AFREZZA- insulin human powder, metered
AFREZZA- insulin
MannKind Corporation
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use AFREZZA® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AFREZZA.
AFREZZA® (insulin human) Inhalation Powder. Initial U.S. Approval: 06/2014
WARNING: RISK OF ACUTE BRONCHOSPASM IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE
|
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: RISK OF ACUTE BRONCHOSPASM IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE
- Acute bronchospasm has been observed in patients with asthma and COPD using AFREZZA. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease such as asthma or COPD. [see Contraindications (4)]
- Before initiating AFREZZA, perform a detailed medical history, physical examination, and spirometry (FEV1) to identify potential lung disease in all patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AFREZZA® is a rapid acting inhaled insulin indicated to improve glycemic control in adult patients with diabetes mellitus.
Limitations of Use:
- AFREZZA is not a substitute for long-acting insulin. AFREZZA must be used in combination with long-acting insulin in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- AFREZZA is not recommended for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis [see Warning and Precautions (5.6)].
- The safety and efficacy of AFREZZA in patients who smoke has not been established. The use of AFREZZA is not recommended in patients who smoke or who have recently stopped smoking.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Route of Administration
AFREZZA should only be administered via oral inhalation using the AFREZZA Inhaler. AFREZZA is administered using a single inhalation per cartridge.
2.2 Dosage Information
Administer AFREZZA at the beginning of the meal.
Dosage adjustment may be needed when switching from another insulin to AFREZZA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Starting Mealtime Dose:
- Insulin Naïve Individuals: Start on 4 units of AFREZZA at each meal.
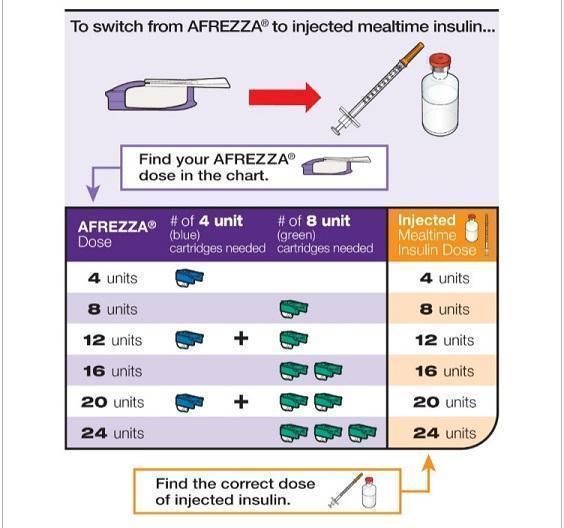
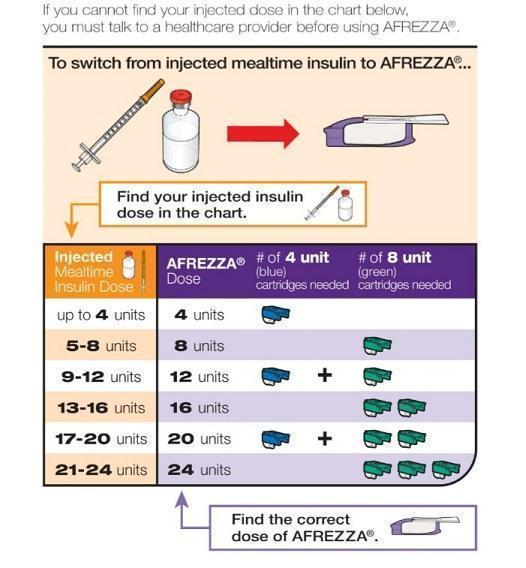
- Individuals Using Subcutaneous Mealtime (Prandial) Insulin: Determine the appropriate AFREZZA dose for each meal by converting from the injected dose using Figure 1.
- Individuals Using Subcutaneous Pre-mixed Insulin: Estimate the mealtime injected dose by dividing half of the total daily injected pre-mixed insulin dose equally among the three meals of the day. Convert each estimated injected mealtime dose to an appropriate AFREZZA dose using Figure 1. Administer half of the total daily injected pre-mixed dose as an injected basal insulin dose.
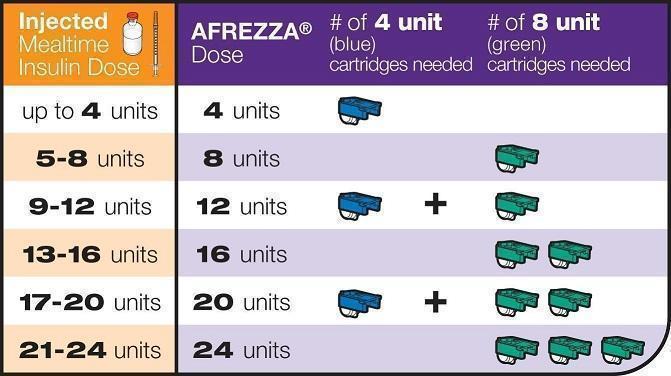
Figure 1. Mealtime AFREZZA Dose Conversion Table
Mealtime Dose Adjustment
Adjust the dosage of AFREZZA based on the individual's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results and glycemic control goal.
Dosage adjustments may be needed with changes in physical activity, changes in meal patterns (i.e., macronutrient content or timing of food intake), changes in renal or hepatic function or during acute illness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), and Use in Specific Populations (8.5, 8.6)] .
Carefully monitor blood glucose control in patients requiring high doses of AFREZZA. If, in these patients, blood glucose control is not achieved with increased AFREZZA doses, consider use of subcutaneous mealtime insulin.
2.3 AFREZZA Administration for Doses Exceeding 8 units
For AFREZZA doses exceeding 8 units, inhalations from multiple cartridges are necessary. To achieve the required total mealtime dose, patients should use a combination of 4 unit and 8 unit cartridges. Examples of cartridge combinations for doses of up to 24 units are shown in Figure 1. For doses above 24 units, combinations of different multiple cartridges can be used.
2.4 Dosage Adjustment due to Drug Interactions
Dosage adjustment may be needed when AFREZZA is coadministered with certain drugs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
2.5 Lung Function Assessment Prior to Administration
AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease because of the risk of acute bronchospasm in these patients. Before initiating AFREZZA, perform a medical history, physical examination and spirometry (FEV1) in all patients to identify potential lung disease [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.6 Important Administration Instructions
See Patient Instructions for Use for complete administration instructions with illustrations.
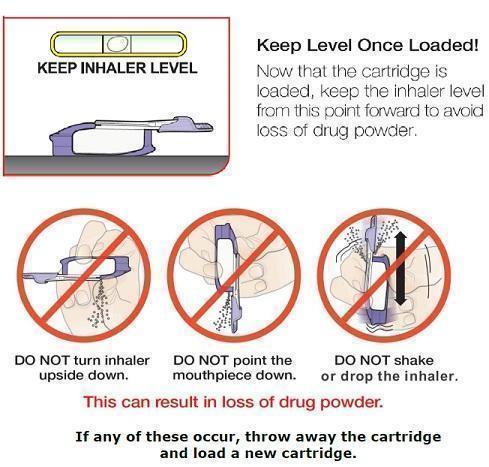
Keep the inhaler level and white mouthpiece on top and purple base on the bottom after a cartridge has been inserted into the inhaler. Loss of drug effect can occur if the inhaler is turned upside down, held with the mouthpiece pointing down, shaken (or dropped) after the cartridge has been inserted but before the dose has been administered. If any of the above occur, the cartridge should be replaced before use.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
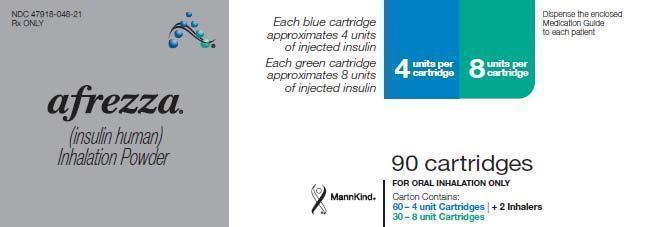
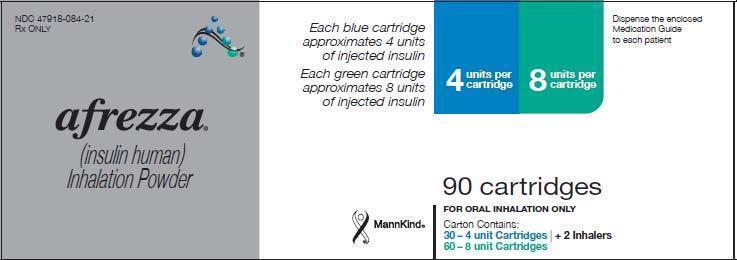
AFREZZA (insulin human) Inhalation Powder is available as 4 unit and 8 unit single use cartridges to be administered via oral inhalation with the AFREZZA Inhaler only. [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with the following:
- During episodes of hypoglycemia
- Chronic lung disease, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), because of the risk of acute bronchospasm [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Hypersensitivity to regular human insulin or any of the AFREZZA excipients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Acute Bronchospasm in Patients with Chronic Lung Disease
Because of the risk of acute bronchospasm, AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients with chronic lung disease such as asthma or COPD [see Contraindications (4)].
Before initiating therapy with AFREZZA, evaluate all patients with a medical history, physical examination and spirometry (FEV1) to identify potential underlying lung disease.
Acute bronchospasm has been observed following AFREZZA dosing in patients with asthma and patients with COPD. In a study of patients with asthma, bronchoconstriction and wheezing following AFREZZA dosing was reported in 29% (5 out of 17) and 0% (0 out of 13) of patients with and without a diagnosis of asthma, respectively. In this study, a mean decline in FEV1 of 400 mL was observed 15 minutes after a single dose in patients with asthma. In a study of patients with COPD (n=8), a mean decline in FEV1 of 200 mL was observed 18 minutes after a single dose of AFREZZA. The long-term safety and efficacy of AFREZZA in patients with chronic lung disease has not been established.
5.2 Changes in Insulin Regimen
Glucose monitoring is essential for patients receiving insulin therapy. Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type, or method of administration may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] or hyperglycemia. These changes should be made under close medical supervision and the frequency of blood glucose monitoring should be increased. Concomitant oral antidiabetic treatment may need to be adjusted.
5.3 Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction associated with insulins, including AFREZZA. Severe hypoglycemia can cause seizures, may be life-threatening, or cause death. Hypoglycemia can impair concentration ability and reaction time; this may place an individual and others at risk in situations where these abilities are important (e.g., driving or operating other machinery).
The timing of hypoglycemia usually reflects the time-action profile of the administered insulin formulation. AFREZZA has a distinct time action profile [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)], which impacts the timing of hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia can happen suddenly and symptoms may differ across individuals and change over time in the same individual. Symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia may be less pronounced in patients with longstanding diabetes, in patients with diabetic nerve disease, in patients using certain medications [see Drug Interactions (7)], or in patients who experience recurrent hypoglycemia. Other factors which may increase the risk of hypoglycemia include changes in meal pattern (e.g., macronutrient content or timing of meals), changes in level of physical activity, or changes to co-administered medication [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Patients with renal or hepatic impairment may be at higher risk of hypoglycemia [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5, 8.6)].
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Hypoglycemia
Patients and caregivers must be educated to recognize and manage hypoglycemia. Self-monitoring of blood glucose plays an essential role in the prevention and management of hypoglycemia. In patients at higher risk for hypoglycemia and patients who have reduced symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia, increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring is recommended.
5.4 Decline in Pulmonary Function
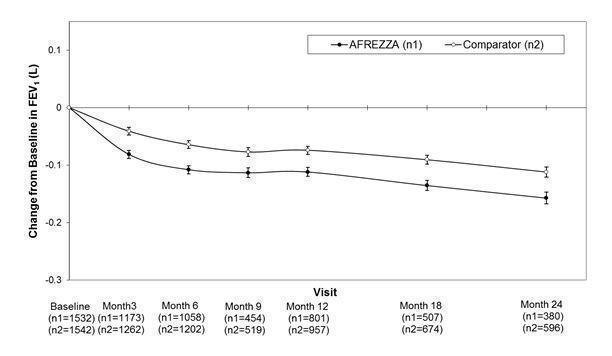
AFREZZA causes a decline in lung function over time as measured by FEV1. In clinical trials excluding patients with chronic lung disease and lasting up to 2 years, AFREZZA-treated patients experienced a small [40 mL (95% CI: -80, -1)] but greater FEV1 decline than comparator-treated patients. The FEV1 decline was noted within the first 3 months, and persisted for the entire duration of therapy (up to 2 years of observation). In this population, the annual rate of FEV1 decline did not appear to worsen with increased duration of use. The effects of AFREZZA on pulmonary function for treatment duration longer than 2 years has not been established. There are insufficient data in long term studies to draw conclusions regarding reversal of the effect on FEV1 after discontinuation of AFREZZA. The observed changes in FEV1 were similar in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Assess pulmonary function (e.g., spirometry) at baseline, after the first 6 months of therapy, and annually thereafter, even in the absence of pulmonary symptoms. In patients who have a decline of ≥ 20% in FEV1 from baseline, consider discontinuing AFREZZA. Consider more frequent monitoring of pulmonary function in patients with pulmonary symptoms such as wheezing, bronchospasm, breathing difficulties, or persistent or recurring cough. If symptoms persist, discontinue AFREZZA. [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.5 Lung Cancer
In clinical trials, two cases of lung cancer, one in controlled trials and one in uncontrolled trials (2 cases in 2,750 patient-years of exposure), were observed in participants exposed to AFREZZA while no cases of lung cancer were observed in comparators (0 cases in 2,169 patient-years of exposure). In both cases, a prior history of heavy tobacco use was identified as a risk factor for lung cancer. Two additional cases of lung cancer (squamous cell) occurred in non-smokers exposed to AFREZZA and were reported by investigators after clinical trial completion. These data are insufficient to determine whether AFREZZA has an effect on lung or respiratory tract tumors. In patients with active lung cancer, a prior history of lung cancer, or in patients at risk for lung cancer, consider whether the benefits of AFREZZA use outweigh this potential risk.
5.6 Diabetic Ketoacidosis
In clinical trials enrolling subjects with type 1 diabetes, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) was more common in subjects receiving AFREZZA (0.43%; n=13) than in subjects receiving comparators (0.14%; n=3). In patients at risk for DKA, such as those with an acute illness or infection, increase the frequency of glucose monitoring and consider delivery of insulin using an alternate route of administration if indicated [see Limitations of Use (1)].
5.7 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulin products, including AFREZZA. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue AFREZZA, treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. AFREZZA is contraindicated in patients who have had hypersensitivity reactions to AFREZZA or any of its excipients [see Contraindications (4)].
5.8 Hypokalemia
All insulin products, including AFREZZA, cause a shift in potassium from the extracellular to intracellular space, possibly leading to hypokalemia. Untreated hypokalemia may cause respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia, and death. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia (e.g., patients using potassium-lowering medications, patients taking medications sensitive to serum potassium concentrations and patients receiving intravenously administered insulin).
5.9 Fluid Retention and Heart Failure with Concomitant Use of PPAR-gamma Agonists
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), which are peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma agonists, can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Fluid retention may lead to or exacerbate heart failure. Patients treated with insulin, including AFREZZA, and a PPAR-gamma agonist should be observed for signs and symptoms of heart failure. If heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care, and discontinuation or dose reduction of the PPAR-gamma agonist must be considered.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Acute bronchospasm in patients with chronic lung disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Decline in pulmonary function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Lung cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Diabetic ketoacidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying designs, the incidence of adverse reactions reported in one clinical trial may not be easily compared to the incidence reported in another clinical trial, and may not reflect what is observed in clinical practice.
The data described below reflect exposure of 3017 patients to AFREZZA and include 1026 patients with type 1 diabetes and 1991 patients with type 2 diabetes. The mean exposure duration was 8.17 months for the overall population and 8.16 months and 8.18 months for type 1 and 2 diabetes patients, respectively. In the overall population, 1874 were exposed to AFREZZA for 6 months and 724 for greater than one year. 620 and 1254 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, respectively, were exposed to AFREZZA for up to 6 months. 238 and 486 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, respectively, were exposed to AFREZZA for greater than one year (median exposure = 1.8 years). AFREZZA was studied in placebo and active-controlled trials (n = 3 and n = 10, respectively).
The mean age of the population was 50.2 years and 20 patients were older than 75 years of age. 50.8% of the population were men; 82.6% were White, 1.8% were Asian, and 4.9% were Black or African American. 9.7% were Hispanic. At baseline, the type 1 diabetes population had diabetes for an average of 16.6 years and had a mean HbA1c of 8.3%, and the type 2 diabetes population had diabetes for an average of 10.7 years and had a mean HbA1c of 8.8%. At baseline, 33.4% of the population reported peripheral neuropathy, 32.0% reported retinopathy and 19.6% had a history of cardiovascular disease.
Table 1 shows common adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, associated with the use of AFREZZA in the pool of controlled trials in type 2 diabetes patients. These adverse reactions were not present at baseline, occurred more commonly on AFREZZA than on placebo and/or comparator and occurred in at least 2% of patients treated with AFREZZA.
|
Placebo* (n = 290) |
AFREZZA (n = 1991) |
Non-placebo comparators (n=1363) |
|
|
Cough |
19.7% |
25.6% |
5.4% |
|
Throat pain or irritation |
3.8% |
4.4% |
0.9% |
|
Headache |
2.8% |
3.1% |
1.8% |
|
Diarrhea |
1.4% |
2.7% |
2.2% |
|
Productive cough |
1.0% |
2.2% |
0.9% |
|
Fatigue |
0.7% |
2.0% |
0.6% |
|
Nausea |
0.3% |
2.0% |
1.0% |
|
*Carrier particle without insulin was used as placebo [Description (11)]. |
|||
Table 2 shows common adverse reactions, excluding hypoglycemia, associated with the use of AFREZZA in the pool of active-controlled trials in type 1 diabetes patients. These adverse reactions were not present at baseline, occurred more commonly on AFREZZA than on comparator, and occurred in at least 2% of patients treated with AFREZZA.
|
Subcutaneous Insulin (n = 835) |
AFREZZA (n = 1026) |
|
| Cough | 4.9% | 29.4% |
| Throat pain or irritation | 1.9% | 5.5% |
| Headache | 2.8% | 4.7% |
| Pulmonary function test decreased | 1.0% | 2.8% |
| Bronchitis | 2.0% | 2.5% |
| Urinary tract infection | 1.9% | 2.3% |
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most commonly observed adverse reaction in patients using insulin, including AFREZZA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. The incidence of severe and non-severe hypoglycemia of AFREZZA versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes is shown in Table 3. A hypoglycemic episode was recorded if a patient reported symptoms of hypoglycemia with or without a blood glucose value consistent with hypoglycemia. Severe hypoglycemia was defined as an event with symptoms consistent with hypoglycemia requiring the assistance of another person and associated with either a blood glucose value consistent with hypoglycemia or prompt recovery after treatment for hypoglycemia.
|
Placebo (n = 176) |
AFREZZA (n = 177) |
|
| Severe Hypoglycemia | 1.7% | 5.1% |
| Non-Severe Hypoglycemia | 30% | 67% |
Cough
Approximately 27% of patients treated with AFREZZA reported cough, compared to approximately 5.2% of patients treated with comparator. In clinical trials, cough was the most common reason for discontinuation of AFREZZA therapy (2.8% of AFREZZA-treated patients).
Pulmonary Function Decline
In clinical trials lasting up to 2 years, excluding patients with chronic lung disease, patients treated with AFREZZA had a 40 mL (95% CI: -80, -1) greater decline from baseline in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) compared to patients treated with comparator anti-diabetes treatments. The decline occurred during the first 3 months of therapy and persisted over 2 years (Figure 2). A decline in FEV1 of ≥ 15% occurred in 6% of AFREZZA-treated subjects compared to 3% of comparator-treated subjects.
Figure 2. Mean (+/-SE) Change in FEV1 (Liters) from Baseline for Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Weight gain
Weight gain may occur with some insulin therapies, including AFREZZA. Weight gain has been attributed to the anabolic effects of insulin and the decrease in glycosuria. In a clinical trial of patients with type 2 diabetes [see Clinical Studies (14.3)], there was a mean 0.49 kg weight gain among AFREZZA-treated patients compared with a mean 1.13 kg weight loss among placebo-treated patients.
Antibody Production
Increases in anti-insulin antibody concentrations have been observed in patients treated with AFREZZA. Increases in anti-insulin antibodies are observed more frequently with AFREZZA than with subcutaneously injected mealtime insulins. Presence of antibody did not correlate with reduced efficacy, as measured by HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose, or specific adverse reactions.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs That May Increase the Risk of Hypoglycemia
The risk of hypoglycemia associated with AFREZZA use may be increased with antidiabetic agents, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blocking agents, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, pentoxifylline, pramlintide, propoxyphene, salicylates, somatostatin analogs (e.g., octreotide), and sulfonamide antibiotics. Dose adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when AFREZZA is co-administered with these drugs.
7.2 Drugs That May Decrease the Blood Glucose Lowering Effect of AFREZZA
The glucose lowering effect of AFREZZA may be decreased when co-administered with atypical antipsychotics (e.g., olanzapine and clozapine), corticosteroids, danazol, diuretics, estrogens, glucagon, isoniazid, niacin, oral contraceptives, phenothiazines, progestogens (e.g., in oral contraceptives), protease inhibitors, somatropin, sympathomimetic agents (e.g., albuterol, epinephrine, terbutaline) and thyroid hormones. Dose adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when AFREZZA is co-administered with these drugs.
7.3 Drugs That May Increase or Decrease the Blood Glucose Lowering Effect of AFREZZA
The glucose lowering effect of AFREZZA may be increased or decreased when co-administered with alcohol, beta-blockers, clonidine, and lithium salts. Pentamidine may cause hypoglycemia, which may sometimes be followed by hyperglycemia. Dose adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when AFREZZA is co-administered with these drugs.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category C
AFREZZA has not been studied in pregnant women. AFREZZA should not be used during pregnancy unless the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
In pregnant rats given subcutaneous doses of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg/day of carrier particles (vehicle without insulin) from gestation day 6 through 17 (organogenesis), no major malformations were observed at up to 100 mg/kg/day (a systemic exposure 14-21 times the human systemic exposure, resulting from the maximum recommended daily dose of 99 mg AFREZZA based on AUC).
In pregnant rabbits given subcutaneousdoses of 2, 10, and 100 mg/kg/day of carrier particles (vehicle without insulin) from gestation day 7 through 19 (organogenesis), adverse maternal effects were observed at all dose groups (at human systemic exposure following a 99 mg AFREZZA dose, based on AUC).
In pregnant rats given subcutaneous doses of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg/day of carrier particles (vehicle without insulin) from gestation day 7 through lactation day 20 (weaning), decreased epididymis and testes weights, however, no decrease in fertility was noted, and impaired learning were observed in pups at ≥ 30 mg/kg/day (a systemic exposure 6 times human systemic exposure at the maximum daily AFREZZAdose of 99 mg based on AUC).
8.2 Nursing Mothers
Many drugs are excreted in human milk. A study in rats indicated that the carrier is excreted in milk at approximately 10% of maternal exposure levels. It is therefore highly likely that the insulin and carrier in AFREZZA is excreted in human milk. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or suspend use of the drug since AFREZZA has not been studied in lactating women.
8.4 Geriatric Use
In the AFREZZA clinical studies, 381 patients were 65 years of age or older, of which 20 were 75 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between patients over 65 and younger patients.
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic studies to assess the effect of age have not been conducted.
8.5 Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of AFREZZA has not been studied. Frequent glucose monitoring and dose adjustment may be necessary for AFREZZA in patients with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of AFREZZA has not been studied. Some studies with human insulin have shown increased circulating levels of insulin in patients with renal failure. Frequent glucose monitoring and dose adjustment may be necessary for AFREZZA in patients with renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Excess insulin administration may cause hypoglycemia and hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), (5.8)].
Mild episodes of hypoglycemia can usually be treated with oral glucose. Adjustments in drug dosage, meal patterns, or exercise, may be needed.
Severe episodes of hypoglycemia with coma, seizure, or neurologic impairment may be treated with intramuscular / subcutaneous glucagon or concentrated intravenous glucose. After apparent clinical recovery from hypoglycemia, continued observation and additional carbohydrate intake may be necessary to avoid recurrence of hypoglycemia. Hypokalemia must be corrected appropriately.
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 AFREZZA Cartridges
AFREZZA consists of single-use plastic cartridges filled with a white powder containing insulin (human), which is administered via oral inhalation using the AFREZZA Inhaler only.
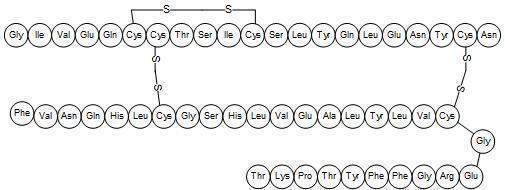
AFREZZA cartridges contain human insulin produced by recombinant DNA technology utilizing a non-pathogenic laboratory strain of Escherichia coli (K12). Chemically, human insulin has the empirical formula C257H383N65O77S6 and a molecular weight of 5808. Human insulin has the following primary amino acid sequence:
Insulin is adsorbed onto carrier particles consisting of fumaryl diketopiperazine (FDKP) and polysorbate 80.
AFREZZA Inhalation Powder is a dry powder supplied as 4 unit or 8 unit cartridges. The 4 unit cartridge contains 0.35 mg of insulin. The 8 unit cartridge contains 0.7 mg of insulin.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Insulin lowers blood glucose levels by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production. Insulin inhibits lipolysis in adipocytes, inhibits proteolysis, and enhances protein synthesis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
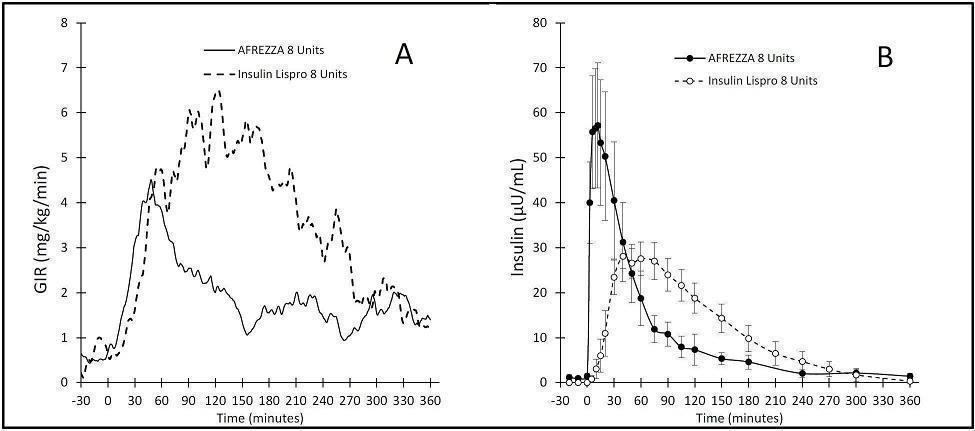
The pharmacodynamic profile for orally inhaled AFREZZA 8 units relative to subcutaneously administered insulin lispro 8 units from a study in 12 patients with type 1 diabetes is shown in Figure 3(A). The median time to maximum effect of AFREZZA (measured by the peak rate of glucose infusion) was approximately 53 minutes (standard deviation of 74 minutes) and the effect then declined to near baseline levels by about 160 minutes.
Figure 3. Baseline-Corrected Glucose Infusion Rate (A) and Baseline-Corrected Serum Insulin Concentrations (B) after Administration of AFREZZA or Subcutaneous Insulin Lispro in Type 1 Diabetes Patients*
* Despite the faster absorption of insulin (PK) from Afrezza, the onset of activity (PD) was comparable to insulin lispro.
In a study of 32 healthy subjects, the pharmacodynamic effect of AFREZZA, measured as area under the glucose infusion rate - time curve (AUC-GIR) from an euglycemic clamp, increased in a less than dose-proportional manner. This effect has been observed for subcutaneously administered insulins, but it is unknown if the diminishing pharmacodynamic benefit at higher dosage of AFREZZA parallels that which is seen with subcutaneously administered insulin.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The insulin contained in AFREZZA is regular human insulin. Following pulmonary absorption into systemic circulation, the metabolism and elimination are comparable to regular human insulin.
Absorption: The pharmacokinetic profiles for orally inhaled AFREZZA 8 units relative to subcutaneously administered insulin lispro 8 units from a study in 12 patients with type 1 diabetes are shown in Figure 3(B). The maximum serum insulin concentration was reached by 12-15 minutes after inhalation of AFREZZA 8 units and serum insulin concentrations declined to baseline by approximately 180 minutes. However, the faster absorption of insulin from Afrezza [see Figure 3(B)] did not result in a faster onset of activity compared to insulin lispro [see Figure 3(A)].
Disposition: Systemic insulin disposition (median terminal half-life) following oral inhalation of AFREZZA 4 and 32 units was 28-39 minutes, and 145 minutes for subcutaneous regular human insulin 15 units.
Carrier Particles
Clinical pharmacology studies showed that carrier particles [see Description (11)] are not metabolized and are eliminated unchanged in the urine following the lung absorption. Following oral inhalation of AFREZZA, a mean of 39% of the inhaled dose of carrier particles was distributed to the lungs and a mean of 7% of the dose was swallowed. The swallowed fraction was not absorbed from the GI tract and was eliminated unchanged in the feces.
Drug Interaction: Bronchodilators and Inhaled Steroids
Albuterol increased the AUC insulin administered by AFREZZA by 25% in patients with asthma. Effect of fluticasone on insulin exposures following AFREZZA administration has not been evaluated in patients with asthma; however, no significant change in insulin exposure was observed in a study in healthy volunteers. Frequent glucose monitoring and dose reduction may be necessary for AFREZZA if it is co-administered with albuterol.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
In a 104 week carcinogenicity study, rats were given doses up to 46 mg/kg/day of the carrier and up to 1.23 mg/kg/day of insulin, by nose-only inhalation. No increased incidence of tumors was observed at systemic exposures equivalent to the insulin at a maximum daily AFREZZA dose of 99 mg based on a comparison of relative body surface areas across species.
In a 26 week carcinogenicity study, transgenic mice (Tg-ras-H2) given doses up to 75 mg/kg/day of carrier and up to 5 mg/kg/day of AFREZZA. No increased incidence of tumors was observed.
AFREZZA was not genotoxic in Ames bacterial mutagenicity assay and in the chromosome aberration assay, using human peripheral lymphocytes with or without metabolic activation. The carrier alone was not genotoxic in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
In female rats given subcutaneous doses of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg/day of carrier (vehicle without insulin) beginning 2 weeks prior to mating until gestation day 7, there were no adverse effects on male fertility at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (a systemic exposure 14-21 times that following the maximum daily AFREZZA dose of 99 mg based on AUC). In female rats there was increased pre- and post-implantation loss at 100 mg/kg/day but not at 30 mg/kg/day (14-21 times higher systemic exposure than the maximum daily AFREZZA dose of 99 mg based on AUC).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Overview of Clinical Studies of AFREZZA for Diabetes Mellitus
AFREZZA has been studied in adults with type 1 diabetes in combination with basal insulin. The efficacy of AFREZZA in type 1 diabetes patients was compared to insulin aspart in combination with basal insulin. AFREZZA has been studied in adults with type 2 diabetes in combination with oral antidiabetic drugs. The efficacy of AFREZZA in type 2 diabetes patients was compared to placebo inhalation.
14.2 Type 1 Diabetes
Patients with inadequately controlled type 1 diabetes participated in a 24-week, open-label, active-controlled study to evaluate the glucose lowering effect of mealtime AFREZZA used in combination with a basal insulin. Following a 4-week basal insulin optimization period, 344 patients were randomized to AFREZZA (n=174) or insulin aspart (n=170)administered at each meal of the day. Mealtime insulin doses were titrated to glycemic goals for the first 12 weeks and kept stable for the last 12 weeks of the study. At Week 24, treatment with basal insulin and mealtime AFREZZA provided a mean reduction in HbA1c that met the pre-specified non-inferiority margin of 0.4%. AFREZZA provided less HbA1c reduction than insulin aspart, and the difference was statistically significant. More subjects in the insulin aspart group achieved the HbA1c target of ≤7% (Table 4).
|
Efficacy Parameter |
AFREZZA + Basal Insulin |
Insulin Aspart + Basal Insulin |
||
|
(N=174) |
(N=170) |
|||
|
HbA1c (%) | ||||
|
Baseline (adjusted meana) |
7.94 |
7.92 |
||
|
Change from baseline (adjusted meana,b) |
-0.21 |
-0.40 |
||
|
Difference from insulin aspart (adjusted meana,b) (95% CI) |
0.19 (0.02, 0.36) |
|||
|
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c ≤ 7%c |
13.8 |
27.1 |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) Mean | ||||
|
Baseline (adjusted meana) |
153.9 |
151.6 |
||
|
Change from baseline (adjusted meana)b |
-25.3 |
10.2 |
||
|
Difference from insulin aspart (adjusted meana,b) (95% CI) |
-35.4 (-56.3, -14.6) |
|||
|
a Adjusted mean was obtained using a Mixed Model Repeated Measures (MMRM) approach with HbA1c or FPG as the dependent variable and treatment, visit, region, basal insulin stratum, and treatment by visit interaction as fixed factors, and corresponding baseline as a covariate. An autoregression (1) [AR(1)] covariance structure was used. b Data at 24 weeks were available from 131 (75 %) and 150 (88% ) subjects randomized to the AFREZZA and insulin aspart groups, respectively. c The percentage was calculated based on the number of patients randomized to the trial. |
||||
14.3 Type 2 Diabetes
A total of 479 adult patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on optimal/maximally tolerated doses of metformin only, or 2 or more oral antidiabetic (OAD) agents participated in a 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Following a 6-week run-in period, 353 patients were randomized to AFREZZA (n=177) or an inhaled placebo powder without insulin (n=176). Insulin doses were titrated for the first 12 weeks and kept stable for the last 12 weeks of the study. OADs doses were kept stable. At Week 24, treatment with AFREZZA plus OADs provided a mean reduction in HbA1c that was statistically significantly greater compared to the HbA1c reduction observed in the placebo group (Table 5).
|
Efficacy Parameter |
AFREZZA + Oral Anti-Diabetic Agents |
Placebo + Oral Anti-Diabetic Agents |
||
|
(N=177) |
(N=176) |
|||
|
HbA1c (%) | ||||
|
Baseline (adjusted meana) |
8.25 |
8.27 |
||
|
Change from baseline (adjusted meana,b) |
-0.82 |
-0.42 |
||
|
Difference from placebo (adjusted meana,b) (95% CI) |
-0.40 (-0.57, -0.23) |
|||
|
Percentage of patients achieving HbA1c ≤ 7%c |
32.2 |
15.3 |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL) Mean | ||||
|
Baseline (adjusted meana) |
175.9 |
175.2 |
||
|
Change from baseline (adjusted meana)b |
-11.2 |
-3.8 |
||
|
Difference from placebo (adjusted meana,b) (95% CI) |
-7.4 (-18.0, 3.2) |
|||
|
a Adjusted mean was obtained using a Mixed Model Repeated Measures (MMRM) approach with HbA1c or FPG as the dependent variable and treatment, visit, region, basal insulin stratum, and treatment by visit interaction as fixed factors, and corresponding baseline as a covariate. An autoregression (1) [AR(1)] covariance structure was used. b Data at 24 weeks without rescue therapy were available from 139 (79%) and 129 (73%) subjects randomized to the AFREZZA and placebo groups, respectively. c The percentage was calculated based on the number of patients randomized to the trial. |
||||
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
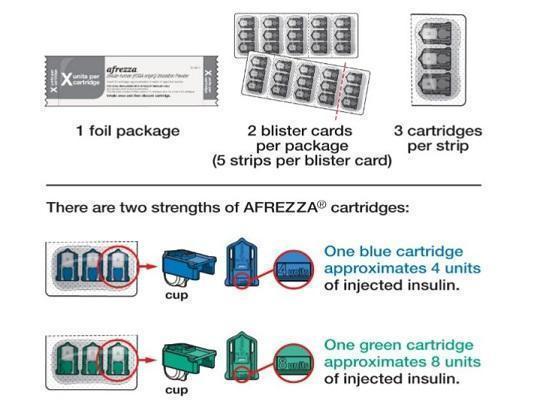
AFREZZA (insulin human) Inhalation Powder is available as 4 unit and 8 unit single-use cartridges. Three cartridges are contained in a single cavity of a blister strip. Each card contains 5 blister strips separated by perforations for a total of 15 cartridges. For convenience, the perforation allows users to remove a single strip containing 3 cartridges. Two cards of the same cartridge strength are packaged in a foil laminate overwrap (30 cartridges per foil package).
The cartridges are color-coded, blue for 4 units and green for 8 units. Each cartridge is marked with “afrezza” and “4 units” or “8 units”.
The AFREZZA Inhaler is individually packaged in a translucent overwrap. The inhaler is fully assembled with a removable mouthpiece cover. The AFREZZA Inhaler can be used for up to 15 days from the date of first use. After 15 days of use, the inhaler must be discarded and replaced with a new inhaler.
AFREZZA is available in the following configurations:
- NDC 47918-004-02, AFREZZA (insulin human [rDNA origin]) Inhalation Powder:
60 − 4 unit cartridges and 2 inhalers - NDC 47918-004-03, AFREZZA (insulin human [rDNA origin]) Inhalation Powder: 90 − 4 unit cartridges and 2 inhalers
- NDC 47918-008-03, AFREZZA (insulin human [rDNA origin]) Inhalation Powder: 90 − 8 unit cartridges and 2 inhalers
- NDC 47918-048-21, AFREZZA (insulin human [rDNA origin]) Inhalation Powder: 90 cartridges; 60 – 4 unit cartridges and 30 − 8 unit cartridges and 2 inhalers
- NDC 47918-084-21, AFREZZA (insulin human [rDNA origin]) Inhalation Powder: 90 cartridges; 30 – 4 unit cartridges and 60 − 8 unit cartridges and 2 inhalers
- NDC 47918-840-33, AFREZZA (insulin human [rDNA origin]) Inhalation Powder: 180 cartridges; 90 - 4 unit cartridges and 90 – 8 unit cartridges and 2 inhalers
Storage
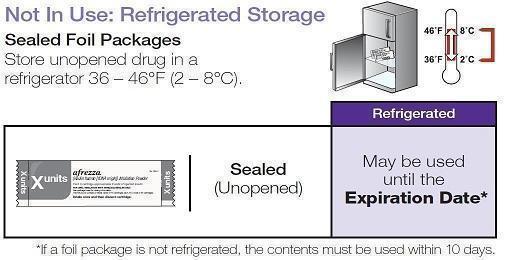
Not in Use: Refrigerated Storage 2-8ºC (36-46ºF)
|
Sealed (Unopened) Foil Package |
May be stored until the Expiration Date* |
* If a foil package is not refrigerated, the contents must be used within 10 days.
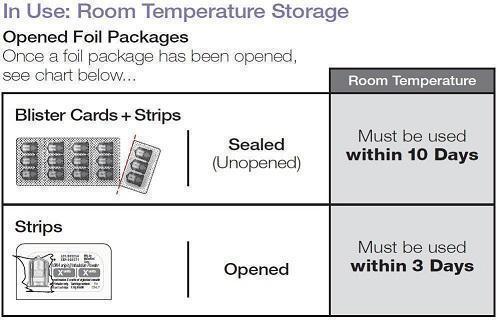
In Use: Room Temperature Storage 25ºC (77ºF), excursions permitted 15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
|
Sealed (Unopened) Blister Cards + Strips |
Must be used within 10 days |
|
Opened Strips |
Must be used within 3 days |
Inhaler Storage:
Store at 2-25ºC (36-77ºF); excursions permitted. Inhaler may be stored refrigerated, but should be at room temperature before use.
Handling:
Before use, cartridges should be at room temperature for 10 minutes.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)
Instructions
Instruct patients to read the Medication Guide before starting AFREZZA therapy and to reread it each time the prescription is renewed, because information may change. Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider or pharmacist if they develop any unusual symptom, or if any known symptom persists or worsens.
Inform patients of the potential risks and benefits of AFREZZA and of alternative modes of therapy. Inform patients about the importance of adherence to dietary instructions, regular physical activity, periodic blood glucose monitoring and HbA1c testing, recognition and management of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, and assessment for diabetes complications. Advise patients to seek medical advice promptly during periods of stress such as fever, trauma, infection, or surgery, as medication requirements may change.
Instruct patients to use AFREZZA only with the AFREZZA inhaler.
Inform patients that the most common adverse reactions associated with the use of AFREZZA are hypoglycemia, cough, and throat pain or irritation.
Advise women with diabetes to inform their physician if they are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant while using AFREZZA.
Acute Bronchospasm in Patients with Chronic Lung Disease
Advise patients to inform their physicians if they have a history of lung disease, because AFREZZA should not be used in patients with chronic lung disease (e.g., asthma, COPD, or other chronic lung disease(s)) [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Advise patients that if they experience any respiratory difficulty after inhalation of AFREZZA, they should report it to their physician immediately for assessment.
Hypoglycemia
Instruct patients on self-management procedures including glucose monitoring, proper inhalation technique, and management of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia especially at initiation of AFREZZA therapy. Instruct patients on handling of special situations such as intercurrent conditions (illness, stress, or emotional disturbances), an inadequate or skipped insulin dose, inadvertent administration of an increased insulin dose, inadequate food intake, and skipped meals.
Instruct patients on the management of hypoglycemia. Inform patients that their ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycemia. Advise patients who have frequent hypoglycemia or reduced or absent warning signs of hypoglycemia to use caution when driving or operating machinery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Decline in Pulmonary Function and Monitoring
Inform patients that AFREZZA can cause a decline in lung function and their lung function will be evaluated by spirometry before initiation of AFREZZA treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Lung Cancer
Inform patients to promptly report any signs or symptoms potentially related to lung cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Instruct patients to carefully monitor their blood glucose during illness, infection, and other risk situations for diabetic ketoacidosis and to contact their healthcare provider if their blood glucose control worsens [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients that hypersensitivity reactions can occur with insulin therapy including AFREZZA. Inform patients on the symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
© MannKind Corporation
Registered trademark owned by MannKind Corporation
Patented: http://www.mannkindcorp.com/our-technology-patent-notices.htm
Distributed by:

MannKindCorporation™
Danbury, CT 06810
06/2014
17.1 Medication Guide
|
Medication Guide AFREZZA® (uh-FREZZ-uh) (insulin human) inhalation powder |
|
What is the most important information I should know about AFREZZA? AFREZZA can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
What is AFREZZA?
|
|
Who should not use AFREZZA? Do not use AFREZZA if you:
|
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using AFREZZA? Before using AFREZZA, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
Before you start using AFREZZA, talk to your healthcare provider about low blood sugar and how to manage it. |
|
How should I use AFREZZA?
|
|
Your dose of AFREZZA may need to change because of:
|
|
What should I avoid while using AFREZZA? While using AFREZZA do not:
|
|
What are the possible side effects of AFREZZA? AFREZZA may cause serious side effects that can lead to death, including: See “What is the most important information I should know about AFREZZA?”
Treatment with TZDs and AFREZZA may need to be changed or stopped by your healthcare provider if you have new or worse heart failure. Get emergency medical help if you have:
The most common side effects of AFREZZA include:
These are not all the possible side effects of AFREZZA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 (1-800-332-1088). |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of AFREZZA. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use AFREZZA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give AFREZZA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about AFREZZA. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about AFREZZA that is written for health professionals. For more information, go to www.AFREZZA.com or call 1-877-323-8505. |
|
What are the ingredients in AFREZZA? Active ingredient: human insulin Inactive ingredients: fumaryl diketopiperazine, polysorbate 80 |
|
Manufactured By: © MannKind Corporation Registered trademark owned by MannKind Corporation Patented: http://www.mannkindcorp.com/our-technology-patent-notices.htm Distributed by:
MannKind Corporation™ |
17.2 Instruction for Use
Instructions for Use
AFREZZA® (uh-FREZZ-uh)
(insulin human) inhalation powder
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using AFREZZA and each time you get a new AFREZZA inhaler. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
Your healthcare provider should show you how to use your AFREZZA inhaler the right way before you use it for the first time.
Important information about AFREZZA:
-
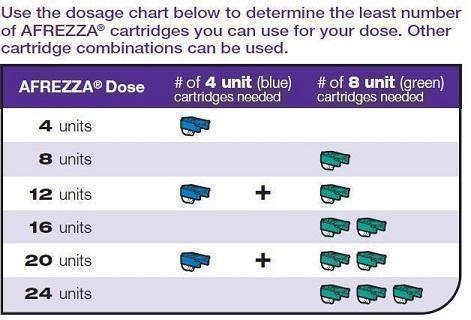
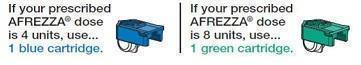
AFREZZA comes in 2 strengths (See Figure A):
- 4 units (blue cartridge)
- 8 units (green cartridge)
(Figure A)
- If your prescribed AFREZZA dose is higher than 8 units, you will need to use more than 1 cartridge.
- If you need to use more than 1 cartridge for your dose, throw away the used cartridge before getting a new one. You can tell when a cartridge has been used, because the cup has moved to the center.
- Do not try to open the AFREZZA cartridges. The AFREZZA Inhaler opens the cartridge automatically during use.
- AFREZZA cartridges should only be used with the AFREZZA Inhaler.Do not try to breathe in the AFREZZA insulin powder in any other way. Do not put cartridges in your mouth and do not swallow cartridges.
- Use only 1 AFREZZA Inhaler at a time. The same inhaler should be used for the 4 unit or 8 unit cartridges.
- Throw away your AFREZZA Inhaler after 15 days and get a new one.
If you are having problems with your AFREZZA inhaler or if it breaks and you need a new one, call 1-877-323-8505.
Know your AFREZZA® inhaler:
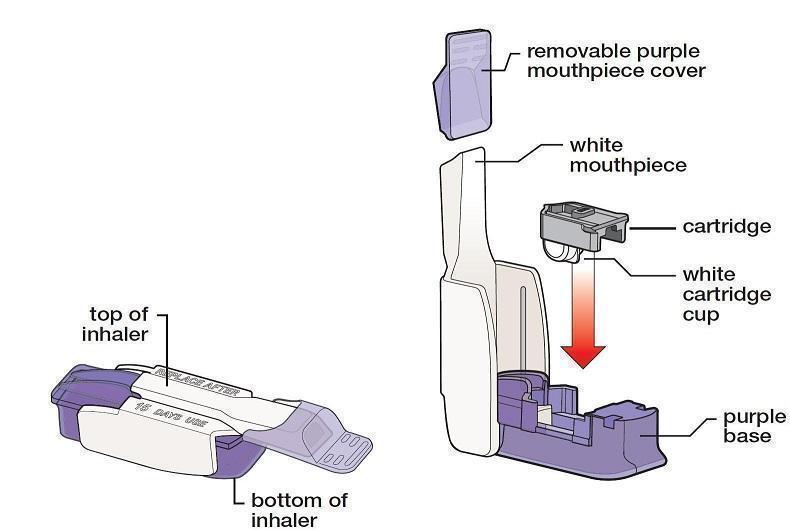
Know your AFREZZA® cartridges:
|
How to take your dose of AFREZZA: Always be sure you have the right number of AFREZZA cartridges for your dose available before you start. AFREZZA cartridges must only be used with the AFREZZA Inhaler. |
|||
|
Step 1: Select the AFREZZA cartridges for your dose |
|||
 | |||
|
If your prescribed AFREZZA® dose is more than 8 units you will need to use more than 1 cartridge to get your right dose. |
|||
|
(Figure B) |
|||
|
Example |
|||
|
Select Cartridges Important: Use the AFREZZA dose chart above (See Figure B) to help you choose the right number of AFREZZA cartridges needed for your dose. |
|||
|
|
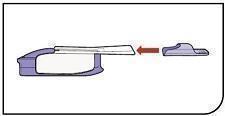
Open Packages Remove a blister card from the foil package. Tear along perforation to remove one strip. |
||
|
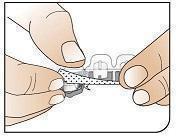
|
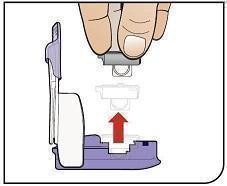
Push Cartridges to Remove Remove a cartridge from the strip by pressing on the clear side to push the cartridge out. Remove the right number of cartridges for your dose. Pushing on the cup will not damage the cartridge. AFREZZA cartridges left over in an opened strip must be used within 3 days. |
||

|
|||
|
Before Proceeding: Check that you have the right AFREZZA cartridge(s) for your dose. Use only 1 inhaler for multiple cartridges. Throw away your AFREZZA inhaler after 15 days and get a new one. |
|||
|
Step 2: Loading a cartridge |
|
|
|
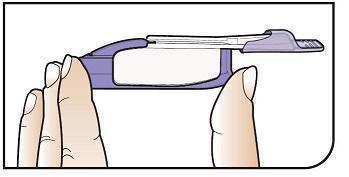
Hold Inhaler Hold the inhaler level in one (1) hand with the white mouthpiece on the top and purple base on the bottom. |
|
|
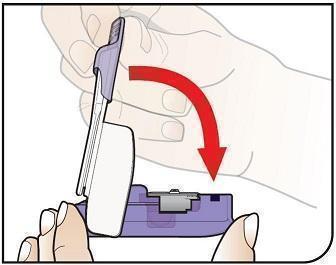
Open Inhaler Open the inhaler by lifting the white mouthpiece to a vertical position. Before you put the AFREZZA cartridge in your inhaler, make sure it has been at room temperature for 10 minutes. |
|
|
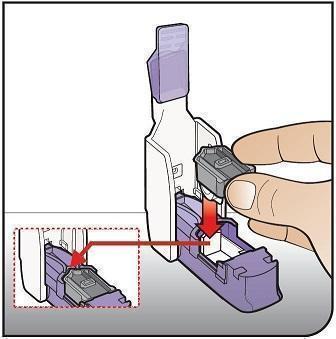
Place Cartridge Hold the cartridge with the cup facing down. Line up the cartridge with the opening in the inhaler. The pointed end of the cartridge should line up with the pointed end in the inhaler. Place the cartridge into the inhaler. Be sure that the cartridge lies flat in the inhaler. |
|
|
|
|
|
Close Inhaler Lower the mouthpiece to close the inhaler (this will open the drug cartridge). You should feel a snap when the inhaler is closed. |
|
Step 3: Inhaling AFREZZA |
|
|
|
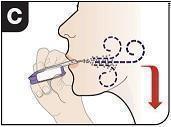
Remove the Mouthpiece Cover Important: Keep the inhaler level during and after removal of the purple mouthpiece cover. |
|
|
|
|
|
Exhale Hold the inhaler away from your mouth and fully blow out (exhale). |
|
|
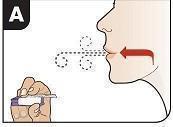
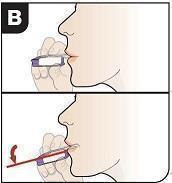
Position Inhaler in Mouth Keeping your head level, place the mouthpiece in your mouth and tilt the inhaler down towards your chin, as shown. Close your lips around the mouthpiece to form a seal. Tilt the inhaler downward while keeping your head level. |
|
|
Inhale Deeply and Hold Breath With your mouth closed around the mouthpiece, inhale deeply through the inhaler. Hold your breath for as long as comfortable and at the same time remove the inhaler from your mouth. After holding your breath, exhale and continue to breathe normally. |
|
Step 4: Removing a used cartridge |
|
|
|
Replace Mouthpiece Cover Place the purple mouthpiece cover back onto the inhaler. |
|
|
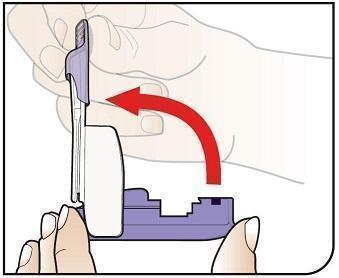
Open Inhaler Open the inhaler by lifting up the white mouthpiece. |
|
|
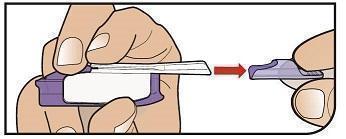
Remove Cartridge Remove the cartridge from the purple base. |
|
|
Throw away the Cartridge Throw away the used cartridge in your regular household trash. |
|
Multiple cartridge dosing |
|
|
If you need more than one (1) AFREZZA cartridge for your dose, See the AFREZZA dosage chart above (Figure B). |
|
|
Repeat steps 2 through 4 for each AFREZZA cartridge you need for your prescribed AFREZZA dose. |
|
 |
|
|
How should I store AFREZZA? |
|
|
|
|

|
Caring for your AFREZZA inhaler: |
|
|
|
|
|
Switching between AFREZZA and injected insulin: |
|
|
|
Contact your healthcare provide before switching insulins. AFREZZA® is a mealtime insulin. Do not switch from AFREZZA to a long acting insulin. Do not switch from a long acting insulin to AFREZZA®. |
|
|
|
This Medication Guide and Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Patented: See http://www.mannkindcorp.com/our-technology-patent-notices.htm
Distributed by:

MannKind Corporation™
Danbury, CT 06810
Approved: 6/2014
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - carton - 4 unit cartridges 60-count
NDC 47918-004-02
Afrezza®
insulin human Inhalation Powder
60 4 unit cartridges + 2 inhalers
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Rx Only
Mannkind

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - carton - 4 unit cartridges 90-count
NDC 47918-004-03
Afrezza®
insulin human Inhalation Powder
90 4 unit cartridges + 2 inhalers
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Rx Only
Mannkind

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - carton - 8 unit cartridges 90-count
NDC 47918-008-03
Afrezza®
insulin human Inhalation Powder
90 8 unit cartridges + 2 inhalers
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Rx Only
Mannkind

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - carton - 4 unit cartridges 30-count - 8 unit cartridges 60-count
NDC 47918-084-21
Afrezza®
insulin human Inhalation Powder
30 4 unit cartridges + 60 8 unit cartridges + 2 inhalers
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Rx Only
Mannkind
| AFREZZA
insulin powder, metered |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AFREZZA
insulin powder, metered |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AFREZZA
insulin kit |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AFREZZA
insulin kit |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AFREZZA
insulin kit |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - MannKind Corporation (128576977) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MannKind Corporation | 099981040 | MANUFACTURE(47918-004, 47918-008, 47918-048, 47918-084, 47918-840) | |