NOVOLIN R
-
insulin human injection, solution
Novo Nordisk Inc.
----------
DESCRIPTION
Novolin®R Regular, Human Insulin Injection (rDNA origin) USP is a polypeptide hormone structurally identical to natural human insulin and is produced by rDNA technology, utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae (bakers' yeast) as the production organism. Human insulin has the empirical formula C257H383N65O77S6 and a molecular weight of 5808 Da.
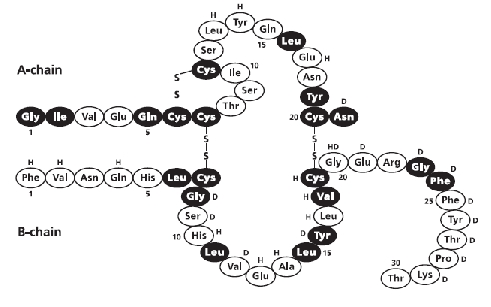
Figure 1. Structural formula of human insulin
Novolin R is a sterile, clear, aqueous, and colorless solution, that contains human insulin (rDNA origin) 100 units/mL, glycerin 16 mg/ml, metacresol 3 mg/mL and zinc chloride approximately 7 µg/mL. The pH is adjusted to 7.4. Hydrochloric acid 2N and/or sodium hydroxide 2N may be added to adjust pH.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Insulin is a polypeptide hormone that controls the storage and metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This activity occurs primarily in the liver, in muscle, and in adipose tissues after binding of the insulin molecules to receptor sites on cellular plasma membranes.
Insulin promotes uptake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in most tissues. Also, insulin influences carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism by stimulating protein and free fatty acid synthesis, and by inhibiting release of free fatty acid from adipose cells. Insulin increases active glucose transport through muscle and adipose cellular membranes, and promotes conversion of intracellular glucose and free fatty acid to the appropriate storage forms (glycogen and triglyceride, respectively). Although the liver does not require active glucose transport, insulin increases hepatic glucose conversion to glycogen and suppresses hepatic glucose output. Even though the actions of exogenous insulin are identical to those of endogenous insulin, the ability to negatively affect hepatic glucose output differs on a unit per unit basis because a smaller quantity of an exogenous insulin dose reaches the portal vein.
Administered insulin, including Novolin R, substitutes for inadequate endogenous insulin secretion and partially corrects the disordered metabolism and inappropriate hyperglycemia of diabetes mellitus, which are caused by either a deficiency or a reduction in the biologic effectiveness of insulin. When administered in appropriate doses at prescribed intervals to patients with diabetes mellitus, Novolin R temporarily restores their ability to metabolize carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
Novolin R is a sterile, aqueous, and colorless solution of human insulin with a short duration of action. The pharmacologic effect of Novolin R begins approximately one-half (½) hour after subcutaneous administration. The effect is maximal between 2½ and 5 hours and terminates after approximately 8 hours. The onset of action of intravenous insulin is more rapid.
Novolin R is indicated for subcutaneous administration for the treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus, for the control of hyperglycemia. Treatment with Novolin R is as an adjunct to diet and exercise for lowering blood glucose in patients with Type 1 diabetes or in patients with Type 2 diabetes for whom oral antidiabetic therapy is inadequate.
Novolin R may be administered intravenously under proper medical supervision in a clinical setting for glycemic control. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION and RECOMMENDED STORAGE.)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Insulin is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia and in patients hypersensitive to Novolin R or one of its excipients.
Warnings
Any change of insulin dose should be made cautiously and only under medical supervision. Changes in insulin strength, manufacturer, type (e.g. regular, NPH, analog, etc.), species (animal, human), or method of manufacture (rDNA versus animal-source insulin) may result in the need for a change in dosage.
Special care should be taken when the transfer is from a standard beef or mixed species insulin to a purified pork or human insulin. If a dosage adjustment is needed, it will usually become apparent either in the first few days or over a period of several weeks. Any change in treatment should be carefully monitored.
General
Hypoglycemia, hypokalemia, lipodystrophy and hypersensitivity are among the potential clinical adverse effects associated with the use of all insulins.
As with all insulin preparations, the time course of Novolin R action may vary in different individuals or at different times in the same individual and is dependent on dose, site of injection, blood supply, temperature, and physical activity.
Adjustment of dosage of any insulin may be necessary if patients change their physical activity or their usual meal plan. Insulin requirements may be altered during illness, emotional disturbances, or other stresses.
Novolin R should only be used if it is clear and colorless. Due to the risk of precipitation in some pump catheters, Novolin R is not recommended for use in insulin pumps.
Hypoglycemia and hypokalemia - As with all insulin preparations, hypoglycemic and hypokalemic reactions may be associated with the administration of Novolin R, particularly via the IV route. Rapid changes in serum glucose levels may induce symptoms of hypoglycemia in persons with diabetes, regardless of the glucose value. Early warning symptoms of hypoglycemia may be different or less pronounced under certain conditions, such as long duration of diabetes, diabetic nerve disease, use of medications such as beta-blockers, or intensified diabetes control (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions). Such situations may result in severe hypoglycemia (and, possibly, loss of consciousness) prior to patients' awareness of hypoglycemia. Severe hypoglycemia can result in temporary or permanent impairment of brain function and death. Insulin stimulates potassium movement into the cells, possibly leading to hypokalemia that left untreated may cause respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia, and death. Since intravenously administered insulin has a rapid onset of action, increased attention to hypoglycemia and hypokalemia is necessary. Therefore, glucose and potassium levels must be monitored closely when Novolin R or any other insulin is administered intravenously.
In certain cases, the nature and intensity of the warning symptoms of hypoglycemia may change. A few patients have reported that after being transferred to human insulin, the early warning symptoms for hypoglycemia had been less pronounced than they were with animal-source insulin.
Hyperglycemia and ketosis - Hyperglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, or diabetic coma may develop if the patient takes less Novolin R than needed to control blood glucose levels. This could be due to insulin demand during illness or infection, neglect of diet, omission or improper administration of prescribed insulin doses. A developing ketoacidosis will be revealed by urine tests which show large amounts of sugar and acetone. The symptoms of polydipsia, polyurea, loss of appetite, fatigue, dry skin and deep and rapid breathing come on gradually, usually over a period of some hours or days. Severe sustained hyperglycemia may result in diabetic coma or death.
Renal Impairment - As with other insulins, the dose requirements for Novolin R may be reduced in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment - As with other insulins, the dose requirements for Novolin R may be reduced in patients with hepatic impairment.
Allergy
Local Allergy - As with other insulin therapy, patients may experience redness, swelling, or itching at the site of injection. These minor reactions usually resolve in a few days to a few weeks, but in some occasions, may require discontinuation of Novolin R. In some instances, these reactions may be related to factors other than insulin, such as irritants in a skin cleansing agent or poor injection technique.
Systemic Allergy - Less common, but potentially more serious, is generalized allergy to insulin, which may cause rash (including pruritus) over the whole body, shortness of breath, wheezing, reduction in blood pressure, rapid pulse, or sweating. Severe cases of generalized allergy, including anaphylactic reaction, may be life threatening. Localized reactions and generalized myalgias have been reported with the use of cresol as an injectable excipient.
Usage in Pregnancy
It is particularly important for patients to maintain good control of diabetes during pregnancy and special attention must be paid to diet, exercise and insulin regimens. Female patients should be advised to tell their physician if they intend to become, or if they become pregnant.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed about potential risks and advantages of Novolin R therapy including the possible side effects. Patients should also be offered continued education and advice on insulin therapies, injection technique, life-style management, regular glucose monitoring, periodic glycosylated hemoglobin testing, recognition and management of hypo- and hyperglycemia, adherence to meal planning, complications of insulin therapy, timing of dose, instruction in the use of injection devices, and proper storage of insulin. Patients should be informed that frequent, patient performed blood glucose measurements are needed to achieve optimal glycemic control and avoid both hyper- and hypoglycemia. Female patients should be advised to tell their physician if they intend to become, or if they become pregnant.
Laboratory Tests
As with all insulin therapy, the therapeutic response to Novolin R should be monitored by periodic blood glucose tests. Periodic measurement of glycosylated hemoglobin is recommended for the monitoring of long-term glycemic control. Urine ketones should be monitored frequently.
When Novolin R is administered intravenously, glucose and potassium levels must be closely monitored to avoid potentially fatal hypoglycemia and hypokalemia.
Drug Interactions
A number of substances affect glucose metabolism and may require insulin dose adjustment and particularly close monitoring.
- The following are examples of substances that may reduce insulin requirement: oral hypoglycemic agents (OHA), octreotide, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), non-selective beta-blocking agents, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, salicylates, alcohol, sulphonamide antibiotics, anabolic steroids, quinine, quinidine and alpha-adrenergic blocking agents.
- The following are examples of substances that may increase insulin requirement: oral contraceptives, thiazides, glucocorticoids, thryroid hormones and sympathomimetics, growth hormone, diazoxide, asparaginase and nicotinic acid.
- Beta-blocking agents may mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia and delay recovery from hypoglycemia.
- Alcohol may intensify and prolong the hypoglycemic effect of insulin.
Mixing of Insulins
- Novolin R should only be mixed as directed by the physician.
- Novolin R is a short-acting insulin and is often used in combination with intermediate- or long-acting insulins.
- The order of mixing and brand or model of syringe should be specified by the physician. A U-100 insulin syringe should always be used. Failure to use the correct syringe can lead to dosage errors.
- In general, when a longer-acting insulin (e.g. NPH insulin isophane suspensions) is mixed with short-acting soluble insulin (e.g., regular), the short-acting insulin should be drawn into the syringe first.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse events commonly associated with human insulin therapy include the following:
Body as Whole - Allergic reactions (see PRECAUTIONS, Allergy).
Skin and Appendages - Injection site reaction, lipodystrophy, pruritus, rash (see PRECAUTIONS, Allergy).
Other - Hypoglycemia, Hyperglycemia and ketosis (see PRECAUTIONS).
OVERDOSAGE
Excess insulin may cause hypoglycemia and hypokalemia, particularly after IV administration. Hypoglycemia may occur as a result of an excess of insulin relative to food intake, energy expenditure, or both. Mild episodes of hypoglycemia usually can be treated with oral glucose. Adjustments in drug dosage, meal patterns, or exercise, may be needed. More severe episodes with coma, seizure, or neurologic impairment may be treated with intramuscular/subcutaneous glucagon or concentrated intravenous glucose. Sustained carbohydrate intake and observation may be necessary because hypoglycemia may recur after apparent clinical recovery. Hypokalemia must be corrected appropriately.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Novolin R, when used alone subcutaneously, is usually given three or more times daily before meals. The dosage and timing of Novolin R should be individualized and determined, based on the physician's advice, in accordance with the needs of the patient. Novolin R may also be used in combination with oral antidiabetic agents or longer-acting insulin products to suit the needs of the individual patients. The injection of Novolin R should be followed by a meal within approximately 30 minutes of administration.
The average range of total daily insulin requirement for maintenance therapy in insulin-treated patients lies between 0.5 and 1.0 IU/kg. However, in pre-pubertal children it usually varies from 0.7 to 1.0 IU/kg, but can be much lower during the period of partial remission. In severe insulin resistance, e.g. during puberty or due to obesity, the daily insulin requirement may be substantially higher. Initial dosages for Type 2 diabetes patients are often lower, e.g. 0.2 to 0.4 IU/kg/day.
Novolin R should be administered by subcutaneous injection in the abdominal wall, the thigh, the gluteal region or in the upper arm. Subcutaneous injection into the abdominal wall ensures a faster absorption than from other injection sites. Injection into a lifted skin fold minimizes the risk of intramuscular injection. Injection sites should be rotated within the same region. As with all insulins, the duration of action will vary according to the dose, injection site, blood flow, temperature, and level of physical activity.
Intramuscular and intravenous administrations of Novolin R are possible under medical supervision with close monitoring of blood glucose and potassium levels to avoid hypoglycemia and hypokalemia.
For intravenous use, Novolin R should be used at concentrations from 0.05 U/mL to 1.0 U/mL in infusion systems with the infusion fluids 0.9% sodium chloride, 5% dextrose, or 10% dextrose with 40 mmol/l potassium chloride using polypropylene infusion bags.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Never use Novolin R if it has become viscous (thickened) or cloudy; use it only if it is clear and colorless. Novolin R should not be used after the printed expiration date.
RECOMMENDED STORAGE
Novolin R vials, Novolin® R PenFill® cartridges, and Novolin® R InnoLet® prefilled insulin syringes should be stored in a cold (36° - 46°F [2° - 8°C]) place, preferably in a refrigerator, but not in the freezer. Do not freeze. Keep Novolin R vials, Novolin R PenFill cartridges and Novolin R InnoLet in their cartons so that they will stay clean and protected from light. They should not be exposed to heat or sunlight. A Novolin R vial in use can be kept unrefrigerated as long as it is kept as cool as possible and away from heat or sunlight. A Novolin R PenFill cartridge and Novolin R InnoLet in use should not be refrigerated but should be kept as cool as possible (below 86°F [30°C]) and away from direct heat and light. Unrefrigerated Novolin R PenFill cartridges and Novolin R InnoLet must be discarded 28 days after the first use, even if they still contain Novolin R insulin.
Infusion bags prepared as indicated under DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION are stable at room temperature for 24 hours. A certain amount of insulin will be initially adsorbed to the material of the infusion bag.
Never use insulin after the expiration date which is printed on the label and carton.
HOW SUPPLIED
Novolin R, Regular, Human Insulin Injection (rDNA origin) USP, 100 units/mL, is supplied as follows:
10 mL vial NDC 0169-1833-11
3 mL PenFill cartridges* NDC 0169-3473-18
3 mL Novolin R InnoLet NDC 0169-2313-21
*Novolin R PenFill 3 mL cartridges are designed for use with Novo Nordisk 3 mL PenFill cartridge compatible insulin delivery devices, the NovoPen® 3 PenMate® and with NovoFine® disposable needles.
Date of issue: October 21, 2005
ReliOn®
For information contact: Novo Nordisk Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540
1-800-727-6500
www.novonordisk-us.com
Manufactured by: Novo Nordisk A/S, DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
Novo Nordisk®, Novolin®, PenFill®, InnoLet®, NovoPen®, PenMate® and NovoFine® are trademarks owned by Novo Nordisk A/S.
ReliOn® trademark owned by Access LLC
ReliOn® is licensed by Novo Nordisk Inc.
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
R Human
Patient Information for Novolin® R
NOVOLIN® R (NO-voe-lin)
Regular,
Human Insulin Injection
(recombinant DNA origin) USP 100 units/mL
Important:
Know your insulin. Do not change the type of insulin you use unless told to do so by your healthcare provider. The amount of insulin you take as well as the best time for you to take your insulin may need to change if you take a different type of insulin.
Make sure that you know the type and strength of insulin that is prescribed for you.
Read the Patient Information leaflet that comes with Novolin R before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your diabetes or your treatment. Make sure you know how to manage your diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider if you have any questions about managing your diabetes.
What is Novolin R?
Novolin R is a man-made insulin (recombinant DNA origin) that is structurally identical to the insulin produced by the human pancreas that is used to control high blood sugar in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Who should not use Novolin R?
Do not take Novolin R if:
- Your blood sugar is too low (hypoglycemia).
- You are allergic to anything in Novolin R. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Novolin R. Check with your healthcare provider if you are not sure.
Tell your healthcare provider:
- about all of your medical conditions. Medical conditions can affect your insulin needs and your dose of Novolin R.
- if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. You and your healthcare provider should talk about the best way to manage your diabetes while you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Novolin R has not been studied in pregnant or nursing women.
- about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Many medicines can affect your blood sugar levels and your insulin needs. Your Novolin R dose may need to change if you take other medicines.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show all your healthcare providers when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Novolin R?
Only use Novolin R if it appears clear and colorless. There may be air bubbles. This is normal. If it looks cloudy, thickened, or colored, or if it contains solid particles do not use it, and call Novo Nordisk at 1-800-727-6500.
Novolin R comes in:
- 10 mL vials (small bottles) for use with syringe
Read the instructions for use that come with your Novolin R product. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any questions. Your healthcare provider should show you how to inject Novolin R before you start taking it. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions to make changes to your insulin dose.
- Take Novolin R exactly as prescribed.
- Novolin R is a fast-acting insulin. The effects of Novolin R start working ½ hour after injection.
- The greatest blood sugar lowering effect is between 2½ and 5 hours after the injection. This blood sugar lowering lasts for 8 hours.
- While using Novolin R you may have to change your total dose of insulin, your dose of longer-acting insulin, or the number of injections of longer-acting insulin you use.
- Do not mix Novolin R with any insulins other than NPH in the same syringe.
- Inject Novolin R into the skin of your stomach area, upper arms, buttocks or upper legs. Novolin R may affect your blood sugar levels sooner if you inject it into the skin of your stomach area. Never inject Novolin R into a vein or into a muscle.
- Due to risk of precipitation in some pump catheters, Novolin R is not recommended for use in insulin pumps.
- Change (rotate) your injection site within the chosen area (for example, stomach or upper arm) with each dose. Do not inject into the same spot for each injection.
- If you take too much Novolin R, your blood sugar may fall low (hypoglycemia). You can treat mild low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) by drinking or eating something sugary right away (fruit juice, sugar candies, or glucose tablets). It is important to treat low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) right away because it could get worse and you could pass out (become unconscious). If you pass out, you will need help from another person or emergency medical services right away, and will need treatment with a glucagon injection or treatment at a hospital. See "What are the possible side effects of Novolin R?" for more information on low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
- If you forget to take your dose of Novolin R, your blood sugar may go too high (hyperglycemia). If high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) is not treated it can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which can lead to serious problems, like loss of consciousness (passing out), coma or even death. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions for treating high blood sugar (hyperglycemia), and talk to your healthcare provider if high blood sugar is a problem for you. Severe or continuing high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) requires prompt evaluation and treatment by your healthcare provider. Know your symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) and diabetic ketoacidosis which may include:
| • increased thirst | • fruity smell on breath |
| • frequent urination and dehydration | • high amounts of sugar and ketones in your urine |
| • confusion or drowsiness | • nausea, vomiting (throwing up) or stomach pain |
| • loss of appetite | • a hard time breathing |
- Check your blood sugar levels. Ask your healthcare provider how often you should check your blood sugar levels for hypoglycemia (too low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (too high blood sugar).
Your insulin dosage may need to change because of:
| • illness | • change in diet |
| • stress | • change in physical activity or exercise |
| • other medicines you take | • surgery |
See the end of this patient information for instructions about preparing and giving the injection.
What should I avoid while using Novolin R?
- Alcohol. Alcohol, including beer and wine, may affect your blood sugar when you take Novolin R.
-
Driving and operating machinery. You may have difficulty concentrating or reacting if you have low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Be careful when you drive a car or operate machinery. Ask your healthcare provider if it is alright to drive if you often have:
- low blood sugar
- decreased or no warning signs of low blood sugar
What are the possible side effects of Novolin R?
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) may include:
| • sweating | • trouble concentrating or confusion |
| • dizziness or lightheadedness | • blurred vision |
| • shakiness | • slurred speech |
| • hunger | • anxiety, irritability or mood changes |
| • fast heart beat | • headache |
| • tingling of lips and tongue |
Severe low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can cause unconsciousness (passing out), seizures, and death. Know your symptoms of low blood sugar. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for treating low blood sugar. Talk to your healthcare provider if low blood sugar is a problem for you.
- Serious allergic reaction (whole body reaction). Get medical help right away if you develop a rash over your whole body, have trouble breathing, a fast heartbeat, or sweating.
- Reactions at the injection site (local allergic reaction). You may get redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site. If you keep having skin reactions, or they are serious, talk to your healthcare provider. You may need to stop using Novolin R and use a different insulin. Do not inject insulin into skin that is red, swollen, or itchy.
- Skin thickens or pits at the injection site (lipodystrophy). Change (rotate) where you inject your insulin to help prevent these skin changes from happening. Do not inject insulin into this type of skin.
- Swelling of your hands and feet
- Vision changes
- Low potassium in your blood (hypokalemia)
These are not all of the possible side effects from Novolin R. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Novolin R?
All Unopened Novolin R:
- Keep all unopened Novolin R in the refrigerator between 36° to 46°F (2° to 8°C).
- Do not freeze. Do not use Novolin R if it has been frozen.
- If refrigeration is not possible, the unopened vial may be kept at room temperature for up to 6 weeks (42 days), as long as it is kept at or below 77°F (25°C).
- Keep unopened Novolin R in the carton to protect from light.
Novolin R in use:
Vials
- Keep at room temperature below 77°F (25°C) for up to 6 weeks (42 days).
- Keep vials away from direct heat or light.
- Throw away an opened vial after 6 weeks (42 days) of use, even if there is insulin left in the vial.
- Unopened vials can be used until the expiration date on the Novolin R label, if the medicine has been stored in a refrigerator.
General advice about Novolin R
Novolin R is used for the treatment of diabetes only. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in the patient leaflet. Do not use Novolin R for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Novolin R to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Novolin R. If you would like more information about Novolin R or diabetes, talk with your healthcare provider. For more information, call 1-800-727-6500 or visit www.novonordisk-us.com.
Helpful information for people with diabetes is published by the American Diabetes Association, 1701 N Beauregard Street, Alexandria, VA 22311 and on www.diabetes.org.
Novolin R ingredients include:
| • Regular Human Insulin Injection (recombinant DNA origin) USP | • Metacresol |
| • Zinc chloride | • Glycerol |
| • Sodium hydroxide | • Hydrochloric acid |
| • Water for injections |
All Novolin R vials are latex-free.
ReliOn®
Date of issue: May 14, 2010
Version: 5
Novolin® and Novo Nordisk® are trademarks of Novo Nordisk A/S.
ReliOn® is a trademark owned by Access LLC
ReliOn® is licensed by Novo Nordisk Inc.
© 2005-2010 Novo Nordisk A/S
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
For information about Novolin R contact:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
100 College Road West
Princeton, New Jersey 08540
Patient Instructions for Use
Novolin® R 10 mL vial (100 Units/mL, U-100)
Before starting, gather all of the supplies that you will need to use for preparing and giving your insulin injection.
Never re-use syringes and needles.
How should I use the Novolin R vial?
- Check to make sure that you have the correct type of insulin. This is especially important if you use different types of insulin.
- Look at the vial and the insulin. The insulin should be clear and colorless. The tamper-resistant cap should be in place before the first use. If the cap had been removed before your first use of the vial, or if the insulin is cloudy, colored, or contains any particles, do not use it and call Novo Nordisk at 1-800-727-6500.
- Wash your hands with soap and water. If you clean your injection site with an alcohol swab, let the injection site dry before you inject. Talk with your healthcare provider about how to rotate injection sites and how to give an injection.
- If you are using a new vial, pull off the tamper-resistant cap. Wipe the rubber stopper with an alcohol swab.
- Do not roll or shake the vial. Shaking right before the dose is drawn into the syringe may cause bubbles or froth. This can cause you to draw up the wrong dose of insulin.
- Pull back the plunger on the syringe until the black tip reaches the marking for the number of units you will inject.
- Push the needle through the rubber stopper of the vial, and push the plunger all the way in to force air into the vial.
- Turn the vial and syringe upside down and slowly pull the plunger back to a few units beyond the correct dose.
- If there are any air bubbles, tap the syringe gently with your finger to raise the air bubbles to the top. Then slowly push the plunger to the marking for your correct dose. This process should move any air bubbles present in the syringe back into the vial.
- Check to make sure you have the right dose of Novolin R in the syringe.
- Pull the syringe with needle out of the vial’s rubber stopper.
- Your doctor should tell you if you need to pinch the skin before inserting the needle. This can vary from patient to patient so it is important to ask your doctor if you did not receive instructions on pinching the skin. Insert the needle into the skin. Press the plunger of the syringe to inject the insulin. When you are finished injecting the insulin, pull the needle out of your skin. You may see a drop of Novolin R at the needle tip. This is normal and has no effect on the dose you just received. If you see blood after you take the needle out of your skin, press the injection site lightly with a piece of gauze or an alcohol wipe. Do not rub the area.
- After your injection, do not recap the needle. Place used syringes, needles and used insulin vials in a disposable puncture-resistant sharps container, or some type of hard plastic or metal container with a screw on cap such as a detergent bottle or coffee can.
- Ask your healthcare provider about the right way to throw away used syringes and needles. There may be state or local laws about the right way to throw away used syringes and needles. Do not throw away used needles and syringes in household trash or recycle.
How should I mix Novolin R with NPH insulin?
Different insulins should be mixed only under instruction from a healthcare provider. Do not mix Novolin R with any other type of insulin besides NPH insulin. Novolin R should be mixed only when injections with syringes are used. Insulin syringes may vary in the amount of space between the bottom line and the needle (“dead space”), so if you are mixing two types of insulin be sure to discuss any change in the model and brand of syringe you are using with your healthcare provider. Novolin R can be mixed with NPH insulin right before use. When you are mixing Novolin R insulin with NPH insulin, always draw the Novolin R (clear) insulin into the syringe first.
- Add together the doses (total number of units) of NPH and Novolin R that you need to inject. The total dose will determine the final amount (volume) in the syringe after drawing up both insulins into the syringe. For example, if you need 5 units of NPH and 2 units of Novolin R, the total dose of insulin in the syringe would be 7 units.
- Roll the NPH vial between your hands until the liquid is equally cloudy throughout.
- Draw into the syringe the same amount of air as the NPH dose. Inject this air into the NPH vial and then remove the needle from the vial but do not withdraw any of the NPH insulin. (Transferring NPH to the Novolin R vial will contaminate the Novolin R vial and may change how quickly it works.)
- Draw into the syringe the same amount of air as the Novolin R dose. Inject this air into the Novolin R vial. With the needle in place, turn the vial upside down and withdraw the correct dose of Novolin R. The tip of the needle must be in the Novolin R to get the full dose and not an air dose.
- After withdrawing the needle from the Novolin R vial, insert the needle into the NPH vial. Turn the NPH vial upside down with the syringe and needle still in it. Withdraw the correct dose of NPH.
- Inject right away to avoid changes in how quickly the insulin works.
Package/Label Principal Display Panel
NDC 59060-1833-2
Novolin®R
Regular Human Insulin Injection
(recombinant DNA origin) USP
100 units/mL • 10mL
ReliOn®
| NOVOLIN
R
regular human insulin injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA019938 | 06/15/2000 | 06/30/2012 |
| Labeler - Novo Nordisk Inc. (012177531) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Novo Nordisk Pharmaceuticals Industries Inc. | 622920320 | MANUFACTURE | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Novo Nordisk A/S | 305156788 | API MANUFACTURE | |
Revised: 12/2011 Novo Nordisk Inc.