PROMETHAZINE VC WITH CODEINE- promethazine and phenylephrine hydrochloride and codeine phosphate solution
A-S Medication Solutions
----------
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution
(Promethazine HCl, Phenylephrine HCl and Codeine Phosphate Oral Solution)
WARNING: ULTRA RAPID METABOLISM OF CODEINE AND OTHER RISK FACTORS FOR LIFE-THREATENING RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION IN CHILDREN and RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH BENZODIAZEPINES OR OTHER CNS DEPRESSANTS
Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Other Risk Factors for Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Children
Life-threatening respiratory depression and death have occurred in children who received codeine. Most of the reported cases occurred following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy, and many of the children had evidence of being an ultra-rapid metabolizer of codeine due to a CYP2D6 polymorphism. Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated in children younger than 12 years of age and in children younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). Avoid the use of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution in adolescents 12 to 18 years of age who have other risk factors that may increase their sensitivity to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine. (See WARNINGS - Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression).
Promethazine and Respiratory Depression in Children
Postmarketing cases of respiratory depression, including fatalities have been reported with use of promethazine in pediatric patients. Children may be particularly sensitive to the additive respiratory depressant effects when promethazine is combined with other respiratory depressants, including codeine. (See WARNINGS - Promethazine and Respiratory Depression in Children).
Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants
Concomitant use of opioids with benzodiazepines or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death (see WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS - Drug Interactions). Avoid use of opioid cough medications in patients taking benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol.
DESCRIPTION
Each 5 mL (one teaspoonful), for oral administration contains: Codeine phosphate 10 mg; promethazine hydrochloride 6.25 mg; phenylephrine hydrochloride 5 mg in a flavored syrup base with a pH between 4.4 and 5.2. Alcohol 7%.
Inactive ingredients: Ascorbic acid, citric acid, D&C Red #33, FD&C Yellow #6, menthol, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, saccharin sodium, sodium benzoate, sodium citrate, strawberry flavor and sucrose.
Codeine is one of the naturally occurring phenanthrene alkaloids of opium derived from the opium poppy, it is classified pharmacologically as a narcotic analgesic. Codeine phosphate may be chemically designated as 7,8-Didehydro-4, 5α-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6α-ol phosphate (1:1) (salt) hemihydrate.
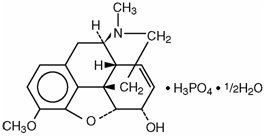
The phosphate salt of codeine occurs as white, needle-shaped crystals or white crystalline powder. Codeine phosphate is freely soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. It has a molecular weight of 406.37, a molecular formula of C18H21NO3 • H3PO4 • ½ H2O and the following structural formula:
Promethazine hydrochloride, a phenothiazine derivative, is chemically designated as (±)-10-[2- (Dimethylamino)propyl] phenothiazine monohydrochloride.
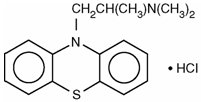
Promethazine hydrochloride occurs as a white to faint yellow, practically odorless, crystalline powder which slowly oxidizes and turns blue on prolonged exposure to air. It is soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol. It has a molecular weight of 320.88, a molecular formula of C17H20N2S • HCl, and the following structural formula:
Phenylephrine hydrochloride is a sympathomimetic amine salt which is chemically designated as (-)-m-hydroxy-α-[(methyl-amino) methyl] benzyl alcohol hydrochloride. It occurs as white or nearly white crystals, having a bitter taste. It is freely soluble in water and alcohol.
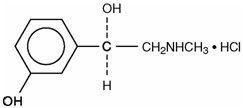
Phenylephrine hydrochloride is subject to oxidation and must be protected from light and air. It has a molecular weight of 203.67, a molecular formula of C9H13NO2 • HCl and the following structural formula:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Codeine
Narcotic analgesics, including codeine, exert their primary effects on the central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. The analgesic effects of codeine are due to its central action; however, the precise sites of action have not been determined, and the mechanisms involved appear to be quite complex. Codeine resembles morphine both structurally and pharmacologically, but its actions at the doses of codeine used therapeutically are milder, with less sedation, respiratory depression and gastrointestinal, urinary, and pupillary effects. Codeine produces an increase in biliary tract pressure, but less than morphine or meperidine. Codeine is less constipating than morphine.
Codeine has good antitussive activity, although less than that of morphine at equal doses. It is used in preference to morphine, because side effects are infrequent at the usual antitussive dose of codeine.
Codeine in oral therapeutic dosage does not usually exert major effects on the cardiovascular system. Narcotic analgesics may cause nausea and vomiting by stimulating the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ); however, they also depress the vomiting center, so that subsequent doses are unlikely to produce vomiting. Nausea is minimal after usual oral doses of codeine.
Narcotic analgesics cause histamine release, which appears to be responsible for wheals or urticaria sometimes seen at the site of injection on parenteral administration. Histamine release may also produce dilation of cutaneous blood vessels, with resultant flushing of the face and neck, pruritus, and sweating.
Codeine and its salts are well absorbed following both oral and parenteral administration. Codeine is about 2/3 as effective orally as parenterally. Codeine is metabolized primarily in the liver by enzymes of the endoplasmic reticulum, where it undergoes O-demethylation, N-demethylation, and partial conjugation with glucuronic acid. The drug is excreted primarily in the urine, largely as inactive metabolites and small amounts of free and conjugated morphine. Negligible amounts of codeine and its metabolites are found in the feces.
Following oral or subcutaneous administration of codeine, the onset of analgesia occurs within 15 to 30 minutes and lasts for four to six hours.
The cough-depressing action, in animal studies, was observed to occur 15 minutes after oral administration of codeine, peak action at 45 to 60 minutes after ingestion. The duration of action, which is dose-dependent, usually did not exceed 3 hours.
Promethazine
Promethazine is a phenothiazine derivative which differs structurally from the antipsychotic phenothiazines by the presence of a branched side chain and no ring substitution. It is thought that this configuration is responsible for its relative lack (1/10 that of chlorpromazine) of dopamine antagonist properties.
Promethazine is an H1 receptor blocking agent. In addition to its antihistaminic action, it provides clinically useful sedative and antiemetic effects. Promethazine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Clinical effects are apparent within 20 minutes after oral administration and generally last four to six hours, although they may persist as long as 12 hours. Promethazine is metabolized by the liver to a variety of compounds; the sulfoxides of promethazine and N-demethylpromethazine are the predominant metabolites appearing in the urine.
Phenylephrine
Phenylephrine is a potent postsynaptic-α-receptor agonist with little effect on β receptors of the heart. Phenylephrine has no effect on β-adrenergic receptors of the bronchi or peripheral blood vessels. A direct action at receptors accounts for the greater part of its effects, only a small part being due to its ability to release norepinephrine.
Therapeutic doses of phenylephrine mainly cause vasoconstriction. Phenylephrine increases resistance and, to a lesser extent, decreases capacitance of blood vessels. Total peripheral resistance is increased, resulting in increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Pulmonary arterial pressure is usually increased, and renal blood flow is usually decreased. Local vasoconstriction and hemostasis occur following topical application or infiltration of phenylephrine into tissues.
The main effect of phenylephrine on the heart is bradycardia; it produces a positive inotropic effect on the myocardium in doses greater than those usually used therapeutically. Rarely, the drug may increase the irritability of the heart, causing arrhythmias. Cardiac output is decreased slightly. Phenylephrine increases the work of the heart by increasing peripheral arterial resistance. Phenylephrine has a mild central stimulant effect.
Following oral administration or topical application of phenylephrine to the mucosa, constriction of blood vessels in the nasal mucosa relieves nasal congestion associated with allergy or head colds. Following oral administration, nasal decongestion may occur within 15 or 20 minutes and may persist for up to 4 hours.
Phenylephrine is irregularly absorbed from and readily metabolized in the gastrointestinal tract. Phenylephrine is metabolized in the liver and intestine by monoamine oxidase. The metabolites and their route and rate of excretion have not been identified. The pharmacologic action of phenylephrine is terminated at least partially by uptake of the drug into tissues.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is indicated for the temporary relief of coughs and upper respiratory symptoms, including nasal congestion, associated with allergy or the common cold.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age. (See WARNINGS - Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression).
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated for post-operative management in children younger than 18 years of age who following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy. (See WARNINGS - Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression).
Codeine is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to the drug.
Promethazine is contraindicated in comatose states, and in individuals known to be hypersensitive or to have had an idiosyncratic reaction to promethazine or to other phenothiazines.
Antihistamines and codeine are both contraindicated for use in the treatment of lower respiratory tract symptoms, including asthma.
Phenylephrine is contraindicated in patients with hypertension or with peripheral vascular insufficiency (ischemia may result with risk of gangrene or thrombosis of compromised vascular beds). Phenylephrine should not be used in patients known to be hypersensitive to the drug or in those receiving a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI).
WARNINGS
Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Other Risk Factors for Life-threatening Respiratory Depression in Children
Life-threatening respiratory depression and death have occurred in children who received codeine. Codeine is subject to variability in metabolism based upon CYP2D6 genotype (described below), which can lead to an increased exposure to the active metabolite morphine. Based upon post-marketing reports, children less than 12 years old appear to be more susceptible to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine, particularly if there are risk factors for respiratory depression. For example, many reported cases of death occurred in the post-operative period following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy, and many of the children had evidence of being ultra-rapid metabolizers of codeine. Furthermore, children with obstructive sleep apnea who are treated with codeine for post-tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy pain may be particularly sensitive to its respiratory depressant effect. Because of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression and death:
-
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated in all children younger than 12 years of age. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS).
-
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated for post-operative management in pediatric patients younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS).
-
Avoid the use of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution in adolescents 12 to 18 years of age who have other risk factors that may increase their sensitivity to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine. Risk factors include conditions associated with hypoventilation, such as postoperative status, obstructive sleep apnea, obesity, severe pulmonary disease, neuromuscular disease, and concomitant use of other medications that cause respiratory depression.
-
When prescribing codeine for adolescents, healthcare providers should choose the lowest effective dose for the shortest period of time and inform patients and caregivers about these risks and the signs of morphine overdose. (See OVERDOSAGE).
Nursing Mothers
At least one death was reported in a nursing infant who was exposed to high levels of morphine in breast milk because the mother was an ultra-rapid metabolizer of codeine. Breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution. (See PRECAUTIONS -Nursing Mothers).
CYP2D6 Genetic Variability: Ultra-rapid metabolizer
Some individuals may be ultra-rapid metabolizers because of a specific CYP2D6 genotype (e.g., gene duplications denoted as *1/*1xN or *1/*2xN). The prevalence of this CYP2D6 phenotype varies widely and has been estimated at 1 to 10% for Whites (European, North American), 3-4% for Blacks (African Americans), 1-2% for East Asians (Chinese, Japanese, Korean), and may be greater than 10% in certain ethnic groups (i.e., Oceanian, Northern African, Middle Eastern, Ashkenazi Jews, Puerto Rican). These individuals convert codeine into its active metabolite, morphine, more rapidly and completely than other people. This rapid conversion results in higher than expected serum morphine levels. Even at labeled dosage regimens, individuals who are ultra-rapid metabolizers may have life-threatening or fatal respiratory depression or experience signs of overdose (such as extreme sleepiness, confusion, or shallow breathing). (See OVERDOSAGE). Therefore, individuals who are ultra-rapid metabolizers should not use codeine.
Promethazine and Respiratory Depression in Children
Postmarketing cases of respiratory depression, including fatalities have been reported with use of promethazine in pediatric patients. Concomitant administration with other respiratory depressants may increase the risk of respiratory depression. Children may be particularly sensitive to the additive respiratory depressant effects when promethazine is combined with other respiratory depressants, including codeine. See WARNINGS -Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression for limitations on the use of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution in children.
-
Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants Concomitant use of opioids, including Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution, with benzodiazepines, or other CNS depressants, including alcohol, may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Because of these risks, avoid use of opioid cough medications in patients taking benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol. (See PRECAUTIONS - Drug Interactions).
Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioids alone. Because of similar pharmacologic properties, it is reasonable to expect similar risk with concomitant use of opioid cough medications and benzodiazepines, other CNS depressants, or alcohol.
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation if Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is used with benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other CNS depressants. (See PRECAUTIONS -Information for Patients).
-
Dosage of codeine SHOULD NOT BE INCREASED if cough fails to respond; an unresponsive cough should be re-evaluated in 5 days or sooner for possible underlying pathology, such as a foreign body or lower respiratory tract disease.
-
Codeine may cause or aggravate constipation.
-
Administration of codeine may be accomplished by histamine release and should be used with caution in atopic children.
-
Head Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure
The respiratory-depressant effects of narcotic analgesics and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, intracranial lesions, or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. Narcotics may produce adverse reactions which may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries.
-
Asthma and Other Respiratory Conditions
Narcotic analgesics or cough suppressants, including codeine, should not be used in asthmatic patients (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). Nor should they be used in acute febrile illness associated with productive cough or in chronic respiratory disease where interference with ability to clear the tracheobronchial tree of secretions would have a deleterious effect on the patient's respiratory function.
- Hypotensive Effect
Codeine may produce orthostatic hypotension in ambulatory patients.
Promethazine
• CNS Depression
Promethazine may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks, such as driving a vehicle or operating machinery. The impairment may be amplified by concomitant use of other central nervous system depressants such as alcohol, sedatives/hypnotics (including barbiturates), narcotics, narcotic analgesics, general anesthetics, tricyclic antidepressants, and tranquilizers; therefore avoid use of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution in patients on these medications. (See PRECAUTIONS - Information for Patients and Drug Interactions).
• Respiratory Depression
Promethazine may lead to potentially fatal respiratory depression. Use of promethazine in patients with compromised respiratory function (e.g. COPD, sleep apnea) should be avoided.
• Lower Seizure Threshold
Promethazine may lower seizure threshold. It should be used with caution in persons with seizure disorders or in persons who are using concomitant medications, such as narcotics or local anesthetics, which may also affect seizure threshold.
• Bone-Marrow Depression
Promethazine should be used with caution in patients with bone marrow depression. Leukopenia and agranulocytosis have been reported, usually when promethazine HCl has been used in association with other known marrow toxic agents.
• Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
A potentially fatal symptom complex sometimes referred to as Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) has been reported in association with promethazine HCl alone or in combination with antipsychotic drugs. Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status and evidence of autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis and cardiac dysrhythmias).
The diagnostic evaluation of patients with this syndrome is complicated. In arriving at a diagnosis, it is important to identify cases where the clinical presentation includes both serious medical illness (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection, etc.) and untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal signs and symptoms (EPS). Other important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever and primary central nervous system (CNS) pathology.
The management of NMS should include 1) immediate discontinuation of promethazine HCl, antipsychotic drugs, if any, and other drugs not essential to concurrent therapy, 2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring, and 3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens for uncomplicated NMS.
Since recurrences of NMS have been reported with phenothiazines, the reintroduction of promethazine HCl should be carefully considered.
Use in Pediatric Patients
Life-threatening respiratory depression and death have occurred in children who received codeine. (See WARNINGS - Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression). In most of the reported cases, these events followed tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy, and many of the children had evidence of being ultra-rapid metabolizers of codeine (i.e., multiple copies of the gene for cytochrome P450 isoenzyme 2D6 or high morphine concentrations). Children with sleep apnea may be particularly sensitive to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine. Postmarketing cases of respiratory depression, including fatalities have been reported with use of promethazine in pediatric patients. (See WARNINGS - Promethazine and Respiratory Depression in Children). Because of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression and death:
-
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated in all children younger than 12 years of age. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS).
-
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated for post-operative pain management in pediatric patients of any age undergoing tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Avoid the use of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution in adolescents 12 to 18 years of age who have other risk factors that may increase their sensitivity to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine. Risk factors include postoperative status, obstructive sleep apnea, obesity and other conditions associated with hypoventilation syndromes (e.g. neuromuscular disease), concomitant use of other medications that cause respiratory depression, and severe pulmonary disease. (See WARNINGS - Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression).
Excessively large dosages of antihistamines, including promethazine hydrochloride, in pediatric patients may cause sudden death (see OVERDOSAGE). Hallucinations and convulsions have occurred with therapeutic doses and overdoses of promethazine hydrochloride in pediatric patients. In pediatric patients who are acutely ill associated with dehydration, there is an increased susceptibility to dystonias with the use of promethazine HCl.
Other Considerations
Administration of promethazine has been associated with reported cholestatic jaundice.
Phenylephrine
Because phenylephrine is an adrenergic agent, it should be given with caution to patients with thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus and heart diseases or those receiving tricyclic antidepressants.
Men with symptomatic, benign prostatic hypertrophy can experience urinary retention when given oral nasal decongestants.
Phenylephrine can cause a decrease in cardiac output, and extreme caution should be used when administering the drug parenterally or orally to patients with arteriosclerosis, to elderly individuals, and/or to patients with initially poor cerebral or coronary circulation.
Phenylephrine should be used with caution in patients taking diet preparations, such as amphetamines or phenylpropanolamine, because synergistic adrenergic effects could result in serious hypertensive response and possible stroke.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Narcotic analgesics, including codeine, should be administered with caution and the initial dose reduced in patients with acute abdominal conditions, convulsive disorders, significant hepatic or renal impairment, fever, hypothyroidism, Addison’s disease, ulcerative colitis, prostatic hypertrophy, in patients with recent gastrointestinal or urinary tract surgery and in the very young or elderly or debilitated patients.
Drugs having anticholinergic properties should be used with caution in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, stenosing peptic ulcer, pyloroduodenal obstruction, and bladder-neck obstruction.
Promethazine should be used cautiously in persons with cardiovascular disease, or with impairment of liver function.
Phenylephrine should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disease.
Information for Patients
Patients should be advised to measure Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution with an accurate measuring device. A household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and could lead to overdosage, especially when a half a teaspoon is measured. A pharmacist can recommend an appropriate measuring device and can provide instructions for measuring the correct dose.
Advise caregivers that Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated in all children younger than 12 years of age and in children younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy. Advise caregivers of children 12- 18 years of age receiving Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution to monitor for signs of respiratory depression. (See WARNINGS -Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression).
Advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution. (See WARNINGS - Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression).
Promethazine, phenylephrine and codeine may cause marked drowsiness or may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks, such as driving a vehicle or operating machinery. Ambulatory patients should be told to avoid engaging in such activities until it is known that they do not become drowsy or dizzy from promethazine, phenylephrine and codeine therapy. Pediatric patients should be supervised to avoid potential harm in bike riding or in other hazardous activities.
Inform patients and caregivers that potentially fatal additive effects may occur if Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is used with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol. Because of this risk, patients should avoid concomitant use of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol. (See WARNINGS - Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants).
Patients should be advised to report any involuntary muscle movements.
Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun.
Codeine, like other narcotic analgesics, may produce orthostatic hypotension in some ambulatory patients. Patients should be cautioned accordingly. Nursing mothers taking codeine can also have higher morphine levels in their breast milk if they are ultra-rapid metabolizers. These higher levels of morphine in breast milk may lead to life-threatening or fatal side effects in nursing babies. Instruct nursing mothers to watch for signs of morphine toxicity in their infants including increased sleepiness (more than usual), difficulty breastfeeding, breathing difficulties, or limpness. Instruct nursing mothers to talk to the baby's doctor immediately if they notice these signs and, if they can not reach the doctor right away, to take the baby to an emergency room or call 911 (or local emergency services).
Drug Interactions
Codeine
In patients receiving MAO inhibitors, an initial small test dose is advisable to allow observation of any excessive narcotic effects or MAOI interaction.
The use of benzodiazepines, opioids, antihistamines, antipsychotics, anti-anxiety agents, or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution may cause an additive CNS depressant effect, profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death and should be avoided. (See WARNINGS - Risks from Concomitant Use with Benzodiazepines or Other CNS Depressants).
Promethazine
Epinephrine: Because of the potential for promethazine to reverse epinephrine’s vasopressor effect, epinephrine should NOT be used to treat hypotension associated with promethazine overdose.
Anticholinergics: Concomitant use of other agents with anticholinergic properties should be undertaken with caution.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI): Drug interactions, including an increased incidence of extrapyramidal effects, have been reported when some MAOI and phenothiazines are used concomitantly.
Phenylephrine
| Drug | Effect |
| Phenylephrine with prior administration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI). | Cardiac pressor response potentiated. May cause acute hypertensive crisis. |
| Phenylephrine with tricyclic antidepressants. | Pressor response increased. |
| Phenylephrine with ergot alkaloids. | Excessive rise in blood pressure. |
| Phenylephrine with bronchodilator sympathomimetic agents and with epinephrine or other sympathomimetics. | Tachycardia or other arrhythmias may occur. |
| Phenylephrine with prior administration of propranolol or other β-adrenergic blockers. | Cardiostimulating effects blocked. |
| Phenylephrine with atropine sulfate. | Reflex bradycardia blocked; pressor response enhanced. |
| Phenylephrine with prior administration of phentolamine or other α-adrenergic blockers. | Pressor response decreased. |
| Phenylephrine with diet preparations, such as amphetamines or phenylpropanolamine. | Synergistic adrenergic response. |
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Because narcotic analgesics may increase biliary tract pressure, with resultant increase in plasma amylase or lipase levels, determination of these enzyme levels may be unreliable for 24 hours after a narcotic analgesic has been given.
The following laboratory tests may be affected in patients who are receiving therapy with promethazine hydrochloride.
Pregnancy Tests: Diagnostic pregnancy tests based on immunological reactions between HCG and anti-HCG may result in false-negative or false-positive interpretations.
Glucose Tolerance Test: An increase in blood glucose has been reported in patients receiving promethazine.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Codeine and Promethazine: Long-term animal studies have not been performed to assess the carcinogenic potential of codeine or of promethazine, nor are there other animal or human data concerning carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or impairment of fertility with these agents. Codeine has been reported to show no evidence of carcinogenicity or mutagenicity in a variety of test systems, including the micronucleus and sperm abnormality assays and the Salmonella assay. Promethazine was nonmutagenic in the Salmonella test system of Ames.
Phenylephrine: A study which followed the development of cancer in 143,574 patients over a four-year period indicated that in 11,981 patients who received phenylephrine (systemic or topical), there was no statistically significant association between the drug and cancer at any or all sites.
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to assess the carcinogenic potential of phenylephrine, nor are there other animal or human data concerning mutagenicity.
A study of the effects of adrenergic drugs on ovum transport in rabbits indicated that treatment with phenylephrine did not alter incidence of pregnancy; the number of implantations was significantly reduced when high doses of the drug were used.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C:
Codeine: A study in rats and rabbits reported no teratogenic effect of codeine administered during the period of organogenesis in doses ranging from 5 to 120 mg/kg. In the rat, doses at the 120-mg/kg level, in the toxic range for the adult animal, were associated with an increase in embryo resorption at the time of implantation. In another study a single 100-mg/kg dose of codeine administered to pregnant mice reportedly resulted in delayed ossification in the offspring.
There are no studies in humans, and the significance of these findings to humans, if any, is not known.
Promethazine: Teratogenic effects have not been demonstrated in rat-feeding studies at doses of 6.25 and 12.5 mg/kg of promethazine HCl. These doses are from approximately 2.1 to 4.2 times the maximum recommended total daily dose of promethazine for a 50-kg subject, depending on the indication for which the drug is prescribed. Daily doses of 25 mg/kg intraperitoneally have been found to produce fetal mortality in rats.
Specific studies to test the action of the drug on parturition, lactation, and development of the animal neonate were not done, but a general preliminary study in rats indicated no effect on these parameters. Although antihistamines have been found to produce fetal mortality in rodents, the pharmacological effects of histamine in the rodent do not parallel those in man. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of promethazine in pregnant women.
Phenylephrine: A study in rabbits indicated that continued moderate overexposure to phenylephrine (3 mg/day) during the second half of pregnancy (22nd day of gestation to delivery) may contribute to perinatal wastage, prematurity, premature labor, and possibly fetal anomalies; when phenylephrine (3 mg/day) was given to rabbits during the first half of pregnancy (3rd day after mating for seven days), a significant number gave birth to litters of low birth weight. Another study showed that phenylephrine was associated with anomalies of aortic arch and with ventricular septal defect in the chick embryo.
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with the drug combination – promethazine, phenylephrine and codeine. It is not known whether this drug combination can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Dependence has been reported in newborns whose mothers took opiates regularly during pregnancy. Withdrawal signs include irritability, excessive crying, tremors, hyperreflexia, fever, vomiting and diarrhea. Signs usually appear during the first few days of life.
Promethazine administered to a pregnant woman within two weeks of delivery may inhibit platelet aggregation in the newborn.
Labor and Delivery
Narcotic analgesics cross the placental barrier. The closer to delivery and the larger the dose used, the greater the possibility of respiratory depression in the newborn. Narcotic analgesics should be avoided during labor if delivery of a premature infant is anticipated. If the mother has received narcotic analgesics during labor, newborn infants should be observed closely for signs of respiratory depression. Resuscitation may be required (see OVERDOSAGE).
Limited data suggest that use of promethazine hydrochloride during labor and delivery does not have an appreciable effect on the duration of labor or delivery and does not increase the risk of need for intervention in the newborn.
The effect of promethazine and/or codeine on later growth and development of the newborn is unknown.
Administration of phenylephrine to patients in late pregnancy or labor may cause fetal anoxia or bradycardia by increasing contractility of the uterus and decreasing uterine blood flow.
See also Nonteratogenic Effects.
Nursing Mothers
Codeine and its active metabolite, morphine, are present in human milk. There are published studies and cases that have reported excessive sedation, respiratory depression, and death in infants exposed to codeine via breast milk. Women who are ultra-rapid metabolizers of codeine achieve higher than expected serum levels of morphine, potentially leading to higher levels of morphine in breast milk that can be dangerous in their breastfed infants. In women with normal codeine metabolism (normal CYP2D6 activity), the amount of codeine secreted into human milk is low and dose-dependent. There is no information on the effects of the codeine on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including excess sedation, respiratory depression, and death in a breastfed infant, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution. (See WARNINGS -Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression).
If infants are exposed to Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution through breast milk, they should be monitored for excess sedation and respiratory depression. Withdrawal symptoms can occur in breastfed infants when maternal administration of an opioid analgesic is stopped, or when breast-feeding is stopped.
It is not known whether phenylephrine or promethazine are excreted in human milk.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Promethazine HCl, Phenylephrine HCl and Codeine Phosphate Oral Solution in pediatric patients below the age of 18 have not been established.
Life-threatening respiratory depression and death have occurred in children who received codeine. (See WARNINGS -Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression). Postmarketing cases of respiratory depression, including fatalities have been reported with use of promethazine in pediatric patients. (See WARNINGS -Promethazine and Respiratory Depression in Children). Because of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression and death:
- Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated in all children younger than 12 years of age. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS).
- Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated for post-operative management in pediatric patients younger than 18 years of age following tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS).
- Avoid the use of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution in adolescents 12 to 18 years of age who have other risk factors that may increase their sensitivity to the respiratory depressant effects of codeine. Risk factors include conditions associated with hypoventilation, such as postoperative status, obstructive sleep apnea, obesity, severe pulmonary disease, neuromuscular disease, and concomitant use of other medications that cause respiratory depression. (See WARNINGS - Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression).
- When prescribing codeine for adolescents, healthcare providers should choose the lowest effective dose for the shortest period of time and inform patients and caregivers about these risks and the signs of morphine overdose. (See OVERDOSAGE).
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Promethazine HCl, Phenylephrine HCl and Codeine Phosphate Oral Solution did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Sedating drugs may cause confusion and over-sedation in the elderly; elderly patients generally should be started on low doses of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution and observed closely.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Codeine
Central Nervous System: CNS depression, particularly respiratory depression, and to a lesser extent circulatory depression; light-headedness, dizziness, sedation, euphoria, dysphoria, headache, transient hallucination, disorientation, visual disturbances and convulsions.
Cardiovascular: Tachycardia, bradycardia, palpitation, faintness, syncope, orthostatic hypotension (common to narcotic analgesics).
Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, constipation, and biliary tract spasm. Patients with chronic ulcerative colitis may experience increased colonic motility; in patients with acute ulcerative colitis, toxic dilation has been reported.
Genitourinary: Oliguria, urinary retention; antidiuretic effect has been reported (common to narcotic analgesics).
Allergic: Infrequent pruritus, giant urticaria, angioneurotic edema, and laryngeal edema.
Other: Flushing of the face, sweating and pruritus (due to opiate-induced histamine release); weakness.
Promethazine
Central Nervous System: Drowsiness is the most prominent CNS effect of this drug. Sedation, somnolence, blurred vision, dizziness; confusion, disorientation and extrapyramidal symptoms such as oculogyric crisis, torticollis, and tongue protrusion; lassitude, tinnitus, incoordination, fatigue, euphoria, nervousness, diplopia, insomnia, tremors, convulsive seizures, excitation, catatonic-like states, hysteria. Hallucinations have also been reported.
Cardiovascular: Increased or decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, bradycardia, faintness.
Dermatologic: Dermatitis, photosensitivity, urticaria.
Hematologic: Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, agranulocytosis.
Gastrointestinal: Dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, jaundice.
Respiratory: Asthma, nasal stuffiness, respiratory depression (potentially fatal) and apnea (potentially fatal) (see WARNINGS – Promethazine; Respiratory Depression).
Other: Angioneurotic edema. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (potentially fatal) has also been reported (see WARNINGS – Promethazine; Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome).
Paradoxical Reactions: Hyperexcitability and abnormal movements have been reported in patients following a single administration of promethazine HCl. Consideration should be given to the discontinuation of promethazine HCl and to the use of other drugs if these reactions occur. Respiratory depression, nightmares, delirium and agitated behavior have also been reported in some of these patients.
Phenylephrine
Central Nervous System: Restlessness, anxiety, nervousness and dizziness.
Cardiovascular: Hypertension (see WARNINGS).
Other: Primordial pain, respiratory distress, tremor and weakness.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Controlled Substance
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is a Schedule V Controlled Substance.
Abuse
Codeine is known to be subject to abuse; however, the abuse potential of oral codeine appears to be quite low. Even parenteral codeine does not appear to offer the psychic effects sought by addicts to the same degree as heroin or morphine. However, codeine must be administered only under close supervision to patients with a history of drug abuse or dependence.
OVERDOSAGE
Codeine
Serious overdose with codeine is characterized by respiratory depression (a decrease in respiratory rate and/or tidal volume, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, cyanosis), extreme somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin and sometimes bradycardia and hypotension. The triad of coma, pinpoint pupils and respiratory depression is strongly suggestive of opiate poisoning. In severe overdosage, particularly by the intravenous route, apnea, circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest, and death may occur. Promethazine is additive to the depressant effects of codeine.
It is difficult to determine what constitutes a standard toxic or lethal dose. However, the lethal oral dose of codeine in an adult is reported to be in the range of 0.5 to 1.0 gram. Infants and children are believed to be relatively more sensitive to opiates on a body-weight basis. Elderly patients are also comparatively intolerant to opiates.
Promethazine
Signs and symptoms of overdosage with promethazine HCl range from mild depression of the central nervous system and cardiovascular system to profound hypotension, respiratory depression, unconsciousness and sudden death. Other reported reactions include hyperreflexia, hypertonia, ataxia, athetosis and extensor-plantar reflexes (Babinski reflex).
Stimulation may be evident, especially in children and geriatric patients. Convulsions may rarely occur. A paradoxical reaction has been reported in children receiving single doses of 75 mg to 125 mg orally, characterized by hyperexcitability and nightmares.
Atropine-like signs and symptoms – dry mouth, fixed dilated pupils, flushing, as well as gastrointestinal symptoms, may occur.
Phenylephrine
Signs and symptoms of overdosage with phenylephrine include hypertension, headache, convulsions, cerebral hemorrhage, and vomiting. Ventricular premature beats and short paroxysms of ventricular tachycardia may also occur. Headache may be a symptom of hypertension. Bradycardia may also be seen early in phenylephrine overdosage through stimulation of baroreceptors.
Treatment
The treatment of overdosage with promethazine, phenylephrine and codeine is essentially symptomatic and supportive. Only in cases of extreme overdosage or individual sensitivity do vital signs including respiration, pulse, blood pressure, temperature, and EKG need to be monitored. Activated charcoal orally or by lavage may be given, or sodium or magnesium sulfate orally as a cathartic. Attention should be given to the re-establishment of adequate respiratory exchange through provision of a patent airway and institution of assisted or controlled ventilation. The narcotic antagonist, naloxone hydrochloride, may be administered when significant respiratory depression occurs with promethazine, phenylephrine and codeine; any depressant effects of promethazine are not reversed by naloxone. Diazepam may be used to control convulsions. Avoid analeptics, which may cause convulsions. Acidosis and electrolyte losses should be corrected. A rise in temperature or pulmonary complications may signal the need for institution of antibiotic therapy.
Severe hypotension usually responds to the administration of norepinephrine or phenylephrine. EPINEPHRINE SHOULD NOT BE USED, since its use in a patient with partial adrenergic blockade may further lower the blood pressure.
Limited experience with dialysis indicates that it is not helpful.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
It is important that Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is measured with an accurate measuring device (see PRECAUTIONS-Information for Patients). A household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and could lead to overdosage, especially when half a teaspoon is to be measured. It is strongly recommended that an accurate measuring device be used. A pharmacist can provide an appropriate device and can provide instructions for measuring the correct dose.
Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution is contraindicated in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age. (See WARNINGS - Ultra-Rapid Metabolism of Codeine and Respiratory Depression).
The average effective dose is given in the following table:
| Adults (12 years of age and over) | 5 mL (1 teaspoonful) every 4 to 6 hours, not to exceed 30.0 mL in 24 hours. |
|
MEDICATION GUIDE Promethazine (proe METH a zeen) VC with Codeine (KOE deen) Oral Solution, C-V (Promethazine Hydrochloride, Phenylephrine Hydrochloride and Codeine Phosphate Oral Solution) |
|
What is the most important information I should know about Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution?
You should not breastfeed during treatment with Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution.
|
|
What is Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution?
|
|
Who should not take Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution?
|
|
Before you take Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Taking Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution or the other medicines work. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you:
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if you take one of these medicines. |
|
How should I take Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution?
|
|
What should I avoid while taking Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution?
|
|
What are the possible side effects of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution? Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution may cause serious side effects, including:
if you have any of the following symptoms of NMS:
The most common side effects of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution include:
These are not all the possible side effects of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
How should I store Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution?
|
|
General information about the safe and effective use of Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution that is written for health professionals. |
|
What are the ingredients in Promethazine VC with Codeine Oral Solution? Active ingredients: codeine phosphate, promethazine hydrochloride, and phenylephrine hydrochloride Inactive ingredients: Ascorbic acid, citric acid, D&C Red #33, FD&C Yellow #6, menthol, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, saccharin sodium, sodium benzoate, sodium citrate, strawberry flavor and sucrose.
For more information, call 1-800-828-9393. |
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Issued: 07/2017 R4 |
| PROMETHAZINE VC WITH CODEINE
promethazine and phenylephrine hydrochloride and codeine phosphate solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - A-S Medication Solutions (830016429) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-S Medication Solutions | 830016429 | RELABEL(50090-0223) , REPACK(50090-0223) | |
