RIBAVIRIN- ribavirin tablet, coated
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA Inc
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use ribavirin tablets safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ribavirin tablets.
RIBAVIRIN tablets for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2002 WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS DISORDERS AND RIBAVIRIN-ASSOCIATED EFFECTSSee full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
RECENT MAJOR CHANGESINDICATIONS AND USAGERibavirin tablets are a nucleoside analogue indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) virus infection in combination with peginterferon alfa-2a in adults with compensated liver disease not previously treated with interferon alpha, and in CHC patients coinfected with HIV (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Peginterferon alfa-2a/Ribavirin: Patients exhibiting the following conditions should be closely monitored and may require dose reduction or discontinuation of therapy:
ADVERSE REACTIONSThe most common adverse reactions (frequency > 40%) in adults receiving combination therapy are fatigue/asthenia, pyrexia, myalgia, and headache (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact TEVA USA, PHARMACOVIGILANCE at 1-888-838-2872, X6351 or drug.safety@tevausa.com; or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSSee 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide. Revised: 2/2016 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS DISORDERS AND RIBAVIRIN-ASSOCIATED EFFECTS
- •
- Ribavirin monotherapy is not effective for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection and should not be used alone for this indication.
- •
- The primary clinical toxicity of ribavirin is hemolytic anemia. The anemia associated with ribavirin therapy may result in worsening of cardiac disease and lead to fatal and nonfatal myocardial infarctions. Patients with a history of significant or unstable cardiac disease should not be treated with ribavirin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Adverse Reactions (6.1), and Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- •
- Significant teratogenic and/or embryocidal effects have been demonstrated in all animal species exposed to ribavirin. In addition, ribavirin has a multiple dose half-life of 12 days, and it may persist in non-plasma compartments for as long as 6 months. Therefore, ribavirin, including ribavirin tablets, is contraindicated in women who are pregnant and in the male partners of women who are pregnant. Extreme care must be taken to avoid pregnancy during therapy and for 6 months after completion of therapy in both female patients and in female partners of male patients who are taking ribavirin therapy. At least two reliable forms of effective contraception must be utilized during treatment and during the 6 month post treatment follow-up period [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ribavirin tablets in combination with peginterferon alfa-2a is indicated for the treatment of adults with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) virus infection who have compensated liver disease and have not been previously treated with interferon alpha.
The following points should be considered when initiating ribavirin tablet combination therapy with peginterferon alfa-2a:
- •
- This indication is based on clinical trials of combination therapy in patients with CHC and compensated liver disease, some of whom had histological evidence of cirrhosis (Child-Pugh class A), and in patients with clinically stable HIV disease and CD4 count > 100 cells/mm2.
- •
- This indication is based on achieving undetectable HCV-RNA after treatment for 24 or 48 weeks, based on HCV genotype, and maintaining a Sustained Virologic Response (SVR) 24 weeks after the last dose.
- •
- Safety and efficacy data are not available for treatment longer than 48 weeks.
- •
- The safety and efficacy of ribavirin tablet and peginterferon alfa-2a therapy have not been established in liver or other organ transplant recipients, patients with decompensated liver disease, or previous non-responders to interferon therapy.
- •
- The safety and efficacy of ribavirin tablet therapy for the treatment of adenovirus, RSV, parainfluenza or influenza infections have not been established. Ribavirin tablets should not be used for these indications. Ribavirin for inhalation has a separate package insert, which should be consulted if ribavirin inhalation therapy is being considered.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Chronic Hepatitis C Monoinfection
The recommended dose of ribavirin tablets is provided in Table 1. The recommended duration of treatment for patients previously untreated with ribavirin and interferon is 24 to 48 weeks.
The daily dose of ribavirin tablets is 800 mg to 1200 mg administered orally in two divided doses. The dose should be individualized to the patient depending on baseline disease characteristics (e.g., genotype), response to therapy, and tolerability of the regimen (see Table 1).
Ribavirin tablets should be taken with food.
|
|||
|
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Genotype |
Peginterferon alfa-2a Dose* |
Ribavirin Tablet Dose |
Duration |
|
Genotypes 1, 4 |
180 mcg |
< 75 kg = 1000 mg |
48 weeks |
|
≥ 75 kg = 1200 mg |
48 weeks |
||
|
Genotypes 2, 3 |
180 mcg |
800 mg |
24 weeks |
Genotypes 2 and 3 showed no increased response to treatment beyond 24 weeks (see Table 6).
Data on genotypes 5 and 6 are insufficient for dosing recommendations.
2.2 Chronic Hepatitis C With HIV Coinfection
The recommended dose for treatment of chronic hepatitis C in patients coinfected with HIV is peginterferon alfa-2a 180 mcg subcutaneous once weekly and ribavirin tablets, 800 mg by mouth daily for a total duration of 48 weeks, regardless of HCV genotype.
Ribavirin tablets should be taken with food.
2.3 Dose Modifications
If severe adverse reactions or laboratory abnormalities develop during combination ribavirin tablet/peginterferon alfa-2a therapy, the dose should be modified or discontinued, if appropriate, until the adverse reactions abate or decrease in severity. If intolerance persists after dose adjustment, ribavirin tablet/peginterferon alfa-2a therapy should be discontinued. Table 2 provides guidelines for dose modifications and discontinuation based on the patient’s hemoglobin concentration and cardiac status.
Ribavirin tablets should be administered with caution to patients with preexisting cardiac disease. Patients should be assessed before commencement of therapy and should be appropriately monitored during therapy. If there is any deterioration of cardiovascular status, therapy should be stopped [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
|
||
|
Laboratory Values |
Reduce Only Ribavirin Tablet Dose to 600 mg/day* if: |
Discontinue Ribavirin Tablets if: |
|
Hemoglobin in patients with no cardiac disease |
< 10 g/dL |
< 8.5 g/dL |
|
Hemoglobin in patients with history of stable cardiac disease |
≥ 2 g/dL decrease in hemoglobin during any 4 week period treatment |
< 12 g/dL despite 4 weeks at reduced dose |
Once ribavirin tablets have been withheld due to either a laboratory abnormality or clinical manifestation, an attempt may be made to restart ribavirin tablets at 600 mg daily and further increase the dose to 800 mg daily. However, it is not recommended that ribavirin tablets be increased to the original assigned dose (1000 mg to 1200 mg).
See peginterferon alfa-2a full prescribing information for recommendations on peginterferon alfa-2a dose modification.
2.4 Discontinuation of Dosing
Discontinuation of peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin tablet therapy should be considered if the patient has failed to demonstrate at least a 2 log10 reduction from baseline in HCV RNA by 12 weeks of therapy, or undetectable HCV RNA levels after 24 weeks of therapy.
Peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin tablet therapy should be discontinued in patients who develop hepatic decompensation during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.5 Renal Impairment
Ribavirin tablets should not be used in patients with creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Ribavirin tablets are available as a light-pink to pink, round standard normal convex, coated tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 200 mg of ribavirin.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Ribavirin tablets are contraindicated in:
- •
- Women who are pregnant. Ribavirin tablets may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Ribavirin tablets are contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.1), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
- •
- Men whose female partners are pregnant.
- •
- Patients with hemoglobinopathies (e.g., thalassemia major or sickle-cell anemia).
- •
- In combination with didanosine. Reports of fatal hepatic failure, as well as peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis, and symptomatic hyperlactatemia/lactic acidosis have been reported in clinical trials [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Ribavirin tablets and peginterferon alfa-2a combination therapy is contraindicated in patients with:
- •
- Autoimmune hepatitis.
- •
- Hepatic decompensation (Child-Pugh score greater than 6; class B and C) in cirrhotic CHC monoinfected patients before treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- •
- Hepatic decompensation (Child-Pugh score greater than or equal to 6) in cirrhotic CHC patients coinfected with HIV before treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Significant adverse reactions associated with ribavirin/peginterferon alfa-2a combination therapy include severe depression and suicidal ideation, hemolytic anemia, suppression of bone marrow function, autoimmune and infectious disorders, ophthalmologic disorders, cerebrovascular disorders, pulmonary dysfunction, colitis, pancreatitis, and diabetes.
The peginterferon alfa-2a Package Insert should be reviewed in its entirety for additional safety information prior to initiation of combination treatment.
5.1 Pregnancy
Ribavirin may cause birth defects and/or death of the exposed fetus. Ribavirin has demonstrated significant teratogenic and/or embryocidal effects in all animal species in which adequate studies have been conducted. These effects occurred at doses as low as one twentieth of the recommended human dose of ribavirin.
Ribavirin therapy should not be started unless a report of a negative pregnancy test has been obtained immediately prior to planned initiation of therapy. Extreme care must be taken to avoid pregnancy in female patients and in female partners of male patients. Patients should be instructed to use at least two forms of effective contraception during treatment and for 6 months after treatment has been stopped. Pregnancy testing should occur monthly during ribavirin therapy and for 6 months after therapy has stopped [see Boxed Warning, Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.2 Anemia
The primary toxicity of ribavirin is hemolytic anemia, which was observed in approximately 13% of all ribavirin/peginterferon alfa-2a-treated subjects in clinical trials. Anemia associated with ribavirin occurs within 1 to 2 weeks of initiation of therapy. Because the initial drop in hemoglobin may be significant, it is advised that hemoglobin or hematocrit be obtained pretreatment and at week 2 and week 4 of therapy or more frequently if clinically indicated. Patients should then be followed as clinically appropriate. Caution should be exercised in initiating treatment in any patient with baseline risk of severe anemia (e.g., spherocytosis, history of gastrointestinal bleeding) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Fatal and nonfatal myocardial infarctions have been reported in patients with anemia caused by ribavirin. Patients should be assessed for underlying cardiac disease before initiation of ribavirin therapy. Patients with preexisting cardiac disease should have electrocardiograms administered before treatment, and should be appropriately monitored during therapy. If there is any deterioration of cardiovascular status, therapy should be suspended or discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Because cardiac disease may be worsened by drug-induced anemia, patients with a history of significant or unstable cardiac disease should not use ribavirin [see Boxed Warning, and Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Hepatic Failure
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including peginterferon alfa-2a. Cirrhotic CHC patients coinfected with HIV receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) and interferon alfa-2a with or without ribavirin appear to be at increased risk for the development of hepatic decompensation compared to patients not receiving HAART. In Study NR15961 [see Clinical Studies (14.3)], among 129 CHC/HIV cirrhotic patients receiving HAART, 14 (11%) of these patients across all treatment arms developed hepatic decompensation resulting in 6 deaths. All 14 patients were on NRTIs, including stavudine, didanosine, abacavir, zidovudine, and lamivudine. These small numbers of patients do not permit discrimination between specific NRTIs or the associated risk. During treatment, patients’ clinical status and hepatic function should be closely monitored for signs and symptoms of hepatic decompensation. Treatment with ribavirin/peginterferon alfa-2a should be discontinued immediately in patients with hepatic decompensation [see Contraindications (4)].
5.4 Hypersensitivity
Severe acute hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., urticaria, angioedema, bronchoconstriction, and anaphylaxis) have been observed during alpha interferon and ribavirin therapy. If such a reaction occurs, therapy with peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin should be discontinued immediately and appropriate medical therapy instituted. Serious skin reactions including vesiculobullous eruptions, reactions in the spectrum of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (erythema multiforme major) with varying degrees of skin and mucosal involvement and exfoliative dermatitis (erythroderma) have been reported in patients receiving peginterferon alfa-2a with and without ribavirin. Patients developing signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions must discontinue therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.5 Renal Impairment
Ribavirin should not be used in patients with creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
5.6 Pulmonary Disorders
Dyspnea, pulmonary infiltrates, pneumonitis, pulmonary hypertension, and pneumonia have been reported during therapy with ribavirin and interferon. Occasional cases of fatal pneumonia have occurred. In addition, sarcoidosis or the exacerbation of sarcoidosis has been reported. If there is evidence of pulmonary infiltrates or pulmonary function impairment, patients should be closely monitored and, if appropriate, combination ribavirin/peginterferon alfa-2a treatment should be discontinued.
5.7 Bone Marrow Suppression
Pancytopenia (marked decreases in RBCs, neutrophils and platelets) and bone marrow suppression have been reported in the literature to occur within 3 to 7 weeks after the concomitant administration of pegylated interferon/ribavirin and azathioprine. In this limited number of patients (n = 8), myelotoxicity was reversible within 4 to 6 weeks upon withdrawal of both HCV antiviral therapy and concomitant azathioprine and did not recur upon reintroduction of either treatment alone. Peginterferon alfa-2a, ribavirin, and azathioprine should be discontinued for pancytopenia, and pegylated interferon/ribavirin should not be re-introduced with concomitant azathioprine [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
5.8 Pancreatitis
Ribavirin and peginterferon alfa-2a therapy should be suspended in patients with signs and symptoms of pancreatitis, and discontinued in patients with confirmed pancreatitis.
5.9 Laboratory Tests
Before beginning peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin combination therapy, standard hematological and biochemical laboratory tests are recommended for all patients. Pregnancy screening for women of childbearing potential must be performed. Patients who have preexisting cardiac abnormalities should have electrocardiograms administered before treatment with peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin.
After initiation of therapy, hematological tests should be performed at 2 weeks and 4 weeks and biochemical tests should be performed at 4 weeks. Additional testing should be performed periodically during therapy. In the clinical studies, the CBC (including hemoglobin level and white blood cell and platelet counts) and chemistries (including liver function tests and uric acid) were measured at 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 weeks, and then every 4 to 6 weeks or more frequently if abnormalities were found. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) was measured every 12 weeks. Monthly pregnancy testing should be performed during combination therapy and for 6 months after discontinuing therapy.
The entrance criteria used for the clinical studies of ribavirin and peginterferon alfa-2a may be considered as a guideline to acceptable baseline values for initiation of treatment:
- •
- Platelet count ≥ 90,000 cells/mm3 (as low as 75,000 cells/mm3 in HCV patients with cirrhosis or 70,000 cells/mm3 in patients with CHC and HIV)
- •
- Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) ≥ 1500 cells/mm3
- •
- TSH and T4 within normal limits or adequately controlled thyroid function
- •
- CD4+ cell count ≥ 200 cells/μL or CD4+ cell count ≥ 100 cells/μL but < 200 cells/μL and HIV-1 RNA < 5000 copies/mL in patients coinfected with HIV
- •
- Hemoglobin ≥ 12 g/dL for women and ≥ 13 g/dL for men in CHC monoinfected patients
- •
- Hemoglobin ≥ 11 g/dL for women and ≥ 12 g/dL for men in patients with CHC and HIV
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Peginterferon alfa-2a in combination with ribavirin causes a broad variety of serious adverse reactions [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5)]. The most common serious or life-threatening adverse reactions induced or aggravated by ribavirin/peginterferon alfa-2a include depression, suicide, relapse of drug abuse/overdose, and bacterial infections each occurring at a frequency of < 1%. Hepatic decompensation occurred in 2% (10/574) CHC/HIV patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
In the pivotal registration trials NV15801 and NV15942, 886 patients received ribavirin for 48 weeks at doses of 1000/1200 mg based on body weight. In these trials, one or more serious adverse reactions occurred in 10% of CHC monoinfected subjects and in 19% of CHC/HIV subjects receiving peginterferon alfa-2a alone or in combination with ribavirin. The most common serious adverse event (3% in CHC and 5% in CHC/HIV) was bacterial infection (e.g., sepsis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, pyelonephritis, pneumonia).
Other serious adverse reactions occurred at a frequency of < 1% and included: suicide, suicidal ideation, psychosis, aggression, anxiety, drug abuse and drug overdose, angina, hepatic dysfunction, fatty liver, cholangitis, arrhythmia, diabetes mellitus, autoimmune phenomena (e.g., hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis), peripheral neuropathy, aplastic anemia, peptic ulcer, gastrointestinal bleeding, pancreatitis, colitis, corneal ulcer, pulmonary embolism, coma, myositis, cerebral hemorrhage, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, psychotic disorder, and hallucination.
The percentage of patients in clinical trials who experienced one or more adverse events was 98%. The most commonly reported adverse reactions were psychiatric reactions, including depression, insomnia, irritability, anxiety, and flu-like symptoms such as fatigue, pyrexia, myalgia, headache and rigors. Other common reactions were anorexia, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, arthralgias, injection site reactions, alopecia, and pruritus. Table 3 shows rates of adverse events occurring in ≥ 5% subjects receiving pegylated interferon and ribavirin combination therapy in the CHC Clinical Trial, NV15801.
Ten percent of CHC monoinfected patients receiving 48 weeks of therapy with peginterferon alfa-2a in combination with ribavirin discontinued therapy; 16% of CHC/HIV coinfected patients discontinued therapy. The most common reasons for discontinuation of therapy were psychiatric, flu-like syndrome (e.g., lethargy, fatigue, headache), dermatologic and gastrointestinal disorders and laboratory abnormalities (thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and anemia).
Overall 39% of patients with CHC or CHC/HIV required modification of peginterferon alfa-2a and/or ribavirin therapy. The most common reason for dose modification of peginterferon alfa-2a in CHC and CHC/HIV patients was for laboratory abnormalities; neutropenia (20% and 27%, respectively) and thrombocytopenia (4% and 6%, respectively). The most common reason for dose modification of ribavirin in CHC and CHC/HIV patients was anemia (22% and 16%, respectively).
Peginterferon alfa-2a dose was reduced in 12% of patients receiving 1000 mg to 1200 mg ribavirin for 48 weeks and in 7% of patients receiving 800 mg ribavirin for 24 weeks. Ribavirin dose was reduced in 21% of patients receiving 1000 mg to 1200 mg ribavirin for 48 weeks and in 12% of patients receiving 800 mg ribavirin for 24 weeks.
Chronic hepatitis C monoinfected patients treated for 24 weeks with peginterferon alfa-2a and 800 mg ribavirin were observed to have lower incidence of serious adverse events (3% vs. 10%), hemoglobin < 10 g/dL (3% vs. 15%), dose modification of peginterferon alfa-2a (30% vs. 36%) and ribavirin (19% vs. 38%), and of withdrawal from treatment (5% vs. 15%) compared to patients treated for 48 weeks with peginterferon alfa-2a and 1000 mg or 1200 mg ribavirin. On the other hand, the overall incidence of adverse events appeared to be similar in the two treatment groups.
|
||
|
Body System |
CHC Combination Therapy Study NV15801 |
|
|
Peginterferon alfa-2a 180 mcg + 1000 mg or 1200 mg Ribavirin Tablets 48 weeks |
Interferon alfa-2b + 1000 mg or 1200 mg Ribavirin Capsules 48 weeks |
|
|
N = 451 |
N = 443 |
|
|
% |
% |
|
|
Application Site Disorders |
|
|
|
Injection site reaction |
23 |
16 |
|
Endocrine Disorders |
|
|
|
Hypothyroidism |
4 |
5 |
|
Flu-like Symptoms and Signs |
|
|
|
Fatigue/Asthenia |
65 |
68 |
|
Pyrexia |
41 |
55 |
|
Rigors |
25 |
37 |
|
Pain |
10 |
9 |
|
Gastrointestinal |
|
|
|
Nausea/Vomiting |
25 |
29 |
|
Diarrhea |
11 |
10 |
|
Abdominal pain |
8 |
9 |
|
Dry mouth |
4 |
7 |
|
Dyspepsia |
6 |
5 |
|
Hematologic* |
|
|
|
Lymphopenia |
14 |
12 |
|
Anemia |
11 |
11 |
|
Neutropenia |
27 |
8 |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
5 |
< 1 |
|
Metabolic and Nutritional |
|
|
|
Anorexia |
24 |
26 |
|
Weight decrease |
10 |
10 |
|
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue and Bone |
|
|
|
Myalgia |
40 |
49 |
|
Arthralgia |
22 |
23 |
|
Back pain |
5 |
5 |
|
Neurological |
|
|
|
Headache |
43 |
49 |
|
Dizziness (excluding vertigo) |
14 |
14 |
|
Memory impairment |
6 |
5 |
|
Psychiatric |
|
|
|
Irritability/Anxiety/Nervousness |
33 |
38 |
|
Insomnia |
30 |
37 |
|
Depression |
20 |
28 |
|
Concentration impairment |
10 |
13 |
|
Mood alteration |
5 |
6 |
|
Resistance Mechanism Disorders |
|
|
|
Overall |
12 |
10 |
|
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal |
|
|
|
Dyspnea |
13 |
14 |
|
Cough |
10 |
7 |
|
Dyspnea exertional |
4 |
7 |
|
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue |
|
|
|
Alopecia |
28 |
33 |
|
Pruritus |
19 |
18 |
|
Dermatitis |
16 |
13 |
|
Dry skin |
10 |
13 |
|
Rash |
8 |
5 |
|
Sweating increased |
6 |
5 |
|
Eczema |
5 |
4 |
|
Visual Disorders |
|
|
|
Vision blurred |
5 |
2 |
Common Adverse Reactions in CHC With HIV Coinfection
The adverse event profile of coinfected patients treated with peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin in Study NR15961 was generally similar to that shown for monoinfected patients in Study NV15801 (Table 3). Events occurring more frequently in coinfected patients were neutropenia (40%), anemia (14%), thrombocytopenia (8%), weight decrease (16%), and mood alteration (9%).
Laboratory Test Abnormalities
Anemia due to hemolysis is the most significant toxicity of ribavirin therapy. Anemia (hemoglobin < 10 g/dL) was observed in 13% of all ribavirin and peginterferon alfa-2a combination-treated patients in clinical trials. The maximum drop in hemoglobin occurred during the first 8 weeks of initiation of ribavirin therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
|
Laboratory Parameter |
Peginterferon alfa-2a + Ribavirin 1000/1200 mg 48 wks |
Interferon alfa-2b + Ribavirin 1000/1200 mg 48 wks |
|
(N = 887) |
(N = 443) |
|
|
Neutrophils (x 109/L) | ||
|
1.0 to 1.49 |
34% |
38% |
|
0.5 to 0.99 |
49% |
21% |
|
< 0.5 |
5% |
1% |
|
Platelets (x 109/L) | ||
|
50 to 74.9 |
11% |
4% |
|
20 to 49.9 |
5% |
< 1% |
|
< 20 |
0 |
0 |
|
Hemoglobin (g/dL) | ||
|
8.5 to 9.9 |
11% |
11% |
|
< 8.5 |
2% |
< 1% |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified and reported during post-approval use of peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin combination therapy. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System disorders
Pure red cell aplasia
Ear and Labyrinth disorders
Hearing impairment, hearing loss
Eye disorders
Serous retinal detachment
Immune disorders
Liver and renal graft rejection
Metabolism and Nutrition disorders
Dehydration
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue disorders
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Results from a pharmacokinetic sub-study demonstrated no pharmacokinetic interaction between peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin.
7.1 Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
In vitro data indicate ribavirin reduces phosphorylation of lamivudine, stavudine, and zidovudine. However, no pharmacokinetic (e.g., plasma concentrations or intracellular triphosphorylated active metabolite concentrations) or pharmacodynamic (e.g., loss of HIV/HCV virologic suppression) interaction was observed when ribavirin and lamivudine (n = 18), stavudine (n = 10), or zidovudine (n = 6) were coadministered as part of a multi-drug regimen to HCV/HIV coinfected patients.
In Study NR15961 among the CHC/HIV coinfected cirrhotic patients receiving NRTIs cases of hepatic decompensation (some fatal) were observed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Patients receiving peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin and NRTIs should be closely monitored for treatment associated toxicities. Physicians should refer to prescribing information for the respective NRTIs for guidance regarding toxicity management. In addition, dose reduction or discontinuation of peginterferon alfa-2a, ribavirin or both should also be considered if worsening toxicities are observed, including hepatic decompensation (e.g., Child-Pugh ≥ 6) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Didanosine
Coadministration of ribavirin and didanosine is contraindicated. Didanosine or its active metabolite (dideoxyadenosine 5’-triphosphate) concentrations are increased when didanosine is coadministered with ribavirin, which could cause or worsen clinical toxicities. Reports of fatal hepatic failure, as well as peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis, and symptomatic hyperlactatemia/lactic acidosis have been reported in clinical trials [see Contraindications (4)].
Zidovudine
In Study NR15961, patients who were administered zidovudine in combination with peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin developed severe neutropenia (ANC < 500) and severe anemia (hemoglobin < 8 g/dL) more frequently than similar patients not receiving zidovudine (neutropenia 15% vs. 9%) (anemia 5% vs. 1%). Discontinuation of zidovudine should be considered as medically appropriate.
7.2 Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome P450
In vitro studies indicate that ribavirin does not inhibit CYP 2C9, CYP 2C19, CYP 2D6 or CYP 3A4.
7.3 Azathioprine
The use of ribavirin to treat chronic hepatitis C in patients receiving azathioprine has been reported to induce severe pancytopenia and may increase the risk of azathioprine-related myelotoxicity. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMDH) is required for one of the metabolic pathways of azathioprine. Ribavirin is known to inhibit IMDH, thereby leading to accumulation of an azathioprine metabolite, 6-methylthioinosine monophosphate (6-MTITP), which is associated with myelotoxicity (neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia). Patients receiving azathioprine with ribavirin should have complete blood counts, including platelet counts, monitored weekly for the first month, twice monthly for the second and third months of treatment, then monthly or more frequently if dosage or other therapy changes are necessary [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy category X [See Contraindications (4).]
Ribavirin produced significant embryocidal and/or teratogenic effects in all animal species in which adequate studies have been conducted. Malformations of the skull, palate, eye, jaw, limbs, skeleton, and gastrointestinal tract were noted. The incidence and severity of teratogenic effects increased with escalation of the drug dose.
Survival of fetuses and offspring was reduced [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
In conventional embryotoxicity/teratogenicity studies in rats and rabbits, observed no-effect dose levels were well below those for proposed clinical use (0.3 mg/kg/day for both the rat and rabbit; approximately 0.06 times the recommended daily human dose of ribavirin). No maternal toxicity or effects on offspring were observed in a peri/postnatal toxicity study in rats dosed orally at up to 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.01 times the maximum recommended daily human dose of ribavirin).
Treatment and Post treatment: Potential Risk to the Fetus
Ribavirin is known to accumulate in intracellular components from where it is cleared very slowly. It is not known whether ribavirin is contained in sperm, and if so, will exert a potential teratogenic effect upon fertilization of the ova. However, because of the potential human teratogenic effects of ribavirin, male patients should be advised to take every precaution to avoid risk of pregnancy for their female partners.
Ribavirin should not be used by pregnant women or by men whose female partners are pregnant. Female patients of childbearing potential and male patients with female partners of childbearing potential should not receive ribavirin unless the patient and his/her partner are using effective contraception (two reliable forms) during therapy and for 6 months post therapy [see Contraindications (4)].
Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry
A Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry has been established to monitor maternal-fetal outcomes of pregnancies of female patients and female partners of male patients exposed to ribavirin during treatment and for 6 months following cessation of treatment. Healthcare providers and patients are encouraged to report such cases by calling 1-800-593-2214.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether ribavirin is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and to avoid any potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from ribavirin, a decision should be made either to discontinue nursing or therapy with ribavirin, based on the importance of the therapy to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Pharmacokinetic evaluations in pediatric patients have not been performed.
Safety and effectiveness of ribavirin have not been established in patients below the age of 18.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of ribavirin and peginterferon alfa-2a did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 or over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Specific pharmacokinetic evaluations for ribavirin in the elderly have not been performed. The risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Ribavirin should not be administered to patients with creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min.
8.6 Race
A pharmacokinetic study in 42 subjects demonstrated there is no clinically significant difference in ribavirin pharmacokinetics among Black (n = 14), Hispanic (n = 13) and Caucasian (n = 15) subjects.
8.7 Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of ribavirin following administration of ribavirin have not been studied in patients with renal impairment and there are limited data from clinical trials on administration of ribavirin in patients with creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min. Therefore, patients with creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min should not be treated with ribavirin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) and Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
8.8 Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of ribavirin following administration of ribavirin has not been evaluated. The clinical trials of ribavirin were restricted to patients with Child-Pugh class A disease.
8.9 Gender
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of ribavirin were observed between male and female subjects.
Ribavirin pharmacokinetics, when corrected for weight, are similar in male and female patients.
8.10 Organ Transplant Recipients
The safety and efficacy of peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin treatment have not been established in patients with liver and other transplantations. As with other alpha interferons, liver and renal graft rejections have been reported on peginterferon alfa-2a, alone or in combination with ribavirin [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
No cases of overdose with ribavirin have been reported in clinical trials. Hypocalcemia and hypomagnesemia have been observed in persons administered greater than the recommended dosage of ribavirin. In most of these cases, ribavirin was administered intravenously at dosages up to and in some cases exceeding four times the recommended maximum oral daily dose.
11 DESCRIPTION
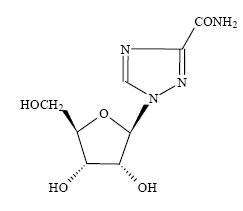
Ribavirin is a nucleoside analogue with antiviral activity. The chemical name of ribavirin is 1-β-D-ribofuranosyl-1 H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide and has the following structural formula:
C8H12N4O5 M.W. 244.2
Ribavirin is a white to off-white powder. It is freely soluble in water and slightly soluble in anhydrous alcohol.
Ribavirin is available as a light-pink to pink, round standard normal convex, coated tablet for oral administration. Each tablet contains 200 mg of ribavirin and the following inactive ingredients: calcium phosphate dibasic, croscarmellose sodium, iron oxide black, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, povidone, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Multiple dose ribavirin pharmacokinetic data are available for HCV patients who received ribavirin in combination with peginterferon alfa-2a. Following administration of 1200 mg/day with food for 12 weeks mean ± SD (n = 39; body weight > 75 kg) AUC0-12hr was 25,361 ± 7110 ng•hr/mL and Cmax was 2748 ± 818 ng/mL. The average time to reach Cmax was 2 hours. Trough ribavirin plasma concentrations following 12 weeks of dosing with food were 1662 ± 545 ng/mL in HCV infected patients who received 800 mg/day (n = 89), and 2112 ± 810 ng/mL in patients who received 1200 mg/day (n = 75; body weight > 75 kg).
The terminal half-life of ribavirin following administration of a single oral dose of ribavirin is about 120 to 170 hours. The total apparent clearance following administration of a single oral dose of ribavirin is about 26 L/h. There is extensive accumulation of ribavirin after multiple dosing (twice daily) such that the Cmax at steady state was four-fold higher than that of a single dose.
Effect of Food on Absorption of Ribavirin
Bioavailability of a single oral dose of ribavirin was increased by coadministration with a high-fat meal. The absorption was slowed (Tmax was doubled) and the AUC0-192h and Cmax increased by 42% and 66%, respectively, when ribavirin was taken with a high-fat meal compared with fasting conditions [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Elimination and Metabolism
The contribution of renal and hepatic pathways to ribavirin elimination after administration of ribavirin is not known. In vitro studies indicate that ribavirin is not a substrate of CYP450 enzymes.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which ribavirin contributes to its antiviral efficacy in the clinic is not fully understood. Ribavirin has direct antiviral activity in tissue culture against many RNA viruses. Ribavirin increases the mutation frequency in the genomes of several RNA viruses and ribavirin triphosphate inhibits HCV polymerase in a biochemical reaction.
Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture
In the stable HCV cell culture model system (HCV replicon), ribavirin inhibited autonomous HCV RNA replication with a 50% effective concentration (EC50) value of 11 to 21 mcM. In the same model, PEG-IFN α-2a also inhibited HCV RNA replication, with an EC50 value of 0.1 to 3 ng/mL. The combination of PEG-IFN α-2a and ribavirin was more effective at inhibiting HCV RNA replication than either agent alone.
Resistance
Different HCV genotypes display considerable clinical variability in their response to PEG-IFN-α and ribavirin therapy. Viral genetic determinants associated with the variable response have not been definitively identified.
Cross-Resistance
Cross-resistance between IFN α and ribavirin has not been observed.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a p53 (+/-) mouse carcinogenicity study up to the maximum tolerated dose of 100 mg/kg/day, ribavirin was not oncogenic. Ribavirin was also not oncogenic in a rat 2 year carcinogenicity study at doses up to the maximum tolerated dose of 60 mg/kg/day. On a body surface area basis, these doses are approximately 0.5 and 0.6 times the maximum recommended daily human dose of ribavirin, respectively.
Mutagenesis
Ribavirin demonstrated mutagenic activity in the in vitro mouse lymphoma assay. No clastogenic activity was observed in an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay at doses up to 2000 mg/kg. However, results from studies published in the literature show clastogenic activity in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay at oral doses up to 2000 mg/kg. A dominant lethal assay in rats was negative, indicating that if mutations occurred in rats they were not transmitted through male gametes. However, potential carcinogenic risk to humans cannot be excluded.
Impairment of Fertility
In a fertility study in rats, ribavirin showed a marginal reduction in sperm counts at the dose of 100 mg/kg/day with no effect on fertility. Upon cessation of treatment, total recovery occurred after 1 spermatogenesis cycle. Abnormalities in sperm were observed in studies in mice designed to evaluate the time course and reversibility of ribavirin-induced testicular degeneration at doses of 15 to 150 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.1 to 0.8 times the maximum recommended daily human dose of ribavirin) administered for 3 to 6 months. Upon cessation of treatment, essentially total recovery from ribavirin-induced testicular toxicity was apparent within 1 or 2 spermatogenic cycles.
Female patients of childbearing potential and male patients with female partners of childbearing potential should not receive ribavirin unless the patient and his/her partner are using effective contraception (two reliable forms). Based on a multiple dose half-life (t1/2) of ribavirin of 12 days, effective contraception must be utilized for 6 months post therapy (i.e., 15 half-lives of clearance for ribavirin).
No reproductive toxicology studies have been performed using peginterferon alfa-2a in combination with ribavirin. However, peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin when administered separately, each has adverse effects on reproduction. It should be assumed that the effects produced by either agent alone would also be caused by the combination of the two agents.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In a study in rats, it was concluded that dominant lethality was not induced by ribavirin at doses up to 200 mg/kg for 5 days (up to 1.7 times the maximum recommended human dose of ribavirin).
Long-term studies in the mouse and rat (18 to 24 months; dose 20 to 75, and 10 to 40 mg/kg/day, respectively, approximately 0.1 to 0.4 times the maximum daily human dose of ribavirin) have demonstrated a relationship between chronic ribavirin exposure and an increased incidence of vascular lesions (microscopic hemorrhages) in mice. In rats, retinal degeneration occurred in controls, but the incidence was increased in ribavirin-treated rats.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Chronic Hepatitis C Patients
The safety and effectiveness of peginterferon alfa-2a in combination with ribavirin for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection were assessed in two randomized controlled clinical trials. All patients were adults, had compensated liver disease, detectable hepatitis C virus, liver biopsy diagnosis of chronic hepatitis, and were previously untreated with interferon. Approximately 20% of patients in both studies had compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh class A). Patients coinfected with HIV were excluded from these studies.
In Study NV15801, patients were randomized to receive either peginterferon alfa-2a 180 mcg subcutaneous once weekly with an oral placebo, peginterferon alfa-2a 180 mcg once weekly with ribavirin 1000 mg by mouth (body weight < 75 kg) or 1200 mg by mouth (body weight ≥ 75 kg) or interferon alfa-2b 3 MIU subcutaneous three times a week plus ribavirin 1000 mg or 1200 mg by mouth. All patients received 48 weeks of therapy followed by 24 weeks of treatment-free follow-up. Ribavirin or placebo treatment assignment was blinded. Sustained virological response was defined as undetectable (< 50 IU/mL) HCV RNA on or after study week 68. Peginterferon alfa-2a in combination with ribavirin resulted in a higher SVR compared to peginterferon alfa-2a alone or interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin (Table 5). In all treatment arms, patients with viral genotype 1, regardless of viral load, had a lower response rate to peginterferon alfa-2a in combination with ribavirin compared to patients with other viral genotypes.
|
Interferon alfa-2b + Ribavirin 1000 mg or 1200 mg |
Peginterferon alfa-2a + placebo |
Peginterferon alfa-2a + Ribavirin 1000 mg or 1200 mg |
|
|
All patients |
197/444 (44%) |
65/224 (29%) |
241/453 (53%) |
|
Genotype 1 |
103/285 (36%) |
29/145 (20%) |
132/298 (44%) |
|
Genotypes 2 to 6 |
94/159 (59%) |
36/79 (46%) |
109/155 (70%) |
Difference in overall treatment response (peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin – Interferon alfa-2b/ribavirin) was 9% (95% CI 2.3, 15.3).
In Study NV15942, all patients received peginterferon alfa-2a 180 mcg subcutaneous once weekly and were randomized to treatment for either 24 or 48 weeks and to a ribavirin dose of either 800 mg or 1000 mg/1200 mg (for body weight < 75 kg/≥ 75 kg). Assignment to the four treatment arms was stratified by viral genotype and baseline HCV viral titer. Patients with genotype 1 and high viral titer (defined as > 2 x 106 HCV RNA copies/mL serum) were preferentially assigned to treatment for 48 weeks.
Sustained Virologic Response (SVR) and HCV Genotype
HCV 1 and 4- Irrespective of baseline viral titer, treatment for 48 weeks with peginterferon alfa-2a and 1000 mg or 1200 mg of ribavirin resulted in higher SVR (defined as undetectable HCV RNA at the end of the 24 week treatment-free follow-up period) compared to shorter treatment (24 weeks) and/or 800 mg ribavirin.
HCV 2 and 3- Irrespective of baseline viral titer, treatment for 24 weeks with peginterferon alfa-2a and 800 mg of ribavirin resulted in a similar SVR compared to longer treatment (48 weeks) and/or 1000 mg or 1200 mg of ribavirin (see Table 6).
The numbers of patients with genotype 5 and 6 were too few to allow for meaningful assessment.
|
||||
|
|
24 Weeks Treatment |
48 Weeks Treatment |
||
|
Peginterferon alfa-2a + Ribavirin 800 mg (N = 207) |
Peginterferon alfa-2a + Ribavirin 1000 mg or 1200 mg* (N = 280) |
Peginterferon alfa-2a + Ribavirin 800 mg (N = 361) |
Peginterferon alfa-2a + Ribavirin 1000 mg or 1200 mg* (N = 436) |
|
|
Genotype 1 |
29/101 (29%) |
48/118 (41%) |
99/250 (40%) |
138/271 (51%) |
|
Genotypes 2, 3 |
79/96 (82%) |
116/144 (81%) |
75/99 (76%) |
117/153 (76%) |
|
Genotype 4 |
0/5 (0%) |
7/12 (58%) |
5/8 (63%) |
9/11 (82%) |
14.2 Other Treatment Response Predictors
Treatment response rates are lower in patients with poor prognostic factors receiving pegylated interferon alpha therapy. In studies NV15801 and NV15942, treatment response rates were lower in patients older than 40 years (50% vs. 66%), in patients with cirrhosis (47% vs. 59%), in patients weighing over 85 kg (49% vs. 60%), and in patients with genotype 1 with high vs. low viral load (43% vs. 56%). African-American patients had lower response rates compared to Caucasians.
In studies NV15801 and NV15942, lack of early virologic response by 12 weeks (defined as HCV RNA undetectable or > 2 log10 lower than baseline) was grounds for discontinuation of treatment. Of patients who lacked an early viral response by 12 weeks and completed a recommended course of therapy despite a protocol-defined option to discontinue therapy, 5/39 (13%) achieved an SVR. Of patients who lacked an early viral response by 24 weeks, 19 completed a full course of therapy and none achieved an SVR.
14.3 Chronic Hepatitis C/HIV Coinfected Patients
In Study NR15961, patients with CHC/HIV were randomized to receive either peginterferon alfa-2a 180 mcg subcutaneous once weekly plus an oral placebo, peginterferon alfa-2a 180 mcg once weekly plus ribavirin 800 mg by mouth daily or interferon alfa-2a, 3 MIU subcutaneous three times a week plus ribavirin 800 mg by mouth daily. All patients received 48 weeks of therapy and sustained virologic response (SVR) was assessed at 24 weeks of treatment-free follow-up. Ribavirin or placebo treatment assignment was blinded in the peginterferon alfa-2a treatment arms. All patients were adults, had compensated liver disease, detectable hepatitis C virus, liver biopsy diagnosis of chronic hepatitis C, and were previously untreated with interferon. Patients also had CD4+ cell count ≥ 200 cells/mcL or CD4+ cell count ≥ 100 cells/mcL but < 200 cells/mcL and HIV-1 RNA < 5000 copies/mL, and stable status of HIV. Approximately 15% of patients in the study had cirrhosis. Results are shown in Table 7.
|
|
Interferon alfa-2a + Ribavirin 800 mg (N = 289) |
Peginterferon alfa-2a + Placebo
|
Peginterferon alfa-2a + Ribavirin 800 mg
|
|
All patients |
33 (11%) |
58 (20%) |
116 (40%) |
|
Genotype 1 |
12/171 (7%) |
24/175 (14%) |
51/176 (29%) |
|
Genotypes 2, 3 |
18/89 (20%) |
32/90 (36%) |
59/95 (62%) |
Treatment response rates were lower in CHC/HIV patients with poor prognostic factors (including HCV genotype 1, HCV RNA > 800,000 IU/mL, and cirrhosis) receiving pegylated interferon alpha therapy.
Of the patients who did not demonstrate either undetectable HCV RNA or at least a 2 log10 reduction from baseline in HCV RNA titer by 12 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin combination therapy, 2% (2/85) achieved an SVR.
In CHC patients with HIV coinfection who received 48 weeks of peginterferon alfa-2a alone or in combination with ribavirin treatment, mean and median HIV RNA titers did not increase above baseline during treatment or 24 weeks post treatment.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Ribavirin tablets, 200 mg for oral administration are available as follows:
Each tablet contains 200 mg of ribavirin and is light-pink to pink, round standard normal convex, coated tablet, debossed with “93” on one side and “7232” on the other side in bottles of 168.
Storage and Handling
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep bottle tightly closed.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required).
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See Medication Guide
Pregnancy
Patients must be informed that ribavirin may cause birth defects and/or death of the exposed fetus. Ribavirin therapy must not be used by women who are pregnant or by men whose female partners are pregnant. Extreme care must be taken to avoid pregnancy in female patients and in female partners of male patients taking ribavirin therapy and for 6 months post therapy. Ribavirin therapy should not be initiated until a report of a negative pregnancy test has been obtained immediately prior to initiation of therapy. Patients must perform a pregnancy test monthly during therapy and for 6 months post therapy.
Female patients of childbearing potential and male patients with female partners of childbearing potential must be advised of the teratogenic/embryocidal risks and must be instructed to practice effective contraception during ribavirin therapy and for 6 months post therapy. Patients should be advised to notify the healthcare provider immediately in the event of a pregnancy [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Anemia
The most common adverse event associated with ribavirin is anemia, which may be severe [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Patients should be advised that laboratory evaluations are required prior to starting ribavirin therapy and periodically thereafter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]. It is advised that patients be well hydrated, especially during the initial stages of treatment.
Patients who develop dizziness, confusion, somnolence, and fatigue should be cautioned to avoid driving or operating machinery.
Patients should be advised to take ribavirin with food.
Patients should be questioned about prior history of drug abuse before initiating ribavirin/peginterferon alfa-2a, as relapse of drug addiction and drug overdoses have been reported in patients treated with interferons.
Patients should be advised not to drink alcohol, as alcohol may exacerbate chronic hepatitis C infection.
Patient should be informed about what to do in the event they miss a dose of ribavirin. The missed doses should be taken as soon as possible during the same day. Patients should not double the next dose. Patients should be advised to call their healthcare provider if they have questions.
Patients should be informed that the effect of peginterferon alfa-2a/ribavirin treatment of hepatitis C infection on transmission is not known, and that appropriate precautions to prevent transmission of hepatitis C virus should be taken.
Patients should be informed regarding the potential benefits and risks attendant to the use of ribavirin. Instructions on appropriate use should be given, including review of the contents of the enclosed MEDICATION GUIDE, which is not a disclosure of all or possible adverse effects.
Manufactured In Israel By:
TEVA PHARMACEUTICAL IND. LTD.
Jerusalem, 91010, Israel
Manufactured For:
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA
Sellersville, PA 18960
Rev. J 12/2010
FDA-approved Medication Guide
MEDICATION GUIDE
Ribavirin Tablets
Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking ribavirin tablets and read the Medication Guide each time you get more ribavirin tablets. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
Also read the Medication Guide for PEGASYS® (peginterferon alfa-2a).
What is the most important information I should know about ribavirin tablets?
- 1.
- You should not take ribavirin tablets alone to treat chronic hepatitis C infection. Ribavirin tablets should be used with peginterferon alfa-2a to treat chronic hepatitis C infection.
- 2.
- Ribavirin tablets may cause you to have a blood problem (hemolytic anemia) that can worsen any heart problems you have, and cause you to have a heart attack or die. Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had any heart problems. Ribavirin tablets may not be right for you. If you have chest pain while you take ribavirin tablets, get emergency medical attention right away.
- 3.
- Ribavirin tablets may cause birth defects or death of your unborn baby. If you are pregnant or your sexual partner is pregnant, do not take ribavirin tablets. You or your sexual partner should not become pregnant while you take ribavirin tablets and for 6 months after treatment is over. You must use two forms of birth control when you take ribavirin tablets and for the 6 months after treatment.
- •
- Females must have a pregnancy test before starting ribavirin tablets, every month while treated with ribavirin tablets, and every month for the 6 months after treatment with ribavirin tablets.
- •
- If you or your female sexual partner becomes pregnant while taking ribavirin tablets or within 6 months after you stop taking ribavirin tablets, tell your healthcare provider right away. You or your healthcare provider should contact the Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry by calling 1-800-593-2214. The Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry collects information about what happens to mothers and their babies if the mother takes ribavirin tablets while she is pregnant.
What are ribavirin tablets?
Ribavirin tablets is a medicine used with another medicine called peginterferon alfa-2a to treat chronic (lasting a long time) hepatitis C infection in people whose liver still works normally, and who have not been treated before with a medicine called an interferon alpha. It is not known if ribavirin tablets are safe and will work in children under 18 years of age.
Who should not take ribavirin tablets?
See “What is the most important information I should know about ribavirin tablets?”
Do not take ribavirin tablets if you:
- •
- have certain types of hepatitis caused by your immune system attacking your liver (autoimmune hepatitis)
- •
- have certain blood disorders, such as thalassemia major or sickle-cell anemia (hemoglobinopathies)
- •
- have severe kidney disease
- •
- take didanosine (Videx® or Videx EC®)
Talk to your healthcare provider before starting treatment with ribavirin tablets if you have any of these medical conditions.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking ribavirin tablets?
Before you take ribavirin tablets, tell your healthcare provider if you have or have had:
- •
- treatment for hepatitis C that did not work for you
- •
- serious allergic reactions to ribavirin tablets or to any of the ingredients in ribavirin tablets. See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of ingredients.
- •
- breathing problems. Ribavirin tablets may cause or worsen your breathing problems you already have.
- •
- vision problems. Ribavirin tablets may cause eye problems or worsen eye problems you already have. You should have an eye exam before you start treatment with ribavirin tablets.
- •
- certain blood disorders such as anemia
- •
- high blood pressure, heart problems or have had a heart attack. Your healthcare provider should test your blood and heart before you start treatment with ribavirin tablets.
- •
- thyroid problems
- •
- diabetes. Ribavirin tablets and peginterferon alfa-2a combination therapy may make your diabetes worse or harder to treat.
- •
- liver problems other than hepatitis C virus infection
- •
- human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or other immunity problems
- •
- mental health problems, including depression or thoughts of suicide
- •
- kidney problems
- •
- an organ transplant
- •
- drug addiction or abuse
- •
- infection with hepatitis B virus
- •
- any other medical condition
- •
- are breast feeding. It is not known if ribavirin passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take ribavirin tablets or breast-feed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Some medicines can cause serious side effects if taken while you also take ribavirin tablets. Some medicines may affect how ribavirin tablets work or ribavirin tablets may affect how your other medicines work.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take any medicines to treat HIV, including didanosine (Videx® or Videx EC®), or if you take azathioprine (Imuran® or Azasan®).
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take ribavirin tablets?
- •
- Take ribavirin tablets exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Your healthcare provider will tell you how many ribavirin tablets to take and when to take it.
- •
- Take ribavirin tablets with food.
- •
- If you miss a dose of ribavirin tablets, take the missed dose as soon as possible during the same day. Do not double the next dose. If you have questions about what to do, call your healthcare provider.
- •
- If you take too many ribavirin tablets, call your healthcare provider or local Poison Control Center right away, or go the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
- •
- Your healthcare provider should do blood tests before you start treatment with ribavirin tablets, at weeks 2 and 4 of treatment, and then as needed to see how well you are tolerating treatment and to check for side effects. Your healthcare provider may change your dose of ribavirin tablets based on blood test results or side effects you may have.
- •
- If you have heart problems, your healthcare provider should check your heart by doing an electrocardiogram before you start treatment with ribavirin tablets, and if needed during treatment.
What should I avoid while taking ribavirin tablets?
- •
- Ribavirin tablets can make you feel tired, dizzy, or confused. You should not drive or operate machinery if you have any of these symptoms.
- •
- Do not drink alcohol, including beer, wine, and liquor. This may make your liver disease worse.
What are the possible side effects of ribavirin tablets?
Ribavirin tablets may cause serious side effects including:
See “What is the most important information I should know about ribavirin tablets?”
- •
- Swelling and irritation of your pancreas (pancreatitis). You may have stomach pain, nausea, vomiting or diarrhea.
- •
- Severe allergic reactions. Symptoms may include hives, wheezing, trouble breathing, chest pain, swelling of your mouth, tongue, or lips, or severe rash.
- •
- Serious breathing problems. Difficulty breathing may be a sign of a serious lung infection (pneumonia) that can lead to death.
- •
- Serious eye problems that may lead to vision loss or blindness.
- •
- Liver problems. Some people may get worsening of liver function. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms: stomach bloating, confusion, brown urine, and yellow eyes.
- •
- Severe depression
- •
- Suicidal thoughts and attempts
Call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you have any of the symptoms listed above. These may be signs of a serious side effect of ribavirin tablet treatment.
Common side effects of ribavirin tablets taken with peginterferon alfa-2a include:
- •
- flu-like symptoms-feeling tired, headache, shaking along with high temperature (fever), and muscle or joint aches
- •
- mood changes, feeling irritable, anxiety, and difficulty sleeping
- •
- loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- •
- hair loss
- •
- itching
Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of ribavirin tablet treatment. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to Teva Pharmaceuticals USA at 1-888-838-2872, X6351.
How should I store ribavirin tablets?
- •
- Store ribavirin tablets tablets between 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
- •
- Keep the bottle tightly closed.
Keep ribavirin tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of ribavirin tablets
It is not known if treatment with ribavirin tablets can cure hepatitis C or if it can prevent liver damage (cirrhosis), liver failure or liver cancer that is caused by hepatitis C virus infections. It is not known if treatment with ribavirin tablets will prevent an infected person from spreading the hepatitis C virus to another person.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use ribavirin tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ribavirin tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about ribavirin tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about ribavirin tablets that is written for healthcare professionals.
What are the ingredients in ribavirin tablets?
Active Ingredient: ribavirin
Inactive Ingredients: calcium phosphate dibasic, croscarmellose sodium, iron oxide black, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, povidone, talc, and titanium dioxide.
All brand names listed are the registered trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Teva Pharmaceuticals USA.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured In Israel By:
TEVA PHARMACEUTICAL IND. LTD.
Jerusalem, 91010, Israel
Manufactured For:
TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA
Sellersville, PA 18960
Rev. E 10/2010
| RIBAVIRIN
ribavirin tablet, coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Teva Pharmaceuticals USA Inc (001627975) |