OFLOXACIN- ofloxacin solution
REMEDYREPACK INC.
----------
Ofloxacin Ophthalmic Solution USP 0.3%
DESCRIPTION
Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.3% is a sterile ophthalmic solution. It is a fluorinated carboxyquinolone anti-infective for topical ophthalmic use.
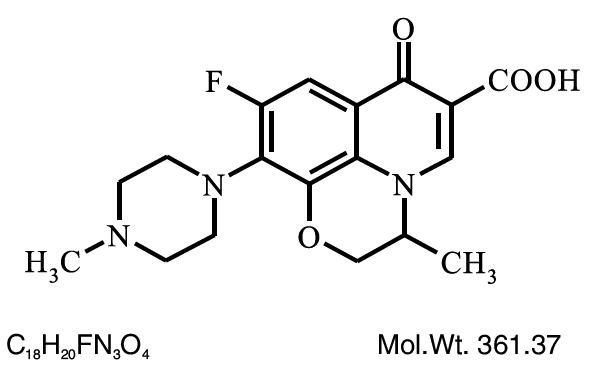
Chemical Name: (±)-9-Fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H pyrido [1,2,3-de]-1,4 benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid.
Contains: Active: ofloxacin 0.3% (3 mg/mL)
Preservative: benzalkonium chloride (0.005%)
Inactives: sodium chloride and water for injection. May also contain hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide to adjust pH.
Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution is unbuffered and formulated with a pH of 6.4 (range 6.0 to 6.8). It has an osmolality of 300 mOsm/kg. Ofloxacin is a fluorinated 4-quinolone which differs from other fluorinated 4-quinolones in that there is a six member (pyridobenzoxazine) ring from positions 1 to 8 of the basic ring structure.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Serum, urine and tear concentrations of ofloxacin were measured in 30 healthy women at various time points during a ten-day course of treatment with ofloxacin ophthalmic solution. The mean serum ofloxacin concentration ranged from 0.4 ng/mL to 1.9 ng/mL. Maximum ofloxacin concentration increased from 1.1 ng/mL on day one to 1.9 ng/mL on day 11 after QID dosing for 10 1/2 days. Maximum serum ofloxacin concentrations after ten days of topical ophthalmic dosing were more than 1000 times lower than those reported after standard oral doses of ofloxacin.
Tear ofloxacin concentrations ranged from 5.7 to 31 mcg/g during the 40 minute period following the last dose on day 11. Mean tear concentration measured four hours after topical ophthalmic dosing was 9.2 mcg/g.
Corneal tissue concentrations of 4.4 mcg/mL were observed four hours after beginning topical ocular application of two drops of ofloxacin ophthalmic solution every 30 minutes. Ofloxacin was excreted in the urine primarily unmodified.
Ofloxacin has in vitro activity against a broad range of gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Ofloxacin is bactericidal at concentrations equal to or slightly greater than inhibitory concentrations. Ofloxacin is thought to exert a bactericidal effect on susceptible bacterial cells by inhibiting DNA gyrase, an essential bacterial enzyme which is a critical catalyst in the duplication, transcription, and repair of bacterial DNA.
Cross-resistance has been observed between ofloxacin and other fluoroquinolones. There is generally no cross-resistance between ofloxacin and other classes of antibacterial agents such as beta-lactams or aminoglycosides.
Ofloxacin has been shown to be active against most strains of the following organisms both in vitro and clinically, in conjunctival and/or corneal ulcer infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section.
| AEROBES, GRAM-POSITIVE: | AEROBES, GRAM-NEGATIVE: |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Enterobacter cloacae |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | Haemophilus influenzae |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Proteus mirabilis |
| ANAEROBIC SPECIES: | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| Propionibacterium acnes | Serratia marcescens * |
|
|
The safety and effectiveness of ofloxacin ophthalmic solution in treating ophthalmologic infections due to the following organisms have not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials. Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution has been shown to be active in vitro against most strains of these organisms but the clinical significance in ophthalmologic infections is unknown.
| AEROBES, GRAM-POSITIVE: | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | Staphylococcus hominus |
| Listeria monocytogenes | Staphylococcus simulans |
| Staphylococcus capitis | Streptococcus pyogenes |
| AEROBES, GRAM-NEGATIVE: | |
| Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. anitratus | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| Acinetobacter calcoaceticus var. lwoffii | Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis |
| Citrobacter diversus | Moraxella lacunata |
| Citrobacter freundii | Morganella morganii |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
| Enterobacter agglomerans | Pseudomonas acidovorans |
| Escherichia coli | Pseudomonas fluorescens |
| Haemophilus parainfluenzae | Shigella sonnei |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | |
| OTHER: | |
| Chlamydia trachomatis |
Conjunctivitis: In a randomized, double-masked, multicenter clinical trial, ofloxacin ophthalmic solution was superior to its vehicle after 2 days of treatment in patients with conjunctivitis and positive conjunctival cultures. Clinical outcomes for the trial demonstrated a clinical improvement rate of 86% (54/63) for the ofloxacin treated group versus 72% (48/67) for the placebo treated group after 2 days of therapy. Microbiological outcomes for the same clinical trial demonstrated an eradication rate for causative pathogens of 65% (41/63) for the ofloxacin treated group versus 25% (17/67) for the vehicle treated group after 2 days of therapy. Please note that microbiologic eradication does not always correlate with clinical outcome in anti-infective trials.
Corneal Ulcers: In a randomized, double-masked, multi-center clinical trial of 140 subjects with positive cultures, ofloxacin ophthalmic solution treated subjects had an overall clinical success rate (complete reepithelialization and no progression of the infiltrate for two consecutive visits) of 82% (61/74) compared to 80% (53/66) for the fortified antibiotic group, consisting of 1.5% tobramycin and 10% cefazolin solutions. The median time to clinical success was 11 days for the ofloxacin treated group and 10 days for the fortified treatment group.
- 1
- Efficacy for this organism was studied in fewer than 10 infections
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the following bacteria in the conditions listed below:
| CONJUNCTIVITIS: | |
| Gram-positive bacteria: | Gram-negative bacteria: |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Enterobacter cloacae |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | Haemophilus influenzae |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Proteus mirabilis |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |
| CORNEAL ULCERS: | |
| Gram-positive bacteria: | Gram-negative bacteria: |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | Serratia marcescens * |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | Anaerobic species: |
| Propionibacterium acnes | |
|
|
- 2
- Efficacy for this organism was studied in fewer than 10 infections
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Ofloxacin Ophthalmic Solution is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to ofloxacin, to other quinolones, or to any of the components in this medication.
WARNINGS
NOT FOR INJECTION.
Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution should not be injected subconjunctivally, nor should it be introduced directly into the anterior chamber of the eye.
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions, some following the first dose, have been reported in patients receiving systemic quinolones, including ofloxacin. Some reactions were accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, angioedema (including laryngeal, pharyngeal or facial edema), airway obstruction, dyspnea, urticaria, and itching. A rare occurrence of Stevens-Johnson syndrome, which progressed to toxic epidermal necrolysis, has been reported in a patient who was receiving topical ophthalmic ofloxacin. If an allergic reaction to ofloxacin occurs, discontinue the drug. Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions may require immediate emergency treatment. Oxygen and airway management, including intubation should be administered as clinically indicated.
PRECAUTIONS
As with other anti-infectives, prolonged use may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi. If superinfection occurs discontinue use and institute alternative therapy. Whenever clinical judgement dictates, the patient should be examined with the aid of magnification, such as slit lamp biomicroscopy and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining. Ofloxacin should be discontinued at the first appearance of a skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity reaction.
The systemic administration of quinolones, including ofloxacin, has led to lesions or erosions of the cartilage in weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature animals of various species. Ofloxacin, administered systemically at 10 mg/kg/day in young dogs (equivalent to 110 times the maximum recommended daily adult ophthalmic dose) has been associated with these types of effects.
Avoid contaminating the applicator tip with material from the eye, fingers or other source.
Systemic quinolones, including ofloxacin, have been associated with hypersensitivity reactions, even following a single dose. Discontinue use immediately and contact your physician at the first sign of a rash or allergic reaction.
Specific drug interaction studies have not been conducted with ofloxacin ophthalmic solution. However, the systemic administration of some quinolones has been shown to elevate plasma concentrations of theophylline, interfere with the metabolism of caffeine, and enhance the effects of the oral anticoagulant warfarin and its derivatives, and has been associated with transient elevations in serum creatinine in patients receiving cyclosporine concomitantly.
Long term studies to determine the carcinogenic potential of ofloxacin have not been conducted.
Ofloxacin was not mutagenic in the Ames test, in vitro and in vivo cytogenic assay, sister chromatid exchange assay (Chinese hamster and human cell lines), unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) assay using human fibroblasts, the dominant lethal assay, or mouse micronucleus assay. Ofloxacin was positive in the UDS test using rat hepatocyte, and in the mouse lymphoma assay.
In fertility studies in rats, ofloxacin did not affect male or female fertility or morphological or reproductive performance at oral dosing up to 360 mg/kg/day (equivalent to 4000 times the maximum recommended daily ophthalmic dose).
Pregnancy Category C: Ofloxacin has been shown to have an embryocidal effect in rats and in rabbits when given in doses of 810 mg/kg/day (equivalent to 9000 times the maximum recommended daily ophthalmic dose) and 160 mg/kg/day (equivalent to 1800 times the maximum recommended daily ophthalmic dose). These dosages resulted in decreased fetal body weight and increased fetal mortality in rats and rabbits, respectively. Minor fetal skeletal variations were reported in rats receiving doses of 810 mg/kg/day. Ofloxacin has not been shown to be teratogenic at doses as high as 810 mg/kg/day and 160 mg/kg/day when administered to pregnant rats and rabbits, respectively.
Additional studies in rats with doses up to 360 mg/kg/day during late gestation showed no adverse effect on late fetal development, labor, delivery, lactation, neonatal viability, or growth of the newborn.
There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
In nursing women a single 200 mg oral dose resulted in concentrations of ofloxacin in milk which were similar to those found in plasma. It is not known whether ofloxacin is excreted in human milk following topical ophthalmic administration. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from ofloxacin in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Safety and effectiveness in infants below the age of one year have not been established.
Quinolones, including ofloxacin, have been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals after oral administration; however, topical ocular administration of ofloxacin to immature animals has not shown any arthropathy. There is no evidence that the ophthalmic dosage form of ofloxacin has any effect on weight bearing joints.
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Ophthalmic Use: The most frequently reported drug-related adverse reaction was transient ocular burning or discomfort. Other reported reactions include stinging, redness, itching, chemical conjunctivitis/keratitis, ocular/periocular/facial edema, foreign body sensation, photophobia, blurred vision, tearing, dryness, and eye pain. Rare reports of dizziness and nausea have been reported.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage regimen for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis is:
| Days 1 and 2 | Instill one to two drops every two to four
hours in the affected eye(s). |
| Days 3 through 7 | Instill one to two drops four times daily. |
| The recommended dosage regimen for the treatment of bacterial corneal ulcer is: | |
| Days 1 and 2 | Instill one to two drops into the affected eye
every 30 minutes, while awake. Awaken at approximately four and six hours after retiring and instill one to two drops. |
| Days 3 through 7 to 9 | Instill one to two drops hourly, while awake. |
| Days 7 to 9 through
treatment completion | Instill one to two drops, four times daily. |
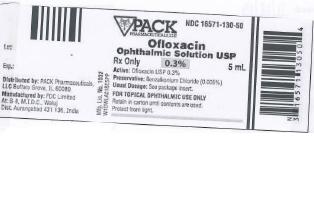
HOW SUPPLIED
Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution 0.3% is supplied sterile in translucent LDPE plastic ophthalmic dispensers with tan coloured high impact polystyrene (HIPS) spike caps as follows:
5 mL in 5 mL bottle NDC 16571-130-50
10 mL in 10 mL bottle NDC 16571-130-11
Note: Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F)[see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Rx Only
Manufactured for:
PACK Pharmaceuticals, LLC
1110 W.Lake Cook Rd., Ste 152
Buffalo Grove, IL 60031
MADE IN INDIA
Revision 03/09
SPL UNCLASSIFIED
Please follow these instructions carefully when using Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution. Use Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution as prescribed by your doctor.
- If you use other topically applied ophthalmic medications, they should be administered at least 10 minutes before or after the use of Ofloxacin ophthalmic solution.
- Wash hands before each use.
-

Tighten the cap on the nozzle till the cap touches the shoulder.
-

The spike in the cap will pierce the tip of the bottle. To open the bottle unscrew the cap
-
Tilt your head back and pull your lower eyelid down slightly to form a pocket between your eyelid and your eye.
Invert the bottle and press lightly until a single drop is dispensed into the eye as directed by your doctor.
Do not touch your eye or eyelid with the dropper tip.
Repeat steps 5 with the other eye if instructed to do so by your doctor. -
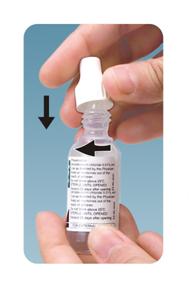
Replace the cap by turning until it is firmly touching the bottle.
Do not overtighten the cap. - OPHTHALMIC MEDICATIONS, IF HANDLED IMPROPERLY, CAN BECOME CONTAMINATED BY COMMON BACTERIA KNOWN TO CAUSE EYE INFECTIONS. SERIOUS DAMAGE TO THE EYE AND SUBSEQUENT LOSS OF VISION MAY RESULT FROM USING CONTAMINATED OPHTHALMIC MEDICATIONS. IF YOU THINK YOUR MEDICATION MAY BE CONTAMINATED, OR IF YOU DEVELOP AN EYE INFECTION, CONTACT YOUR DOCTOR IMMEDIATELY CONCERNING CONTINUED USE OF THIS BOTTLE
- The dispenser tip is designed to provide a premeasured drop; therefore, do NOT enlarge the hole of the dispenser tip.
- After you have used all doses, there will be some timolol left in the bottle. You should not be concerned since an extra amount of timolol has been added and you will get the full amount of timolol that your doctor prescribed. Do not attempt to remove excess medicine from the bottle.
WARNING: KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
IF YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS ABOUT THE USE OF TIMOLOL MALEATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION, PLEASE CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR.
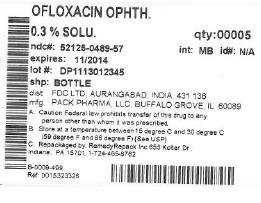
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
DRUG: ofloxacin
GENERIC: ofloxacin
DOSAGE: SOLUTION
ADMINSTRATION: OPHTHALMIC
NDC: 52125-489-57
ACTIVE INGREDIENT(S):
- ofloxacin 3mg in 1mL
INACTIVE INGREDIENT(S):
- benzalkonium chloride
- sodium hydroxide
- hydrochloric acid
- sodium chloride
PACKAGING: 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC
| OFLOXACIN
ofloxacin solution |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - REMEDYREPACK INC. (829572556) |