TRETINOIN- tretinoin gel
Spear Dermatology Products
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRETINOIN GEL (microsphere) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRETINOIN GEL (microsphere).
TRETINOIN gel (microsphere), for topical use Initial U.S. Approval: 1997 INDICATIONS AND USAGETretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and 0.04%, is a retinoid, indicated for topical treatment of acne vulgaris. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONDOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSGel, 0.04% and 0.1% (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSNone. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions are skin pain, pruritus, skin irritation/subcutaneous irritation, pharyngitis, and erythema. (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Spear Dermatology Products at 1-866-SPEAR-RX (773-2279) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 5/2016 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and 0.04%, is a retinoid indicated for topical application in the treatment of acne vulgaris.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For topical use only. Not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use.
Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and 0.04%, should be applied once a day, in the evening, to the skin where acne lesions appear, using enough to cover the entire affected area in a thin layer. Areas to be treated should be cleansed thoroughly before the medication is applied. If medication is applied excessively, no more rapid or better results will be obtained and marked redness, peeling, or discomfort may occur. A transitory feeling of warmth or slight stinging may be noted on application. In cases where it has been necessary to temporarily discontinue therapy or to reduce the frequency of application, therapy may be resumed or the frequency of application increased as the patient becomes able to tolerate the treatment. Frequency of application should be closely monitored by careful observation of the clinical therapeutic response and skin tolerance. Efficacy has not been established for less than once daily dosing frequencies.
During the early weeks of therapy, an apparent exacerbation of inflammatory lesions may occur. If tolerated, this should not be considered a reason to discontinue therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Therapeutic results may be noticed after two weeks, but more than seven weeks of therapy are required before consistent beneficial effects are observed.
Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and 0.04% should be kept away from the eyes, the mouth, paranasal creases of the nose, and mucous membranes.
Patients treated with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and 0.04% may use cosmetics.
Concomitant topical medication, medicated or abrasive soaps and cleansers, products that have a strong drying effect, products with high concentrations of alcohol, astringents, or spices should be used with caution because of possible interaction with tretinoin. Avoid contact with the peel of limes. Particular caution should be exercised with the concomitant use of topical over-the-counter acne preparations containing benzoyl peroxide, sulfur, resorcinol, or salicylic acid with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and 0.04%. It also is advisable to allow the effects of such preparations to subside before use of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and 0.04%, is begun.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) is a white to very pale yellow opaque gel. Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) is available in two strengths: 0.04% and 0.1%.
Each gram of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% contains 1 mg of tretinoin.
Each gram of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04% contains 0.4 mg of tretinoin.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Local Irritation
The skin of certain individuals may become excessively dry, red, swollen, or blistered.
Tretinoin has been reported to cause severe irritation on eczematous skin and should be used with utmost caution in patients with this condition.
If the degree of irritation warrants, patients should be directed to temporarily reduce the amount or frequency of application of the medication, discontinue use temporarily, or discontinue use all together. Efficacy at reduced frequencies of application has not been established. If a reaction suggesting sensitivity occurs, use of the medication should be discontinued.
To help limit skin irritation, patients must
- wash the treated skin gently, using a mild, non-medicated soap, and pat it dry, and
- avoid washing the treated skin too often or scrubbing it hard when washing.
Patients should apply a topical moisturizer if dryness is bothersome.
5.2 Exposure to Ultraviolet Light or Weather Extremes
Unprotected exposure to sunlight, including sunlamps (UV light) should be avoided or minimized during the use of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and 0.04%, and patients with sunburn should be advised not to use the product until fully recovered because of heightened susceptibility to sunlight as a result of the use of tretinoin. Patients who may be required to have extended periods of UV exposure (e.g., due to occupation or sports), or those with inherent sensitivity to the sun, or those using medications that cause photosensitivity, should exercise particular caution. Use of sunscreen products (SPF15 or higher) and protective clothing over treated areas are recommended when exposure cannot be avoided [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Weather extremes, such as wind or cold, also may be irritating to tretinoin-treated skin.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Clinical Trials in Subjects with Acne
In separate clinical trials for each concentration, acne subjects treated with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% or 0.04%, over the twelve week period showed that cutaneous irritation scores for erythema, peeling, dryness, burning/stinging, or itching peaked during the initial two weeks of therapy, decreasing thereafter.
Approximately half of the subjects treated with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04% had cutaneous irritation at Week 2. Of those subjects who did experience cutaneous side effects, most had signs or symptoms that were mild in severity (severity was ranked on a 4-point ordinal scale: 0=none, 1=mild, 2=moderate, and 3=severe). Less than 10% of patients experienced moderate cutaneous irritation and there was no severe irritation at Week 2.
In trials of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04%, throughout the treatment period the majority of subjects experienced some degree of irritation (mild, moderate, or severe) with 1% (2/225) of subjects having scores indicative of a severe irritation; 1.3% (3/225) of subjects treated with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04%, discontinued treatment due to irritation, which included dryness in one patient and peeling and urticaria in another.
In trials of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1%, no more than 3% of subjects had cutaneous irritation scores indicative of severe irritation; 6% (14/224) of subjects treated with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% discontinued treatment due to irritation. Of these 14 subjects, four had severe irritation after 3 to 5 days of treatment, with blistering in one subject.
In a double-blind trial with 156 acne subjects comparing 12 weeks of treatment with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04% or 0.1% (78 subjects each group), the most frequently-reported adverse events affected the skin and subcutaneous tissue (15.4% in the 0.04% group, and 20.5% in the 0.1% group). The most prevalent of the dermatologic adverse events in the 0.04% group was skin irritation (6.4%); and in the 0.1% group skin burning (7.7%), erythema (5.1%), skin irritation (3.8%), and dermatitis (3.8%). Most adverse events were of mild intensity (63.4%), and 34.4% were moderate. One subject in each group had adverse events characterized as severe, neither were dermatologic findings and neither was characterized as related to drug by the investigator.
Trials in Subjects Without Acne
In a half-face comparison trial conducted for up to 14 days in women with sensitive skin, but without acne, tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% was statistically less irritating than tretinoin cream, 0.1%. In addition, a cumulative 21 day irritation evaluation in subjects with normal skin showed that tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1%, had a lower irritation profile than tretinoin cream, 0.1%. The clinical significance of these irritation trials for patients with acne is not established. Comparable effectiveness of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and tretinoin cream, 0.1%, has not been established. The lower irritancy of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% in subjects without acne may be attributable to the properties of its vehicle. The contribution of decreased irritancy by the methyl methacrylate/glycol dimethacrylate crosspolymer porous microspheres has not been established. No irritation trials have been performed to compare tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04%, with either tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1%, or tretinoin cream, 0.1%.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere). Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a casual relationship to drug exposure.
Temporary hyper- or hypopigmentation has been reported with repeated application of tretinoin.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Thirty human cases of temporally associated congenital malformations have been reported during two decades of clinical use of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and 0.04%. Although no definite pattern of teratogenicity and no causal association has been established from these cases, five of the reports describe the rare birth defect category holoprosencephaly (defects associated with incomplete midline development of the forebrain). The significance of these spontaneous reports in terms of risk to the fetus is not known.
For purposes of comparison of the animal exposure to systemic human exposure, the Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) applied topically is defined as 1 gram of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% applied daily to a 60 kg person (0.017 mg tretinoin/kg body weight).
Pregnant rats were treated with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% at daily dermal doses of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/day on gestation days 6-15. Alterations were seen in vertebrae and ribs of offspring at 5 to 10 times the MRHD based on the body surface area (BSA) comparison.
Pregnant New Zealand White rabbits were treated with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% at daily dermal doses of 0.2, 0.5, and 1.0 mg/kg/day tretinoin on gestation days 7-19. Doses were administered topically for 24 hours a day while wearing Elizabethan collars to prevent ingestion of the drug. Increased incidences of certain alterations, including domed head and hydrocephaly, typical of retinoid-induced fetal malformations in this species, were observed at 0.5 and 1.0 mg/kg/day. Similar malformations were not observed at 0.2 mg/kg/day, 4 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison. Other pregnant rabbits exposed topically for six hours per day to 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg/day tretinoin while restrained in stocks to prevent ingestion, did not show any teratogenic effects at doses up to 19 times (1.0 mg/kg/day) the MRHD based on BSA comparison, but fetal resorptions were increased at 0.5 mg/kg (10 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison).
Oral tretinoin has been shown to be teratogenic in rats, mice, rabbits, hamsters, and nonhuman primates.
Tretinoin was teratogenic in Wistar rats when given orally in doses greater than 1 mg/kg/day (10 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison). In the cynomolgus monkey, fetal malformations were reported for doses of 10 mg/kg/day but none were observed at 5 mg/kg/day (95 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison), although increased skeletal variations were observed at all doses. Dose-related increases in embryolethality and abortion also were reported. Similar results have also been reported in pigtail macaques.
There is evidence for teratogenicity (shortened or kinked tail) of topical tretinoin in Wistar rats at doses greater than 1 mg/kg/day (10 times the maximum MRHD based on BSA comparison). Anomalies (humerus: short 13%, bent 6%, os parietal incompletely ossified 14%) have also been reported when 10 mg/kg/day was topically applied. Supernumerary ribs have been a consistent finding in rats when dams were treated topically or orally with retinoids.
In oral peri- and postnatal development studies in rats with tretinoin, decreased survival of neonates and growth retardation were observed at doses in excess of 2 mg/kg/day (19 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison).
Nonteratogenic effects on fetus
Oral tretinoin has been shown to be fetotoxic when administered (in doses 24 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison).
Topical tretinoin has been shown to be fetotoxic in rabbits when administered in doses 10 times the MHRD based on BSA comparison.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% or 0.04%, is administered to a nursing woman.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Oral ingestion of large amounts of the drug may lead to the same side effects as those associated with excessive oral intake of Vitamin A.
11 DESCRIPTION
Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% and 0.04%, is a a white to very pale yellow opaque gel for topical treatment of acne vulgaris.
Chemically, tretinoin is all-trans-retinoic acid, also known as (all-E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid. It is a member of the retinoid class of compounds, and a metabolite of naturally occurring Vitamin A. Tretinoin has a molecular weight of 300.44, a molecular formula of C20H28O2 and the following chemical structure:
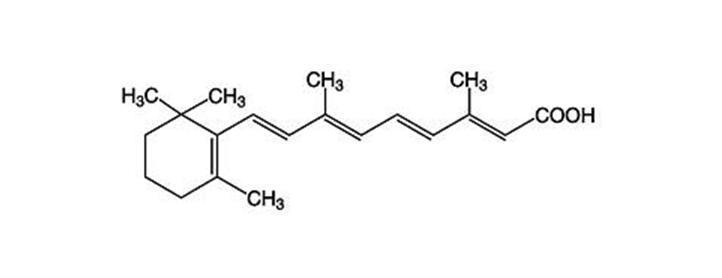
Each gram of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% contains 1 mg of tretinoin.
Each gram of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04% contains 0.4 mg of tretinoin.
The formulation uses methyl methacrylate/glycol dimethacrylate crosspolymer porous microspheres to enable inclusion of the active ingredient, tretinoin, in an aqueous gel. Other components consist of benzyl alcohol, butylated hydroxytoluene, carbomer 974P, cyclomethicone and dimethicone copolyol, disodium EDTA, glycerin, PPG-20 methyl glucose ether distearate, propylene glycol, purified water, sorbic acid, and trolamine.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Although tretinoin activates three members of the retinoic acid (RAR) nuclear receptors (RARα, RARβ, and RARγ) which may act to modify gene expression, subsequent protein synthesis, and epithelial cell growth and differentiation, it has not been established whether the clinical effects of tretinoin are mediated through activation of retinoic acid receptors and/or other mechanisms.
The exact mode of action of tretinoin is unknown. Current evidence suggests that topical tretinoin decreases cohesiveness of follicular epithelial cells with decreased microcomedone formation. Additionally, tretinoin stimulates mitotic activity and increased turnover of follicular epithelial cells causing extrusion of the comedones.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Tretinoin is a metabolite of Vitamin A metabolism in man. Percutaneous absorption, as determined by the cumulative excretion of radiolabeled drug into urine and feces, was assessed in 44 healthy men and women after single and repeated daily applications of 500 mg of a 0.1% tretinoin gel formulation. Estimates of in vivo bioavailability, mean (SD)%, following both single and multiple daily applications, for a period of 28 days with the 0.1% gel, were 0.82 (0.11)% and 1.41 (0.54)%, respectively. The plasma concentrations of tretinoin and its metabolites, 13-cis-retinoic acid, all-trans-4-oxo-retinoic acid, and 13-cis-4-oxo-retinoic acid, generally ranged from 1 to 3 ng/mL and were essentially unaltered after either single or multiple daily applications of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% relative to baseline levels. Clinical pharmacokinetic studies have not been performed with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04%.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Dermal carcinogenicity testing has not been performed with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% or 0.04%.
In a 91-week dermal study in which CD-1 mice were administered 0.017% and 0.035% formulations of tretinoin, cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas and papillomas in the treatment area were observed in some female mice. These concentrations are near the tretinoin concentration of the 0.04% and 0.1% clinical formulations. A dose-related incidence of liver tumors in male mice was observed at those same doses. The maximum systemic doses associated with the administered 0.017% and 0.035% formulations are 0.5 and 1.0 mg/kg/day tretinoin, respectively. These doses are two and four times the MHRD based on BSA comparison.
The biological significance of these findings is not clear because they occurred at doses that exceeded the dermal maximally tolerated dose of tretinoin and because they were within the background natural occurrence rate for these tumors in this strain of mice.
There was no evidence of carcinogenic potential when 0.025 mg/kg/day of tretinoin was administered topically to mice (0.1 times the MHRD based on BSA comparison).
Studies in hairless albino mice suggest that concurrent exposure to tretinoin may enhance the tumorigenic potential of carcinogenic doses of UVB and UVA light from a solar simulator. This effect has been confirmed in a later study in pigmented mice, and dark pigmentation did not overcome the enhancement of photocarcinogenesis by 0.05% tretinoin. Although the significance of these studies to humans is not clear, patients should minimize exposure to sunlight or artificial ultraviolet irradiation sources [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
The genotoxic potential of tretinoin was evaluated in the Ames assay and in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay, both of which were negative.
The components of the microspheres have shown potential for genetic toxicity and teratogenesis. EGDMA, a component of the excipient acrylates copolymer, was positive for induction of structural chromosomal aberrations in the in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in mammalian cells in the absence of metabolic activation, and negative for genetic toxicity in the Ames assay, and the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
In oral fertility studies in rats with tretinoin, the no-observable effect level was 2 mg/kg/day (19 times the MHRD based on BSA comparison).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Tretinoin Gel, USP (Microsphere) 0.1%
In two vehicle-controlled trials, tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% applied once daily was significantly more effective than vehicle in reducing the severity of acne lesion counts. The mean reductions in lesion counts from baseline after treatment for 12 weeks are shown in the following table:
|
Table 1: Mean Percent Reduction in Lesion Counts Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% |
||||
|
|
Tretinoin gel, USP |
Vehicle gel |
||
|
Study #1
|
Study #2
|
Study #1
|
Study #2
|
|
|
Non-inflammatory |
49% |
32% |
22% |
3% |
|
Inflammatory |
37% |
29% |
18% |
24% |
|
Total lesion counts |
45% |
32% |
23% |
16% |
Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% was also significantly superior to the vehicle in the investigator’s global evaluation of the clinical response. In Study #1, thirty-five percent (35%) of patients using tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% achieved an excellent result, as compared to eleven percent (11%) of patients on the vehicle control. In Study #2, twenty-eight percent (28%) of patients using tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.1% achieved an excellent result, as compared to nine percent (9%) of the patients on vehicle control.
14.2 Tretinoin Gel, USP (Microsphere) 0.04%
In two vehicle-controlled clinical studies, studies, tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04%, applied once daily, was more effective (p<0.05) than vehicle in reducing the acne lesion counts. The mean reductions in lesion counts from baseline after treatment for 12 weeks are shown in the following table:
| Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04% | Vehicle gel | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *- That is, a mean percent increase of 2% | ||||
| Study #1
108 pts | Study #2
111 pts | Study #1
110 pts | Study #2
103 pts |
|
| Non-inflammatory lesion counts | 37% | 29% | -2%* | 14% |
| Inflammatory lesion counts | 44% | 41% | 13% | 30% |
| Total lesion counts | 40% | 35% | 8% | 20% |
Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04% was also superior (p<0.05) to the vehicle in the investigator’s global evaluation of the clinical response. In Study #1, fourteen percent (14%) of patients using tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04% achieved an excellent result, as compared to five percent (5%) of patients on vehicle control. In Study #2, nineteen percent (19%) of patients using tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 0.04% achieved an excellent result compared to nine percent (9%) of the patients on vehicle control.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Tretinoin Gel, USP (Microsphere) is opaque and white to very pale yellow in color.
Tretinoin Fel, USP (Microsphere) 0.1% is supplied in
20 gram tube (NDC 66530-250-20),
45 gram tube (NDC 66530-250-45), and
50 gram pump (NDC 66530-250-50).
Tretinoin Gel, USP (Microsphere) 0.04% is supplied in
20 gram tube (NDC 66530-251-20),
45 gram tube (NDC 66530-251-45), and
50 gram pump (NDC 66530-251-50).
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information)
The patient should be instructed to:
Cleanse the treatment area thoroughly, before treatment with a mild, non-medicated cleanser. Do not to use more than the recommended amount and do not to apply tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) more than once daily as this will not produce faster or better results, but may increase irritation.
Minimize exposure to sunlight, including sunlamps. Recommend the use of sunscreen products and protective apparel (e.g., hat) when exposure cannot be avoided.
Manufactured by: DPT Laboratories, San Antonio, TX 78215
Distributed by: Spear Dermatology Products, Randolph, NJ 07869
140321
Rev 05-16
PATIENT INFORMATION
Tretinoin (TREH-tih-noyn) Gel, USP (Microsphere) (MY-kroe-sfeer) 0.1% and 0.04% for topical use
Important Information: Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) is for use on skin only. Do not get tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) in your eyes, mouth, vagina or the corners of your nose.
What is tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere)?
Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) is a prescription medicine used on the skin (topical) to treat acne. Acne is a condition in which the skin has blackheads, whiteheads, and other pimples.
It is not known if tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere)is safe and effective in the treatment of other conditions.
It is not known if tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) is safe and effective in children under 12 years of age.
What should I tell my doctor before using tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere)?
Before using tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere), tell your doctor if you:
- have a skin condition called eczema
- have a sunburn. You should not use tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) until your skin has healed.
- have any other medical condition.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) passes into your breast milk.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, herbal supplements, and any skin products that you use.
Especially tell your doctor if you use any other medicines to treat your acne, including medicated cleansers or soaps. Using other topical acne products may increase the irritation of your skin when used with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere).
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere)?
- Use tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) exactly as your doctor tells you to use it.
- Your doctor may change your dose of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) if you have skin irritation.
- Before you apply tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere), gently wash the affected area with a mild, non-medicated soap. Rinse and pat your skin dry.
- Apply tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) 1 time a day in the evening, or as prescribed by your doctor.
- Do not use more tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) than you need to cover the affected area and do not apply tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) more than 1 time a day. Using too much tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) or using it too often will not give you faster or better results and you may get skin redness, peeling, or discomfort.
- You may have a brief feeling of warmth of slight stinging after applying tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere).
- You may use moisturizers and cosmetics.
- Early in your treatment, you may get new pimples. At this stage, it is important to continue using tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere).
- Your acne may not get better right away. Use tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) even after your acne improves. Your acne may get better after two weeks of treatment, but more than seven weeks of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) treatment are needed before you get the full benefit.
Applying tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere):
- Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) comes in a tube and a pump. If you have been prescribed the:
Tube: Squeeze the gel from the tube onto a fingertip. Apply a thin layer to cover the affected area, as prescribed by your doctor. Spread tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) evenly over the affected area.
Pump: Fully depress the pump twice to dispense tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) onto fingertip. Apply a thin layer to cover the affected area, as prescribed by your doctor. Spread tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) evenly over the affected area.
- Wash your hands after applying tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere).
What should I avoid while using tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere)?
- Avoid washing your skin too often and scrubbing the affected skin area.
- You should avoid sunlamps, tanning beds, and ultraviolet light during treatment with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere).
- Minimize exposure to sunlight.
- If you have to be in the sunlight or are sensitive to sunlight, use a sunscreen with SPF (sun protection factor) of 15 or more and wear a wide-brimmed hat or other protective clothing to cover the treated areas.
- If you do get sunburned, stop using tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) until your skin has healed and is back to normal.
- Cold weather and wind may irritate skin treated with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere). Talk to your doctor about ways to manage skin irritation.
- Avoid contact with the peels of limes.
What are the possible side effects of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere)?
Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) may cause serious side effects, including:
Skin irritation. Tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) may cause skin dryness, redness, swelling, and blistering. If you develop these symptoms, your doctor may tell you to stop using tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) for a while, change your dose, decrease the number of times you apply tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere), or completely stop treatment with tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere). It is not known if tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) is effective when used less than 1 time a day.
The most common side effects of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) include skin burning and itching.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere). For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere)?
- Store tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Store tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) pump upright.
Keep tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere).
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in Patient Information leaflets. Do not use tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere) that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients of tretinoin gel, USP (microsphere)?
Active ingredient: tretinoin
Inactive ingredients: benzyl alcohol, butylated hydroxytoluene, carbomer 974P, cyclomethicone and dimethicone copolyol, disodium EDTA, glycerin, PPG-20 methyl glucose ether distearate, propylene glycol, purified water, sorbic acid and trolamine
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by: DPT Laboratories, San Antonio, TX 78215
Distributed by: Spear Dermatology Products, Randolph, NJ 07869
05/2016
| TRETINOIN
tretinoin gel |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRETINOIN
tretinoin gel |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Spear Dermatology Products (066551941) |
| Registrant - DPT Laboratories, Ltd (832224526) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPT Laboratories, Ltd | 832224526 | MANUFACTURE(66530-250, 66530-251) | |

