Label: HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE solution
HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE cream
HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE ointment
-
NDC Code(s):
51672-4061-2,
51672-4061-4,
51672-4074-1,
51672-4074-2, view more51672-4074-5, 51672-4074-6, 51672-4074-7, 51672-4083-1, 51672-4083-2, 51672-4083-5, 51672-4083-6, 51672-4083-7
- Packager: Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated April 6, 2021
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Ointment, Cream and Topical Solution contain the topical corticosteroid, hydrocortisone butyrate, a non-fluorinated hydrocortisone ester. It has the chemical name: 11β,17,21-Trihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione 17-butyrate; the molecular formula: C25H36O6; the molecular weight: 432.54; and the CAS registry number: 13609-67-1.
Its structural formula is:
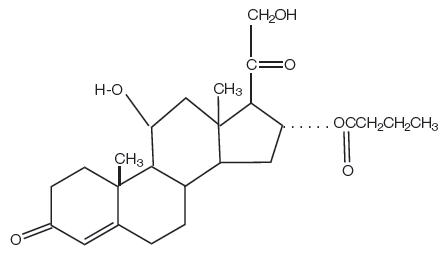
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Ointment, 0.1%
Each gram of hydrocortisone butyrate ointment contains 1 mg of hydrocortisone butyrate in a base consisting of mineral oil and polyethylene.
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Cream USP, 0.1%
Each gram of hydrocortisone butyrate cream contains 1 mg of hydrocortisone butyrate in a hydrophilic base consisting of anhydrous citric acid, cetomacrogol 1000, cetostearyl alcohol, light mineral oil, propylparaben and butylparaben (preservatives), purified water, sodium citrate anhydrous and white petrolatum.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Topical corticosteroids share anti-inflammatory, anti-pruritic and vasoconstrictive actions. The mechanism of anti-inflammatory activity of the topical corticosteroids is unclear. Various laboratory methods, including vasoconstrictor assays, are used to compare and predict potencies and/or clinical efficacies of the topical corticosteroids. There is some evidence to suggest that a recognizable correlation exists between vasoconstrictor potency and therapeutic efficacy in man.
Pharmacokinetics
The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors including the vehicle, the integrity of the epidermal barrier, and the use of occlusive dressings.
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin increase percutaneous absorption. Occlusive dressings substantially increase the percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids.
Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are bound to plasma proteins in varying degrees. Corticosteroids are metabolized primarily in the liver and are then excreted by the kidneys. Some of the topical corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted into the bile.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Ointment, 0.1% and Hydrocortisone Butyrate Cream USP, 0.1% are indicated for the relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses.
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Topical Solution, 0.1% is indicated for the relief of the inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids has produced reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria in some patients. Conditions which augment systemic absorption include the application of the more potent corticosteroids, use over large surface areas, prolonged use, and the addition of occlusive dressings.
Therefore, patients receiving a large dose of a potent topical corticosteroid applied to a large surface area or under an occlusive dressing should be evaluated periodically for evidence of HPA axis suppression by using ACTH stimulation tests.
If HPA axis suppression is noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or to substitute a less potent corticosteroid.
Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of the drug. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of corticosteroid withdrawal may occur, requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids.
Children may absorb proportionally larger amounts of topical corticosteroids and thus be more susceptible to systemic toxicity. (See PRECAUTIONS – Pediatric Use).
If irritation develops, topical corticosteroids should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. In the presence of dermatological infections, the use of an appropriate antifungal or antibacterial agent should be instituted. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, the corticosteroid should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled.
Information for Patients
Patients using topical corticosteroids should receive the following information and instructions:
- This medication is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the eyes.
- Patients should be advised not to use this medication for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed.
- The treated skin area should not be bandaged or otherwise covered or wrapped as to be occlusive unless directed by the physician.
- Patients should report any signs of local adverse reactions especially under occlusive dressing.
- Parents of pediatric patients should be advised not to use tight-fitting diapers or plastic pants on a child being treated in the diaper area, as these garments may constitute occlusive dressings.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Note: The animal multiples of human exposure calculations in this label were based on body surface area comparisons for an adult (i.e., mg/m2/day dose comparisons) assuming 100% human percutaneous absorption of a maximum topical human dose (MTHD) for hydrocortisone butyrate cream, ointment and topical solution (25 g).
In a 2-year dermal rat carcinogenicity study with hydrocortisone butyrate lotion, hydrocortisone butyrate was administered to Sprague-Dawley rats at topical doses of 0.05, 0.15, and 0.3 mg/kg/day in males and 0.1, 0.25, and 0.5 mg/kg/day in females (0.1% lotion). No drug-related tumors were noted in this study up to the highest doses evaluated in this study of 0.3 mg/kg/day in males (0.1× MTHD) and 0.5 mg/kg/day in females (0.2× MTHD).
Hydrocortisone butyrate revealed no evidence of mutagenic or clastogenic potential based on the results of two in vitro genotoxicity tests (Ames test and L5178Y/TK+/- mouse lymphoma assay) and one in vivo genotoxicity test (mouse micronucleus assay).
No evidence of impairment of fertility or effect on mating performance was observed in a fertility and general reproductive performance study conducted in male and female rats at subcutaneous doses up to and including 1.8 mg/kg/day (0.7× MTHD). Mild effects on maternal animals, such as reduced food consumption and a subsequent reduction in body weight gain, were seen at doses ≥0.6 mg/kg/day (0.2× MTHD).
Pregnancy
Corticosteroids are generally teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels. The more potent corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic after dermal application in laboratory animals. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women on teratogenic effects from topically applied corticosteroids. Therefore, topical corticosteroids should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Drugs of this class should not be used extensively on pregnant patients, in large amounts, or for prolonged periods of time.
Systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits. Subcutaneous doses of 0.6, 1.8 and 5.4 mg/kg/day hydrocortisone butyrate were administered to pregnant female rats during gestation days 6 – 17. In the presence of maternal toxicity, fetal effects noted at 5.4 mg/kg/day (2× MTHD) included an increased incidence of ossification variations and unossified sternebra. No treatment-related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at doses of 5.4 and 1.8 mg/kg/day, respectively (2× MTHD and 0.7× MTHD, respectively).
Subcutaneous doses of 0.1, 0.2 and 0.3 mg/kg/day hydrocortisone butyrate were administered to pregnant female rabbits during gestation days 7 – 20. An increased incidence of abortion was noted at 0.3 mg/kg/day (0.2× MTHD). In the absence of maternal toxicity, a dose-dependent decrease in fetal body weight was noted at doses ≥0.1 mg/kg/day (0.1× MTHD). Additional indicators of embryofetal toxicity (reduction in litter size, decreased number of viable fetuses, increased post-implantation loss) were noted at doses ≥0.2 mg/kg/day (0.2× MTHD). Additional fetal effects noted in this study included delayed ossification noted at doses ≥0.1 mg/kg/day and an increased incidence of fetal malformations (primarily skeletal malformations) noted at doses ≥0.2 mg/kg/day. A dose at which no treatment-related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were observed was not established in this study.
Additional systemic embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and mice. Subcutaneous doses of 0.1 and 9 mg/kg/day hydrocortisone butyrate were administered to pregnant female rats during gestation days 9 – 15. In the presence of maternal toxicity, an increase in fetal deaths and fetal resorptions and an increase in the number of ossifications in caudal vertebrae were noted at a dose of 9 mg/kg/day (3× MTHD). No treatment-related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at 0.1 mg/kg/day (0.1× MTHD).
Subcutaneous doses of 0.2 and 1 mg/kg/day hydrocortisone butyrate were administered to pregnant female mice during gestation days 7 – 13. In the absence of maternal toxicity, an increased number of cervical ribs and one fetus with clubbed legs were noted at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day (0.2× MTHD). No treatment-related effects on embryofetal toxicity or teratogenicity were noted at doses of 1 and 0.2 mg/kg/day, respectively (0.2× MTHD and 0.1× MTHD, respectively).
No topical embryofetal development studies were conducted with hydrocortisone butyrate cream and hydrocortisone butyrate topical solution. However, topical embryofetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits with a hydrocortisone butyrate ointment formulation. Topical doses of 1% and 10% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment were administered to pregnant female rats during gestation days 6 – 15 or pregnant female rabbits during gestation days 6 – 18. A dose-dependent increase in fetal resorptions was noted in rabbits (0.2 – 2× MTHD) and fetal resorptions were noted in rats at the 10% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment dose (80× MTHD).
No treatment-related effects on embryofetal toxicity were noted at the 1% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment dose in rats (8× MTHD). A dose at which no treatment-related effects on embryofetal toxicity were observed in rabbits after topical administration of hydrocortisone butyrate ointment was not established in this study.
No treatment-related effects on teratogenicity were noted at a dose of 10% hydrocortisone butyrate ointment in rats or rabbits (80× MTHD and 2× MTHD, respectively).
A peri- and post-natal development study was conducted in rats. Subcutaneous doses of 0.6, 1.8 and 5.4 mg/kg/day hydrocortisone butyrate were administered to pregnant female rats from gestation day 6 – lactation day 20. In the presence of maternal toxicity, a dose-dependent decrease in fetal weight was noted at doses ≥1.8 mg/kg/day (0.7× MTHD). No treatment-related effects on fetal toxicity were noted at 0.6 mg/kg/day (0.2× MTHD). A delay in sexual maturation was noted at 5.4 mg/kg/day (2× MTHD). No treatment-related effects on sexual maturation were noted at 1.8 mg/kg/day. No treatment-related effects on behavioral development or subsequent reproductive performance were noted at 5.4 mg/kg/day.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether topical administration of corticosteroids could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in breast milk. Systemically administered corticosteroids are secreted into breast milk, in quantities not likely to have a deleterious effect on the infant. Nevertheless, caution should be exercised when topical corticosteroids are administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Pediatric patients may demonstrate greater susceptibility to topical corticosteroid-induced HPA axis suppression and Cushing's syndrome than mature patients because of a larger skin surface area to body weight ratio.
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, Cushing's syndrome, linear growth retardation, delayed weight gain, and intracranial hypertension have been reported in children receiving topical corticosteroids.
Manifestations of adrenal suppression in children include low plasma cortisol levels and absence of response to ACTH stimulation. Manifestations of intracranial hypertension include bulging fontanelles, headaches, and bilateral papilledema.
Administration of topical corticosteroids to children should be limited to the least amount compatible with an effective therapeutic regimen. Chronic corticosteroid therapy may interfere with the growth and development of children.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following local adverse reactions are reported infrequently with topical corticosteroids but may occur more frequently with the use of occlusive dressings. These reactions are listed in an approximate decreasing order of occurrence: burning, itching, irritation, dryness, folliculitis, hypertrichosis, acneiform eruptions, hypopigmentation, perioral dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, maceration of the skin, secondary infection, skin atrophy, striae and miliaria.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Ointment, 0.1% or Hydrocortisone Butyrate Cream USP, 0.1% should be applied to the affected area as a thin film two or three times daily depending on the severity of the condition. Occlusive dressings may be used for the management of psoriasis or recalcitrant conditions.
If an infection develops, the use of occlusive dressings should be discontinued and appropriate antimicrobial therapy instituted.
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Topical Solution, 0.1% should be applied to the affected area as a thin film two or three times daily depending on the severity of the condition.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Hydrocortisone Butyrate Ointment, 0.1% is supplied in tubes containing: 5 g NDC 51672-4083-5 (as physician samples) 10 g NDC 51672-4083-7 15 g NDC 51672-4083-1 30 g NDC 51672-4083-2 45 g NDC 51672-4083-6 Hydrocortisone Butyrate Cream USP, 0.1% is supplied in tubes containing: 5 g NDC 51672-4074-5 (as physician samples) 10 g NDC 51672-4074-7 15 g NDC 51672-4074-1 30 g NDC 51672-4074-2 45 g NDC 51672-4074-6 Hydrocortisone Butyrate Topical Solution, 0.1% is supplied in polyethylene bottles containing: 20 mL NDC 51672-4061-2 60 mL NDC 51672-4061-4 - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mL Bottle Carton
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15 g Tube Carton - Cream
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15 g Tube Carton - Ointment
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE
hydrocortisone butyrate solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:51672-4061 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Hydrocortisone Butyrate (UNII: 05RMF7YPWN) (Hydrocortisone - UNII:WI4X0X7BPJ) Hydrocortisone Butyrate 1 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength citric acid monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) glycerin (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) isopropyl alcohol (UNII: ND2M416302) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) trisodium citrate dihydrate (UNII: B22547B95K) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:51672-4061-2 1 in 1 CARTON 01/14/2004 1 20 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:51672-4061-4 1 in 1 CARTON 01/14/2004 2 60 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076364 01/14/2004 HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE
hydrocortisone butyrate creamProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:51672-4074 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Hydrocortisone Butyrate (UNII: 05RMF7YPWN) (Hydrocortisone - UNII:WI4X0X7BPJ) Hydrocortisone Butyrate 1 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength anhydrous citric acid (UNII: XF417D3PSL) ceteth-20 (UNII: I835H2IHHX) cetostearyl alcohol (UNII: 2DMT128M1S) light mineral oil (UNII: N6K5787QVP) propylparaben (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) butylparaben (UNII: 3QPI1U3FV8) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) anhydrous trisodium citrate (UNII: RS7A450LGA) petrolatum (UNII: 4T6H12BN9U) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:51672-4074-5 5 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/04/2005 2 NDC:51672-4074-7 1 in 1 CARTON 08/04/2005 2 10 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC:51672-4074-1 1 in 1 CARTON 08/04/2005 3 15 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 4 NDC:51672-4074-2 1 in 1 CARTON 08/04/2005 4 30 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 5 NDC:51672-4074-6 1 in 1 CARTON 08/04/2005 5 45 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076654 08/04/2005 HYDROCORTISONE BUTYRATE
hydrocortisone butyrate ointmentProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:51672-4083 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Hydrocortisone Butyrate (UNII: 05RMF7YPWN) (Hydrocortisone - UNII:WI4X0X7BPJ) Hydrocortisone Butyrate 1 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength mineral oil (UNII: T5L8T28FGP) high density polyethylene (UNII: UG00KM4WR7) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:51672-4083-5 5 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/27/2004 2 NDC:51672-4083-7 1 in 1 CARTON 12/27/2004 2 10 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC:51672-4083-1 1 in 1 CARTON 12/27/2004 3 15 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 4 NDC:51672-4083-2 1 in 1 CARTON 12/27/2004 4 30 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 5 NDC:51672-4083-6 1 in 1 CARTON 12/27/2004 5 45 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076842 12/27/2004 Labeler - Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. (145186370) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. 600072078 MANUFACTURE(51672-4061, 51672-4074, 51672-4083)






