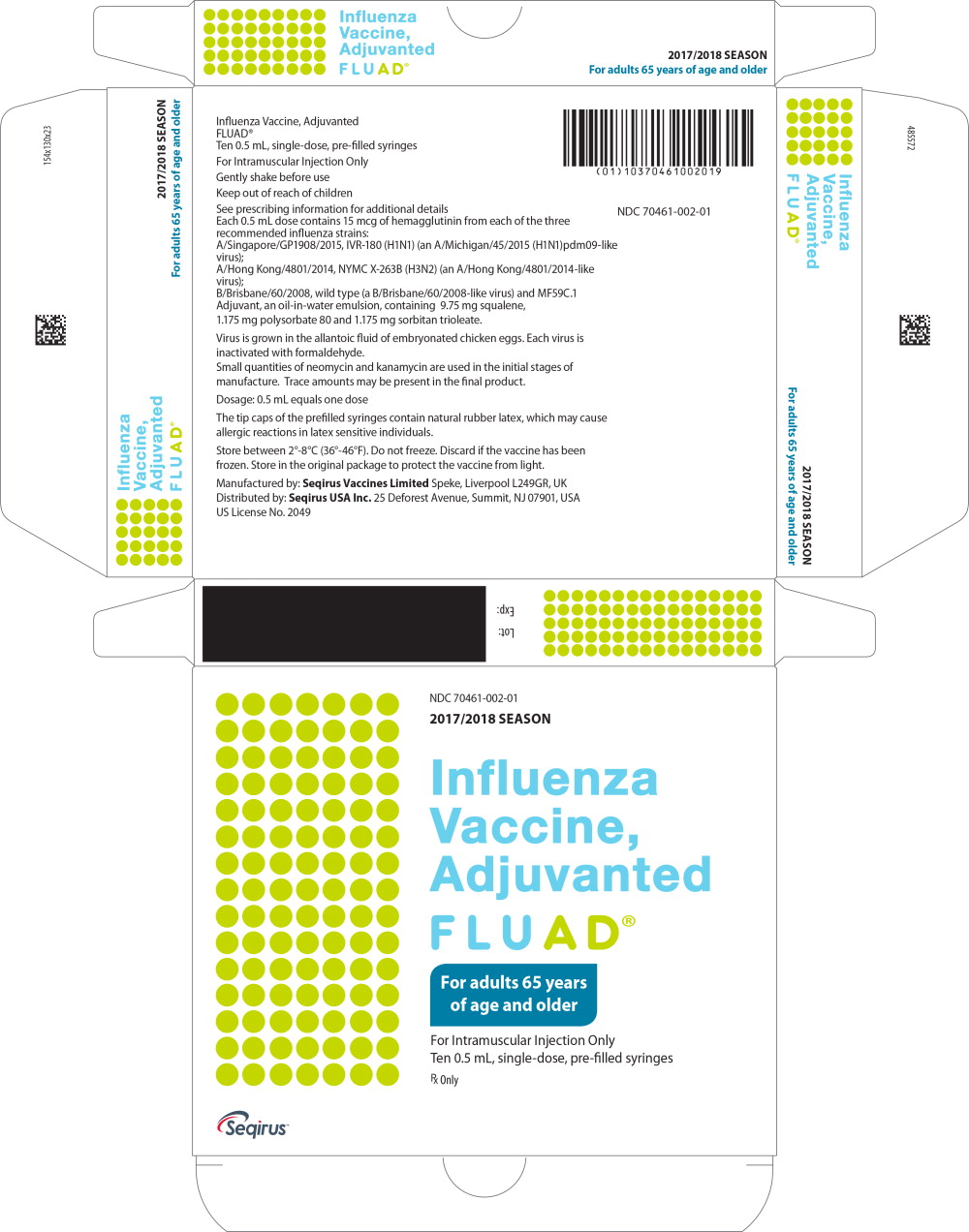
FLUAD- a/singapore/gp1908/2015 ivr-180 (h1n1) (an a/michigan/45/2015 (h1n1)pdm09-like virus), a/hong kong/4801/2014, nymc x-263b (h3n2) (an a/hong kong/4801/2014-like virus), and b/brisbane/60/2008, wild type (a b/brisbane/60/2008-like virus) injection, suspension
Seqirus Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use FLUAD® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FLUAD.
FLUAD® (Influenza Vaccine, Adjuvanted) Suspension for Intramuscular Injection 2017-2018 Formula Initial U.S. Approval: 2015 INDICATIONS AND USAGEFLUAD is an inactivated influenza vaccine indicated for active immunization against influenza disease caused by influenza virus subtypes A and type B contained in the vaccine. FLUAD is approved for use in persons 65 years of age and older. (1) Approval is based on the immune response elicited by FLUAD. Data demonstrating a decrease in influenza disease after vaccination with FLUAD are not available. (14) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONA single 0.5 mL dose for intramuscular injection. (2.1) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSSuspension for injection supplied in 0.5 mL single-dose pre-filled syringes. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Seqirus at 1-855-358-8966 or VAERS at 1-800-822-7967 and www.vaers.hhs.gov. See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 5/2017 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FLUAD is an inactivated influenza vaccine indicated for active immunization against influenza disease caused by influenza virus subtypes A and type B contained in the vaccine. FLUAD is approved for use in persons 65 years of age and older. Approval is based on the immune response elicited by FLUAD. Data demonstrating a decrease in influenza disease after vaccination with FLUAD are not available. [see Clinical Studies (14)]
2. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intramuscular injection only
2.1. Dosage and Schedule
Administer FLUAD as a single 0.5 mL intramuscular injection in adults 65 years of age and older.
2.2. Administration
- Gently shake each syringe. FLUAD has a milky white appearance. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit [see Description (11)]. If either condition exists, FLUAD should not be administered.
- The vaccine should be administered by intramuscular injection, preferably in the region of the deltoid muscle of the upper arm. Do not inject the vaccine in the gluteal region or areas where there may be a major nerve trunk.
3. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
FLUAD is a sterile suspension for intramuscular injection supplied in 0.5 mL single-dose pre-filled syringes.
4. CONTRAINDICATIONS
Do not administer FLUAD to anyone with a history of severe allergic reaction (e.g. anaphylaxis) to any component of the vaccine, including egg protein [see Description (11)], or to a previous influenza vaccine.
5. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1. Guillain-Barré Syndrome
If Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) has occurred within 6 weeks of receipt of prior influenza vaccine, the decision to give FLUAD should be based on careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks. The 1976 swine influenza vaccine was associated with an elevated risk of GBS. Evidence for a causal relationship of GBS with other influenza vaccines is inconclusive; if an excess risk exists, it is probably slightly more than 1 additional case per 1 million persons vaccinated. [see References (1)]
5.2. Preventing and Managing Allergic Reactions
Appropriate medical treatment and supervision must be available to manage possible anaphylactic reactions following administration of the vaccine.
5.3. Latex
The tip caps of the prefilled syringes contain natural rubber latex which may cause allergic reactions in latex sensitive individuals. [see Description (11)]
5.4. Altered Immunocompetence
Theimmuneresponseto FLUADinimmunocompromisedpersons, including individuals receiving immunosuppressive therapy, may be lower than in immunocompetent individuals. [see Concurrent Use With Immunosuppressive Therapies (7.2)]
6. ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1. Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a vaccine cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another vaccine and may not reflect rates observed in clinical practice.
Solicited adverse reactions were assessed in a multicenter, observer-blind, randomized controlled study (Study 1) conducted in the United States, Colombia, Panama and the Philippines. The safety analysis set included 3545 FLUAD recipients and 3537 AGRIFLU (Influenza Vaccine) recipients. The enrolled subject population in Study 1 was 65 to 97 years of age (mean 72 years) and 64% were female. Within each treatment group, 53% were Asian, 28% were Caucasian, 18% were Hispanic, 1% were Black, and fewer than 1% each were Native American/Alaskan, Pacific Islander/Hawaiian, or Other.
Solicited local (injection site) and systemic adverse reactions were collected from subjects in Study 1 who completed a symptom diary card for seven days following vaccination. The reported frequencies of solicited local and systemic adverse events from Study 1 are presented in Table 1.
|
a N = number of subjects with safety data. |
|||
|
b Moderate: pain, tenderness, myalgia, fatigue, headache, arthralgia, chills, nausea, vomiting defined as “some limitation in normal daily activity”, diarrhea defined as“4 to 5 stools a day”. |
|||
|
c Severe: pain, tenderness, myalgia, fatigue, headache, arthralgia, chills, nausea, vomiting defined as “unable to perform normal daily activity”, diarrhea defined as“6 or more watery stools a day”. |
|||
|
d Potentially life threatening (PLT) reaction defined as requiring emergency room visit or hospitalization. |
|||
| Study 1 | |||
| FLUAD (Na=3418-3496) Percentage | AGRIFLU (Na=3420-3488) Percentage |
||
| Local | |||
| Injection site Pain | Any | 25.0 | 12.2 |
| Moderateb | 3.9 | 1.9 | |
| Severec | 0.3 | 0.2 | |
| Tenderness | Any | 21.1 | 11.2 |
| Moderate | 3.0 | 1.0 | |
| Severe | 0.1 | 0.2 | |
| Erythema | Any | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| 25 to < 50 mm | 1.1 | 0.5 | |
| 51 to < 100 mm | 0.2 | <0.1 | |
| > 100 mm | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Induration | Any | 1.3 | 0.5 |
| 25 to < 50 mm | 1.0 | 0.5 | |
| 51 to < 100 mm | 0.3 | 0.0 | |
| > 100 mm | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Swelling | Any | 1.2 | 0.4 |
| 25 to < 50 mm | 1.0 | 0.4 | |
| 51 to < 100 mm | 0.2 | <0.1 | |
| > 100 mm | <0.1 | 0.0 | |
| Systemic | |||
| Myalgia | Any | 14.7 | 9.7 |
| Moderate | 2.6 | 1.8 | |
| Severe | 0.3 | 0.7 | |
| Fatigue | Any | 13.3 | 10.4 |
| Moderate | 3.1 | 2.4 | |
| Severe | 0.4 | 0.6 | |
| PLTd | 0.0 | <0.1 | |
| Headache | Any | 13.2 | 11.2 |
| Moderate | 3.0 | 2.6 | |
| Severe | 0.4 | 0.6 | |
| PLT | 0.0 | <0.1 | |
| Arthralgia | Any | 8.5 | 7.8 |
| Moderate | 1.6 | 1.6 | |
| Severe | 0.2 | 0.6 | |
| Chills | Any | 6.7 | 4.7 |
| Moderate | 1.5 | 1.2 | |
| Severe | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| PLT | <0.1 | 0.0 | |
| Diarrhea | Any | 4.8 | 4.5 |
| Moderate | 1.3 | 0.9 | |
| Severe | 0.3 | 0.2 | |
| PLT | <0.1 | <0.1 | |
| Fever | Any | 3.6 | 3.4 |
| ≥ 38.0°C to ≤ 38.4°C | 1.8 | 1.7 | |
| ≥ 38.5°C to ≤ 38.9°C | 1.3 | 1.3 | |
| 39.0°C to ≤ 40.0°C | 0.4 | 0.4 | |
| ≥ 40.0°C | 0.1 | 0.0 | |
| Nausea | Any | 2.9 | 2.8 |
| Moderate | 0.4 | 0.6 | |
| Severe | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| PLT | <0.1 | 0.0 | |
| Vomiting | Any | 1.4 | 1.7 |
| Moderate | 0.4 | 0.5 | |
| Severe | <0.1 | 0.1 | |
| PLT | <0.1 | 0.0 | |
Unsolicited Adverse Events (AEs): The clinical safety of FLUAD was assessed in fifteen (15) randomized, controlled studies. The total safety population in these trials included 10,952 adults 65 years of age and older, comprising 5,754 who received FLUAD and 5,198 who received other US licensed influenza vaccines. The percentage of subjects with an unsolicited AE within 30 days following vaccination was similar between vaccine groups (16.9% FLUAD vs. 18.0% active comparator).
Serious Adverse Events (SAEs) and Deaths: In Study 1, in which subjects were followed for SAEs and deaths for one year following vaccination (N=3,545 FLUAD, N=3,537 AGRIFLU), the percentages of subjects with an SAE were similar between vaccine groups (7% FLUAD vs. 7% AGRIFLU). Four SAEs (1 FLUAD and 3 AGRIFLU) were assessed as related to study vaccination over one year of observation and 2 of these occurred (1 FLUAD and 1 AGRIFLU) within 21 days following study vaccination. There were 98 deaths (n=52 FLUAD, n=46 AGRIFLU) over one year of which none occurred within the first 21 days following vaccination.
In 14 additional randomized, controlled studies, SAEs were collected over a 3 to 4-week period in 4 studies, over a 8-week period in 1 study, and over a 6-month period in 9 studies (N= 2,209 FLUAD, N=1,661 US licensed influenza vaccines). The percentages of subjects with an SAE within 30 days (1.1% FLUAD vs. 1.8% AGRIFLU) or within 6 months (4.3% FLUAD vs. 5.9% AGRIFLU) were similar between vaccine groups. The percentages of deaths within 30 days (0.3% FLUAD vs. 0.6% active comparator) or within 6 months (1.0% FLUAD vs. 1.5% active comparator) were also similar.
Adverse Events of Special Interest (AESIs): Rates of new onset neuroinflammatory and immune mediated diseases were assessed in a post hoc analysis of the 15 randomized controlled studies over the time periods specified above for SAEs. The percentage of subjects with an AESI at any time after vaccination was similar between vaccine groups (0.9% FLUAD vs. 0.9% active comparator). There were no notable imbalances for specific AESIs.
Safety of Annual Revaccination: In 5 of the randomized, controlled trials, subjects were followed for SAEs and deaths for 6 months following revaccination (N=492 FLUAD, N=330 US licensed and non-US licensed influenza vaccines). After the second annual vaccination, the percentages of subjects with an SAE were similar between vaccine groups (6.1% FLUAD vs. 5.5% comparator influenza vaccines); 23 deaths (n=17 FLUAD, n=6 comparator influenza vaccines) were reported. Causes of death included cardiovascular events, malignancy, trauma, gastrointestinal disorders, and respiratory failure. Clinical characteristics of the deaths, including the variable causes, timing since vaccination, and underlying medical conditions, do not provide evidence for a causal relationship with FLUAD.
6.2. Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse events have been spontaneously reported during post-approval use of FLUAD in Europe and other regions since 1997. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to the vaccine.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Thrombocytopenia (some cases were severe with platelet counts less than 5,000 per mm3), lymphadenopathy
General disorders and administration site conditions:
Extensive swelling of injected limb lasting more than one week, injection site cellulitis-like reactions (some cases of swelling, pain, and redness extending more than 10 cm and lasting more than 1 week)
Immune system disorders:
Allergic reactions including anaphylactic shock, anaphylaxis and angioedema
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders:
Muscular weakness
Nervous system disorders:
Encephalomyelitis, Guillain-Barré Syndrome, convulsions, neuritis, neuralgia, paraesthesia, syncope, presyncope
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
Generalized skin reactions including erythema multiforme, urticaria, pruritis or non-specific rash
Vascular disorders:
Vasculitis with transient renal involvement
7. DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1. Concomitant Use With Other Vaccines
There are no data to assess the concomitant administration of FLUAD with other vaccines. If FLUAD is given at the same time as other injectable vaccine(s), the vaccine(s) should be administered at different injection sites.
Do not mix FLUAD with any other vaccine in the same syringe.
8. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1. Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B: A reproductive and developmental toxicity study has been performed in rabbits with a dose level that was approximately 15 times the human dose based on body weight. The study revealed no evidence of impaired female fertility or harm to the fetus due to FLUAD. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this vaccine should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
In a reproductive and developmental toxicity study, the effect of FLUAD on embryo-fetal and post-natal development was evaluated in pregnant rabbits. Animals were administered FLUAD by intramuscular injection twice prior to gestation, during the period of organogenesis (gestation day 7) and later in pregnancy (gestation day 20), 0.5 mL (45 mcg)/rabbit/occasion (approximately 15-fold excess relative to the adult human dose based on body weight). No adverse effects on mating, female fertility, pregnancy, embryo-fetal development, or post-natal development were observed. There were no vaccine-related fetal malformations or other evidence of teratogenesis.
11. DESCRIPTION
FLUAD (Influenza Vaccine, Adjuvanted), a sterile suspension for intramuscular injection, is a trivalent, inactivated influenza vaccine prepared from virus propagated in the allantoic cavity of embryonated hens' eggs inoculated with a specific type of influenza virus suspension.
Each 0.5 mL dose contains at least 15 mcg of hemagglutinin (HA) from each of the following three influenza strains recommended for the 2017/2018 influenza season: A/Singapore/GP1908/2015, IVR-180 (H1N1) (an A/ Michigan/45/2015 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus); A/Hong Kong/4801/2014, NYMC X-263B (H3N2) (an A/Hong Kong/4801/2014-like virus); and B/Brisbane/60/2008, wild type (a B/Brisbane/60/2008-like virus). FLUAD also contains MF59C.1 adjuvant (MF59®), a squalene based oil-in-water emulsion. Each of the strains is harvested and clarified separately by centrifugation and filtration prior to inactivation with formaldehyde. The inactivated virus is concentrated and purified by zonal centrifugation. The surface antigens, hemagglutinin and neuraminidase, are obtained from the influenza virus particle by further centrifugation in the presence of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB). The antigen preparation is further purified.
FLUAD is prepared by combining the three virus antigens with the MF59C.1 adjuvant. After combining, FLUAD is a sterile, milky-white suspension supplied in 0.5 mL single-dose pre-filled syringe. Each 0.5 mL dose contains 15 mcg of hemagglutinin (HA) from each of the three recommended influenza strains and MF59C.1 adjuvant (9.75 mg squalene, 1.175 mg of polysorbate 80, 1.175 mg of sorbitan trioleate, 0.66 mg of sodium citrate dihydrate and 0.04 mg of citric acid monohydrate) at pH 6.9-7.7.
FLUAD may contain trace amounts of neomycin (≤ 0.02 mcg by calculation), kanamycin (≤ 0.03 mcg by calculation) and barium (< 0.5 mcg by calculation), which are used during the initial stages of manufacture, as well as residual egg proteins (< 0.4 mcg), formaldehyde (≤ 10 mcg), or CTAB (≤ 12 mcg).
FLUAD does not contain a preservative.
The tip caps of the prefilled syringes contain natural rubber latex. The syringe and syringe plunger stopper are not made with natural rubber latex.
12. CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1. Mechanism of Action
Influenza illness and its complications follow infection with influenza viruses. Global surveillance of influenza identifies yearly antigenic variants. For example, since 1977, antigenic variants of influenza A (H1N1 and H3N2) viruses and influenza B viruses have been in global circulation. Specific levels of hemagglutination inhibition (HI) antibody titers induced by vaccination with inactivated influenza virus vaccine have not been correlated with protection from influenza illness. In some human studies, HI antibody titers of 1:40 or greater have been associated with protection from influenza illness in up to 50% of subjects. [see References (2, 3)]
Antibody against one influenza virus type or subtype confers limited or no protection against another. Furthermore, antibody to one antigenic variant of influenza virus might not protect against a new antigenic variant of the same type or subtype. Frequent development of antigenic variants through antigenic drift is the virologic basis for seasonal epidemics and the reason for the usual change of one or more new strains in each year's influenza vaccine. Therefore, inactivated trivalent influenza vaccines are standardized to contain the hemagglutinin of influenza virus strains (two subtypes A and one type B), representing the influenza viruses likely to be circulating in the United States in the upcoming winter.
Annual influenza vaccination is recommended because immunity declines during the year after vaccination, and because circulating strains of influenza virus change from year to year.
14. CLINICAL STUDIES
Study 1 (NCT01162122) evaluated the safety and immunogenicity of FLUAD in comparison to AGRIFLU. A total of 7,082 subjects were randomized and vaccinated with FLUAD (N=3,541) or AGRIFLU (N=3,541). The primary immunogenicity analyses were conducted on all vaccinated subjects with a blood sample collected at Day 22 (N=3,225-3,227 [91%] and 3,256-3,259 [92%] in the FLUAD and AGRIFLU groups, respectively). Non-inferiority of FLUAD compared with AGRIFLU was demonstrated for all three vaccine strains based on pre-defined thresholds for seroconversion rate differences and GMT ratios (Table 2).
|
GMT = Geometric mean antibody titer; CI = Confidence Interval. |
|||
|
a Results obtained following vaccination with influenza vaccine formulated for the 2010-2011 season. |
|||
|
b N is the number of vaccinated participants with available data for the immunologic endpoint listed. |
|||
|
c FLUAD met non-inferiority criteria based on GMT ratios if the lower limit of the 95% CI [FLUAD:AGRIFLU] for each strain was > 0.67. |
|||
|
d Seroconversion was defined as prevaccination HI titer <10 and postvaccination HI titer ≥ 40 or at least a 4-fold increase in HI from prevaccination HI titer ≥ 10. |
|||
|
e FLUAD met non-inferiority criteria based on seroconversion rate differences if the lower limit of the 95% CI [FLUAD -AGRIFLU] for each strain was >-10% . |
|||
| FLUAD | AGRIFLU | ||
| GMTs Against | GMT
N b= 3225-3227 (95% CI) | GMT
N b =3256-3259 (95% CI) | GMT Ratioc
(95% CI) |
| A/California/7/2009-like (H1N1) | 99 (93-106) | 70 (66-75) | 1.4 (1.32-1.49) |
| A/Perth/16/2009-like (H3N2) | 272 (257-288) | 169 (159-179) | 1.61 (1.52-1.7) |
| B/Brisbane/60/2008- like | 28 (26-29) | 24 (23-26) | 1.15 (1.08-1.21) |
| Seroconversiond to: | % of Subjects (95% CI) | % of Subjects (95% CI) | Difference in Seroconversion Ratee (95% CI) |
| A/California/7/2009-like (H1N1) | 69% (67%–70%) | 58% (57%–60%) | 9.8% (7.5%–12.1%) |
| A/Perth/16/2009-like (H3N2) | 73% (71%–74%) | 58% (56%–60%) | 13.9% (11.7%–16.1%) |
| B/Brisbane/60/2008-like | 33% (31%–35%) | 29% (28%–31%) | 3.2% (1.1%–5.3%) |
15. REFERENCES
- Lasky T, Terracciano GJ, Magder L, et al. The Guillain-Barre syndrome and the 1992-1993 and 1993-1994 influenza vaccines. N Engl J Med 1998; 339(25): 1797-1802.
-
Hannoun C, Megas F, Piercy J. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of influenza vaccination. Virus Res 2004; 103:133-138.
-
Hobson D, Curry RL, Beare A, et. al. The role of serum hemagglutinin-inhibiting antibody in protection against challenge infection with influenza A2 and B viruses. J Hyg Camb 1972; 767-777.
16. HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
FLUAD is supplied as a 0.5 mL pre-filled needleless syringe:
- package of 10 pre-filled syringes per carton (NDC number: 70461-002-01)
- pre-filled single syringe (NDC number: 70461-002-11)
Store FLUAD refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Protect from light. Do not freeze. Discard if the vaccine has been frozen. Do not use after expiration date.
The tip caps of prefilled syringes contain natural rubber latex. The syringe and syringe plunger stopper are not made with natural rubber latex.
17. PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Inform vaccine recipients of the potential benefits and risks of immunization with FLUAD.
- Educate vaccine recipients regarding the potential side effects. Clinicians should emphasize that (1) FLUAD contains non-infectious particles and cannot cause influenza and (2) FLUAD is intended to help provide protection against illness due to influenza viruses only, and cannot provide protection against other respiratory illnesses.
- Instruct vaccine recipients to report adverse reactions to their healthcare provider and/or to Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) at 1-800-822-7967 and www.vaers.hhs.gov. Provide vaccine recipients with the Vaccine Information Statements which are required by the National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act of 1986. These materials are available free of charge at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website (www.cdc.gov/vaccines).
- Inform vaccine recipients that annual vaccination is recommended.
FLUAD is a registered trademark of Seqirus UK Limited or its affiliates.
Manufactured by: Seqirus Vaccines Limited Speke, Liverpool, L249GR, UK
US License No. 2049
Distributed by: Seqirus USA Inc. 25 Deforest Avenue, Summit, NJ 07901, USA
1-855-358-8966
| FLUAD
a/singapore/gp1908/2015 ivr-180 (h1n1) (an a/michigan/45/2015 (h1n1)pdm09-like virus), a/hong kong/4801/2014, nymc x-263b (h3n2) (an a/hong kong/4801/2014-like virus), and b/brisbane/60/2008, wild type (a b/brisbane/60/2008-like virus) injection, suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Seqirus Inc. (080102141) |