SEEBRI NEOHALER- glycopyrrolate capsule
Sunovion Pharmacueticals Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use SEEBRI NEOHALER safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SEEBRI NEOHALER.
SEEBRI® NEOHALER® (glycopyrrolate) inhalation powder, for oral inhalation use Initial U.S. Approval: 1961 INDICATIONS AND USAGESEEBRI NEOHALER is an anticholinergic indicated for the long-term, maintenance treatment of airflow obstruction in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONDOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 2% and higher than placebo) are upper respiratory tract infection and nasopharyngitis. (6.1)
DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 7/2021 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SEEBRI® NEOHALER® is indicated for the long-term, maintenance treatment of airflow obstruction in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Administration Overview
For oral inhalation only. Do not swallow SEEBRI capsules, as the intended effects on the lungs will not be obtained. SEEBRI capsules should only be used with the NEOHALER device [see Overdosage (10)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage is one capsule of SEEBRI (15.6 mcg glycopyrrolate) inhalation powder twice daily by oral inhalation using the NEOHALER device. SEEBRI NEOHALER should be administered at the same time of the day, (1 capsule in the morning and 1 capsule in the evening), every day. More frequent administration or a greater number of inhalations (more than 1 capsule twice -daily) of SEEBRI NEOHALER is not recommended.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Inhalation powder: SEEBRI capsule contains15.6 mcg of glycopyrrolate in an orange transparent hypromellose (HPMC) capsule with the product code “GPL15.6” printed in black and the logo ( ) printed with two radial black bars.
) printed with two radial black bars.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
SEEBRI NEOHALER is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to glycopyrrolate or to any of the ingredients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Deterioration of Disease and Acute Episodes
SEEBRI NEOHALER should not be initiated in patients during acutely deteriorating or potentially life-threatening episodes of COPD. SEEBRI NEOHALER has not been studied in subjects with acutely deteriorating COPD. The initiation of SEEBRI NEOHALER in this setting is not appropriate.
SEEBRI NEOHALER should not be used for the relief of acute symptoms, i.e., as rescue therapy for the treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm. SEEBRI NEOHALER has not been studied in the relief of acute symptoms and extra doses should not be used for that purpose. Acute symptoms should be treated with an inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist.
COPD may deteriorate acutely over a period of hours or chronically over several days or longer. If SEEBRI NEOHALER no longer controls symptoms of bronchoconstriction; the patient's inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist becomes less effective; or the patient needs more inhalation of a short-acting beta2-agonist than usual, these may be markers of deterioration of disease. In this setting, a reevaluation of the patient and the COPD treatment regimen should be undertaken at once. Increasing the daily dose of SEEBRI NEOHALER beyond the recommended dose is not appropriate in this situation.
5.2 Paradoxical Bronchospasm
As with other inhaled medicines, SEEBRI NEOHALER can produce paradoxical bronchospasm that may be life-threatening. If paradoxical bronchospasm occurs following dosing with SEEBRI NEOHALER, it should be treated immediately with an inhaled, short-acting bronchodilator; SEEBRI NEOHALER should be discontinued immediately, and alternative therapy instituted.
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions have been reported after administration of SEEBRI NEOHALER. If signs suggesting allergic reactions occur, in particular, angioedema (including difficulties in breathing or swallowing, swelling of the tongue, lips, and face), urticaria, or skin rash, SEEBRI NEOHALER should be discontinued immediately and alternative therapy instituted. SEEBRI NEOHALER should be used with caution in patients with severe hypersensitivity to milk proteins.
5.4 Worsening of Narrow-Angle Glaucoma
SEEBRI NEOHALER should be used with caution in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma. Prescribers and patients should be alert for signs and symptoms of acute narrow-angle glaucoma (e.g., eye pain or discomfort, blurred vision, visual halos or colored images in association with red eyes from conjunctival congestion and corneal edema). Instruct patients to consult a physician immediately should any of these signs or symptoms develop.
5.5 Worsening of Urinary Retention
SEEBRI NEOHALER should be used with caution in patients with urinary retention. Prescribers and patients should be alert for signs and symptoms of urinary retention (e.g., difficulty passing urine, painful urination), especially in patients with prostatic hyperplasia or bladder-neck obstruction. Instruct patients to consult a physician immediately should any of these signs or symptoms develop.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described in greater detail, in other sections:
- Paradoxical Bronchospasm [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions, including Anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Worsening of Narrow-Angle Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Worsening of Urinary Retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The SEEBRI NEOHALER safety database included 3415 subjects with COPD in four 12-week lung function trials and one 52-week long-term safety study. A total of 1202 subjects received treatment with SEEBRI NEOHALER 15.6 mcg twice daily. The safety data described below are based on the four 12-week trials and the one 52-week trial.
12-Week Trials
The incidence of adverse reactions associated with SEEBRI NEOHALER in Table 1 is based on four 12-week, placebo-controlled trials in 2908 subjects with COPD. In the total population, 61.2% of patients had moderate COPD and 37.8% had severe COPD. In these trials, 951 subjects received SEEBRI NEOHALER 15.6 mcg twice daily, 511 subjects received indacaterol 27.5 mcg twice daily, 508 subjects received a fixed-dose combination of indacaterol/glycopyrrolate 27.5 mcg/15.6 mcg twice daily, and 938 subjects received placebo. Overall, 62% were males, 90% were Caucasian, and the mean age was 63 years (ranging from 41 to 89 years). In this population, 53% were identified as current smokers with an average smoking history of 48 pack-years.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 2% and higher than placebo) were upper respiratory tract infection and nasopharyngitis.
The proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions was 2.4% for the SEEBRI NEOHALER-treated patients and 3.8% for placebo-treated patients.
| Abbreviation: COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. | ||
|
Adverse Reaction | SEEBRI NEOHALER
15.6 mcg twice daily (N = 951) n (%) | Placebo
(N = 938) n (%) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 32 (3.4) | 22 (2.3) |
| Nasopharyngitis | 20 (2.1) | 18 (1.9) |
| Urinary tract infection | 13 (1.4) | 12 (1.3) |
| Sinusitis | 13 (1.4) | 7 (0.7) |
| Oropharyngeal pain | 17 (1.8) | 11 (1.2) |
Other adverse reactions occurring more frequently with SEEBRI NEOHALER than with placebo, but with an incidence of less than 1% include rash, pruritus, gastroenteritis, hypersensitivity, atrial fibrillation, insomnia, pain in extremity, dysuria, vomiting, productive cough, and diabetes mellitus/hyperglycemia.
52-Week Trial
In a long-term safety trial, 507 subjects were treated for up to 52 weeks with glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg twice daily or indacaterol 75 mcg once daily. The demographic and baseline characteristics of the long-term safety trial were similar to those of the placebo-controlled efficacy trials described above. The adverse reactions reported in the long-term safety trial were consistent with those observed in the placebo-controlled trials of 12 weeks. Additional adverse reactions that occurred with a frequency greater than or equal to 2% in the group receiving glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg twice daily that exceeded the frequency of indacaterol 75 mcg once daily in this trial were: diarrhea, nausea, upper abdominal pain, fatigue, bronchitis, pneumonia, rhinitis, back pain, arthralgia, dyspnea, and wheezing.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during worldwide post-approval use of glycopyrrolate, the active ingredient in SEEBRI NEOHALER, at higher than the recommended dose. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These adverse reactions are: angioedema, paradoxical bronchospasm and dysphonia.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Sympathomimetics, Methylxanthines, Steroids
In clinical studies, concurrent administration of short-acting and long-acting sympathomimetic (beta-agonists) bronchodilators (including indacaterol), methylxanthines, oral and inhaled steroids with SEEBRI NEOHALER showed no increases in adverse drug reactions.
7.2 Anticholinergics
There is a potential for an additive interaction with concomitantly used anticholinergic medications. Therefore, avoid coadministration of SEEBRI NEOHALER with other anticholinergic-containing drugs as this may lead to an increase in anticholinergic effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.5) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with SEEBRI NEOHALER in pregnant women. Women should be advised to contact their physician if they become pregnant while taking SEEBRI NEOHALER.
In animal reproduction studies, there were no evidence of fetal harm or structural abnormalities in Wistar rats or New Zealand White rabbits at inhaled doses approximately 1,400 and 530 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD of 31.2 mcg) on an area under the curve (AUC) basis (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Labor or Delivery
The potential effect of SEEBRI NEOHALER on labor and delivery is unknown. SEEBRI NEOHALER should be used during labor and delivery only if the potential benefit to the patient justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Data
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies, pregnant Wistar rats received daily inhalation doses of glycopyrrolate, during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 7 to 17, at exposures up to 1,400 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis with maternal inhaled doses up to 3.83 mg/kg) and pregnant New Zealand White rabbits received daily inhalation doses of glycopyrrolate, during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 7 to 19, at exposures up to 530 times the MRHD on an AUC basis with maternal inhaled doses up to 4.4 mg/kg). Glycopyrrolate produced no evidence of teratogenicity in Wistar rats or New Zealand White rabbits at exposures up to approximately 1,400 and 530 times, respectively the MRHD.
In a pre- and postnatal development study in pregnant Wistar rats, glycopyrrolate was administered subcutaneously daily throughout the periods of organogenesis and lactation from gestation day 6 through lactation day 23 at exposures up to 1,100 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis with maternal subcutaneous doses up to 1.88 mg/kg/day). Glycopyrrolate had no effects on physical, neurological, or reproductive development in rats following exposures up to approximately 1,100 times the MRHD.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of glycopyrrolate or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, in a study of lactating rats, glycopyrrolate was present in the milk (see Data). The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for SEEBRI NEOHALER and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from SEEBRI NEOHALER or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Animal Data
Glycopyrrolate and its metabolites were detected in the milk of lactating rats following a single intravenous injection of 4 mg/kg of radiolabeled glycopyrrolate.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SEEBRI NEOHALER in pediatric patients have not been established. SEEBRI NEOHALER is not indicated for use in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Based on available data, no adjustment of the dosage of SEEBRI NEOHALER in geriatric patients is warranted. SEEBRI NEOHALER can be used at the recommended dose in elderly patients 75 years of age and older.
Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of SEEBRI NEOHALER, 45% were aged 65 and older, while 10% were aged 75 and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild and moderate renal impairment. Use SEEBRI NEOHALER in patients with severe renal impairment [estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2], including those with end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis, only if the expected benefit outweighs the potential risk since the systemic exposure to glycopyrrolate may be increased in this population [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with hepatic impairment. The effects of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of glycopyrrolate have not been studied [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
An overdosage of glycopyrrolate may lead to anticholinergic signs and symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, lightheadedness, blurred vision, increased intraocular pressure (causing pain, vision disturbances, or reddening of the eye), obstipation or difficulties in voiding.
Accidental Ingestion: Acute intoxication by inadvertent oral ingestion of SEEBRI NEOHALER capsules is unlikely due to the low oral bioavailability (about 5%) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
11 DESCRIPTION
SEEBRI NEOHALER consists of SEEBRI capsules and a NEOHALER device. Each SEEBRI capsule contains a dry powder formulation of glycopyrrolate packaged in orange transparent hypromellose (HPMC) capsules for oral inhalation with the NEOHALER device only.
Each orange transparent HPMC capsule contains 15.6 mcg of glycopyrrolate blended with approximately 25 mg of lactose monohydrate (which contains trace levels of milk protein) and 0.04 mg of magnesium stearate.
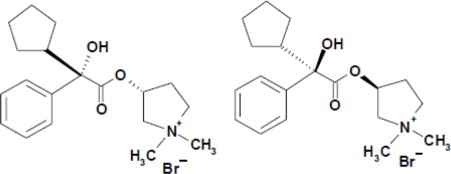
Glycopyrrolate, the active component of SEEBRI NEOHALER, is chemically described as (3RS)-3-[(2SR)-(2-cyclopentyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetyl) oxy]-1,1-dimethylpyrrolidinium bromide. This synthetic quaternary ammonium compound acts as a competitive antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, also referred to as anticholinergic. Glycopyrrolate, C19H28BrNO3, is a white powder that is freely soluble in water and sparingly soluble in absolute ethanol. It has a molecular mass of 398.33 g/mol. The structural formula is:
The NEOHALER device is an inhalation device used to inhale the dry powder within the SEEBRI capsule. The amount of drug delivered to the lung will depend on patient factors, such as inspiratory flow rate and inspiratory time. Under standardized in vitro testing at a fixed flow rate of 90 L/min for 1.3 seconds, the NEOHALER device delivered 13.1 mcg for the 15.6 mcg dose strength (equivalent to 12.5 mcg of glycopyrronium) from the mouthpiece. This in vitro testing revealed that the NEOHALER device had a specific resistance of 0.07 cm H2O1/2/L/min. Peak inspiratory flow rates (PIFR) achievable through the NEOHALER device were evaluated in 26 adult patients with COPD of varying severity. Mean PIFR was 95 L/min (range, 52 to 133 L/min) for adult patients. Twenty-five of 26 patients (96%) in this study generated a PIFR through the device exceeding 60 L/min.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Glycopyrrolate is a long-acting muscarinic antagonist which is often referred to as an anticholinergic. It has similar affinity to the subtypes of muscarinic receptors M1 to M5. In the airways, it exhibits pharmacological effects through inhibition of M3 receptor at the smooth muscle leading to bronchodilation. The competitive and reversible nature of antagonism was shown with human and animal origin receptors and isolated organ preparations. In preclinical in vitro as well as in vivo studies, prevention of methacholine and acetylcholine-induced bronchoconstrictive effects was dose-dependent and lasted longer than 24 hours. The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown. The bronchodilation following inhalation of glycopyrrolate is predominantly a site-specific effect.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of SEEBRI NEOHALER on the QTc interval was evaluated in a Phase 1 randomized placebo and positive controlled double-blind, single-dose, crossover thorough QTc study in 73 healthy subjects. At the dose 16-fold the therapeutic daily dose, SEEBRI NEOHALER did not prolong QTc to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Linear pharmacokinetics of glycopyrrolate was observed following inhalation of daily doses of 31.2 mcg to 249.6 mcg.
Absorption
Following oral inhalation using the NEOHALER inhaler, glycopyrrolate was rapidly absorbed and reached peak plasma levels at 5 minutes post dose.
The absolute bioavailability of glycopyrrolate inhaled via SEEBRI NEOHALER was estimated to be about 40%. About 90% of systemic exposure following inhalation is due to lung absorption and 10% is due to gastrointestinal absorption.
Following repeated once-daily inhalation in patients with COPD, PK steady-state of glycopyrrolate was reached within 1 week of treatment. There was no indication that the glycopyrrolate pharmacokinetics changes over time.
Distribution
After intravenous administration, the steady-state volume of distribution of glycopyrrolate was 83 L and the volume of distribution in the terminal phase was 376 L. The in vitro human plasma protein binding of glycopyrrolate was 38% to 41% at concentrations of 1 to 10 ng/mL.
Elimination
Renal elimination of parent drug accounts for about 60% to 70% of total clearance of systemically available glycopyrrolate whereas non-renal clearance processes account for about 30% to 40%. Biliary clearance contributes to the non-renal clearance, but the majority of non-renal clearance is thought to be due to metabolism.
Following inhalation of single and repeated once-daily doses between 62.4 mcg and 249.6 mcg glycopyrrolate by healthy volunteers and patients with COPD, mean renal clearance of glycopyrrolate was in the range of 17.4 L/h and 24.4 L/h indicating active tubular secretion contributes to the renal elimination of glycopyrrolate.
Glycopyrrolate plasma concentrations declined in a multi-phasic manner. The mean terminal elimination half-life was much longer after inhalation (33 to 53 hours) than after intravenous (6.2 hours) and oral (2.8 hours) administration.
Metabolism
In vitro metabolism studies show glycopyrrolate hydroxylation resulting in a variety of mono- and bis-hydroxylated metabolites and direct hydrolysis resulting in the formation of a carboxylic acid derivative (M9). Further in vitro investigations showed that multiple CYP isoenzymes contribute to the oxidative biotransformation of glycopyrrolate and the hydrolysis to M9 is likely to be catalyzed by members from the cholinesterase family pre-systemically and/or via first pass metabolism from the swallowed dose fraction of orally inhaled glycopyrrolate. Glucuronide and/or sulfate conjugates of glycopyrrolate were found in urine of humans after repeated inhalation, accounting for about 3% of the dose.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro inhibition studies demonstrated that glycopyrrolate has no relevant capacity to inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 or CYP3A4/5, the efflux transporters MDR1, MRP2 or MXR, and the uptake transporters OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT1 or OCT2. In vitro enzyme induction studies did not indicate a clinically relevant induction by glycopyrrolate for any of the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes tested as well as for UGT1A1 and the transporters MDR1 and MRP2.
In a clinical study in healthy volunteers, cimetidine, an inhibitor of organic cation transport which is thought to contribute to the renal excretion of glycopyrrolate, increased total systemic exposure (AUC) to glycopyrrolate by 22% and decreased renal clearance by 23%.
Specific Populations
Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed no evidence of a clinically relevant effect of age (40 to 85 years) or body weight (45 to 120 kg) on systemic exposure to glycopyrrolate. In addition, there was no evidence of a clinically significant ethnic/race effect (across Caucasian, Chinese, Hispanic/Latino, Japanese subjects). Gender, smoking status, and baseline FEV1 have no apparent effect on maximal or average glycopyrrolate systemic exposure.
Patients with Renal Impairment: Renal impairment has an impact on the systemic exposure to glycopyrrolate. A moderate mean increase in total systemic exposure (AUClast) of up to 1.4-fold was seen in subjects with mild and moderate renal impairment [estimated GFR greater than or equal to 30 mL/min/1.73m2] and up to 2.2-fold in subjects with severe renal impairment and end stage renal disease [estimated GFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73m2] [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment: The effects of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of glycopyrrolate have not been studied. Glycopyrrolate is cleared predominantly from systemic circulation by renal excretion [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Glycopyrrolate produced no treatment-related increases in the incidence of tumors in a 2-year inhalation study in Wistar rats at inhaled doses up to 0.56 mg/kg/day approximately 170 times the MRHD on an AUC basis. No evidence of tumorigenicity occurred in a 26-week oral (gavage) study in male and female TgrasH2 mice that received glycopyrrolate at doses up to 93.8 and 125.1 mg/kg/day, respectively.
Glycopyrrolate tested negative in the following genotoxicity assays: the in vitro Ames assay, in vitro human lymphocyte chromosomal aberration assay, and in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Impairment of fertility was observed in male and female Wistar rats at a subcutaneous glycopyrrolate dose of 1.88 mg/kg/day (approximately 1,900 and 1,100 times, respectively the MRHD on an AUC basis) based upon findings of decreased implantation sites and corresponding reduction of live fetuses. No effects on fertility and reproductive performance occurred in male and female rats at a subcutaneous glycopyrrolate dose of 0.63 mg/kg/day, approximately 350 times the MRHD on an AUC basis.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of SEEBRI NEOHALER were evaluated in a clinical development program that included 2 dose-ranging trials, 4 efficacy and safety trials of 12 weeks duration (placebo-controlled), and a 52-week long-term safety trial. Two of these efficacy and safety trials were conducted in support of the UTIBRON NEOHALER clinical development program, included glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg twice daily treatment arms, and are included in the overall safety database. Therefore, the efficacy of SEEBRI NEOHALER is based primarily on the dose-ranging trials in 471 subjects with COPD and the 2 placebo-controlled confirmatory trials in 867 subjects with COPD.
14.1 Dose Ranging Trial
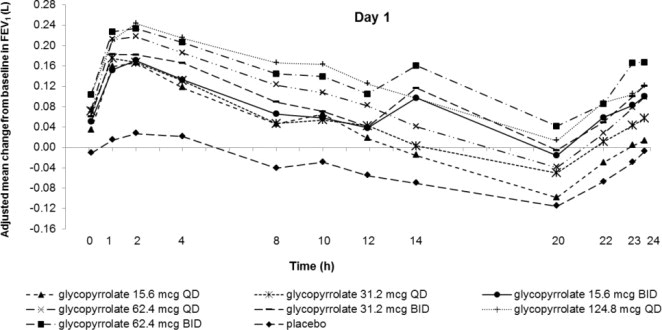
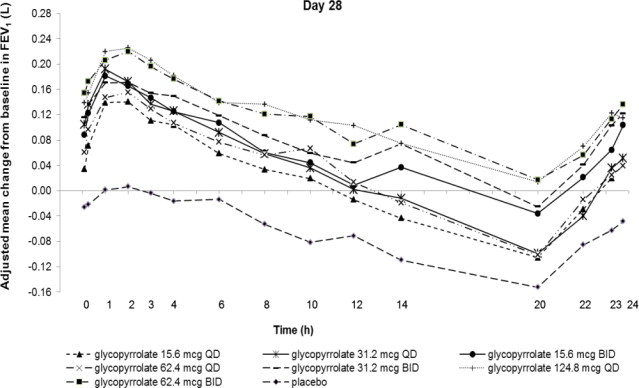
Dose selection for glycopyrrolate in COPD was supported by a 28-day, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2-period, crossover study evaluating 7 doses of glycopyrrolate (15.6 mcg, 31.2 mcg, 62.4 mcg, and 124.8 mcg once daily and 15.6 mcg, 31.2 mcg, and 62.4 mcg twice daily) or placebo in 388 subjects with COPD. The differences in trough FEV1 from baseline after 28 days compared to placebo for the 15.6 mcg, 31.2 mcg, 62.4 mcg, and 124.8 mcg once daily and for 15.6 mcg, 31.2 mcg, and 62.4 mcg twice-daily doses were 0.083 L (95% CI: 0.030, 0.136), 0.098 L (0.048, 0.148), 0.090 L (0.038, 0.142), 0.176 L (0.132, 0.220) 0.139 L (0.089, 0.189), 0.167 L (0.115, 0.219), and 0.177 L (0.132, 0.222), respectively. The dose-ranging results supported the evaluation of glycopyrrolate 15.6 mcg twice daily in the confirmatory COPD trials.
Figure 1. Adjusted Mean Change From Baseline in FEV1 (L) Over 24 Hours on Days 1 and 28
14.2 Confirmatory Trials
The clinical development program for SEEBRI NEOHALER included two (Trial 1 and Trial 2) similar 12-week, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trials in subjects with COPD designed to evaluate the efficacy of SEEBRI NEOHALER on lung function.
The 12-week trials treated 867 subjects that had a clinical diagnosis of COPD, were 40 years of age or older, had a history of smoking greater than 10 pack-years, had a post-bronchodilator FEV1 greater than or equal to 30% and less than 80% of predicted normal values, had a ratio of FEV1/FVC of less than 0.7, and were symptomatic as determined by a Modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) score greater than or equal to 2. Of the 867 subjects included in the efficacy analysis, 58% were male and 89% were Caucasian. They had a mean age of 63 years and an average smoking history of 53 pack-years, with 57% identified as current smokers, and 29% using inhaled corticosteroids. At screening, the mean post-bronchodilator percent predicted FEV1 was 55% (range, 30% to 83%), the mean post-bronchodilator percent FEV1/FVC was 51% (range, 24% to 69%), and the mean percent reversibility was 20% (0% to 169%).
Trial 1 and Trial 2 evaluated SEEBRI NEOHALER (glycopyrrolate) 15.6 mcg twice daily and placebo twice daily. The primary endpoint was the change from baseline in FEV1 AUC0-12h following the morning dose at Day 85 (defined as the mean FEV1 change from baseline over 0 to 12 hours divided by 12 hours) compared with placebo. In both trials, SEEBRI NEOHALER twice daily demonstrated a larger increase in mean change from baseline in FEV1 AUC0-12h compared to placebo (see Table 2).
| Abbreviation: CI, confidence interval; SE, standard error. | ||||||
| Treatment | N | Change from baseline
LS Mean (SE) | Comparison | Treatment difference
LS Mean (SE) | (95% CI) | |
| Trial 1 | ||||||
| SEEBRI NEOHALER | 222 | 0.125 L (0.0162) | SEEBRI NEOHALER - Placebo | 0.139 L (0.0225) | (0.095, 0.184) | |
| Placebo | 216 | -0.014 L (0.0165) | ||||
| Trial 2 | ||||||
| SEEBRI NEOHALER | 215 | 0.115 L (0.0153) | SEEBRI NEOHALER - Placebo | 0.123 L (0.0213) | (0.081, 0.165) | |
| Placebo | 213 | - 0.008 L (0.0153) | ||||
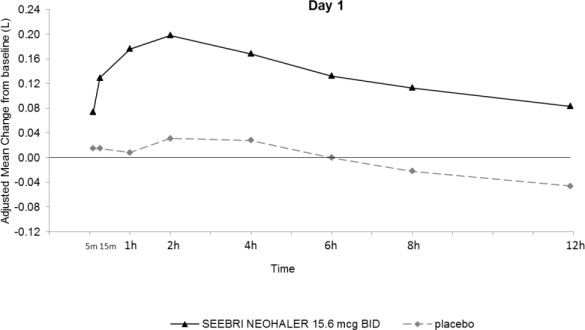
In Trial 1 and Trial 2, serial spirometric evaluations throughout the 12-hour dosing interval were performed in all subjects at Days 1 and 85. The spirometric curves from Trial 1 at Days 1 and 85 are displayed in Figure 2. In Trial 2, the results for SEEBRI NEOHALER in FEV1 AUC0-12h were similar to those observed in Trial 1.
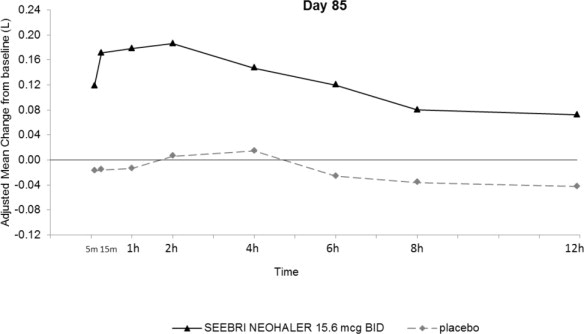
Figure 2. Adjusted Mean Change From Baseline in FEV1 (L) Over 12 Hours on Days 1 and 85 in Trial 1 (All Patient Population)
The peak FEV1 was defined as the maximum FEV1 recorded within 4 hours after the morning dose on Days 1 and 85. The mean peak FEV1 improvement from baseline for SEEBRI NEOHALER compared with placebo at Day 1 and at Day 85 was 0.142L and 0.163L (Trial 1), and 0.137L and 0.148L (Trial 2), respectively.
In Trials 1 and 2, patients treated with SEEBRI NEOHALER used less daily rescue albuterol during the trial compared to patients treated with placebo.
The St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) was assessed in Trials 1 and 2. In Trial 1, the SGRQ responder rate (defined as an improvement in score of 4 or more as threshold) for the SEEBRI NEOHALER treatment arm was 49% compared to 41% for placebo [Odds Ratio: 1.43, 95% CI: 0.95, 2.15]. In Trial 2, the SGRQ responder rate for the SEEBRI NEOHALER treatment arm was 55% compared to 42% for placebo [Odds Ratio: 1.78; 95% CI: 1.17, 2.71].
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
- SEEBRI NEOHALER contains SEEBRI (15.6 mcg glycopyrrolate inhalation powder) orange transparent capsules packaged in aluminum blister cards, one NEOHALER device, and FDA approved Patient Labeling.
- Unit Dose (blister pack), Box of 60 (10 blister cards with 6 orange transparent capsules each) NDC 63402-815-60
- Unit Dose (blister pack), Box of 6 (1 blister card with 6 orange transparent capsules) NDC 63402-815-06
- The NEOHALER device consists of a white protective cap and a base with mouthpiece, capsule chamber and 2 orange push buttons.
Storage and Handling
Store in a dry place at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- SEEBRI capsules should be used with the NEOHALER device only. Do not use the NEOHALER device with any other capsules.
- Store SEEBRI capsules in the blister protected from moisture. Remove the SEEBRI capsules from the blister immediately before use.
- Always use the new NEOHALER inhaler provided with each new prescription.
Keep out of the reach of children.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Not for Acute Symptoms
Inform patients that SEEBRI NEOHALER is not meant to relieve acute symptoms of COPD and extra doses should not be used for that purpose. Advise them to treat acute symptoms with a rescue inhaler, such as albuterol. Provide patients with such medicine and instruct them in how it should be used [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of the following:
- Symptoms get worse
- Need for more inhalations than usual of their rescue inhaler
Patients should not stop therapy with SEEBRI NEOHALER without physician/healthcare provider guidance since symptoms may recur after discontinuation.
Paradoxical Bronchospasm
Inform patients that, SEEBRI NEOHALER can produce paradoxical bronchospasm. Advise patients that if paradoxical bronchospasm occurs, patients should discontinue SEEBRI NEOHALER [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Worsening of Narrow-Angle Glaucoma
Instruct patients to be alert for signs and symptoms of acute narrow-angle glaucoma (e.g. eye pain or discomfort, blurred vision, visual halos or colored images in association with red eyes from conjunctival congestion and corneal edema). Instruct patients to consult a physician immediately should any of these signs or symptoms develop [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Worsening of Urinary Retention
Instruct patients to be alert for signs and symptoms of urinary retention (e.g. difficulty passing urine, painful urination). Instruct patients to consult a physician immediately should any of these signs or symptoms develop [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Instructions for Administering SEEBRI NEOHALER
It is important for patients to understand how to correctly administer SEEBRI capsules using the NEOHALER device [see Instructions for Use]. Instruct patients that SEEBRI capsules should only be administered via the NEOHALER device and the NEOHALER device should not be used for administering other medications. Remind patients that the contents of SEEBRI capsules are for oral inhalation only and must not be swallowed.
Instruct patients always to store SEEBRI capsules in sealed blisters and to only remove a SEEBRI capsule immediately before use or it may not be as effective. Instruct patients to discard unused additional SEEBRI capsules that are exposed to air (i.e., not intended for immediate use).
Inform patients to use one inhalation of SEEBRI NEOHALER orally twice daily (1 capsule in the morning and 1 capsule in the evening) at the same time every day.
Inform patients that if they miss a dose of SEEBRI NEOHALER, they should use their next capsule at the usual time. Instruct patients to not use 2 capsules at one time and to not use more than 2 capsules in a day.
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
T2021-109
T2021-110
| This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: July 2021 |
| INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
SEEBRI® NEOHALER® (SEE-Bri) (glycopyrrolate) inhalation powder, for oral inhalation use |
|
| For Oral Inhalation Only
Do not swallow SEEBRI capsules. |
|
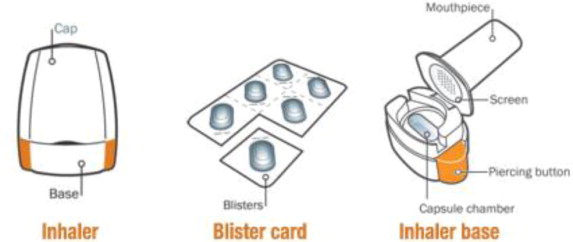
| Your SEEBRI NEOHALER
SEEBRI NEOHALER consists of both the inhaler and the blister-packaged capsules. Each package contains SEEBRI capsules and a NEOHALER inhaler.
|
|
| Your inhaler is made to give you the medicine contained in the capsules. | |
 |
|
| Only use the NEOHALER inhaler contained in this pack. Do not use SEEBRI NEOHALER capsules with any other inhaler; do not use NEOHALER inhaler to take any other capsule medicine. | |
| How to use your inhaler: | |
|
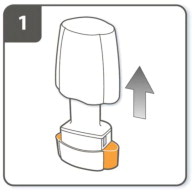
| Step 1. Pull off cap.
|
|
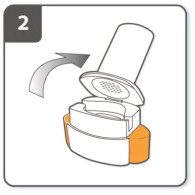
| Step 2. Open inhaler:
Hold the base of the inhaler firmly and tilt the mouthpiece to open the inhaler. |
|
| Step 3. Prepare capsule:
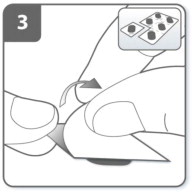
Separate 1 of the blisters from the blister card by tearing along the perforation. Take 1 blister and peel away the protective backing to expose the capsule. Do not push the capsule through the foil to remove it from the blister. |
|
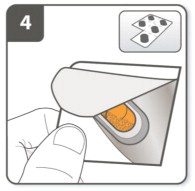
| Step 4. Remove a SEEBRI capsule:
Capsules should always be stored in the blister and only removed immediately before use. With dry hands, remove 1 capsule from the blister. Do not swallow the SEEBRI capsule. |
|
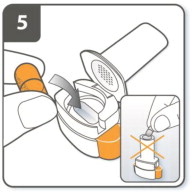
| Step 5. Insert capsule:
Place the capsule into the capsule chamber. Do not place a capsule directly into the mouthpiece. |
|
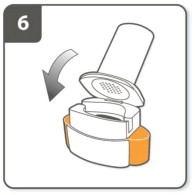
| Step 6. Close the inhaler:
Close the inhaler fully. You should hear a ‘click' as it fully closes. |
|
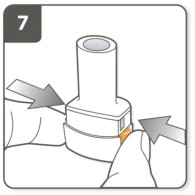
| Step 7. Pierce the capsule:
Hold the inhaler upright with the mouthpiece pointing up. Press both piercing buttons together firmly at the same time. You should hear a ‘click' as the capsule is being pierced. Do not press the piercing buttons more than 1 time. |
|
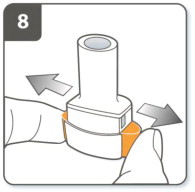
| Step 8. Release the piercing buttons fully.
|
|
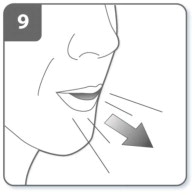
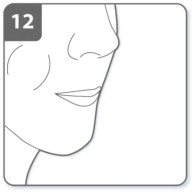
| Step 9. Breathe out:
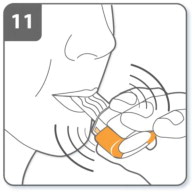
Before placing the mouthpiece in your mouth, breathe out fully. Do not blow into the mouthpiece. |
|
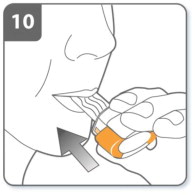
| Step 10. Inhale the medicine:
Before breathing in:
|
|
| Step 11. Note:
As you breathe in through the inhaler, the capsule spins around in the chamber and you should hear a whirring noise. You may experience a sweet flavor as you inhale the medicine. If you do not hear a whirring noise, the capsule may be stuck in the capsule chamber. If this occurs, open the inhaler and carefully loosen the capsule by tapping the base of the inhaler. Do not press the piercing buttons to loosen the capsule. (Repeat steps 9 and 10 if necessary). |
|
| Step 12. Hold breath:
Continue to hold your breath for at least 5 to 10 seconds or as long as comfortably possible while removing the inhaler from your mouth. Then breathe out. Open the inhaler to see if any powder is left in the capsule. If there is powder left in the capsule, close the inhaler and repeat steps 9 to 12. Most people are able to empty the capsule with 1 or 2 inhalations. Some people may cough soon after inhaling the medicine. If you cough, don't worry; as long as the capsule is empty, you have received 1 full dose. |
|
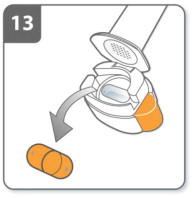
| Step 13. Remove capsule:
After you have finished taking your dose of SEEBRI NEOHALER, open the mouthpiece again, remove the empty capsule by tipping it out of the capsule chamber, and throwing it away. Close the inhaler and replace the cap. Do not leave the used capsules in the NEOHALER inhaler. |
| Additional Information:
Occasionally, very small pieces of the capsule can get past the screen and enter your mouth. If this happens, you may be able to feel these pieces on your tongue. It is not harmful if these pieces are swallowed or inhaled. The chances of the capsule shattering (breaking apart) will be increased if the capsule is pierced more than once (see Step 7). Therefore, it is recommended that you follow the storage directions, remove the capsule from the blister immediately before use, and pierce each capsule only once. How to clean your inhaler: Cleaning the inhaler device is not necessary; however, if you want to clean your inhaler, wipe the mouthpiece inside and outside with a clean, dry, lint-free cloth, or you may use a clean, dry, soft brush to wipe the inhaler between uses to remove any powder residue. Keep the inhaler dry. REMEMBER:
|
|
How should I store SEEBRI NEOHALER?
|
|
| SEEBRI is a trademark of Novartis AG. NEOHALER is a registered trademark of Novartis AG. | |
| Distributed by: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation East Hanover, New Jersey 07936 © Novartis |
|
T2021-111
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 15.6 mcg per capsule – 12 SAMPLE Capsule Carton
NDC 63402-815-12
12 Capsules
PROFESSIONAL SAMPLE
NOT FOR SALE OR REIMBURSEMENT
Seebri™ Neohaler®
(glycopyrrolate) inhalation powder
15.6 mcg per capsule
Rx only
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Do not swallow the SEEBRI capsules
SEEBRI capsules are for use with NEOHALER Inhaler only
Manufactured for Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
EXP/LOT
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
BLISTER LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 15.6 mcg SAMPLE Blister
NDC 63402-815-02
2 blister cards of 6
SAMPLE
NOT FOR SALE OR DISTRIBUTION
Seebri™ Neohaler®
(glycopyrrolate) inhalation powder
15.6 mcg per capsule
For use with NEOHALER only
Do not swallow capsule
Do not push capsule through foil
Rx only
EXP/LOT
Mfd for Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
CARTON LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15.6 mcg per capsule - 60 capsule Trade Carton
NDC 63402-815-60
60 Capsules
Rx only
Seebri™ Neohaler®
(glycopyrrolate) inhalation powder
15.6 mcg per capsule
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Do not swallow the SEEBRI capsules
SEEBRI capsules are for use with the NEOHALER Inhaler only
Manufactured for Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
GTIN: 00363402815604
EXP/LOT
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
CARTON LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 15.6 mcg per capsule - 6 capsule Carton
NDC 63402-815-06
6 Capsules
Rx only
Seebri™ Neohaler®
(glycopyrrolate) inhalation powder
15.6 mcg per capsule
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Do not swallow the SEEBRI capsules
SEEBRI capsules are for use with the NEOHALER Inhaler only
Manufactured for Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
GTIN: 00363402815062
EXP/LOT
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
BLISTER LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 15.6 mcg Trade Blister
NDC 63402-815-01
1 blister card of 6 capsules (2 blister cards displayed)
Seebri™ Neohaler®
(glycopyrrolate) inhalation powder
15.6 mcg per capsule
Do not push the capsule through foil
For use with NEOHALER only
Do not swallow capsule
Rx only
EXP/LOT
Mfd for Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
| SEEBRI NEOHALER
glycopyrrolate capsule |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Sunovion Pharmacueticals Inc. (131661746) |
| Registrant - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |