PROPYLTHIOURACIL- propylthiouracil tablet
REMEDYREPACK INC.
----------
BOXED WARNING
Severe liver injury and acute liver failure, in some cases fatal, have been reported in patients treated with propylthiouracil. These reports of hepatic reactions include cases requiring liver transplantation in adult and pediatric patients.
Propylthiouracil should be reserved for patients who can not tolerate methimazole and in whom radioactive iodine therapy or surgery are not appropriate treatments for the management of hyperthyroidism.
Because of the risk of fetal abnormalities associated with methimazole, propylthiouracil may be the treatment of choice when an antithyroid drug is indicated during or just prior to the first trimester of pregnancy (seeWarningsandPrecautions).
DESCRIPTION
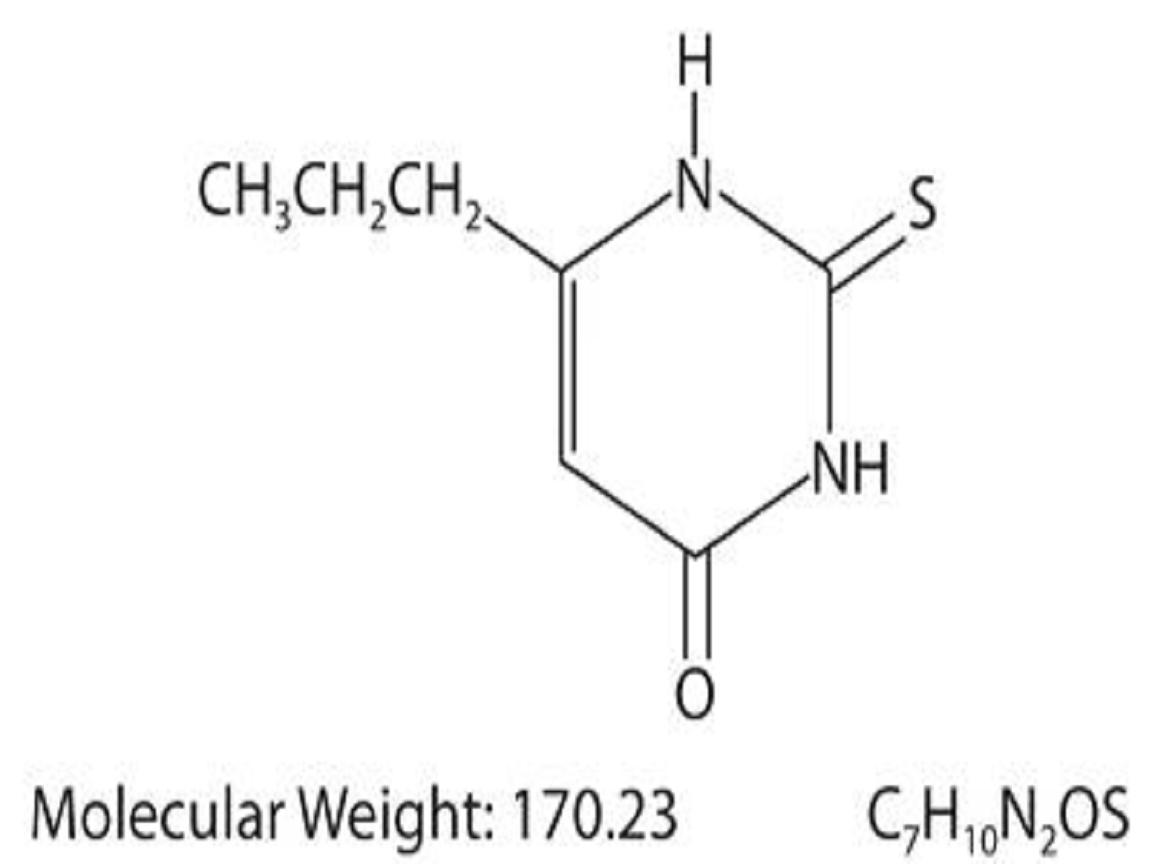
Propylthiouracil, USP is one of the thiocarbamide compounds. It is a white, crystalline substance that has a bitter taste and is very slightly soluble in water. Propylthiouracil is an antithyroid drug administered orally. The structural formula is:
Each tablet contains propylthiouracil, USP 50 mg and the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, corn starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, povidone, pregelatinized starch, and magnesium stearate.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Propylthiouracil inhibits the synthesis of thyroid hormones and thus is effective in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. The drug does not inactivate existing thyroxine and triiodothyronine that are stored in the thyroid or circulating in the blood, nor does it interfere with the effectiveness of thyroid hormones given by mouth or by injection. Propylthiouracil inhibits the conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in peripheral tissues and may therefore be an effective treatment for thyroid storm.
Propylthiouracil is readily absorbed and is extensively metabolized. Approximately 35% of the drug is excreted in the urine, in intact and conjugated forms, within 24 hours.
INDICATIONS & USAGE
Propylthiouracil tablets, USP are indicated:
- in patients with Graves'disease with hyperthyroidism or toxic multinodular goiter who are intolerant of methimazole and for whom surgery or radioactive iodine therapy is not an appropriate treatment option
- to ameliorate symptoms of hyperthyroidism in preparation for thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy in patients who are intolerant of methimazole
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Propylthiouracil is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug or any of the other product components.
WARNINGS
Liver Toxicity
Liver injury resulting in liver failure, liver transplantation, or death, has been reported with propylthiouracil therapy in adult and pediatric patients. No cases of liver failure have been reported with the use of methimazole in pediatric patients. For this reason, propylthiouracil is not recommended for pediatric patients except when methimazole is not well-tolerated and surgery or radioactive iodine therapy are not appropriate therapies.
There are cases of liver injury, including liver failure and death, in women treated with propylthiouracil during pregnancy. Two reports of in utero exposure with liver failure and death of a newborn have been reported. The use of an alternative antithyroid medication (e.g., methimazole) may be advisable following the first trimester of pregnancy (see
PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy
).
Biochemical monitoring of liver function (bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase) and hepatocellular integrity (ALT, AST) is not expected to attenuate the risk of severe liver injury due to its rapid and unpredictable onset. Patients should be informed of the risk of liver failure. Patients should be instructed to report any symptoms of hepatic dysfunction (anorexia, pruritus, right upper quadrant pain, etc.), particularly in the first six months of therapy. When these symptoms occur, propylthiouracil should be discontinued immediately and liver function tests and ALT and AST levels obtained.
Agranulocytosis
Agranulocytosis occurs in approximately 0.2% to 0.5% of patients and is a potentially life-threatening side effect of propylthiouracil therapy. Agranulocytosis typically occurs within the first 3 months of therapy. Patients should be instructed to immediately report any symptoms suggestive of agranulocytosis, such as fever or sore throat. Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and aplastic anemia (pancytopenia) may also occur. Propylthiouracil should be discontinued if agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia (pancytopenia), ANCA-positive vasculitis, hepatitis, interstitial pneumonitis, fever, or exfoliative dermatitis is suspected, and the patient's bone marrow indices should be obtained.
Hypothyroidism
Propylthiouracil can cause hypothyroidism necessitating routine monitoring of TSH and free T4 levels with adjustments in dosing to maintain a euthyroid state. Because the drug readily crosses placental membranes, propylthiouracil can cause fetal goiter and cretinism when administered to a pregnant woman (see
PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant while taking an antithyroid drug, they should contact their physician immediately about their therapy.
Patients should report immediately any evidence of illness, in particular sore throat, skin eruptions, fever, headache, or general malaise. They also should report symptoms suggestive of hepatic dysfunction (anorexia, pruritus, right upper quadrant pain, etc.).
LABORATORY TESTS
Because propylthiouracil may cause hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding, monitoring of prothrombin time should be considered during therapy with the drug, especially before surgical procedures.
Thyroid function tests should be monitored periodically during therapy. Once clinical evidence of hyperthyroidism has resolved, the finding of an elevated serum TSH indicates that a lower maintenance dose of propylthiouracil should be employed.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Beta-adrenergic Blocking Agents: Hyperthyroidism may cause an increased clearance of beta blockers with a high extraction ratio. A reduced dose of beta-adrenergic blockers may be needed when a hyperthyroid patient becomes euthyroid.
Digitalis Glycosides: Serum digitalis levels may be increased when hyperthyroid patients on a stable digitalis glycoside regimen become euthyroid; a reduced dose of digitalis glycosides may be needed.
Theophylline: Theophylline clearance may decrease when hyperthyroid patients on a stable theophylline regimen become euthyroid; a reduced dose of theophylline may be needed
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
Laboratory animals treated with propylthiouracil for > 1 year have demonstrated thyroid hyperplasia and carcinoma formation. Such animal findings are seen with continuous suppression of thyroid function by sufficient doses of a variety of antithyroid agents, as well as in dietary iodine deficiency, subtotal thyroidectomy, and implantation of autonomous thyrotropic hormone-secreting pituitary tumors. Pituitary adenomas have also been described.
PREGNANCY
If propylthiouracil is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking propylthiouracil, the patient should be warned of the rare potential hazard to the mother and fetus of liver damage.
Since methimazole may be associated with the rare development of fetal abnormalities such as aplasia cutis and choanal atresia, propylthiouracil may be the preferred agent during organogenesis, in the first trimester of pregnancy. Given the potential maternal adverse effects of propylthiouracil (e.g., hepatotoxicity), it may be preferable to switch from propylthiouracil to methimazole for the second and third trimesters.
Pregnancy Category D: See
WARNINGS
NURSING MOTHERS
Propylthiouracil is transferred to breast milk to a small extent and therefore likely results in clinically insignificant doses to the suckling infant. In one study, nine lactating women were administered 400 mg of propylthiouracil by mouth. The mean amount of propylthiouracil excreted during 4 hours after drug administration was 0.025% of the administered dose.
PEDIATRIC USE
Postmarketing reports of severe liver injury including hepatic failure requiring liver transplantation or resulting in death have been reported in the pediatric population. No such reports have been observed with methimazole. As such, propylthiouracil is not recommended for use in the pediatric population except in rare instances in which methimazole is not well-tolerated and surgery or radioactive iodine therapy are not appropriate.
When used in children, parents and patients should be informed of the risk of liver failure. If patients taking propylthiouracil develop tiredness, nausea, anorexia, fever, pharyngitis, or malaise, propylthiouracil should be discontinued immediately by the patient, a physician should be contacted, and a white blood cell count, liver function tests, and transaminase levels obtained.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
It should be noted that about 10% of patients with untreated hyperthyroidism have leukopenia (white blood cell count of less than 4,000/mm3), often with relative granulopenia.
OVERDOSAGE
Signs and Symptoms
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritus, edema, and pancytopenia. Agranulocytosis is the most serious effect. Rarely, exfoliative dermatitis, hepatitis, neuropathies, or CNS stimulation or depression may occur.
No information is available on the following: LD50; concentration of propylthiouracil in biologic fluids associated with toxicity and/or death; the amount of drug in a single dose usually associated with symptoms of overdosage; or the amount of propylthiouracil in a single dose likely to be life-threatening.
Treatment
To obtain up-to-date information about the treatment of overdose, a good resource is the certified Regional Poison Control Center. In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug overdoses, interaction among drugs, and unusual drug kinetics in the patient.
In the event of an overdose, appropriate supportive treatment should be initiated as dictated by the patient's medical status.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Propylthiouracil is administered orally. The total daily dosage is usually given in 3 equal doses at approximately 8-hour intervals.
Adults
Pediatric Use
Propylthiouracil is generally not recommended for use in the pediatric patient population except in rare instances in which other alternative therapies are not appropriate options. Studies evaluating appropriate dosing regimen have not been conducted in the pediatric population although general practice would suggest initiation of therapy in patients 6 years or older at a dosage of 50 mg daily with careful upward titration based on clinical response and evaluation of TSH and free T4 levels. Although cases of severe liver injury have been reported with doses as low as 50 mg/day, most cases were associated with doses of
300 mg/day and higher.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of propylthiouracil did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
HOW SUPPLIED
50 mgEach white, round, tablet imprinted with "R" on one side and 348 and partial bisect on the other side contains 50 mg of Propylthiouracil, USP. Tablets are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC 0228-2348-10).
| PROPYLTHIOURACIL
propylthiouracil tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - REMEDYREPACK INC. (829572556) |