SUSTIVA- efavirenz tablet, film coated
REMEDYREPACK INC.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use SUSTIVA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SUSTIVA.
SUSTIVA ® (efavirenz) capsules for oral use SUSTIVA ® (efavirenz) tablets for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1998 INDICATIONS AND USAGESUSTIVA is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in adults and in pediatric patients at least 3 months old and weighing at least 3.5 kg. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
CONTRAINDICATIONSSUSTIVA is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity (eg, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, or toxic skin eruptions) to any of the components of this product. (4.1) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions (>5%, moderate-severe) are impaired concentration, abnormal dreams, rash, dizziness, nausea, headache, fatigue, insomnia, and vomiting.
(5.5,
6)
DRUG INTERACTIONSCoadministration of efavirenz can alter the concentrations of other drugs and other drugs may alter the concentrations of efavirenz. The potential for drug-drug interactions should be considered before and during therapy. (7.1, 12.3) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 7/2016 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
SUSTIVA ® (efavirenz) in combination with other antiretroviral agents is indicated for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in adults and in pediatric patients at least 3 months old and weighing at least 3.5 kg.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adults
The recommended dosage of SUSTIVA (efavirenz) is 600 mg orally, once daily, in combination with a protease inhibitor and/or nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). It is recommended that SUSTIVA be taken on an empty stomach, preferably at bedtime. The increased efavirenz concentrations observed following administration of SUSTIVA with food may lead to an increase in frequency of adverse reactions [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Dosing at bedtime may improve the tolerability of nervous system symptoms [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Adverse Reactions (6.1), and Patient Counseling Information (17)]. SUSTIVA capsules or tablets should be swallowed intact with liquid. For patients who cannot swallow capsules or tablets, the capsule sprinkle method of administration is recommended [ see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Concomitant Antiretroviral Therapy
SUSTIVA must be given in combination with other antiretroviral medications [ see Indications and Usage (1), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Dosage Adjustment
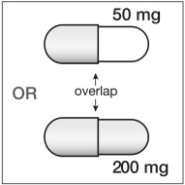
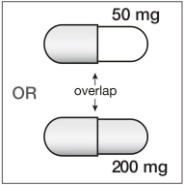
If SUSTIVA is coadministered with voriconazole, the voriconazole maintenance dose should be increased to 400 mg every 12 hours and the SUSTIVA dose should be decreased to 300 mg once daily using the capsule formulation (one 200 mg and two 50 mg capsules or six 50 mg capsules). SUSTIVA tablets must not be broken. [ See Drug Interactions (7.1, Table 5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3, Tables 7 and 8).]
If SUSTIVA is coadministered with rifampin to patients weighing 50 kg or more, an increase in the dose of SUSTIVA to 800 mg once daily is recommended [ see Drug Interactions (7.1, Table 5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3, Table 8)].
2.2 Pediatric Patients
It is recommended that SUSTIVA be taken on an empty stomach, preferably at bedtime. Table 1 describes the recommended dose of SUSTIVA for pediatric patients 3 months of age or older and weighing between 3.5 kg and 40 kg [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The recommended dosage of SUSTIVA for pediatric patients weighing 40 kg or greater is 600 mg once daily. For pediatric patients who cannot swallow capsules, the capsule contents can be administered with a small amount of food or infant formula using the capsule sprinkle method of administration [ see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
| Patient Body Weight | SUSTIVA Daily Dose | Number of Capsules
a or Tablets
b
and Strength to Administer |
|---|---|---|
| a Capsules can be administered intact or as sprinkles [
see
Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
b Tablets must not be crushed. |
||
|
3.5 kg to less than 5 kg |
100 mg |
two 50 mg capsules |
|
5 kg to less than 7.5 kg |
150 mg |
three 50 mg capsules |
|
7.5 kg to less than 15 kg |
200 mg |
one 200 mg capsule |
|
15 kg to less than 20 kg |
250 mg |
one 200 mg + one 50 mg capsule |
|
20 kg to less than 25 kg |
300 mg |
one 200 mg + two 50 mg capsules |
|
25 kg to less than 32.5 kg |
350 mg |
one 200 mg + three 50 mg capsules |
|
32.5 kg to less than 40 kg |
400 mg |
two 200 mg capsules |
|
at least 40 kg |
600 mg |
one 600 mg tablet OR
|
2.3 Capsule Sprinkle Method of Administration
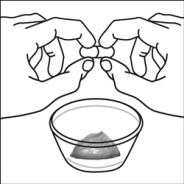
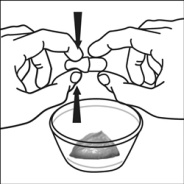
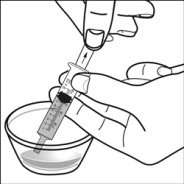
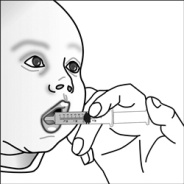
For pediatric patients at least 3 months old and weighing at least 3.5 kg and adults who cannot swallow capsules or tablets, the capsule contents may be administered with a small amount (1 to 2 teaspoons) of food. Use of infant formula for mixing should only be considered for those young infants who cannot reliably consume solid foods. Patients and caregivers should be instructed to open the capsule carefully to avoid spillage or dispersion of the capsule contents into the air. The capsule should be held horizontally over a small container and carefully twisted to open. For patients able to tolerate solid foods, the entire capsule contents should be gently mixed with an age-appropriate soft food, such as applesauce, grape jelly, or yogurt, in the small container. For young infants receiving the capsule sprinkle-infant formula mixture, the entire capsule contents should be gently mixed into 2 teaspoons of reconstituted room temperature infant formula in a small container by carefully stirring with a small spoon, and then drawing up the mixture into a 10 mL oral dosing syringe for administration. After administration of the SUSTIVA-food or -formula mixture, an additional small amount (approximately 2 teaspoons) of food or formula must be added to the empty mixing container, stirred to disperse any remaining SUSTIVA residue, and administered to the patient. The SUSTIVA-food or -formula mixture should be administered within 30 minutes of mixing. No additional food should be consumed for 2 hours after administration of SUSTIVA.
Further patient instructions on the capsule sprinkle method of administration are provided in the FDA-approved patient labeling (see Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
• Capsules
200 mg capsules are gold color, reverse printed with “SUSTIVA” on the body and imprinted “200 mg” on the cap.
50 mg capsules are gold color and white, printed with “SUSTIVA” on the gold color cap and reverse printed “50 mg” on the white body.
• Tablets
600 mg tablets are yellow, capsular-shaped, film-coated tablets, with “SUSTIVA” printed on both sides.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Drug Interactions
Efavirenz plasma concentrations may be altered by substrates, inhibitors, or inducers of CYP3A. Likewise, efavirenz may alter plasma concentrations of drugs metabolized by CYP3A or CYP2B6. The most prominent effect of efavirenz at steady-state is induction of CYP3A and CYP2B6. [ See Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Drug Interactions (7.1).]
5.2 Resistance
SUSTIVA must not be used as a single agent to treat HIV-1 infection or added on as a sole agent to a failing regimen. Resistant virus emerges rapidly when efavirenz is administered as monotherapy. The choice of new antiretroviral agents to be used in combination with efavirenz should take into consideration the potential for viral cross-resistance.
5.3 Coadministration with Related Products
Coadministration of SUSTIVA with ATRIPLA (efavirenz 600 mg/emtricitabine 200 mg/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate 300 mg) is not recommended unless needed for dose adjustment (eg, with rifampin), since efavirenz is one of its active ingredients.
5.4 Psychiatric Symptoms
Serious psychiatric adverse experiences have been reported in patients treated with SUSTIVA. In controlled trials of 1008 patients treated with regimens containing SUSTIVA for a mean of 2.1 years and 635 patients treated with control regimens for a mean of 1.5 years, the frequency (regardless of causality) of specific serious psychiatric events among patients who received SUSTIVA or control regimens, respectively, were severe depression (2.4%, 0.9%), suicidal ideation (0.7%, 0.3%), nonfatal suicide attempts (0.5%, 0), aggressive behavior (0.4%, 0.5%), paranoid reactions (0.4%, 0.3%), and manic reactions (0.2%, 0.3%). When psychiatric symptoms similar to those noted above were combined and evaluated as a group in a multifactorial analysis of data from Study 006, treatment with efavirenz was associated with an increase in the occurrence of these selected psychiatric symptoms. Other factors associated with an increase in the occurrence of these psychiatric symptoms were history of injection drug use, psychiatric history, and receipt of psychiatric medication at study entry; similar associations were observed in both the SUSTIVA and control treatment groups. In Study 006, onset of new serious psychiatric symptoms occurred throughout the study for both SUSTIVA-treated and control-treated patients. One percent of SUSTIVA-treated patients discontinued or interrupted treatment because of one or more of these selected psychiatric symptoms. There have also been occasional postmarketing reports of death by suicide, delusions, and psychosis-like behavior, although a causal relationship to the use of SUSTIVA cannot be determined from these reports. Patients with serious psychiatric adverse experiences should seek immediate medical evaluation to assess the possibility that the symptoms may be related to the use of SUSTIVA, and if so, to determine whether the risks of continued therapy outweigh the benefits. [ See Adverse Reactions (6.1).]
5.5 Nervous System Symptoms
Fifty-three percent (531/1008) of patients receiving SUSTIVA in controlled trials reported central nervous system symptoms (any grade, regardless of causality) compared to 25% (156/635) of patients receiving control regimens [ see Adverse Reactions (6.1, Table 3)]. These symptoms included, but were not limited to, dizziness (28.1% of the 1008 patients), insomnia (16.3%), impaired concentration (8.3%), somnolence (7.0%), abnormal dreams (6.2%), and hallucinations (1.2%). These symptoms were severe in 2.0% of patients; and 2.1% of patients discontinued therapy as a result. These symptoms usually begin during the first or second day of therapy and generally resolve after the first 2-4 weeks of therapy. After 4 weeks of therapy, the prevalence of nervous system symptoms of at least moderate severity ranged from 5% to 9% in patients treated with regimens containing SUSTIVA and from 3% to 5% in patients treated with a control regimen. Patients should be informed that these common symptoms were likely to improve with continued therapy and were not predictive of subsequent onset of the less frequent psychiatric symptoms [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Dosing at bedtime may improve the tolerability of these nervous system symptoms [ see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Analysis of long-term data from Study 006 (median follow-up 180 weeks, 102 weeks, and 76 weeks for patients treated with SUSTIVA + zidovudine + lamivudine, SUSTIVA + indinavir, and indinavir + zidovudine + lamivudine, respectively) showed that, beyond 24 weeks of therapy, the incidences of new-onset nervous system symptoms among SUSTIVA-treated patients were generally similar to those in the indinavir-containing control arm.
Patients receiving SUSTIVA should be alerted to the potential for additive central nervous system effects when SUSTIVA is used concomitantly with alcohol or psychoactive drugs.
Patients who experience central nervous system symptoms such as dizziness, impaired concentration, and/or drowsiness should avoid potentially hazardous tasks such as driving or operating machinery.
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Efavirenz may cause fetal harm when administered during the first trimester to a pregnant woman. Advise females of reproductive potential who are receiving SUSTIVA to avoid pregnancy. [ See Use in Specific Populations (8.1 and 8.3).]
5.7 Rash
In controlled clinical trials, 26% (266/1008) of adult patients treated with 600 mg SUSTIVA experienced new-onset skin rash compared with 17% (111/635) of those treated in control groups [ see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Rash associated with blistering, moist desquamation, or ulceration occurred in 0.9% (9/1008) of patients treated with SUSTIVA. The incidence of Grade 4 rash (eg, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome) in adult patients treated with SUSTIVA in all studies and expanded access was 0.1%. Rashes are usually mild-to-moderate maculopapular skin eruptions that occur within the first 2 weeks of initiating therapy with efavirenz (median time to onset of rash in adults was 11 days) and, in most patients continuing therapy with efavirenz, rash resolves within 1 month (median duration, 16 days). The discontinuation rate for rash in adult clinical trials was 1.7% (17/1008).
Rash was reported in 59 of 182 pediatric patients (32%) treated with SUSTIVA [ see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Two pediatric patients experienced Grade 3 rash (confluent rash with fever, generalized rash), and four patients had Grade 4 rash (erythema multiforme). The median time to onset of rash in pediatric patients was 28 days (range 3-1642 days). Prophylaxis with appropriate antihistamines before initiating therapy with SUSTIVA in pediatric patients should be considered.
SUSTIVA can generally be reinitiated in patients interrupting therapy because of rash. SUSTIVA should be discontinued in patients developing severe rash associated with blistering, desquamation, mucosal involvement, or fever. Appropriate antihistamines and/or corticosteroids may improve the tolerability and hasten the resolution of rash. For patients who have had a life-threatening cutaneous reaction (eg, Stevens-Johnson syndrome), alternative therapy should be considered [ see also Contraindications (4.1)].
5.8 Hepatotoxicity
Monitoring of liver enzymes before and during treatment is recommended for patients with underlying hepatic disease, including hepatitis B or C infection; patients with marked transaminase elevations; and patients treated with other medications associated with liver toxicity [ see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. A few of the postmarketing reports of hepatic failure occurred in patients with no pre-existing hepatic disease or other identifiable risk factors [ see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Liver enzyme monitoring should also be considered for patients without pre-existing hepatic dysfunction or other risk factors. In patients with persistent elevations of serum transaminases to greater than five times the upper limit of the normal range, the benefit of continued therapy with SUSTIVA needs to be weighed against the unknown risks of significant liver toxicity.
5.9 Convulsions
Convulsions have been observed in adult and pediatric patients receiving efavirenz, generally in the presence of known medical history of seizures [ see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.2)]. Caution should be taken in any patient with a history of seizures. Patients who are receiving concomitant anticonvulsant medications primarily metabolized by the liver, such as phenytoin and phenobarbital, may require periodic monitoring of plasma levels [ see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.10 Lipid Elevations
Treatment with SUSTIVA has resulted in increases in the concentration of total cholesterol and triglycerides [ see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Cholesterol and triglyceride testing should be performed before initiating SUSTIVA therapy and at periodic intervals during therapy.
5.11 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including SUSTIVA. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections [such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PCP), or tuberculosis], which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves’ disease, polymyositis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
5.12 Fat Redistribution
Redistribution/accumulation of body fat including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and “cushingoid appearance” have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. The mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are currently unknown. A causal relationship has not been established.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most significant adverse reactions observed in patients treated with SUSTIVA are:
- psychiatric symptoms [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)],
- nervous system symptoms [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)],
- rash [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates reported cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical studies and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Adverse Reactions in Adults
The most common (>5% in either efavirenz treatment group) adverse reactions of at least moderate severity among patients in Study 006 treated with SUSTIVA in combination with zidovudine/lamivudine or indinavir were rash, dizziness, nausea, headache, fatigue, insomnia, and vomiting.
Selected clinical adverse reactions of moderate or severe intensity observed in ≥2% of SUSTIVA-treated patients in two controlled clinical trials are presented in Table 2.
| Study 006
LAM-, NNRTI-, and Protease Inhibitor-Naive Patients | Study ACTG 364
NRTI-experienced, NNRTI-, and Protease Inhibitor-Naive Patients |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUSTIVA
b
+ ZDV/LAM (n=412) | SUSTIVA
b
+ Indinavir (n=415) | Indinavir
+ ZDV/LAM (n=401) | SUSTIVA
b
+ Nelfinavir + NRTIs (n=64) | SUSTIVA
b
+ NRTIs (n=65) | Nelfinavir
+ NRTIs (n=66) |
|
| Adverse Reactions | 180 weeks c | 102 weeks c | 76 weeks c | 71.1 weeks c | 70.9 weeks c | 62.7 weeks c |
| a Includes adverse events at least possibly related to study drug or of unknown relationship for Study 006. Includes all adverse events regardless of relationship to study drug for Study ACTG 364.
b SUSTIVA provided as 600 mg once daily. c Median duration of treatment. d Includes erythema multiforme, rash, rash erythematous, rash follicular, rash maculopapular, rash petechial, rash pustular, and urticaria for Study 006 and macules, papules, rash, erythema, redness, inflammation, allergic rash, urticaria, welts, hives, itchy, and pruritus for ACTG 364. — = Not Specified. ZDV = zidovudine, LAM = lamivudine. |
||||||
|
Body as a Whole |
||||||
|
Fatigue |
8% |
5% |
9% |
0 |
2% |
3% |
|
Pain |
1% |
2% |
8% |
13% |
6% |
17% |
|
Central and Peripheral Nervous System |
||||||
|
Dizziness |
9% |
9% |
2% |
2% |
6% |
6% |
|
Headache |
8% |
5% |
3% |
5% |
2% |
3% |
|
Insomnia |
7% |
7% |
2% |
0 |
0 |
2% |
|
Concentration impaired |
5% |
3% |
<1% |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Abnormal dreams |
3% |
1% |
0 |
— |
— |
— |
|
Somnolence |
2% |
2% |
<1% |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Anorexia |
1% |
<1% |
<1% |
0 |
2% |
2% |
|
Gastrointestinal |
||||||
|
Nausea |
10% |
6% |
24% |
3% |
2% |
2% |
|
Vomiting |
6% |
3% |
14% |
— |
— |
— |
|
Diarrhea |
3% |
5% |
6% |
14% |
3% |
9% |
|
Dyspepsia |
4% |
4% |
6% |
0 |
0 |
2% |
|
Abdominal pain |
2% |
2% |
5% |
3% |
3% |
3% |
|
Psychiatric |
||||||
|
Anxiety |
2% |
4% |
<1% |
— |
— |
— |
|
Depression |
5% |
4% |
<1% |
3% |
0 |
5% |
|
Nervousness |
2% |
2% |
0 |
2% |
0 |
2% |
|
Skin & Appendages |
||||||
|
Rash d |
11% |
16% |
5% |
9% |
5% |
9% |
|
Pruritus |
<1% |
1% |
1% |
9% |
5% |
9% |
Pancreatitis has been reported, although a causal relationship with efavirenz has not been established. Asymptomatic increases in serum amylase levels were observed in a significantly higher number of patients treated with efavirenz 600 mg than in control patients (see Laboratory Abnormalities).
Nervous System Symptoms
For 1008 patients treated with regimens containing SUSTIVA and 635 patients treated with a control regimen in controlled trials, Table 3 lists the frequency of symptoms of different degrees of severity and gives the discontinuation rates for one or more of the following nervous system symptoms: dizziness, insomnia, impaired concentration, somnolence, abnormal dreaming, euphoria, confusion, agitation, amnesia, hallucinations, stupor, abnormal thinking, and depersonalization [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. The frequencies of specific central and peripheral nervous system symptoms are provided in Table 2.
| Percent of Patients with: | SUSTIVA 600 mg Once Daily
(n=1008) | Control Groups
(n=635) |
|---|---|---|
| % | % | |
| a Includes events reported regardless of causality.
b Data from Study 006 and three Phase 2/3 studies. c “Mild” = Symptoms which do not interfere with patient’s daily activities. d “Moderate” = Symptoms which may interfere with daily activities. e “Severe” = Events which interrupt patient’s usual daily activities. |
||
|
Symptoms of any severity |
52.7 |
24.6 |
|
Mild symptoms c |
33.3 |
15.6 |
|
Moderate symptoms d |
17.4 |
7.7 |
|
Severe symptoms e |
2.0 |
1.3 |
|
Treatment discontinuation as a result of symptoms |
2.1 |
1.1 |
Psychiatric Symptoms
Serious psychiatric adverse experiences have been reported in patients treated with SUSTIVA. In controlled trials, psychiatric symptoms observed at a frequency greater than 2% among patients treated with SUSTIVA or control regimens, respectively, were depression (19%, 16%), anxiety (13%, 9%), and nervousness (7%, 2%).
Rash
In controlled clinical trials, the frequency of rash (all grades, regardless of causality) was 26% for 1008 adults treated with regimens containing SUSTIVA and 17% for 635 adults treated with a control regimen. Most reports of rash were mild or moderate in severity. The frequency of Grade 3 rash was 0.8% for SUSTIVA-treated patients and 0.3% for control groups, and the frequency of Grade 4 rash was 0.1% for SUSTIVA and 0 for control groups. The discontinuation rates as a result of rash were 1.7% for SUSTIVA-treated patients and 0.3% for control groups [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Experience with SUSTIVA in patients who discontinued other antiretroviral agents of the NNRTI class is limited. Nineteen patients who discontinued nevirapine because of rash have been treated with SUSTIVA. Nine of these patients developed mild-to-moderate rash while receiving therapy with SUSTIVA, and two of these patients discontinued because of rash.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Selected Grade 3-4 laboratory abnormalities reported in ≥2% of SUSTIVA-treated patients in two clinical trials are presented in Table 4.
| Study 006
LAM-, NNRTI-, and Protease Inhibitor-Naive Patients | Study ACTG 364
NRTI-experienced, NNRTI-, and Protease Inhibitor-Naive Patients |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Limit | SUSTIVA
a
+ ZDV/LAM (n=412) | SUSTIVA
a
+ Indinavir (n=415) | Indinavir
+ ZDV/LAM (n=401) | SUSTIVA
a
+ Nelfinavir + NRTIs (n=64) | SUSTIVA
a
+ NRTIs (n=65) | Nelfinavir
+ NRTIs (n=66) |
| 180 weeks b | 102 weeks b | 76 weeks b | 71.1 weeks b | 70.9 weeks b | 62.7 weeks b | ||
| a SUSTIVA provided as 600 mg once daily.
b Median duration of treatment. c Isolated elevations of GGT in patients receiving SUSTIVA may reflect enzyme induction not associated with liver toxicity. d Nonfasting. ZDV = zidovudine, LAM = lamivudine, ULN = upper limit of normal, ALT = alanine aminotransferase, AST = aspartate aminotransferase, GGT = gamma-glutamyltransferase. |
|||||||
|
Chemistry |
|||||||
|
ALT |
>5 × ULN |
5% |
8% |
5% |
2% |
6% |
3% |
|
AST |
>5 × ULN |
5% |
6% |
5% |
6% |
8% |
8% |
|
GGT c |
>5 × ULN |
8% |
7% |
3% |
5% |
0 |
5% |
|
Amylase |
>2 × ULN |
4% |
4% |
1% |
0 |
6% |
2% |
|
Glucose |
>250 mg/dL |
3% |
3% |
3% |
5% |
2% |
3% |
|
Triglycerides d |
≥751 mg/dL |
9% |
6% |
6% |
11% |
8% |
17% |
|
Hematology |
|||||||
|
Neutrophils |
<750/mm 3 |
10% |
3% |
5% |
2% |
3% |
2% |
Patients Coinfected with Hepatitis B or C
Liver function tests should be monitored in patients with a history of hepatitis B and/or C. In the long-term data set from Study 006, 137 patients treated with SUSTIVA-containing regimens (median duration of therapy, 68 weeks) and 84 treated with a control regimen (median duration, 56 weeks) were seropositive at screening for hepatitis B (surface antigen positive) and/or C (hepatitis C antibody positive). Among these coinfected patients, elevations in AST to greater than five times ULN developed in 13% of patients in the SUSTIVA arms and 7% of those in the control arm, and elevations in ALT to greater than five times ULN developed in 20% of patients in the SUSTIVA arms and 7% of patients in the control arm. Among coinfected patients, 3% of those treated with SUSTIVA-containing regimens and 2% in the control arm discontinued from the study because of liver or biliary system disorders [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Lipids
Increases from baseline in total cholesterol of 10-20% have been observed in some uninfected volunteers receiving SUSTIVA. In patients treated with SUSTIVA + zidovudine + lamivudine, increases from baseline in nonfasting total cholesterol and HDL of approximately 20% and 25%, respectively, were observed. In patients treated with SUSTIVA + indinavir, increases from baseline in nonfasting cholesterol and HDL of approximately 40% and 35%, respectively, were observed. Nonfasting total cholesterol levels ≥240 mg/dL and ≥300 mg/dL were reported in 34% and 9%, respectively, of patients treated with SUSTIVA + zidovudine + lamivudine; 54% and 20%, respectively, of patients treated with SUSTIVA + indinavir; and 28% and 4%, respectively, of patients treated with indinavir + zidovudine + lamivudine. The effects of SUSTIVA on triglycerides and LDL in this study were not well characterized since samples were taken from nonfasting patients. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, the adverse reaction rates reported cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical studies and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Assessment of adverse reactions is based on three clinical trials in 182 HIV-1 infected pediatric patients (3 months to 21 years of age) who received SUSTIVA in combination with other antiretroviral agents for a median of 123 weeks. The adverse reactions observed in the three trials were similar to those observed in clinical trials in adults except that rash was more common in pediatric patients (32% for all grades regardless of causality) and more often of higher grade (ie, more severe). Two (1.1%) pediatric patients experienced Grade 3 rash (confluent rash with fever, generalized rash), and four (2.2%) pediatric patients had Grade 4 rash (all erythema multiforme). Five pediatric patients (2.7%) discontinued from the study because of rash [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of SUSTIVA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Body as a Whole: allergic reactions, asthenia, redistribution/accumulation of body fat [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
Central and Peripheral Nervous System: abnormal coordination, ataxia, cerebellar coordination and balance disturbances, convulsions, hypoesthesia, paresthesia, neuropathy, tremor, vertigo
Endocrine: gynecomastia
Gastrointestinal: constipation, malabsorption
Cardiovascular: flushing, palpitations
Liver and Biliary System: hepatic enzyme increase, hepatic failure, hepatitis. A few of the postmarketing reports of hepatic failure, including cases in patients with no pre-existing hepatic disease or other identifiable risk factors, were characterized by a fulminant course, progressing in some cases to transplantation or death.
Metabolic and Nutritional: hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, myalgia, myopathy
Psychiatric: aggressive reactions, agitation, delusions, emotional lability, mania, neurosis, paranoia, psychosis, suicide
Respiratory: dyspnea
Skin and Appendages: erythema multiforme, photoallergic dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Special Senses: abnormal vision, tinnitus
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drug-Drug Interactions
Efavirenz has been shown in vivo to induce CYP3A and CYP2B6. Other compounds that are substrates of CYP3A or CYP2B6 may have decreased plasma concentrations when coadministered with SUSTIVA. Drugs that induce CYP3A activity (eg, phenobarbital, rifampin, rifabutin) would be expected to increase the clearance of efavirenz resulting in lowered plasma concentrations [ see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Drug interactions with SUSTIVA are summarized in Table 5 [for pharmacokinetics data see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3, Tables 7 and 8)]. This table includes potentially significant interactions, but is not all inclusive.
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| * The interaction between SUSTIVA and the drug was evaluated in a clinical study. All other drug interactions shown are predicted.
This table is not all-inclusive. |
||
|
HIV antiviral agents |
||
|
Protease inhibitor:
|
|
Fosamprenavir (unboosted): Appropriate doses of the combinations with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established.
|
|
Protease inhibitor:
|
|
Treatment-naive patients: When coadministered with SUSTIVA, the recommended dose of atazanavir is 400 mg with ritonavir 100 mg (together once daily with food) and SUSTIVA 600 mg (once daily on an empty stomach, preferably at bedtime).
|
|
Protease inhibitor:
|
|
The optimal dose of indinavir, when given in combination with SUSTIVA, is not known. Increasing the indinavir dose to 1000 mg every 8 hours does not compensate for the increased indinavir metabolism due to SUSTIVA. When indinavir at an increased dose (1000 mg every 8 hours) was given with SUSTIVA (600 mg once daily), the indinavir AUC and C min were decreased on average by 33-46% and 39-57%, respectively, compared to when indinavir (800 mg every 8 hours) was given alone. |
|
Protease inhibitor:
|
|
Dose increase of lopinavir/ritonavir is recommended for all patients. Lopinavir/ritonavir tablets should not be administered once daily in combination with SUSTIVA. See the lopinavir/ritonavir prescribing information for dose adjustments of lopinavir/ritonavir when coadministered with efavirenz in adult and pediatric patients. |
|
Protease inhibitor:
|
|
When ritonavir 500 mg q12h was coadministered with SUSTIVA 600 mg once daily, the combination was associated with a higher frequency of adverse clinical experiences (eg, dizziness, nausea, paresthesia) and laboratory abnormalities (elevated liver enzymes). Monitoring of liver enzymes is recommended when SUSTIVA is used in combination with ritonavir. |
|
Protease inhibitor:
|
|
Appropriate doses of the combination of SUSTIVA and saquinavir/ritonavir with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. |
|
NNRTI:
|
↑ or ↓ efavirenz
|
Combining two NNRTIs has not been shown to be beneficial. SUSTIVA should not be coadministered with other NNRTIs. |
|
CCR5 co-receptor antagonist:
|
|
Refer to the full prescribing information for maraviroc for guidance on coadministration with efavirenz. |
|
Hepatitis C antiviral agents |
||
|
Protease inhibitor:
|
|
Plasma trough concentrations of boceprevir were decreased when boceprevir was coadministered with SUSTIVA, which may result in loss of therapeutic effect. The combination should be avoided. |
|
Protease inhibitor:
|
|
Concomitant administration of simeprevir with SUSTIVA is not recommended because it may result in loss of therapeutic effect of simeprevir. |
|
Other agents |
||
|
Anticoagulant:
|
|
Plasma concentrations and effects potentially increased or decreased by SUSTIVA. |
|
Anticonvulsants:
|
|
|
|
Phenytoin
|
↓ anticonvulsant
|
Potential for reduction in anticonvulsant and/or efavirenz plasma levels; periodic monitoring of anticonvulsant plasma levels should be conducted. |
|
Antidepressants:
|
|
|
|
Sertraline |
↓ sertraline* |
Increases in sertraline dosage should be guided by clinical response. |
|
Antifungals:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ketoconazole |
↓ ketoconazole |
Drug interaction studies with SUSTIVA and ketoconazole have not been conducted. SUSTIVA has the potential to decrease plasma concentrations of ketoconazole. |
|
Posaconazole |
↓ posaconazole* |
Avoid concomitant use unless the benefit outweighs the risks. |
|
Anti-infective:
|
|
Plasma concentrations decreased by SUSTIVA; clinical significance unknown. In uninfected volunteers, 46% developed rash while receiving SUSTIVA and clarithromycin. No dose adjustment of SUSTIVA is recommended when given with clarithromycin. Alternatives to clarithromycin, such as azithromycin, should be considered (see Other Drugs, following table). Other macrolide antibiotics, such as erythromycin, have not been studied in combination with SUSTIVA. |
|
Antimycobacterials:
|
|
Increase daily dose of rifabutin by 50%. Consider doubling the rifabutin dose in regimens where rifabutin is given 2 or 3 times a week. |
|
Rifampin |
↓ efavirenz* |
If SUSTIVA is coadministered with rifampin to patients weighing 50 kg or more, an increase in the dose of SUSTIVA to 800 mg once daily is recommended. |
|
Antimalarials:
|
↓ lumefantrine* |
Artemether/lumefantrine should be used cautiously with efavirenz because decreased artemether, dihydroartemisinin (active metabolite of artemether), and/or lumefantrine concentrations may result in a decrease of antimalarial efficacy of artemether/lumefantrine. |
|
Atovaquone/proguanil |
↑ atovaquone*
|
Concomitant administration is not recommended. |
|
Calcium channel blockers:
|
|
Diltiazem dose adjustments should be guided by clinical response (refer to the full prescribing information for diltiazem). No dose adjustment of efavirenz is necessary when administered with diltiazem. |
|
Others (eg, felodipine, nicardipine, nifedipine, verapamil) |
|
No data are available on the potential interactions of efavirenz with other calcium channel blockers that are substrates of CYP3A. The potential exists for reduction in plasma concentrations of the calcium channel blocker. Dose adjustments should be guided by clinical response (refer to the full prescribing information for the calcium channel blocker). |
|
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors:
|
|
Plasma concentrations of atorvastatin, pravastatin, and simvastatin decreased. Consult the full prescribing information for the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor for guidance on individualizing the dose. |
|
Hormonal contraceptives:
|
|
|
|
Implant
|
|
|
|
Immunosuppressants:
|
|
Decreased exposure of the immunosuppressant may be expected due to CYP3A induction. These immunosuppressants are not anticipated to affect exposure of efavirenz. Dose adjustments of the immunosuppressant may be required. Close monitoring of immunosuppressant concentrations for at least 2 weeks (until stable concentrations are reached) is recommended when starting or stopping treatment with efavirenz. |
|
Narcotic analgesic:
|
|
Coadministration in HIV-infected individuals with a history of injection drug use resulted in decreased plasma levels of methadone and signs of opiate withdrawal. Methadone dose was increased by a mean of 22% to alleviate withdrawal symptoms. Patients should be monitored for signs of withdrawal and their methadone dose increased as required to alleviate withdrawal symptoms. |
Other Drugs
Based on the results of drug interaction studies [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3, Tables 7 and 8)], no dosage adjustment is recommended when SUSTIVA is given with the following: aluminum/magnesium hydroxide antacids, azithromycin, cetirizine, famotidine, fluconazole, lamivudine, lorazepam, nelfinavir, paroxetine, raltegravir, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, and zidovudine.
Specific drug interaction studies have not been performed with SUSTIVA and NRTIs other than lamivudine and zidovudine. Clinically significant interactions would not be expected since the NRTIs are metabolized via a different route than efavirenz and would be unlikely to compete for the same metabolic enzymes and elimination pathways.
7.2 Cannabinoid Test Interaction
Efavirenz does not bind to cannabinoid receptors. False-positive urine cannabinoid test results have been reported with some screening assays in uninfected and HIV-infected subjects receiving efavirenz. Confirmation of positive screening tests for cannabinoids by a more specific method is recommended.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to SUSTIVA during pregnancy. Physicians are encouraged to register patients by calling the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry at 1-800-258-4263.
Risk Summary
There are retrospective case reports of neural tube defects in infants whose mothers were exposed to efavirenz containing regimens in the first trimester of pregnancy. Prospective pregnancy data from the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry are not sufficient to adequately assess this risk. Available data from the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry show no difference in the risk of overall major birth defects compared to the background rate for major birth defects of 2.7% in the U.S. reference population of the Metropolitan Atlanta Congenital Defects Program (MACDP). Although a causal relationship has not been established between exposure to efavirenz in the first trimester and neural tube defects, similar malformations have been observed in studies conducted in monkeys at doses similar to the human dose. In addition, fetal and embryonic toxicities occurred in rats, at a dose ten times less than the human exposure at recommended clinical dose. Because of the potential risk of neural tube defects, efavirenz should not be used in the first trimester of pregnancy. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
Data
Human Data
There are retrospective postmarketing reports of findings consistent with neural tube defects, including meningomyelocele, all in infants of mothers exposed to efavirenz-containing regimens in the first trimester.
Based on prospective reports from the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry (APR) of approximately 1000 live births following exposure to efavirenz containing regimens (including over 800 live births exposed in the first trimester), there was no difference between efavirenz and overall birth defects compared with the background birth defect rate of 2.7% in the U.S. reference population of the Metropolitan Atlanta Congenital Defects Program. As of the interim APR report issued December 2014, the prevalence of birth defects following first-trimester exposure was 2.3% (95% CI: 1.4%-3.6%). One of these prospectively reported defects with first-trimester exposure was a neural tube defect. A single case of anophthalmia with first-trimester exposure to efavirenz has also been prospectively reported. This case also included severe oblique facial clefts and amniotic banding, which have a known association with anophthalmia.
Animal Data
Effects of efavirenz on embryo-fetal development have been studied in three nonclinical species (cynomolgus monkeys, rats, and rabbits). In monkeys, efavirenz 60 mg/kg/day was administered to pregnant females throughout pregnancy (gestation days 20 through 150). The maternal systemic drug exposures (AUC) were 1.3 times the exposure in humans at the recommended clinical dose (600 mg/day), with fetal umbilical venous drug concentrations approximately 0.7 times the maternal values. Three of 20 fetuses/infants had one or more malformations; there were no malformed fetuses or infants from placebo-treated mothers. The malformations that occurred in these three monkey fetuses included anencephaly and unilateral anophthalmia in one fetus, microphthalmia in a second, and cleft palate in the third. There was no NOAEL (no observable adverse effect level) established for this study because only one dosage was evaluated. In rats, efavirenz was administered either during organogenesis (gestation days 7 to 18) or from gestation day 7 through lactation day 21 at 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg/day. Administration of 200 mg/kg/day in rats was associated with increase in the incidence of early resorptions; and doses 100 mg/kg/day and greater were associated with early neonatal mortality. The AUC at the NOAEL (50 mg/kg/day) in this rat study was 0.1 times that in humans at the recommended clinical dose. Drug concentrations in the milk on lactation day 10 were approximately 8 times higher than those in maternal plasma. In pregnant rabbits, efavirenz was neither embryo lethal nor teratogenic when administered at doses of 25, 50, and 75 mg/kg/day over the period of organogenesis (gestation days 6 through 18). The AUC at the NOAEL (75 mg/kg/day) in rabbits was 0.4 times that in humans at the recommended clinical dose.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-infected mothers not breastfeed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV. Because of the potential for HIV transmission in breastfed infants, advise women not to breastfeed.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Because of potential teratogenic effects, pregnancy should be avoided in women receiving SUSTIVA. [ See Use in Specific Populations (8.1). ]
Pregnancy Testing
Females of reproductive potential should undergo pregnancy testing before initiation of SUSTIVA.
Contraception
Females of reproductive potential should use effective contraception during treatment with SUSTIVA and for 12 weeks after discontinuing SUSTIVA due to the long half-life of efavirenz. Barrier contraception should always be used in combination with other methods of contraception. Hormonal methods that contain progesterone may have decreased effectiveness [ see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety, pharmacokinetic profile, and virologic and immunologic responses of SUSTIVA were evaluated in antiretroviral-naive and -experienced HIV-1 infected pediatric patients 3 months to 21 years of age in three open-label clinical trials [ see Adverse Reactions (6.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.2)]. The type and frequency of adverse reactions in these trials were generally similar to those of adult patients with the exception of a higher frequency of rash, including a higher frequency of Grade 3 or 4 rash, in pediatric patients compared to adults [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Use of SUSTIVA in patients younger than 3 months of age OR less than 3.5 kg body weight is not recommended because the safety, pharmacokinetics, and antiviral activity of SUSTIVA have not been evaluated in this age group and there is a risk of developing HIV resistance if SUSTIVA is underdosed. See Dosage and Administration (2.2) for dosing recommendations for pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of SUSTIVA did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other therapy.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
SUSTIVA is not recommended for patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment because there are insufficient data to determine whether dose adjustment is necessary. Patients with mild hepatic impairment may be treated with efavirenz without any adjustment in dose. Because of the extensive cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of efavirenz and limited clinical experience in patients with hepatic impairment, caution should be exercised in administering SUSTIVA to these patients [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Some patients accidentally taking 600 mg twice daily have reported increased nervous system symptoms. One patient experienced involuntary muscle contractions.
Treatment of overdose with SUSTIVA should consist of general supportive measures, including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the patient’s clinical status. Administration of activated charcoal may be used to aid removal of unabsorbed drug. There is no specific antidote for overdose with SUSTIVA. Since efavirenz is highly protein bound, dialysis is unlikely to significantly remove the drug from blood.
11 DESCRIPTION
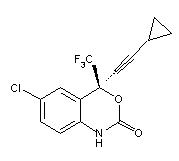
SUSTIVA ® (efavirenz) is an HIV-1 specific, non-nucleoside, reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI). Efavirenz is chemically described as (S)-6-chloro-4-(cyclopropylethynyl)-1,4-dihydro-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one. Its empirical formula is C 14H 9ClF 3NO 2 and its structural formula is:
Efavirenz is a white to slightly pink crystalline powder with a molecular mass of 315.68. It is practically insoluble in water (<10 microgram/mL).
Capsules: SUSTIVA is available as capsules for oral administration containing either 50 mg or 200 mg of efavirenz and the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate, and sodium starch glycolate. The capsule shell contains the following inactive ingredients and dyes: gelatin, sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide, and/or yellow iron oxide. The capsule shells may also contain silicon dioxide. The capsules are printed with ink containing carmine 40 blue, FD&C Blue No. 2, and titanium dioxide.
Tablets: SUSTIVA is available as film-coated tablets for oral administration containing 600 mg of efavirenz and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The film coating contains Opadry Yellow and Opadry Clear. The tablets are polished with carnauba wax and printed with purple ink, Opacode WB.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Peak efavirenz plasma concentrations of 1.6-9.1 μM were attained by 5 hours following single oral doses of 100 mg to 1600 mg administered to uninfected volunteers. Dose-related increases in C max and AUC were seen for doses up to 1600 mg; the increases were less than proportional suggesting diminished absorption at higher doses.
In HIV-1-infected patients at steady state, mean C max, mean C min, and mean AUC were dose proportional following 200 mg, 400 mg, and 600 mg daily doses. Time-to-peak plasma concentrations were approximately 3-5 hours and steady-state plasma concentrations were reached in 6-10 days. In 35 patients receiving SUSTIVA 600 mg once daily, steady-state C max was 12.9 ± 3.7 μM (mean ± SD), steady-state C min was 5.6 ± 3.2 μM, and AUC was 184 ± 73 μM•h.
Effect of Food on Oral Absorption:
Capsules: Administration of a single 600 mg dose of efavirenz capsules with a high-fat/high-caloric meal (894 kcal, 54 g fat, 54% calories from fat) or a reduced-fat/normal-caloric meal (440 kcal, 2 g fat, 4% calories from fat) was associated with a mean increase of 22% and 17% in efavirenz AUC ∞ and a mean increase of 39% and 51% in efavirenz C max, respectively, relative to the exposures achieved when given under fasted conditions. [ See Dosage and Administration (2) and Patient Counseling Information (17).]
Tablets: Administration of a single 600 mg efavirenz tablet with a high-fat/high-caloric meal (approximately 1000 kcal, 500-600 kcal from fat) was associated with a 28% increase in mean AUC ∞ of efavirenz and a 79% increase in mean C max of efavirenz relative to the exposures achieved under fasted conditions. [ See Dosage and Administration (2) and Patient Counseling Information (17).]
Bioavailability of capsule contents mixed with food vehicles: In healthy adult subjects, the efavirenz AUC when administered as the contents of three 200 mg capsules mixed with 2 teaspoons of certain food vehicles (applesauce, grape jelly or yogurt, or infant formula) met bioequivalency criteria for the AUC of the intact capsule formulation administered under fasted conditions.
Distribution
Efavirenz is highly bound (approximately 99.5-99.75%) to human plasma proteins, predominantly albumin. In HIV-1 infected patients (n=9) who received SUSTIVA 200 to 600 mg once daily for at least one month, cerebrospinal fluid concentrations ranged from 0.26 to 1.19% (mean 0.69%) of the corresponding plasma concentration. This proportion is approximately 3-fold higher than the non-protein-bound (free) fraction of efavirenz in plasma.
Metabolism
Studies in humans and in vitro studies using human liver microsomes have demonstrated that efavirenz is principally metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system to hydroxylated metabolites with subsequent glucuronidation of these hydroxylated metabolites. These metabolites are essentially inactive against HIV-1. The in vitro studies suggest that CYP3A and CYP2B6 are the major isozymes responsible for efavirenz metabolism.
Efavirenz has been shown to induce CYP enzymes, resulting in the induction of its own metabolism. Multiple doses of 200-400 mg per day for 10 days resulted in a lower than predicted extent of accumulation (22-42% lower) and a shorter terminal half-life of 40-55 hours (single dose half-life 52-76 hours).
Elimination
Efavirenz has a terminal half-life of 52-76 hours after single doses and 40-55 hours after multiple doses. A one-month mass balance/excretion study was conducted using 400 mg per day with a 14C-labeled dose administered on Day 8. Approximately 14-34% of the radiolabel was recovered in the urine and 16-61% was recovered in the feces. Nearly all of the urinary excretion of the radiolabeled drug was in the form of metabolites. Efavirenz accounted for the majority of the total radioactivity measured in feces.
Special Populations
Pediatric: The pharmacokinetic parameters for efavirenz at steady state in pediatric patients were predicted by a population pharmacokinetic model and are summarized in Table 6 by weight ranges that correspond to the recommended doses.
| Body Weight | Dose | Mean AUC
(0-24)
µM•h | Mean C
max
µg/mL | Mean C
min
µg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
3.5-5 kg |
100 mg |
220.52 |
5.81 |
2.43 |
|
5-7.5 kg |
150 mg |
262.62 |
7.07 |
2.71 |
|
7.5-10 kg |
200 mg |
284.28 |
7.75 |
2.87 |
|
10-15 kg |
200 mg |
238.14 |
6.54 |
2.32 |
|
15-20 kg |
250 mg |
233.98 |
6.47 |
2.3 |
|
20-25 kg |
300 mg |
257.56 |
7.04 |
2.55 |
|
25-32.5 kg |
350 mg |
262.37 |
7.12 |
2.68 |
|
32.5-40 kg |
400 mg |
259.79 |
6.96 |
2.69 |
|
>40 kg |
600 mg |
254.78 |
6.57 |
2.82 |
Gender and race: The pharmacokinetics of efavirenz in patients appear to be similar between men and women and among the racial groups studied.
Renal impairment: The pharmacokinetics of efavirenz have not been studied in patients with renal insufficiency; however, less than 1% of efavirenz is excreted unchanged in the urine, so the impact of renal impairment on efavirenz elimination should be minimal.
Hepatic impairment: A multiple-dose study showed no significant effect on efavirenz pharmacokinetics in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) compared with controls. There were insufficient data to determine whether moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B or C) affects efavirenz pharmacokinetics.
Drug Interaction Studies
Efavirenz has been shown in vivo to cause hepatic enzyme induction, thus increasing the biotransformation of some drugs metabolized by CYP3A and CYP2B6. In vitro studies have shown that efavirenz inhibited CYP isozymes 2C9 and 2C19 with K i values (8.5-17 μM) in the range of observed efavirenz plasma concentrations. In in vitro studies, efavirenz did not inhibit CYP2E1 and inhibited CYP2D6 and CYP1A2 (K i values 82-160 μM) only at concentrations well above those achieved clinically. Coadministration of efavirenz with drugs primarily metabolized by CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A, or CYP2B6 isozymes may result in altered plasma concentrations of the coadministered drug. Drugs which induce CYP3A and CYP2B6 activity would be expected to increase the clearance of efavirenz resulting in lowered plasma concentrations.
Drug interaction studies were performed with efavirenz and other drugs likely to be coadministered or drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interaction. The effects of coadministration of efavirenz on the C max, AUC, and C min are summarized in Table 7 (effect of efavirenz on other drugs) and Table 8 (effect of other drugs on efavirenz). For information regarding clinical recommendations see Drug Interactions (7.1).
| ↑ Indicates increase ↓ Indicates decrease ↔ Indicates no change or a mean increase or decrease of <10%.
a Compared with atazanavir 400 mg qd alone. b Comparator dose of indinavir was 800 mg q8h × 10 days. c Parallel-group design; n for efavirenz + lopinavir/ritonavir, n for lopinavir/ritonavir alone. d Values are for lopinavir; the pharmacokinetics of ritonavir in this study were unaffected by concurrent efavirenz. e 95% CI. f Soft Gelatin Capsule. g Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. h 90% CI not available. i Relative to steady-state administration of voriconazole (400 mg for 1 day, then 200 mg po q12h for 2 days). j Not available because of insufficient data. NA = not available. |
||||||
|
Coadministered Drug
|
||||||
|
Coadministered Drug |
Dose |
Efavirenz Dose |
Number of Subjects |
C
max
|
AUC
|
C
min
|
|
Atazanavir |
400 mg qd with a light meal d 1-20 |
600 mg qd with a light meal d 7-20 |
27 |
↓ 59%
|
↓ 74%
|
↓ 93%
|
|
|
400 mg qd d 1-6, then 300 mg qd d 7-20 with ritonavir 100 mg qd and a light meal |
600 mg qd 2 h after atazanavir and ritonavir d 7-20 |
13 |
↑ 14%
a
|
↑ 39%
a
|
↑ 48%
a
|
|
|
300 mg qd/ritonavir 100 mg qd d 1-10 (pm), then 400 mg qd/ritonavir 100 mg qd d 11-24 (pm) (simultaneous with efavirenz) |
600 mg qd with a light snack d 11-24 (pm) |
14 |
↑ 17%
|
↔ |
↓ 42%
|
|
Indinavir |
1000 mg q8h × 10 days |
600 mg qd × 10 days |
20 |
|
||
|
|
After morning dose |
↔ b |
↓ 33%
b
|
↓ 39%
b
|
||
|
|
After afternoon dose |
↔ b |
↓ 37%
b
|
↓ 52%
b
|
||
|
|
After evening dose |
↓ 29%
b
|
↓ 46%
b
|
↓ 57%
b
|
||
|
Lopinavir/
|
400/100 mg capsule
|
600 mg qd × 9 days |
11,7 c |
↔ d |
↓ 19%
d
|
↓ 39%
d
|
|
|
500/125 mg tablet q12h × 10 days with efavirenz compared to 400/100 mg q12h alone |
600 mg qd × 9 days |
19 |
↑ 12%
d
|
↔ d |
↓ 10%
d
|
|
|
600/150 mg tablet q12h × 10 days with efavirenz compared to 400/100 mg q12h alone |
600 mg qd × 9 days |
23 |
↑ 36%
d
|
↑ 36%
d
|
↑ 32%
d
|
|
Nelfinavir |
750 mg q8h × 7 days |
600 mg qd × 7 days |
10 |
↑ 21%
|
↑ 20%
|
↔ |
|
Metabolite
|
|
↓ 40%
|
↓ 37%
|
↓ 43%
|
||
|
Ritonavir |
500 mg q12h × 8 days |
600 mg qd × 10 days |
11 |
|
||
|
|
After AM dose |
↑ 24%
|
↑ 18%
|
↑ 42%
|
||
|
|
After PM dose |
↔ |
↔ |
↑ 24%
|
||
|
Saquinavir
|
1200 mg q8h × 10 days |
600 mg qd × 10 days |
12 |
↓ 50%
|
↓ 62%
|
↓ 56%
|
|
Lamivudine |
150 mg q12h × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
9 |
↔ |
↔ |
↑ 265%
|
|
Tenofovir g |
300 mg qd |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
29 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|
Zidovudine |
300 mg q12h × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
9 |
↔ |
↔ |
↑ 225%
|
|
Maraviroc |
100 mg bid |
600 mg qd |
12 |
↓ 51%
|
↓ 45%
|
↓ 45%
|
|
Raltegravir |
400 mg single dose |
600 mg qd |
9 |
↓ 36%
|
↓ 36%
|
↓ 21%
|
|
Boceprevir |
800 mg tid × 6 days |
600 mg qd × 16 days |
NA |
↓ 8%
|
↓ 19%
|
↓ 44%
|
|
Simeprevir |
150 mg qd × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
23 |
↓ 51%
|
↓ 71%
|
↓ 91%
|
|
Azithromycin |
600 mg single dose |
400 mg qd × 7 days |
14 |
↑ 22%
|
↔ |
NA |
|
Clarithromycin |
500 mg q12h × 7 days |
400 mg qd × 7 days |
11 |
↓ 26%
|
↓ 39%
|
↓ 53%
|
|
14-OH metabolite |
|
↑ 49%
|
↑ 34%
|
↑ 26%
|
||
|
Fluconazole |
200 mg × 7 days |
400 mg qd × 7 days |
10 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|
Itraconazole |
200 mg q12h × 28 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
18 |
↓ 37%
|
↓ 39%
|
↓ 44%
|
|
Hydroxy-itraconazole |
|
↓ 35%
|
↓ 37%
|
↓ 43%
|
||
|
Posaconazole |
400 mg (oral suspension) bid × 10 and 20 days |
400 mg qd × 10 and 20 days |
11 |
↓ 45%
|
↓ 50%
|
NA |
|
Rifabutin |
300 mg qd × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
9 |
↓ 32%
|
↓ 38%
|
↓ 45%
|
|
Voriconazole |
400 mg po q12h × 1 day, then 200 mg po q12h × 8 days |
400 mg qd × 9 days |
NA |
↓ 61% h |
↓ 77% h |
NA |
|
|
300 mg po q12h days 2-7 |
300 mg qd × 7 days |
NA |
↓ 36%
i
|
↓ 55%
i
|
NA |
|
|
400 mg po q12h days 2-7 |
300 mg qd × 7 days |
NA |
↑ 23%
i
|
↓ 7%
i
|
NA |
|
Artemether/lumefantrine |
Artemether 20 mg/lumefantrine 120 mg tablets (6 4-tablet doses over 3 days) |
600 mg qd × 26 days |
12 | |||
|
Artemether |
↓ 21% |
↓ 51% |
NA |
|||
|
dihydroartemisinin |
↓ 38% |
↓ 46% |
NA |
|||
|
lumefantrine |
↔ |
↓ 21% |
NA |
|||
|
Atorvastatin |
10 mg qd × 4 days |
600 mg qd × 15 days |
14 |
↓ 14%
|
↓ 43%
|
↓ 69%
|
|
Total active
|
|
↓ 15%
|
↓ 32%
|
↓ 48%
|
||
|
Pravastatin |
40 mg qd × 4 days |
600 mg qd × 15 days |
13 |
↓ 32%
|
↓ 44%
|
↓ 19%
|
|
Simvastatin |
40 mg qd × 4 days |
600 mg qd × 15 days |
14 |
↓ 72%
|
↓ 68%
|
↓ 45%
|
|
Total active
|
|
↓ 68%
|
↓ 60%
|
NA j |
||
|
Carbamazepine |
200 mg qd × 3 days, 200 mg bid × 3 days, then 400 mg qd × 29 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
12 |
↓ 20%
|
↓ 27%
|
↓ 35%
|
|
Epoxide metabolite |
|
↔ |
↔ |
↓ 13%
|
||
|
Cetirizine |
10 mg single dose |
600 mg qd × 10 days |
11 |
↓ 24%
|
↔ |
NA |
|
Diltiazem |
240 mg × 21 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
13 |
↓ 60%
|
↓ 69%
|
↓ 63%
|
|
Desacetyl
|
|
↓ 64%
|
↓ 75%
|
↓ 62%
|
||
|
N-
|
|
↓ 28%
|
↓ 37%
|
↓ 37%
|
||
|
Ethinyl estradiol/
|
0.035 mg/
|
600 mg qd × 14 days | ||||
|
Ethinyl
|
|
21 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|
|
Norelgestromin |
|
21 |
↓ 46%
|
↓ 64%
|
↓ 82%
|
|
|
Levonorgestrel |
|
6 |
↓ 80%
|
↓ 83%
|
↓ 86%
|
|
|
Lorazepam |
2 mg single dose |
600 mg qd × 10 days |
12 |
↑ 16%
|
↔ |
NA |
|
Methadone |
Stable
|
600 mg qd × 14-21 days |
11 |
↓ 45%
|
↓ 52%
|
NA |
|
Bupropion |
150 mg single dose
|
600 mg qd × 14 days |
13 |
↓ 34%
|
↓ 55%
|
NA |
|
Hydroxy-
|
|
↑ 50%
|
↔ |
NA |
||
|
Paroxetine |
20 mg qd × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
16 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|
Sertraline |
50 mg qd × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
13 |
↓ 29%
|
↓ 39%
|
↓ 46%
|
| Efavirenz
(mean % change) |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coadministered Drug | Dose | Efavirenz Dose | Number of Subjects | C
max
(90% CI) | AUC
(90% CI) | C
min
(90% CI) |
|||||||
| ↑ Indicates increase ↓ Indicates decrease ↔ Indicates no change or a mean increase or decrease of <10%.
a Parallel-group design; n for efavirenz + lopinavir/ritonavir, n for efavirenz alone. b 95% CI. c Soft Gelatin Capsule. d Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. e 90% CI not available. f Relative to steady-state administration of efavirenz (600 mg once daily for 9 days). NA = not available. |
|||||||||||||
|
Indinavir |
800 mg q8h × 14 days |
200 mg qd × 14 days |
11 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||||||
|
Lopinavir/ritonavir |
400/100 mg q12h × 9 days |
600 mg qd × 9 days |
11,12 a |
↔ |
↓ 16%
|
↓ 16%
|
|||||||
|
Nelfinavir |
750 mg q8h × 7 days |
600 mg qd × 7 days |
10 |
↓ 12%
|
↓ 12%
|
↓ 21%
|
|||||||
|
Ritonavir |
500 mg q12h × 8 days |
600 mg qd × 10 days |
9 |
↑ 14%
|
↑ 21%
|
↑ 25%
|
|||||||
|
Saquinavir
|
1200 mg q8h × 10 days |
600 mg qd × 10 days |
13 |
↓ 13%
|
↓ 12%
|
↓ 14%
|
|||||||
|
Tenofovir d |
300 mg qd |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
30 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||||||
|
Boceprevir |
800 mg tid × 6 days |
600 mg qd × 16 days |
NA |
↑ 11%
|
↑ 20%
|
NA |
|||||||
|
Simeprevir |
150 mg qd × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
23 |
↔ |
↓ 10%
|
↓ 13%
|
|||||||
|
Azithromycin |
600 mg single dose |
400 mg qd × 7 days |
14 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||||||
|
Clarithromycin |
500 mg q12h × 7 days |
400 mg qd × 7 days |
12 |
↑ 11%
|
↔ |
↔ |
|||||||
|
Fluconazole |
200 mg ×
|
400 mg qd × 7 days |
10 |
↔ |
↑ 16%
|
↑ 22%
|
|||||||
|
Itraconazole |
200 mg q12h × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 28 days |
16 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||||||
|
Rifabutin |
300 mg qd × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
11 |
↔ |
↔ |
↓ 12%
|
|||||||
|
Rifampin |
600 mg ×
|
600 mg qd × 7 days |
12 |
↓ 20%
|
↓ 26%
|
↓ 32%
|
|||||||
|
Voriconazole |
400 mg po q12h
|
400 mg qd × 9 days |
NA |
↑ 38% e |
↑ 44% e |
NA |
|||||||
|
|
300 mg po q12h days 2-7 |
300 mg qd × 7 days |
NA |
↓ 14%
f
|
↔ f |
NA |
|||||||
|
|
400 mg po q12h days 2-7 |
300 mg qd × 7 days |
NA |
↔ f |
↑ 17%
f
|
NA |
|||||||
|
Artemether/Lumefantrine |
Artemether 20 mg/lumefantrine 120 mg tablets (6 4-tablet doses over 3 days) |
600 mg qd × 26 days |
12 |
↔ |
↓ 17% |
NA |
|||||||
|
Atorvastatin |
10 mg qd ×
|
600 mg qd × 15 days |
14 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||||||
|
Pravastatin |
40 mg qd ×
|
600 mg qd × 15 days |
11 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||||||
|
Simvastatin |
40 mg qd ×
|
600 mg qd × 15 days |
14 |
↓ 12%
|
↔ |
↓ 12%
|
|||||||
|
Aluminum hydroxide 400 mg, magnesium hydroxide 400 mg, plus simethicone 40 mg |
30 mL single dose |
400 mg single dose |
17 |
↔ |
↔ |
NA |
|||||||
|
Carbamazepine |
200 mg qd × 3 days, 200 mg
|
|
14 |
↓ 21%
|
↓ 36%
|
↓ 47%
|
|||||||
|
Cetirizine |
10 mg single dose |
600 mg qd × 10 days |
11 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||||||
|
Diltiazem |
240 mg ×
|
600 mg qd × 28 days |
12 |
↑ 16%
|
↑ 11%
|
↑ 13%
|
|||||||
|
Famotidine |
40 mg single dose |
400 mg single dose |
17 |
↔ |
↔ |
NA |
|||||||
|
Paroxetine |
20 mg qd × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
12 |
↔ |
↔ |
↔ |
|||||||
|
Sertraline |
50 mg qd × 14 days |
600 mg qd × 14 days |
13 |
↑ 11%
|
↔ |
↔ |
|||||||
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Efavirenz is an NNRTI of HIV-1. Efavirenz activity is mediated predominantly by noncompetitive inhibition of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. HIV-2 reverse transcriptase and human cellular DNA polymerases α, β, γ, and δ are not inhibited by efavirenz.
Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture
The concentration of efavirenz inhibiting replication of wild-type laboratory adapted strains and clinical isolates in cell culture by 90-95% (EC 90-95) ranged from 1.7 to 25 nM in lymphoblastoid cell lines, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), and macrophage/monocyte cultures. Efavirenz demonstrated antiviral activity against clade B and most non-clade B isolates (subtypes A, AE, AG, C, D, F, G, J, N), but had reduced antiviral activity against group O viruses. Efavirenz demonstrated additive antiviral activity without cytotoxicity against HIV-1 in cell culture when combined with the NNRTIs delavirdine and nevirapine, NRTIs (abacavir, didanosine, emtricitabine, lamivudine, stavudine, tenofovir, zalcitabine, zidovudine), PIs (amprenavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir), and the fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide. Efavirenz demonstrated additive to antagonistic antiviral activity in cell culture with atazanavir. Efavirenz was not antagonistic with adefovir, used for the treatment of hepatitis B virus infection, or ribavirin, used in combination with interferon for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection.
Resistance
In cell culture
In cell culture, HIV-1 isolates with reduced susceptibility to efavirenz (>380-fold increase in EC 90 value) emerged rapidly in the presence of drug. Genotypic characterization of these viruses identified single amino acid substitutions L100I or V179D, double substitutions L100I/V108I, and triple substitutions L100I/V179D/Y181C in reverse transcriptase.
Clinical studies
Clinical isolates with reduced susceptibility in cell culture to efavirenz have been obtained. One or more substitutions at amino acid positions 98, 100, 101, 103, 106, 108, 188, 190, 225, and 227 in reverse transcriptase were observed in patients failing treatment with efavirenz in combination with indinavir, or with zidovudine plus lamivudine. The K103N substitution was the most frequently observed. Long-term resistance surveillance (average 52 weeks, range 4-106 weeks) analyzed 28 matching baseline and virologic failure isolates. Sixty-one percent (17/28) of these failure isolates had decreased efavirenz susceptibility in cell culture with a median 88-fold change in efavirenz susceptibility (EC 50 value) from reference. The most frequent NNRTI substitution to develop in these patient isolates was K103N (54%). Other NNRTI substitutions that developed included L100I (7%), K101E/Q/R (14%), V108I (11%), G190S/T/A (7%), P225H (18%), and M230I/L (11%).
Cross-Resistance
Cross-resistance among NNRTIs has been observed. Clinical isolates previously characterized as efavirenz-resistant were also phenotypically resistant in cell culture to delavirdine and nevirapine compared to baseline. Delavirdine- and/or nevirapine-resistant clinical viral isolates with NNRTI resistance-associated substitutions (A98G, L100I, K101E/P, K103N/S, V106A, Y181X, Y188X, G190X, P225H, F227L, or M230L) showed reduced susceptibility to efavirenz in cell culture. Greater than 90% of NRTI-resistant clinical isolates tested in cell culture retained susceptibility to efavirenz.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats were carried out with efavirenz. Mice were dosed with 0, 25, 75, 150, or 300 mg/kg/day for 2 years. Incidences of hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas and pulmonary alveolar/bronchiolar adenomas were increased above background in females. No increases in tumor incidence above background were seen in males. There was no NOAEL in females established for this study because tumor findings occurred at all doses. AUC at the NOAEL (150 mg/kg) in the males was approximately 0.9 times that in humans at the recommended clinical dose. In the rat study, no increases in tumor incidence were observed at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day, for which AUCs were 0.1 (males) or 0.2 (females) times those in humans at the recommended clinical dose.
Mutagenesis
Efavirenz tested negative in a battery of in vitro and in vivo genotoxicity assays. These included bacterial mutation assays in S. typhimurium and E. coli, mammalian mutation assays in Chinese hamster ovary cells, chromosome aberration assays in human peripheral blood lymphocytes or Chinese hamster ovary cells, and an in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
Efavirenz did not impair mating or fertility of male or female rats, and did not affect sperm of treated male rats. The reproductive performance of offspring born to female rats given efavirenz was not affected. The AUCs at the NOAEL values in male (200 mg/kg) and female (100 mg/kg) rats were approximately ≤0.15 times that in humans at the recommended clinical dose.
13.2 Animal Toxicology
Nonsustained convulsions were observed in 6 of 20 monkeys receiving efavirenz at doses yielding plasma AUC values 4- to 13-fold greater than those in humans given the recommended dose [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adults
Study 006, a randomized, open-label trial, compared SUSTIVA (600 mg once daily) + zidovudine (ZDV, 300 mg q12h) + lamivudine (LAM, 150 mg q12h) or SUSTIVA (600 mg once daily) + indinavir (IDV, 1000 mg q8h) with indinavir (800 mg q8h) + zidovudine (300 mg q12h) + lamivudine (150 mg q12h). Twelve hundred sixty-six patients (mean age 36.5 years [range 18-81], 60% Caucasian, 83% male) were enrolled. All patients were efavirenz-, lamivudine-, NNRTI-, and PI-naive at study entry. The median baseline CD4+ cell count was 320 cells/mm 3 and the median baseline HIV-1 RNA level was 4.8 log 10 copies/mL. Treatment outcomes with standard assay (assay limit 400 copies/mL) through 48 and 168 weeks are shown in Table 9. Plasma HIV RNA levels were quantified with standard (assay limit 400 copies/mL) and ultrasensitive (assay limit 50 copies/mL) versions of the AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR assay. During the study, version 1.5 of the assay was introduced in Europe to enhance detection of non-clade B virus.
| SUSTIVA + ZDV
+ LAM (n=422) | SUSTIVA + IDV
(n=429) | IDV + ZDV + LAM
(n=415) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Week 48 | Week 168 | Week 48 | Week 168 | Week 48 | Week 168 |
| a Patients achieved and maintained confirmed HIV-1 RNA <400 copies/mL through Week 48 or Week 168.
b Includes patients who rebounded, patients who were on study at Week 48 and failed to achieve confirmed HIV-1 RNA <400 copies/mL at time of discontinuation, and patients who discontinued due to lack of efficacy. c Includes consent withdrawn, lost to follow-up, noncompliance, never treated, missing data, protocol violation, death, and other reasons. Patients with HIV-1 RNA levels <400 copies/mL who chose not to continue in the voluntary extension phases of the study were censored at date of last dose of study medication. |
||||||
|
Responder a |
69% |
48% |
57% |
40% |
50% |
29% |
|
Virologic failure b |
6% |
12% |
15% |
20% |
13% |
19% |
|
Discontinued for adverse events |
7% |
8% |
6% |
8% |
16% |
20% |
|
Discontinued for other reasons c |
17% |
31% |
22% |
32% |
21% |
32% |
|
CD4+ cell count (cells/mm 3) |
||||||
|
Observed subjects (n) |
(279) |
(205) |
(256) |
(158) |
(228) |
(129) |
|
Mean change from baseline |
190 |
329 |
191 |
319 |
180 |
329 |
For patients treated with SUSTIVA + zidovudine + lamivudine, SUSTIVA + indinavir, or indinavir + zidovudine + lamivudine, the percentage of responders with HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL was 65%, 50%, and 45%, respectively, through 48 weeks, and 43%, 31%, and 23%, respectively, through 168 weeks. A Kaplan-Meier analysis of time to loss of virologic response (HIV RNA <400 copies/mL) suggests that both the trends of virologic response and differences in response continue through 4 years.
ACTG 364 is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 48-week study in NRTI-experienced patients who had completed two prior ACTG studies. One-hundred ninety-six patients (mean age 41 years [range 18-76], 74% Caucasian, 88% male) received NRTIs in combination with SUSTIVA (600 mg once daily), or nelfinavir (NFV, 750 mg three times daily), or SUSTIVA (600 mg once daily) + nelfinavir in a randomized, double-blinded manner. The mean baseline CD4+ cell count was 389 cells/mm 3 and mean baseline HIV-1 RNA level was 8130 copies/mL. Upon entry into the study, all patients were assigned a new open-label NRTI regimen, which was dependent on their previous NRTI treatment experience. There was no significant difference in the mean CD4+ cell count among treatment groups; the overall mean increase was approximately 100 cells at 48 weeks among patients who continued on study regimens. Treatment outcomes are shown in Table 10. Plasma HIV RNA levels were quantified with the AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR assay using a lower limit of quantification of 500 copies/mL.
| Outcome | SUSTIVA + NFV
+ NRTIs (n=65) | SUSTIVA + NRTIs
(n=65) | NFV + NRTIs
(n=66) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| * For some patients, Week 56 data were used to confirm the status at Week 48.
a Subjects achieved virologic response (two consecutive viral loads <500 copies/mL) and maintained it through Week 48. b Includes viral rebound and failure to achieve confirmed <500 copies/mL by Week 48. c See Adverse Reactions (6.1) for a safety profile of these regimens. d Includes loss to follow-up, consent withdrawn, noncompliance. |
||||||||||
|
HIV-1 RNA <500 copies/mL a |
71% |
63% |
41% |
|||||||
|
HIV-1 RNA ≥500 copies/mL b |
17% |
34% |
54% |
|||||||
|
CDC Category C Event |
2% |
0% |
0% |
|||||||
|
Discontinuations for adverse events c |
3% |
3% |
5% |
|||||||
|
Discontinuations for other reasons d |
8% |
0% |
0% |
|||||||
A Kaplan-Meier analysis of time to treatment failure through 72 weeks demonstrates a longer duration of virologic suppression (HIV RNA <500 copies/mL) in the SUSTIVA-containing treatment arms.
14.2 Pediatric Patients
Study AI266922 is an open-label study to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, safety, tolerability, and antiviral activity of SUSTIVA in combination with didanosine and emtricitabine in antiretroviral-naive and -experienced pediatric patients. Thirty-seven patients 3 months to 6 years of age (median 0.7 years) were treated with SUSTIVA. At baseline, median plasma HIV-1 RNA was 5.88 log 10 copies/mL, median CD4+ cell count was 1144 cells/mm 3, and median CD4+ percentage was 25%. The median time on study therapy was 60 weeks; 27% of patients discontinued before Week 48. Using an ITT analysis, the overall proportions of patients with HIV RNA <400 copies/mL and <50 copies/mL at Week 48 were 57% (21/37) and 46% (17/37), respectively. The median increase from baseline in CD4+ count at 48 weeks was 196 cells/mm 3 and the median increase in CD4+ percentage was 6%.
Study PACTG 1021 was an open-label study to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, safety, tolerability, and antiviral activity of SUSTIVA in combination with didanosine and emtricitabine in pediatric patients who were antiretroviral therapy naive. Forty-three patients 3 months to 21 years of age (median 9.6 years) were dosed with SUSTIVA. At baseline, median plasma HIV-1 RNA was 4.8 log 10 copies/mL, median CD4+ cell count was 367 cells/mm 3, and median CD4+ percentage was 18%. The median time on study therapy was 181 weeks; 16% of patients discontinued before Week 48. Using an ITT analysis, the overall proportions of patients with HIV RNA <400 copies/mL and <50 copies/mL at Week 48 were 77% (33/43) and 70% (30/43), respectively. The median increase from baseline in CD4+ count at 48 weeks of therapy was 238 cells/mm 3 and the median increase in CD4+ percentage was 13%.
Study PACTG 382 was an open-label study to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, safety, tolerability, and antiviral activity of SUSTIVA in combination with nelfinavir and an NRTI in antiretroviral-naive and NRTI-experienced pediatric patients. One hundred two patients 3 months to 16 years of age (median 5.7 years) were treated with SUSTIVA. Eighty-seven percent of patients had received prior antiretroviral therapy. At baseline, median plasma HIV-1 RNA was 4.57 log 10 copies/mL, median CD4+ cell count was 755 cells/mm 3, and median CD4+ percentage was 30%. The median time on study therapy was 118 weeks; 25% of patients discontinued before Week 48. Using an ITT analysis, the overall proportion of patients with HIV RNA <400 copies/mL and <50 copies/mL at Week 48 were 57% (58/102) and 43% (44/102), respectively. The median increase from baseline in CD4+ count at 48 weeks of therapy was 128 cells/mm 3 and the median increase in CD4+ percentage was 5%.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 Capsules
SUSTIVA ® (efavirenz) capsules are available as follows:
Capsules 200 mg are gold color, reverse printed with “SUSTIVA” on the body and imprinted “200 mg” on the cap.
Bottles of 90 NDC 0056-0474-92
Capsules 50 mg are gold color and white, printed with “SUSTIVA” on the gold color cap and reverse printed “50 mg” on the white body.
Bottles of 30 NDC 0056-0470-30
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Drug Interactions
A statement to patients and healthcare providers is included on the product’s bottle labels: ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with SUSTIVA.
SUSTIVA may interact with some drugs; therefore, patients should be advised to report to their doctor the use of any other prescription or nonprescription medication.
General Information for Patients
Patients should be informed that SUSTIVA is not a cure for HIV‑1 infection and patients may continue to experience illnesses associated with HIV‑1 infection, including opportunistic infections. Patients should remain under the care of a physician while taking SUSTIVA.
Patients should be advised to avoid doing things that can spread HIV-1 infection to others.
- Do not share or reuse needles or other injection equipment.
- Do not share personal items that can have blood or body fluids on them, like toothbrushes and razor blades.
- Do not have any kind of sex without protection. Always practice safer sex by using a latex or polyurethane condom to lower the chance of sexual contact with semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
- Do not breastfeed. Mothers with HIV-1 should not breastfeed because HIV-1 can be passed to the baby in breast milk.
Dosing Instructions
Patients should be advised to take SUSTIVA every day as prescribed. If a patient forgets to take SUSTIVA, tell the patient to take the missed dose right away, unless it is almost time for the next dose. Advise the patient not to take 2 doses at one time and to take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time. Advise the patient to ask a healthcare provider if he/she needs help in planning the best times to take his/her medicine.
SUSTIVA must always be used in combination with other antiretroviral drugs. Patients should be advised to take SUSTIVA on an empty stomach, preferably at bedtime. Taking SUSTIVA with food increases efavirenz concentrations and may increase the frequency of adverse reactions. Dosing at bedtime may improve the tolerability of nervous system symptoms [ seeDosage and Administration (2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Healthcare providers should assist parents or caregivers in determining the best SUSTIVA dosing schedule for infants and young children.
For adult and pediatric patients who cannot swallow capsules or tablets, patients or their caregivers should be advised to read and carefully follow the instructions for administering the capsule contents in a small amount of food or infant formula [ seeDosage and Administration (2.3) and FDA-approved patient labeling ( Patient Information and Instructions for Use)]. Patients should call their healthcare provider or pharmacist if they have any questions.
Nervous System Symptoms
Patients should be informed that central nervous system symptoms (NSS) including dizziness, insomnia, impaired concentration, drowsiness, and abnormal dreams are commonly reported during the first weeks of therapy with SUSTIVA [ seeWarnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Dosing at bedtime may improve the tolerability of these symptoms, which are likely to improve with continued therapy. Patients should be alerted to the potential for additive effects when SUSTIVA is used concomitantly with alcohol or psychoactive drugs. Patients should be instructed that if they experience NSS they should avoid potentially hazardous tasks such as driving or operating machinery.
Psychiatric Symptoms
Patients should be informed that serious psychiatric symptoms including severe depression, suicide attempts, aggressive behavior, delusions, paranoia, and psychosis-like symptoms have been reported in patients receiving SUSTIVA [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. If they experience severe psychiatric adverse experiences they should seek immediate medical evaluation. Patients should be advised to inform their physician of any history of mental illness or substance abuse.
Rash
Patients should be informed that a common side effect is rash [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. Rashes usually go away without any change in treatment. However, since rash may be serious, patients should be advised to contact their physician promptly if rash occurs.
Females of Reproductive Potential
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception as well as a barrier method during treatment with SUSTIVA and for 12 weeks after discontinuing SUSTIVA. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they plan to become pregnant, become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected during treatment with SUSTIVA [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)and Use in Specific Populations (8.1,8.3)].
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to SUSTIVA during pregnancy [ see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Fat Redistribution
Patients should be informed that redistribution or accumulation of body fat may occur in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy and that the cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
SUSTIVA is a registered trademark of Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma Company. ATRIPLA is a trademark of Bristol-Myers Squibb & Gilead Sciences, LLC.
Distributed by:
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
Princeton, NJ 08543 USA
SUSTIVA ® (efavirenz) capsules made in India.
© Bristol-Myers Squibb Company 2015
Patient Information
SUSTIVA® (sus-TEE-vah)
(efavirenz)
capsules
SUSTIVA® (sus-TEE-vah)
(efavirenz)
tablets
Important: Ask your doctor or pharmacist about medicines that should not be taken with SUSTIVA. For more information, see the section “ What should I tell my doctor before taking SUSTIVA?”
Read this Patient Information before you start taking SUSTIVA and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or treatment.
What is SUSTIVA?
SUSTIVA is a prescription HIV-1 (Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1) medicine used with other antiretroviral medicines to treat HIV-1 infection in adults and in children who are at least 3 months old and who weigh at least 7 pounds 12 ounces (3.5 kg). HIV is the virus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome).
It is not known if SUSTIVA is safe and effective in children younger than 3 months of age or who weigh less than 7 pounds 12 ounces (3.5 kg).
When used with other antiretroviral medicines to treat HIV-1 infection, SUSTIVA may help:
- reduce the amount of HIV-1 in your blood. This is called viral load.
- increase the number of CD4+ (T) cells in your blood that help fight off other infections.
Reducing the amount of HIV-1 and increasing the CD4+ (T) cells in your blood may help improve your immune system. This may reduce your risk of death or getting infections that can happen when your immune system is weak (opportunistic infections).
SUSTIVA does not cure HIV-1 infection or AIDS. You should keep taking HIV-1 medicines to control HIV-1 infection and decrease HIV-related illnesses.
Avoid doing things that can spread HIV-1 infection to others:
- Do not share or reuse needles or other injection equipment.
- Do not share personal items that can have blood or body fluids on them, like toothbrushes and razor blades.
- Do not have any kind of sex without protection. Always practice safer sex by using a latex or polyurethane condom to lower the chance of sexual contact with any body fluids such as semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about how to prevent passing HIV to other people.
Who should not take SUSTIVA?
Do not take SUSTIVA if you are allergic to efavirenz or any of the ingredients in SUSTIVA. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in SUSTIVA.
What should I tell my doctor before taking SUSTIVA?
Before taking SUSTIVA, tell your doctor if you have any medical conditions and in particular, if you:
- have ever had a mental health problem
- have ever used street drugs or large amounts of alcohol
- have liver problems, including hepatitis B or C virus infection
- have a history of seizures
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. SUSTIVA may harm your unborn baby. If you are able to become pregnant your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start SUSTIVA. You should not become pregnant while taking SUSTIVA and for 12 weeks after stopping treatment with SUSTIVA.
-
Females who are able to become pregnant should use 2 effective forms of birth control during treatment and for 12 weeks after stopping treatment with SUSTIVA. A barrier form of birth control should always be used along with another type of birth control.
- Barrier forms of birth control may include latex or polyurethane condom, contraceptive sponge, diaphragm with spermicide, and cervical cap.
- Hormonal forms of birth control, such as birth control pills, injections, vaginal rings, or implants may not work during treatment with SUSTIVA.
- Talk to your doctor about forms of birth control that may be used during treatment with SUSTIVA.
- Pregnancy Registry. There is a pregnancy registry for women who take antiretroviral medicines during pregnancy. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. Talk to your doctor about how you can take part in this registry.
- Do not breastfeed if you take SUSTIVA.
- You should not breastfeed if you have HIV because of the risk of passing HIV to your baby.
Tell your doctor and pharmacist about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
SUSTIVA may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how SUSTIVA works, and may cause serious side effects. If you take certain medicines with SUSTIVA, the amount of SUSTIVA in your body may be too low and it may not work to help control your HIV infection. The HIV virus in your body may become resistant to SUSTIVA or other HIV medicines that are like it.
You should not take SUSTIVA if you take ATRIPLA (efavirenz, emtricitabine, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) unless your doctor tells you to.
Tell your doctor and pharmacist about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicines interact with SUSTIVA.
Keep a list of your medicines to show your doctor and pharmacist.
- You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of medicines that interact with SUSTIVA.
- Do not start taking a new medicine without telling your doctor. Your doctor can tell you if it is safe to take SUSTIVA with other medicines.
How should I take SUSTIVA?
- Take SUSTIVA exactly as your doctor tells you to.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking SUSTIVA unless your doctor tells you to.
- Stay under the care of your doctor during treatment with SUSTIVA.
- SUSTIVA must be used with other antiretroviral medicines.
- Take SUSTIVA 1 time each day.
- SUSTIVA comes as tablets or capsules.
- SUSTIVA tablets must not be broken.
- Swallow SUSTIVA tablets or capsules whole with liquid.
How and when to take SUSTIVA.
- You should take SUSTIVA on an empty stomach at bedtime. Taking SUSTIVA with food increases the amount of medicine in your body. Some side effects may bother you less if you take SUSTIVA on an empty stomach and at bedtime.
- Your child’s doctor will prescribe the right dose of SUSTIVA based on your child’s weight.
- If you have difficulty swallowing tablets or capsules, tell your doctor. Your doctor may recommend opening the SUSTIVA capsule and mixing the contents with food or infant formula. See the detailed “Instructions for Use” at the end of this Patient Information to learn the right way to take SUSTIVA using the capsule sprinkle method.
- Adults and children who take SUSTIVA using the capsule sprinkle method should not eat for 2 hours after taking a dose of SUSTIVA.
- Babies should not be given infant formula for 2 hours after taking a dose of SUSTIVA using the capsule sprinkle method.
- Do not miss a dose of SUSTIVA. If you forget to take SUSTIVA, take the missed dose right away, unless it is almost time for your next dose. Do not take 2 doses at one time. Just take your next dose at your regularly scheduled time. If you need help in planning the best times to take your medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- If you take too much SUSTIVA, call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
- When your SUSTIVA supply starts to run low, get more from your doctor or pharmacy. It is important not to run out of SUSTIVA. The amount of HIV-1 in your blood may increase if the medicine is stopped for even a short time. The virus may become resistant to SUSTIVA and harder to treat.
What are the possible side effects of SUSTIVA?
SUSTIVA may cause serious side effects, including:
- Serious mental health problems can happen in people who take SUSTIVA. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Nervous system symptoms are common in people who take SUSTIVA and can be severe. These symptoms usually begin during the first or second day of treatment with SUSTIVA and usually go away after 2 to 4 weeks of treatment. These symptoms may become worse if you drink alcohol, take a medicine for mental health problems, or use certain street drugs during treatment with SUSTIVA. Symptoms may include:
|
|
|
|
|
If you have dizziness, trouble concentrating or drowsiness, do not drive a car, use machinery, or do anything that needs you to be alert.
- Skin rash is common with SUSTIVA but can sometimes be severe. Skin rash usually goes away without any change in treatment. If you develop a rash with any of the following symptoms, tell your doctor right away:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Liver problems, including liver failure and death. If you have liver problems, including hepatitis B or C infection or take another medicine that can cause liver problems, your doctor may do blood tests to check your liver before you start SUSTIVA and during treatment. Liver problems can also happen in people without a history of liver problems. Tell your doctor right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Seizures can happen in people who take SUSTIVA. Seizures are more likely to happen if you have had seizures in the past. Tell your doctor if you have had a seizure or if you take a medicine to help prevent seizures.
- Changes in your immune system (Immune Reconstitution Syndrome) can happen when you start taking HIV-1 medicines. Your immune system may get stronger and begin to fight infections that have been hidden in your body for a long time. Tell your doctor if you start having new symptoms after starting your HIV-1 medicine.
- Changes in body fat can happen in people who take HIV-1 medicine. These changes may include increased amount of fat in the upper back and neck (“buffalo hump”), breast, and around the main part of your body (trunk). Loss of fat from the legs, arms, and face may also happen. The cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known.
The most common side effects of SUSTIVA include:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Some patients taking SUSTIVA have experienced increased levels of lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) in the blood. Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of SUSTIVA. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store SUSTIVA?
- Store SUSTIVA capsules and tablets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep SUSTIVA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about SUSTIVA
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use SUSTIVA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SUSTIVA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about SUSTIVA that is written for health professionals. For more information, go to www.sustiva.com or call 1-800-321-1335.
What are the ingredients in SUSTIVA?
Active ingredient: efavirenz
Inactive ingredients:
SUSTIVA capsules: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate, and sodium starch glycolate. The capsule shell contains gelatin, sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide, and/or yellow iron oxide. The capsule shell may also contain silicon dioxide. The capsules are printed with ink containing carmine 40 blue, FD&C Blue No. 2, and titanium dioxide.
SUSTIVA tablets: croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The tablet film coating contains Opadry Yellow and Opadry Clear. The tablets are polished with carnauba wax and printed with purple ink, Opacode WB.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
Princeton, NJ 08543 USA
SUSTIVA ® (efavirenz) capsules made in India.
© Bristol-Myers Squibb Company 2015
Revised: March 2016
SUSTIVA is a registered trademark of Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma Company. ATRIPLA is a registered trademark of Bristol-Myers Squibb & Gilead Sciences, LLC.
Instructions for Use
SUSTIVA (sus-TEE-vah)
(efavirenz)
capsules
Preparing a dose of SUSTIVA using the capsule sprinkle method
Read this Instructions for Use before you prepare your first dose of SUSTIVA mixed with food or infant formula using the capsule sprinkle method, each time you get a refill, and as needed. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your medical condition or treatment. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions about how to mix or give a dose of SUSTIVA using the capsule sprinkle method.
Important Information:
- For more information about SUSTIVA capsules, see the Patient Information leaflet.
- The capsule sprinkle method for mixing the contents of SUSTIVA capsules with soft food or infant formula may be used for adults or children who cannot swallow capsules or tablets.
- You should take SUSTIVA on an empty stomach at bedtime.
- You should not eat for 2 hours after taking SUSTIVA mixed with food.
- Babies who are old enough to swallow food should be given SUSTIVA using the capsule sprinkle method mixed with food instead of with infant formula.
- Talk with your doctor to help decide the best schedule for giving your baby SUSTIVA mixed with infant formula using the capsule sprinkle method.
Preparing a dose of SUSTIVA mixed with food using the capsule sprinkle method.
Before you prepare a dose of SUSTIVA mixed with food using the capsule sprinkle method, gather the following supplies:
- paper towels
- teaspoon for measuring
- small spoon for stirring and feeding
- small clean container (such as a small cup or bowl)
- soft food such as applesauce, grape jelly, or yogurt
|
Step 1. Choose a clean, flat work surface. Place a clean paper towel on the work surface. Then place the other supplies on the paper towel. | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 2. Wash and dry your hands well. |
||
|
|
||
|
Step 3. Place 1 to 2 teaspoons of soft food such as applesauce, grape jelly, or yogurt in the small container (see Figure A). The color and thickness of the food may change when mixed with the medicine. | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 4. There are 2 parts of the SUSTIVA capsule. Look at the SUSTIVA capsule to see which part of the capsule overlaps the other part (see Figure B). | ||
|
Step 5. Hold the SUSTIVA capsule in a sideways (horizontal) position directly over the container of food. Hold each end of the SUSTIVA capsule between your thumbs and index (pointer) fingers (see Figure C). | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 6. Use your thumb and index finger to pinch near the end of the overlapping part of the SUSTIVA capsule (see Figure D). | ||
|
|
||
|
Then, carefully twist both ends of the SUSTIVA capsule in opposite directions to open it (see Figure E). Be careful not to spill the capsule contents or spread it in the air. | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 7. Sprinkle the contents of the SUSTIVA capsule onto the food (see Figure F).
| ||
|
|
||
|
If the total prescribed dose is more than 1 capsule, follow Steps 4 through 7 for each capsule. Do not add more food. |
||
|
|
||
|
Steps 8 through 11 should be completed within 30 minutes of mixing the medicine (see Figure G). | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 8. Use the small spoon to gently mix the capsule contents and food together (see Figure H). Sprinkles will not dissolve. Mixture will look grainy but should not be lumpy. | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 9. Use the small spoon to give or take the food and capsule contents mixture. Make sure that all of the mixture is swallowed. |
||
|
|
||
|
Step 10. Add about 2 teaspoons more of the food to the empty container and gently stir with the small spoon to mix with any capsule contents that may still be in the container. |
||
|
|
||
|
Step 11. Use the small spoon to give or take the food and capsule contents mixture. Make sure all of the mixture is swallowed. |
||
|
|
||
|
Step 12. Wash the container and spoons. Throw away the paper towel and clean the work surface. Wash your hands. |
||
|
|
||
|
Preparing a dose of SUSTIVA mixed with infant formula using the capsule sprinkle method |
||
|
To make sure that your baby gets all of the medicine, do not give SUSTIVA capsule contents to your baby in a bottle. |
||
|
Before you prepare a dose of SUSTIVA mixed with infant formula using the capsule sprinkle method, gather the following supplies: |
||
| ||
|
|
||
|
Step 1. Prepare the infant formula according to the directions on the infant formula package. You will use about 1 ounce of the formula to give the medicine. Any remaining formula should not be given to the child for 2 hours. |
||
|
|
||
|
Step 2. Choose a clean, flat work surface. Place a clean paper towel on the work surface. Place the supplies you will need on the paper towel. |
||
|
|
||
|
Step 3. Wash and dry your hands well. |
||
|
|
||
|
Step 4. Pour 2 teaspoons of room temperature infant formula into the container (see Figure J). | ||
|
Step 5. There are 2 parts of the SUSTIVA capsule. Look at the SUSTIVA capsule to see which part of the capsule overlaps the other part (see Figure K). | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 6. Hold the SUSTIVA capsule in a sideways (horizontal) position directly over the container with the infant formula. Hold each end of the SUSTIVA capsule between your thumbs and index (pointer) fingers (see Figure L). | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 7. Use your thumb and index finger to pinch near the end of the overlapping part of the SUSTIVA capsule (see Figure M). | ||
|
|
||
|
Then, carefully twist both ends of the SUSTIVA capsule in opposite directions to open it (see Figure N). Be careful not to spill the capsule contents or spread it in the air. | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 8. Sprinkle the contents of the SUSTIVA capsule onto the infant formula (see Figure O).
| ||
|
|
||
|
If the total prescribed dose is more than 1 capsule, follow Steps 5 through 8 for each capsule. Do not add more infant formula. |
||
|
|
||
|
Steps 9 through 12 should be completed within 30 minutes of mixing the medicine (see Figure P). | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 9. Hold the container with one hand. With your other hand, use the teaspoon to gently mix the capsule contents and the infant formula (see Figure Q). Sprinkles will not dissolve. Mixture will look grainy but should not be lumpy. | ||
|
|
||
|
Step 10. To draw up all of the mixture into the oral dosing syringe:
| ||
|
|
||
| ||
|
|
||
| ||
|
|
||
|
Step 11. Place the tip of the syringe in your baby’s mouth along the inner cheek (see Figure U). Slowly push on the plunger to give your baby all of the mixture. | ||
|
Step 12. To make sure all of the medicine is given to your baby:
| ||
|
Step 13. Remove the plunger from the oral dosing syringe. Wash the container, teaspoon, and oral dosing syringe. Allow the plunger and the syringe barrel to dry before putting them back together. |
||
|
|
||
|
Step 14. Throw away the paper towel and clean the work surface. Wash your hands. |
||
How should I store SUSTIVA capsules?
- Store SUSTIVA capsules at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep SUSTIVA capsules and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
Princeton, NJ 08543 USA
SUSTIVA ® (efavirenz) capsules made in India.
Revised: March 2016
DRUG: SUSTIVA
GENERIC: efavirenz
DOSAGE: TABLET, FILM COATED
ADMINSTRATION: ORAL
NDC: 24236-282-02
COLOR: yellow
SHAPE: OVAL
SCORE: No score
SIZE: 19 mm
IMPRINT: SUSTIVA;SUSTIVA
PACKAGING: 30 in 1 BLISTER PACK
ACTIVE INGREDIENT(S):
- efavirenz 600mg in 1
INACTIVE INGREDIENT(S):
- carnauba wax
- cellulose, microcrystalline
- sodium lauryl sulfate
- croscarmellose sodium
- HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (TYPE H)
- lactose monohydrate
- magnesium stearate

| SUSTIVA
efavirenz tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - REMEDYREPACK INC. (829572556) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| RemedyRepack Inc. | 829572556 | repack(24236-282) | |