POLY HIST PD- pyrilamine maleate, chlorpheniramine maleate, and phenylephrine hydrochloride liquid
Poly Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Disclaimer: This drug has not been found by FDA to be safe and effective, and this labeling has not been approved by FDA. For further information about unapproved drugs, click here.
----------
POLY HIST PD
POLY HIST PD
Antihistamine / Decongestant
Sugar Free / Alcohol Free / Dye Free
DESCRIPTION: POLY HIST PD
is a sugar free, alcohol free, dye free, clear and colorless liquid with a
bubble gum odor and flavor. Each 5 mL (1 teaspoonful) contains:
Pyrilamine Maleate.................... 12.5 mg
Chlorpheniramine Maleate........... 2 mg
Phenylephrine HCl...................... 7.5 mg
Pyrilamine Maleate is an antihistamine that occurs as a white crystalline powder, usually having a faint odor.
It is very soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol and chloroform, and slightly soluble in ether and benzene.
The chemical name is 1,2-Ethanediamine, N-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-N', N'dimethyl-N-2-pyridinyl-, (Z)-2-
butenedioate (1:1). Its structural formula is as follows:
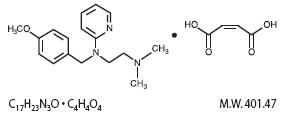
Chlorpheniramine Maleate is an antihistaminic that occurs as a white, odorless crystalline powder. Its solutions
have a pH between 4 and 5. It is freely soluble in water, soluble in alcohol and chloroform, and slightly soluble
in ether and benzene. The chemical name is 2-Pyridinepropanamine, gamma-(4-chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-,
(Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1). Its structural formula is as follows:
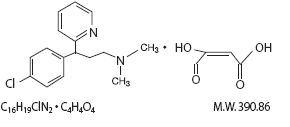
Phenylephrine hydrochloride is an adrenergic that occurs as white or practically white, odorless crystals, having
a bitter taste. It is freely soluble in water and alcohol. It is affected by light. The chemical name is benzenemethanol, 3-hydroxy-alpha[(methylamino)methyl]-, hydrochloride (R)-. Its structural formula is as follows:
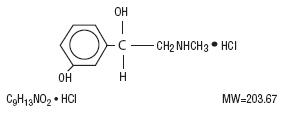
Inactive ingredients:
Propylene glycol, sorbitol, glycerin, sodium saccharin, purified water, and bubble gum flavoring.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Pyrilamine Maleate:
Pyrilamine is an antihistamine belonging to the ethylenediamine class. Pyrilamine is a
highly effective H
1 blocker which possesses local anesthetic activity. Pyrilamine antagonizes most of the
smooth muscle stimulating actions of histamine on the H
1 receptors of the gastrointestinal tract, blood
vessels and bronchial muscle. It also antagonizes the actions of histamine that result in increased capillary
permeability and the formation of edema. Pyrilamine has a duration of action of 4 to 6 hours in clinical studies.
Chlorpheniramine Maleate:
Chlorpheniramine is an antihistamine belonging to the alkylamine class. It possesses anticholinergic and
sedative effects. Antihistamines appear to compete with histamine for H
1 cell receptor sites on effector cells.
Chlorpheniramine Maleate does not prevent the release of histamine in response to injury, drugs or antigens.
Antihistamines effectively block most smooth muscle responses to histamine and acts as an antagonist of
the constrictor action of histamine on respiratory smooth muscle. Antihistamines counteract edema formation
and whealing in response to injury, antigens, or histamine-liberating drugs. Chlorpheniramine is readily absorbed
from the gastrointestinal tract and has a duration of 4 to 6 hours. Plasma half-life is approximately 22 hours.
Degradation products of chlorpheniramine's metabolic transformation by the liver are almost completely excreted
in 24 hours via the kidney. The alkylamines of which chlorpheniramine is the prototype, are among the most
potent H
1 blockers. Although not so prone as others to cause drowsiness, a significant proportion of patients
do experience this effect. CNS stimulation is more common in chlorpheniramine than in other groups of H
1 blockers.
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride:
Phenylephrine is a potent postsynaptic alpha-receptor agonist with little effect on beta-receptors on the heart.
Phenylephrine has no effect on beta-adrenergic receptors of the bronchi or peripheral blood vessels. A direct
action at receptors accounts for the greater part of its effects; only a small part is due to its ability to release
norepinephrine. Therapeutic doses of phenylephrine mainly cause vasoconstriction. It increases resistance,
and to a lesser extent, decreases capacitance of blood vessels. Total peripheral resistance is increased,
resulting in increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Pulmonary arterial pressure is usually increased,
and renal blood flow is usually decreased. Following oral administration of phenylephrine, constriction of blood
vessels in the nasal mucosa relieves nasal congestion associated with allergy or head colds. Following oral
administration of phenylephrine, nasal decongestion may occur within 15 to 20 minutes and may persist for up
to 4 hours. Phenylephrine is irregularly absorbed from and readily metabolized in the gastrointestinal tract.
Phenylephrine is metabolized in the liver and intestine by monoamine oxidase. The metabolites and their route
and rate of excretion have not been identified. The pharmacologic action of phenylephrine is terminated at least
partially by uptake of the drug into the tissues.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE:
Poly Hist PD is indicated for symptomatic relief of seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis, and vasomotor rhinitis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients. Patients known to be sensitive to other sympathomimetic amines
may exhibit cross sensitivity with this drug. Poly Hist PD is contraindicated in patients with severe hypertension,
severe coronary artery disease and patients on monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor therapy. It is also
contraindicated in patients with diabetes or hyperthyroidism. Antihistamines should not be administered to premature
or newborn infants or be used to treat lower respiratory tract symptoms or asthma.
WARNINGS:
Pyrilamine Maleate and Chlorpheniramine Maleate:
Antihistamines should be used with considerable caution in patients with narrow angle glaucoma, stenosing peptic
ulcer, pyloroduodenal obstruction, symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy, and bladder neck obstruction. In infants and
children especially, antihistamine overdosage may cause hallucinations, convulsions or death. As in adults,
antihistamines may diminish mental alertness in children. Chlorpheniramine Maleate has additional effects with
alcohol and other CNS depressants (hypnotics, sedatives, tranquilizers) Patients should be warned about engaging
in activities requiring mental alertness, such as driving a car or operating appliances, machinery, etc.
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride:
Sympathomimetic amines should be used with considerable caution in patients with hypertension, ischemic heart
disease, diabetes mellitus, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism or prostatic hypertrophy.
Sympathomimetics may produce central nervous system stimulation with convulsions or cardiovascular collapse
with accompanying hypotension. DO NOT EXCEED RECOMMENDED DOSAGE. Hypertensive crisis could occur
with concurrent use of phenylephrine and monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, indomethacin or with beta blockers
and methyldopa. If a hypertensive crisis occurs, this drug should be discontinued immediately and therapy to lower
blood pressure should be instituted. Fever should be managed by means of external cooling. The elderly
(approximately sixty years or older) are more likely to have adverse reactions to sympathomimetics. Overdosage of
sympathomimetics in this age group may cause hallucinations, convulsions, CNS depression and death. Therefore,
safe use of a short-acting sympathomimetic should be demonstrated in the individual elderly patient before
considering the use of a sustained-release formulation. Discontinue use if adverse reaction(s) occur.
PRECAUTIONS:
General:
Antihistamines have an atropine-like action and therefore should be used with caution in patients with a
history of bronchial asthma, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, cardiovascular disease and
hypertension. Phenylephrine should be used with caution in patients with diabetes, hypertension,
cardiovascular disease and hyper-reactivity to ephedrine.
Information for Patients:
Antihistamines may impair the mental and physical abilities required for the performance of potentially
hazardous tasks such as driving a vehicle or operating machinery. Patients should also be warned about
possible additive effects with alcohol and other central nervous system depressants (hypnotics, sedatives
and tranquilizers).
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions:
MAO inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants may prolong and intensify the anticholinergic (drying) effects
of antihistamines. Beta-adrenergic blockers and MAO inhibitors may potentiate the pressor effect of
phenylephrine. Concurrent use of digitalis glycosides may increase the possibility of cardiac arrhythmias.
Sympathomimetics may reduce the antihypertensive effects of methyldopa, mecamylamine, reserpine and
veratrum alkaloids. Concurrent use of tricyclic antidepressants may antagonize the effects of phenylephrine.
Concomitant use of antihistamines with alcohol, tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, and other CNS
depressants may have an additive effect.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
No long-term studies have been performed using Poly Hist PD to determine the long-term potential for
carcinogenesis, mutagenesis and impairment of fertility. In a four-year evaluation of phenylephrine, no
statistically significant associated between the drug and cancer was found.
Usage in Pregnancy:
Pregnancy Category C: Moderate overexposure to phenylephrine has been found to contribute to birth defects
in rabbits. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with the other ingredients in Poly Hist PD.
Poly Hist PD should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the possible risk to the fetus.
Labor and Delivery:
Administration of phenylephrine to patients in late pregnancy or labor may cause fetal anoxia or bradycardia by
increasing contractility of the uterus and decreasing uterine blood flow.
Nursing Mothers:
Due to the possible passage of antihistamines into breast milk, and because of the higher than usual risk for
infants from sympathomimetic amines and antihistamines, a decision should be made whether to discontinue
nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of both.
Pediatric Use:
In infants and children especially, antihistamines in overdosage may cause hallucination, convulsions or death.
As in adults, antihistamines may diminish mental alertness in children. In the young child particularly, they may
produce excitation.
Geriatric Use:
The elderly (60 years and older) are more likely to experience adverse reactions from sympathomimetics and
antihistamines. Overdosage of sympathomimetics in this age group may cause hallucinations, convulsions,
CNS depression and death.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Pyrilamine Maleate and Chlorpheniramine Maleate:
Chlorpheniramine maleate may cause slight to moderate drowsiness relatively infrequently. Other possible side effects
of antihistamines in general include: urticaria, drug rash, anaphylactic shock, photosensitivity, excessive perspiration,
chills, dryness or the mouth, nose and throat; cardiovascular effects (hypotension, headache, palpitation, tachycardia,
extrasystoles); hematological effects (hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis); CNS disturbances (sedation,
dizziness, disturbed coordination, fatigue, confusion, restlessness, excitation, nervousness, tremor, irritability, insomnia,
euphoria, paresthesias, blurred vision, diplopia, vertigo, tinnitus, acute labyrinthitis, hysteria, neuritis, convulsions);
gastrointestinal effects (epigastric distress, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation); genitourinary effects
(urinary frequency, difficult urination, urinary retention, early menses) and respiratory effects (thickening of bronchial
secretions, tightness of the chest, wheezing and nasal stuffiness).
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride:
Hyper-reactive individuals may display ephedrine-like reactions such as tachycardia, palpitations, headache, dizziness,
or nausea. Sympathomimetic amines have been associated with certain untoward reactions including fear, anxiety,
nervousness, restlessness, tremor, weakness, pallor, respiratory difficulty, dysuria, insomnia, hallucinations, convulsions,
CNS depression, arrhythmias, and cardiovascular collapse with hypotension. Phenylephrine may cause precordial pain,
respiratory distress, tremor, weakness, hypertension, restlessness, anxiety, nervousness and dizziness.
OVERDOSAGE:
Signs and symptoms:
Pyrilamine Maleate and Chlorpheniramine Maleate:
Manifestations of antihistamine overdosage may vary from central nervous system depression (sedation, apnea,
cardiovascular collapse) to stimulation (insomnia, hallucinations, tremors or convulsions). Other signs and
symptoms may be dizziness, tinnitus, ataxia, blurred vision and hypotension. Stimulation is particularly likely
in children, as are atropine-like signs and symptoms (dry mouth, fixed dilated pupils, flushing, hypothermia and
gastrointestinal symptoms.
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride:
May cause hypertension, headache, convulsions, cerebral hemorrhage and vomiting. Ventricular premature beats
and short paroxysms of ventricular tachycardia may also occur. Headache may be a symptom of hypertension.
Bradycardia may also be seen early in phenylephrine overdosage through stimulation of baroreceptors. Excessive
CNS stimulation may result in excitement, tremor, restlessness and insomnia. Other effects may include pallor,
mydriasis, hyperglycemia and urinary retention. Severe overdosage may cause tachypnea or hyperpnea,
hallucination, convulsions or delirium but in some individuals, there may be CNS depression with somnolence,
stupor or respiratory depression. Arrhythmias (including ventricular fibrillation) may lead to hypotension and
circulatory collapse. Severe hypokalemia can occur, probably due to compartmental shift rather than a depletion
of potassium.
Treatment:
The patient should be induced to vomit even if emesis has occurred spontaneously. Pharmacologic vomiting by
the administration of ipecac is facilitated by physical activity and by the administration of eight to twelve ounces
of water. If emesis does not occur within fifteen minutes, the dose of ipecac should be repeated.
Precautions against aspiration must be taken especially in infants and children. Following emesis, any drug remaining
in the stomach may be absorbed by activated charcoal administered as a slurry with water. If vomiting is unsuccessful
or contraindicated, gastric lavage should be performed. Isotonic and one-half isotonic saline are the lavage solution of
choice. Saline cathartics, such as milk of magnesia, draw water into the bowel by osmosis and therefore, may be
valuable for their action in rapid dilution of bowel content. After emergency treatment, the patient should continue to
be medically monitored. Treatment of the signs and symptoms of overdosage is symptomatic and supportive.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Adults and Children 12 years of age and over:
1-2 teaspoonfuls every 4-6 hours.
Children 6 to under 12 years of age:
1/2 teaspoonful every 4-6 hours.
Not recommended for Children under 6 years of age.
HOW SUPPLIED:
16 fluid ounce bottles, NDC 50991-405-16 and 20 mL bottles, NDC 50991-405-20.
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
IN CASE OF ACCIDENTAL OVERDOSE, CONTACT A POISON
CONTROL
CENTER OR SEEK PROFESSIONAL ASSISTANCE IMMEDIATELY.
Storage:
Store at controlled room temperature, 15
o-30
oC (59
o-86
oF).
DISPENSE IN TIGHT, LIGHT-RESISTANT CONTAINER WITH A CHILD-RESISTANT
CLOSURE AS DESCRIBED IN THE USP/NF.
CAUTION: FEDERAL LAW PROHIBITS DISPENSING WITHOUT A PRESCRIPTION.
Manufactured by:
Great Southern Laboratories,
Houston, TX 77099
Distributed by:
Poly Pharmaceuticals, Inc.,
Mobile, AL 36619
Rev. 11/09
PRODUCT PACKAGING:
The packaging below represents the labeling currently used:
Principal Display Panel and Side Panel for 473 mL Label:
NDC 50991-405-16
POLY HIST
PD
EACH TEASPOONFUL (5 mL)
FOR ORAL ADIMISTRATION CONTAINS:
PYRILAMINE MALEATE..................12.5 mg
CHLORPHENIRAMINE MALEATE...... 2 mg
PHENYLEPHRINE HCl......................7.5 mg
- SUGAR FREE
- ALCOHOL FREE
- DYE FREE
Rx Only
16 fl oz (473 mL)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Adults and Children 12 years of age and over: 1-2 teaspoonfuls every 4-6 hours.
Children 6 to under 12 years of age:
1/2 teaspoonful every 4-6 hours.
Not recommended for Children under 6 years of age.
SEE LABEL FOLDOUT FOR FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION.
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
IN CASE OF ACCIDENTAL OVERDOSE, SEEK PROFESSIONAL
ASSISTANCE
OR CONTACT A POISON CONTROL CENTER IMMEDIATELY.
Store at controlled room temperature, 15
o-30
oC (59
o-86
oF).
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP/NF with a child-resistant closure.
This bottle is not to be dispensed to consumer.
Tamper evident by heat seal under cap. Do not use if there is evidence of tampering.
POLY HIST PD is a product of POLY PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
Mfg. by: Great Southern Labroatories, Houston, TX 77099
Distributed by: Poly Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Mobile, AL 36619
Rev. 11/09



| POLY HIST
PD
pyrilamine maleate, chlorpheniramine maleate, and phenylephrine hydrochloride liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Poly Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (198449894) |