DESCRIPTION
Losartan potassium is an angiotensin II receptor (type AT1) antagonist. Losartan potassium, a non-peptide molecule, is chemically described as 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[p-(o-1H-tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]imidazole-5-methanol monopotassium salt.
Its empirical formula is C22H22ClKN6O, and its structural formula is:
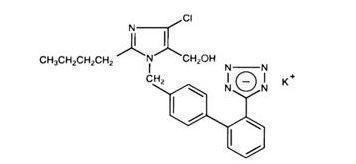
Losartan potassium, USP is a white to off-white free-flowing crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 461.01. It is freely soluble in water, soluble in alcohols, and slightly soluble in common organic solvents, such as acetonitrile and methyl ethyl ketone. Oxidation of the 5-hydroxymethyl group on the imidazole ring results in the active metabolite of losartan.
Losartan potassium is available as tablets for oral administration containing either 25 mg, 50 mg or 100 mg of losartan potassium and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, talc and titanium dioxide.
Losartan potassium 25 mg, 50 mg and 100 mg tablets contain potassium in the following amounts: 2.12 mg (0.054 mEq), 4.24 mg (0.108 mEq) and 8.48 mg (0.216 mEq), respectively.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
-
Mechanism of Action
Angiotensin II [formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE, kininase II)], is a potent vasoconstrictor, the primary vasoactive hormone of the renin-angiotensin system and an important component in the pathophysiology of hypertension. It also stimulates aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex. Losartan and its principal active metabolite block the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone-secreting effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor found in many tissues, (e.g., vascular smooth muscle, adrenal gland). There is also an AT2 receptor found in many tissues but it is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Both losartan and its principal active metabolite do not exhibit any partial agonist activity at the AT1 receptor and have much greater affinity (about 1000-fold) for the AT1 receptor than for the AT2 receptor. In vitro binding studies indicate that losartan is a reversible, competitive inhibitor of the AT1 receptor. The active metabolite is 10 to 40 times more potent by weight than losartan and appears to be a reversible, non-competitive inhibitor of the AT1 receptor.
Neither losartan nor its active metabolite inhibits ACE (kininase II, the enzyme that converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II and degrades bradykinin); nor do they bind to or block other hormone receptors or ion channels known to be important in cardiovascular regulation.
Pharmacokinetics
General
Losartan is an orally active agent that undergoes substantial first-pass metabolism by cytochrome P450 enzymes. It is converted, in part, to an active carboxylic acid metabolite that is responsible for most of the angiotensin II receptor antagonism that follows losartan treatment. Losartan metabolites have been identified in human plasma and urine. In addition to the active carboxylic acid metabolite, several inactive metabolites are formed. Following oral and intravenous administration of 14C-labeled losartan potassium, circulating plasma radioactivity is primarily attributed to losartan and its active metabolite. In vitro studies indicate that cytochrome P450 2C9 and 3A4 are involved in the biotransformation of losartan to its metabolites. Minimal conversion of losartan to the active metabolite (less than 1% of the dose compared to 14% of the dose in normal subjects) was seen in about one percent of individuals studied.
The terminal half-life of losartan is about 2 hours and of the metabolite is about 6-9 hours.
The pharmacokinetics of losartan and its active metabolite are linear with oral losartan doses up to 200 mg and do not change over time. Neither losartan nor its metabolite accumulates in plasma upon repeated once-daily dosing.
Following oral administration, losartan is well absorbed (based on absorption of radiolabeled losartan) and undergoes substantial first-pass metabolism; the systemic bioavailability of losartan is approximately 33%. About 14% of an orally-administered dose of losartan is converted to the active metabolite. Mean peak concentrations of losartan and its active metabolite are reached in 1 hour and in 3-4 hours, respectively. While maximum plasma concentrations of losartan and its active metabolite are approximately equal, the AUC of the metabolite is about 4 times as great as that of losartan. A meal slows absorption of losartan and decreases its Cmax but has only minor effects on losartan AUC or on the AUC of the metabolite (about 10% decreased).
The pharmacokinetics of losartan and its active metabolite were also determined after IV doses of each component separately in healthy volunteers. The volume of distribution of losartan and the active metabolite is about 34 liters and 12 liters, respectively. Total plasma clearance of losartan and the active metabolite is about 600 mL/min and 50 mL/min, respectively, with renal clearance of about 75 mL/min and 25 mL/min, respectively. After single doses of losartan administered orally, about 4% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine and about 6% is excreted in urine as active metabolite. Biliary excretion contributes to the elimination of losartan and its metabolites. Following oral 14C-labeled losartan, about 35% of radioactivity is recovered in the urine and about 60% in the feces. Following an intravenous dose of 14C-labeled losartan, about 45% of radioactivity is recovered in the urine and 50% in the feces.
Both losartan and its active metabolite are highly bound to plasma proteins, primarily albumin, with plasma free fractions of 1.3% and 0.2%, respectively. Plasma protein binding is constant over the concentration range achieved with recommended doses. Studies in rats indicate that losartan crosses the blood-brain barrier poorly, if at all.
Special Populations
Pediatric: Pharmacokinetic parameters after multiple doses of losartan (average dose 0.7 mg/kg, range 0.36 to 0.97 mg/kg) as a tablet to 25 hypertensive patients aged 6 to 16 years are shown in Table 1 below. Pharmacokinetics of losartan and its active metabolite were generally similar across the studied age groups and similar to historical pharmacokinetic data in adults. The principal pharmacokinetic parameters in adults and children are shown in the table below.
Table 1: Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Hypertensive Adults and Children Age 6-16 Following Multiple Dosing
* Mean ± standard deviation
† Harmonic mean and standard deviation
‡ Median
Adults given 50 mg once daily for 7 days
N=12Age 6-16 given 0.7 mg/kg once daily for 7 days
N=25Parent Active Metabolite Parent Active Metabolite AUC0-24* (ng•h/mL) 442 ± 173 1685 ± 452 368 ± 169 1866 ± 1076 CMAX (ng/mL)* 224 ± 82 212 ± 73 141 ± 88 222 ± 127 T½ (h)† 2.1 ± 0.70 7.4 ± 2.4 2.3 ± 0.8 5.6 ± 1.2 TPEAK (h)‡ 0.9 3.5 2.0 4.1 CLREN (mL/min)* 56 ± 23 20 ± 3 53 ± 33 17 ± 8 The bioavailability of the suspension formulation was compared with losartan tablets in healthy adults. The suspension and tablet are similar in their bioavailability with respect to both losartan and the active metabolite (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Preparation of Suspension).
Geriatric and Gender: Losartan pharmacokinetics have been investigated in the elderly (65-75 years) and in both genders. Plasma concentrations of losartan and its active metabolite are similar in elderly and young hypertensives. Plasma concentrations of losartan were about twice as high in female hypertensives as male hypertensives, but concentrations of the active metabolite were similar in males and females. No dosage adjustment is necessary (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Race: Pharmacokinetic differences due to race have not been studied (see also PRECAUTIONS, Race and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, Reduction in the Risk of Stroke, Race).
Renal Insufficiency: Following oral administration, plasma concentrations and AUCs of losartan and its active metabolite are increased by 50-90% in patients with mild (creatinine clearance of 50 to 74 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance 30 to 49 mL/min) renal insufficiency. In this study, renal clearance was reduced by 55-85% for both losartan and its active metabolite in patients with mild or moderate renal insufficiency. Neither losartan nor its active metabolite can be removed by hemodialysis. No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with renal impairment unless they are volume-depleted (see WARNINGS, Hypotension ─ Volume-Depleted Patients and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Hepatic Insufficiency: Following oral administration in patients with mild to moderate alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver, plasma concentrations of losartan and its active metabolite were, respectively, 5-times and about 1.7-times those in young male volunteers. Compared to normal subjects the total plasma clearance of losartan in patients with hepatic insufficiency was about 50% lower and the oral bioavailability was about 2-times higher. A lower starting dose is recommended for patients with a history of hepatic impairment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Drug Interactions
Losartan, administered for 12 days, did not affect the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of a single dose of warfarin. Losartan did not affect the pharmacokinetics of oral or intravenous digoxin. There is no pharmacokinetic interaction between losartan and hydrochlorothiazide. Coadministration of losartan and cimetidine led to an increase of about 18% in AUC of losartan but did not affect the pharmacokinetics of its active metabolite. Coadministration of losartan and phenobarbital led to a reduction of about 20% in the AUC of losartan and that of its active metabolite. A somewhat greater interaction (approximately 40% reduction in the AUC of active metabolite and approximately 30% reduction in the AUC of losartan) has been reported with rifampin. Fluconazole, an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 2C9, decreased the AUC of the active metabolite by approximately 40%, but increased the AUC of losartan by approximately 70% following multiple doses. Conversion of losartan to its active metabolite after intravenous administration is not affected by ketoconazole, an inhibitor of P450 3A4. The AUC of active metabolite following oral losartan was not affected by erythromycin, another inhibitor of P450 3A4, but the AUC of losartan was increased by 30%.
Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects
Adult HypertensionLosartan inhibits the pressor effect of angiotensin II (as well as angiotensin I) infusions. A dose of 100 mg inhibits the pressor effect by about 85% at peak with 25-40% inhibition persisting for 24 hours. Removal of the negative feedback of angiotensin II causes a 2- to 3-fold rise in plasma renin activity and consequent rise in angiotensin II plasma concentration in hypertensive patients. Losartan does not affect the response to bradykinin, whereas ACE inhibitors increase the response to bradykinin. Aldosterone plasma concentrations fall following losartan administration. In spite of the effect of losartan on aldosterone secretion, very little effect on serum potassium was observed.
In a single-dose study in normal volunteers, losartan had no effects on glomerular filtration rate, renal plasma flow or filtration fraction. In multiple-dose studies in hypertensive patients, there were no notable effects on systemic or renal prostaglandin concentrations, fasting triglycerides, total cholesterol or HDL-cholesterol or fasting glucose concentrations. There was a small uricosuric effect leading to a minimal decrease in serum uric acid (mean decrease <0.4 mg/dL) during chronic oral administration.
The antihypertensive effects of losartan potassium tablets were demonstrated principally in 4 placebo-controlled, 6- to 12-week trials of dosages from 10 to 150 mg per day in patients with baseline diastolic blood pressures of 95-115. The studies allowed comparisons of two doses (50-100 mg/day) as once-daily or twice-daily regimens, comparisons of peak and trough effects, and comparisons of response by gender, age, and race. Three additional studies examined the antihypertensive effects of losartan and hydrochlorothiazide in combination.
The 4 studies of losartan monotherapy included a total of 1075 patients randomized to several doses of losartan and 334 to placebo. The 10- and 25-mg doses produced some effect at peak (6 hours after dosing) but small and inconsistent trough (24 hour) responses. Doses of 50, 100 and 150 mg once daily gave statistically significant systolic/diastolic mean decreases in blood pressure, compared to placebo in the range of 5.5-10.5/3.5-7.5 mmHg, with the 150-mg dose giving no greater effect than 50-100 mg. Twice-daily dosing at 50-100 mg/day gave consistently larger trough responses than once-daily dosing at the same total dose. Peak (6 hour) effects were uniformly, but moderately, larger than trough effects, with the trough-to-peak ratio for systolic and diastolic responses 50-95% and 60-90%, respectively.
Addition of a low dose of hydrochlorothiazide (12.5 mg) to losartan 50 mg once daily resulted in placebo-adjusted blood pressure reductions of 15.5/9.2 mmHg.
Analysis of age, gender, and race subgroups of patients showed that men and women, and patients over and under 65, had generally similar responses. Losartan potassium tablets were effective in reducing blood pressure regardless of race, although the effect was somewhat less in Black patients (usually a low-renin population).
The effect of losartan is substantially present within one week but in some studies the maximal effect occurred in 3-6 weeks. In long-term follow-up studies (without placebo control) the effect of losartan appeared to be maintained for up to a year. There is no apparent rebound effect after abrupt withdrawal of losartan. There was essentially no change in average heart rate in losartan-treated patients in controlled trials.
Pediatric HypertesionThe antihypertensive effect of losartan was studied in one trial enrolling 177 hypertensive pediatric patients aged 6 to 16 years old. Children who weighed <50 kg received 2.5, 25 or 50 mg of losartan daily and patients who weighed ≥50 kg received 5, 50 or 100 mg of losartan daily. Children in the lowest dose group were given losartan in a suspension formulation (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION, Preparation of Suspension). The majority of the children had hypertension associated with renal and urogenital disease. The sitting diastolic blood pressure (SiDBP) on entry into the study was higher than the 95th percentile level for the patient's age, gender, and height. At the end of three weeks, losartan reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure, measured at trough, in a dose-dependent manner. Overall, the two higher doses (25 to 50 mg in patients <50 kg; 50 to 100 mg in patients ≥50 kg) reduced diastolic blood pressure by 5 to 6 mmHg more than the lowest dose used (2.5 mg in patients <50 kg; 5 mg in patients ≥50 kg). The lowest dose, corresponding to an average daily dose of 0.07 mg/kg, did not appear to offer consistent antihypertensive efficacy. When patients were randomized to continue losartan at the two higher doses or to placebo after 3 weeks of therapy, trough diastolic blood pressure rose in patients on placebo between 5 and 7 mmHg more than patients randomized to continuing losartan. When the low dose of losartan was randomly withdrawn, the rise in trough diastolic blood pressure was the same in patients receiving placebo and in those continuing losartan, again suggesting that the lowest dose did not have significant antihypertensive efficacy. Overall, no significant differences in the overall antihypertensive effect of losartan were detected when the patients were analyzed according to age (<, ≥12 years old) or gender. While blood pressure was reduced in all racial subgroups examined, too few non-White patients were enrolled to compare the dose-response of losartan in the non-White subgroup.
Reduction in the Risk of Stroke
The Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension (LIFE) study was a multinational, double-blind study comparing losartan potassium tablets and atenolol in 9193 hypertensive patients with ECG-documented left ventricular hypertrophy. Patients with myocardial infarction or stroke within six months prior to randomization were excluded. Patients were randomized to receive once daily losartan potassium tablets 50 mg or atenolol 50 mg. If goal blood pressure (<140/90 mmHg) was not reached, hydrochlorothiazide (12.5 mg) was added first and, if needed, the dose of losartan potassium tablets or atenolol was then increased to 100 mg once daily. If necessary, other antihypertensive treatments (e.g., increase in dose of hydrochlorothiazide therapy to 25 mg or addition of other diuretic therapy, calcium-channel blockers, alpha-blockers, or centrally acting agents, but not ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II antagonists, or beta-blockers) were added to the treatment regimen to reach the goal blood pressure.
Of the randomized patients, 4963 (54%) were female and 533 (6%) were Black. The mean age was 67 with 5704 (62%) age ≥65. At baseline, 1195 (13%) had diabetes, 1326 (14%) had isolated systolic hypertension, 1469 (16%) had coronary heart disease, and 728 (8%) had cerebrovascular disease. Baseline mean blood pressure was 174/98 mmHg in both treatment groups. The mean length of follow-up was 4.8 years. At the end of study or at the last visit before a primary endpoint, 77% of the group treated with losartan potassium tablets and 73% of the group treated with atenolol were still taking study medication. Of the patients still taking study medication, the mean doses of losartan potassium tablets and atenolol were both about 80 mg/day, and 15% were taking atenolol or losartan as monotherapy, while 77% were also receiving hydrochlorothiazide (at a mean dose of 20 mg/day in each group). Blood pressure reduction measured at trough was similar for both treatment groups but blood pressure was not measured at any other time of the day. At the end of study or at the last visit before a primary endpoint, the mean blood pressures were 144.1/81.3 mmHg for the group treated with losartan potassium tablets and 145.4/80.9 mmHg for the group treated with atenolol [the difference in systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 1.3 mmHg was significant (p<0.001), while the difference of 0.4 mmHg in diastolic blood pressure (DBP) was not significant (p=0.098)].
The primary endpoint was the first occurrence of cardiovascular death, nonfatal stroke, or nonfatal myocardial infarction. Patients with nonfatal events remained in the trial, so that there was also an examination of the first event of each type even if it was not the first event (e.g., a stroke following an initial myocardial infarction would be counted in the analysis of stroke). Treatment with losartan potassium tablets resulted in a 13% reduction (p=0.021) in risk of the primary endpoint compared to the atenolol group (see Figure 1 and Table 2); this difference was primarily the result of an effect on fatal and nonfatal stroke. Treatment with losartan potassium tablets reduced the risk of stroke by 25% relative to atenolol (p=0.001) (see Figure 2 and Table 2).
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier estimates of the primary endpoint of time to cardiovascular death, nonfatal stroke, or nonfatal myocardial infarction in the groups treated with losartan potassium tablets and atenolol. The Risk Reduction is adjusted for baseline Framingham risk score and level of electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy.
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier estimates of the time to fatal/nonfatal stroke in the groups treated with losartan potassium tablets and atenolol. The Risk Reduction is adjusted for baseline Framingham risk score and level of electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy.
Table 2 shows the results for the primary composite endpoint and the individual endpoints. The primary endpoint was the first occurrence of stroke, myocardial infarction or cardiovascular death, analyzed using an intention-to-treat (ITT) approach. The table shows the number of events for each component in two different ways. The Components of Primary Endpoint (as a first event) counts only the events that define the primary endpoint, while the Secondary Endpoints count all first events of a particular type, whether or not they were preceded by a different type of event.
Table 2: Incidence of Primary Endpoint Events
Losartan Potassium Tablets Atenolol Risk Reduction† 95 % CI p-Value N (%) Rate* N (%) Rate* Primary Composite Endpoint 508 (11) 23.8 588 (13) 27.9 13% 2% to 23% 0.021 Components of Primary Composite Endpoint (as a first event) Stroke (nonfatal‡) 209 (5) 286 (6) Myocardial infarction (nonfatal‡) 174 (4) 168 (4) Cardiovascular mortality 125 (3) 134 (3) Secondary Endpoints (any time in study) Stroke (fatal/nonfatal) 232 (5) 10.8 309 (7) 14.5 25% 11% to 37% 0.001 Myocardial infarction (fatal/nonfatal) 198 (4) 9.2 188 (4) 8.7 -7% -13% to 12% 0.491 Cardiovascular mortality 204 (4) 9.2 234 (5) 10.6 11% -7% to 27% 0.206 Due to CHD 125 (3) 5.6 124(3) 5.6 -3% -32% to 20% 0.839 Due to Stroke 40 (1) 1.8 62 (1) 2.8 35% 4% to 67% 0.032 Other§ 39 (1) 1.8 48 (1) 2.2 16% -28% to 45% 0.411 *Rate per 1000 patient-years of follow-up † Adjusted for baseline Framingham risk score and level of electrocardiogram left ventricular hypertrophy ‡ First report of an event, in some cases the patient died subsequently to the event reported § Death due to heart failure, non-coronary vascular disease, pulmonary embolism, or a cardiovascular cause other than stroke or coronary heart disease Although the LIFE study favored losartan potassium tablets over atenolol with respect to the primary endpoint (p=0.021), this result is from a single study and, therefore, is less compelling than the difference between losartan potassium tablets and placebo. Although not measured directly, the difference between losartan potassium tablets and placebo is compelling because there is evidence that atenolol is itself effective (vs. placebo) in reducing cardiovascular events, including stroke, in hypertensive patients.
Other clinical endpoints of the LIFE study were: total mortality, hospitalization for heart failure or angina pectoris, coronary or peripheral revascularization procedures, and resuscitated cardiac arrest. There were no significant differences in the rates of these endpoints between the losartan potassium tablets and atenolol groups.
For the primary endpoint and stroke, the effects of losartan potassium tablets in patient subgroups defined by age, gender, race and presence or absence of isolated systolic hypertension (ISH), diabetes, and history of cardiovascular disease (CVD) are shown in Figure 3 below. Subgroup analyses can be difficult to interpret and it is not known whether these represent true differences or chance effects.
Figure 3. Primary Endpoint Events† within Demographic Subgroups
Symbols are proportional to sample size.
# Other includes Asian, Hispanic, Asiatic, Multi-race, Indian, Native American, European.
†Adjusted for baseline Framingham risk score and level of electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertophy.
Race
In the LIFE study, Black patients treated with atenolol were at lower risk of experiencing the primary composite endpoint compared with Black patients treated with losartan potassium tablets. In the subgroup of Black patients (n=533; 6% of the LIFE study patients), there were 29 primary endpoints among 263 patients on atenolol (11%, 26 per 1000 patient-years) and 46 primary endpoints among 270 patients (17%, 42 per 1000 patient-years) on losartan potassium tablets. This finding could not be explained on the basis of differences in the populations other than race or on any imbalances between treatment groups. In addition, blood pressure reductions in both treatment groups were consistent between Black and non-Black patients. Given the difficulty in interpreting subset differences in large trials, it cannot be known whether the observed difference is the result of chance. However, the LIFE study provides no evidence that the benefits of losartan potassium tablets on reducing the risk of cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy apply to Black patients.
Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
The Reduction of Endpoints in NIDDM with the Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist Losartan (RENAAL) study was a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter study conducted worldwide in 1513 patients with type 2 diabetes with nephropathy (defined as serum creatinine 1.3 to 3.0 mg/dl in females or males ≤60 kg and 1.5 to 3.0 mg/dl in males >60 kg and proteinuria [urinary albumin to creatinine ratio ≥300 mg/g]).
Patients were randomized to receive losartan potassium tablets 50 mg once daily or placebo on a background of conventional antihypertensive therapy excluding ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II antagonists. After one month, investigators were instructed to titrate study drug to 100 mg once daily if the trough blood pressure goal (140/90 mmHg) was not achieved. Overall, 72% of patients received the 100-mg daily dose more than 50% of the time they were on study drug. Because the study was designed to achieve equal blood pressure control in both groups, other antihypertensive agents (diuretics, calcium-channel blockers, alpha- or beta-blockers, and centrally acting agents) could be added as needed in both groups. Patients were followed for a mean duration of 3.4 years.
The study population was diverse with regard to race (Asian 16.7%, Black 15.2%, Hispanic 18.3%, White 48.6%). Overall, 63.2% of the patients were men, and 66.4% were under the age of 65 years. Almost all of the patients (96.6%) had a history of hypertension, and the patients entered the trial with a mean serum creatinine of 1.9 mg/dl and mean proteinuria (urinary albumin/creatinine) of 1808 mg/g at baseline.
The primary endpoint of the study was the time to first occurrence of any one of the following events: doubling of serum creatinine, end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (need for dialysis or transplantation), or death. Treatment with losartan potassium tablets resulted in a 16% risk reduction in this endpoint (see Figure 4 and Table 3). Treatment with losartan potassium tablets also reduced the occurrence of sustained doubling of serum creatinine by 25% and ESRD by 29% as separate endpoints, but had no effect on overall mortality (see Table 3).
The mean baseline blood pressures were 152/82 mmHg for losartan potassium tablets plus conventional antihypertensive therapy and 153/82 mmHg for placebo plus conventional antihypertensive therapy. At the end of the study, the mean blood pressures were 143/76 mmHg for the group treated with losartan potassium tablets and 146/77 mmHg for the group treated with placebo.
Figure 4. Kaplan-Meier curve for the primary composite endpoint of doubling of serum creatinine, end stage renal disease (need for dialysis or transplantation) or death.
Table 3: Incidence of Primary Endpoint Events Incidence Risk Reduction 95 % C.l. p-Value Losartan Placebo Primary Composite Endpoint 43.5% 47.1% 16.1% 2.3% to 27.9% 0.022 Doubling of Serum Creatinine, ESRD and Death Occurring as a First Event Doubling of Serum Creatinine 21.6% 26.0% ESRD 8.5% 8.5% Death 13.4% 12.6% Overall Incidence of Doubling of Serum Creatinine, ESRD and Death Doubling of Serum Creatinine 21.6% 26.0% 25.3% 7.8% to 39.4% 0.006 ESRD 19.6% 25.5% 28.6% 11.5% to 42.4% 0.002 Death 21.0% 20.3% -1.7% -26.9% to 18.6% 0.884 The secondary endpoints of the study were change in proteinuria, change in the rate of progression of renal disease, and the composite of morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular causes (hospitalization for heart failure, myocardial infarction, revascularization, stroke, hospitalization for unstable angina, or cardiovascular death). Compared with placebo, losartan potassium tablets significantly reduced proteinuria by an average of 34%, an effect that was evident within 3 months of starting therapy, and significantly reduced the rate of decline in glomerular filtration rate during the study by 13%, as measured by the reciprocal of the serum creatinine concentration. There was no significant difference in the incidence of the composite endpoint of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
The favorable effects of losartan potassium tablets were seen in patients also taking other anti-hypertensive medications (angiotensin II receptor antagonists and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors were not allowed), oral hypoglycemic agents and lipid-lowering agents.
For the primary endpoint and ESRD, the effects of losartan potassium tablets in patient subgroups defined by age, gender and race are shown in Table 4 below. Subgroup analyses can be difficult to interpret and it is not known whether these represent true differences or chance effects.
Table 4: Efficacy Outcomes within Demographic Subgroups Primary Composite Endpoint ESRD No. of
PatientsLosartan Potassium
Tablets Event Rate %Placebo Event
Rate %Hazard Ratio
(95% CI)Losartan Potassium Tablets
Event Rate %Placebo Event
Rate %Hazard Ratio
(95% CI)Overall Results 1513 43.5 47.1 0.839 (0.721, 0.977) 19.6 25.5 0.714 (0.576, 0.885) Age <65 years 1005 44.1 49.0 0.784 (0.653, 0.941) 21.1 28.5 0.670 (0.521, 0.863) ≥65 years 508 42.3 43.5 0.978 (0.749, 1.277) 16.5 19.6 0.847 (0.560, 1.281) Gender Female 557 47.8 54.1 0.762 (0.603, 0.962) 22.8 32.8 0.601 (0.436, 0.828) Male 956 40.9 43.3 0.892 (0.733, 1.085) 17.5 21.5 0.809 (0.605, 1.081) Race Asian 252 41.9 54.8 0.655 (0.453, 0.947) 18.8 27.4 0.625 (0.367, 1.066) Black 230 40.0 39.0 0.983 (0.647, 1.495) 17.6 21.0 0.831 (0.456, 1.516) Hispanic 277 55.0 54.0 1.003 (0.728, 1.380) 30.0 28.5 1.024 (0.661, 1.586) White 735 40.5 43.2 0.809 (0.645, 1.013) 16.2 23.9 0.596 (0.427, 0.831)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
Hypertension
Losartan potassium tablets are indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, including diuretics.
Hypertensive Patients with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Losartan potassium tablets are indicated to reduce the risk of stroke in patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy, but there is evidence that this benefit does not apply to Black patients. (See PRECAUTIONS, Race and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, Reduction in the Risk of Stroke, Race.)
Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Losartan potassium tablets are indicated for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy with an elevated serum creatinine and proteinuria (urinary albumin to creatinine ratio ≥300 mg/g) in patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of hypertension. In this population, losartan potassium tablets reduce the rate of progression of nephropathy as measured by the occurrence of doubling of serum creatinine or end stage renal disease (need for dialysis or renal transplantation) (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
Losartan potassium tablets are contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to any component of this product.
Do not co-administer aliskiren with losartan potassium tablets in patients with diabetes.
WARNINGS
-
Fetal Toxicity
Pregnancy Category D
Use of drugs that act on the renin-angiotensin system during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. Resulting oligohydramnios can be associated with fetal lung hypoplasia and skeletal deformations. Potential neonatal adverse effects include skull hypoplasia, anuria, hypotension, renal failure, and death. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue losartan potassium tablets as soon as possible. These adverse outcomes are usually associated with the use of these drugs in the second and third trimester of pregnancy. Most epidemiologic studies examining fetal abnormalities after exposure to antihypertensive use in the first trimester have not distinguished drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system from other antihypertensive agents. Appropriate management of maternal hypertension during pregnancy is important to optimize outcomes for both mother and fetus.
In the unusual case that there is no appropriate alternative to therapy with drugs affecting the rennin-angiotensin system for a particular patient, apprise the mother of the potential risk to the fetus. Perform serial ultrasound examinations to assess the intra-amniotic environment.
If oligohydramnios is observed, discontinue losartan potassium tablets, unless it is considered life-saving for the mother. Fetal testing may be appropriate, based on the week of pregnancy. Patients and physicians should be aware, however, that oligohydramnios may not appear until after the fetus has sustained irreversible injury.
Closely observe infants with histories of in utero exposure to losartan potassium tablets for hypotension, oliguria, and hyperkalemia (see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use).
Losartan potassium has been shown to produce adverse effects in rat fetuses and neonates, including decreased body weight, delayed physical and behavioral development, mortality and renal toxicity. With the exception of neonatal weight gain (which was affected at doses as low as 10 mg/kg/day), doses associated with these effects exceeded 25 mg/kg/day (approximately three times the maximum recommended human dose of 100 mg on a mg/m2 basis). These findings are attributed to drug exposure in late gestation and during lactation. Significant levels of losartan and its active metabolite were shown to be present in rat fetal plasma during late gestation and in rat milk.
Hypotension ─ Volume-Depleted Patients
In patients who are intravascularly volume-depleted (e.g., those treated with diuretics), symptomatic hypotension may occur after initiation of therapy with losartan potassium tablets. These conditions should be corrected prior to administration of losartan potassium tablets, or a lower starting dose should be used (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
PRECAUTIONS
-
General
Hypersensitivity: Angioedema. See ADVERSE REACTIONS, Postmarketing Experience.
Impaired Hepatic Function
Based on pharmacokinetic data which demonstrate significantly increased plasma concentrations of losartan in cirrhotic patients, a lower dose should be considered for patients with impaired liver function (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics).
Impaired Renal Function
As a consequence of inhibiting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, changes in renal function have been reported in susceptible individuals treated with losartan potassium tablets; in some patients, these changes in renal function were reversible upon discontinuation of therapy.
In patients whose renal function may depend on the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (e.g., patients with severe congestive heart failure), treatment with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors has been associated with oliguria and/or progressive azotemia and (rarely) with acute renal failure and/or death. Similar outcomes have been reported with losartan potassium tablets.
In studies of ACE inhibitors in patients with unilateral or bilateral renal artery stenosis, increases in serum creatinine or blood urea nitrogen (BUN) have been reported. Similar effects have been reported with losartan potassium tablets; in some patients, these effects were reversible upon discontinuation of therapy.
Electrolyte Imbalance
Electrolyte imbalances are common in patients with renal impairment, with or without diabetes, and should be addressed. In a clinical study conducted in type 2 diabetic patients with proteinuria, the incidence of hyperkalemia was higher in the group treated with losartan potassium tablets as compared to the placebo group; however, few patients discontinued therapy due to hyperkalemia (see ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Information for Patients
Pregnancy: Female patients of childbearing age should be told about the consequences of exposure to losartan potassium tablets during pregnancy. Discuss treatment options with women planning to become pregnant. Patients should be asked to report pregnancies to their physicians as soon as possible.
Potassium Supplements: A patient receiving losartan potassium tablets should be told not to use potassium supplements or salt substitutes containing potassium without consulting the prescribing physician (see PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
Drug Interactions
No significant drug-drug pharmacokinetic interactions have been found in interaction studies with hydrochlorothiazide, digoxin, warfarin, cimetidine and phenobarbital. Rifampin, an inducer of drug metabolism, decreased the concentrations of losartan and its active metabolite. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Drug Interactions.) In humans, two inhibitors of P450 3A4 have been studied. Ketoconazole did not affect the conversion of losartan to the active metabolite after intravenous administration of losartan, and erythromycin had no clinically significant effect after oral administration. Fluconazole, an inhibitor of P450 2C9, decreased active metabolite concentration and increased losartan concentration. The pharmacodynamic consequences of concomitant use of losartan and inhibitors of P450 2C9 have not been examined. Subjects who do not metabolize losartan to active metabolite have been shown to have a specific, rare defect in cytochrome P450 2C9. These data suggest that the conversion of losartan to its active metabolite is mediated primarily by P450 2C9 and not P450 3A4.
As with other drugs that block angiotensin II or its effects, concomitant use of potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride), potassium supplements, or salt substitutes containing potassium may lead to increases in serum potassium.
Lithium: Increases in serum lithium concentrations and lithium toxicity have been reported during concomitant administration of lithium with angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Monitor serum lithium levels during concomitant use.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Including Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors (COX-2 Inhibitors): In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or with compromised renal function, co-administration of NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors, with angiotensin II receptor antagonists (including losartan) may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. These effects are usually reversible. Monitor renal function periodically in patients receiving losartan and NSAID therapy.
The antihypertensive effect of angiotensin II receptor antagonists, including losartan, may be attenuated by NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors.
Dual Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS): Dual blockade of the RAS with angiotensin receptor blockers, ACE inhibitors, or aliskiren is associated with increased risks of hypotension, syncope, hyperkalemia, and changes in renal function (including acute renal failure) compared to monotherapy. The Veterans Affairs Nephropathy in Diabetes (VA NEPHRON-D) trial enrolled 1448 patients with type 2 diabetes, elevated urinary-albumin-to-creatinine ratio, and decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR 30 to 89.9 ml/min), randomized them to lisinopril or placebo on a background of losartan therapy and followed them for a median of 2.2 years. Patients receiving the combination of losartan and lisinopril did not obtain any additional benefit compared to monotherapy for the combined endpoint of decline in GFR, end stage renal disease, or death, but experienced an increased incidence of hyperkalemia and acute kidney injury compared with the monotherapy group.
Do not co-administer aliskiren with losartan potassium in patients with diabetes. Avoid use of aliskiren with losartan potassium in patients with renal impairment (GFR <60 ml/min).
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Losartan potassium was not carcinogenic when administered at maximally tolerated dosages to rats and mice for 105 and 92 weeks, respectively. Female rats given the highest dose (270 mg/kg/day) had a slightly higher incidence of pancreatic acinar adenoma. The maximally tolerated dosages (270 mg/kg/day in rats, 200 mg/kg/day in mice) provided systemic exposures for losartan and its pharmacologically active metabolite that were approximately 160- and 90-times (rats) and 30- and 15-times (mice) the exposure of a 50 kg human given 100 mg per day.
Losartan potassium was negative in the microbial mutagenesis and V-79 mammalian cell mutagenesis assays and in the in vitro alkaline elution and in vitro and in vivo chromosomal aberration assays. In addition, the active metabolite showed no evidence of genotoxicity in the microbial mutagenesis, in vitro alkaline elution, and in vitro chromosomal aberration assays.
Fertility and reproductive performance were not affected in studies with male rats given oral doses of losartan potassium up to approximately 150 mg/kg/day. The administration of toxic dosage levels in females (300/200 mg/kg/day) was associated with a significant (p<0.05) decrease in the number of corpora lutea/female, implants/female, and live fetuses/female at C-section. At 100 mg/kg/day only a decrease in the number of corpora lutea/female was observed. The relationship of these findings to drug-treatment is uncertain since there was no effect at these dosage levels on implants/pregnant female, percent post-implantation loss, or live animals/litter at parturition. In nonpregnant rats dosed at 135 mg/kg/day for 7 days, systemic exposure (AUCs) for losartan and its active metabolite were approximately 66 and 26 times the exposure achieved in man at the maximum recommended human daily dosage (100 mg).
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether losartan is excreted in human milk, but significant levels of losartan and its active metabolite were shown to be present in rat milk. Because of the potential for adverse effects on the nursing infant, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Neonates with a history of in utero exposure to losartan potassium tablets:
If oliguria or hypotension occurs, direct attention toward support of blood pressure and renal perfusion. Exchange transfusions or dialysis may be required as a means of reversing hypotension and/or substituting for disordered renal function.
Antihypertensive effects of losartan potassium tablets have been established in hypertensive pediatric patients aged 6 to 16 years. There are no data on the effect of losartan potassium tablets on blood pressure in pediatric patients under the age of 6 or in pediatric patients with glomerular filtration rate <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics, Special Populations and Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients receiving losartan potassium tablets in controlled clinical studies for hypertension, 391 patients (19%) were 65 years and over, while 37 patients (2%) were 75 years and over. In a controlled clinical study for renal protection in type 2 diabetic patients with proteinuria, 248 patients (33%) were 65 years and over. In a controlled clinical study for the reduction in the combined risk of cardiovascular death, stroke and myocardial infarction in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy, 2857 patients (62%) were 65 years and over, while 808 patients (18%) were 75 years and over. No overall differences in effectiveness or safety were observed between these patients and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Race
In the LIFE study, Black patients with hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy had a lower risk of stroke on atenolol than on losartan potassium tablets. Given the difficulty in interpreting subset differences in large trials, it cannot be known whether the observed difference is the result of chance. However, the LIFE study does not provide evidence that the benefits of losartan potassium tablets on reducing the risk of cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy apply to Black patients. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects; Reduction in the Risk of Stroke.)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Hypertension
Losartan potassium tablets have been evaluated for safety in more than 3300 adult patients treated for essential hypertension and 4058 patients/subjects overall. Over 1200 patients were treated for over 6 months and more than 800 for over one year. In general, treatment with losartan potassium tablets were well-tolerated. The overall incidence of adverse experiences reported with losartan potassium tablets were similar to placebo.
In controlled clinical trials, discontinuation of therapy due to clinical adverse experiences was required in 2.3 percent of patients treated with losartan potassium tablets and 3.7 percent of patients given placebo.
The following table of adverse events is based on four 6- to 12-week, placebo-controlled trials involving over 1000 patients on various doses (10-150 mg) of losartan and over 300 patients given placebo. All doses of losartan are grouped because none of the adverse events appeared to have a dose-related frequency. The adverse experiences reported in ≥1% of patients treated with losartan potassium tablets and more commonly than placebo are shown in the table below.
Table 5
Losartan
(n=1075)
Incidence %
Placebo
(n=334)
Incidence %
Musculoskeletal
Cramp, muscle
1
0
Pain, back
2
1
Pain, leg
1
0
Nervous System/Psychiatric
Dizziness
3
2
Respiratory
Congestion, nasal
2
1
Infection, upper respiratory
8
7
Sinusitis
1
0
The following adverse events were also reported at a rate of 1% or greater in patients treated with losartan, but were as, or more frequent, in the placebo group: asthenia/fatigue, edema/swelling, abdominal pain, chest pain, nausea, headache, pharyngitis, diarrhea, dyspepsia, myalgia, insomnia, cough, sinus disorder.
Adverse events occurred at about the same rates in men and women, older and younger patients, and Black and non-Black patients.
A patient with known hypersensitivity to aspirin and penicillin, when treated with losartan potassium tablets, was withdrawn from study due to swelling of the lips and eyelids and facial rash, reported as angioedema, which returned to normal 5 days after therapy was discontinued.
Superficial peeling of palms and hemolysis were reported in one subject.
In addition to the adverse events above, potentially important events that occurred in at least two patients/subjects exposed to losartan or other adverse events that occurred in <1% of patients in clinical studies are listed below. It cannot be determined whether these events were causally related to losartan : Body as a Whole: facial edema, fever, orthostatic effects, syncope; Cardiovascular: angina pectoris, second degree AV block, CVA, hypotension, myocardial infarction, arrhythmias including atrial fibrillation, palpitation, sinus bradycardia, tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation; Digestive: anorexia, constipation, dental pain, dry mouth, flatulence, gastritis, vomiting; Hematologic: anemia; Metabolic: gout; Musculoskeletal: arm pain, hip pain, joint swelling, knee pain, musculoskeletal pain, shoulder pain, stiffness, arthralgia, arthritis, fibromyalgia, muscle weakness; Nervous System/Psychiatric: anxiety, anxiety disorder, ataxia, confusion, depression, dream abnormality, hypesthesia, decreased libido, memory impairment, migraine, nervousness, paresthesia, peripheral neuropathy, panic disorder, sleep disorder, somnolence, tremor, vertigo; Respiratory: dyspnea, bronchitis, pharyngeal discomfort, epistaxis, rhinitis, respiratory congestion; Skin: alopecia, dermatitis, dry skin, ecchymosis, erythema, flushing, photosensitivity, pruritus, rash, sweating, urticaria; Special Senses: blurred vision, burning/stinging in the eye, conjunctivitis, taste perversion, tinnitus, decrease in visual acuity; Urogenital: impotence, nocturia, urinary frequency, urinary tract infection.
Persistent dry cough (with an incidence of a few percent) has been associated with ACE-inhibitor use and in practice can be a cause of discontinuation of ACE-inhibitor therapy. Two prospective, parallel-group, double-blind, randomized, controlled trials were conducted to assess the effects of losartan on the incidence of cough in hypertensive patients who had experienced cough while receiving ACE-inhibitor therapy. Patients who had typical ACE-inhibitor cough when challenged with lisinopril, whose cough disappeared on placebo, were randomized to losartan 50 mg, lisinopril 20 mg, or either placebo (one study, n=97) or 25 mg hydrochlorothiazide (n=135). The double-blind treatment period lasted up to 8 weeks. The incidence of cough is shown below.
Table 6
* Demographics = (89% caucasian, 64% female)
† Demographics = (90% caucasian, 51% female)
Study 1* HCTZ
Losartan
Lisinopril
Cough
25%
17%
69%
Study 2† Placebo
Losartan
Lisinopril
Cough
35%
29%
62%
These studies demonstrate that the incidence of cough associated with losartan therapy, in a population that all had cough associated with ACE-inhibitor therapy, is similar to that associated with hydrochlorothiazide or placebo therapy.
Cases of cough, including positive re-challenges, have been reported with the use of losartan in postmarketing experience.
Pediatric Patients: No relevant differences between the adverse experience profile for pediatric patients and that previously reported for adult patients were identified.
Hypertensive Patients with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
In the LIFE study, adverse events with losartan potassium tablets were similar to those reported previously for patients with hypertension.
Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
In the RENAAL study involving 1513 patients treated with losartan potassium tablets or placebo, the overall incidences of reported adverse experiences were similar for the two groups. Losartan potassium tablets were generally well tolerated as evidenced by a similar incidence of discontinuations due to side effects compared to placebo (19% for losartan potassium tablets, 24% for placebo). The adverse experiences, regardless of drug relationship, reported with an incidence of ≥4% of patients treated with losartan potassium tablets and occurring more commonly than placebo, on a background of conventional antihypertensive therapy, are shown in the table below.
Table 7
Losartan and Conventional
Antihypertensive Therapy Incidence %
(n=751)
Placebo and Conventional
Antihypertensive Therapy Incidence %
(n=762)
Body as a Whole
Asthenia/Fatigue
14
10
Chest Pain
12
8
Fever
4
3
Infection
5
4
Influenza-like disease
10
9
Trauma
4
3
Cardiovascular
Hypotension
7
3
Orthostatic hypotension
4
1
Digestive
Diarrhea
15
10
Dyspepsia
4
3
Gastritis
5
4
Endocrine
Diabetic neuropathy
4
3
Diabetic vascular disease
10
9
Eyes, Ears, Nose and Throat
Cataract
7
5
Sinusitis
6
5
Hemic
Anemia
14
11
Metabolic and Nutrition
Hyperkalemia
7
3
Hypoglycemia
14
10
Weight gain
4
3
Musculoskeletal
Back pain
12
10
Leg pain
5
4
Knee pain
5
4
Muscular weakness
7
4
Nervous System
Hypesthesia
5
4
Respiratory
Bronchitis
10
9
Cough
11
10
Skin
Cellulitis
7
6
Urogenital
Urinary tract infection
16
13
Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported in postmarketing experience:
Digestive: Hepatitis (reported rarely).
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Malaise.
Hemic: Thrombocytopenia (reported rarely).
Hypersensitivity: Angioedema, including swelling of the larynx and glottis, causing airway obstruction and/or swelling of the face, lips, pharynx, and/or tongue has been reported rarely in patients treated with losartan; some of these patients previously experienced angioedema with other drugs including ACE inhibitors. Vasculitis, including Henoch-Sch nlein purpura, has been reported. Anaphylactic reactions have been reported.
Metabolic and Nutrition: Hyperkalemia, hyponatremia have been reported with losartan.
Musculoskeletal: Rare cases of rhabdomyolysis have been reported in patients receiving angiotensin II receptor blockers.
Nervous system disorders: Dysgeusia.
Respiratory: Dry cough (see above).
Skin: Erythroderma.
Laboratory Test Findings
In controlled clinical trials, clinically important changes in standard laboratory parameters were rarely associated with administration of losartan potassium tablets.
Creatinine, Blood Urea Nitrogen: Minor increases in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) or serum creatinine were observed in less than 0.1 percent of patients with essential hypertension treated with losartan potassium tablets alone (see PRECAUTIONS, Impaired Renal Function).
Hemoglobin and Hematocrit: Small decreases in hemoglobin and hematocrit (mean decreases of approximately 0.11 grams percent and 0.09 volume percent, respectively) occurred frequently in patients treated with losartan potassium tablets alone, but were rarely of clinical importance. No patients were discontinued due to anemia.
Liver Function Tests: Occasional elevations of liver enzymes and/or serum bilirubin have occurred. In patients with essential hypertension treated with losartan potassium tablets alone, one patient (<0.1%) was discontinued due to these laboratory adverse experiences.
OVERDOSAGE
-
Significant lethality was observed in mice and rats after oral administration of 1000 mg/kg and 2000 mg/kg, respectively, about 44 and 170 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis.
Limited data are available in regard to overdosage in humans. The most likely manifestation of overdosage would be hypotension and tachycardia; bradycardia could occur from parasympathetic (vagal) stimulation. If symptomatic hypotension should occur, supportive treatment should be instituted.
Neither losartan nor its active metabolite can be removed by hemodialysis.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
-
Adult Hypertensive Patients
Losartan potassium tablets may be administered with other antihypertensive agents, and with or without food.
Dosing must be individualized. The usual starting dose of losartan potassium tablets is 50 mg once daily, with 25 mg used in patients with possible depletion of intravascular volume (e.g., patients treated with diuretics) (see WARNINGS, Hypotension ─ Volume-Depleted Patients) and patients with a history of hepatic impairment (see PRECAUTIONS, General). Losartan potassium tablets can be administered once or twice daily with total daily doses ranging from 25 mg to 100 mg.
If the antihypertensive effect measured at trough using once-a-day dosing is inadequate, a twice-a-day regimen at the same total daily dose or an increase in dose may give a more satisfactory response. The effect of losartan is substantially present within one week but in some studies the maximal effect occurred in 3-6 weeks (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, Hypertension).
If blood pressure is not controlled by losartan potassium tablets alone, a low dose of a diuretic may be added. Hydrochlorothiazide has been shown to have an additive effect (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, Hypertension).
No initial dosage adjustment is necessary for elderly patients or for patients with renal impairment, including patients on dialysis.
Pediatric Hypertensive Patients greater than or equal to 6 years of age
The usual recommended starting dose is 0.7 mg/kg once daily (up to 50 mg total) administered as a tablet or a suspension (see Preparation of Suspension). Dosage should be adjusted according to blood pressure response. Doses above 1.4 mg/kg (or in excess of 100 mg) daily have not been studied in pediatric patients (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics, Special Populations and Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, and WARNINGS, Hypotension ─ Volume-Depleted Patients.)
Losartan potassium tablets are not recommended in pediatric patients less than 6 years of age or in pediatric patients with glomerular filtration rate less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacokinetics, Special Populations, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, and PRECAUTIONS).
Preparation of Suspension (for 200 mL of a 2.5 mg/mL suspension)
Add 10 mL of Purified Water USP to an 8 ounce (240 mL) amber polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottle containing ten 50 mg losartan potassium tablets. Immediately shake for at least 2 minutes. Let the concentrate stand for 1 hour and then shake for 1 minute to disperse the tablet contents. Separately prepare a 50/50 volumetric mixture of Ora-PlusTM and Ora-Sweet SFTM. Add 190 mL of the 50/50 Ora-PlusTM/Ora-Sweet SFTM mixture to the tablet and water slurry in the PET bottle and shake for 1 minute to disperse the ingredients. The suspension should be refrigerated at 2-8°C (36-46°F) and can be stored for up to 4 weeks. Shake the suspension prior to each use and return promptly to the refrigerator.
Hypertensive Patients with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
The usual starting dose is 50 mg of losartan potassium tablets once daily. Hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg daily should be added and/or the dose of losartan potassium tablets should be increased to 100 mg once daily followed by an increase in hydrochlorothiazide to 25 mg once daily based on blood pressure response (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, Reduction in the Risk of Stroke).
Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
The usual starting dose is 50 mg once daily. The dose should be increased to 100 mg once daily based on blood pressure response (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Pharmacodynamics and Clinical Effects, Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients). Losartan potassium tablets may be administered with insulin and other commonly used hypoglycemic agents (e.g., sulfonylureas, glitazones and glucosidase inhibitors).
HOW SUPPLIED
-
Losartan potassium tablets, USP 25 mg, are white to off-white colored, oval shaped, biconvex, film coated tablets debossed with "25" on one side and "113" on the other side.
Bottles of 90 NDC 13668-113-90 Bottles of 1000 NDC 13668-113-10 100 Unit Dose Tablets NDC 13668-113-74 Losartan potassium tablets, USP 50 mg, are white to off-white colored, oval shaped, biconvex, film coated tablets debossed with "114" on one side and breakline on the other side.
Bottles of 30 NDC 13668-409-30 Bottles of 90 NDC 13668-409-90 Bottles of 1000 NDC 13668-409-10 100 Unit Dose Tablets NDC 13668-409-74 Losartan potassium tablets, USP 100 mg, are white to off-white colored, oval shaped, biconvex, film coated tablets debossed with "100" on one side and "115" on the other side.
Bottles of 30 NDC 13668-115-30 Bottles of 90 NDC 13668-115-90 Bottles of 1000 NDC 13668-115-10 100 Unit Dose Tablets NDC 13668-115-74 Storage
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F). [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep container tightly closed. Protect from light.
Manufactured by:TORRENT PHARMACEUTICALS LTD., Indrad-382 721, Dist. Mehsana, INDIA.
For:
TORRENT PHARMA INC., 150 Allen Road, Suite 102, Basking Ridge, NJ 07920.
8051805 Revised October 2014
Patient Information
-
Losartan Potassium (loe SAR tan poe TASS ee um) Tablets, USP
25mg, 50mg, 100mg
Rx only
Read the Patient Information that comes with losartan potassium tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your condition and treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about losartan potassium tablets?
- Losartan potassium tablets can cause harm or death to an unborn baby.
- Talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your blood pressure if you plan to become pregnant.
- If you get pregnant while taking losartan potassium tablets, tell your doctor right away.
What are losartan potassium tablets?
Losartan potassium tablets are prescription medicine called an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB). It is used:
- alone or with other blood pressure medicines to lower high blood pressure (hypertension).
- to lower the chance of stroke in patients with high blood pressure and a heart problem called left ventricular hypertrophy. Losartan potassium tablets may not help Black patients with this problem.
- to slow the worsening of diabetic kidney disease (nephropathy) in patients with type 2 diabetes who have or had high blood pressure.
Losartan potassium tablets have not been studied in children less than 6 years old or in children with certain kidney problems.
High Blood Pressure (hypertension). Blood pressure is the force in your blood vessels when your heart beats and when your heart rests. You have high blood pressure when the force is too much. Losartan potassium tablets can help your blood vessels relax so your blood pressure is lower.
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) is an enlargement of the walls of the left chamber of the heart (the heart's main pumping chamber). LVH can happen from several things. High blood pressure is the most common cause of LVH.
Type 2 Diabetes with Nephropathy. Type 2 diabetes is a type of diabetes that happens mainly in adults. If you have diabetic nephropathy it means that your kidneys do not work properly because of damage from the diabetes.
Who should not take losartan potassium tablets?
- Do not take losartan potassium tablets if you are allergic to any of the ingredients in losartan potassium tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in losartan potassium tablets.
- Do not take losartan potassium tablets if you have diabetes and are taking a medicine called aliskiren to reduce blood pressure.
What should I tell my doctor before taking losartan potassium tablets?
Tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions including if you:
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. See "What is the most important information I should know about losartan potassium tablets?"
- are breastfeeding. It is not known if losartan potassium tablets passes into your breast milk. You should choose either to take losartan potassium tablets or breastfeed, but not both.
- are vomiting a lot or having a lot of diarrhea
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non- prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Losartan potassium tablets and certain other medicines may interact with each other.
Especially tell your doctor if you are taking:
- potassium supplements
- salt substitutes containing potassium
- water pills (diuretics)
- lithium (a medicine used to treat a certain kind of depression)
- medicines used to treat pain and arthritis, called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including COX-2 inhibitors
- other medicines to reduce blood pressure
How should I take losartan potassium tablets?
- Take losartan potassium tablets exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor may change your dose if needed.
- Losartan potassium tablets can be taken with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is close to your next dose, do not take the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time.
- If you take too much losartan potassium tablets, call your doctor or Poison Control Center, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of losartan potassium tablets?
Losartan potassium tablets may cause the following side effects that may be serious:
- Injury or death of unborn babies. See "What is the most important information I should know about losartan potassium tablets?"
- Allergic reaction. Symptoms of an allergic reaction are swelling of the face, lips, throat or tongue. Get emergency medical help right away and stop taking losartan potassium tablets.
- Low blood pressure (hypotension). Low blood pressure may cause you to feel faint or dizzy. Lie down if you feel faint or dizzy. Call your doctor right away.
- For people who already have kidney problems, you may see a worsening in how well your kidneys work. Call your doctor if you get swelling in your feet, ankles, or hands, or unexplained weight gain.
The most common side effects of losartan potassium tablets in people with high blood pressure are:
- "colds" (upper respiratory infection)
- dizziness
- stuffy nose
- back pain
The most common side effects of losartan potassium tablets in people with type 2 diabetes with diabetic kidney disease are:
- diarrhea
- tiredness
- low blood sugar
- chest pain
- high blood potassium
- low blood pressure
Tell your doctor if you get any side effect that bothers you or that won’t go away.
This is not a complete list of side effects. For a complete list, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How do I store losartan potassium tablets?
- Store losartan potassium tablets at 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
- Keep losartan potassium tablets in a tightly closed container that protects the medicine from light.
- Keep losartan potassium tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about losartan potassium tablets
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use losartan potassium tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give losartan potassium tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about losartan potassium tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about losartan potassium tablets that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in losartan potassium tablets?
Active ingredients: losartan potassium, USP
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, talc and titanium dioxide.
Trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
This medication guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.

