GLUCAGEN- glucagon hydrochloride
Bedford Laboratories
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use GlucaGen safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GlucaGen.
GlucaGen® (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection) Initial U.S. Approval: 1998 INDICATIONS AND USAGEDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONTreatment of severe hypoglycemia (GlucaGen HypoKit)
Use as a diagnostic aid (GlucaGen Diagnostic Kit and GlucaGen 10-Pack)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSAdverse reactions seen with GlucaGen are:
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novo Nordisk Inc. at 1-800-727-6500 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSSee 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 12/2014 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Treatment of severe hypoglycemia
GlucaGen is used to treat severe hypoglycemic (low blood sugar) reactions which may occur in patients with diabetes mellitus treated with insulin. Because GlucaGen depletes glycogen stores, the patient should be given supplemental carbohydrates as soon as he/she awakens and is able to swallow, especially children or adolescents. Medical evaluation is recommended for all patients who experience severe hypoglycemia.
1.2 Use as a diagnostic aid
GlucaGen is indicated for use during radiologic examinations to temporarily inhibit movement of the gastrointestinal tract. Glucagon is as effective for this examination as are the anticholinergic drugs. However, the addition of the anticholinergic agent may result in increased side effects. After the end of the diagnostic procedure, give oral carbohydrates to patients who have been fasting, if this is compatible with the diagnostic procedure applied.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For GlucaGen HypoKit:
2.1 Treatment of severe hypoglycemia
- 1.
- Using the supplied prefilled syringe, carefully insert the needle through the rubber stopper of the vial containing GlucaGen powder and inject all the liquid from the syringe into the vial.
- 2.
- Shake the vial gently until the powder is completely dissolved and no particles remain in the fluid. The reconstituted fluid should be clear and of water-like consistency.
- 3.
- The reconstituted GlucaGen gives a concentration of approximately 1 mg/mL glucagon.
- 4.
- The reconstituted GlucaGen should be used immediately after reconstitution.
- 5.
- Inject 1 mL (adults and children, weighing more than 55 lbs (25 kg)) or 0.5 mL (children weighing less than 55 lbs (25 kg)) subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intravenously. If the weight is not known: children younger than 6 years should be given a 0.5 mL and children 6 years and older should be given 1 mL.
- 6.
- Discard any unused portion.
- 7.
- Emergency assistance should be sought immediately after subcutaneous or intramuscular injection of glucagon.
- 8.
- The glucagon injection may be repeated using a new kit while waiting for emergency assistance.
- 9.
- Intravenous glucose MUST be administered if the patient fails to respond to glucagon.
- 10.
- When the patient has responded to the treatment, give oral carbohydrates to restore the liver glycogen and prevent recurrence of hypoglycemia.
For GlucaGen Diagnostic Kit and the GlucaGen 10-pack:
2.2 Use as a diagnostic aid
- 1.
- GlucaGen should be reconstituted with 1 mL of Sterile Water for Reconstitution (if supplied) or 1 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP. Using a syringe, withdraw all of the Sterile Water for Reconstitution (if supplied) or 1 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP and inject into the GlucaGen vial.
- 2.
- Shake the vial gently until the powder is completely dissolved and no particles remain in the fluid. The reconstituted fluid should be clear and of water-like consistency.
- 3.
- The reconstituted GlucaGen gives a concentration of approximately 1 mg/mL glucagon.
- 4.
- The reconstituted GlucaGen should be used immediately after reconstitution.
- 5.
- GlucaGen must be administered by medical personnel.
- 6.
- Discard any unused portion.
- 7.
- Onset of action after an injection will depend on the organ under examination and route of administration [see Pharmacodynamics (12.2)].
- 8.
- The usual diagnostic dose for relaxation of the stomach, duodenal bulb, duodenum, and small bowel is 0.2 mg to 0.5 mg given intravenously or 1 mg given intramuscularly; the usual dose to relax the colon is 0.5 mg to 0.75 mg intravenously and 1 mg to 2 mg intramuscularly [see Pharmacodynamics (12.2)].
- 9.
- After the end of the diagnostic procedure, give oral carbohydrates to patients who have been fasting, if this is compatible with the diagnostic procedure applied.
The GlucaGen Diagnostic Kit and the GlucaGen 10-pack presentations are intended only for use by healthcare providers as a diagnostic aid. The GlucaGen Diagnostic Kit and the GlucaGen 10-pack presentations are not intended for use by patients to treat severe hypoglycemia because they are not packaged with a syringe and diluent necessary for rapid preparation and administration during an emergency outside of a healthcare facility.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
GlucaGen is supplied in a vial, alone, or accompanied by Sterile Water for Reconstitution (1 mL) also in a vial (10 pack or diagnostic kit). It is also supplied as GlucaGen HypoKit®, a presentation with a disposable prefilled syringe containing 1 mL Sterile Water for Reconstitution. When the glucagon powder is reconstituted with Sterile Water for Reconstitution (if supplied) or with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, it forms a solution of 1 mg/mL (1 unit/mL) glucagon for subcutaneous, intramuscular, or intravenous injection.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
GlucaGen is contraindicated in patients with:
- •
- Known hypersensitivity to glucagon, lactose or any other constituent in GlucaGen
- •
- Pheochromocytoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- •
- Insulinoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Pheochromocytoma
Glucagon is contraindicated in patients with pheochromocytoma because Glucagon may stimulate the release of catecholamines from the tumor. If the patient develops a dramatic increase in blood pressure, 5 to 10 mg of phentolamine mesylate has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure for the short time that control would be needed.
5.2 Insulinoma and Glucagonoma
GlucaGen should be administered cautiously to patients suspected of having insulinoma or glucagonoma. In patients with insulinoma, intravenous administration of glucagon may produce an initial increase in blood glucose; however, glucagon administration may directly or indirectly (through an initial rise in blood glucose) stimulate exaggerated insulin release from an insulinoma. A patient developing symptoms of hypoglycemia after a dose of glucagon should be given glucose orally or intravenously, whichever is most appropriate. Caution should also be observed in administering GlucaGen to patients with glucagonoma.
5.3 Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions may occur and include generalized rash, and in some cases anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties, and hypotension. The anaphylactic reactions have generally occurred in association with endoscopic examination during which patients often received other agents including contrast media and local anesthetics. The patients should be given standard treatment for anaphylaxis including an injection of epinephrine if they encounter respiratory difficulties after GlucaGen injection.
5.4 Glycogen Stores and Hypoglycemia
In order for GlucaGen treatment to reverse hypoglycemia, adequate amounts of glucose must be stored in the liver (as glycogen). Therefore, GlucaGen should be used with caution in patients with conditions such as prolonged fasting, starvation, adrenal insufficiency or chronic hypoglycemia because these conditions result in low levels of releasable glucose in the liver and an inadequate reversal of hypoglycemia by GlucaGen treatment.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Side effects may include nausea and vomiting at doses above 1 mg or with rapid injection. Hypotension has been reported up to 2 hours after administration in patients receiving GlucaGen as premedication for upper GI endoscopy procedures. Glucagon exerts positive inotropic and chronotropic effects and may, therefore, cause tachycardia and hypertension. Adverse reactions indicating toxicity of GlucaGen have not been reported. A temporary increase in both blood pressure and pulse rate may occur following the administration of glucagon. Patients taking beta-blockers might be expected to have a greater increase in both pulse and blood pressure, an increase of which will be temporary because of glucagon’s short half-life [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. The increase in blood pressure and pulse rate may require therapy in patients with pheochromocytoma or coronary artery disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Anaphylactic reactions may occur in some cases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of GlucaGen. Because these adverse reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency.
|
Treatment of severe hypoglycemia |
|
|
Frequency (%) |
Adverse Reaction |
|
< 10 |
Nausea |
|
< 1 |
Vomiting |
|
Use as a diagnostic aid |
|
|
< 10 |
Nausea |
|
< 1 |
Vomiting |
|
< 1 |
Hypoglycemia |
|
<1 |
Hypoglycemic coma |
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Beta-blockers
Patients taking beta-blockers might be expected to have a greater increase in both pulse and blood pressure, an increase of which will be temporary because of glucagon’s short half-life. The increase in blood pressure and pulse rate may require therapy in patients with pheochromocytoma or coronary artery disease.
7.2 Indomethacin
When used with indomethacin, glucagon may lose its ability to raise blood glucose or may even produce hypoglycemia. Therefore, caution should be exercised for patients taking indomethacin when glucagon will be administered.
7.3 Anticholinergic Drugs
Coadministration with an anticholinergic drug is not recommended due to increased gastrointestinal side effects.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B. Reproduction studies were performed in rats and rabbits at GlucaGen doses of 0.4, 2.0, and 10 mg/kg. These doses represent exposures of up to 100 and 200 times the human dose based on mg/m2 for rats and rabbits, respectively, and revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Glucagon does not cross the human placenta barrier.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when GlucaGen is administered to a nursing woman. No clinical studies have been performed in nursing mothers, however, GlucaGen is a peptide and intact glucagon is not absorbed from the GI tract. Therefore, even if the infant ingested glucagon it would be unlikely to have any effect on the infant. Additionally, GlucaGen has a short plasma half-life thus limiting amounts available to the child. Glucagon does not cross the human placental barrier.
10 OVERDOSAGE
No reports of overdosage with GlucaGen have been reported. If overdosage occurs, the patient may experience nausea, vomiting, inhibition of GI tract motility, increase in blood pressure and pulse rate. In case of suspected overdosing, the serum potassium may decrease and should be monitored and corrected if needed. If the patient develops a dramatic increase in blood pressure, phentolamine mesylate has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure for the short time that control would be needed.
11 DESCRIPTION
GlucaGen (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection) is an antihypoglycemic agent and a gastrointestinal motility inhibitor. It is produced by expression of recombinant DNA in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae vector with subsequent purification. The chemical structure of the glucagon in GlucaGen is identical to human glucagon and to glucagon extracted from beef and pork pancreas. Glucagon with the empirical formula of C153H225N43O49S, and a molecular weight of 3483, is a single-chain polypeptide containing 29 amino acid residues. The structure of glucagon is:
GlucaGen is a sterile, lyophilized white powder in a 2 mL vial. The reconstituted solution contains glucagon as hydrochloride 1 mg/mL (1 unit/mL) and lactose monohydrate (107 mg). GlucaGen is supplied at pH 2.5-3.5 and is soluble in water.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Antihypoglycemic Action: Glucagon induces liver glycogen breakdown, releasing glucose from the liver. Hepatic stores of glycogen are necessary for glucagon to produce an antihypoglycemic effect.
Gastrointestinal Motility Inhibition: Extra hepatic effects of glucagon include relaxation of the smooth muscle of the stomach, duodenum, small bowel, and colon.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
For the treatment of severe hypoglycemia:
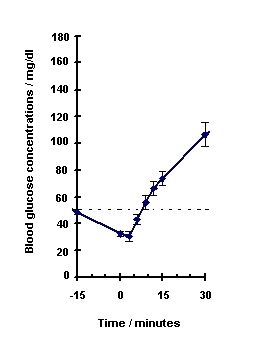
Blood glucose concentration rises within 10 minutes of injection and maximal concentrations are attained at approximately 30 minutes after injection (see Figure 1). The duration of hyperglycemic action after intravenous or intramuscular injection is 60 – 90 minutes.
Figure 1. Recovery from Insulin Induced Hypoglycemia (mean blood glucose) After Intramuscular Injection of 1 mg GlucaGen in Type I Diabetic Men
For use as a diagnostic aid:
|
||||
|
Route of Administration |
Dose* |
Time of Maximal Glucose Concentration |
Time of Onset of Action for GI Smooth Muscle Relaxation |
Duration of Smooth Muscle Relaxation† |
|
IV |
0.25-0.5 mg (0.25-0.5 units) |
5-20 minutes |
45 seconds |
9-17 minutes |
|
2 mg (2 units) |
5-20 minutes |
45 seconds |
22-25 minutes |
|
|
IM |
1 mg (1 unit) |
30 minutes |
8-10 minutes |
12-27 minutes |
|
2 mg (2 units) |
30 minutes |
4-7 minutes |
21-32 minutes |
|
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Intramuscular injection of 1 mg GlucaGen resulted in a mean Cmax (CV%) of 1686 pg/mL (43%) and median Tmax of 12.5 minutes. The mean apparent half-life of 45 minutes after intramuscular injection probably reflects prolonged absorption from the injection site. Glucagon is degraded in the liver, kidney, and plasma.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been performed. Several studies have been conducted to evaluate the mutagenic potential of glucagon. The mutagenic potential tested in the Ames and human lymphocyte assays, was borderline positive under certain conditions for both glucagon (pancreatic) and glucagon (rDNA) origin. In vivo, very high doses (100 and 200 mg/kg) of glucagon (both origins) gave a slightly higher incidence of micronucleus formation in male mice but there was no effect in females. The weight of evidence indicates that GlucaGen is not different from glucagon pancreatic origin and does not pose a genotoxic risk to humans. GlucaGen (rDNA origin) was not tested in animal fertility studies. Studies in rats have shown that pancreatic glucagon does not cause impaired fertility.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
GlucaGen is supplied as a sterile, lyophilized white powder in a vial, alone, or accompanied by Sterile Water for Reconstitution also in a vial (Diagnostic Kit or 10-pack). It is also supplied as GlucaGen HypoKit with a disposable prefilled syringe containing Sterile Water for Reconstitution.
GlucaGen HypoKit includes:
1 vial containing 1 mg (1 unit) GlucaGen (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection)
1 disposable syringe containing 1 mL Sterile Water for Reconstitution
NDC 0169-7065-15
GlucaGen Diagnostic Kit (NDC 0597-0260-10) includes:
1 vial containing 1 mg (1 unit) GlucaGen(glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection)
NDC 0597-0053-01
1 vial containing 1 mL Sterile Water for Reconstitution
NDC 0597-0265-94
GlucaGen Diagnostic Kit is also available as (NDC 55390-004-01) and includes:
1 vial containing 1 mg (1 unit) GlucaGen(glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection)
NDC 55390-004-01
1 vial containing 1 mL Sterile Water for Reconstitution
GlucaGen HypoKit (Two-Pack) includes: 2 packs of GlucaGen HypoKit,
Each HypoKit contains:
1 vial containing 1 mg (1 unit) GlucaGen (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection)
1 disposable syringe containing 1 mL Sterile Water for Reconstitution
NDC 0169-7065-21
The GlucaGen 10-pack includes:
10 vials, each containing 1 mg (1 unit) GlucaGen (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection)
NDC 55390-004-10
NDC 0597-0053-45
16.2 Recommended Storage
Before Reconstitution:
The GlucaGen package may be stored up to 24 months at controlled room temperature 20o to 25o C (68o to 77o F) prior to reconstitution. Do not freeze. Keep in the original package to protect from light. GlucaGen should not be used after the expiry date on the vials.
After Reconstitution:
Reconstituted GlucaGen should be used immediately. Discard any unused portion. If the solution shows any sign of gel formation or particles, it should be discarded.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
[See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Instructions for Emergency Use).]
17.1 Physician Instructions
Refer patients and family members to the FDA-approved patient labeling for instructions describing the method of preparing and injecting GlucaGen. Advise the patient and family members to become familiar with the technique of preparing glucagon before an emergency arises. Instruct patients to use 1 mg for adults or ½ the adult dose (0.5 mg) for children weighing less than 55 lb (25 kg). To prevent severe hypoglycemia, patients and family members should be informed of the symptoms of mild hypoglycemia and how to treat it appropriately. Family members should be informed to arouse the patient as quickly as possible because prolonged hypoglycemia may result in damage to the central nervous system. Patients should be advised to inform their physician when hypoglycemic reactions occur so that the treatment regimen may be adjusted if necessary.
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed. After diagnostic procedures, hypoglycemia has been reported infrequently. The patient’s ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycemia. This may present a risk in situations where these abilities are especially important, such as driving or operating machinery. Therefore, these activities should be avoided until the patient has had a meal with oral carbohydrates.
Date of issue: December 12, 2014
Version: 6
GlucaGen® and HypoKit® are registered trademarks of Novo Nordisk A/S
© 1998-2014 Novo Nordisk
For information contact:
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Ridgefield, CT 06877
1-800-243-0127
Manufactured for:
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Ridgefield, CT 06877
By:
Novo Nordisk A/S
2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - GlucaGen diagnostic kit
NDC 55390-004-01
GlucaGen®
[glucagon (rDNA origin) for injection]
1 mg per vial
For intramuscular or intravenous injection
GlucaGen® should be reconstituted
with Sterile Water for Reconstitution
immediately before use
Single use only. Discard unused portion.
Protect from Light.
See package insert for complete product
information.
FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE ONLY - NOT INTENDED FOR
USE BY PATIENTS TO TREAT SEVERE
HYPOGLYCEMIA
Rx ONLY
BEDFORD
Laboratories™
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - GlucaGen diagnostic kit - (10 Pack)
NDC 55390-004-10
10 vials each containing 1 mg per vial
GlucaGen®
[glucagon (rDNA origin) for injection]
1 mg per vial
For intramuscular or intravenous injection
Protect from Light
FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE ONLY - NOT INTENDED FOR
USE BY PATIENTS TO TREAT SEVERE HYPOGLYCEMIA
Rx ONLY
BEDFORD
Laboratories™
| GLUCAGEN
glucagon hydrochloride kit |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Bedford Laboratories (884528407) |
| Registrant - Novo Nordisk (622920320) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Novo Nordisk A/S | 306711800 | MANUFACTURE(55390-004) | |