DEXTROSE- dextrose monohydrate injection, solution
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DEXTROSE INJECTION 70% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DEXTROSE INJECTION 70%.
DEXTROSE injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 1940 INDICATIONS AND USAGEDextrose Injection is indicated as a source of calories when mixed with amino acids or other compatible intravenous fluids for patients requiring parenteral nutrition when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient or contraindicated. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSInjection: 70% (0.7 grams/mL), 70 grams of dextrose hydrous per 100 mL in a single-dose, partial-fill flexible container with 500 mL fill volume in 1000 mL flexible container. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSSevere dehydration. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSThe most common adverse reactions are, hyperglycemia, hypersensitivity reactions, infection both systemic and at the injection site, and vein thrombosis or phlebitis. (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Baxter Healthcare at 1-866-888-2472 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 3/2018 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Dextrose Injection is indicated as source of calories and fluid replenishment when mixed with amino acids or other compatible intravenous fluids for patients requiring parenteral nutrition when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient or contraindicated.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Preparation Prior to Administration
Prior to administration, Dextrose Injection must be diluted with other compatible intravenous fluids or used as an admixture with amino acids. It is not for direct intravenous infusion.
- •
- Do not remove from overpouch until ready to use. Tear protective foil overwrap across top at slit and remove solution container. Small amounts of moisture may be found on the solution container from water permeating from inside the container. The amount of permeated water is insufficient to affect the solution significantly. If larger amounts of water are found, the container should be checked for tears or leaks.
- •
- Inspect the container prior to activation. Some opacity of the plastic due to moisture absorption during the sterilization process may be observed. This is normal and does not affect the solution quality or safety. The opacity will diminish gradually. Evaluate the following:
- •
- If the outlet port protector is damaged, detached, or not present, discard container as solution path sterility may be impaired.
- •
- Check for minute leaks by separately squeezing the inner bag firmly. If leaks are found, discard solution as sterility may be impaired.
- •
- Additives can be introduced to the container; however, some additives may be incompatible. Evaluate all additions to the plastic container for compatibility and stability of the resulting preparation. Consult with a pharmacist, if available.
- •
- Activate chambers of bag prior to introduction of additives. Supplemental medication may be added with a 19 to 22 gauge needle through the medication port using aseptic technique. Mix thoroughly when additives have been introduced. For high density medications, such as potassium chloride, squeeze ports while ports are upright and mix thoroughly.
- •
- Calcium and phosphate ratios must be considered. Excess addition of calcium and phosphate, especially in the form of mineral salts, may result in the formation of calcium phosphate precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- •
- Inspect the container to ensure precipitates have not formed during the mixing or addition of additives and that the solution has not changed color. Discard the admixture if either are observed.
- •
- Insert transfer set into prepared solution container to be transferred. Follow directions accompanying transfer set.
- •
- Remove protector from extended middle port of Dextrose Injection container and insert connector of transfer set.
- •
- Transfer solution by gravity.
- •
- After desired solution has been transferred, mix thoroughly and seal extension tubing of extended middle port. Cut between seal and connector of transfer set.
- •
- Check for leaks.
- •
- Use promptly after admixing or dilution.
- •
- Single-dose container.
- •
- Discard unused portion.
2.2 Important Administration Instructions
- •
- Do not administer Dextrose 70% Injection simultaneously with blood products through the same administration set because of the possibility of pseudoagglutination or hemolysis.
- •
- Set the vent to the closed position on a vented intravenous administration set to prevent air embolism.
- •
- Use a dedicated line without any connections to avoid air embolism.
- •
- The choice of a central or peripheral venous route of infusion should depend on the osmolarity of the final infusate. Solutions with greater than 5% dextrose or with osmolarity of greater than or equal to approximately 900 mOsm/L must be infused through a central catheter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- •
- Prior to infusion, visually inspect the diluted dextrose solution for particulate matter. The solution should be clear and there should be no precipitates. Do not administer unless solution is clear and container is undamaged.
2.3 Dosing Information
Caution: Dextrose Injection is not for direct intravenous infusion. Prior to administration, Dextrose Injection must be diluted with other compatible intravenous fluids or used as an admixture with amino acids.
Dextrose Injection is a part of the parenteral nutrition (PN) regimen which also includes amino acids, electrolytes, and possibly lipid emulsion. Protein, caloric, fluid and electrolyte requirements all need to be taken into consideration when determining individual patient dosage needs.
Individualize the dosage of Dextrose Injection based on the patient’s clinical condition (ability to adequately metabolize dextrose), body weight, nutritional and fluid requirements, as well as additional energy given orally or enterally to the patient. Vitamins and trace elements and other components (including amino acids, electrolytes, and lipid emulsion) can be added to the PN solution to meet nutrient needs and prevent deficiencies and complications from developing.
The administration rate should be governed, especially during the first few day of therapy, by the patient’s tolerance to dextrose. Daily intake of amino acids and dextrose should be increased gradually to the maximum required dose as indicated by frequent determinations of blood glucose levels.
In many patients, provision of adequate calories in the form of hypertonic dextrose may require the administration of exogenous insulin to prevent hyperglycemia and glycosuria.
2.4 Discontinuation of Dextrose Injection
To reduce the risk of hypoglycemia, a gradual decrease in flow rate in the last hour of infusion should be considered [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10, Pediatric Use (8.4)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Dextrose Injection 70%, USP is a sterile, non-pyrogenic, hypertonic solution of 70 grams of dextrose hydrous per 100 mL (0.7 grams/mL) of 500 mL fill volume in 1000 mL flexible container.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
The use of Dextrose Injection is contraindicated in patients:
- •
- Who are severely dehydrated as hypertonic dextrose solution can worsen the patient’s hyperosmolar state [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
- •
- Known hypersensitivity to dextrose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates
Pulmonary vascular precipitates causing pulmonary vascular emboli and pulmonary distress have been reported in patients receiving parenteral nutrition. In some cases, fatal outcomes due to pulmonary embolism have occurred. Patients, especially those with hypophosphatemia, may require the addition of phosphate. To prevent hypocalcemia, calcium supplementation should always accompany phosphate administration. Excessive addition of calcium and phosphate increases the risk of the formation of calcium phosphate precipitates. Precipitates have been reported even in the absence of phosphate salt in the solution. Precipitation following passage through an in-line filter and suspected in vivo precipitate formation has also been reported. If signs of pulmonary distress occur, stop the infusion and initiate a medical evaluation. In addition to inspection of the solution [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)], the infusion set and catheter should also periodically be checked for precipitates.
5.2 Hyperglycemia and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State
The use of dextrose infusions in patients with impaired glucose tolerance may worsen hyperglycemia. Administration of dextrose at a rate exceeding the patient’s utilization rate may lead to hyperglycemia, coma, and death.
Hyperglycemia is associated with an increase in serum osmolality, resulting in osmotic diuresis, dehydration and electrolyte losses [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. Patients with underlying CNS disease and renal impairment who receive dextrose infusions, may be at greater risk of developing hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state.
Monitor blood glucose levels and treat hyperglycemia to maintain levels within normal limits while administering Dextrose Injection. Insulin may be administered or adjusted to maintain optimal blood glucose levels during Dextrose Injection administration.
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity and infusion reactions including anaphylaxis have been reported with dextrose injection [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Stop infusion immediately and treat patient accordingly if signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction develop. Signs or symptoms may include: pruritis, bronchospasm, cyanosis, angioedema, hypotension, pyrexia, chills, and rash.
5.4 Risk of Infections
Patients who require parenteral nutrition are at high risk of infections because the nutritional components of these solutions can support microbial growth. Infection and sepsis may also occur as a result of the use of intravenous catheters to administer parenteral nutrition.
The risk of infection is increased in patients with malnutrition-associated immunosuppression, hyperglycemia exacerbated by dextrose infusion, long-term use and poor maintenance of intravenous catheters, or immunosuppressive effects of other concomitant conditions, drugs, or other components of the parenteral formulation (e.g., lipid emulsion).
To decrease the risk of infectious complications, ensure aseptic technique in catheter placement and maintenance, as well as aseptic technique in the preparation and administration of the nutritional formula.
Monitor for signs and symptoms (including fever and chills) of early infections, including laboratory test results (including leukocytosis and hyperglycemia) and frequent checks of the parenteral access device and insertion site for edema, redness and discharge.
5.5 Refeeding Syndrome
Refeeding severely undernourished patients may result in refeeding syndrome, characterized by the intracellular shift of potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium as the patient becomes anabolic. Thiamine deficiency and fluid retention may also develop. To prevent these complications, monitor severely undernourished patients and slowly increase nutrient intakes including Dextrose Injection.
5.6 Vein Damage and Thrombosis
Dextrose Injection is for admixture with amino acids or dilution with other compatible intravenous fluids. It is not for direct intravenous infusion. Administer solutions containing more than 5% dextrose or with an osmolarity of ≥ 900 mOsm/L through a central vein [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. The infusion of hypertonic solutions into a peripheral vein may result in vein irritation, vein damage, and/or thrombosis. The primary complication of peripheral access is venous thrombophlebitis, which manifests as pain, erythema, tenderness or a palpable cord. Remove the catheter as soon as possible, if thrombophlebitis develops.
5.7 Hepatobiliary Disorders
Hepatobiliary disorders are known to develop in some patients without preexisting liver disease who receive parenteral nutrition, including cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, cholestasis, hepatic steatosis, fibrosis and cirrhosis, possibly leading to hepatic failure. The etiology of these disorders is thought to be multifactorial and may differ between patients.
Monitor liver function parameters and ammonia levels. Patients developing signs of hepatobiliary disorders should be assessed early by a clinician knowledgeable in liver diseases in order to identify possible causative and contributory factors, and possible therapeutic and prophylactic interventions.
5.8 Aluminum Toxicity
Dextrose Injection contains no more than 25 mcg/L of aluminum. However, with prolonged parenteral administration in patients with renal impairment, the aluminum contained in Dextrose Injection may reach toxic levels. Preterm infants are at greater risk because their kidneys are immature, and they require large amounts of concomitant calcium and phosphate solutions that contain aluminum. Patients with renal impairment, including preterm infants, who receive parenteral levels of aluminum at greater than 4 to 5 mcg/kg/day, accumulate aluminum at levels associated with central nervous system (CNS) and bone toxicity. Tissue loading may occur at even lower rates of administration of total parenteral nutrition products [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.9 Risk of Parenteral Nutrition Associated Liver Disease
Parenteral Nutrition Associated Liver Disease (PNALD) has been reported in patients who receive parenteral nutrition for extended periods of time, especially preterm infants, and can present as cholestasis or steatohepatitis. The exact etiology is not entirely clear and is likely multifactorial. If Dextrose Injection-treated patients develop abnormal liver function tests, consider discontinuation or dosage reduction.
5.10 Electrolyte Imbalance and Fluid Overload
Electrolyte deficits, particularly in serum potassium and phosphate, may occur during prolonged use of concentrated dextrose solutions.
Depending on the volume and rate of infusion, the intravenous administration of concentrated dextrose solutions can cause fluid and/or solute overloading resulting in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations (including hypoosmotic hyponatremia), overhydration, congested states or pulmonary edema. The risk of dilutional states is inversely proportional to the electrolyte concentrations in the administered solution. The risk of solute overload causing congested states with peripheral and pulmonary edema is directly proportional to the electrolyte concentrations in the solution.
Monitor blood electrolyte levels, glucose, acid-base balance, correct fluid and electrolyte imbalances, and administer essential vitamins and minerals as needed. Monitor daily fluid balance. Additional monitoring is recommended for patients with water and electrolyte disturbances that could be aggravated by increased glucose and/or free water load. Patients at increased risk for developing hyponatremic encephalopathy include pediatric patients; elderly patients, women, in particular premenopausal women; patients with hypoxemia; and patients with underlying CNS disease [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4,8.5)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of dextrose injection were identified in clinical trials or postmarketing reports. Because these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency, reliably, or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- •
- Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- •
- Hyperglycemia and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- •
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- •
- Risk of infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- •
- Refeeding syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- •
- Vein damage and thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- •
- Hepatobiliary disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- •
- Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- •
- Risk of parenteral nutrition associated liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
- •
- Electrolyte imbalance and fluid overload [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Appropriate administration of Dextrose Injection during pregnancy is not expected to cause adverse developmental outcomes, including congenital malformations. However, maternal hyperglycemia secondary to infusion of glucose-containing products at the time of delivery has been associated with adverse neonatal outcomes such as neonatal hypoglycemia. Malnutrition in pregnant women is associated with adverse maternal and fetal outcomes (see Clinical Considerations). Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with injectable dextrose solutions.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Severe malnutrition in pregnant women is associated with preterm delivery, low birth weight, intrauterine growth restriction, congenital malformations and perinatal mortality. Parenteral nutrition should be considered if a pregnant woman’s nutritional requirements cannot be fulfilled by oral or enteral intake.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of dextrose in human milk, the effects on a breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear determination of the risk of Dextrose Injection to an infant during lactation; therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Dextrose Injection and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Dextrose Injection or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety profile of Dextrose Injection in pediatric patients is similar to adults. Neonates, especially premature infants with low birth weight, are at increased risk of developing hypo- or hyperglycemia and therefore need close monitoring during treatment with intravenous glucose infusions to ensure adequate glycemic control in order to avoid potential long term adverse effects.
Plasma electrolyte concentrations should be closely monitored in pediatric patients who may have impaired ability to regulate fluids and electrolytes. In very low birth weight infants, excessive or rapid administration of Dextrose Injection may result in increased serum osmolality and risk of intracerebral hemorrhage.
Because of immature renal function, preterm infants receiving prolonged treatment with
dextrose injection, may be at risk of aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. Patients, including pediatric patients, may be at risk for Parenteral Nutrition Associated Liver Disease (PNALD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Dextrose Injection did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Elderly patients are at increased risk of developing hyponatremia as well as for developing hyponatremic encephalopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
10 OVERDOSAGE
An increased infusion rate of Dextrose Injection or administration of a concentrated dextrose solution can cause hyperglycemia, hyperosmolality, and adverse effects on water and electrolyte balance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2,5.10)].
Severe hyperglycemia and severe dilutional hyponatremia, and their complications, can be fatal. Discontinue infusion and institute appropriate corrective measures such as administration of exogenous insulin.
Discontinue infusion and institute appropriate corrective measures in the event of overhydration or solute overload during therapy, with particular attention to CNS, respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
If over-exposure occurs, call your Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222 for current information on the management of poisoning or overdosage.
11 DESCRIPTION
Dextrose Injection 70%, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, hypertonic solutions of Dextrose, USP in Water for Injection in a polyvinylchloride flexible plastic container for intravenous administration after appropriate admixture or dilution [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Partial-fill container, designed to facilitate admixture or dilution to provide dextrose in various concentrations, is available in 500 mL size. See Table 1 for the content and characteristics of this solution.
The solution contains no bacteriostatic, antimicrobial agent or added buffer and is intended only for use as a single-dose injection following admixture or dilution. The pH range is 4.0 (3.2 to 6.5).
Water can permeate from inside the container into the overwrap but not in amounts sufficient to affect the solution significantly.
| Strength | Fill Volume | Amount of Dextrose Hydrous per Container | kcal* per Container | mOsmol per liter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
|
Dextrose Injection 70%, USP |
500 mL |
350 grams |
1195 |
3530 |
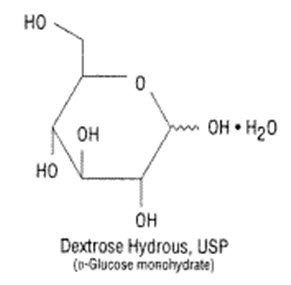
Dextrose, USP is chemically designated D-glucose, monohydrate (C6H12O6 • H2O), a hexose sugar freely soluble in water. The molecular weight of dextrose (D-glucose) monohydrate is 198.17. It has the following structural formula:
Water for Injection, USP is chemically designated H2O.
Dextrose Injection 70%, USP contains no more than 25 mcg/L of aluminum.
Dextrose is derived from corn.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Dextrose Injection 70%, USP (0.7 grams/mL) is a sterile hypertonic solutions of dextrose supplied in a single-dose, 500 mL partial-fill flexible container for intravenous administration after appropriate admixture or dilution [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
|
Product Description |
Code |
NDC |
|
Dextrose Injection 70%, USP (0.7 grams/mL) |
2B0114 |
0338-0719-13 |
Do not remove container from the overwrap until intended for use.
Use the product immediately after mixing and the introduction of additives.
Store between 20ºC to 25°C (68º F to 77°F). [See USP controlled room temperature.]
Do not freeze.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform patients, caregivers, or home healthcare providers of the following risks of Dextrose Injection:
- •
- Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- •
- Hyperglycemia and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- •
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- •
- Risk of infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- •
- Refeeding syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- •
- Vein damage and thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- •
- Hepatobiliary disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
- •
- Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- •
- Risk of parenteral nutrition associated liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
- •
- Electrolyte imbalance and fluid overload [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
- Manufactured by, Packed by, Distributed by:
-
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL 60015 USA
Printed in USA - 07-19-73-115
- Baxter and Viaflex are trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
LOT EXP
2B0114 500 mL in 1000 mL
NDC 0338-0719-13
70% Dextrose
Injection USP
70%
(70% Dextrose in Water)
Rx Only
EACH 100 mL CONTAINS 70 g DEXTROSE HYDROUS USP
pH 4.0 (3.2 to 6.5)
HYPERTONIC OSMOLARITY 3530 mOsmol/L (CALC)
STERILE NONPYROGENIC SINGLE DOSE CONTAINER
A PARENTERAL NUTRIENT COLOR VARIATION
FROM LIGHT YELLOW TO AMBER IS NORMAL AND
DOES NOT ALTER EFFICACY WARNING DILUTE PRIOR TO USE
ADDITIVES MAY BE INCOMPATIBLE
CONSULT WITH PHARMACIST IF AVAILABLE
WHEN INTRODUCING ADDITIVES USE ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE
MIX THOROUGHLY DO NOT STORE
DOSAGE ADMIX FOR INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION
AS DIRECTED BY A PHYSICIAN SEE ACCOMPANYING
DIRECTIONS FOR USE
CAUTIONS MUST NOT BE USED IN SERIES CONNECTIONS
DO NOT USE UNLESS SOLUTION IS CLEAR AND SEAL
IS INTACT
VIAFLEX CONTAINER PL 146 PLASTIC
Baxter Logo
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
CLINTEC NUTRITION DIVISION
DEERFIELD IL 60015 USA
MADE IN USA
BAXTER PL 146 AND VIAFLEX
ARE TRADEMARKS OF
BAXTER INTERNATIONAL INC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2B0114 12 - 500 ML IN 1000 ML
VIAFEX CONTAINER
70% DEXTROSE INJECTION, USP
EXP
XXXXX
SECONDARY BAR CODE
(17) YYMM00 (10) XXXXX
LOT
XXXXX
PRIMARY BAR CODE
(01) 50303380719131
| DEXTROSE
dextrose monohydrate injection, solution |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Baxter Healthcare Corporation (005083209) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baxter Healthcare Corporation | 059140764 | ANALYSIS(0338-0719) , LABEL(0338-0719) , MANUFACTURE(0338-0719) , PACK(0338-0719) , STERILIZE(0338-0719) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baxter Healthcare Corporation | 194684502 | ANALYSIS(0338-0719) | |