TOPOTECAN- topotecan injection
Sandoz Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Topotecan Injection safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Topotecan Injection.
Topotecan Injection Must be diluted before intravenous infusion Initial U.S. Approval: 1996 WARNING: BONE MARROW SUPPRESSIONSee full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.Do not give Topotecan to patients with baseline neutrophil counts less than 1,500 cells/mm3. In order to monitor the occurrence of bone marrow suppression, primarily neutropenia, which may be severe and result in infection and death, monitor peripheral blood cell counts frequently on all patients receiving Topotecan Injection. (5.1) INDICATIONS AND USAGETopotecan is a topoisomerase inhibitor indicated for: (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
See Dosage Modification Guidelines for patients with neutropenia or reduced platelets. (2.1, 2.2) (2) See Dosage Adjustment in Renal Impairment. (2.3) (2) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Each mL contains topotecan hydrochloride equivalent to 1 mg of topotecan free base. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSSmall cell lung cancer:
Cervical cancer (Topotecan Injection plus cisplatin):
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sandoz Inc. at 1-800-525-8747 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 9/2011 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: BONE MARROW SUPPRESSION
Do not give Topotecan Injection to patients with baseline neutrophil counts less than 1,500 cells/mm3. In order to monitor the occurrence of bone marrow suppression, primarily neutropenia, which may be severe and result in infection and death, monitor peripheral blood counts frequently on all patients receiving Topotecan Injection. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Topotecan Injection is indicated for the treatment of:
- •
- small cell lung cancer sensitive disease after failure of first-line chemotherapy. In clinical studies submitted to support approval, sensitive disease was defined as disease responding to chemotherapy but subsequently progressing at least 60 days (in the Phase 3 study) or at least 90 days (in the Phase 2 studies) after chemotherapy [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Topotecan Injection in combination with cisplatin is indicated for the treatment of:
- •
- stage IV-B, recurrent, or persistent carcinoma of the cervix which is not amenable to curative treatment with surgery and/or radiation therapy.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Prior to administration of the first course of Topotecan Injection, patients must have a baseline neutrophil count of >1,500 cells/mm3 and a platelet count of >100,000 cells/mm3.
2.1 Small Cell Lung Cancer
Recommended Dosage
- •
- The recommended dose of topotecan is 1.5 mg/m2 by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes daily for 5 consecutive days, starting on day 1 of a 21-day course.
- •
- In the absence of tumor progression, a minimum of 4 courses is recommended because tumor response may be delayed. The median time to response in 4 small cell lung cancer trials was 5 to 7 weeks.
Dosage Modification Guidelines
- •
- In the event of severe neutropenia (defined as <500 cells/mm3) during any course, reduce the dose by 0.25 mg/m2 (to 1.25 mg/m2) for subsequent courses.
- •
- Alternatively, in the event of severe neutropenia, administer G-CSF (granulocyte-colony stimulating factor) following the subsequent course (before resorting to dose reduction) starting from day 6 of the course (24 hours after completion of topotecan administration).
- •
- In the event the platelet count falls below 25,000 cells/mm3, reduce doses by 0.25 mg/m2 (to 1.25 mg/m2) for subsequent courses.
2.2 Cervical Cancer
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of Topotecan Injection is 0.75 mg/m2 by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes daily on days 1, 2, and 3; followed by cisplatin 50 mg/m2 by intravenous infusion on day 1 repeated every 21 days (a 21-day course).
Dosage Modification Guidelines
Dosage adjustments for subsequent courses of Topotecan Injection in combination with cisplatin are specific for each drug. See manufacturer’s prescribing information for cisplatin administration and hydration guidelines and for cisplatin dosage adjustment in the event of hematologic toxicity.
- •
- In the event of severe febrile neutropenia (defined as <1000 cells/mm3 with temperature of 38°C or 100.4°F), reduce the dose of Topotecan Injection to 0.60 mg/m2 for subsequent courses.
- •
- Alternatively, in the event of severe febrile neutropenia, administer G-CSF following the subsequent course (before resorting to dose reduction) starting from day 4 of the course (24 hours after completion of administration of Topotecan Injection).
- •
- If febrile neutropenia occurs despite the use of G-CSF, reduce the dose of Topotecan Injection to 0.45 mg/m2 for subsequent courses.
- •
- In the event the platelet count falls below 25,000 cells/mm3, reduce doses to 0.60 mg/m2 for subsequent courses.
2.3 Dosage Adjustment in Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of Topotecan Injection appears to be required for patients with mild renal impairment (Clcr 40 to 60 mL/min.). Dosage adjustment of Topotecan Injection to 0.75 mg/m2 is recommended for patients with moderate renal impairment (20 to 39 mL/min.). Insufficient data are available in patients with severe renal impairment to provide a dosage recommendation for Topotecan Injection. [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
Topotecan Injection in combination with cisplatin for the treatment of cervical cancer should only be initiated in patients with serum creatinine ≤1.5 mg/dL. In the clinical trial, cisplatin was discontinued for a serum creatinine >1.5 mg/dL. Insufficient data are available regarding continuing monotherapy with Topotecan Injection after cisplatin discontinuation in patients with cervical cancer.
2.4 Instructions for Handling, Preparation and Intravenous Administration
Handling
Topotecan is a cytotoxic anticancer drug. Prepare Topotecan Injection under a vertical laminar flow hood while wearing gloves and protective clothing. If Topotecan Injection solution contacts the skin, wash the skin immediately and thoroughly with soap and water. If Topotecan Injection contacts mucous membranes, flush thoroughly with water.
Use procedures for proper handling and disposal of anticancer drugs. Several guidelines on this subject have been published.1-4
Preparation and Administration
The appropriate volume of the Topotecan Injection is diluted in a minimum of 50 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP prior to administration. Infuse over 30 minutes. Topotecan Injection diluted for infusion is stable for 4 hours at room temperature or 24 hours at refrigerated temperature in ambient lighting conditions.
Topotecan Injection is supplied as a multiple dose vial. Studies have shown the product is stable for 28 days after initial puncture when stored under refrigerated conditions.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Topotecan Injection is available in the following strengths:
4 mg/4 mL (1 mg/mL) Multiple Dose Vial
Each mL contains topotecan hydrochloride equivalent to 1 mg of topotecan free base for intravenous infusion only following dilution.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Topotecan Injection is contraindicated in patients who have a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylactoid reactions) to topotecan or to any of its ingredients. Topotecan Injection should not be used in patients with severe bone marrow depression.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Bone Marrow Suppression
Bone marrow suppression (primarily neutropenia) is the dose-limiting toxicity of Topotecan Injection. Neutropenia is not cumulative over time. In the comparative study, in small cell lung cancer, the treatment-related death rates were 5% for topotecan and 4% for CAV (cyclophosphamide-doxorubicin-vincristine).
Neutropenia
- •
- From a combined experience of patients receiving topotecan which included patients treated for small cell lung cancer: Grade 4 neutropenia (<500 cells/mm3) was most common during course 1 of treatment (60% of patients) and occurred in 39% of all courses, with a median duration of 7 days. The nadir neutrophil count occurred at a median of 12 days. Therapy-related sepsis or febrile neutropenia occurred in 23% of patients, and sepsis was fatal in 1%. Pancytopenia has been reported.
- •
- Cervical cancer experience: Grade 3 and grade 4 neutropenia affected 26% and 48% of patients, respectively.
Thrombocytopenia
- •
- From a combined experience of patients receiving topotecan which included patients treated for small cell lung cancer: Grade 4 thrombocytopenia (<25,000/mm3) occurred in 27% of patients and in 9% of courses, with a median duration of 5 days and platelet nadir at a median of 15 days. Platelet transfusions were given to 15% of patients in 4% of courses.
- •
- Cervical cancer experience: Grade 3 and grade 4 thrombocytopenia affected 26% and 7% of patients, respectively.
Anemia
- •
- From a combined experience of patients receiving topotecan which included patients treated for small cell lung cancer: Grade 3/4 anemia (<8 g/dL) occurred in 37% of patients and in 14% of courses. Median nadir was at day 15. Transfusions were needed in 52% of patients in 22% of courses.
- •
- Cervical cancer experience: Grade 3 and grade 4 anemia affected 34% and 6% of patients, respectively.
Monitoring of Bone Marrow Function
Administer Topotecan Injection only in patients with adequate bone marrow reserves, including baseline neutrophil count of at least 1,500 cells/mm3 and platelet count at least 100,000/mm3.
Monitor peripheral blood counts frequently during treatment with Topotecan Injection. Do not treat patients with subsequent courses of Topotecan Injection until neutrophils recover to >1,000 cells/mm3, platelets recover to >100,000 cells/mm3, and hemoglobin levels recover to 9 g/dL (with transfusion if necessary). Severe myelotoxicity has been reported when Topotecan Injection is used in combination with cisplatin [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.2 Neutropenic Colitis
Topotecan-induced neutropenia can lead to neutropenic colitis. Fatalities due to neutropenic colitis have been reported in clinical trials with Topotecan Injection. In patients presenting with fever, neutropenia, and a compatible pattern of abdominal pain, consider the possibility of neutropenic colitis.
5.3 Interstitial Lung Disease
Topotecan Injection has been associated with reports of interstitial lung disease (ILD), some of which have been fatal [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Underlying risk factors include history of ILD, pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer, thoracic exposure to radiation, and use of pneumotoxic drugs and/or colony stimulating factors. Monitor patients for pulmonary symptoms indicative of interstitial lung disease (e.g., cough, fever, dyspnea, and/or hypoxia), and discontinue Topotecan Injection if a new diagnosis of ILD is confirmed.
5.4 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D
Topotecan Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman.
Topotecan caused embryolethality, fetotoxicity, and teratogenicity in rats and rabbits when administered during organogenesis. There are no adequate and well controlled studies of Topotecan Injection in pregnant women. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if a patient becomes pregnant while receiving Topotecan Injection, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. [see Use in Specific Populations, Pregnancy (8.1)]
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Small Cell Lung Cancer
Data in the following section are based on the combined experiences of the 879 patients studied, including 426 patients with small cell lung cancer treated with topotecan. Table 1 lists the principle hematologic adverse reactions and Table 2 lists non-hematologic adverse reactions occurring in at least 15% of patients.
Table 1. Hematologic Adverse Reactions Experienced in ≥15% of Patients, Including 426 Patients With Small Cell Lung Cancer, Receiving Topotecan
|
Hematologic Adverse Reaction |
Patients (n=879) % Incidence |
|
Neutropenia <1,500 cells/mm3 <500 cells/mm3 |
97 78 |
|
Leukopenia <3,000 cells/mm3 <1,000 cells/mm3 |
97 32 |
|
Thrombocytopenia <75,000/mm3 <25,000/mm3 |
69 27 |
|
Anemia <10 g/dL <8 g/dL |
89 37 |
Table 2. Non-hematologic Adverse Reactions Experienced by ≥15% of 879 Patients, Including 426 Patients With Small Cell Lung Cancer, Receiving Topotecan
|
Non-hematologic Adverse Reaction |
Percentage of Patients with Adverse Reaction (879 Patients) |
||
|
All Grades |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 |
|
|
Infections and infestations | |||
|
Sepsis or pyrexia/infection with neutropeniaa |
43 |
NR |
23 |
|
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | |||
|
Anorexia |
19 |
2 |
<1 |
|
Nervous system disorders | |||
|
Headache |
18 |
1 |
<1 |
|
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | |||
|
Dyspnea |
22 |
5 |
3 |
|
Coughing |
15 |
1 |
0 |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders | |||
|
Nausea |
64 |
7 |
1 |
|
Vomiting |
45 |
4 |
1 |
|
Diarrhea |
32 |
3 |
1 |
|
Constipation |
29 |
2 |
1 |
|
Abdominal pain |
22 |
2 |
2 |
|
Stomatitis |
18 |
1 |
<1 |
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | |||
|
Alopecia |
49 |
NA |
NA |
|
Rashb |
16 |
1 |
0 |
|
General disorders and administrative site conditions | |||
|
Fatigue |
29 |
5 |
0 |
|
Pyrexia |
28 |
1 |
<1 |
|
Painc |
23 |
2 |
1 |
|
Asthenia |
25 |
4 |
2 |
NA = Not applicable
NR = Not reported separately
a Does not include Grade 1 sepsis or pyrexia
b Rash also includes pruritus, rash erythematous, urticaria, dermatitis, bullous eruption, and maculopapular rash.
c Pain includes body pain, back pain, and skeletal pain.
Nervous System Disorders
Paresthesia occurred in 7% of patients but was generally grade 1.
Hepatobiliary Disorders
Grade 1 transient elevations in hepatic enzymes occurred in 8% of patients. Greater elevations, grade 3/4, occurred in 4%. Grade 3/4 elevated bilirubin occurred in <2% of patients.
Table 3 shows the grade 3/4 hematologic and major non-hematologic adverse reactions in the topotecan/CAV comparator trial in small cell lung cancer.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions Experienced by ≥5% of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Randomized to Receive Topotecan or CAV
|
Adverse Reaction |
Topotecan (n=107) |
CAV (n=104) |
|
Hematologic Grade 3/4 |
% |
% |
|
Grade 4 neutropenia (<500 cells/mm3) |
70 |
72 |
|
Grade 3/4 anemia (Hgb <8 g dL) |
42 |
20 |
|
Grade 4 thrombocytopenia (<25,000 plts/mm3) |
29 |
5 |
|
Pyrexia/Grade 4 neutropenia |
28 |
26 |
|
Non-hematologic Grade 3/4 |
% |
% |
|
Infections and infestations Documented sepsisa |
5 |
5 |
|
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders Dyspnea |
9 |
14 |
|
Pneumonia |
8 |
6 |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders Abdominal pain |
6 |
4 |
|
Nausea |
8 |
6 |
|
General disorders and administrative site conditions Fatigue |
6 |
10 |
|
Asthenia |
9 |
7 |
|
Painb |
5 |
7 |
a Death related to sepsis occurred in 3% of patients receiving topotecan, and 1% of patients receiving CAV
b Pain includes body pain, skeletal pain, and back pain.
Cervical Cancer
In the comparative trial with Topotecan Injection plus cisplatin versus cisplatin in patients with cervical cancer, the most common dose-limiting adverse reaction was myelosuppression. Table 4 shows the hematologic adverse reactions and Table 5 shows the non-hematologic adverse reactions in patients with cervical cancer.
Table 4. Hematologic Adverse Reactions in Patients with Cervical Cancer Treated with Topotecan Injection Plus Cisplatin or Cisplatin Monotherapya
|
Hematologic Adverse Reaction |
Topotecan Injection Plus Cisplatin (n = 140) |
Cisplatin (n = 144) |
|
Anemia | ||
|
All grades (Hgb <12 g/dL) |
131 (94%) |
130 (90%) |
|
Grade 3 (Hgb <8 to 6.5 g/dL) |
47 (34%) |
28 (19%) |
|
Grade 4 (Hgb <6.5 g/dL) |
9 (6%) |
5 (3%) |
|
Leukopenia | ||
|
All grades (<3,800 cells/mm3) |
128 (91%) |
43 (30%) |
|
Grade 3 (<2,000 to 1,000 cells/mm3) |
58 (41%) |
1 (1%) |
|
Grade 4 (<1,000 cells/mm3) |
35 (25%) |
0 (0%) |
|
Neutropenia | ||
|
All grades (<2,000 cells/mm3) |
125 (89%) |
28 (19%) |
|
Grade 3 (<1,000 to 500 cells/mm3) |
36 (26%) |
1 (1%) |
|
Grade 4 (<500 cells/mm3) |
67 (48%) |
1 (1%) |
|
Thrombocytopenia | ||
|
All grades (<130,000 cells/mm3) |
104 (74%) |
21 (15%) |
|
Grade 3 (<50,000 to 10,000 cells/mm3) |
36 (26%) |
5 (3%) |
|
Grade 4 (<10,000 cells/mm3) |
10 (7%) |
0 (0%) |
a Includes patients who were eligible and treated.
Table 5. Non-hematologic Adverse Reactions Experienced by ≥5% of Patients with Cervical Cancer Treated with Topotecan Injection Plus Cisplatin or Cisplatin Monotherapya
|
Topotecan Injection Plus Cisplatin |
Cisplatin |
|||||
|
(n = 140) |
(n = 144) |
|||||
|
Adverse Reaction |
All Gradesb |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 |
All Gradesb |
Grade 3 |
Grade 4 |
|
General disorders and administrative site conditions | ||||||
|
Constitutionalc |
96 (69%) |
11 (8%) |
0 |
89 (62%) |
17 (12%) |
0 |
|
Paind |
82 (59%) |
28 (20%) |
3 (2%) |
72 (50%) |
18 (13%) |
5 (3%) |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders | ||||||
|
Vomiting |
56 (40%) |
20 (14%) |
2 (1%) |
53 (37%) |
13 (9%) |
0 |
|
Nausea |
77 (55%) |
18 (13%) |
2 (1%) |
79 (55%) |
13 (9%) |
0 |
|
Stomatitis-pharyngitis |
8 (6%) |
1 (<1%) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Other |
88 (63%) |
16 (11%) |
4 (3%) |
80 (56%) |
12 (8%) |
3 (2%) |
|
Dermatology |
67 (48%) |
1 (<1%) |
0 |
29 (20%) |
0 |
0 |
|
Metabolic-Laboratory |
55 (39%) |
13 (9%) |
7 (5%) |
44 (31%) |
14 (10%) |
1 (<1%) |
|
Genitourinary |
51 (36%) |
9 (6%) |
9 (6%) |
49 (34%) |
7 (5%) |
7 (5%) |
|
Nervous system disorders | ||||||
|
Neuropathy |
4 (3%) |
1 (<1%) |
0 |
3 (2%) |
1 (<1%) |
0 |
|
Other |
49 (35%) |
3 (2%) |
1 (<1%) |
43 (30%) |
7 (5%) |
2 (1%) |
|
Infection-febrile neutropenia |
39 (28%) |
21 (15%) |
5 (4%) |
26 (18%) |
11 (8%) |
0 |
|
Cardiovascular |
35 (25%) |
7 (5%) |
6 (4%) |
22 (15%) |
8 (6%) |
3 (2%) |
|
Hepatic |
34 (24%) |
5 (4%) |
2 (1%) |
23 (16%) |
2 (1%) |
0 |
|
Pulmonary |
24 (17%) |
4 (3%) |
0 |
23 (16%) |
5 (3%) |
3 (2%) |
|
Vascular disorders | ||||||
|
Hemorrhage |
21 (15%) |
8 (6%) |
1 (<1%) |
20 (14%) |
3 (2%) |
1 (<1%) |
|
Coagulation |
8 (6%) |
4 (3%) |
3 (2%) |
10 (7%) |
7 (5%) |
0 |
|
Musculoskeletal |
19 (14%) |
3 (2%) |
0 |
7 (5%) |
1 (<1%) |
1 (<1%) |
|
Allergy-Immunology |
8 (6%) |
2 (1%) |
1 (<1%) |
4 (3%) |
0 |
1 (<1%) |
|
Endocrine |
8 (6%) |
0 |
0 |
4 (3%) |
2 (1%) |
0 |
|
Sexual reproduction function |
7 (5%) |
0 |
0 |
10 (7%) |
1 (<1%) |
0 |
|
Ocular-visual |
7 (5%) |
0 |
0 |
7 (5%) |
1 (<1%) |
0 |
Data were collected using NCI Common Toxicity Criteria, v. 2.
a Includes patients who were eligible and treated.
b Grades 1 through 4 only. There were 3 patients who experienced grade 5 deaths with investigator-designated attribution. One was a grade 5 hemorrhage in which the drug-related thrombocytopenia aggravated the event. A second patient experienced bowel obstruction, cardiac arrest, pleural effusion and respiratory failure which were not treatment related but probably aggravated by treatment. A third patient experienced a pulmonary embolism and adult respiratory distress syndrome, the latter was indirectly treatment-related.
c Constitutional includes fatigue (lethargy, malaise, asthenia), fever (in the absence of neutropenia), rigors, chills, sweating, and weight gain or loss.
d Pain includes abdominal pain or cramping, arthralgia, bone pain, chest pain (non-cardiac and non-pleuritic), dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, earache, headache, hepatic pain, myalgia, neuropathic pain, pain due to radiation, pelvic pain, pleuritic pain, rectal or perirectal pain, and tumor pain.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials or listed in other sections of the prescribing information, the following reactions have been identified during post-marketing use of Topotecan Injection. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. These reactions have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of their seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal connection to Topotecan Injection.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders:Severe bleeding (in association with thrombocytopenia). [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Immune System Disorders:Allergic manifestations; Anaphylactoid reactions.
Gastrointestinal Disorders:Abdominal pain potentially associated with neutropenic colitis. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Pulmonary Disorders:Interstitial lung disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders:Angioedema, severe dermatitis, severe pruritus
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions:Inadvertent extravasation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
G-CSF: Concomitant administration of G-CSF can prolong the duration of neutropenia, so if G-CSF is to be used, do not initiate it until day 6 of the course of therapy, 24 hours after completion of treatment with Topotecan Injection.
Platinum and Other Cytotoxic Agents:Myelosuppression was more severe when topotecan, at a dose of 1.25 mg/m2/day for 5 days, was given in combination with cisplatin at a dose of 50 mg/m2 in Phase 1 studies. In one study, 1 of 3 patients had severe neutropenia for 12 days and a second patient died with neutropenic sepsis.
Greater myelosuppression is also likely to be seen when Topotecan Injection is used in combination with other cytotoxic agents, thereby necessitating a dose reduction. However, when combining topotecan with platinum agents (e.g., cisplatin or carboplatin), a distinct sequence-dependent interaction on myelosuppression has been reported. Coadministration of a platinum agent on day 1 of dosing with topotecan required lower doses of each agent compared to co-administration on day 5 of the dosing schedule for topotecan.
For information on the pharmacokinetics, efficacy, safety, and dosing of Topotecan Injection at a dose of 0.75 mg/m2/day on days 1, 2, and 3 in combination with cisplatin 50 mg/m2 on day 1 for cervical cancer, see Dosage and Administration (2), Adverse Reactions (6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14).
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Topotecan Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In rabbits, a dose of 0.1 mg/kg/day (about equal to the clinical dose of 1.5 mg/m2) given on days 6 through 20 of gestation caused maternal toxicity, embryolethality, and reduced fetal body weight. In the rat, a dose of 0.23 mg/kg/day (about equal to the clinical dose of 1.5 mg/m2) given for 14 days before mating through gestation day 6 caused fetal resorption, microphthalmia, pre-implant loss, and mild maternal toxicity. A dose of 0.1 mg/kg/day (about half the clinical dose of 1.5 mg/m2) given to rats on days 6 through 17 of gestation caused an increase in post-implantation mortality. This dose also caused an increase in total fetal malformations. The most frequent malformations were of the eye (microphthalmia, anophthalmia, rosette formation of the retina, coloboma of the retina, ectopic orbit), brain (dilated lateral and third ventricles), skull, and vertebrae.
There are no adequate and well controlled studies of Topotecan Injection in pregnant women. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if a patient becomes pregnant while receiving Topotecan Injection, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Rats excrete high concentrations of topotecan into milk. Lactating female rats given 4.72 mg/m2 IV (about three times the clinical dose of 1.5 mg/m2) excreted topotecan into milk at concentrations up to 48-fold higher than those in plasma. It is not known whether the drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Topotecan Injection, discontinue breastfeeding when women are receiving Topotecan Injection.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 879 patients in a combined experience of topotecan which included patients with small cell lung cancer, 32% (n=281) were 65 years of age and older, while 3.8% (n=33) were 75 years of age and older. Of the 140 patients with stage IV-B, relapsed, or refractory cervical cancer in clinical studies of Topotecan Injection who received Topotecan Injection plus cisplatin in the randomized clinical trial, 6% (n = 9) were 65 years of age and older, while 3% (n = 4) were 75 years of age and older.
No overall differences in effectiveness or safety were observed between these patients and younger adult patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger adult patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
There were no apparent differences in the pharmacokinetics of topotecan in elderly patients, once the age-related decrease in renal function was considered [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of Topotecan Injection appears to be required for patients with mild renal impairment (Clcr 40 to 60 mL/min.). Dosage reduction is recommended for patients with moderate renal impairment (Clcr 20 to 39 mL/min.). Insufficient data are available in patients with severe renal impairment to provide a dosage recommendation for Topotecan Injection. [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no known antidote for overdosage with Topotecan Injection. The primary anticipated complication of overdosage would consist of bone marrow suppression.
One patient on a single-dose regimen of 17.5 mg/m2 given on day 1 of a 21-day cycle had received a single dose of 35 mg/m2. This patient experienced severe neutropenia (nadir of 320/mm3) 14 days later but recovered without incident.
Observe patients closely for bone marrow suppression, and consider supportive measures (such as the prophylactic use of G-CSF and/or antibiotic therapy).
11 DESCRIPTION
Topotecan is a semi-synthetic derivative of camptothecin and is an anti-tumor drug with topoisomerase I-inhibitory activity.
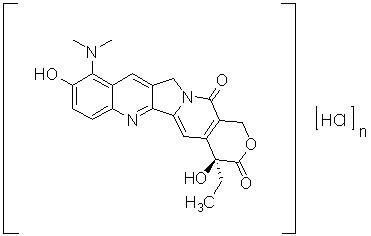
The chemical name for topotecan free base is (S)-10-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-4-ethyl-4,9-dihydroxy-1H-pyrano[3’,4’:6,7]indolizino[1,2-b]quinoline-3,14-(4H,12H)-dione. It has the molecular formula C23H23N3O5 and a molecular weight of 421.45.
Topotecan has three pKa values: pKa1 = 10.50 corresponding to the benzyldimethylamino group, pKa2 = 6.99 corresponding to the phenol group and pKa3 = 0.60 corresponding to the quinoline group.
As formulated in Topotecan Injection, topotecan has the following structural formula:
where n is >1, corresponding to HCl added to adjust the pH to approximately 2 to 2.5.
Topotecan Injection is supplied as a sterile, non-pyrogenic, clear, yellow solution at a topotecan free base concentration of 4 mg/4 mL (1 mg/mL), in multiple dose vials. Each mL of Topotecan Injection contains topotecan hydrochloride equivalent to 1 mg of topotecan as free base, 5 mg tartaric acid, NF, and water for injection, USP. Hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may be used to adjust the pH.. The hydrochloride salt of topotecan is soluble in water and melts with decomposition at 213°C to 218°C.
The solution must be diluted before administration by intravenous infusion.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Topoisomerase I relieves torsional strain in DNA by inducing reversible single strand breaks. Topotecan binds to the topoisomerase I-DNA complex and prevents religation of these single strand breaks. The cytotoxicity of topotecan is thought to be due to double strand DNA damage produced during DNA synthesis, when replication enzymes interact with the ternary complex formed by topotecan, topoisomerase I, and DNA. Mammalian cells cannot efficiently repair these double strand breaks.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The dose-limiting toxicity of topotecan is leukopenia. White blood cell count decreases with increasing topotecan dose or topotecan AUC. When topotecan is administered at a dose of 1.5 mg/m2/day for 5 days, an 80% to 90% decrease in white blood cell count at nadir is typically observed after the first cycle of therapy.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of topotecan have been evaluated in cancer patients following doses of 0.5 to 1.5 mg/m2 administered as a 30-minute infusion. Topotecan exhibits multiexponential pharmacokinetics with a terminal half-life of 2 to 3 hours. Total exposure (AUC) is approximately dose-proportional.
Distribution:Binding of topotecan to plasma proteins is about 35%.
Metabolism:Topotecan undergoes a reversible pH dependent hydrolysis of its lactone moiety; it is the lactone form that is pharmacologically active. At pH ≤ 4, the lactone is exclusively present, whereas the ring-opened hydroxy-acid form predominates at physiologic pH. In vitro studies in human liver microsomes indicate topotecan is metabolized to an N-demethylated metabolite. The mean metabolite:parent AUC ratio was about 3% for total topotecan and topotecan lactone following IV administration.
Excretion:Renal clearance is an important determinant of topotecan elimination.
In a mass balance/excretion study in 4 patients with solid tumors, the overall recovery of total topotecan and its N-desmethyl metabolite in urine and feces over 9 days averaged 73.4 ± 2.3% of the administered IV dose. Mean values of 50.8 ± 2.9% as total topotecan and 3.1 ± 1% as N-desmethyl topotecan were excreted in the urine following IV administration. Fecal elimination of total topotecan accounted for 17.9 ± 3.6% while fecal elimination of N-desmethyl topotecan was 1.7 ± 0.6%. An O-glucuronidation metabolite of topotecan and N-desmethyl topotecan has been identified in the urine. These metabolites, topotecan-O-glucuronide and N-desmethyl topotecan-O-glucuronide, were less than 2% of the administered dose.
Effect of Gender:The overall mean topotecan plasma clearance in male patients was approximately 24% higher than that in female patients, largely reflecting difference in body size.
Effect of Age:Topotecan pharmacokinetics have not been specifically studied in an elderly population, but population pharmacokinetic analysis in female patients did not identify age as a significant factor. Decreased renal clearance, which is common in the elderly, is a more important determinant of topotecan clearance [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Effect of Race:The effect of race on topotecan pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
Effect of Renal Impairment:In patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 40 to 60 mL/min.), topotecan plasma clearance was decreased to about 67% of the value in patients with normal renal function. In patients with moderate renal impairment (Clcr of 20 to 39 mL/min.), topotecan plasma clearance was reduced to about 34% of the value in control patients, with an increase in half-life. Mean half-life, estimated in 3 renally impaired patients, was about 5 hours. Dosage adjustment is recommended for these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Effect of Hepatic Impairment:Plasma clearance in patients with hepatic impairment (serum bilirubin levels between 1.7 and 15 mg/dL) was decreased to about 67% of the value in patients without hepatic impairment. Topotecan half-life increased slightly, from 2 hours to 2.5 hours, but these hepatically impaired patients tolerated the usual recommended topotecan dosage regimen.
Drug Interactions:Pharmacokinetic studies of the interaction of topotecan with concomitantly administered medications have not been formally investigated.
In vitro inhibition studies using marker substrates known to be metabolized by human P450 CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C8/9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E, CYP3A, or CYP4A or dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase indicate that the activities of these enzymes were not altered by topotecan. Enzyme inhibition by topotecan has not been evaluated in vivo.
Cisplatin:No pharmacokinetic data are available following topotecan (0.75 mg/m2/day for 3 consecutive days) and cisplatin (50 mg/m2/day on day 1) in patients with cervical cancer.
Myelosuppression was more severe when topotecan was given in combination with cisplatin. [see Drug Interactions (7)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity testing of topotecan has not been performed. Topotecan is known to be genotoxic to mammalian cells and is a probable carcinogen. Topotecan was mutagenic to L5178Y mouse lymphoma cells and clastogenic to cultured human lymphocytes with and without metabolic activation. It was also clastogenic to mouse bone marrow. Topotecan did not cause mutations in bacterial cells.
Topotecan given to female rats prior to mating at a dose of 1.4 mg/m2 IV (about equal to the clinical dose of 1.5 mg/m2) caused superovulation possibly related to inhibition of follicular atresia. This dose given to pregnant female rats also caused increased pre-implantation loss. Studies in dogs given 0.4 mg/m2 IV (about 1/4th the clinical dose of 1.5 mg/m2) of topotecan daily for a month suggest that treatment may cause an increase in the incidence of multinucleated spermatogonial giant cells in the testes. Topotecan may impair fertility in women and men.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Small Cell Lung Cancer
Topotecan was studied in 426 patients with recurrent or progressive small cell lung cancer in 1 randomized, comparative study and in 3 single-arm studies.
Randomized Comparative Study
In a randomized, comparative, Phase 3 trial, 107 patients were treated with topotecan (1.5 mg/m2/day x 5 days starting on day 1 of a 21-day course) and 104 patients were treated with CAV (1,000 mg/m2 cyclophosphamide, 45 mg/m2 doxorubicin, 2 mg vincristine administered sequentially on day 1 of a 21-day course). All patients were considered sensitive to first-line chemotherapy (responders who then subsequently progressed ≥60 days after completion of first-line therapy). A total of 77% of patients treated with topotecan and 79% of patients treated with CAV received platinum/etoposide with or without other agents as first-line chemotherapy.
Response rates, response duration, time to progression, and survival are shown in Table 6.
Table 6. Efficacy of Topotecan Versus CAV (cyclophosphamide-doxorubicin-vincristine) in Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Sensitive to First-Line Chemotherapy
|
Parameter |
Topotecan (n = 107) |
CAV (n = 104) |
|
Complete response rate |
0% |
1% |
|
Partial response rate |
24% |
17% |
|
Overall response rate |
24% |
18% |
|
Difference in overall response rates |
6% |
|
|
95% Confidence interval of the difference |
(–6 to 18%) |
|
|
Response durationa (weeks) |
n = 26 |
n = 19 |
|
Median |
14.4 |
15.3 |
|
95% Confidence interval hazard-ratio |
13.1 to 18 |
13.1 to 23.1 |
|
(Topotecan:CAV) (95% CI) |
1.42 (0.73 to 2.76) |
|
|
(P-value) |
(0.30) |
|
|
Time to progression (weeks) | ||
|
Median |
13.3 |
12.3 |
|
95% Confidence interval hazard-ratio |
11.4 to 16.4 |
11 to 14.1 |
|
(Topotecan:CAV) (95% CI) |
0.92 (0.69 to 1.22) |
|
|
(P-value) |
(0.55) |
|
|
Survival (weeks) | ||
|
Median |
25 |
24.7 |
|
95% Confidence interval |
20.6 to 29.6 |
21.7 to 30.3 |
|
hazard-ratio | ||
|
(Topotecan:CAV) (95% CI) |
1.04 (0.78 to 1.39) |
|
|
(P-value) |
(0.80) |
|
a The calculation for duration of response was based on the interval between first response and time to progression.
The time to response was similar to both arms: topotecan median of 6 weeks (range 2.4 to 15.7) versus CAV median 6 weeks (range 5.1 to 18.1).
Changes on a disease-related symptom scale in patients who received topotecan or who received CAV are presented in Table 7. It should be noted that not all patients had all symptoms, nor did all patients respond to all questions. Each symptom was rated on a 4-category scale with an improvement defined as a change in 1 category from baseline sustained over 2 courses. Limitations in interpretation of the rating scale and responses preclude formal statistical analysis.
Table 7. Percentage of Patients with Symptom Improvementa: Topotecan Versus CAV in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer
|
Symptom |
Topotecan Injection (n=107) |
CAV (n=104) |
||
|
nb |
(%) |
nb |
(%) |
|
|
Shortness of breath |
68 |
(28) |
61 |
(7) |
|
Interference with daily activity |
67 |
(27) |
63 |
(11) |
|
Fatigue |
70 |
(23) |
65 |
(9) |
|
Hoarseness |
40 |
(33) |
38 |
(13) |
|
Cough |
69 |
(25) |
61 |
(15) |
|
Insomnia |
57 |
(33) |
53 |
(19) |
|
Anorexia |
56 |
(32) |
57 |
(16) |
|
Chest pain |
44 |
(25) |
41 |
(17) |
|
Hemoptysis |
15 |
(27) |
12 |
(33) |
a Defined as improvement sustained over at least 2 courses compared to baseline.
b Number of patients with baseline and at least 1 post-baseline assessment.
Single-Arm Studies
Topotecan was also studied in 3 open-label, non-comparative trials in a total of 319 patients with recurrent or progressive small cell lung cancer after treatment with first-line chemotherapy. In all 3 studies, patients were stratified as either sensitive (responders who then subsequently progressed ≥90 days after completion of first-line therapy) or refractory (no response to first-line chemotherapy or who responded to first-line therapy and then progressed within 90 days of completing first-line therapy). Response rates ranged from 11% to 31% for sensitive patients and 2% to 7% for refractory patients. Median time to progression and median survival were similar in all 3 studies and the comparative study.
14.2 Cervical Cancer
In a comparative trial, 147 eligible women were randomized to Topotecan Injection (0.75 mg/m2/day IV over 30 minutes × 3 consecutive days starting on day 1 of a 21-day course) plus cisplatin (50 mg/m2 on day 1) and 146 eligible women were randomized to cisplatin (50 mg/m2 IV on day 1 of a 21-day course). All patients had histologically confirmed Stage IV-B, recurrent, or persistent carcinoma of the cervix considered not amenable to curative treatment with surgery and/or radiation. Fifty-six percent (56%) of patients treated with Topotecan Injection plus cisplatin and 56% of patients treated with cisplatin had received prior cisplatin with or without other agents as first-line chemotherapy.
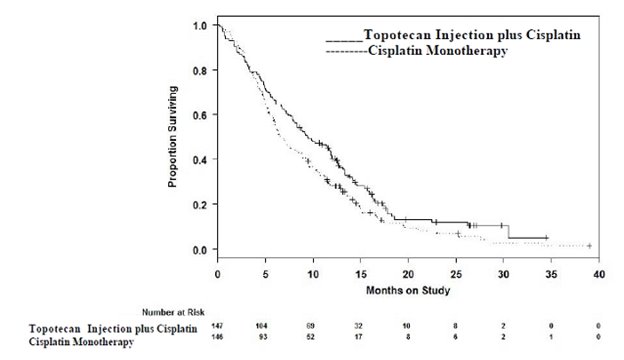
Median survival of eligible patients receiving Topotecan Injection plus cisplatin was 9.4 months (95% CI: 7.9 to 11.9) compared to 6.5 months (95% CI: 5.8 to 8.8) among patients randomized to cisplatin alone with a log rank P-value of 0.033 (significance level was 0.044 after adjusting for the interim analysis). The unadjusted hazard ratio for overall survival was 0.76 (95% CI: 0.59 to 0.98).
Figure 1. Overall Survival Curves Comparing Topotecan Injection plus Cisplatin versus Cisplatin Monotherapy in Cervical Cancer Patients
15 REFERENCES
1. Preventing Occupational Exposures to Antineoplastic and Other Hazardous Drugs in Health Care Settings. NIOSH Alert 2004-165.
2.OSHA Technical Manual, TED 1-0.15A, Section VI: Chapter 2. Controlling Occupational Exposure to Hazardous Drugs. OSHA, 1999. http://www.osha.gov/ dts/osta/otm/otm_vi/otm_vi_2.html
3. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. ASHP Guidelines on Handling Hazardous Drugs. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2006;63:1172-1193.
4. Polovich M, White JM, Kelleher LO (eds.) 2005. Chemotherapy and Biotherapy Guidelines and Recommendations for Practice. (2nd ed) Pittsburgh, PA: Oncology Nursing Society.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Topotecan Injection is supplied in the following:
4 mg/4 mL (1 mg/mL) Multiple Dose Vial
NDC 66758-051-05 (package of 1)
Unopened vials of Topotecan Injection are stable until the date indicated on the package when stored between 2ºC and 8°C (36°F and 46°F) and protected from light in the original package.
Topotecan Injection is supplied as a multiple dose vial. Studies have shown the product is stable for 28 days after initial puncture when stored under refrigerated conditions.
Topotecan Injection diluted for infusion is stable for 4 hours at room temperature or 24 hours at refrigerated temperature in ambient lighting conditions.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Bone Marrow Suppression
Inform patients that Topotecan Injection decreases blood cell counts such as white blood cells, platelets, and red blood cells. Patients who develop fever, other signs of infection (e.g., chills, cough, or burning pain on urination), or bleeding while on therapy should notify their physician promptly. Inform patients that frequent blood tests will be performed while taking Topotecan Injection to monitor for the occurrence of bone marrow suppression.
17.2 Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Advise patients to use effective contraceptive measures to prevent pregnancy and to avoid breastfeeding during treatment with Topotecan Injection.
17.3 Asthenia and Fatigue
Inform patients that Topotecan Injection may cause asthenia or fatigue. If these symptoms occur, caution should be observed when driving or operating machinery.
Rx only
For Sandoz Inc. customer service call 1-800-525-8747.
Revised: September 2011
Manufactured by: Ebewe Pharma, A-4866 Unterach, Austria
Manufactured for: Sandoz Inc., Princeton, NJ 08540
| TOPOTECAN
topotecan injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Sandoz Inc. (005387188) |