KIONEX
-
sodium polystyrene sulfonate suspension
Paddock Laboratories, Inc.
----------
Kionex®
Sodium Polystyrene
Sulfonate Suspension, USP
| CATION-EXCHANGE RESIN |
DESCRIPTION
Kionex® (Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Suspension, USP) can be administered orally or in an enema. It is a raspberry-flavored suspension containing 15 grams of cation-exchange resin (Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate, USP); 21.5 mL of Sorbitol Solution USP (equivalent to approximately 19.3 grams of Sorbitol); 0.12 mL (0.2%) of Alcohol per 60 mL of suspension. Also contains Purified Water USP, Propylene Glycol USP, Magnesium Aluminum Silicate NF, Xanthan Gum NF, Sodium Saccharin USP, Sorbic Acid NF, Methylparaben NF, Propylparaben NF, and Flavor.
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is a benzene, diethenyl-, polymer with ethenylbenzene, sulfonated, sodium salt and has the following structural formula:
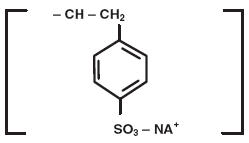
The sodium content of the suspension is 1500 mg (65 mEq) per 60 mL. It is a brown, slightly viscous suspension with an in vitro exchange capacity of approximately 3.1 mEq (in vivo approximately 1 mEq) of potassium per 4 mL (1 gram) of suspension.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
As the resin passes along the intestine or is retained in the colon after administration by enema, the sodium ions are partially released and are replaced by potassium ions. For the most part, this action occurs in the large intestine, which excretes potassium ions to a greater degree than does the small intestine. The efficiency of this process is limited and unpredictably variable. It commonly approximates the order of 33%, but the range is so large that definitive indices of electrolyte balance must be clearly monitored.
Metabolic data are unavailable.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Kionex® Suspension is indicated for the treatment of hyperkalemia.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Kionex® Suspension is contraindicated in patients with hypokalemia or those patients who are hypersensitive to it.
WARNINGS
Alternative Therapy in Severe Hyperkalemia:
Since the effective lowering of serum potassium with sodium polystyrene sulfonate may take hours to days, treatment with this drug alone may be insufficient to rapidly correct severe hyperkalemia associated with states of rapid tissue breakdown (e.g., burns and renal failure) or hyperkalemia so marked as to constitute a medical emergency. Therefore, other definitive measures, including dialysis, should always be considered and may be imperative.
Hypokalemia:
Serious potassium deficiency can occur from sodium polystyrene sulfonate therapy. The effect must be carefully controlled by frequent serum potassium determinations within each 24 hour period. Since intracellular potassium deficiency is not always reflected by serum potassium levels, the level at which treatment with sodium polystyrene sulfonate should be discontinued must be determined individually for each patient. Important aids in making this determination are the patient's clinical condition and electrocardiogram. Early clinical signs of severe hypokalemia include a pattern of irritable confusion and delayed thought processes. Electrocardiographically, severe hypokalemia is often associated with a lengthened Q-T interval, widening, flattening, or inversion of the T wave, and prominent U waves. Also, cardiac arrhythmias may occur, such as premature atrial, nodal, and ventricular contractions, and supraventricular and ventricular tachycardias. The toxic effects of digitalis are likely to be exaggerated. Marked hypokalemia can also be manifested by severe muscle weakness, at times extending into frank paralysis.
Electrolyte Disturbances:
Like all cation-exchange resins, sodium polystyrene sulfonate is not totally selective (for potassium) in its actions, and small amounts of other cations such as magnesium and calcium can also be lost during treatment. Accordingly, patients receiving sodium polystyrene sulfonate should be monitored for all applicable electrolyte disturbances.
Systemic Alkalosis:
Systemic alkalosis has been reported after cation-exchange resins were administered orally in combination with nonabsorbable cation-donating antacids and laxatives such as magnesium hydroxide and aluminum carbonate. Magnesium hydroxide should not be administered with sodium polystyrene sulfonate. One case of grand mal seizure has been reported in a patient with chronic hypocalcemia of renal failure who was given sodium polystyrene sulfonate with magnesium hydroxide as a laxative. (See PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
PRECAUTIONS
Caution is advised when sodium polystyrene sulfonate is administered to patients who cannot tolerate even a small increase in sodium loads (i.e., severe congestive heart failure, severe hypertension, or marked edema). In such instances, compensatory restriction of sodium intake from other sources may be indicated.
If constipation occurs, patients should be treated with sorbitol (from 10 to 20 mL of 70 percent syrup every 2 hours or as needed to produce 1 or 2 watery stools daily), a measure which also reduces any tendency to fecal impaction.
Drug Interactions
Antacids:
The simultaneous oral administration of sodium polystyrene sulfonate with nonabsorbable cation-donating antacids and laxatives may reduce the resin's potassium exchange capability.
Systemic alkalosis has been reported after cation exchange resins were administered orally in combination with nonabsorbable cation-donating antacids and laxatives such as magnesium hydroxide and aluminum carbonate. Magnesium hydroxide should not be administered with sodium polystyrene sulfonate. One case of grand mal seizure has been reported in a patient with chronic hypocalcemia of renal failure who was given sodium polystyrene sulfonate with magnesium hydroxide as a laxative.
Intestinal obstruction due to concretions of aluminum hydroxide when used in combination with sodium polystyrene sulfonate has been reported.
Digitalis:
The toxic effects of digitalis on the heart, especially various ventricular arrhythmias and A-V nodal dissociation, are likely to be exaggerated by hypokalemia, even in the face of serum digoxin concentrations in the "normal range" (See WARNINGS).
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Studies have not been performed.
Pregnancy Category C:
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with sodium polystyrene sulfonate. It is also not known whether sodium polystyrene sulfonate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers:
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when sodium polystyrene sulfonate is administered to a nursing woman.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Kionex® Suspension may cause some degree of gastric irritation. Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and constipation may occur especially if high doses are given. Also, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and significant sodium retention may occur. Occasionally diarrhea develops. Large doses in elderly individuals may cause fecal impaction (See PRECAUTIONS). This effect may be obviated through usage of the resin in enemas as described under DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION. Rare instances of colonic necrosis have been reported. Intestinal obstruction due to concretions of aluminum hydroxide, when used in combination with sodium polystyrene sulfonate, has been reported.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The average daily adult dose is 15 g (60 mL) to 60 g (240 mL) of suspension. This is best provided by administering 15 g (60 mL) of Kionex® Suspension one to four times daily. Each 60 mL of Kionex® Suspension contains 1500 mg (65 mEq) of sodium. Since the in vivo efficiency of sodium-potassium exchange resins is approximately 33%, about one-third of the resin's actual sodium content is being delivered to the body.
In smaller children and infants, lower doses should be employed by using as a guide a rate of 1 mEq of potassium per gram of resin as the basis for calculation.
Kionex® Suspension may be introduced into the stomach through a plastic tube and, if desired, given with a diet appropriate for a patient in renal failure.
Kionex® Suspension may also be given, although with less effective results, as an enema consisting (for adults) of 30 g (120 mL) to 50 g (200 mL) every six hours. The enema should be retained as long as possible and followed by a cleansing enema.
After an initial cleansing enema, a soft, large size (French 28) rubber tube is inserted into the rectum for a distance of about 20 cm, with the tip well into the sigmoid colon, and taped into place. The suspension is introduced at body temperature by gravity. The suspension is flushed with 50 or 100 mL of fluid, following which the tube is clamped and left in place. If back leakage occurs, the hips are elevated on pillows or a knee-chest position is taken temporarily. The suspension is kept in the sigmoid colon for several hours, if possible. Then the colon is irrigated with nonsodium containing solution at body temperature in order to remove the resin. Two quarts of flushing solution may be necessary. The returns are drained constantly through a Y tube connection. Particular attention should be paid to the cleansing enema, because sorbitol is present in the vehicle.
The intensity and duration of therapy depend upon the severity and resistance of hyperkalemia.
HOW SUPPLIED
Kionex® Suspension is a light brown, raspberry-flavored suspension supplied as follows:
Kionex® Suspension (Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Suspension, USP)
| 480 mL (16 Fluid Ounce) | NDC 0574-2002-16 |
| Unit-Dose 60 mL (2 Fluid Ounce) | NDC 0574-2002-02 |
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]
Kionex® Suspension should not be heated for to do so may alter the exchange properties of the resin.
Dispense in a tight container, as defined in the USP.
If repackaging into other containers, store in refrigerator and use within 14 days of packaging.
Paddock Laboratories, Inc.
Minneapolis, MN 55427
(09-07)
| KIONEX
sodium polystyrene sulfonate suspension |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revised: 11/2008Paddock Laboratories, Inc.