EXELON- rivastigmine patch, extended release
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EXELON PATCH safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EXELON PATCH.
EXELON® PATCH (rivastigmine transdermal system) Initial U.S. Approval: 2000 RECENT MAJOR CHANGESDosage and Administration (2.1) 08/2012 INDICATIONS AND USAGEDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSExelon Patch: 4.6 mg/24 hours or 9.5 mg/24 hours or 13.3 mg/24 hours (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost commonly observed adverse reactions (>5% and higher than with placebo): Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea (6.1)
DRUG INTERACTIONSCholinomimetic and anticholinergic drugs: Avoid concomitant use unless clinically necessary (7.1) See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 08/2012 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
The effective dosage of Exelon Patch is 9.5 mg/24 hours or 13.3 mg/24 hours administered once per day; replace with a new patch every 24 hours.
Initial Dose
Initiate treatment with one 4.6 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch applied to the skin once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Dose Titration
Increase the dose only after a minimum of 4 weeks at the previous dose, and only if the previous dose has been well tolerated. Continue the recommended effective dose of 9.5 mg/24 hours for as long as therapeutic benefit persists. Patients can then be increased to the maximum effective dose of 13.3 mg/24 hours dose. Doses higher than 13.3 mg/24 hours confer no appreciable additional benefit, and are associated with an increase in the incidence of adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Interruption of Treatment
If dosing is interrupted for three days or fewer, restart treatment with the same or lower strength Exelon Patch. If dosing is interrupted for more than three days, restart treatment with the 4.6 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch and titrate as described above.
2.2 Dosing in Specific Populations
Dosing Modifications in Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Consider using the 4.6 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch as both the initial and maximum dose in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment and in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Pharmacokinetic studies of oral rivastigmine in these patient populations showed reduced clearance of the drug [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Dosing Modifications in Patients with Low Body Weight
Because rivastigmine blood levels vary with weight [see Use in Specific Populations (8.8), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], carefully titrate and monitor patients with low body weight (<50kg) for toxicities (e.g., excessive nausea, vomiting) and consider reducing the maintenance dose to the 4.6 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch if such toxicities develop.
2.3 Switching to Exelon Patch from Exelon Capsules or Exelon Oral Solution
Patients treated with Exelon capsules or oral solution may be switched to Exelon Patch as follows:
- A patient who is on a total daily dose of <6 mg of oral rivastigmine can be switched to the 4.6 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch.
- A patient who is on a total daily dose of 6-12 mg of oral rivastigmine can be switched to the 9.5 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch.
Instruct patients or caregivers to apply the first patch on the day following the last oral dose.
2.4 Important Administration Instructions
Exelon Patch is for transdermal use on intact skin.
(a) Do not use the patch if the pouch seal is broken or the patch is cut, damaged, or changed in any way.
(b) Apply the Exelon Patch once a day
- Press down firmly until the edges stick well when applying to clean, dry, hairless, intact healthy skin in a place that will not be rubbed against by tight clothing.
- Use the upper or lower back as the site of application because the patch is less likely to be removed by the patient. If sites on the back are not accessible, apply the patch to the upper arm or chest.
- Do not apply to a skin area where cream, lotion, or powder has recently been applied.
(c) Do not apply to skin that is red, irritated, or cut.
(d) Replace the Exelon Patch with a new patch every 24 hours. If taking 4.6 mg/24 hours, instruct patients to only wear one patch at a time (remove the previous day's patch before applying a new patch) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Overdosage (10)]. If a dose is missed, apply a new patch immediately.
(e) Change the site of patch application daily to minimize potential irritation, although a new patch can be applied to the same general anatomic site (e.g., another spot on the upper back) on consecutive days. Do not apply a new patch to the same location for at least 14 days.
(f) May wear the patch during bathing and in hot weather. But avoid long exposure to external heat sources (excessive sunlight, saunas, solariums).
(g) Place used patches in the previously saved pouch and discard in the trash, away from pets or children.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Exelon Patch is available in three strengths. Each patch has a beige backing layer labeled as either:
- EXELON® PATCH 4.6 mg/24 hours, AMCX
- EXELON® PATCH 9.5 mg/24 hours, BHDI
- EXELON® PATCH 13.3 mg/24 hours, CNFU
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Exelon Patch (rivastigmine transdermal system) is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to rivastigmine, other carbamate derivatives, or other components of the formulation [see Description (11)]. Isolated cases of generalized skin reactions have been described in post-marketing experience [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Medication Errors Resulting in Overdose
Medication errors with Exelon Patch have resulted in serious adverse reactions; some cases have required hospitalization, and rarely, led to death. The majority of medication errors have involved not removing the old patch when putting on a new one and the use of multiple patches at one time. Instruct patients and their caregivers on important administration instructions for Exelon Patch. [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.2 Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Exelon Patch can cause gastrointestinal adverse reactions, including significant nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia/decreased appetite, and weight loss. Dehydration may result from prolonged vomiting or diarrhea and can be associated with serious outcomes. The incidence and severity of these reactions are dose-related [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. For this reason, initiate treatment with Exelon Patch at a dose of 4.6 mg/24 hours and titrate to a dose of 9.5 mg/24 hours and then to a dose of 13.3 mg/24 hours, if appropriate [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
If treatment is interrupted for more than three days because of intolerance, reinitiate Exelon Patch with the 4.6 mg/24 hours dose to reduce the possibility of severe vomiting and its potentially serious sequelae. A postmarketing report described a case of severe vomiting with esophageal rupture following inappropriate reinitiation of treatment of an oral formulation of rivastigmine without retitration after 8 weeks of treatment interruption.
Inform caregivers to monitor for gastrointestinal adverse reactions and to inform the physician if they occur. It is critical to inform caregivers that if therapy has been interrupted for more than three days because of intolerance, the next dose should not be administered without contacting the physician regarding proper retitration.
5.3 Other Adverse Reactions from Increased Cholinergic Activity
Neurologic Effects
Extrapyramidal Symptoms: Like other cholinomimetics, rivastigmine may exacerbate or induce extrapyramidal symptoms. Worsening of parkinsonian symptoms, particularly tremor, has been observed in patients with dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease who were treated with Exelon capsules.
Seizures: Drugs that increase cholinergic activity are believed to have some potential for causing seizures. However, seizure activity also may be a manifestation of Alzheimer's disease.
Peptic Ulcers/Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Cholinesterase inhibitors, including rivastigmine, may increase gastric acid secretion due to increased cholinergic activity. Monitor patients using Exelon Patch for symptoms of active or occult gastrointestinal bleeding, especially those at increased risk for developing ulcers, e.g., those with a history of ulcer disease or those receiving concurrent nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Clinical studies of rivastigmine have shown no significant increase, relative to placebo, in the incidence of either peptic ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding.
Use with Anesthesia
Rivastigmine, as a cholinesterase inhibitor, is likely to exaggerate succinylcholine-type muscle relaxation during anesthesia.
Cardiac Conduction Effects
Because rivastigmine increases cholinergic activity, use of the Exelon Patch may have vagotonic effects on heart rate (e.g., bradycardia). The potential for this action may be particularly important in patients with sick sinus syndrome or other supraventricular cardiac conduction conditions. In clinical trials, rivastigmine was not associated with any increased incidence of cardiovascular adverse events, heart rate or blood pressure changes, or ECG abnormalities.
Genitourinary Effects
Although not observed in clinical trials of rivastigmine, drugs that increase cholinergic activity may cause urinary obstruction.
Pulmonary Effects
Like other drugs that increase cholinergic activity, Exelon Patch should be used with care in patients with a history of asthma or obstructive pulmonary disease.
5.4 Impairment in Driving or Use of Machinery
Dementia may cause gradual impairment of driving performance or compromise the ability to use machinery. The administration of rivastigmine may also result in adverse reactions that are detrimental to these functions. During treatment with the Exelon Patch, routinely evaluate the patient's ability to continue driving or operating machinery.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Significant gastrointestinal adverse reactions including nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and weight loss are described below and elsewhere in the labeling [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Exelon Patch has been administered to 1634 patients with Alzheimer's disease during clinical trials worldwide. Of these, 1388 patients have been treated for at least 12 weeks, 1182 patients have been treated for at least 24 weeks, and 582 patients have been treated for at least 48 weeks.
24-Week International Placebo-Controlled Trial (Study 1)
Most Commonly Observed Adverse Reactions
The most commonly observed adverse reactions in patients administered Exelon Patch in Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14.1)], defined as those occurring at a frequency of at least 5% in the 9.5 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch arm and at a frequency at higher than in the placebo group, were nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These reactions were dose-related, with each being more common in patients using the 17.4 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch than in those using the 9.5 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch.
Discontinuation Rates
In Study 1, which randomized a total of 1195 patients, the proportions of patients in the Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours, Exelon capsules 6 mg twice daily, and placebo groups who discontinued treatment due to adverse events were 9.6%, 8.1%, and 5.0%, respectively.
The most common adverse reactions in the Exelon Patch-treated groups that led to treatment discontinuation in this study were nausea and vomiting. The proportions of patients who discontinued treatment due to nausea were 0.7%, 1.7%, and 1.3% in the Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours, Exelon capsules 6 mg twice daily, and placebo groups, respectively. The proportions of patients who discontinued treatment due to vomiting were 0%, 2.0%, and 0.3% in the Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours, Exelon capsules 6 mg twice daily, and placebo groups, respectively.
Adverse Reactions Observed at an Incidence of ≥2%
Table 1 lists adverse reactions seen at an incidence of ≥2% in either Exelon Patch-treated group in Study 1 and for which the rate of occurrence was greater for patients treated with that dose of Exelon Patch than for those treated with placebo. The unapproved 17.4 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch arm is included to demonstrate the increased rates of gastrointestinal adverse reactions over those seen with the 9.5 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch.
| Exelon Patch
9.5 mg/24 hours | Exelon Patch
17.4 mg/24 hours | Exelon capsule
6 mg twice daily | Placebo | |
| Total Patients Studied | 291 | 303 | 294 | 302 |
| Total Percentage of Patients with ARs (%) | 51 | 66 | 63 | 46 |
| Nausea | 7 | 21 | 23 | 5 |
| Vomiting* | 6 | 19 | 17 | 3 |
| Diarrhea | 6 | 10 | 5 | 3 |
| Depression | 4 | 4 | 4 | 1 |
| Headache | 3 | 4 | 6 | 2 |
| Anxiety | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Anorexia/Decreased Appetite | 3 | 9 | 9 | 2 |
| Weight Decreased ** | 3 | 8 | 5 | 1 |
| Dizziness | 2 | 7 | 7 | 2 |
| Abdominal Pain | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Urinary Tract Infection | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Asthenia | 2 | 3 | 6 | 1 |
| Fatigue | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Insomnia | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Abdominal Pain Upper | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Vertigo | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
*Vomiting was severe in 0% of patients who received Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours, 1% of patients who received Exelon Patch 17.4 mg/24 hours, 1% of patients who received the Exelon capsule at doses up to 6 mg BID, and 0% of those who received placebo.
**Weight Decreased as presented in Table 1 is based upon clinical observations and/or adverse events reported by patients or caregivers. Body weight was also monitored at pre-specified time points throughout the course of the clinical study. The proportion of patients who had weight loss equal to or greater than 7% of their baseline weight was 8% of those treated with Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours, 12% of those treated with Exelon Patch 17.4 mg/24 hours, 11% of patients who received the Exelon capsule at doses up to 6 mg BID and 6% of those who received placebo. It is not clear how much of the weight loss was associated with anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and the diarrhea associated with the drug.
48-Week International Active Comparator-Controlled Trial (Study 2)
Most Commonly Observed Adverse Reactions
In Study 2 [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] of the commonly observed adverse reactions (≥ 3% in any treatment group) the most frequent event in the Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours group was nausea, followed by vomiting, fall, weight decreased, application site erythema, decreased appetite, diarrhea and urinary tract infection (Table 2). The percentage of patients with these events was higher in the Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours group than in the Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours group. Patients with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and decreased appetite experienced these reactions more often during the first 4 weeks of the double-blind treatment phase. These reactions decreased over time in each treatment group. Weight decreased was reported to have increased over time in each treatment group.
Discontinuation Rates
Table 2 displays the most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation during the 48-week double-blind treatment phase in Study 2.
| Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours | Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours | Total | |
| Total Patients Studied | 280 | 283 | 563 |
| Total Percentage of Patients with ARs Leading to Discontinuation (%) | 9.6 | 12.7 | 11.2 |
| Vomiting | 1.4 | 0.4 | 0.9 |
| Application site pruritus | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| Aggression | 0.4 | 1.1 | 0.7 |
Most Commonly Observed Adverse Reactions ≥3%
Other adverse reactions of interest which occurred less frequently, but which were observed in a markedly higher percentage of patients in the Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours group than in the Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours group in Study 2, included dizziness and upper abdominal pain. The percentage of patients with these reactions decreased over time in each treatment group (Table 3). The majority of patients reported adverse events of mild to moderate severity. The adverse event severity profile was generally similar for both the Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours and 9.5 mg/24 hours groups.
| Cumulative Week 0-48 (DB Phase) | Week 0- 24 (DB Phase) | Week > 24 to 48 (DB Phase) | ||||
| Preferred Term | Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours | Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours | Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours | Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours | Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours | Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours |
| Total Patients Studied | 280 | 283 | 280 | 283 | 241 | 246 |
| Total Percentage of Patients with ARs (%) | 75 | 68 | 65 | 55 | 42 | 40 |
| Nausea | 12 | 5 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| Vomiting | 10 | 5 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Fall | 8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| Weight decreased* | 7 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 2 |
| Application site erythema | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 2 |
| Decreased appetite | 6 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 2 | <1 |
| Diarrhea | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 2 | <1 |
| Urinary tract infection | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Agitation | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Depression | 5 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Dizziness | 4 | 1 | 3 | <1 | 2 | <1 |
| Application site pruritus | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | <1 | 1 |
| Headache | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | <1 | <1 |
| Insomnia | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| Abdominal pain upper | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | <1 |
| Anxiety | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Hypertension | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Urinary incontinence | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | <1 |
| Psychomotor hyperactivity | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Aggression | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| *Decreased Weight as presented in Table 3 is based upon clinical observations and/or adverse events reported by patients or caregivers. Body weight was monitored as a vital sign at pre-specified time points throughout the course of the clinical study. The proportion of patients who had weight loss equal to or greater than 7% of their baseline weight was 15.2% of those treated with Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours and 18.6% of those treated with Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours during the 48 week double-blind treatment period | ||||||
Application Site Reactions in the 24-Week and 48-Week Studies (Studies 1 and 2)
A direct comparison of the rates of application site reactions reported in the placebo-controlled and active comparator controlled clinical trials cannot be made due to differences in the method of data collection employed in each of the trials.
In Study 1, cases of skin irritation were captured separately on an investigator-rated skin irritation scale and not as adverse events unless they fulfilled the criteria for a serious adverse event. Skin irritation, when observed, was mostly slight or mild in severity and was rated as severe in ≤2.2% of Exelon Patch patients, versus ≤1.0% of placebo patch patients. Among the skin reactions reported were the following: application site reactions, application site dermatitis and application site irritation.
In Study 2, cases of application site reactions were captured as patient or caregiver reported adverse events. The most commonly reported skin irritation events for both treatment groups were application site erythema and application site pruritus. These events occurred more frequently during the first 24 weeks of the double-blind period and decreased over time in each treatment group after 24 weeks (Table 3). The most common reason for discontinuation due to application site reactions was application site pruritus which occurred in 1.1% of the patients in each treatment group (Table 2). Application site reactions were mostly mild or moderate in severity and were rated as severe in less than 2% of patients.
Other Adverse Events Observed During Clinical Trials
The frequencies represent the proportion of 1634 patients from 2 controlled and 4 open-label trials in North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia and Japan who experienced that event while receiving Exelon Patch. All patch doses are pooled.
All adverse events occurring in approximately 0.1% are included, except for those already listed elsewhere in labeling, too general to be informative, or relatively minor events.
Events are classified by system organ class and listed using the following definitions: Frequent – those occurring in at least 1/100 patients; Infrequent – those occurring in 1/100 to 1/1000 patients. These adverse events are not necessarily related to Exelon Patch treatment and in most cases were observed at a similar frequency in placebo-treated patients in the controlled studies.
Cardiac Disorders: Infrequent: Bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrioventricular block, arrhythmia, supraventricular extrasystole.
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: Infrequent: Tinnitus.
Eye Disorders: Infrequent: Vision blurred.
Gastrointestinal System: Frequent: Constipation, gastritis. Infrequent: Gastroesophageal reflux disease, hematochezia, hematemesis, pancreatitis, salivary hypersecretion.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Infrequent: Chest pain.
Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications: Infrequent: Hip fracture.
Investigations: Infrequent: Blood creatine phosphokinase increased, lipase increased, blood amylase increased, electrocardiogram QT prolonged.
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders: Frequent: Dehydration. Infrequent: Hypokalemia, hyponatremia.
Nervous System Disorders: Infrequent: Migraine.
Psychiatric Disorders: Infrequent: Delirium
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders: Infrequent: Dyspnea, bronchospasm.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Frequent: Pruritus. Infrequent: Erythema, eczema, dermatitis, rash erythematous, skin ulcer.
Vascular Disorders: Infrequent: Hypotension, cerebrovascular accident.
Other Adverse Reactions Observed with Exelon Capsules or Oral Solution
The following additional adverse reactions have been observed with Exelon capsules/oral solution:
Confusion, abnormal liver function tests, duodenal ulcers, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, tremor
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified based on postmarketing spontaneous reports and are not listed above. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypertension, application site hypersensitivity, urticaria, blister, allergic dermatitis, seizure, worsening of Parkinson’s disease in patients with Parkinson’s disease who were treated with Exelon Patch, tachycardia.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Cholinomimetic and Anticholinergic Drugs
Rivastigmine may increase the cholinergic effects of other cholinomimetic drugs. Rivastigmine may also interfere with the activity of anticholinergic medications. Avoid concomitant use of rivastigmine with drugs having these pharmacologic effects unless deemed clinically necessary.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. No dermal reproduction studies in animals have been conducted. Oral reproduction studies conducted in pregnant rats and rabbits revealed no evidence of teratogenicity. Studies in rats showed slightly decreased fetal/pup weight, usually at doses causing some maternal toxicity. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Rivastigmine and its metabolites are excreted in rat milk following oral administration of rivastigmine; levels of rivastigmine plus metabolites in rat milk are approximately two times that in maternal plasma. It is not known whether rivastigmine is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Exelon Patch, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. Use of Exelon Patch in children and adolescents (below 18 years of age) is not recommended.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of Exelon Patch, 88% were 65 and over, while 53% were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
8.6 Renal Impairment
In patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (glomerular filtration rate [GFR] <50 mL/min), clearance of oral rivastigmine was reduced [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In these patients, consider using the lowest dose Exelon Patch (4.6 mg/24 hours) for both initial and maintenance therapy.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
In patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 5-9), clearance of oral rivastigmine was reduced [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In these patients, consider using the lowest dose Exelon Patch (4.6 mg/24 hours) for both initial and maintenance therapy. No data are available on the use of rivastigmine in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
8.8 Low or High Body Weight
Because rivastigmine blood levels vary with weight [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], careful titration and monitoring should be performed in patients with low or high body weights. In patients with low body weight (<50 kg), monitor closely for toxicities (e.g., excessive nausea, vomiting), and consider reducing the maintenance dose to the 4.6 mg/24 hour Exelon Patch if such toxicities develop. In patients with body weight >100 kg, consider the use of doses higher than 9.5 mg/24 hours.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdose with Exelon Patch has been reported in the postmarketing setting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Overdoses have occurred from application of more than one patch at one time and not removing the previous day’s patch before applying a new patch. The symptoms reported in these overdose cases are similar to those seen in cases of overdose associated with rivastigmine oral formulations.
Because strategies for the management of overdose are continually evolving, it is advisable to contact a Poison Control Center to determine the latest recommendations for the management of an overdose of any drug. As rivastigmine has a plasma half-life of about 3.4 hours after patch administration and a duration of acetylcholinesterase inhibition of about 9 hours, it is recommended that in cases of asymptomatic overdose the patch should be immediately removed and no further patch should be applied for the next 24 hours.
As in any case of overdose, general supportive measures should be utilized. Overdosage with cholinesterase inhibitors can result in cholinergic crisis characterized by severe nausea, vomiting, salivation, sweating, bradycardia, hypotension, respiratory depression, and convulsions. Increasing muscle weakness is a possibility and may result in death if respiratory muscles are involved. Atypical responses in blood pressure and heart rate have been reported with other drugs that increase cholinergic activity when coadministered with quaternary anticholinergics such as glycopyrrolate. Due to the short plasma elimination half-life of rivastigmine after patch administration, dialysis (hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, or hemofiltration) would not be clinically indicated in the event of an overdose.
In overdose accompanied by severe nausea and vomiting, the use of antiemetics should be considered.
11 DESCRIPTION
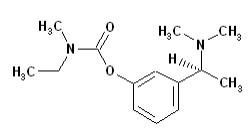
Exelon Patch (rivastigmine transdermal system) contains rivastigmine, a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor known chemically as (S)- 3-[1-(dimethylamino) ethyl]phenyl ethylmethylcarbamate. It has an empirical formula of C14H22N2O2 as the base and a molecular weight of 250.34 (as the base). Rivastigmine is a viscous, clear, and colorless to yellow to very slightly brown liquid that is sparingly soluble in water and very soluble in ethanol, acetonitrile, n-octanol and ethyl acetate.
The distribution coefficient at 37°C in n-octanol/phosphate buffer solution pH 7 is 4.27.
Exelon Patch is for transdermal administration. The patch is a four-layer laminate containing the backing layer, drug matrix, adhesive matrix and overlapping release liner (see Figure 1). The release liner is removed and discarded prior to use.
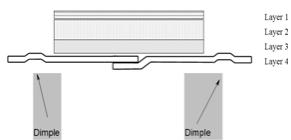
Figure 1: Cross Section of the Exelon Patch
| Layer 1: | Backing Film |
| Layer 2: | Drug Product (Acrylic) Matrix |
| Layer 3: | Adhesive (Silicone) Matrix |
| Layer 4: | Release Liner (removed at time of use) |
Excipients within the formulation include acrylic copolymer, poly(butylmethacrylate, methylmethacrylate), silicone adhesive applied to a flexible polymer backing film, silicone oil, and vitamin E.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Although the precise mechanism of action of rivastigmine is unknown, it is thought to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by cholinesterase. If this mechanism is correct, the effect of rivastigmine may lessen as the disease process advances and fewer cholinergic neurons remain functionally intact. There is no evidence that rivastigmine alters the course of the underlying dementing process.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
After a 6-mg oral dose of rivastigmine in humans, anticholinesterase activity is present in cerebrospinal fluid for about 10 hours, with a maximum inhibition of about 60% 5 hours after dosing.
In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrate that the inhibition of cholinesterase by rivastigmine is not affected by the concomitant administration of memantine, an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After the initial application of Exelon Patch, there is a lag time of 0.5-1 hour in the absorption of rivastigmine. Concentrations then rise slowly typically reaching a maximum after 8 hours, although maximum values (Cmax) can also occur later (at 10-16 hours). After the peak, plasma concentrations slowly decrease over the remainder of the 24-hour period of application. At steady state, trough levels are approximately 60-80% of peak levels.
Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours gave exposure approximately the same as that provided by an oral dose of 6 mg twice daily (i.e., 12 mg/day). Inter-subject variability in exposure was lower (43-49%) for the Exelon Patch formulation as compared with the oral formulations (73-103%). Fluctuation (between Cmax and Cmin) is less for Exelon Patch than for the oral formulation of rivastigmine.
Figure 2 displays rivastigmine plasma concentrations over 24 hours for the three available patch strengths.
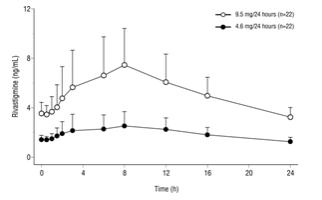
Figure 2: Rivastigmine Plasma Concentrations Following Dermal 24-Hour Patch Application
Over a 24-hour dermal application, approximately 50% of the drug content of the patch is released from the system.
Exposure (AUC∞) to rivastigmine (and metabolite NAP266-90) was highest when the patch was applied to the upper back, chest, or upper arm. Two other sites (abdomen and thigh) could be used if none of the three other sites is available, but the practitioner should be aware that the rivastigmine plasma exposure associated with these sites was approximately 20-30% lower.
There was no relevant accumulation of rivastigmine or the metabolite NAP226-90 in plasma in patients with Alzheimer’s disease with daily dosing.
Distribution
Rivastigmine is weakly bound to plasma proteins (approximately 40%) over the therapeutic range. It readily crosses the blood-brain barrier, reaching CSF peak concentrations in 1.4-2.6 hours. It has an apparent volume of distribution in the range of 1.8-2.7 L/kg.
Metabolism
Rivastigmine is extensively metabolized primarily via cholinesterase-mediated hydrolysis to the decarbamylated metabolite NAP226-90. In vitro, this metabolite shows minimal inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (<10%). Based on evidence from in vitro and animal studies, the major cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are minimally involved in rivastigmine metabolism.
The metabolite-to-parent AUC∞ ratio was about 0.7 after Exelon Patch application versus 3.5 after oral administration, indicating that much less metabolism occurred after dermal treatment. Less NAP226-90 is formed following patch application, presumably because of the lack of presystemic (hepatic first pass) metabolism. Based on in vitro studies, no unique metabolic routes were detected in human skin.
Elimination
Renal excretion of the metabolites is the major route of elimination. Unchanged rivastigmine is found in trace amounts in the urine. Following administration of 14C-rivastigmine, renal elimination was rapid and essentially complete (>90%) within 24 hours. Less than 1% of the administered dose is excreted in the feces. The apparent elimination half-life in plasma is approximately 3 hours after patch removal. Renal clearance was approximately
2.1-2.8 L/hr.
Renal Impairment
No study was conducted with Exelon Patch in subjects with renal impairment. Following a single 3-mg dose, mean oral clearance of rivastigmine is 64% lower in moderately impaired renal patients (n=8, GFR=10-50 mL/min) than in healthy subjects (n=10, GFR≥60 mL/min); Cl/F=1.7 L/min and 4.8 L/min, respectively. In patients with severe renal impairment (n=8, GFR<10 mL/min), mean oral clearance of rivastigmine is 43% higher than in healthy subjects (n=10, GFR≥60 mL/min); Cl/F=6.9 L/min and 4.8 L/min, respectively. For unexplained reasons, the severely impaired renal patients had a higher clearance of rivastigmine than moderately impaired patients. Despite this finding, consider a reduced dose in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Hepatic Impairment
No pharmacokinetic study was conducted with Exelon Patch in subjects with hepatic impairment. After multiple 6-mg twice daily oral dosing, the mean clearance of rivastigmine was 65% lower in mild (n=7, Child-Pugh score 5-6) and moderate (n=3, Child-Pugh score 7-9) hepatically impaired patients (biopsy proven, liver cirrhosis) than in healthy subjects (n=10).
Body Weight
A relationship between drug exposure at steady state (rivastigmine and metabolite NAP226-90) and body weight was observed in Alzheimer’s dementia patients. Rivastigmine exposure is higher in subjects with low body weight. Compared to a patient with a body weight of 65 kg, the rivastigmine steady-state concentrations in a patient with a body weight of 35 kg would be approximately doubled, while for a patient with a body weight of 100 kg the concentrations would be approximately halved [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Age
Age had no impact on the exposure to rivastigmine in Alzheimer’s disease patients treated with Exelon Patch.
Gender or Race
No specific pharmacokinetic study was conducted to investigate the effect of gender and race on the disposition of Exelon Patch. A population pharmacokinetic analysis of oral rivastigmine indicated that neither gender (n=277 males and 348 females) nor race (n=575 White, 34 Black, 4 Asian, and 12 Other) affected clearance of the drug. Similar results were seen with analyses of pharmacokinetic data obtained after the administration of Exelon Patch.
Smoking
Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that nicotine use increased the oral clearance of rivastigmine by 23% (n=75 smokers and 549 nonsmokers).
Drug Interaction Studies
No specific interaction studies have been conducted with Exelon Patch. Information presented below is from studies with oral rivastigmine.
Effect of Rivastigmine on the Metabolism of Other Drugs
Rivastigmine is primarily metabolized through hydrolysis by esterases. Minimal metabolism occurs via the major cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. Based on in vitro studies, no pharmacokinetic drug interactions with drugs metabolized by the following isoenzyme systems are expected: CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP3A4/5, CYP2E1, CYP2C9, CYP2C8, CYP2C19, or CYP2B6.
No pharmacokinetic interaction was observed between rivastigmine taken orally and digoxin, warfarin, diazepam or fluoxetine in studies in healthy volunteers. The increase in prothrombin time induced by warfarin is not affected by administration of rivastigmine.
Effect of Other Drugs on the Metabolism of Rivastigmine
Drugs that induce or inhibit CYP450 metabolism are not expected to alter the metabolism of rivastigmine.
Population pharmacokinetic analysis with a database of 625 patients showed that the pharmacokinetics of rivastigmine taken orally were not influenced by commonly prescribed medications such as antacids (n=77), antihypertensives (n=72), ß-blockers (n=42), calcium channel blockers (n=75), antidiabetics (n=21), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (n=79), estrogens (n=70), salicylate analgesics (n=177), antianginals (n=35) and antihistamines (n=15).
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In oral carcinogenicity studies conducted at doses up to 1.1 mg base/kg/day in rats and 1.6 mg base/kg/day in mice, rivastigmine was not carcinogenic.
In a dermal carcinogenicity study conducted at doses up to 0.75 mg base/kg/day in mice, rivastigmine was not carcinogenic. The mean rivastigmine plasma exposure (AUC) at this dose was less than that in humans at the maximum recommended human dose (13.3 mg/24 hours).
Mutagenesis
Rivastigmine was clastogenic in in vitro chromosomal aberration assays in mammalian cells in the presence, but not the absence, of metabolic activation. Rivastigmine was negative in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay, an in vitro HGPRT assay, and in an in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
No fertility or reproduction studies of dermal rivastigmine have been conducted in animals. Rivastigmine had no effect on fertility or reproductive performance in rats at oral doses up to 1.1 mg base/kg/day.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The effectiveness of the Exelon Patch in dementia of the Alzheimer’s type and dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease was based on the results of two controlled trials of Exelon Patch in patients with Alzheimer’s disease (Studies 1 and 2) (see below); three controlled trials of oral rivastigmine in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer’s type; and one controlled trial of oral rivastigmine in patients with dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease. See the prescribing information for oral rivastigmine for details of the four studies of oral rivastigmine.
International 24-Week Study of Exelon Patch in Dementia of the Alzheimer’s Type (Study 1)
This study was a randomized double-blind, double dummy clinical investigation in patients with Alzheimer’s disease [diagnosed by NINCDS-ADRDA and DSM-IV criteria, Mini-Mental Status Examination (MMSE) score ≥10 and ≤20] (Study 1). The mean age of patients participating in this trial was 74 years with a range of 50-90 years. Approximately 67% of patients were women, and 33% were men. The racial distribution was White 75%, Black 1%, Asian 9%, and other races 15%.
The effectiveness of the Exelon Patch was evaluated in Study 1 using a dual outcome assessment strategy, evaluating for changes in both cognitive performance and overall clinical effect.
The ability of the Exelon Patch to improve cognitive performance was assessed with the cognitive subscale of the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-Cog), a multi-item instrument that has been extensively validated in longitudinal cohorts of Alzheimer’s disease patients. The ADAS-Cog examines selected aspects of cognitive performance including elements of memory, orientation, attention, reasoning, language, and praxis. The ADAS-Cog scoring range is from 0-70, with higher scores indicating greater cognitive impairment. Elderly normal adults may score as low as 0 or 1, but it is not unusual for non-demented adults to score slightly higher.
The ability of the Exelon Patch to produce an overall clinical effect was assessed using the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study-Clinical Global Impression of Change (ADCS-CGIC). The ADCS-CGIC is a more standardized form of the Clinician's Interview-Based Impression Of Change-Plus (CIBIC-Plus) and is also scored as a seven-point categorical rating; scores range from 1, indicating “markedly improved,” to 4, indicating “no change,” to 7, indicating “marked worsening.”
In Study 1, 1195 patients were randomized to one of the following four treatments: Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours, Exelon Patch 17.4 mg/24 hours, Exelon capsules in a dose of 6 mg twice daily, or placebo. This 24-week study was divided into a 16-week titration phase followed by an 8-week maintenance phase. In the active treatment arms of this study, doses below the target dose were permitted during the maintenance phase in the event of poor tolerability.
Figure 3 illustrates the time course for the change from baseline in ADAS-Cog scores for all 4 treatment groups over the 24-week study. At 24 weeks, the mean differences in the ADAS-Cog change scores for the Exelon-treated patients compared to the patients on placebo, were 1.8, 2.9, and 1.8 units for the Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours, Exelon Patch 17.4 mg/24 hours, and Exelon capsule 6 mg twice daily groups, respectively. The difference between each of these groups and placebo was statistically significant. Although a slight improvement was observed with the 17.4 mg/24 hours patch compared to the 9.5 mg/24 hours patch on this outcome measure, no meaningful difference between the two was seen on the global evaluation (see Figure 4).
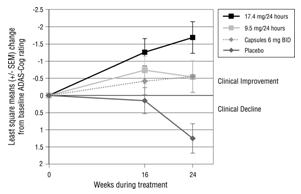
Figure 3: Time Course of the Change from Baseline in ADAS-Cog Score for Patients Observed at Each Time Point in Study 1
Figure 4 presents the distribution of patients’ scores on the ADCS-CGIC for all 4 treatment groups. At 24 weeks, the mean difference in the ADCS-CGIC scores for the comparison of patients in each of the Exelon-treated groups with the patients on placebo was 0.2 units. The difference between each of these groups and placebo was statistically significant.
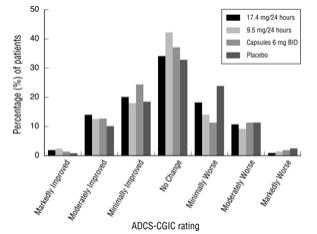
Figure 4: Distribution of ADCS-CGIC Scores for Patients Completing Study 1
International 48-Week Study of Exelon Patch in Dementia of the Alzheimer’s Type (Study 2)
This study was a randomized double-blind clinical investigation in patients with Alzheimer’s disease [diagnosed by NINCDS-ADRDA and DSM-IV criteria, Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score ≥10 and ≤24] (Study 2). The mean age of patients participating in this trial was 76 years with a range of 50-85 years. Approximately 65% of patients were women and 35% were men. The racial distribution was approximately Caucasian 97%, Black 2%, Oriental 0.5% and Other Races 1%. Approximately 27% of the patients were taking memantine throughout the entire duration of the study.
Alzheimer’s disease patients who received 24-48 weeks open label treatment with Exelon Patch 9.5mg/24 hours and who demonstrated functional and cognitive decline were randomized into treatment with either Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours or Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours in a 48-week double blind treatment phase. Functional decline was assessed by the investigator and cognitive decline was defined as a decrease in the MMSE score of >2 points from the previous visit or a decrease of >3 points from baseline.
Study 2 was designed to compare the efficacy of Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/ 24 hours versus that of Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours during the 48-week double blind treatment phase.
The ability of the Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours to improve cognitive performance over that provided by the Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours was assessed by the cognitive subscale of the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS-Cog) [see International 24-Week Study (14.1)].
The ability of the Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours to improve overall function versus that provided by Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours was assessed by the instrumental sub-scale of the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study Activities of Daily Living (ADCS-IADL). The ADCS-IADL sub-scale is composed of items 7 to 23 of the caregiver-based ADCS-ADL scale. The ADCS-IADL assesses activities such as those necessary for communicating and interacting with other people, maintaining a household, and conducting hobbies and interests. A sum score is calculated by adding the scores of the individual items and can range from 0 to 56, with higher scores indicating less impairment.
Out of a total of 1584 patients enrolled in the initial open-label phase of the study, 567 patients were classified as decliners and were randomized into the 48-week double-blind treatment phase of the study. Two hundred eighty-seven (287) patients entered the 9.5 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch treatment group and 280 patients entered the 13.3 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch treatment group.
Figure 5 illustrates the time course for the mean change from double-blind baseline in ADCS-IADL scores for each treatment group over the course of the 48-week treatment phase of the study. Decline in the mean ADCS-IADL score from the double-blind baseline for the Intent to Treat – Last Observation Carried Forward (ITT-LOCF) analysis was less at each timepoint in the 13.3 mg/24 hour Exelon Patch treatment group than in the 9.5 mg/24 hours Exelon Patch treatment group. The between-treatment group differences for Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24hours versus Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours were statistically significant at weeks 16, 24, 32 and 48 (primary endpoint).
Figure 6 illustrates the time course for the mean change from double-blind baseline in ADAS-Cog scores for both treatment groups over the 48-week treatment phase. The between-treatment group difference for Exelon Patch 13.3 mg/24 hours versus Exelon Patch 9.5 mg/24 hours was nominally statistically significant at week 24 (p=0.027), but not at week 48 (p=0.227), which was the primary endpoint.

Figure 5 Time Course of the Change from Double-Blind Baseline in ADCS-IADL Score for Patients Observed at Each Time Point in Study 2

Figure 6 Time Course of the Change from Double-Blind Baseline in ADAS-Cog Score for Patients Observed at Each Time Point in Study 2
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Exelon Patch: 4.6 mg/24 hours
Each patch of 5 cm2 contains 9 mg rivastigmine base with in vivo release rate of 4.6 mg/24 hours.
Carton of 30………………………NDC 0078-0501-15
Exelon Patch: 9.5 mg/24 hours
Each patch of 10 cm2 contains 18 mg rivastigmine base with in vivo release rate of 9.5 mg/24 hours.
Carton of 30………………………..NDC 0078-0502-15
Exelon Patch: 13.3 mg/24 hours
Each patch of 15 cm2 contains 27 mg rivastigmine base with in vivo release rate of 13.3 mg/24 hours.
Carton of 30………………………NDC 0078-0503-15
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep Exelon Patch in the individual sealed pouch until use. Each pouch contains one patch. Used systems should be folded, with the adhesive surfaces pressed together, and discarded safely.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Importance of Correct Usage
Inform patients or caregivers of the importance of applying the correct dose on the correct part of the body. They should be instructed to rotate the application site in order to minimize skin irritation. The same site should not be used within 14 days. The previous day’s patch must be removed before applying a new patch to a different skin location. Exelon Patch should be replaced every 24 hours and the time of day should be consistent. It may be helpful for this to be part of a daily routine, such as the daily bath or shower.
Instruct patients or caregivers to avoid exposure of the patch to external heat sources (excessive sunlight, saunas, solariums) for long periods of time.
Instruct patients who have missed a dose to apply a new patch immediately. They may apply the next patch at the usual time the next day. Instruct patients to not apply two patches to make up for one missed.
Inform the patient or caregiver to contact the physician for retitration instructions if treatment has been interrupted.
Discarding Used Patches
Instruct patients or caregivers to fold the patch in half after use, return the used patch to its original pouch, and discard it out of the reach and sight of children and pets. They should also be informed that drug still remains in the patch after 24-hour usage. They should be instructed to avoid eye contact and to wash their hands after handling the patch.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Inform patients or caregivers of the potential gastrointestinal adverse reactions such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, including the possibility of dehydration due to these symptoms. Explain that Exelon Patch may affect the patient’s appetite and/or the patient’s weight. Patients and caregivers should be instructed to look for these adverse reactions, in particular when treatment is initiated or the dose is increased. Instruct patients and caregivers to inform a physician if these adverse reactions persist.
Concomitant Use of Drugs with Cholinergic Action
Inform patients or caregivers that while wearing Exelon Patch, patients should not be taking Exelon capsules or Exelon oral solution or other drugs with cholinergic effects.
PATIENT INFORMATION
Exelon Patch [ECS-‘el-on]
(rivastigmine
transdermal system)
Exelon Patch is for skin use only.
Read this Patient Information leaflet before you start using Exelon Patch and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment. If you do not understand the information, or have any questions about Exelon Patch, talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Exelon patch is available in 3 dosage strengths
- 4.6 mg per day (4.6 mg/24 hours)
- 9.5 mg per day (9.5 mg/24 hours)
- 13.3 mg per day (13.3 mg/24 hours)
What is Exelon Patch?
Exelon Patch is a prescription medicine used to treat:
- mild to moderate memory problems (dementia) associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
- mild to moderate memory problems (dementia) associated with Parkinson’s disease.
It is not known if Exelon Patch is safe or effective in children.
Who should not use Exelon Patch?
Do not use Exelon Patch if you are allergic to rivastigmine, carbamate derivatives, or any of the ingredients in Exelon Patch. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Exelon Patch.
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using Exelon Patch?
Before you use Exelon Patch, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have or ever had a stomach ulcer
- are planning to have surgery
- have or ever had problems with your heart
- have problems passing urine
- have or ever had seizures
- have problems with movement (tremors)
- have asthma or breathing problems
- have a loss of appetite or are losing weight
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Exelon Patch will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Exelon Patch passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you use Exelon Patch.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- a medicine used to treat inflammation (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- other medicines used to treat Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease
- an anticholinergic medicine, such as an allergy or cold medicine, a medicine to treat bladder or bowel spasms, or certain asthma medicines, or certain medicines to prevent motion or travel sickness
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if your medicine is one listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use Exelon Patch?
- Use Exelon Patch exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose as needed.
- Wear only 1 Exelon Patch at a time.
- Exelon Patch is for skin use only.
- Apply Exelon Patch to clean, dry, hairless, intact skin.
- Avoid applying Exelon Patch to areas on your body that will be rubbed against tight clothing.
- Do not apply Exelon Patch to skin that is red, irritated, or has cuts.
- Do not apply Exelon Patch to skin that has cream, lotion, or powder on it.
- Change your Exelon Patch every 24 hours at the same time of day. You may write the date and time you put on the Exelon Patch with a ballpoint pen before applying the patch to help you remember when to remove it.
- Change your application site every day to avoid skin irritation. You can use the same area, but do not use the same spot for at least 14 days after your last application.
- Check to see if the patch is loosened when engaging in activities such as bathing, swimming, or showering.
- If your Exelon Patch falls off, put on another patch right away and then replace the new patch the next day at the same time as usual. Do not use overlays, bandages, or tape to secure patches that have loosened or reapply patches that have fallen off.
- If you miss a dose or forget to change your Exelon Patch apply your next Exelon Patch as soon as you remember. Do not apply 2 Exelon Patches to make up for the missed dose.
- If you miss more than three days of applying Exelon Patch, call your healthcare provider before putting on another patch.
- You must remove Exelon Patch from the previous day before applying a new one.
- Having more than one patch on your body at the same time can cause you to get too much Exelon. If you accidentally use more than one Exelon Patch at a time call your healthcare provider. If you are unable to reach your healthcare provider, contact your local Poison Control Center or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
Where should I Apply Exelon Patch?
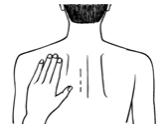
- Apply 1 Exelon Patch to ONLY ONE of the outlined areas shown in the figures below (See figure A):
- upper back, left or right side
- lower back, left or right side
- upper arm, left or right
- chest, left or right side
Figure A
Apply one patch to ONLY ONE of the following possible sites each day
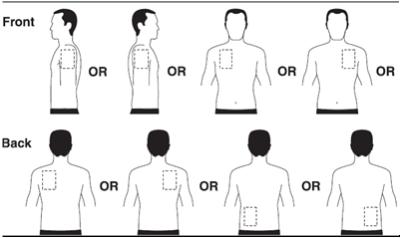
The diagram represents areas on the body where Exelon Patch may be applied. Only one patch should be worn at a time. Do not apply multiple patches to the body.
Apply ONLY ONE patch per day to ONLY ONE of the following locations (as illustrated above): the upper or lower back if it is likely that the patient will remove it. If this is not a concern, the patch can be applied instead to the upper arm or chest. Avoid places where the patch can be rubbed off by tight clothing.
Apply Exelon Patch as follows:
The patch is a thin, beige, plastic patch that sticks to the skin. Each patch is sealed in a pouch that protects it until you are ready to put it on. Do not open the pouch or remove a patch until just before you apply it.
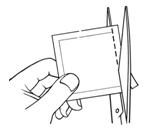
1. Cut the pouch along the dotted line to open and remove the patch (See Figure B). Save the pouch for later use. The patch should not be cut or folded sharply.
Figure B
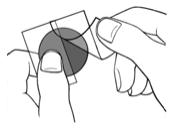
2. A protective liner covers the sticky (adhesive) side of the patch. Peel off one side of the protective cover. Do not touch the sticky part of the patch with your finger (See Figure C).
Figure C
3. Apply the sticky side of the patch onto your chosen skin site.
4. Peel off the other side of the protective cover (See Figure D).
Figure D
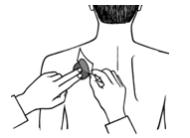
5. Press down on the patch firmly to make sure that the edges stick well (See Figure E).
Figure E
Wash your hands with soap and water after applying the patch.
Removing the Exelon Patch:
- Gently pull on 1 edge of the Exelon Patch to remove it off your skin.
- Fold the Exelon Patch in half and put it back into the pouch that you saved.
- Throw the used Exelon Patch in the trash out of the reach of children and pets.
- Wash your hands with soap and water right away.
What should I avoid while using Exelon Patch?
- Do not touch your eyes after you touch the Exelon Patch.
- Exelon Patch can cause drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, or fainting. Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how Exelon Patch affects you.
- Avoid exposure to external heat sources such as excessive sunlight, saunas, or solariums for long periods of time.
What are the possible side effects of Exelon Patch?
Exelon Patch may cause serious side effects including:
-
Stomach or bowel (intestinal) problems, including:
▪ nausea
▪ vomiting
▪ diarrhea
▪ dehydration
▪ loss of appetite
▪ weight loss
▪ bleeding in your stomach (ulcers)
-
heart problems
-
seizures
- problems with movement (tremors)
The most common side effects of Exelon Patch include:
- depression
- headache
- anxiety
- dizziness
- stomach pain
- urinary tract infections
- muscle weakness
- tiredness
- trouble sleeping
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Exelon Patch. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Exelon Patch?
- Store Exelon Patch at 59oF to 86oF (15oC to 30oC).
- Keep Exelon Patch in the sealed pouch until ready to use.
Keep Exelon Patch and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of Exelon Patch.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in the Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Exelon Patch for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Exelon Patch to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about Exelon Patch. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Exelon Patch that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients of Exelon Patch?
Active ingredient: rivastigmine
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
©Novartis
T2012-155/T2012-156
August 2012/August 2012
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 4.6 mg / 24 hours
Rx Only NDC 0078-0501-15
EXELON® Patch
(rivastigmine transdermal system)
Each System Delivers 4.6 mg/24 hours
Contains 30 Systems

| EXELON
rivastigmine patch, extended release |
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| EXELON
rivastigmine patch, extended release |
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| EXELON
rivastigmine patch, extended release |
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |

