FLUZONE- influenza a virus a/california/7/2009 x-179a (h1n1) antigen (formaldehyde inactivated), influenza a virus a/victoria/361/2011 ivr-165 (h3n2) antigen (formaldehyde inactivated) and influenza b virus b/texas/6/2011 antigen (formaldehyde inactivated) injection, suspension
Sanofi Pasteur Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use Fluzone Intradermal safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Fluzone Intradermal.
Fluzone Intradermal (Influenza Virus Vaccine) Suspension for Intradermal Injection 2012-2013 Formula Initial U.S. Approval: 2011 INDICATIONS AND USAGEDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
A single 0.1 mL dose for intradermal injection in adults 18 through 64 years of age. (2.1) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSSuspension for injection in a prefilled microinjection system, 0.1 mL. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSSevere allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine, including egg protein, or after previous dose of any influenza vaccine. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONSIf Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) has occurred within 6 weeks of previous influenza vaccination, the decision to give Fluzone Intradermal should be based on careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks. (5.1) ADVERSE REACTIONSThe most common injection-site reactions were erythema (>75%), induration (>50%), swelling (>50%), pain (>50%), and pruritus (>40%). Erythema, induration, swelling and pruritus occurred more frequently following Fluzone Intradermal than Fluzone. The most common solicited systemic adverse events were headache, myalgia, and malaise (>20%). (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sanofi Pasteur Inc., Discovery Drive, Swiftwater, PA 18370 at 1-800-822-2463 (1-800-VACCINE) or VAERS at 1-800-822-7967 or www.vaers.hhs.gov. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSSafety and effectiveness of Fluzone Intradermal have not been established in pregnant women. (8.1) Pregnancy registry available for Fluzone Intradermal. Contact Sanofi Pasteur Inc. at 1-800-822-2463. See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 07/2012 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Fluzone® Intradermal is an inactivated influenza virus vaccine indicated for active immunization against influenza disease caused by influenza virus subtypes A and type B contained in the vaccine.
Fluzone Intradermal is approved for use in persons 18 through 64 years of age.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- For intradermal use only
2.1 Dose and Schedule
Fluzone Intradermal should be administered as a single 0.1 mL injection by the intradermal route in adults 18 through 64 years of age.
2.2 Administration
Inspect Fluzone Intradermal microinjection system visually for particulate matter and/or discoloration prior to administration. If either of these conditions exist, the vaccine should not be administered.
The preferred site of injection is the skin in the region of the deltoid.
Fluzone Intradermal vaccine should not be combined through reconstitution or mixed with any other vaccine.
Gently shake the microinjection system before administering the vaccine.
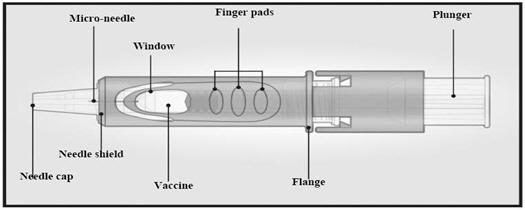
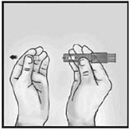
1. Remove Needle Cap
Remove the needle cap from the microinjection system.
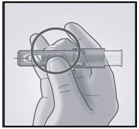
2. Hold Microinjection System Between Thumb and Middle Finger
Hold the system by placing the thumb and middle finger only on the finger pads, the index finger remains free. Do not place fingers on the windows.
3. Insert Needle Rapidly and Perpendicular to the Skin
Insert the needle perpendicular to the skin, in the region of the deltoid, in a short, quick movement.
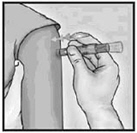
4. Inject Using the Index Finger
Once the needle has been inserted, maintain light pressure on the surface of the skin and inject using the index finger to push on the plunger. Do not aspirate. Once the intradermal vaccine has been administered, a wheal may be visible at the injection site.
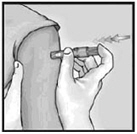
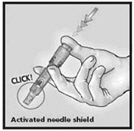
5. Remove Needle from Skin and Activate Needle Shield by Pushing Firmly on Plunger
Remove the needle from the skin. Direct the needle away from you and others. With the same hand, push very firmly with the thumb on the plunger to activate the needle shield. You will hear a click when the shield extends to cover the needle.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Fluzone Intradermal is a suspension for injection.
Fluzone Intradermal is supplied in a single-dose prefilled microinjection system, 0.1 mL, for adults 18 through 64 years of age.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
A severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) to any component of the vaccine [see Description (11)], including egg protein, or to a previous dose of any influenza vaccine is a contraindication to administration of Fluzone Intradermal.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Guillain-Barré Syndrome
The 1976 swine influenza vaccine was associated with an elevated risk of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). Evidence for a causal relation of GBS with other influenza vaccines is inconclusive; if an excess risk exists, it is probably slightly more than 1 additional case per 1 million persons vaccinated. (1) If GBS has occurred within 6 weeks of previous influenza vaccination, the decision to give Fluzone Intradermal should be based on careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks.
5.2 Preventing and Managing Allergic Reactions
Appropriate medical treatment and supervision must be available to manage possible anaphylactic reactions following administration of the vaccine.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse event rates observed in the clinical trials of a vaccine cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trial of another vaccine, and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adults 18 through 64 years of age were randomized to receive Fluzone Intradermal or Fluzone (year 2008-2009 formulation) in a multi-center trial conducted in the US. The trial was open-label for administration route. The safety analysis set included 2855 Fluzone Intradermal recipients and 1421 Fluzone recipients. Table 1 summarizes solicited injection-site reactions and systemic adverse events reported within 7 days post-vaccination via diary cards. With the exception of pain, solicited injection-site reactions were more frequent after vaccination with Fluzone Intradermal compared to Fluzone. Nine percent of Fluzone recipients and 49% of Fluzone Intradermal recipients had an injection-site reaction present beyond Day 3 post-vaccination. Approximately 20% of subjects in both groups had a solicited systemic adverse event present beyond Day 3 post-vaccination.
| Fluzone Intradermal (N*=2798-2802) Percentage | Fluzone (N*=1392-1394) Percentage |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any | Grade 2† | Grade 3‡ | Any | Grade 2† | Grade 3‡ | |
|
||||||
| Injection-Site Erythema | 76.4 | 28.8 | 13.0 | 13.2 | 2.1 | 0.9 |
| Injection-Site Induration | 58.4 | 13.0 | 3.4 | 10.0 | 2.3 | 0.5 |
| Injection-Site Swelling | 56.8 | 13.4 | 5.4 | 8.4 | 2.1 | 0.9 |
| Injection-Site Pain | 51.0 | 4.4 | 0.6 | 53.7 | 5.8 | 0.8 |
| Injection-Site Pruritus | 46.9 | 4.1 | 1.1 | 9.3 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| Injection-Site Ecchymosis | 9.3 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 6.2 | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| Headache | 31.2 | 6.4 | 1.5 | 30.3 | 6.5 | 1.6 |
| Myalgia | 26.5 | 4.6 | 1.5 | 30.8 | 5.5 | 1.4 |
| Malaise | 23.3 | 5.5 | 2.2 | 22.2 | 5.5 | 1.8 |
| Shivering | 7.3 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 6.2 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| Fever§ | 3.9 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 2.6 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
Within 28 days post-vaccination, a serious adverse event was reported by 10 (0.4%) Fluzone Intradermal recipients and 5 (0.4%) Fluzone recipients. Within 6 months post-vaccination, a serious adverse event was reported by 47 (1.6%) Fluzone Intradermal recipients and 20 (1.4%) Fluzone recipients. No deaths were reported during the 6 months post-vaccination. Throughout the study, one reported serious adverse event was considered to be caused by vaccination: a pruritic rash on the extremities and torso that began 48 hours after receipt of Fluzone Intradermal and resulted in hospitalization and treatment with an antihistamine and steroids.
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
Currently, there are no post-marketing data available for Fluzone Intradermal vaccine.
The following events have been spontaneously reported during the post-approval use of Fluzone. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to vaccine exposure. Adverse events were included based on one or more of the following factors: severity, frequency of reporting, or strength of evidence for a causal relationship to Fluzone.
Events Reported During Post-Approval Use of Fluzone.
- Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Thrombocytopenia, lymphadenopathy
- Immune System Disorders: Anaphylaxis, other allergic/hypersensitivity reactions (including urticaria, angioedema)
- Eye Disorders: Ocular hyperemia
- Nervous System Disorders: Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), convulsions, febrile convulsions, myelitis (including encephalomyelitis and transverse myelitis), facial palsy (Bell's palsy), optic neuritis/neuropathy, brachial neuritis, syncope (shortly after vaccination), dizziness, paresthesia
- Vascular Disorders: Vasculitis, vasodilatation/flushing
- Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: Dyspnea, pharyngitis, rhinitis, cough, wheezing, throat tightness
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Pruritus, asthenia/fatigue, pain in extremities, chest pain
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Vomiting
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Data evaluating the concomitant administration of Fluzone Intradermal with other vaccines are not available.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B: A developmental and reproductive toxicity study has been performed in female rabbits at a dose approximately 20 times the human dose (on a mg/kg basis) and has revealed no evidence of impaired female fertility or harm to the fetus due to Fluzone Intradermal. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, Fluzone Intradermal should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Healthcare providers are encouraged to register women who receive Fluzone Intradermal during pregnancy in Sanofi Pasteur Inc.'s vaccination pregnancy registry by calling 1-800-822-2463.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether Fluzone Intradermal is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Fluzone Intradermal is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of Fluzone Intradermal in persons <18 years of age have not been established. In a clinical trial, 97 infants and toddlers 6 months through 35 months of age and 160 children 3 years through 8 years of age were enrolled to receive two injections of Fluzone Intradermal. Infants and children in a control group received two injections of Fluzone. Fluzone Intradermal was associated with increased local reactogenicity relative to Fluzone. The size of the study was not adequate to reliably evaluate serious adverse events or the immune response elicited by Fluzone Intradermal relative to Fluzone.
11 DESCRIPTION
Fluzone Intradermal (Influenza Virus Vaccine) for intradermal injection is an inactivated influenza virus vaccine, prepared from influenza viruses propagated in embryonated chicken eggs. The virus-containing allantoic fluid is harvested and inactivated with formaldehyde. Influenza virus is concentrated and purified in a linear sucrose density gradient solution using a continuous flow centrifuge. The virus is then chemically disrupted using a non-ionic surfactant, Octylphenol Ethoxylate (Triton® X-100), producing a "split virus". The split virus is further purified and then suspended in sodium phosphate-buffered isotonic sodium chloride solution. The Fluzone Intradermal process uses an additional concentration factor after the ultrafiltration step in order to obtain a higher hemagglutinin (HA) antigen concentration.
Fluzone Intradermal is a clear, slightly opalescent suspension for injection.
Neither antibiotics nor preservative are used in the manufacture of Fluzone Intradermal.
Fluzone Intradermal is standardized according to United States Public Health Service requirements and is formulated to contain HA of each of the following three influenza strains recommended for the 2012-2013 influenza season: A/California/07/2009 NYMC X-179A (H1N1), A/Victoria/361/2011 IVR-165 (H3N2) and B/Texas/6/2011 (a B/Wisconsin/1/2010-like virus). The amounts of HA and other ingredients per dose of vaccine are listed in Table 2.
| Quantity (per dose) |
|
|---|---|
| Ingredient | Fluzone Intradermal 0.1 mL Dose |
| Active Substance: Split influenza virus, inactivated strains*: | 27 mcg HA total |
| A (H1N1) | 9 mcg HA |
| A (H3N2) | 9 mcg HA |
| B | 9 mcg HA |
| Other: | |
| Sodium phosphate-buffered isotonic sodium chloride solution | QS† to appropriate volume |
| Formaldehyde | ≤20 mcg |
| Octylphenol Ethoxylate | ≤50 mcg |
| Gelatin | None |
| Preservative | None |
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Influenza illness and its complications follow infection with influenza viruses. Global surveillance of influenza identifies yearly antigenic variants. For example, since 1977, antigenic variants of influenza A (H1N1 and H3N2) viruses and influenza B viruses have been in global circulation. Specific levels of hemagglutination inhibition (HI) antibody titer post-vaccination with inactivated influenza virus vaccines have not been correlated with protection from influenza virus infection. In some human studies, antibody titers ≥1:40 have been associated with protection from influenza illness in up to 50% of subjects. (2) (3)
Antibodies against one influenza virus type or subtype confer limited or no protection against another. Furthermore, antibodies to one antigenic variant of influenza virus might not protect against a new antigenic variant of the same type or subtype. Frequent development of antigenic variants through antigenic drift is the virologic basis for seasonal epidemics and the reason for the usual change of one or more new strains in each year's influenza vaccine. Therefore, influenza vaccines are standardized to contain the hemagglutinins of influenza virus strains (ie, typically two type A and one type B), representing the influenza viruses likely to be circulating in the US in the upcoming winter.
Annual vaccination with the current vaccine is recommended because immunity during the year after vaccination declines, and because circulating strains of influenza virus change from year to year.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Immunogenicity of Fluzone Intradermal in Adults
Adults 18 through 64 years of age were randomized to receive Fluzone Intradermal or Fluzone (year 2008-2009 formulation) in a multi-center trial conducted in the US. The trial was open-label for administration route. For immunogenicity analyses, there were 2581 participants who received Fluzone Intradermal and 1287 participants who received Fluzone in the per protocol analysis set. There were fewer males than females (36.1% and 35.8% males in the Fluzone Intradermal and Fluzone groups, respectively). In the Fluzone Intradermal group, the mean age was 42.7 years (ranged from 18.1 through 65.0 years), and in the Fluzone group, the mean age was 42.6 years (ranged from 18.2 through 65.0 years). Most participants in the Fluzone Intradermal and Fluzone groups, respectively, were Caucasian (79.6% and 80.0%), followed by Hispanic (10.2% and 11.0%), and Black (7.7% and 6.3%). HI antibody geometric mean titers (GMTs) following Fluzone Intradermal were non-inferior to those following Fluzone for all three strains. (See Table 3) Seroconversion rates following Fluzone Intradermal were non-inferior to those following Fluzone for strains A (H1N1) and A (H3N2), but not for strain B. (See Table 4) At 28 days following vaccination with either Fluzone or Fluzone Intradermal, the percentages of subjects with a serum HI antibody titer of at least 1:40 ranged from 87% to 92%, depending on the influenza strain.
| Influenza Strain | GMT | GMT Ratio (95% CI) | Non- inferior* |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluzone Intradermal N=2575-2579 | Fluzone N=1283-1285 | Fluzone GMT divided by Fluzone Intradermal GMT | ||
|
||||
| A (H1N1) | 193.2 | 178.3 | 0.92 (0.85; 1.01) | Yes |
| A (H3N2) | 246.7 | 230.7 | 0.94 (0.85; 1.03) | Yes |
| B | 102.5 | 126.9 | 1.24 (1.15; 1.33) | Yes |
| Influenza Strain | Seroconversion* % | Difference (95% CI) | Non-inferior† | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluzone Intradermal N=2573-2578 | Fluzone N=1283-1285 | Fluzone minus Fluzone Intradermal |
||
|
||||
| A (H1N1) | 61.2 | 60.5 | -0.69 (-3.97; 2.56) | Yes |
| A (H3N2) | 75.3 | 74.8 | -0.55 (-3.49; 2.31) | Yes |
| B | 46.2 | 54.2 | 7.99 (4.64; 11.31) | No |
15 REFERENCES
- 1
- Lasky T, Terracciano GJ, Magder L, et al. The Guillain-Barre´ syndrome and the 1992-1993 and 1993-1994 influenza vaccines. N Engl J Med 1998;339(25):1797-802.
- 2
- Hannoun C, Megas F, Piercy J. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of influenza vaccination. Virus Res 2004;103:133-138.
- 3
- Hobson D, Curry RL, Beare AS, Ward-Gardner A. The role of serum haemagglutination-inhibiting antibody in protection against challenge infection with influenza A2 and B viruses. J Hyg Camb 1972;767-777.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
- Inform the patient that Fluzone Intradermal contains killed viruses and cannot cause influenza.
- Fluzone Intradermal stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies that help protect against influenza, but do not prevent other respiratory infections.
- Annual influenza vaccination is recommended.
- Instruct vaccine recipients to report adverse reactions to their healthcare provider and/or to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). Inform the patient about the Sanofi Pasteur Inc. pregnancy registry for Fluzone Intradermal as appropriate.
Fluzone is a registered trademark of Sanofi Pasteur Inc.
Manufactured by:
Sanofi Pasteur Inc.
Swiftwater PA 18370 USA
6221
Patient Information Sheet
Fluzone® Intradermal
Influenza Virus Vaccine
Please read this information sheet before getting Fluzone Intradermal vaccine. This summary is not intended to take the place of talking with your healthcare provider. If you have questions or would like more information, please talk with your healthcare provider.
What is Fluzone Intradermal vaccine?
Fluzone Intradermal is a vaccine that helps protect against influenza illness (flu).
Fluzone Intradermal vaccine is for people 18 through 64 years of age.
Vaccination with Fluzone Intradermal vaccine may not protect all people who receive the vaccine.
Who should not get Fluzone Intradermal vaccine?
You should not get Fluzone Intradermal vaccine if you:
- ever had a severe allergic reaction to eggs or egg products.
- ever had a severe allergic reaction after getting any flu shot.
- are younger than 18 years of age.
- are 65 years of age or older.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have or have had:
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (severe muscle weakness) after getting a flu shot.
- problems with your immune system as the immune response may be diminished.
How is Fluzone Intradermal vaccine given?
Fluzone Intradermal vaccine is a shot given into the skin of the arm.
What are the possible side effects of Fluzone Intradermal vaccine?
The most common side effects of Fluzone Intradermal vaccine are:
- pain, redness, swelling, hardness, and itching where you got the shot
- muscle ache
- tiredness
- headache
These are not all of the possible side effects of Fluzone Intradermal vaccine. You can ask your healthcare provider for a list of other side effects that is available to healthcare professionals.
Call your healthcare provider for advice about any side effects that concern you. You may report side effects to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) at 1-800-822-7967 or http://vaers.hhs.gov. A pregnancy registry is available for Fluzone Intradermal by contacting Sanofi Pasteur Inc. at 1-800-822-2463.
What are the ingredients in Fluzone Intradermal vaccine?
Fluzone Intradermal vaccine contains 3 killed flu virus strains.
Inactive ingredients include formaldehyde, and octylphenol ethoxylate.
Manufactured by: Sanofi Pasteur Inc.
Swiftwater, PA 18370 USA
6621
| FLUZONE
influenza a virus a/california/7/2009 x-179a (h1n1) antigen (formaldehyde inactivated), influenza a virus a/victoria/361/2011 ivr-165 (h3n2) antigen (formaldehyde inactivated), and influenza b virus b/texas/6/2011 antigen (formaldehyde inactivated) injection, suspension |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Sanofi Pasteur Inc. (086723285) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
| Sanofi Pasteur Inc. | 086723285 | MANUFACTURE | |