benzphetamine hydrochloride (Benzphetamine Hydrochloride) tablet, coated
[Paddock Laboratories, Inc.]
CIII
DESCRIPTION
Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets contain the anorectic agent benzphetamine hydrochloride. Benzphetamine hydrochloride is a white crystalline powder readily soluble in water and 95% ethanol. The chemical name for benzphetamine hydrochloride is d-N,α-Dimethyl-N-(phenylmethyl)-benzeneethanamine hydrochloride and its molecular weight is 275.82.
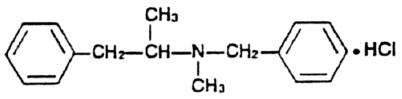
The structural formula (dextro form) is represented below:
Each Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablet, for oral administration, contains 50 mg of benzphetamine hydrochloride.
Inactive Ingredients: Lactose Monohydrate, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Sodium Starch Glycolate, Magnesium Stearate, Colloidal Silicon Dioxide, Titanium Dioxide, Polydextrose, Hypromellose 2910, Triacetin, FD&C Red #40 Aluminum Lake, Polyethylene Glycol 8000 and FD&C Yellow #6 Aluminum Lake.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Benzphetamine hydrochloride is a sympathomimetic amine with pharmacologic activity similar to the prototype drugs of this class used in obesity, the amphetamines. Actions include central nervous system stimulation and elevation of blood pressure. Tachyphylaxis and tolerance have been demonstrated with all drugs of this class in which these phenomena have been looked for.
Drugs of this class used in obesity are commonly known as "anorectics" or "anorexigenics". It has not been established, however, that the action of such drugs in treating obesity is primarily one of appetite suppression. Other central nervous system actions, or metabolic effects, may be involved.
Adult obese subjects instructed in dietary management and treated with "anorectic" drugs, lose more weight on the average than those treated with placebo and diet, as determined in relatively short-term clinical trials.
The magnitude of increased weight loss of drug-treated patients over placebo-treated patients is only a fraction of a pound a week. The rate of weight loss is the greatest in the first weeks of therapy for both drug and placebo subjects and tends to decrease in succeeding weeks. The possible origins of the increased weight loss due to the various drug effects are not established. The amount of weight loss associated with the use of an "anorectic" drug varies from trial to trial, and the increased weight loss appears to be related in part to variables other than the drug prescribed, such as the physician-investigator, the population treated, and the diet prescribed. Studies do not permit conclusions as to the relative importance of the drug and non-drug factors on weight loss.
The natural history of obesity is measured in years, whereas the studies cited are restricted to a few weeks duration; thus, the total impact of drug-induced weight loss over that of diet alone must be considered to be clinically limited.
Pharmacokinetic data in humans are not available.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets are indicated in the management of exogenous obesity as a short term adjunct (a few weeks) in a regimen of weight reduction based on caloric restriction. The limited usefulness of agents of this class (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY) should be weighed against possible risks inherent in their use such as those described below.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets are contraindicated in patients with advanced arteriosclerosis, symptomatic cardiovascular disease, moderate to severe hypertension, hyperthyroidism, known hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to sympathomimetic amines, and glaucoma. Benzphetamine should not be given to patients who are in an agitated state or who have a history of drug abuse.
Hypertensive crises have resulted when sympathomimetic amines have been used concomitantly or within 14 days following use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets should not be used concomitantly with other CNS stimulants.
Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Amphetamines have been shown to be teratogenic and embryotoxic in mammals at high multiples of the human dose. Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets are contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
WARNINGS
When tolerance to the anorectic effect develops, the recommended dose should not be exceeded in an attempt to increase the effect; rather, the drug should be discontinued.
PRECAUTIONS
General:
Insulin requirements in diabetes mellitus may be altered in association with use of anorexigenic drugs and the concomitant dietary restrictions.
Psychological disturbances have been reported in patients who receive an anorectic agent together with a restrictive dietary regime.
Caution is to be exercised in prescribing amphetamines for patients with even mild hypertension. The least amount feasible should be prescribed or dispensed at one time in order to minimize the possibility of overdosage.
Information for Patients:
Amphetamines may impair the ability of the patient to engage in potentially hazardous activities such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle; the patient should therefore be cautioned accordingly.
Drug Interactions:
Hypertensive crises have resulted when sympathomimetic amines have been used concomitantly or within 14 days following use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets should not be used concomitantly with other CNS stimulants.
Amphetamines may decrease the hypotensive effect of antihypertensives. Amphetamines may enhance the effects of tricyclic antidepressants.
Urinary alkalinizing agents increase blood levels and decrease excretion of amphetamines. Urinary acidifying agents decrease blood levels and increase excretion of amphetamines.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Animal studies to evaluate the potential for carcinogenesis, mutagenesis or impairment of fertility have not been performed.
Pregnancy:
Pregnancy Category X (see CONTRAINDICATIONS section).
Nursing Mothers:
Amphetamines are excreted in human milk. Mothers taking amphetamines should be advised to refrain from nursing.
Pediatric Use:
Use of benzphetamine hydrochloride is not recommended in individuals under 12 years of age.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following have been associated with the use of benzphetamine hydrochloride:
Cardiovascular
Palpitation, tachycardia, elevation of blood pressure. There have been isolated reports of cardiomyopathy associated with chronic amphetamine use.
CNS
Overstimulation, restlessness, dizziness, insomnia, tremor, sweating, headache; rarely, psychotic episodes at recommended doses; depression following withdrawal of the drug.
Gastrointestinal
Dryness of the mouth, unpleasant taste, nausea, diarrhea, other gastrointestinal disturbances.
Allergic
Urticaria and other allergic reactions involving the skin.
Endocrine
Changes in libido.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Benzphetamine is a controlled substance under the Controlled Substance Act by the Drug Enforcement Administration and has been assigned to Schedule III.
Benzphetamine hydrochloride is related chemically and pharmacologically to the amphetamines. Amphetamines and related stimulant drugs have been extensively abused, and the possibility of abuse of Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets should be kept in mind when evaluating the desirability of including a drug as part of a weight reduction program. Abuse of amphetamines and related drugs may be associated with intense psychological dependence and severe social dysfunction. There are reports of patients who have increased the dosage to many times that recommended. Abrupt cessation following prolonged high dosage administration results in extreme fatigue and mental depression; changes are also noted on the sleep EEG. Manifestations of chronic intoxication with anorectic drugs include severe dermatoses, marked insomnia, irritability, hyperactivity, and personality changes. The most severe manifestation of chronic intoxication is psychosis, often clinically indistinguishable from schizophrenia.
OVERDOSAGE
Manifestations of Overdosage:
Acute overdosage with amphetamines may result in restlessness, tremor, tachypnea, confusion, assaultiveness and panic states. Fatigue and depression usually follow the central stimulation. Cardiovascular effects include arrhythmias, hypertension or hypotension, and circulatory collapse. Gastrointestinal symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Hyperpyrexia and rhabdomyolysis have been reported and can lead to a number of associated complications. Fatal poisoning is usually preceded by convulsions and coma.
Treatment of Overdosage:
(See WARNINGS)- Information concerning the effects of overdosage with Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets is extremely limited. The following is based on experience with other anorexiants.
Management of acute amphetamine intoxication is largely symptomatic and includes sedation with a barbiturate. If hypertension is marked, the use of a nitrite or rapidly acting alpha receptor blocking agent should be considered. Experience with hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis is inadequate to permit recommendations in this regard.
Acidification of the urine increases amphetamine excretion.
The oral LD50 is 174 mg/kg in mice and 104 mg/kg in rats. The intraperitoneal LD50 in mice is 153 mg/kg.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage should be individualized according to the response of the patient. The suggested dosage ranges from 25 to 50 mg one to three times daily. Treatment should begin with 25 to 50 mg once daily with subsequent increase in individual dose or frequency according to response. A single daily dose is preferably given in mid-morning or mid-afternoon, according to the patient's eating habits. In an occasional patient it may be desirable to avoid late afternoon administration. Use of benzphetamine hydrochloride is not recommended in individuals under 12 years of age.
HOW SUPPLIED
Benzphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets, 50 mg are supplied as round, biconvex, film coated tablets debossed with "PAD" above the score and the number "0116" debossed below the score and plain on the other side.
Bottles of 30 NDC 0574-0116-30
Bottles of 100 NDC 0574-0116-01
Bottles of 500 NDC 0574-0116-05
Store at controlled room temperature 20°- 25°C (68°- 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Manufactured for:
Paddock Laboratories, Inc.
Minneapolis, MN 55427
Manufactured by:
Metrics Inc.
Greenville, NC 27834
May 2007
| Benzphetamine Hydrochloride (Benzphetamine Hydrochloride) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revised: 06/2008Paddock Laboratories, Inc.