sodium chloride (Sodium Chloride) injection
[B. Braun Medical Inc.]
Partial Fill
DESCRIPTION
Each mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP contains:
Sodium Chloride USP 9 mg; Water for Injection USP qs
pH adjusted with Hydrochloric Acid NF
pH: 5.5 (4.5–7.0)
Calculated Osmolarity: 310 mOsmol/liter
Concentration of Electrolytes (mEq/100 mL): Sodium 15.4 Chloride 15.4
This solution is sterile, nonpyrogenic, isotonic and contains no bacteriostatic or antimicrobial agents.
The formula of the active ingredient is:
| Ingredient | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium Chloride USP | NaCl | 58.44 |
The PAB container is Latex-free, DEHP-free, and PVC-free.
The plastic container is a copolymer of ethylene and propylene formulated and developed for parenteral drugs. The copolymer contains no plasticizers and exhibits virtually no leachability. The safety of the plastic container has been confirmed by biological evaluation procedures. The material passes Class VI testing as specified in the U.S. Pharmacopeia for Biological Tests — Plastic Containers. These tests have shown that the container is nontoxic and biologically inert.
The container/solution unit is a closed system and is not dependent upon entry of external air during administration. The container has two ports, one is for the intravenous administration set and the other is a medication addition site. Each is covered by a tamperproof barrier. Refer to the Directions for Use of the container to properly identify the ports.
No vapor barrier is necessary.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP provides electrolytes and is a source of water for hydration. It is capable of inducing diuresis depending on the clinical condition of the patient.
Sodium, the major cation of the extracellular fluid, functions primarily in the control of water distribution, fluid balance, and osmotic pressure of body fluids. Sodium is also associated with chloride and bicarbonate in the regulation of the acid-base equilibrium of body fluid.
Chloride, the major extracellular anion, closely follows the metabolism of sodium, and changes in the acid-base balance of the body are reflected by changes in the chloride concentration.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
This intravenous solution is indicated for use in adults and pediatric patients as a source of electrolytes and water for hydration.
This product is designed for use as a diluent and delivery system for intermittent intravenous administration of compatible drug additives. Consult prescribing information for INDICATIONS AND USAGE of drug additives to be administered in this manner.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
This solution is contraindicated where the administration of sodium or chloride could be clinically detrimental.
WARNINGS
Solutions containing sodium ions should be used with great care, if at all, in patients with congestive heart failure, severe renal insufficiency, and in clinical states in which there is sodium retention with edema. In patients with diminished renal function, administration of solutions containing sodium ions may result in sodium retention.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Clinical evaluation and periodic laboratory determinations are necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance during prolonged parenteral therapy or whenever the condition of the patient warrants such evaluation. Significant deviations from normal concentrations may require tailoring of the electrolyte pattern, in this or an alternative solution(s).
Sodium-containing solutions should be administered with caution to patients receiving corticosteroids or corticotropin, or to other salt-retaining patients. Care should be exercised in administering solutions containing sodium to patients with renal or cardiovascular insufficiency, with or without congestive heart failure, particularly if they are postoperative or elderly. See PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use.
To minimize the risk of possible incompatibilities arising from mixing this solution with other additives that may be prescribed, the final infusate should be inspected for cloudiness or precipitation immediately after mixing, prior to administration, and periodically during administration.
Laboratory Tests
Periodic laboratory determinations are necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance during prolonged parenteral therapy or whenever the condition of the patient warrants such evaluation.
Drug Interactions
Sodium-containing solutions should be administered with caution to patients receiving cortiscosteroids or corticotrophin.
Some additives may be incompatible. Consult with pharmacist. When introducing additives, use aseptic techniques. Mix thoroughly. Do not store.
Studies have not been conducted to evaluate additional drug/drug or drug/food interactions with Sodium Chloride Injection USP.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential or effects on fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP. It is also not known whether 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Labor and Delivery
Studies have not been conducted to evaluate the effects of Sodium Chloride Injection USP on labor and delivery. As reported in the literature, sodium chloride solutions have been administered during labor and delivery. Caution should be exercised, and the fluid balance, glucose and electrolyte concentrations and acid-base balance, of both mother and fetus should be evaluated periodically or whenever warranted by the condition of the patient or fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of sodium chloride injections in pediatric patients have not been established by adequate and well controlled trials, however, the use of Sodium Chloride solutions in the pediatric population is referenced in the medical literature. All Warnings, Precautions and Adverse Reactions described in this label apply to pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
An evaluation of current literature revealed no clinical experience identifying differences in response between elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Reactions which may occur because of the solution or the technique of administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation, and hypervolemia.
The physician should also be alert to the possibility of adverse reactions to drug additives diluted and administered from the plastic partial fill container. Prescribing information for drug additives to be administered in this manner should be consulted.
Symptoms may result from an excess or deficit of one or more of the ions present in the solution; therefore, frequent monitoring of electrolyte levels is essential.
Hypernatremia may be associated with edema and exacerbation of congestive heart failure due to the retention of water, resulting in an expanded extracellular fluid volume.
If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures, and save the remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
OVERDOSAGE
In the event of a fluid or solute overload during parenteral therapy, reevaluate the patient's condition, and institute appropriate corrective treatment.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
This solution is for intravenous use only.
Do not use plastic container in series connection.
If administration is controlled by a pumping device, care must be taken to discontinue pumping action before the container runs dry or air embolism may result.
This solution is intended for intravenous administration using sterile equipment. It is recommended that intravenous administration apparatus be replaced at least once every 24 hours.
Use only if solution is clear and container and seals are intact.
As directed by a physician. Dosage is dependent upon the age, weight, and clinical condition of the patient as well as laboratory determinations.
There is no specific pediatric dose. The dose is dependent on weight, clinical condition, and laboratory results. Follow recommendations of appropriate pediatric reference text. See PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use.
When using this product as a diluent or vehicle for administration of drug additives, consult the prescribing information of the drug to be used.
Addition of medication should be accomplished using aseptic technique in order to assure sterility.
Physicochemical studies have shown that the container and solution can withstand freezing.
Some additives may be incompatible. Consult with pharmacist. When introducing additives, use aseptic techniques. Mix thoroughly. Do not store.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
HOW SUPPLIED
0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP is supplied sterile and nonpyrogenic in partial fill polyolefin containers. The 100/150 mL product is packaged 64 per case. The 50/100 mL product is packaged 84 per case. The 25/100 mL product is packaged 116 per case.
| NDC | Cat. No. | Fill/Container (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP (Canada DIN 01924303) | ||
| 0264-1800-36 | S8004-5410 | 25/100 |
| 0264-1800-31 | S8004-5384 | 50/100 |
| 0264-1800-32 | S8004-5264 | 100/150 |
Exposure of pharmaceutical products to heat should be minimized. Avoid excessive heat. It is recommended that the product be stored at room temperature (25°C); however, brief exposure up to 40°C does not adversely affect the product.
Rx only
Revised: April 2006
PAB® is a registered trademark of B. Braun Medical Inc.
Made in USA
Directions For Use of PAB® Container
Partial Additive Bag
Aseptic technique is required.
Caution: Before use, perform the following checks: Read the label. Ensure solution is the one ordered and is within the expiration date.
Inspect the solution in good light for cloudiness, haze or particulate matter; check the container for leakage or damage. Any container which is suspect should not be used.
Use only if solution is clear and container and seals are intact. Single dose container. Discard unused portion. Consult Package Insert for complete product information.
The physician should also be alert to the possibility of adverse reactions to drug additives diluted and administered from the plastic partial fill container. Prescribing information for drug additives to be administered in this manner should be consulted.
Do not use plastic container in series connection.
This solution is intended for intravenous administration using sterile equipment. It is recommended that intravenous administration apparatus be replaced at least once every 24 hours.
Physicochemical studies have shown that the container and solution can withstand freezing.
-
Identify Two Ports
Remove additive port closure and swab exposed medication site (See Figure A). Using a syringe with 18 gauge or smaller needle, insert cannula through resealable medication site and add desired drug. Mix thoroughly.
Note: Partial fill bags have been designed to accept an overfill of up to 50 mL.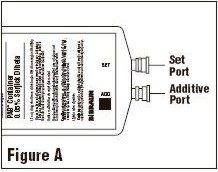
-
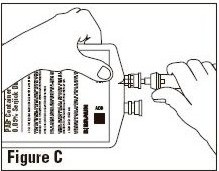
To Attach Solution Set
To aseptically remove set port closure: hold container below set port and grasp cap between thumb and forefinger then roll cap upward (See Figure B). Push spike through diaphragm of the port (See Figure C). Hang container using hole in lower flap. Prime set in accordance with Directions for Use provided with the set in use.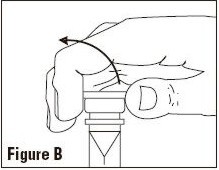
When the container is to be used as a diluent and delivery system for intermittent intravenous administration of compatible drug additives, consult prescribing information for INDICATIONS AND USAGE of drug additives to be administered in this manner.
Warning: Some additives may be incompatible. Consult with pharmacist. When introducing additives, use aseptic techniques. Mix thoroughly. Do not store.
It is not recommended that PAB Containers be transported by pneumatic tube systems.
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Irvine, CA USA 92614-5895
In Canada, distributed by:
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Scarborough, Ontario M1H 2W4
©2006 B. Braun Medical Inc.
Y36-002-583
| Sodium Chloride (Sodium Chloride) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revised: 05/2008B. Braun Medical Inc.