AMTURNIDE
-
aliskiren hemifumarate,
amlodipine besylate and
hydrochlorothiazide tablet, film coated
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
----------
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: FETAL TOXICITY
- When pregnancy is detected, discontinue Amturnide as soon as possible. (5.1)
- Drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and death to the developing fetus. (5.1)
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Amturnide is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, to lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, primarily strokes and myocardial infarctions. These benefits have been seen in controlled trials of antihypertensive drugs from a wide variety of pharmacologic classes, including amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide. There are no controlled trials demonstrating risk reduction with Amturnide.
Control of high blood pressure should be part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk management, including, as appropriate, lipid control, diabetes management, antithrombotic therapy, smoking cessation, exercise, and limited sodium intake. Many patients will require more than one drug to achieve blood pressure goals. For specific advice on goals and management, see published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program’s Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC).
Numerous antihypertensive drugs, from a variety of pharmacologic classes and with different mechanisms of action, have been shown in randomized controlled trials to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that it is blood pressure reduction, and not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, that is largely responsible for those benefits. The largest and most consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit has been a reduction in the risk of stroke, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality also have been seen regularly.
Elevated systolic or diastolic pressure causes increased cardiovascular risk, and the absolute risk increase per mmHg is greater at higher blood pressures, so that even modest reductions of severe hypertension can provide substantial benefit. Relative risk reduction from blood pressure reduction is similar across populations with varying absolute risk, so the absolute benefit is greater in patients who are at higher risk independent of their hypertension (for example, patients with diabetes or hyperlipidemia), and such patients would be expected to benefit from more aggressive treatment to a lower blood pressure goal.
Some antihypertensive drugs have smaller blood pressure effects (as monotherapy) in black patients, and many antihypertensive drugs have additional approved indications and effects (e.g., on angina, heart failure, or diabetic kidney disease). These considerations may guide selection of therapy.
This fixed combination drug is not indicated for initial therapy of hypertension.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Considerations
Dose once-daily. The dosage may be increased after 2 weeks of therapy. The maximum recommended dose of Amturnide is 300/10/25 mg.
2.2 Add-on/Switch Therapy
Use Amturnide for patients not adequately controlled with any two of the following: aliskiren, dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, and thiazide diuretics.
Switch a patient who experiences dose-limiting adverse reactions attributed to an individual component—while on any dual combination of the components of Amturnide—to Amturnide at a lower dose of that component to achieve similar blood pressure reductions.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets are convex ovaloid with a beveled edge, film-coated, and unscored, in the following strengths:
| Aliskiren/Amlodipine/HCTZ
(mg) | Color | Embossing
Side 1/side 2 |
| 150/5/12.5 | Violet white | YIY/NVR |
| 300/5/12.5 | Light pink | LIL/NVR |
| 300/5/25 | Pale orange brown | OIO/NVR |
| 300/10/12.5 | Light red | UIU/NVR |
| 300/10/25 | Brown | VIV/NVR |
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Do not use aliskiren with ARBs or ACEIs in patients with diabetes [see Warnings (5.2), Clinical Trials (14.2)].
Amturnide is contraindicated in patients with anuria or hypersensitivity to sulfonamide-derived drugs like HCTZ [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Hypersensitivity reactions may range from urticaria to anaphylaxis.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fetal Toxicity
Pregnancy Category D
Use of drugs that act on the renin-angiotensin system during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces fetal renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. Resulting oligohydramnios can be associated with fetal lung hypoplasia and skeletal deformations. Potential neonatal adverse effects include skull hypoplasia, anuria, hypotension, renal failure, and death. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue Amturnide as soon as possible [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.2 Renal Impairment/Hyperkalemia/Hypotension when Amturnide is given in combination with ARBs or ACEI
Amturnide is contraindicated in patients with diabetes who are receiving ARBs or ACEI because of the increased risk of renal impairment, hyperkalemia, and hypotension [see Contraindications (4) and Clinical Trials (14.2)].
Avoid use of Amturnide with ARBs or ACEI in patients with moderate renal impairment (GFR <60 ml/min).
5.3 Head and Neck Angioedema
AliskirenAngioedema of the face, extremities, lips, tongue, glottis and/or larynx has been reported in patients treated with aliskiren and has necessitated hospitalization and intubation. This may occur at any time during treatment and has occurred in patients with and without a history of angioedema with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor antagonists. If angioedema involves the throat, tongue, glottis or larynx, or if the patient has a history of upper respiratory surgery, airway obstruction may occur and be fatal. Patients who experience these effects, even without respiratory distress, require prolonged observation since treatment with antihistamines and corticosteroids may not be sufficient to prevent respiratory involvement. Prompt administration of subcutaneous epinephrine solution 1:1000 (0.3 to 0.5 mL) and measures to ensure a patent airway may be necessary.
Discontinue Amturnide immediately in patients who develop angioedema, and do not re-administer.
5.4 Hypotension
In patients with an activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, such as volume- and/or salt-depleted patients receiving high doses of diuretics, symptomatic hypotension may occur in patients receiving renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) blockers. Correct these conditions prior to administration of Amturnide, or start the treatment under close medical supervision.
A transient hypotensive response is not a contraindication to further treatment, which usually can be continued without difficulty once the blood pressure has stabilized.
5.5 Risk of Myocardial Infarction or Increased Angina
Rarely, initiation or change to the dose of a calcium channel blocker has resulted in the development of documented increased frequency, duration or severity of angina or acute myocardial infarction, particularly in patients with severe obstructive coronary artery disease. The mechanism of this effect has not been elucidated.
5.6 Impaired Renal Function
Monitor renal function periodically in patients treated with Amturnide. Changes in renal function, including acute renal failure, can be caused by drugs that affect the renin-angiotensin system and by diuretics. Patients whose renal function may depend in part on the activity of the renin-angiotensin system (e.g., patients with renal artery stenosis, severe heart failure, post-myocardial infarction or volume depletion) or patients receiving ARB, ACEI or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) therapy may be at particular risk of developing acute renal failure on Amturnide [see Contraindications (4), Warnings (5.2), Clinical Trials (14.2)]. Consider withholding or discontinuing therapy in patients who develop a clinically significant decrease in renal function on Amturnide.
5.7 Patients with Heart Failure
Amturnide has not been studied in patients with heart failure.
Amlodipine (5-10 mg per day) has been studied in a placebo-controlled trial of 1153 patients with NYHA Class III or IV heart failure on stable doses of ACE inhibitors, digoxin, and diuretics. Follow-up was at least 6 months, with a mean of about 14 months. There was no overall adverse effect on survival or cardiac morbidity (as defined by life-threatening arrhythmia, acute myocardial infarction, or hospitalization for worsened heart failure). Amlodipine has been compared to placebo in four 8-12 week studies of patients with NYHA Class II/III heart failure, involving a total of 697 patients. In these studies, there was no evidence of worsened heart failure based on measures of exercise tolerance, NYHA classification, symptoms, or left ventricular ejection fraction.
5.8 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions to HCTZ may occur in patients with or without a history of allergy or bronchial asthma, but are more likely in patients with such a history.
5.9 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Thiazide diuretics have been reported to cause exacerbation or activation of systemic lupus erythematosus.
5.10 Lithium Interaction
Lithium generally should not be given with thiazides [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.11 Serum Electrolyte Abnormalities
Amturnide
In a short-term controlled trial the incidence of patients with hypertension not concomitantly treated with an ARB or ACEI who developed hypokalemia (serum potassium <3.5 mEq/L) was 11.0% of Amturnide-treated patients compared to 19.0% of amlodipine/HCTZ patients, 4.4% of aliskiren/HCTZ patients, and 2.1% of aliskiren/amlodipine patients; the incidence of hyperkalemia (serum potassium >5.5 mEq/L) was 3.0% compared to 2.0% of amlodipine/HCTZ patients, 0.7% of aliskiren/HCTZ patients, and 0.7% of aliskiren/amlodipine patients. No Amturnide-treated patients discontinued due to increase or decrease of serum potassium.
Aliskiren
Monitor serum potassium periodically in patients receiving aliskiren. Drugs that affect the renin-angiotensin system can cause hyperkalemia. Risk factors for the development of hyperkalemia include renal insufficiency, diabetes, combination use with ARBs or ACEI [see Contraindications (4), Warnings (5.2), and Clinical Trials (14.2)], NSAIDs, or potassium supplements or potassium sparing diuretics.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide can cause hypokalemia and hyponatremia. Hypomagnesemia can result in hypokalemia which appears difficult to treat despite potassium repletion.
If hypokalemia is accompanied by clinical signs (e.g., muscular weakness, paresis, or ECG alterations), Amturnide should be discontinued. Correction of hypokalemia and any coexisting hypomagnesaemia is recommended prior to the initiation of thiazides.
5.12 Cyclosporine or Itraconazole
When aliskiren was given with cyclosporine or itraconazole, the blood concentrations of aliskiren were significantly increased. Avoid concomitant use of Amturnide with cyclosporine or itraconazole [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.13 Acute Myopia and Secondary Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Hydrochlorothiazide, a sulfonamide, can cause an idiosyncratic reaction, resulting in transient myopia and acute angle-closure glaucoma. Symptoms include acute onset of decreased visual acuity or ocular pain and typically occur within hours to weeks of drug initiation. Untreated acute angle-closure glaucoma can lead to permanent vision loss. The primary treatment is to discontinue hydrochlorothiazide as rapidly as possible. Prompt medical or surgical treatments may need to be considered if the intraocular pressure remains uncontrolled. Risk factors for developing acute angle-closure glaucoma may include a history of sulfonamide or penicillin allergy.
5.14 Metabolic Disturbances
Hydrochlorothiazide
Hydrochlorothiazide may alter glucose tolerance and raise serum levels of cholesterol and triglycerides.
Hydrochlorothiazide may raise the serum uric acid level due to reduced clearance of uric acid and may cause or exacerbate hyperuricemia and precipitate gout in susceptible patients.
Hydrochlorothiazide decreases urinary calcium excretion and may cause elevation of serum calcium. Monitor calcium levels in patients with hypercalcemia receiving Amturnide.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Risk of fetal/neonatal morbidity and mortality [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Head and neck angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Amturnide
Amturnide has been evaluated for safety in 1155 patients treated with Amturnide, including 182 patients for over 1 year.
In a short-term controlled trial, there were 60.5% males, 84.1% Caucasians, 10% Blacks, 6.4% Hispanics, and 19.1% who were ≥ 65 years of age. In this study, the overall incidence of adverse events on therapy with Amturnide was similar to that observed with the individual components. The overall frequency of adverse events was similar between men and women and Black and White patients. Discontinuation of therapy because of a clinical adverse event in this study occurred in 3.6% of patients treated with Amturnide versus 2.4% in aliskiren/amlodipine, 0.7% in aliskiren/HCTZ, and 2.7% in amlodipine/HCTZ.
| Amturnide | Ali/amlo | Ali/HCTZ | Amlo/HCTZ | |
| Edema peripheral | 7.1% | 8.0% | 2.0% | 4.1% |
| Dizziness | 3.6% | 2.4% | 3.4% | 1.7% |
| Headache | 3.6% | 3.1% | 4.0% | 5.1% |
| Nasopharyngitis | 2.6% | 0.7% | 2.0% | 3.4% |
In a long-term safety trial, the safety profile was similar to that seen in the short-term controlled trial.
Aliskiren
Aliskiren has been evaluated for safety in 6460 patients, including 1740 treated for longer than 6 months, and 1250 for longer than 1 year. In placebo-controlled clinical trials, discontinuation of therapy because of a clinical adverse event, including uncontrolled hypertension, occurred in 2.2% of patients treated with aliskiren, versus 3.5% of patients given placebo. These data do not include information from the ALTITUDE study which evaluated the use of aliskiren in combination with ARBs or ACEI [see Contraindications (4), Warnings (5.2), and Clinical Trials (14.2)].
Two cases of angioedema with respiratory symptoms were reported with aliskiren use in the clinical studies. Two other cases of periorbital edema without respiratory symptoms were reported as possible angioedema and resulted in discontinuation. The rate of these angioedema cases in the completed studies was 0.06%.
In addition, 26 other cases of edema involving the face, hands, or whole body were reported with aliskiren use, including 4 leading to discontinuation.
In the placebo-controlled studies, however, the incidence of edema involving the face, hands, or whole body was 0.4% with aliskiren compared with 0.5% with placebo. In a long-term active-controlled study with aliskiren and HCTZ arms, the incidence of edema involving the face, hands, or whole body was 0.4% in both treatment arms.
Aliskiren produces dose-related gastrointestinal (GI) adverse reactions. Diarrhea was reported by 2.3% of patients at 300 mg, compared to 1.2% in placebo patients. In women and the elderly (age ≥65) increases in diarrhea rates were evident starting at a dose of 150 mg daily, with rates for these subgroups at 150 mg similar to those seen at 300 mg for men or younger patients (all rates about 2%). Other GI symptoms included abdominal pain, dyspepsia, and gastroesophageal reflux, although increased rates for abdominal pain and dyspepsia were distinguished from placebo only at 600 mg daily. Diarrhea and other GI symptoms were typically mild and rarely led to discontinuation.
Aliskiren was associated with a slight increase in cough in the placebo-controlled studies (1.1% for any aliskiren use versus 0.6% for placebo). In active-controlled trials with ACE inhibitor (ramipril, lisinopril) arms, the rates of cough for the aliskiren arms were about one-third to one-half the rates in the ACE inhibitor arms.
Other adverse reactions with increased rates for aliskiren compared to placebo included rash (1% versus 0.3%), and renal stones (0.2% versus 0%).
Single episodes of tonic-clonic seizures with loss of consciousness were reported in 2 patients treated with aliskiren in the clinical trials. One patient had predisposing causes for seizures and had a negative electroencephalogram (EEG) and cerebral imaging following the seizures; for the other patient, EEG and imaging results were not reported. Aliskiren was discontinued and there was no re-challenge in either case.
No clinically meaningful changes in vital signs or in ECG (including QTc interval) were observed in patients treated with aliskiren.
Amlodipine
Amlodipine (Norvasc®) has been evaluated for safety in more than 11,000 patients in U.S. and foreign clinical trials. Other adverse events that have been reported at <1% but >0.1% of patients in controlled clinical trials or under conditions of open trials or marketing experience where a causal relationship is uncertain were:
Cardiovascular: arrhythmia (including ventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation), bradycardia, chest pain, peripheral ischemia, syncope, postural hypotension, vasculitis
Central and Peripheral Nervous System: neuropathy peripheral, paresthesia, tremor, vertigo
Gastrointestinal: anorexia, constipation, dyspepsia,** dysphagia, diarrhea, flatulence, pancreatitis, vomiting, gingival hyperplasia
General: allergic reaction, asthenia,** back pain, hot flushes, malaise, pain, rigors, weight gain, weight decrease
Musculoskeletal System: arthralgia, arthrosis, muscle cramps,** myalgia
Psychiatric: sexual dysfunction (male** and female), insomnia, nervousness, depression, abnormal dreams, anxiety, depersonalization
Respiratory System: dyspnea, epistaxis
Skin and Appendages: angioedema, erythema multiforme, pruritus,** rash,** rash erythematous, rash maculopapular
**These events occurred in less than 1% in placebo-controlled trials, but the incidence of these side effects was between 1% and 2% in all multiple dose studies.
Special Senses: abnormal vision, conjunctivitis, diplopia, eye pain, tinnitus
Urinary System: micturition frequency, micturition disorder, nocturia
Autonomic Nervous System: dry mouth, sweating increased
Metabolic and Nutritional: hyperglycemia, thirst
Hemopoietic: leukopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia
Other events reported with amlodipine at a frequency of ≤0.1% of patients include: cardiac failure, pulse irregularity, extrasystoles, skin discoloration, urticaria, skin dryness, alopecia, dermatitis, muscle weakness, twitching, ataxia, hypertonia, migraine, cold and clammy skin, apathy, agitation, amnesia, gastritis, increased appetite, loose stools, rhinitis, dysuria, polyuria, parosmia, taste perversion, abnormal visual accommodation, and xerophthalmia. Other reactions occurred sporadically and cannot be distinguished from medications or concurrent disease states such as myocardial infarction and angina.
HCTZ
Other adverse reactions not listed above that have been reported with HCTZ, without regard to causality, are listed below:
Body as a Whole: weakness
Digestive: pancreatitis, jaundice (intrahepatic cholestatic jaundice), sialadenitis, cramping, gastric irritation
Hematologic: aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, Hypersensitivity: photosensitivity, urticaria, necrotizing angiitis (vasculitis and cutaneous vasculitis), fever, respiratory distress including pneumonitis and pulmonary edema, anaphylactic reactions
Musculoskeletal: muscle spasm
Nervous System/Psychiatric: restlessness
Renal: renal failure, renal dysfunction, interstitial nephritis
Skin: erythema multiforme including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis including toxic epidermal necrolysis
Special Senses: transient blurred vision, xanthopsia
Clinical Laboratory Test Abnormalities
Clinical laboratory findings for Amturnide in patients with hypertension not concomitantly treated with an ARB or ACEI were obtained in a controlled trial of Amturnide administered at the maximal dose of 300/10/25 mg compared to maximal doses of dual therapies, i.e., aliskiren/amlodipine 300/10 mg, aliskiren/HCTZ 300/25 mg and amlodipine/HCTZ 10/25 mg.
RBC Count, Hemoglobin and Hematocrit
Small mean changes from baseline were seen in RBC count, hemoglobin and hematocrit in patients treated with Amturnide. This effect is also seen with other agents acting on the renin angiotensin system. In aliskiren monotherapy trials these decreases led to slight increases in rates of anemia compared to placebo (0.1% for any aliskiren use, 0.3% for aliskiren 600 mg daily, versus 0% for placebo). No patients discontinued Amturnide because of anemia.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)/Creatinine
No patients with hypertension not concomitantly treated with an ARB or ACEI treated with Amturnide had elevations in BUN >40 mg/dL or creatinine >2.0 mg/dL.
Liver Function Tests
Occasional elevations (greater than 150% from baseline) in ALT (SGPT) were observed in 2.7% of patients treated with Amturnide, compared with 1.7-2.7% in patients treated with the dual combinations. No patients were discontinued due to abnormal liver function tests.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of either aliskiren, amlodipine or hydrochlorothiazide. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
Aliskiren:
Hypersensitivity: angioedema requiring airway management and hospitalization.
Peripheral edema, severe cutaneous adverse reactions, including Stevens Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Amlodipine: The following postmarketing event has been reported infrequently where a causal relationship is uncertain: gynecomastia. In postmarketing experience, jaundice and hepatic enzyme elevations (mostly consistent with cholestasis or hepatitis), in some cases severe enough to require hospitalization, have been reported in association with use of amlodipine.
Hydrochlorothiazide:
Acute renal failure, renal disorder, aplastic anemia, erythema multiforme, pyrexia, muscle spasm, asthenia, acute angle-closure glaucoma, bone marrow failure, worsening of diabetes control, hypokalemia, blood lipids increased, hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia, hyperchloremic alkalosis, impotence, visual impairment.
Pathological changes in the parathyroid gland of patients with hypercalcemia and hypophosphatemia have been observed in a few patients on prolonged thiazide therapy. If hypercalcemia occurs, further diagnostic evaluation is necessary.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No drug interaction studies have been conducted between Amturnide and other drugs. In a phase III sub-study, there was no clinically relevant change in the exposure of aliskiren, amlodipine, and HCTZ observed with Amturnide compared to the dual combinations of aliskiren and amlodipine, amlodipine and HCTZ, and aliskiren and HCTZ. Studies with the individual aliskiren, amlodipine, and HCTZ components are described below.
Aliskiren
Cyclosporine: Avoid co-administration of cyclosporine with aliskiren.
Itraconazole: Avoid co-administration of itraconazole with aliskiren [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents(NSAIDS) including selective Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors (COX-2 inhibitors): In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or with compromised renal function, co-administration of NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors with agents that affect the renin-angiotensin system, including aliskiren, may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. These effects are usually reversible. Monitor renal function periodically in patients receiving aliskiren and NSAID therapy.
The antihypertensive effect of aliskiren may be attenuated by NSAIDS.
Amlodipine
In clinical trials, amlodipine has been safely administered with thiazide diuretics, beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, long-acting nitrates, sublingual nitroglycerin, digoxin, warfarin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and oral hypoglycemic drugs.
Cimetidine: Coadministration of amlodipine with cimetidine did not alter the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
Grapefruit juice: Coadministration of 240 mL of grapefruit juice with a single oral dose of amlodipine 10 mg in 20 healthy volunteers had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
Maalox® (antacid): Coadministration of the antacid Maalox with a single dose of amlodipine had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of amlodipine.
Sildenafil: A single 100 mg dose of sildenafil in subjects with essential hypertension had no effect on the pharmacokinetic parameters of amlodipine. When amlodipine and sildenafil were used in combination, each agent independently exerted its own blood pressure lowering effect.
Atorvastatin: Coadministration of multiple 10 mg doses of amlodipine with 80 mg of atorvastatin resulted in no significant change in the steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters of atorvastatin.
Digoxin: Coadministration of amlodipine with digoxin did not change serum digoxin levels or digoxin renal clearance in normal volunteers.
Ethanol (alcohol): Single and multiple 10 mg doses of amlodipine had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of ethanol.
Warfarin: Coadministration of amlodipine with warfarin did not change the warfarin prothrombin response time.
Simvastatin: Co-administration of multiple doses of 10 mg of amlodipine with 80 mg simvastatin resulted in a 77% increase in exposure to simvastatin compared to simvastatin alone. Limit the dose of simvastatin in patients on amlodipine to 20 mg daily.
HCTZ
When administered concurrently, the following drugs may interact with thiazide diuretics.
Antidiabetic drugs (oral agents and insulin): Dosage adjustment of the antidiabetic drug may be required.
Lithium: Diuretic agents increase the risk of lithium toxicity. Refer to the package insert for lithium before use of such preparation with Amturnide. Monitoring of serum lithium concentrations is recommended during concurrent use.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and Cox2 selective agents: When Amturnide and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents are used concomitantly, observe the patient to determine if the desired effect of the diuretic is obtained.
Ion exchange resins: Staggering the dosage of hydrochlorothiazide and resin (e.g., cholestyramine, colestipol) such that hydrochlorothiazide is administered at least 4 hours before or 4-6 hours after the administration of resins would potentially minimize the interaction [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D
Use of drugs that act on the renin-angiotensin system during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy reduces fetal renal function and increases fetal and neonatal morbidity and death. Resulting oligohydramnios can be associated with fetal lung hypoplasia and skeletal deformations. Potential neonatal adverse effects include skull hypoplasia, anuria, hypotension, renal failure, and death. When pregnancy is detected, discontinue Amturnide as soon as possible. These adverse outcomes are usually associated with use of drugs in the second and third trimester of pregnancy. Most epidemiologic studies examining fetal abnormalities after exposure to antihypertensive use in the first trimester have not distinguished drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system from other antihypertensive agents. Appropriate management of maternal hypertension during pregnancy is important to optimize outcomes for both mother and fetus. In the unusual case that there is no appropriate alternative to therapy with drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin system for a particular patient, apprise the mother of the potential risk to the fetus. Perform serial ultrasound examinations to assess the intra-amniotic environment. If oligohydramnios is observed, discontinue Amturnide, unless it is considered lifesaving for the mother. Fetal testing may be appropriate, based on the week of pregnancy. Patients and physicians should be aware, however, that oligohydramnios may not appear until after the fetus has sustained irreversible injury. Closely observe infants with histories of in utero exposure to Amturnide for hypotension, oliguria, and hyperkalemia [see use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Animal Data
No reproductive toxicity studies have been conducted with the combination of aliskiren, amlodipine besylate and HCTZ. However, these studies have been conducted for aliskiren, amlodipine besylate and HCTZ alone.
Aliskiren
In developmental toxicity studies, pregnant rats and rabbits received oral aliskiren hemifumarate during organogenesis at doses up to 20 and 7 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on body surface area (mg/m2), respectively, in rats and rabbits. (Actual animal doses were up to 600 mg/kg/day in rats and up to 100 mg/kg/day in rabbits.) No teratogenicity was observed; however, fetal birth weight was decreased in rabbits at doses 3.2 times the MRHD based on body surface area (mg/m2). Aliskiren was present in placentas, amniotic fluid and fetuses of pregnant rabbits.
Amlodipine
In developmental toxicity studies, pregnant rats and rabbits received oral amlodipine maleate during organogenesis at doses approximately 10 and 20 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on body surface area (mg/m2), respectively, in rats and rabbits. (Actual animal doses were up to 10 mg/kg/day.) No evidence of teratogenicity or other embryofetal toxicity was observed. However, litter size was decreased approximately 50% and the number of intrauterine deaths was increased approximately 5-fold for rats receiving amlodipine maleate at doses approximately 10 times the MRHD based on body surface area (mg/m2) for 14 days before mating and throughout mating and gestation. Amlodipine maleate has been shown to prolong both the gestation period and the duration of labor in rats at this dose.
HCTZ
When pregnant mice and rats were given HCTZ at doses up to 3000 and 1000 mg/kg/day, respectively (about 600 and 400 times the MRHD), during their respective periods of major organogenesis, there was no evidence of fetal harm.
Thiazides can cross the placenta, and concentrations reached in the umbilical vein approach those in the maternal plasma. Hydrochlorothiazide, like other diuretics, can cause placental hypoperfusion. It accumulates in the amniotic fluid, with reported concentrations up to 19 times higher than in umbilical vein plasma. Use of thiazides during pregnancy is associated with a risk of fetal or neonatal jaundice or thrombocytopenia. Since they do not prevent or alter the course of EPH (Edema, Proteinuria, Hypertension) gestosis (pre eclampsia), these drugs should not be used to treat hypertension in pregnant women. The use of hydrochlorothiazide for other indications (e.g. heart disease) in pregnancy should be avoided.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether aliskiren or amlodipine is excreted in human milk, but thiazides are excreted in human milk. Both aliskiren and amlodipine are secreted in the milk of lactating rats. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in human milk-fed infants from Amturnide, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue Amturnide, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of Amturnide in pediatric patients have not been established.
Neonates with a history of in utero exposure to Amturnide:
If oliguria or hypotension occurs, direct attention towards support of blood pressure and renal perfusion. Exchange transfusions or dialysis may be required as a means of reversing hypotension and/or substituting for disordered renal function.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the short-term controlled clinical trial of Amturnide, 19% of patients treated with Amturnide were ≥ 65 years. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Patients ≥ 75 years of age should start amlodipine at 2.5 mg, which is not available with Amturnide.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Aliskiren
Limited data are available related to overdosage in humans. The most likely manifestation of overdosage would be hypotension. If symptomatic hypotension occurs, provide supportive treatment.
Aliskiren is poorly dialyzed. Therefore, hemodialysis is not adequate to treat aliskiren overexposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Amlodipine
Single oral doses of amlodipine maleate equivalent to 40 mg amlodipine/kg and 100 mg amlodipine/kg in mice and rats, respectively, caused deaths. Single oral amlodipine maleate doses equivalent to 4 or more mg amlodipine/kg or higher in dogs (11 or more times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis) caused a marked peripheral vasodilation and hypotension.
Overdosage might be expected to cause excessive peripheral vasodilation with marked hypotension and possibly a reflex tachycardia. In humans, experience with intentional overdosage of amlodipine is limited. Reports of intentional overdosage include a patient who ingested 250 mg and was asymptomatic and was not hospitalized; another (120 mg) was hospitalized, underwent gastric lavage and remained normotensive; the third patient (105 mg) was hospitalized and had hypotension (90/50 mmHg), which normalized following plasma expansion. A case of accidental drug overdose has been documented in a 19-month-old male who ingested 30 mg amlodipine (about 2 mg/kg). During the emergency room presentation, vital signs were stable with no evidence of hypotension but a heart rate of 180 bpm. Ipecac was administered 3.5 hours after ingestion, and on subsequent observation (overnight) no sequelae were noted.
If massive overdose occurs, institute active cardiac and respiratory monitoring. Frequent blood pressure measurements are essential. If hypotension occurs, initiate cardiovascular support including elevation of the extremities and the judicious administration of fluids. If hypotension remains unresponsive to these conservative measures, consider administration of vasopressors (such as phenylephrine), with attention to circulating volume and urine output. Intravenous calcium gluconate may help to reverse the effects of calcium entry blockade. As amlodipine is highly protein bound, hemodialysis is not likely to be of benefit.
HCTZ
The most common signs and symptoms of overdose observed in humans are those caused by electrolyte depletion (hypokalemia, hypochloremia, hyponatremia) and dehydration resulting from excessive diuresis. If digitalis has also been administered, hypokalemia may accentuate cardiac arrhythmias. The degree to which HCTZ is removed by hemodialysis has not been established. The oral LD50 of HCTZ is greater than 10 g/kg in both mice and rats. These doses are 1946 and 3892 times, respectively, the MRHD of 25 mg/day, when based on a mg/m2 basis of a 60-kg individual.
11 DESCRIPTION
Amturnide is a single tablet for oral administration of aliskiren hemifumarate (an orally active, nonpeptide, potent direct renin inhibitor), amlodipine besylate (a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker) and HCTZ (a diuretic).
Aliskiren hemifumarate
Aliskiren hemifumarate is chemically described as (2S,4S,5S,7S)-N-(2-carbamoyl-2-methylpropyl)-5-amino-4-hydroxy-2,7-diisopropyl-8-[4-methoxy-3-(3-methoxypropoxy)phenyl]-octanamide hemifumarate, and its structural formula is
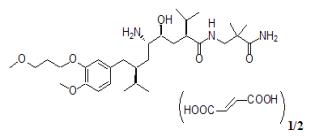
Molecular formula: C30H53N3O6 • 0.5 C4H4O4
Aliskiren hemifumarate is a white to slightly yellowish powder with a molecular weight of 609.8 (free base- 551.8). It is highly soluble in water, and freely soluble in methanol, ethanol and isopropanol.
Amlodipine
Amlodipine besylate, USP is chemically described as 3-ethyl 5-methyl (±)-2-[(2-aminoethoxy)methyl]-4-(o-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, monobenzenesulfonate and its structural formula is
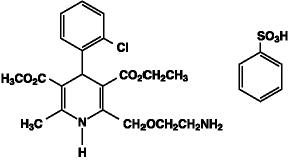
Molecular formula: C20H25CIN2O5•C6H6O3S
Amlodipine besylate is a white to pale yellow crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 567.1. It is slightly soluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol.
HCTZ
HCTZ, USP is a white, or practically white, practically odorless, crystalline powder. It is slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in sodium hydroxide solution, in n-butylamine, and in dimethylformamide; sparingly soluble in methanol; and insoluble in ether, in chloroform, and in dilute mineral acids. HCTZ is chemically described as 6-chloro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide.
HCTZ is a thiazide diuretic. Its empirical formula is C7H8ClN3O4S2, its molecular weight is 297.73, and its structural formula is
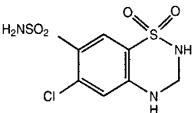
The inactive ingredients for all strengths of the tablets may contain colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hypromellose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, iron oxide black, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Amturnide
The effects of combined treatment of aliskiren, amlodipine and HCTZ arise from the actions of these three agents on different but complementary mechanisms that regulate blood pressure. Together, inhibition of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), inhibition of calcium channel-mediated vasoconstriction, and increase of sodium chloride excretion lowers blood pressure to a greater degree than the individual components.
Aliskiren
Renin is secreted by the kidney in response to decreases in blood volume and renal perfusion. Renin cleaves angiotensinogen to form the inactive decapeptide angiotensin I (Ang I). Ang I is converted to the active octapeptide angiotensin II (Ang II) by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and non-ACE pathways. Ang II is a powerful vasoconstrictor and leads to the release of catecholamines from the adrenal medulla and prejunctional nerve endings. It also promotes aldosterone secretion and sodium reabsorption. Together, these effects increase blood pressure. Ang II also inhibits renin release, thus providing a negative feedback to the system. This cycle, from renin through angiotensin to aldosterone and its associated negative feedback loop, is known as the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Aliskiren is a direct renin inhibitor, decreasing plasma renin activity (PRA) and inhibiting the conversion of angiotensinogen to Ang I. Whether aliskiren affects other RAAS components, e.g., ACE or non-ACE pathways, is not known.
All agents that inhibit the RAAS, including renin inhibitors, suppress the negative feedback loop, leading to a compensatory rise in plasma renin concentration. When this rise occurs during treatment with ACE inhibitors and ARBs, the result is increased levels of PRA. During treatment with aliskiren, however, the effect of increased renin levels is blocked, so that PRA, Ang I and Ang II are all reduced, whether aliskiren is used as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
Amlodipine
Amlodipine is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker that inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. Experimental data suggest that amlodipine binds to both dihydropyridine and nondihydropyridine binding sites. The contractile processes of cardiac muscle and vascular smooth muscle are dependent upon the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels. Amlodipine inhibits calcium ion influx across cell membranes selectively, with a greater effect on vascular smooth muscle cells than on cardiac muscle cells. Negative inotropic effects can be detected in vitro but such effects have not been seen in intact animals at therapeutic doses. Serum calcium concentration is not affected by amlodipine. Within the physiologic pH range, amlodipine is an ionized compound (pKa=8.6), and its kinetic interaction with the calcium channel receptor is characterized by a gradual rate of association and dissociation with the receptor binding site, resulting in a gradual onset of effect.
Amlodipine is a peripheral arterial vasodilator that acts directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause a reduction in peripheral vascular resistance and reduction in blood pressure.
HCTZ
The mechanism of action of the antihypertensive effect of thiazides is unknown.
HCTZ is a thiazide diuretic. Thiazides affect the renal tubular mechanisms of electrolyte reabsorption, directly increasing excretion of sodium and chloride in approximately equivalent amounts. Indirectly, the diuretic action of HCTZ reduces plasma volume, with consequent increases in plasma renin activity, increases in aldosterone secretion, increases in urinary potassium loss, and decreases in serum potassium. The renin-aldosterone link is mediated by angiotensin II, so coadministration of agents that block the production or function of angiotensin II tends to reverse the potassium loss associated with these diuretics.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Amturnide
In an active-controlled trial which established the clinical efficacy of Amturnide in hypertensive patients, Amturnide was associated with a 34% reduction in PRA compared to a 63% reduction with aliskiren/amlodipine, 64% reduction with aliskiren/HCTZ and a 170% elevation with amlodipine/HCTZ.
Aliskiren
PRA reductions in clinical trials ranged from approximately 50% to 80%, were not dose-related and did not correlate with blood pressure reductions. The clinical implications of the differences in effect on PRA are not known.
Amlodipine
Following administration of therapeutic doses to patients with hypertension, amlodipine produces vasodilation resulting in a reduction of supine and standing blood pressures. These decreases in blood pressure are not accompanied by a significant change in heart rate or plasma catecholamine levels with chronic dosing. Although the acute intravenous administration of amlodipine decreases arterial blood pressure and increases heart rate in hemodynamic studies of patients with chronic stable angina, chronic oral administration of amlodipine in clinical trials did not lead to clinically significant changes in heart rate or blood pressures in normotensive patients with angina.
With chronic once-daily administration, antihypertensive effectiveness is maintained for at least 24 hours. Plasma concentrations correlate with effect in both young and elderly patients. The magnitude of reduction in blood pressure with amlodipine is also correlated with the height of pretreatment elevation; thus, individuals with moderate hypertension (diastolic pressure 105-114 mmHg) had about 50% greater response than patients with mild hypertension (diastolic pressure 90-104 mmHg). Normotensive subjects experienced no clinically significant change in blood pressure (+1/-2 mmHg).
In hypertensive patients with normal renal function, therapeutic doses of amlodipine resulted in a decrease in renal vascular resistance and an increase in glomerular filtration rate and effective renal plasma flow without change in filtration fraction or proteinuria.
As with other calcium channel blockers, hemodynamic measurements of cardiac function at rest and during exercise (or pacing) in patients with normal ventricular function treated with amlodipine have generally demonstrated a small increase in cardiac index without significant influence on dP/dt or on left ventricular end diastolic pressure or volume. In hemodynamic studies, amlodipine has not been associated with a negative inotropic effect when administered in therapeutic dose range to intact animals and man, even when co-administered with beta-blockers to man. Similar findings, however, have been observed in normal or well-compensated patients with heart failure with agents possessing significant negative inotropic effects.
Amlodipine does not change sinoatrial nodal function or atrioventricular conduction in intact animals or man. In patients with chronic stable angina, intravenous administration of 10 mg did not significantly alter A-H and H-V conduction and sinus node recovery time after pacing. Similar results were obtained in patients receiving amlodipine and concomitant beta-blockers. In clinical studies in which amlodipine was administered in combination with beta-blockers to patients with either hypertension or angina, no adverse effects of electrocardiographic parameters were observed. In clinical trials with angina patients alone, amlodipine therapy did not alter electrocardiographic intervals or produce higher degrees of AV blocks.
Amlodipine has indications other than hypertension, which can be found in the Norvasc® package insert.
HCTZ
After oral administration of HCTZ, diuresis begins within 2 hours, peaks in about 4 hours, and lasts about 6 to 12 hours.
Drug Interactions
Hydrochlorothiazide
Alcohol, barbiturates, or narcotics: Potentiation of orthostatic hypotension may occur.
Skeletal muscle relaxants: Possible increased responsiveness to muscle relaxants such as curare derivatives.
Digitalis glycosides: Thiazide-induced hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia may predispose the patient to digoxin toxicity.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Distribution
Amturnide
Following oral administration of the fixed combination of aliskiren, amlodipine, and HCTZ, peak concentrations were achieved within 1-2 hours, 6-12 hours, and 1-4 hours for aliskiren, amlodipine and HCTZ, respectively. The rate and extent of absorption of aliskiren, amlodipine, and HCTZ following administration of the fixed combination are similar to when they are administered as individual dosage forms.
When Amturnide is taken with food, mean AUC and Cmax of aliskiren are decreased by 78% and 89%, respectively. There is no impact of food on the exposures of amlodipine and HCTZ.
Aliskiren
Aliskiren is poorly absorbed (bioavailability about 2.5%). Following oral administration, peak plasma concentrations of aliskiren are reached within 1 to 3 hours. When taken with a high fat meal, mean AUC and Cmax of aliskiren are decreased by 71% and 85% respectively. In the clinical trials of aliskiren, it was administered without requiring a fixed relation of administration to meals.
Amlodipine
Peak plasma concentrations of amlodipine are reached 6-12 hours after an oral administration of amlodipine. Absolute bioavailability has been estimated to be between 64% and 90%. The bioavailability of amlodipine is not altered by the presence of food. Steady state plasma levels of amlodipine are reached after 7 to 8 days of consecutive daily dosing.
Approximately 93% of circulating amlodipine is bound to plasma proteins in hypertensive patients.
HCTZ
The estimated absolute bioavailability of hydrochlorothiazide after oral administration is about 70%. Peak plasma hydrochlorothiazide concentrations (Cmax) are reached within 2 to 5 hours after oral administration. There is no clinically significant effect of food on the bioavailability of hydrochlorothiazide.
Hydrochlorothiazide binds to albumin (40 to 70%) and distributes into erythrocytes. Following oral administration, plasma hydrochlorothiazide concentrations decline bi-exponentially, with a mean distribution half-life of about 2 hours and an elimination half-life of about 10 hours.
Metabolism and Elimination
Aliskiren
The effective half-life for aliskiren is 24 hours. Steady state blood levels are reached in about 7 – 8 days. About one-fourth of the absorbed dose appears in the urine as parent drug. How much of the absorbed dose is metabolized is unknown. Based on the in vitro studies, the major enzyme responsible for aliskiren metabolism appears to be CYP 3A4. Aliskiren does not inhibit the CYP450 isoenzymes (CYP 1A2, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A) or induce CYP 3A4.
Transporters: Pgp (MDR1/Mdr1a/1b) was found to be the major efflux system involved in absorption and disposition of aliskiren in preclinical studies. The potential for drug interactions at the Pgp site will likely depend on the degree of inhibition of this transporter.
Amlodipine
Amlodipine is extensively (about 90%) converted to inactive metabolites via hepatic metabolism, with 10% of the parent compound and 60% of the metabolites excreted in the urine.
Elimination of amlodipine from the plasma is biphasic, with a terminal elimination half-life of about 30-50 hours.
HCTZ
About 70% of an orally administered dose of hydrochlorothiazide is eliminated in the urine as unchanged drug.
Drug interactions:
Aliskiren
The effect of co-administered drugs on the pharmacokinetics of aliskiren and vice versa, were studied in several single and multiple dose studies. Pharmacokinetic measures indicating the magnitude of these interactions are presented in Figure 1 (impact of co-administered drugs on aliskiren) and Figure 2 (impact on co-administered drugs).
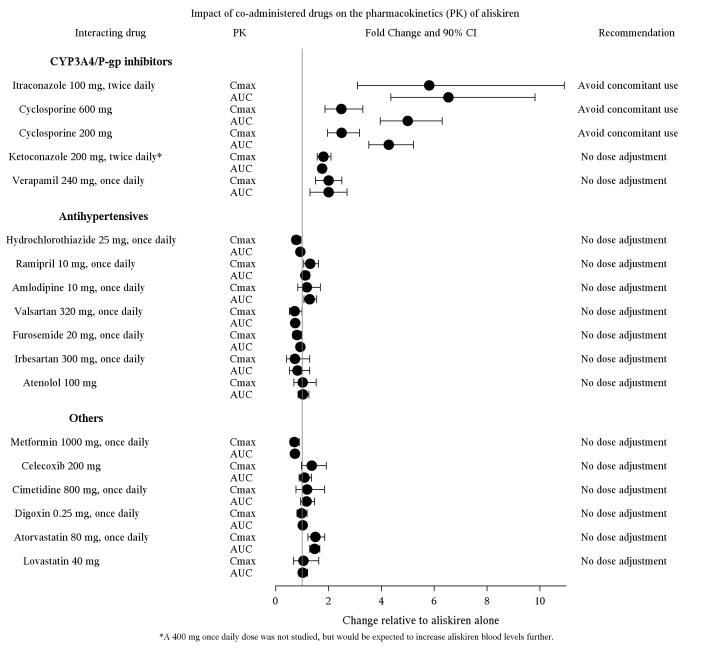
Figure 1: The impact of co-administered drugs on the pharmacokinetics of aliskiren.
Warfarin: There was no clinically significant effect of a single dose of warfarin 25 mg on the pharmacokinetics of aliskiren.
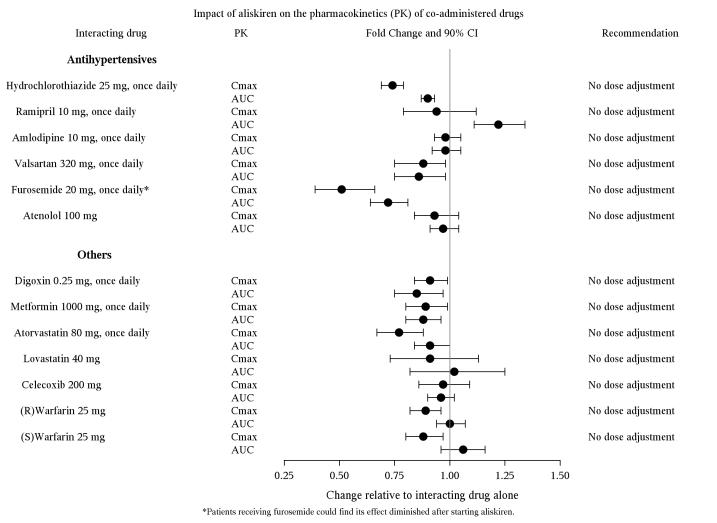
Figure 2: The impact of aliskiren on the pharmacokinetics of co-administered drugs.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Drugs that alter gastrointestinal motility: The bioavailability of thiazide-type diuretics may be increased by anticholinergic agents (e.g. atropine, biperiden), apparently due to a decrease in gastrointestinal motility and the stomach emptying rate. Conversely, pro-kinetic drugs may decrease the bioavailability of thiazide diuretics.
Cholestyramine: In a dedicated drug interaction study, administration of cholestyramine 2 hours before hydrochlorothiazide resulted in a 70% reduction in exposure to hydrochlorothiazide. Further, administration of hydrochlorothiazide 2 hours before cholestyramine, resulted in 35% reduction in exposure to hydrochlorothiazide.
Antineoplastic agents (e.g. cyclophosphamide, methotrexate): Concomitant use of thiazide diuretics may reduce renal excretion of cytotoxic agents and enhance their myelosuppressive effects.
Special Populations
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of Amturnide have not been investigated in patients <18 years of age.
Geriatric Patients
Aliskiren
The pharmacokinetics of aliskiren were studied in the elderly (≥65 years). Exposure (measured by AUC) is increased in elderly patients.
Amlodipine
Elderly patients have decreased clearance of amlodipine, with a resulting increase in AUC of approximately 40%-60%.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Limited data suggest that the systemic clearance of hydrochlorothiazide is reduced in both healthy and hypertensive elderly subjects compared to young healthy volunteers.
Race
With Amturnide, pharmacokinetic differences due to race have not been studied. The pharmacokinetic differences among Blacks, Caucasians, and Japanese are minimal with aliskiren therapy.
Renal Impairment
Aliskiren
The pharmacokinetics of aliskiren were evaluated in patients with varying degrees of renal impairment. Rate and extent of exposure (AUC and Cmax) of aliskiren in subjects with renal impairment did not show a consistent correlation with the severity of renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
The pharmacokinetics of aliskiren following administration of a single oral dose of 300 mg was evaluated in patients with End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) undergoing hemodialysis. When compared to matched healthy subjects, changes in the rate and extent of aliskiren exposure (Cmax and AUC) in ESRD patients undergoing hemodialysis was not clinically significant.
Timing of hemodialysis did not significantly alter the pharmacokinetics of aliskiren in ESRD patients. Therefore, no dose adjustment is warranted in ESRD patients receiving hemodialysis.
Amlodipine
The pharmacokinetics of amlodipine is not significantly influenced by renal impairment. Patients with renal failure may therefore receive the usual initial dose.
Hydrochlorothiazide
In a study in individuals with impaired renal function, the mean elimination half-life of hydrochlorothiazide was doubled in individuals with mild/moderate renal impairment (30 < CLcr < 90 mL/min) and tripled in severe renal impairment (≤ 30 mL/min), compared to individuals with normal renal function (CLcr > 90 mL/min) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Hepatic Impairment
Aliskiren
The pharmacokinetics of aliskiren were not significantly affected in patients with mild-to-severe liver disease [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Amlodipine
Patients with hepatic insufficiency have decreased clearance of amlodipine with resulting increase in AUC of approximately 40%-60%. A lower initial dose of amlodipine is required for patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies with Aliskiren hemifumarate, Amlodipine besylate and HCTZ
No carcinogenicity, mutagenicity or fertility studies have been conducted with the combination of aliskiren hemifumarate, amlodipine besylate and HCTZ. However, these studies have been conducted for aliskiren hemifumarate, amlodipine besylate and HCTZ alone.
Studies with Aliskiren hemifumarate
Carcinogenic potential was assessed in a 2-year rat study and a 6-month transgenic (rasH2) mouse study with aliskiren hemifumarate at oral doses of up to 1500 mg aliskiren/kg/day. Although there were no statistically significant increases in tumor incidence associated with exposure to aliskiren, mucosal epithelial hyperplasia (with or without erosion/ulceration) was observed in the lower gastrointestinal tract at doses of 750 or more mg/kg/day in both species, with a colonic adenoma identified in one rat and a cecal adenocarcinoma identified in another, rare tumors in the strain of rat studied. On a systemic exposure (AUC0-24h) basis, 1500 mg/kg/day in the rat is about 4 times and in the mouse about 1.5 times the maximum recommended human dose (300 mg aliskiren/day). Mucosal hyperplasia in the cecum or colon of rats was also observed at doses of 250 mg/kg/day (the lowest tested dose) as well as at higher doses in 4- and 13-week studies.
Aliskiren hemifumarate was devoid of genotoxic potential in the Ames reverse mutation assay with S. typhimurium and E. coli, the in vitro Chinese hamster ovary cell chromosomal aberration assay, the in vitro Chinese hamster V79 cell gene mutation test and the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Fertility of male and female rats was unaffected at doses of up to aliskiren 250 mg/kg/day (8 times the maximum recommended human dose of aliskiren 300 mg/60 kg on a mg/m2 basis).
Studies with Amlodipine besylate
Rats and mice treated with amlodipine maleate in the diet for up to two years, at concentrations calculated to provide daily dosage levels of 0.5, 1.25, and 2.5 mg amlodipine/kg/day, showed no evidence of a carcinogenic effect of the drug. For the mouse, the highest dose was, on mg/m2 basis, similar to the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 10 mg amlodipine/day. For the rat, the highest dose was, on a mg/m2 basis, about two and half times the MRHD. (Calculations are based on a 60-kg patient.)
Mutagenicity studies conducted with amlodipine maleate revealed no drug-related effects at either the gene or chromosome level.
There was no effect on the fertility of rats treated orally with amlodipine maleate (males for 64 days and females for 14 days prior to mating) at doses of up to 10 mg amlodipine/kg/day (about 10 times the MRHD of 10 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis).
Studies with HCTZ
Two-year feeding studies in mice and rats conducted under the auspices of the National Toxicology Program (NTP) uncovered no evidence of a carcinogenic potential of HCTZ in female mice (at doses of up to approximately 600 mg/kg/day) or in male and female rats (at doses of up to approximately 100 mg/kg/day). These doses in mice and rats are about 117 and 39 times, respectively, the MRHD of 25 mg/day, when based on a mg/m2 basis of a 60 kg individual. The NTP, however, found equivocal evidence for hepatocarcinogenicity in male mice.
HCTZ was not genotoxic in vitro in the Ames mutagenicity assay of S. typhimurium strains TA 98, TA 100, TA 1535, TA 1537, and TA 1538 and in the Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) test for chromosomal aberrations, or in vivo in assays using mouse germinal cell chromosomes, Chinese hamster bone marrow chromosomes, and the Drosophila sex-linked recessive lethal trait gene. Positive test results were obtained only in the in vitro CHO Sister Chromatid Exchange (clastogenicity) and in the Mouse Lymphoma Cell (mutagenicity) assays, using concentrations of HCTZ from 43 to 1300 mcg/mL, and in the Aspergillus Nidulans nondisjunction assay at an unspecified concentration.
HCTZ was not teratogenic and had no adverse effects on the fertility of mice and rats of either sex in studies wherein these species were exposed, via their diet, to doses of up to 100 and 4 mg/kg, respectively, prior to mating and throughout gestation. These doses of HCTZ in mice and rats represent 19 and 1.5 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis. (Calculations assume an oral dose of 25 mg/day and a 60-kg patient.)
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Amturnide
Amturnide
Amturnide was studied in a double-blind, active-controlled study in 1181 treated hypertensive patients, of whom 773 were classified as moderately hypertensive (SBP 160-180 mmHg) and 408 as severely hypertensive (SBP 180-200 mmHg) at baseline. The mean baseline systolic/diastolic blood pressure for all randomized patients was approximately 173/105 mmHg. A total of 61% of patients were male, 19% were 65 years or older, 84% were Caucasian, and 10% were Black.
At study initiation, patients assigned to the dual combination treatments received lower doses of their treatment combination (aliskiren 150 mg plus amlodipine 5 mg, aliskiren 150 mg plus HCTZ 12.5 mg, or amlodipine 5 mg plus HCTZ 12.5 mg), while patients assigned to the Amturnide arm received aliskiren/HCTZ 150/12.5 mg. After 3 days, Amturnide patients were titrated to aliskiren/amlodipine/HCTZ 150/5/12.5 mg, while all other patients continued receiving their initial doses. After 4 weeks, all patients were titrated to their full target doses of aliskiren/amlodipine/HCTZ 300/10/25 mg, aliskiren/amlodipine 300/10, aliskiren/HCTZ 300/25 mg, or amlodipine/HCTZ 10/25 mg.
Amturnide produced greater reductions in blood pressure than did any of the 3 dual combination treatments (p<0.001 for both diastolic and systolic blood pressure reductions). The reductions in systolic/diastolic blood pressure with Amturnide were 9.9/6.3 mmHg greater than with aliskiren/HCTZ, 7.2/3.6 mmHg greater than with amlodipine/HCTZ, and 6.6/2.6 mmHg greater than with aliskiren/amlodipine.
In the severe hypertensive patients, Amturnide produced greater reductions in blood pressure than each of the 3 dual combination treatments (p<0.001 for both diastolic and systolic blood pressure reductions). The reductions in systolic/diastolic blood pressure with Amturnide were 16.3/8.2 mmHg greater than with aliskiren/HCTZ, 9.6/4.8 mmHg greater than with amlodipine/HCTZ, and 11.4/4.9 mmHg greater than with aliskiren/amlodipine.
The distribution of reductions in blood pressure on each treatment are shown in Figure 3 for diastolic blood pressure and in Figure 4 for systolic blood pressure. For example, Figure 3 shows that 50% of patients on Amturnide had more than 20.2 mmHg reduction in diastolic blood pressure compared to 18.7 mmHg on aliskiren/amlodipine combination, 12.7 mmHg on aliskiren/HCTZ combination, and 15.3 mmHg on amlodipine/HCTZ combination. Similarly, Figure 4 shows that 50% of patients on Amturnide had more than 36.3 mmHg reduction in systolic blood pressure compared to 30.8 mmHg on aliskiren/amlodipine combination, 28.3 mmHg on aliskiren/HCTZ combination, and 31.0 mmHg on amlodipine/HCTZ combination. The time course over which blood pressure effects developed is shown in Figures 5 and 6. As the trial had no placebo control, the treatment effects shown in Figures 3-6 include a placebo effect of unknown size.
The antihypertensive effect of Amturnide was similar in patients with and without diabetes, obese and non-obese patients, in patients ≥65 years of age and <65 years of age, and in women and men.
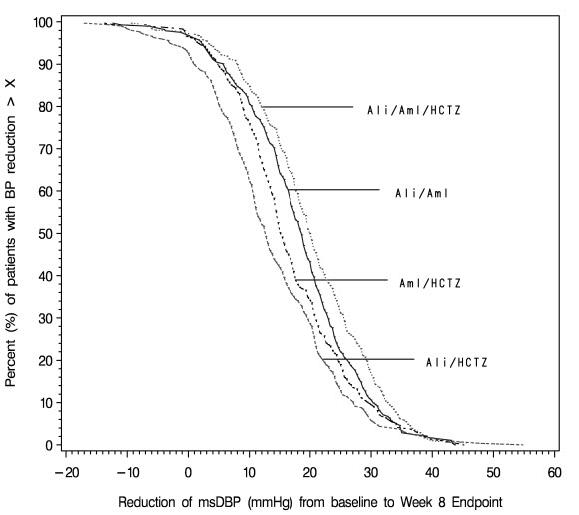
Figure 3. Distribution of diastolic blood pressure responses on Amturnide and combinations of two drugs.
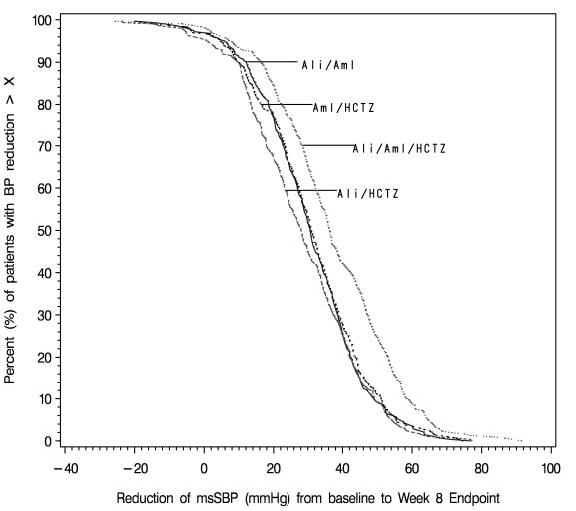
Figure 4. Distribution of systolic blood pressure responses on Amturnide and combinations of two drugs.
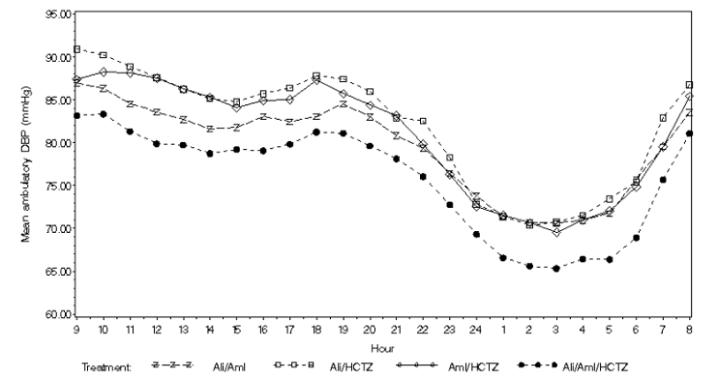
Figure 5. Mean Ambulatory Diastolic Blood Pressure at Endpoint by Treatment and Clock Hour
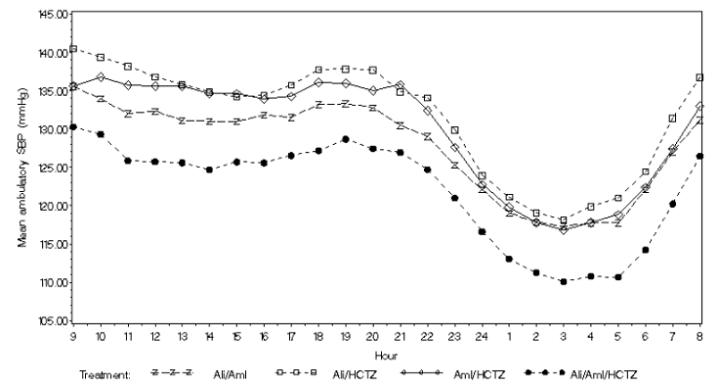
Figure 6. Mean Ambulatory Systolic Blood Pressure at Endpoint by Treatment and Clock Hour
There are no trials of the Amturnide triple combination tablet demonstrating reductions in cardiovascular risk in patients with hypertension, but two of the components, amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide, have demonstrated such benefits.
14.2 Aliskiren in Patients with Diabetes treated with ARB or ACEI (ALTITUDE study)
Patients with diabetes with renal disease (defined either by the presence of albuminuria or reduced GFR) were randomized to aliskiren 300 mg daily (n=4283) or placebo (n=4296). All patients were receiving background therapy with an ARB or ACEI. The primary efficacy outcome was the time to the first event of the primary composite endpoint consisting of cardiovascular death, resuscitated sudden death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke, unplanned hospitalization for heart failure, onset of end stage renal disease, renal death, and doubling of serum creatinine concentration from baseline sustained for at least one month. After a median follow up of about 27 months, the trial was terminated early for lack of efficacy. Higher risk of renal impairment, hypotension and hyperkalemia was observed in aliskiren compared to placebo treated patients, as shown in the table below.
| Aliskiren N=4283 | Placebo N=4296 |
|||
| Serious Adverse Events* (%) | Adverse Events (%) | Serious Adverse Events* (%) | Adverse Events (%) | |
| Renal impairment † | 4.7 | 12.4 | 3.3 | 10.4 |
| Hypotension †† | 2.0 | 18.6 | 1.7 | 14.8 |
| Hyperkalemia ††† | 1.1 | 36.9 | 0.3 | 27.1 |
†renal failure, renal failure acute, renal failure chronic, renal impairment
††dizziness, dizziness postural, hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, presyncope, syncope
††† Given the variable baseline potassium levels of patients with renal insufficiency on dual RAAS therapy, the reporting of adverse event of hyperkalemia was at the discretion of the investigator.
* A Serious Adverse Event (SAE) is defined as: an event which is fatal or life-threatening, results in persistent or significant disability/incapacity, constitutes a congenital anomaly/birth defect, requires inpatient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization, or is medically significant (i.e. defined as an event that jeopardizes the patient or may require medical or surgical intervention to prevent one of the outcomes previously listed).
The risk of stroke (2.7% aliskiren vs 2.0% placebo) and death (6.9% aliskiren vs. 6.4% placebo) were also numerically higher in aliskiren treated patients.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Tablets are convex ovaloid with a beveled edge, film-coated, and unscored, in the following strengths and packages:
| Aliskiren/Amlodipine/HCTZ
(mg) | Color | Embossing
Side 1/side 2 | NDC 0078-XXXX-XX | ||
| Bottle/30 | Bottle/90 | Blister/100 | |||
| 150/5/12.5 | Violet white | YIY/NVR | 0610-15 | 0610-34 | 0610-35 |
| 300/5/12.5 | Light pink | LIL/NVR | 0611-15 | 0611-34 | 0611-35 |
| 300/5/25 | Pale orange brown | OIO/NVR | 0612-15 | 0612-34 | 0612-35 |
| 300/10/12.5 | Light red | UIU/NVR | 0613-15 | 0613-34 | 0613-35 |
| 300/10/25 | Brown | VIV/NVR | 0614-15 | 0614-34 | 0614-35 |
Storage
Store at 25ºC (77ºF); excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF) in original container.
Protect from heat and moisture.
Dispense in original container.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information)
Instruct patients to read the Patient Package Insert before starting Amturnide and to reread each time the prescription is renewed. Instruct patients to inform their doctor or pharmacist if they develop any unusual symptom, or if any known symptom persists or worsens.
Pregnancy
Female patients of childbearing age should be told about the consequences of exposure to Amturnide during pregnancy. Discuss treatment options with women planning to become pregnant. Patients should be asked to report pregnancies to their physicians as soon as possible.
Symptomatic Hypotension
Caution patients receiving Amturnide that lightheadedness can occur, especially during the first days of therapy, and that it should be reported to the prescribing physician. Tell patients that if syncope occurs, discontinue Amturnide until the physician has been consulted.
Caution all patients that inadequate fluid intake, excessive perspiration, diarrhea, or vomiting can lead to an excessive fall in blood pressure, with the same consequences of lightheadedness and possible syncope.
Angioedema
Advise patients to report immediately any signs or symptoms suggesting angioedema (swelling of face, extremities, eyes, lips, tongue, difficulty in swallowing or breathing) and to take no more drug until they have consulted with the prescribing physician.
Potassium Supplements
Tell patients receiving Amturnide not to use potassium supplements or salt substitutes containing potassium without consulting the prescribing physician.
Relationship to Meals
Patient should establish a routine pattern for taking Amturnide either with or without a meal. High-fat meals decrease absorption substantially .
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
Patient Information
Amturnide™ (AM-turn-ide)
Amturnide
(aliskiren, amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide)
Tablets
Read the Patient Information leaflet that comes with Amturnide before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition and treatment. If you have any questions about Amturnide, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
What is the most important information I should know about Amturnide?
Amturnide can cause harm or death to an unborn baby. Talk to your doctor about other ways to lower your blood pressure if you plan to become pregnant. If you get pregnant while taking Amturnide, tell your doctor right away.
What is Amturnide?
Amturnide is a prescription medicine used to lower blood pressure (hypertension). Amturnide is not for use as the first medicine to treat your high blood pressure.
Amturnide contains 3 different prescription medicines:
- aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor (DRI)
- amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker (CCB) and
- hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), a diuretic (water pill)
It is not known if Amturnide is safe and works in children under 18 years of age.
Who should not take Amturnide?
Do not take Amturnide if you:
- If you get pregnant, stop taking Amturnide and call your doctor right away. If you plan to become pregnant, talk to your doctor about other treatment options for your high blood pressure.
- have diabetes and are taking a kind of medicine called an angiotensin-receptor-blocker or angiotensin-converting-enzyme-inhibitor.
- have low or no urine output
- are allergic to any ingredients in Amturnide or other medicines that contain sulfonamide. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Amturnide.
What should I tell my doctor before taking Amturnide?
Before taking Amturnide, tell your doctor if you:
- have kidney problems
- have liver problems
- have lupus
- have had an allergic reaction to another blood pressure medicine. Symptoms may include: swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat, arms and legs, and trouble breathing.
- have any other medical problems
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. See “What is the most important information I should know about Amturnide?”
- are breast-feeding. It is not known if Amturnide passes into your breast milk and if it can harm your baby. You and your doctor should decide if you will take Amturnide or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Amturnide and certain other medicines may affect each other and cause side effects.
Especially tell your doctor if you are taking:
- a kind of medicine called angiotensin receptor blocker or angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor
- water pills (also called “diuretics”)
- medicines for treating fungus or fungal infections
- cyclosporine (Gengraf®, Neoral, Sandimmune), a medicine used to suppress the immune system
- potassium-containing medicines, potassium supplements, or salt substitutes containing potassium
- cholesterol lowering medicines
- atorvastatin (Lipitor®)
- cholestyramine (Questran, Questran Light, Cholestyramine Light, Locholest Light, Locholest, Prevalite)
- colestipol (Colestipol hydrochloride, Colestid, Flavored Colestid)
- atorvastatin (Lipitor®)
- medicines used to treat diabetes, including insulin.
- lithium, a medicine used to treat some types of depression. You should not take Amturnide if you are taking lithium.
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAIDs) medicines. Ask your doctor if you are not sure if you are taking one of these medicines.
- sleeping pills and anti-seizure medicines called barbiturates
- narcotic pain medicines.
Ask your doctor if you are not sure whether you are taking one of the medicines listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor or pharmacist when you get a new medicine. Your doctor or pharmacist will know what medicines are safe to take together.
How should I take Amturnide?
- Take Amturnide exactly as prescribed by your doctor. It is important to take Amturnide every day to control your blood pressure.
- Take Amturnide one time a day, at about the same time each day.
- Take Amturnide the same way every day, either with or without a meal.
- Your doctor may change your dose of Amturnide if needed. Do not change the amount of Amturnide you take without talking to your doctor.
- If you miss a dose of Amturnide, take it as soon as you remember. If it is close to your next dose, do not take the missed dose. Just take the next dose at your regular time.
- If you take too much Amturnide, call your doctor or a Poison Control Center, or go to the nearest hospital emergency room.
What should I avoid while taking Amturnide?
Drinking alcohol. Drinking alcohol during treatment with Amturnide can cause you to have low blood pressure. See “What are the possible side effects of Amturnide?”
What are the possible side effects of Amturnide?
Amturnide may cause serious side effects, including:
-
Harm to an unborn baby causing injury or death. See “What is the most important information I should know about Amturnide?”
-
Angioedema. Aliskiren, one of the medicines in Amturnide, can cause swelling of your face, lips, tongue, throat, arms and legs, or the whole body. Get medical help right away and tell your doctor if you get any one or more of these symptoms. Serious allergic reactions can happen at any time while you are taking Amturnide.
-
Low blood pressure (hypotension). Your blood pressure may get too low if you also take water pills, are on a low-salt diet, get dialysis treatments, have heart problems, or get sick with vomiting or diarrhea. Drinking alcohol and taking certain medicines (barbiturates or narcotics) can cause low blood pressure to get worse. Lie down if you feel faint or dizzy, and call your doctor right away.
-
Worsening chest pain or heart attack. When you first start taking Amturnide or increase your dose, you may have a heart attack or your angina may get worse. If that happens, call your doctor right away or go directly to the nearest hospital emergency room.
-
Allergic reactions. Hydrochlorothiazide, one of the medicines in Amturnide, can cause allergic reactions.
-
Worsening of lupus. One of the medicines in Amturnide may cause your lupus to become active or get worse. Tell your doctor if your lupus gets worse or becomes active while taking Amturnide.
-
Low potassium level (hypokalemia). Your doctor will do blood tests to check your potassium levels.
-
Eye problems. One of the medicines in Amturnide can cause eye problems that may lead to vision loss. Symptoms of eye problems can happen within hours to weeks of starting Amturnide. Tell your doctor right away if you have:
- decrease in vision
- eye pain
- decrease in vision
The most common side effects of Amturnide include:
- swelling of your ankles, feet, and hands
- dizziness
- headache
- stuffy or runny nose and sore throat
Common side effects of Amturnide include:
- diarrhea
- cough
- tiredness
- high levels of potassium in the blood (hyperkalemia)
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of Amturnide. For more information ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Amturnide?
- Store Amturnide tablets at room temperature between 59oF to 86oF (15oC to 30oC).
- Keep Amturnide in the original container.
- Protect Amturnide from heat and moisture.
Keep Amturnide and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about Amturnide
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions not listed in the patient information leaflet. Do not take Amturnide for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Amturnide to other people, even if they have the same condition or symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Amturnide. If you have questions about Amturnide, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information about Amturnide, visit www.Amturnide.com, or call 1-888-NOW-NOVA (1-888-669-6682).
What are the ingredients in Amturnide?
Active ingredients: Aliskiren hemifumarate, amlodipine besylate, and HCTZ.
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, hypromellose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, iron oxide black, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, talc, and titanium dioxide.
What is high blood pressure (hypertension)?
Blood pressure is the force of blood in your blood vessels when your heart beats and when your heart rests. You have high blood pressure when the force is too much.
High blood pressure makes the heart work harder to pump blood through the body and causes damage to blood vessels. Amturnide can help your blood vessels relax so your blood pressure is lower. Medicines that lower your blood pressure may lower your chance of having a stroke or heart attack.
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
© Novartis
T2012-78/T2012-79
March 2012/March 2012
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 150 mg* / 5 mg* / 12.5 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0610-15
Amturnide™
(aliskiren, amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide) Tablets
150 mg* / 5 mg* / 12.5 mg
*each tablet contains 165.8 mg of aliskiren hemifumarate and 6.9 mg of amlodipine besylate
30 Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 300 mg* / 5 mg* / 12.5 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0611-15
Amturnide™
(aliskiren, amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide) Tablets
300 mg* / 5 mg* / 12.5 mg
*each tablet contains 331.5 mg of aliskiren hemifumarate and 6.9 mg of amlodipine besylate
30 Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 300 mg* / 5 mg* / 25 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0612-15
Amturnide™
(aliskiren, amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide) Tablets
300 mg* / 5 mg* / 25 mg
*each tablet contains 331.5 mg of aliskiren hemifumarate and 6.9 mg of amlodipine besylate
30 Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 300 mg* / 10 mg* / 12.5 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0613-15
Amturnide™
(aliskiren, amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide) Tablets
300 mg* / 10 mg* / 12.5 mg
*each tablet contains 331.5 mg of aliskiren hemifumarate and 13.9 mg of amlodipine besylate
30 Tablets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 300 mg* / 10 mg* / 25 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0614-15
Amturnide™
(aliskiren, amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide) Tablets
300 mg* / 10 mg* / 25 mg
*each tablet contains 331.5 mg of aliskiren hemifumarate and 13.9 mg of amlodipine besylate
30 Tablets

| AMTURNIDE
aliskiren hemifumarate and amlodipine besylate and hydrochlorothiazide tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA200045 | 12/21/2010 | |
| AMTURNIDE
aliskiren hemifumarate and amlodipine besylate and hydrochlorothiazide tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA200045 | 12/21/2010 | |
| AMTURNIDE
aliskiren hemifumarate and amlodipine besylate and hydrochlorothiazide tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA200045 | 12/21/2010 | |
| AMTURNIDE
aliskiren hemifumarate and amlodipine besylate and hydrochlorothiazide tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA200045 | 12/21/2010 | |
| AMTURNIDE
aliskiren hemifumarate and amlodipine besylate and hydrochlorothiazide tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA200045 | 12/21/2010 | |
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |
Revised: 03/2012 Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation