CEFAZOLIN SODIUM
-
cefazolin sodium solution
B. Braun Medical Inc.
----------
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP and other antibacterial drugs, Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is indicated for the treatment of the following infections when caused by susceptible bacteria.
1.1 Respiratory Tract Infections
Respiratory tract infections due to Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
Injectable benzathine penicillin is considered the drug of choice in treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections, including the prophylaxis of rheumatic fever.
Cefazolin is effective in the eradication of streptococci from the nasopharynx; however, data establishing the efficacy of cefazolin in the subsequent prevention of rheumatic fever are not available.
1.2 Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections due to Escherichia coli, and Proteus mirabilis.
1.3 Skin And Skin Structure Infections
Skin and skin structure infections due to S. aureus, S. pyogenes, and Streptococcus agalactiae.
1.4 Biliary Tract Infections
Biliary infections due to E. coli, various isolates of streptococci, P. mirabilis, and S. aureus.
1.9 Perioperative Prophylaxis
The prophylactic administration of cefazolin preoperatively, intraoperatively, and postoperatively may reduce the incidence of certain postoperative infections in patients undergoing surgical procedures which are classified as contaminated or potentially contaminated (e.g., vaginal hysterectomy, and cholecystectomy in high-risk patients such as those older than 70 years, with acute cholecystitis, obstructive jaundice, or common duct bile stones).
The perioperative use of cefazolin may also be effective in surgical patients in whom infection at the operative site would present a serious risk (e.g., during open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty).
If there are signs of infection, specimens for cultures should be obtained for the identification of the causative organism so that appropriate therapy may be instituted.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adult Population
Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in the DUPLEX® Container should be used only in patients who require the entire 1 or 2 gram dose and not any fraction thereof. The recommended adult dosages are outlined in Table 1. Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP should be administered intravenously (IV) over approximately 30 minutes.
|
||
| Table 1: Recommended Dosing Schedule in Adult Patients with CrCl Greater Than or Equal To 55 mL/min. | ||
| Site and Type of Infection | Dose | Frequency |
| Moderate to severe infections | 500 mg to 1 gram | every 6 to 8 hours |
| Mild infections caused by susceptible gram-positive cocci | 250 mg to 500 mg | every 8 hours |
| Acute, uncomplicated urinary tract infections | 1 gram | every 12 hours |
| Pneumococcal pneumonia | 500 mg | every 12 hours |
| Severe, life-threatening infections (e.g., endocarditis, septicemia)* | 1 gram to 1.5 grams | every 6 hours |
2.2 Perioperative Prophylactic Use
To prevent postoperative infection in contaminated or potentially contaminated surgery, recommended doses are:
- 1 to 2 gram IV administered 1/2 hour to 1 hour prior to the start of surgery.
- For lengthy operative procedures (e.g., 2 hours or more), 500 mg to 1 gram IV during surgery (administration modified depending on the duration of the operative procedure).
- 500 mg to 1 gram IV every 6 to 8 hours for 24 hours postoperatively.
It is important that (i) the preoperative dose be given just prior (1/2 hour to 1 hour) to the start of surgery so that adequate antibacterial concentrations are present in the serum and tissues at the time of initial surgical incision; and (ii) cefazolin be administered, if necessary, at appropriate intervals during surgery to provide sufficient concentrations of the antibacterial drug at the anticipated moments of greatest exposure to infective organisms.
The prophylactic administration of cefazolin should usually be discontinued within a 24-hour period after the surgical procedure. In surgery where the occurrence of infection may be particularly devastating (e.g., open-heart surgery and prosthetic arthroplasty), the prophylactic administration of cefazolin may be continued for 3 to 5 days following the completion of surgery.
2.3 Patients with Renal Impairment
Cefazolin may be used in patients with renal impairment with the dosage adjustments outlined in Table 2. All reduced dosage recommendations apply after an initial loading dose appropriate to the severity of the infection.
| Table 2: Dosage Adjustment for Patients with Renal Impairment | ||
| Creatinine Clearance | Dose | Frequency |
| 55 mL/min. or greater | full dose | normal frequency |
| 35 to 54 mL/min. | full dose | every 8 hours or longer |
| 11 to 34 mL/min. | 1/2 usual dose | every 12 hours |
| 10 mL/min. or less | 1/2 usual dose | every 18 to 24 hours |
2.4 Preparation for Use of Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in DUPLEX® Container
This reconstituted solution is for intravenous use only.
Do not use plastic containers in series connections. Such use would result in air embolism due to residual air being drawn from the primary container before administration of the fluid from the secondary container is complete. If administration is controlled by a pumping device, care must be taken to discontinue pumping action before the container runs dry or air embolism may result.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Use only if solution is clear and container and seals are intact.
DUPLEX® Drug Delivery System Storage
- To avoid inadvertent activation, the DUPLEX® Container should remain in the folded position until activation is intended.
Patient Labeling and Drug Powder/Diluent Inspection
- Apply patient-specific label on foil side of container. Use care to avoid activation. Do not cover any portion of foil strip with patient label.
- Unlatch side tab and unfold DUPLEX® Container (see Diagram 1).
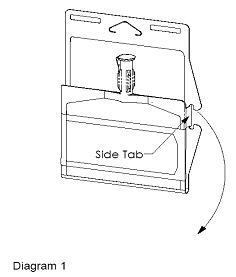
- Visually inspect diluent chamber for particulate matter.
- Use only if container and seals are intact.
- To inspect the drug powder for foreign matter or discoloration, peel foil strip from drug chamber (see Diagram 2).
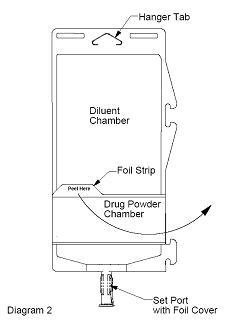
- Protect from light after removal of foil strip.
Note: If foil strip is removed, the container should be re-folded and the side tab latched until ready to activate. The product must then be used within 7 days, but not beyond the labeled expiration date.
Reconstitution (Activation)
- Do not use directly after storage by refrigeration, allow the product to equilibrate to room temperature before patient use.
- Unfold the DUPLEX® container and point the set port in a downward direction. Starting at the hanger tab end, fold the DUPLEX® Container just below the diluent meniscus trapping all air above the fold. To activate, squeeze the folded diluent chamber until the seal between the diluent and powder opens, releasing diluent into the drug powder chamber (see Diagram 3).
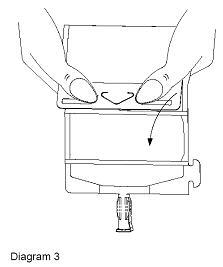
- Agitate the liquid-powder mixture until the drug powder is completely dissolved.
Note: Following reconstitution (activation), product must be used within 24 hours if stored at room temperature or within 7 days if stored under refrigeration.
Administration
- Visually inspect the reconstituted solution for particulate matter.
- Point the set port in a downwards direction. Starting at the hanger tab end, fold the DUPLEX® Container just below the solution meniscus trapping all air above the fold. Squeeze the folded DUPLEX® Container until the seal between reconstituted drug solution and set port opens, releasing liquid to set port (see Diagram 4).
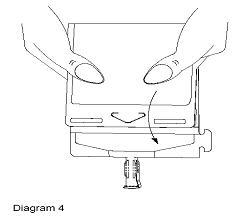
- Prior to attaching the IV set, check for minute leaks by squeezing container firmly. If leaks are found, discard container and solution as sterility may be compromised.
- Using aseptic technique, peel foil cover from the set port and attach sterile administration set (see Diagram 5).
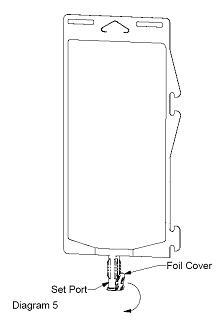
- Refer to directions for use accompanying the administration set.
Important Administration Instructions
- Do not use in series connections.
- Do not introduce additives into the DUPLEX® Container.
- Administer Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP intravenously over approximately 30 minutes.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Dual-chamber, single-use container:
- 1 g Cefazolin for Injection USP and 50 mL 4% Dextrose Injection USP
- 2 g Cefazolin for Injection USP and 50 mL 3% Dextrose Injection USP
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity to Cefazolin or the Cephalosporin Class of Antibacterial Drugs, Penicillins, or Other Beta-lactams
Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is contraindicated in patients who have a history of immediate hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, serious skin reactions) to cefazolin or the cephalosporin class of antibacterial drugs, penicillins, or other beta-lactams [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions to Cefazolin, Cephalosporins, Penicillins, or Other Beta-lactams
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported in patients receiving beta-lactam antibacterial drugs. Before therapy with Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine whether the patient has had previous immediate hypersensitivity reactions to cefazolin, cephalosporins, penicillins, or carbapenems. Exercise caution if this product is to be given to penicillin-sensitive patients because cross-hypersensitivity among beta-lactam antibacterial drugs has been clearly documented and may occur in up to 10% of patients with a history of penicillin allergy. If an allergic reaction to Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP occurs, discontinue the drug.
5.2 Use In Patients with Renal Impairment
As with other beta-lactam antibacterial drugs, seizures may occur if inappropriately high doses are administered to patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance less than 55 mL/min.) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea
Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefazolin, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B, which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin-producing isolates of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial drug use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial drug use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial drug treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
5.4 Hypersensitivity to Dextrose-containing Products
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with administration of dextrose-containing products. These reactions have been reported in patients receiving high concentrations of dextrose (i.e. 50% dextrose)1. The reactions have also been reported when corn-derived dextrose solutions were administered to patients with or without a history of hypersensitivity to corn products.2
5.5 Risk of Development of Drug-resistant Bacteria
Prescribing Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in the absence of proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
As with other antimicrobials, prolonged use of Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible microorganisms. Repeated evaluation of the patient's condition is essential. Should superinfection occur during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
5.6 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Urinary Glucose
The administration of cefazolin may result in a false-positive reaction with glucose in the urine when using CLINITEST® tablets. It is recommended that glucose tests based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions (e.g., CLINISTIX®) be used.
Coombs’ Test
Positive direct Coombs' tests have been reported during treatment with cefazolin. In hematologic studies or in transfusion cross-matching procedures when antiglobulin tests are performed on the minor side or in Coombs' testing of newborns whose mothers have received cephalosporin antibacterial drugs before parturition, it should be recognized that a positive Coombs' test may be due to the drug.
5.7 Patients with Overt or Known Subclinical Diabetes Mellitus or Carbohydrate Intolerance
As with other dextrose-containing solutions, Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP should be prescribed with caution in patients with overt or known subclinical diabetes mellitus or carbohydrate intolerance for any reason.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions to cefazolin are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
The following adverse reactions were reported from clinical trials:
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, oral candidiasis (oral thrush), mouth ulcers, vomiting, nausea, stomach cramps, epigastric pain, heartburn, flatus, anorexia and pseudomembranous colitis. Onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibacterial treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Allergic: Anaphylaxis, eosinophilia, urticaria, itching, drug fever, skin rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Hematologic: Neutropenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocythemia.
Hepatic: Transient rise in SGOT, SGPT, and alkaline phosphatase levels has been observed. As with other cephalosporins, reports of hepatitis have been received.
Renal: As with other cephalosporins, reports of increased BUN and creatinine levels, as well as renal failure, have been received.
Local Reactions: Instances of phlebitis have been reported at site of injection. Some induration has occurred.
Other Reactions: Pruritus (including genital, vulvar and anal pruritus, genital moniliasis, and vaginitis). Dizziness, fainting, lightheadedness, confusion, weakness, tiredness, hypotension, somnolence and headache.
6.2 Cephalosporin-class Adverse Reactions
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above that have been observed in patients treated with cefazolin, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory tests have been reported for cephalosporin-class antibacterials: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, renal impairment, toxic nephropathy, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhage, hepatic impairment including cholestasis, and pancytopenia.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Probenecid may decrease renal tubular secretion of cephalosporins when used concurrently, resulting in increased and more prolonged cephalosporin blood levels.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.2 Labor and Delivery
When cefazolin has been administered prior to caesarean section, drug concentrations in cord blood have been approximately one quarter to one third of maternal drug levels. The drug appears to have no adverse effect on the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Cefazolin is present in very low concentrations in the milk of nursing mothers. Caution should be exercised when Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is designed to deliver a 1 g or 2 g dose of cefazolin. To prevent unintentional overdose, Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP should not be used in pediatric patients who require less than the full adult dose of cefazolin.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 920 subjects who received cefazolin in clinical studies, 313 (34%) were 65 years and over, while 138 (15%) were 75 years and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8.6 Patients with Renal Impairment
When Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is administered to patients with low urinary output because of impaired renal function (creatinine clearance less than 55 mL/min.), lower daily dosage is required [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) andWarnings and Precautions (5.2)].
11 DESCRIPTION
Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, single use, packaged combination of Cefazolin Sodium USP (lyophilized) and sterile iso-osmotic diluent in the DUPLEX® sterile container. The DUPLEX® Container is a flexible dual chamber container.
After reconstitution the approximate osmolality for Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is 290 mOsmol/kg.
The drug chamber is filled with sterile lyophilized Cefazolin Sodium USP, a semi-synthetic cephalosporin and has the following IUPAC nomenclature: Sodium (6R,7R)-3-[[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo-7-[2-(1H-tetrazol-1-yl)acetamido]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate.
Cefazolin Sodium USP has the following structural formula:
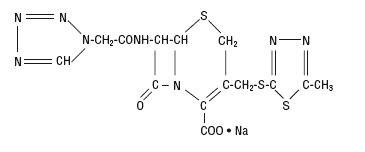
The sodium content is 48 mg/g of cefazolin sodium.
The diluent chamber contains Dextrose Injection USP, an iso-osmotic diluent using Hydrous Dextrose USP in Water for Injection USP. Dextrose Injection USP is sterile, nonpyrogenic, and contains no bacteriostatic or antimicrobial agents.
Hydrous Dextrose USP has the following structural (molecular) formula:
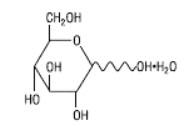
The molecular weight of Hydrous Dextrose USP is 198.17
Cefazolin Sodium USP is supplied as a lyophilized form equivalent to either 1 g or 2 g of cefazolin. Dextrose hydrous USP has been added to the diluent to adjust osmolality (approximately 2 g [4.0% w/v] and 1.5 g [3.0% w/v] for the 1 g and 2 g dosages, respectively).
After removing the peelable foil strip, activating the seals, and thoroughly mixing, the reconstituted drug product is intended for single intravenous use.
The DUPLEX® Container is not manufactured with Latex, PVC or DEHP.
The DUPLEX® dual chamber container is made from a specially formulated material. The product (diluent and drug) contact layer is a mixture of thermoplastic rubber and a polypropylene ethylene copolymer that contains no plasticizers. The safety of the container system is supported by USP biological evaluation procedures.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship for cefazolin has not been evaluated in patients.12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Studies have shown that following intravenous administration of cefazolin to normal volunteers, mean serum concentrations peaked at approximately 185 mcg/mL and were approximately 4 mcg/mL at 8 hours for a 1 g dose.
The serum half-life for cefazolin is approximately 1.8 hours following IV administration.
In a study, using normal volunteers, of constant intravenous infusion with dosages of 3.5 mg/kg for 1 hour (approximately 250 mg) and 1.5 mg/kg the next 2 hours (approximately 100 mg), cefazolin produced a steady serum concentration at the third hour of approximately 28 mcg/mL.
Plasma pharmacokinetic parameters of cefazolin in normal volunteers (N=12) following a single 15-minute IV infusion of 2 g of Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP are summarized in Table 3.
|
|||||||
| Table 3: Mean (Standard Deviation) Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Cefazolin in Normal Volunteers | |||||||
| N |
Cmax (mcg/mL) |
Tmax* | AUC0-inf(mcg*h/mL) |
t1/2
|
CL |
Vz
|
|
| Single 2 g Dose as a 15-Minute IV Infusion | 12 | 280.9 (45.9) | 0.25 (0.25-0.33) | 509.9 (89.3) | 2.01 (0.28) | 4.03 (0.68) | 11.50 (1.53) |
N= number of subjects observed; Cmax = maximum plasma concentration; Tmax = time to maximum plasma concentration; AUC0-inf = area under the plasma concentration-time curve extrapolated to infinity; t1/2 = apparent plasma terminal elimination half-life; CL = total clearance; Vz = volume of distribution
Studies in patients hospitalized with infections indicate that cefazolin produces mean peak serum concentrations approximately equivalent to those seen in normal volunteers.
Bile concentrations in patients without obstructive biliary disease can reach or exceed serum concentrations by up to five times; however, in patients with obstructive biliary disease, bile concentrations of cefazolin are considerably lower than serum concentrations (less than 1.0 mcg/mL).
In synovial fluid, the cefazolin concentration becomes comparable to that reached in serum at about 4 hours after drug administration.
Studies of cord blood show prompt transfer of cefazolin across the placenta. Cefazolin is present in very low concentrations in the milk of nursing mothers.
Cefazolin is excreted unchanged in the urine. In the first 6 hours approximately 60% of the drug is excreted in the urine and this increases to 70% to 80% within 24 hours.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Cefazolin is a bactericidal agent that acts by inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Mechanism of Resistance
Predominant mechanisms of bacterial resistance to cephalosporins include the presence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and enzymatic hydrolysis.
Lists of Microorganisms
Cefazolin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE (1) section.
-
Gram-Positive Bacteria
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus agalactiae
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
Methicillin-resistant staphylococci are uniformly resistant to cefazolin.
-
Gram-Negative Bacteria
- Escherichia coli
- Proteus mirabilis
Most isolates of indole positive Proteus (Proteus vulgaris), Enterobacter spp., Morganella morganii, Providencia rettgeri, Serratia spp., and Pseudomonas spp. are resistant to cefazolin.
Susceptibility Test Methods
When available, the clinical microbiology laboratory should provide the results of in vitro susceptibility test results for antimicrobial drug products used in resident hospitals to the physician as periodic reports that describe the susceptibility profile of nosocomial and community-acquired pathogens. These reports should aid the physician in selecting an antibacterial drug product for treatment.
Dilution Technique
Quantitative methods are used to determine minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standard test 3, 4(broth and/or agar). The MIC values obtained should be interpreted according to criteria as provided in Table 4.Diffusion Techniques
Quantitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The zone size provides an estimate of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The zone size should be interpreted using a standard test method 4, 5. This procedure uses paper disks impregnated with 30 mcg cefazolin to test the susceptibility of microorganisms to cefazolin. The disk diffusion interpretive criteria are provided in Table 4.
| Table 4: Susceptibility Test Interpretive Criteria for Cefazolin* | ||||||
|
Pathogen | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (mcg/ml) | Disk Diffusion Zone Diameter (mm)† | ||||
| S | I | R | S | I | R | |
|
Escherichia coli Proteus mirabilis | ≤1 | 2 | ≥4 | - | - | - |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ≤8 | 16 | ≥32 | ≥18 | 15-17 | ≤14 |
Abbreviations: S= susceptible, I= intermediate, R= resistant
NOTE: S. pyogenes and S. agalactiae that have a penicillin MIC of ≤ 0.12 mcg/ml, or disk diffusion zone diameters of ≥ 24 mm with a 10 mcg penicillin disk, may be interpreted as susceptible to cefazolin. Non-meningitis isolates of S. pneumoniae that have a penicillin MIC of ≤ 0.06 mcg/mL, may be interpreted as susceptible to cefazolin.
A report of Susceptible indicates that the antimicrobial is likely to inhibit growth of the pathogen if the antimicrobial compound reaches the concentrations at the infection site necessary to inhibit growth of the pathogen. A report of Intermediate indicates that the result should be considered equivocal, and, if the microorganism is not fully susceptible to alternative, clinically feasible drugs, the test should be repeated. This category implies possible clinical applicability in body sites where the drug product is physiologically concentrated or in situations where a high dosage of the drug product can be used. This category also provides a buffer zone that prevents small uncontrolled technical factors from causing major discrepancies in interpretation. A report of Resistant indicates that the antimicrobial is not likely to inhibit growth of the pathogen if the antimicrobial compound reaches the concentrations usually achievable at the infection site; other therapy should be selected.
Quality Control
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory controls to monitor and ensure the accuracy and precision of supplies and reagents used in the assay, and the techniques of the individual performing the test 3, 4, 5 .Standard cefazolin powder should provide the following MIC values noted in Table 5. For the diffusion technique using the 30 mcg disk, the criteria in Table 5 should be achieved.
|
||
| Table 5: Acceptable Quality Control Ranges for Cefazolin | ||
| QC Isolate | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration mcg/mL | Disk Diffusion Zone Diameters* (mm) |
| E. coli ATCC® 25922 | 1.0-4.0 | 21-27 |
| S. aureus ATCC® 29213 | 0.25−1.0 | - |
| S. aureus ATCC® 25923 | - | 29-35 |
15 REFERENCES
- Czarny D, Prichard PJ, Fennessy M, Lewis S. Anaphylactoid reaction to 50% solution of dextrose. Med J Aust 1980;2:255-258.
- Guharoy, SR, Barajas M. Probably Anaphylactic Reaction to Corn-Derived Dextrose Solution. Vet Hum Toxicol 1991;33:609-610.
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard-Eighth Edition. CLSI Document M07-A8. CLSI, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, PA 19087-1898 USA, 2009.
- CLSI. Perfomance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-first informational supplement. CLSI document M100-S21. CLSI, 2011.
- CLSI. January 2009. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests; Approved Standard-Tenth Edition. CLSI Document M02-A10. CLSI, 2009.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP in the DUPLEX® Drug Delivery System is a flexible dual chamber container supplied in two concentrations. After reconstitution, the concentrations are equivalent to 1 g and 2 g cefazolin. The diluent chamber contains approximately 50 mL of Dextrose Injection USP. Dextrose Injection USP has been adjusted to 4.0% and 3.0% for the 1 g and 2 g doses, respectively, such that the reconstituted solution is iso-osmotic.
Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is supplied sterile and nonpyrogenic in the DUPLEX® Drug Delivery System containers packaged 24 units per case.
| NDC | REF | Dose | Volume |
| 0264-3103-11 | 3103-11 | 1 g | 50 mL |
| 0264-3105-11 | 3105-11 | 2 g | 50 mL |
Store the unactivated unit at 20-25°C (68-77°F). Excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F).
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Patients should be advised that allergic reactions, including serious allergic reactions could occur and that serious reactions require immediate treatment and discontinuation of cefazolin. Patients should report to their health care provider any previous allergic reactions to cefazolin, cephalosporins, penicillins, or other similar antibacterials.
Patients should be advised that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics, which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterials, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibacterials. If this occurs, patients should contact a physician as soon as possible.
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs, including Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Rx only
DUPLEX is a registered trademark of B. Braun Medical Inc.
ATCC is a registered trademark of American Type Culture Collection.
Clinitest is a registered trademark of Siemens Medical Solutions Diagnostics.
Clinistix is a registered trademark of Bayer Healthcare LLC.
U.S. Patent Nos. 5,944,709, 6,165,161, 6,203,535, 6,846,305, and 6,996,951.
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Irvine, CA 92614-5895 USA
1-800-227-2862
www.bbraun.com
Made in USA.
Y36-002-801 LD-105-5
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1g Cefazolin
Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP
1g*
REF 3103-11
NDC 0264-3103-11
DUPLEX®
DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
50 mL
Use only after mixing contents of both chambers.
For IV Use Only Iso-osmotic Single Dose Sterile/Nonpyrogenic
* Contains Cefazolin Sodium USP equivalent to 1 g cefazolin.
Reconstitution: Hold container with set port in a downward direction and fold the diluent chamber just below the solution meniscus. To activate seal, squeeze folded diluent chamber until seal between diluent and drug chamber opens, releasing diluent into drug chamber. Agitate the reconstituted solution until the drug powder is completely dissolved. Fold the container a second time and squeeze until seal between drug chamber and set port opens.
After reconstitution each 50 mL single dose unit contains: Cefazolin for Injection USP (equivalent to 1 g cefazolin) with approx. 2.0 g (4.0% w/v) Hydrous Dextrose USP in Water for Injection USP. Sodium content is 48 mg/g of cefazolin sodium.
Approximate osmolality: 290 mOsmol/kg
Prior to Reconstitution: Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F). Excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Use only if container and seals are intact. Do not peel foil strip until ready for use. After foil strip removal, product must be used within 7 days, but not beyond the labeled expiration date. Protect from light after removal of foil strip.
After Reconstitution: Use only if prepared solution is clear and free from particulate matter. Use within 24 hours if stored at room temperature or within 7 days if stored under refrigeration. Do not use in a series connection. Do not introduce additives into this container. Prior to administration check for minute leaks by squeezing container firmly. If leaks are found, discard container and solution as sterility may be impaired. Do not freeze.
The DUPLEX Container is not manufactured with Latex, PVC or DEHP.
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Rx only
Made in USA
LD-201-3
Y37-002-416
PEEL HERE
Drug Chamber
Discard unit if foil strip is damaged. Peel foil strip only when ready for use. Visually inspect drug prior to reconstitution.
See package insert for complete directions for reconstitution and administration.
LD-336-1 X27-001-485


PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2g Cefazolin
Cefazolin for Injection USP and Dextrose Injection USP
2g*
REF 3105-11
NDC 0264-3105-11
DUPLEX®
DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
50 mL
Use only after mixing contents of both chambers.
For IV Use Only Iso-osmotic Single Dose Sterile/Nonpyrogenic
* Contains Cefazolin Sodium USP equivalent to 2 g cefazolin.
Reconstitution: Hold container with set port in a downward direction and fold the diluent chamber just below the solution meniscus. To activate seal, squeeze folded diluent chamber until seal between diluent and drug chamber opens, releasing diluent into drug chamber. Agitate the reconstituted solution until the drug powder is completely dissolved. Fold the container a second time and squeeze until seal between drug chamber and set port opens.
After reconstitution each 50 mL single dose unit contains: Cefazolin for Injection USP (equivalent to 2 g cefazolin) with approx. 1.5 g (3.0% w/v) Hydrous Dextrose USP in Water for Injection USP. Sodium content is 48 mg/g of cefazolin sodium.
Approximate osmolality: 290 mOsmol/kg
Prior to Reconstitution: Store at 20-25°C (68-77°F). Excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Use only if container and seals are intact. Do not peel foil strip until ready for use. After foil strip removal, product must be used within 7 days, but not beyond the labeled expiration date. Protect from light after removal of foil strip.
After Reconstitution: Use only if prepared solution is clear and free from particulate matter. Use within 24 hours if stored at room temperature or within 7 days if stored under refrigeration. Do not use in a series connection. Do not introduce additives into this container. Prior to administration check for minute leaks by squeezing container firmly. If leaks are found, discard container and solution as sterility may be impaired. Do not freeze.
The DUPLEX Container is not manufactured with Latex, PVC or DEHP.
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Rx only
Made in USA
LD-200-2
Y37-002-406
PEEL HERE
Drug Chamber
Discard unit if foil strip is damaged. Peel foil strip only when ready for use. Visually inspect drug prior to reconstitution.
See package insert for complete directions for reconstitution and administration.
LD-336-1 X27-001-485


| CEFAZOLIN SODIUM
cefazolin sodium solution |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA050779 | 07/27/2000 | |
| CEFAZOLIN SODIUM
cefazolin sodium solution |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA050779 | 01/13/2012 | |
| Labeler - B. Braun Medical Inc. (002397347) |
Revised: 01/2012 B. Braun Medical Inc.