FERRIPROX
-
deferiprone tablet, film coated
ApoPharma USA, Inc.
----------
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: AGRANULOCYTOSIS/NEUTROPENIA
-
Ferriprox can cause agranulocytosis that can lead to serious infections and death. Neutropenia may precede the development of agranulocytosis. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
Measure the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) before starting Ferriprox therapy and monitor the ANC weekly on therapy. Interrupt Ferriprox therapy if neutropenia develops. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
Interrupt Ferriprox if infection develops, and monitor the ANC more frequently. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
Advise patients taking Ferriprox to report immediately any symptoms indicative of infection. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FERRIPROX® (deferiprone) is indicated for the treatment of patients with transfusional iron overload due to thalassemia syndromes when current chelation therapy is inadequate.
Approval is based on a reduction in serum ferritin levels. There are no controlled trials demonstrating a direct treatment benefit, such as improvement in disease-related symptoms, functioning, or increased survival [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Limitation of Use:
- Safety and effectiveness have not been established for the treatment of transfusional iron overload in patients with other chronic anemias.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended initial dose of Ferriprox is 25 mg/kg, orally, three times per day for a total of 75 mg/kg/day. The maximum dose is 33 mg/kg, three times per day for a total of 99 mg/kg/day.
Dose adjustments up to 33 mg/kg, orally, three times per day should be tailored to the individual patient’s response and therapeutic goals (maintenance or reduction of body iron burden). The maximum recommended total daily dose is 99 mg/kg per day. The dose should be rounded by the prescriber to the nearest 250 mg (half-tablet).
| Body Weight (kg) | Dose (mg) | Number of tablets |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 500 | 1 |
| 30 | 750 | 1.5 |
| 40 | 1000 | 2 |
| 50 | 1250 | 2.5 |
| 60 | 1500 | 3 |
| 70 | 1750 | 3.5 |
| 80 | 2000 | 4 |
| 90 | 2250 | 4.5 |
| Body Weight (kg) | Dose (mg) | Number of tablets |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 660 | 1.5 |
| 30 | 990 | 2 |
| 40 | 1320 | 2.5 |
| 50 | 1650 | 3.5 |
| 60 | 1980 | 4 |
| 70 | 2310 | 4.5 |
| 80 | 2640 | 5.5 |
| 90 | 2970 | 6 |
Monitor serum ferritin concentration every two to three months to assess the effects of Ferriprox on body iron stores. Dose adjustments should be tailored to the individual patient’s response and therapeutic goals (maintenance or reduction of body iron burden). If the serum ferritin falls consistently below 500 mcg/L, consider temporarily interrupting Ferriprox therapy.
2.1 Interactions with Foods, Vitamins and Antacids
Allow at least a 4-hour interval between Ferriprox and other medications or supplements containing polyvalent cations such as iron, aluminum, and zinc [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Ferriprox is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to deferiprone or to any of the excipients in the formulation. The following reactions have been reported in association with the administration of deferiprone: Henoch-Schönlein purpura; urticaria; and periorbital edema with skin rash [see Post Marketing Experience (6.2)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Agranulocytosis/Neutropenia
Fatal agranulocytosis can occur with Ferriprox use. (Ferriprox can also cause neutropenia, which may foreshadow agranulocytosis. Measure the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) before starting Ferriprox therapy and monitor the ANC weekly on therapy [see Boxed Warning].
Interrupt Ferriprox therapy if neutropenia develops (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L).
Interrupt Ferriprox if infection develops, and monitor the ANC more frequently.
Advise patients taking Ferriprox to immediately interrupt therapy and report to their physician if they experience any symptoms indicative of infection.
In pooled clinical trials, the incidence of agranulocytosis was 1.7% of patients. The mechanism of Ferriprox-associated agranulocytosis is unknown. Agranulocytosis and neutropenia usually resolve upon discontinuation of Ferriprox, but there have been reports of agranulocytosis leading to death.
Implement a plan to monitor for and to manage agranulocytosis/neutropenia prior to initiating Ferriprox treatment.
For neutropenia (ANC < 1.5 x 109/L and > 0.5 x 109/L):
Instruct the patient to immediately discontinue Ferriprox and all other medications with a potential to cause neutropenia.
Obtain a complete blood cell (CBC) count, including a white blood cell (WBC) count corrected for the presence of nucleated red blood cells, an absolute neutrophil count (ANC), and a platelet count daily until recovery (ANC ≥ 1.5 x 109/L).
For agranulocytosis (ANC < 0.5 x 109/L):
Consider hospitalization and other management as clinically appropriate.
Do not resume Ferriprox in patients who have developed agranulocytosis unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks. Do not rechallenge patients who develop neutropenia with Ferriprox unless potential benefits outweigh potential risks.
5.2 Cardiac QT Syndrome
A thorough QT study has not been conducted with Ferriprox. One patient with a history of QT prolongation experienced Torsades de Pointes during therapy with Ferriprox. Administer Ferriprox with caution to patients who may be at increased risk of prolongation of the cardiac QT interval (e.g., those with congestive heart failure, bradycardia, use of a diuretic, cardiac hypertrophy, hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia). Instruct any patient taking Ferriprox who experiences symptoms suggestive of an arrhythmia (such as palpitations, dizziness, lightheadedness, syncope, or seizures) to seek medical attention immediately.
5.3 Embryofetal toxicity
Based on evidence of genotoxicity and developmental toxicity in animal studies, Ferriprox can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal studies, administration of deferiprone during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryofetal death and malformations at doses lower than equivalent human clinical doses. If Ferriprox is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking Ferriprox, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. Women of reproductive potential should be advised to avoid pregnancy when taking Ferriprox [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
5.4 Laboratory Tests
Serum liver enzyme activities
In clinical studies, 7.5% of 642 subjects treated with Ferriprox developed increased ALT values. Four (0.62%) Ferriprox-treated subjects discontinued the drug due to increased serum ALT levels and 1 (0.16%) due to an increase in both ALT and AST.
Monitor serum ALT values monthly during therapy with Ferriprox, and consider interruption of therapy if there is a persistent increase in the serum transaminase levels.
Plasma Zinc concentration
Decreased plasma zinc concentrations have been observed on Ferriprox therapy. Monitor plasma zinc, and supplement in the event of a deficiency.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
The following adverse reactions are also discussed in other sections of the labeling: Agranulocytosis/Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Elevated ALT (5.4), Torsades de Pointes (5.2), Decreased plasma zinc concentrations (5.4).
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse reaction information for Ferriprox represents the pooled data collected from 642 patients who participated in single arm or active-controlled clinical studies.
The most serious adverse reaction reported in clinical trials with Ferriprox was agranulocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
The most common adverse reactions reported during clinical trials were chromaturia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, alanine aminotransferase increased, arthralgia and neutropenia.
The table below lists the adverse drug reactions that occurred in at least 1% of patients treated with Ferriprox in clinical trials.
| Body System | % Subjects | |
|---|---|---|
| Preferred Term | ||
| BLOOD AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEM DISORDERS | ||
| Neutropenia | 6.2 | |
| Agranulocytosis | 1.7 | |
| GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS | ||
| Nausea | 12.6 | |
| Abdominal pain/discomfort | 10.4 | |
| Vomiting | 9.8 | |
| Diarrhea | 3.0 | |
| Dyspepsia | 2.0 | |
| INVESTIGATIONS | ||
| Alanine Aminotransferase increased | 7.5 | |
| Neutrophil count decreased | 7.3 | |
| Weight increased | 1.9 | |
| Aspartate Aminotransferase increased | 1.2 | |
| METABOLISM AND NUTRITION DISORDERS | ||
| Increased appetite | 4.0 | |
| Decreased appetite | 1.1 | |
| MUSCULOSKELETAL AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISORDERS | ||
| Arthralgia | 9.8 | |
| Back pain | 2.0 | |
| Pain in extremity | 1.9 | |
| Arthropathy | 1.4 | |
| NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS | ||
| Headache | 2.5 | |
| URINARY DISORDERS | ||
| Chromaturia | 14.6 | |
Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain were the most frequent adverse reactions reported by patients participating in clinical trials and led to the discontinuation of Ferriprox therapy in 1.6% of patients.
Chromaturia (reddish-brown discoloration of the urine) is a result of the excretion of the iron in the urine.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported in patients receiving Ferriprox. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: thrombocytosis, pancytopenia.
Cardiac disorders: atrial fibrillation, cardiac failure.
Congenital, familial and genetic disorders: hypospadias.
Eye disorders: diplopia, papilledema, retinal toxicity.
Gastrointestinal disorders: enterocolitis, rectal hemorrhage, gastric ulcer, pancreatitis, parotid gland enlargement.
General disorders and administration site conditions: chills, pyrexia, edema peripheral, multi-organ failure.
Hepatobiliary disorders: jaundice, hepatomegaly.
Immune system disorders: anaphylactic shock, hypersensitivity.
Infections and infestations: cryptococcal cutaneous infection, enteroviral encephalitis, pharyngitis, pneumonia, sepsis, furuncle, infection hepatitis, rash pustular, subcutaneous abscess.
Investigations: blood bilirubin increased, blood creatinine phosphokinase increased.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: metabolic acidosis, dehydration.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: myositis, chondropathy, trismus.
Nervous system disorders: cerebellar syndrome, cerebral hemorrhage, convulsion, gait disturbance, intracranial pressure increased, psychomotor skills impaired, pyramidal tract syndrome, somnolence.
Psychiatric disorders: bruxism, depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Renal disorders: glycosuria, hemoglobinuria.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: acute respiratory distress syndrome, epistaxis, hemoptysis, pulmonary embolism.
Skin, subcutaneous tissue disorders: hyperhidrosis, periorbital edema, photosensitivity reaction, pruritis, urticaria, rash, Henoch-Schönlein purpura.
Vascular disorders: hypotension, hypertension.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs associated with neutropenia or agranulocytosis
Avoid concomitant use of Ferriprox with other drugs known to be associated with neutropenia or agranulocytosis; however, if this is not possible, closely monitor the absolute neutrophil count [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.2 UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs)
Deferiprone is primarily eliminated via metabolism to the 3-O-glucuronide. In vitro studies suggest that UDP glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A6 is primarily responsible for the glucuronidation of deferiprone. The significance of coadministration of Ferriprox with the UGT 1A6 inhibitor (e.g. silymarin (milk thistle)) on systemic exposure to deferiprone has not been evaluated. Closely monitor patients for adverse reactions that may require downward dose titration or interruption when Ferriprox is concomitantly administered with a UGT 1A6 inhibitor.
7.3 Polyvalent cations
Concurrent use of Ferriprox with foods, mineral supplements, and antacids that contain polyvalent cations has not been studied. However, since deferiprone has the potential to bind polyvalent cations (e.g., iron, aluminum, and zinc), allow at least a 4-hour interval between Ferriprox and other medications (e.g., antacids), or supplements containing these polyvalent cations [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]
Based on evidence of genotoxicity and developmental toxicity in animal studies, Ferriprox can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal studies, administration of deferiprone during the period of organogenesis resulted in embryofetal death and malformations at doses lower than equivalent human clinical doses. There are no studies in pregnant women, and available human data are limited. If Ferriprox is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking Ferriprox, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Skeletal and soft tissue malformations occurred in offspring of rats and rabbits that received deferiprone orally during organogenesis at the lowest doses tested (25 mg/kg per day in rats; 10 mg/kg per day in rabbits). These doses were equivalent to 3% to 4% of the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on body surface area. No maternal toxicity was evident at these doses.
Embryofetal lethality and maternal toxicity occurred in pregnant rabbits given 100 mg/kg/day deferiprone orally during the period of organogenesis. This dose is equivalent to 32% of the MRHD based on body surface area.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether Ferriprox is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for adverse reactions in nursing infants from Ferriprox, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Ferriprox tablets for oral use in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in elderly individuals have not been established. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
10 OVERDOSAGE
No cases of acute overdose have been reported. There is no specific antidote to Ferriprox overdose.
Neurological disorders such as cerebellar symptoms, diplopia, lateral nystagmus, psychomotor slowdown, hand movements and axial hypotonia have been observed in children treated with 2.5 to 3 times the recommended dose for more than one year. The neurological disorders progressively regressed after deferiprone discontinuation.
11 DESCRIPTION
Ferriprox (deferiprone) tablets contain 500 mg deferiprone (3-hydroxy-1,2-dimethylpyridin-4-one), a synthetic, orally active, iron-chelating agent. Deferiprone has the following structural formula:
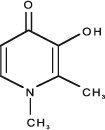
Deferiprone is a white to pinkish-white crystalline powder. It is sparingly soluble in deionized water and has a melting point range of 272°C - 278°C.
Ferriprox tablets are white to off-white, capsule-shaped tablets, and imprinted with “APO” score “500” on one side and plain on the other. The tablets can be broken in half along the score. Each tablet contains 500 mg deferiprone and the following inactive ingredients: Tablet core - microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide; Coating - hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Deferiprone is a chelating agent with an affinity for ferric ion (iron III). Deferiprone binds with ferric ions to form neutral 3:1 (deferiprone:iron) complexes that are stable over a wide range of pH values. Deferiprone has a lower binding affinity for other metals such as copper, aluminum and zinc than for iron.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
No clinical studies were performed to assess the relationship between the dose of Ferriprox and the amount of iron eliminated from the body.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Deferiprone is rapidly absorbed from the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract, appearing in the blood within 5 to 10 minutes of oral administration. Peak serum concentrations occur approximately 1 hour after a single dose in fasted healthy subjects and patients, and up to 2 hours after a single dose in the fed state. Administration with food decreased the Cmax of deferiprone by 38% and the AUC by 10%. While a food effect cannot be ruled out, the magnitude of the exposure change does not warrant dose adjustment.
In healthy subjects, the mean maximum concentration (Cmax) of deferiprone in serum was 20 mcg/mL, and the mean total area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) was 53 mcg∙h/mL following oral administration of a 1,500 mg dose of Ferriprox tablets in the fasting state. Dose proportionality over the labeled dosage range of 25 to 33 mg/kg three times per day (75 to 100 mg/kg per day) has not been studied. The elimination half life (t1/2) of deferiprone was 1.9 hours. The accumulation of deferiprone and its glucuronide metabolite at the highest approved dosage level of 33 mg/kg three times per day has not been studied. The volume of distribution of deferiprone is 1.6 L/kg in thalassemia patients, and approximately 1 L/kg in healthy subjects. The plasma protein binding of deferiprone in humans is less than 10%.
In humans, the majority of the deferiprone is metabolized, primarily by UGT 1A6. The contribution of extrahepatic (e.g., renal) UGT1A6 is unknown. The major metabolite of deferiprone is the 3-O-glucuronide, which lacks iron binding capability. Peak serum concentration of the glucuronide occurs 2 to 4 hours after administration of deferiprone in fasting subjects.
More than 90% of deferiprone is eliminated from plasma within 5 to 6 hours of ingestion. Following oral administration, 75% to 90% is recovered in the urine in the first 24 hours, primarily as metabolite.
Special populations
The pharmacokinetics of deferiprone has not been studied in geriatric or pediatric populations, and the influence of race, gender, or obesity has not been established.
12.6 QT/QTc Prolongation
No clinical studies of the effects of Ferriprox on the cardiac QT interval have been performed in human subjects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with deferiprone. However, in view of the genotoxicity results, and the findings of mammary gland hyperplasia and mammary gland tumors in rats treated with deferiprone in the 52-week toxicology study, tumor formation in carcinogenicity studies must be regarded as likely.
Deferiprone was positive in a mouse lymphoma cell assay in vitro. Deferiprone was clastogenic in an in vitro chromosomal aberration test in mice and in a chromosomal aberration test in Chinese Hamster Ovary cells. Deferiprone given orally or intraperitoneally was clastogenic in a bone marrow micronucleus assay in non-iron-loaded mice. A micronucleus test was also positive when mice predosed with iron dextran were treated with deferiprone. Deferiprone was not mutagenic in the Ames bacterial reverse mutation test.
A fertility and early embryonic development study of deferiprone was conducted in rats. Sperm counts, motility and morphology were unaffected by treatment with deferiprone. There were no effects observed on male or female fertility or reproductive function at the highest dose which was 25% of the MRHD based on body surface area.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
In a prospective, planned, pooled analysis of patients from several studies, the efficacy of Ferriprox was assessed in transfusion-dependent iron overload patients in whom previous iron chelation therapy had failed or was considered inadequate due to poor tolerance. The main criterion for chelation failure was serum ferritin >2,500 mcg/L before treatment with Ferriprox. Ferriprox therapy (35-99 mg/kg/day) was considered successful in individual patients who experienced a ≥20% decline in serum ferritin within one year of starting therapy.
Data from a total of 236 patients were analyzed. Of the 224 patients with thalassemia who received deferiprone monotherapy and were eligible for serum ferritin analysis, 105 (47%) were male and 119 (53%) were female. The mean age of these patients was 18.2 years.
For the patients in the analysis, the endpoint of at least a 20% reduction in serum ferritin was met in 50% (of 236 subjects), with a 95% confidence interval of 43% to 57%.
A small number of patients with thalassemia and iron overload were assessed by measuring the change in the number of milliseconds (ms) in the cardiac MRI T2* value before and after treatment with deferiprone for one year. There was an increase in cardiac MRI T2* from a mean at baseline of 11.8 ± 4.9 ms to a mean of 15.1 ± 7.0 ms after approximately one year of treatment. The clinical significance of this observation is not known.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
FERRIPROX® (deferiprone) tablets are white to off-white, capsule-shaped tablets, film-coated, and have a functional score imprinted with “APO” score “500” on one side and are plain on the other. They are provided in a 100 count HDPE bottle with a child-resistant cap.
500 mg film-coated tablets, 100 tablets NDC 52609-0006-1
Store at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF); excursions permitted to 15º to 30ºC (59º to 86ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep Ferriprox out of the reach and sight of children.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Medication Guide)
- Inform patients of the risks of developing agranulocytosis and instruct them to immediately interrupt therapy and report to their physician if they experience any symptoms of infection such as fever, sore throat or flu-like symptoms.
- Advise patients that the amount of Ferriprox prescribed is based on body weight and on the therapeutic goal (reduction or stabilization of the body iron load).
- Advise patients to take the first dose of Ferriprox in the morning, the second dose at midday, and the third dose in the evening. Clinical experience suggests that taking Ferriprox with meals may reduce nausea. If a dose of this medicine has been missed, take as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to the regular dosing schedule. Do not catch-up or double doses.
- Advise patients to contact their physician in the event of overdose.
- Inform patients that their urine might show a reddish/brown discoloration due to the excretion of the iron-deferiprone complex. This is a very common sign of the desired effect of Ferriprox, and it is not harmful.
- Counsel women of reproductive potential to avoid pregnancy while taking Ferriprox. Advise patients to immediately notify their physician if they become pregnant, or if they plan to become pregnant during therapy.
- Inform patients that they should not breast feed while taking Ferriprox.
- Inform patients that if they experience palpitations, dizziness, lightheadedness, syncope, or seizures to immediately seek medical attention.
Manufactured for ApoPharma USA, Inc., Rockville, MD, United States of America, 20850. Manufactured by Apotex Inc., Toronto, Ontario, Canada, M9L 1T9
MEDICATION GUIDE
FERRIPROX® (Feh’ ri prox)
(deferiprone)
Tablets
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking FERRIPROX and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about FERRIPROX?
FERRIPROX can cause serious side effects, including a very low white blood cell count in your blood. One type of white blood cell that is important for fighting infections is called a neutrophil. If your neutrophil count is low (neutropenia), you may be at risk of developing a serious infection that can lead to death. Neutropenia is common with FERRIPROX and can become severe in some patients. Severe neutropenia is known as agranulocytosis. If you develop agranulocytosis, you will be at risk of developing serious infections that can lead to death.
Your healthcare provider should do a blood test before you start FERRIPROX and weekly during treatment to check your neutrophil count. If you develop neutropenia, your healthcare provider should check your blood counts every day until your white blood cell count improves.
Stop taking FERRIPROX and get medical help right away if you develop any of these symptoms of infection:
- fever
- sore throat or mouth sores
- flu-like symptoms
- chills and severe shaking
See “What are the possible side effects of FERRIPROX?” for more information about side effects.
What is FERRIPROX?
FERRIPROX is a prescription medicine used to treat people with thalassemia syndromes who have iron overload from blood transfusions, when current iron removal (chelation) therapy does not work well enough.
It is not known if FERRIPROX tablets for oral use are safe and effective:
- to treat iron overload due to blood transfusions in people with any other type of anemia that is long lasting (chronic)
- in children
Who should not take FERRIPROX?
Do not take FERRIPROX if you:
- are allergic to deferiprone or any of the ingredients in FERRIPROX. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in FERRIPROX.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking FERRIPROX?
Before you take FERRIPROX, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have liver problems
- have kidney problems
- have any heart problems, especially a heart rhythm problem called QT prolongation or long-QT syndrome
- have been told that you have low levels of potassium or magnesium in your blood
- have any other medical conditions.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. FERRIPROX can harm your unborn baby. You should avoid becoming pregnant while taking FERRIPROX. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or plan to become pregnant while taking FERRIPROX.
- are breastfeeding. It is not known whether FERRIPROX passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take FERRIPROX or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- other medicines that can cause a lowering of your neutrophil count
- antacids or mineral supplements that contain: iron, aluminum, and zinc. Allow at least 4 hours between taking FERRIPROX and any of these products.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if your medicine is one that is listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take FERRIPROX?
- Take FERRIPROX exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not change your dose of FERRIPROX unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how many FERRIPROX tablets to take.
- FERRIPROX is taken 3 times each day. Take your first dose in the morning, the second dose at mid-day, and third dose in the evening.
- You can take FERRIPROX with or without food.
- Taking FERRIPROX with meals may help reduce nausea. If you take too much FERRIPROX, call your healthcare provider.
- If you do miss a dose take it as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and then continue with your regular schedule. Do not try to catch-up or take 2 doses at the same time to make up for a missed dose.
What are the possible side effects of FERRIPROX?
FERRIPROX can cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about FERRIPROX?”
- Increased liver enzyme levels in your blood. Your healthcare provider should do monthly blood test to check your liver function during treatment with FERRIPROX.
The most common side effects of FERRIPROX include:
- reddish-brown colored urine. This is not harmful and is expected when you are taking FERRIPROX.
- nausea
- vomiting
- stomach-area (abdominal) pain
- joint pain
- low neutrophil count. See “What is the most important information I should know about FERRIPROX?”
Your doctor should tell you about symptoms and signs of an irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia). It is not clear if FERRIPROX causes arrhythmia, but it is important that you get medical help right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- irregular or fast heart beat
- dizziness
- lightheadedness or fainting
- seizure
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of FERRIPROX. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1‑800-FDA-1088.
How should I store FERRIPROX?
- Store FERRIPROX at room temperature between 68○F and 77○F (20○C to 25○C).
Keep FERRIPROX and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of FERRIPROX.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use FERRIPROX for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give FERRIPROX to other people, even if they have the same condition.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about FERRIPROX. If you would like more information, talk to your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about FERRIPROX that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information call, 1-866-949-0995.
What are the ingredients in FERRIPROX?
Active ingredients: deferiprone
Inactive ingredients:
Tablet core: microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide.
Coating: hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
ApoPharma USA, Inc., Rockville, MD, United States of America, 20850.
Manufactured by:
Apotex Inc., Toronto, Ontario, Canada, M9L 1T9
Issued October 2011
Trademark disclaimers.
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL SECTION
ApoPharma USA, Inc. NDC 52609-0006-1
Ferriprox tablets
500 mg
Rx only
100 Tablets

| FERRIPROX
deferiprone tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA021825 | 11/25/2011 | |
| Labeler - ApoPharma USA, Inc. (962810821) |
| Registrant - Apotex Inc. (209429182) |
Revised: 11/2011 ApoPharma USA, Inc.