DICLOFENAC SODIUM
-
diclofenac sodium tablet, delayed release
Unit Dose Services
----------
Cardiovascular Risk
- NSAIDs may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk. (See .) WARNINGS
- Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see ). WARNINGS
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal events. (See ). WARNINGS
DESCRIPTION
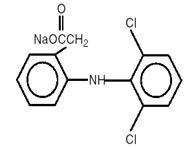
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are a benzene-acetic acid derivative. Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are available as delayed-release tablets of 75 mg for oral administration. The chemical name is 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino] benzeneacetic acid, monosodium salt. The molecular weight is 318.14. Its molecular formula is C H Cl NNaO , and it has the following structural formula 141022
The inactive ingredients in Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets include: lactose (monohydrate), microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, povidone, talc, magnesium stearate, methacrylic acid copolymer, polyethylene glycol, opadry brown (Titanium dioxide, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow) and purified water.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see ). WARNINGS
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, are indicated:
- For relief of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis
- For relief of signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
- For acute or long-term use in the relief of signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to diclofenac.
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients (see and ). WARNINGS, Anaphylactoid Reactions,PRECAUTIONS, Preexisting Asthma
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are contraindicated for the treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see ). WARNINGS
PRECAUTIONS
General
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids.
The pharmacological activity of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets in reducing fever and inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the following information before initiating therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy. Patients should also be encouraged to read the NSAID Medication Guide that accompanies each prescription dispensed.
- Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, like other NSAIDs, may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see ). WARNINGS, CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS
- Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause GI discomfort and, rarely, more serious GI side effects, such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see ). WARNINGS, Gastrointestinal Effects – Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation
- Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, like other NSAIDs, can cause serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, SJS, and TEN, which may result in hospitalizations and even death. Although serious skin reactions may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs of hypersensitivity such as itching, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms. Patients should be advised to stop the drug immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their physicians as soon as possible.
- Patients should promptly report signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or edema to their physicians.
- Patients should be informed of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and “flu-like” symptoms). If these occur, patients should be instructed to stop therapy and seek immediate medical therapy. (See ) WARNINGS; Hepatic Effects
- Patients should be informed of the signs of an anaphylactoid reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, patients should be instructed to seek immediate emergency help (see ). WARNINGS
- In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
Laboratory Tests
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. In patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, the CBC and a chemistry profile (including transaminase levels) should be checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets should be discontinued.
Drug Interactions
When diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are administered with aspirin, its protein binding is reduced. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however, as with other NSAIDs, concomitant administration of diclofenac and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential of increased adverse effects. Aspirin:
NSAIDs have been reported to competitively inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. This may indicate that they could enhance the toxicity of methotrexate. Caution should be used when NSAIDs are administered concomitantly with methotrexate. Methotrexate:
Diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, like other NSAIDs, may affect renal prostaglandins and increase the toxicity of certain drugs. Therefore, concomitant therapy with diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets may increase cyclosporine’s nephrotoxicity. Caution should be used when diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets are administered concomitantly with cyclosporine. Cyclosporine:
Reports suggest that NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. This interaction should be given consideration in patients taking NSAIDs concomitantly with ACE inhibitors. ACE-inhibitor:
Clinical studies, as well as post-marketing observations, have shown that diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets can reduce the natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazides in some patients. This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. During concomitant therapy with NSAIDs, the patient should be observed closely for signs of renal failure (see ), as well as to assure diuretic efficacy. Furosemide:WARNINGS, Renal Effects
NSAIDs have produced an elevation of plasma lithium levels and a reduction in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15% and the renal clearance was decreased by approximately 20%. These effects have been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by the NSAID. Thus, when NSAIDs and lithium are administered concurrently, subjects should be observed carefully for signs of lithium toxicity. Lithium:
The effects of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone. Warfarin:
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects:
Pregnancy Category C
Reproductive studies conducted in rats and rabbits have not demonstrated evidence of developmental abnormalities. However, animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women.
Labor and Delivery
In rat studies with NSAIDs, as with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, an increased incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased pup survival occurred. The effects of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets on labor and delivery in pregnant women are unknown.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In patients taking diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, or other NSAIDs, the most frequently reported adverse experiences occurring in approximately 1%-10% of patients are:
Gastrointestinal experiences including: abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, gross bleeding/perforation, heartburn, nausea, GI ulcers (gastric/duodenal) and vomiting.
Abnormal renal function, anemia, dizziness, edema, elevated liver enzymes, headaches, increased bleeding time, pruritus, rashes and tinnitus.
Additional adverse experiences reported occasionally include:
fever, infection, sepsis Body as a Whole:
congestive heart failure, hypertension, tachycardia, syncope Cardiovascular System:
dry mouth, esophagitis, gastric/peptic ulcers, gastritis, gastrointestinal bleeding, glossitis, hematemesis, hepatitis, jaundice Digestive System:
ecchymosis, eosinophilia, leukopenia, melena, purpura, rectal bleeding, stomatitis, thrombocytopenia Hemic and Lymphatic System:
weight changes Metabolic and Nutritional:
anxiety, asthenia, confusion, depression, dream abnormalities, drowsiness, insomnia, malaise, nervousness, paresthesia, somnolence, tremors, vertigo Nervous System:
asthma, dyspnea Respiratory System:
alopecia, photosensitivity, sweating increased Skin and Appendages:
blurred vision Special Senses:
cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, oliguria/ polyuria, proteinuria, renal failure Urogenital System:
Other adverse reactions, which occur rarely are:
anaphylactic reactions, appetite changes, death Body as a Whole:
arrhythmia, hypotension, myocardial infarction, palpitations, vasculitis Cardiovascular System:
colitis, eructation, liver failure, pancreatitis Digestive System:
agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia Hemic and Lymphatic System:
hyperglycemia Metabolic and Nutritional:
convulsions, coma, hallucinations, meningitis Nervous System:
respiratory depression, pneumonia Respiratory System:
angioedema, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, urticaria Skin and Appendages:
conjunctivitis, hearing impairment Special Senses:
OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdoses are usually limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which are generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression and coma may occur, but are rare. Anaphylactoid reactions have been reported with therapeutic ingestion of NSAIDs, and may occur following an overdose.
Patients should be managed by symptomatic and supportive care following a NSAID overdose. There are no specific antidotes. Emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 g in adults, 1 to 2 g/kg in children) and/or osmotic cathartic may be indicated in patients seen within 4 hours of ingestion with symptoms or following a large overdose (5 to 10 times the usual dose). Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets and other treatment options before deciding to use diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see ). WARNINGS
After observing the response to initial therapy with diclofenac sodium delayed-release tablets, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient’s needs.
For the relief of osteoarthritis, the recommended dosage is 100-150 mg/day in divided doses (50 mg b.i.d. or t.i.d., or 75 mg b.i.d.).
For the relief of rheumatoid arthritis, the recommended dosage is 150-200 mg/day in divided doses (50 mg t.i.d. or q.i.d., or 75 mg b.i.d.).
For the relief of ankylosing spondylitis, the recommended dosage is 100-125 mg/day, administered as 25 mg q.i.d., with an extra 25-mg dose at bedtime if necessary.
Different formulations of diclofenac (diclofenac sodium enteric-coated tablets; diclofenac sodium extended-release tablets, diclofenac potassium immediate-release tablets) are not necessarily bioequivalent even if the milligram strength is the same.
MEDICATION GUIDE for Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
(See the end of this Medication Guide for a list of prescription NSAID medicines.)
| DICLOFENAC SODIUM
diclofenac sodium tablet, delayed release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| ANDA | ANDA077863 | 08/19/2008 | |
| Labeler - Unit Dose Services (831995316) |
| Registrant - Unit Dose Services (831995316) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Unit Dose Services | 831995316 | REPACK | |
Revised: 03/2011 Unit Dose Services
