implanon (etonogestrel) implant
[Organon USA, Inc.]
DESCRIPTION
IMPLANON™ (etonogestrel implant) is an off-white, non-biodegradable, etonogestrel-containing single sterile rod implant for subdermal use. The implant is 4 cm in length with a diameter of 2 mm (see Figure 1). Each IMPLANON™ rod consists of an ethylene vinylacetate (EVA) copolymer core, containing 68 mg of the synthetic progestin etonogestrel (ENG), surrounded by an EVA copolymer skin. The release rate is 60-70 µg/day in week 5-6 and decreases to approximately 35-45 µg/day at the end of the first year, to approximately 30-40 µg/day at the end of the second year, and then to approximately 25-30 µg/day at the end of the third year. IMPLANON™ is a progestin-only contraceptive and does not contain estrogen. IMPLANON™ does not contain latex and is not radio-opaque.
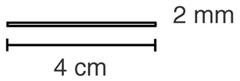
Figure 1 (Not to scale)
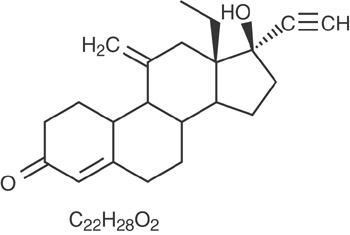
ENG [13-Ethyl-17-hydroxy-11-methylene-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one], structurally derived from 19-nortestosterone, is the synthetic biologically active metabolite of the synthetic progestin desogestrel. It has a molecular weight of 324.46 and the following structural formula:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacodynamics
The contraceptive effect of IMPLANON™ is achieved by several mechanisms that include suppression of ovulation, increased viscosity of the cervical mucus, and alterations in the endometrium.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After subdermal insertion of IMPLANON™, ENG is released into the circulation and is approximately 100% bioavailable.
The mean peak serum concentrations in 3 pharmacokinetic studies ranged between 781 and 894 pg/mL and were reached within the first few weeks after insertion. The mean serum ENG concentration decreases gradually over time declining to 192 - 261 pg/mL at 12 months (n=41), 154 – 194 pg/mL at 24 months (n=35), and 156 – 177 pg/mL at 36 months (n=17). The pharmacokinetic profile of IMPLANON™ from one of 3 pharmacokinetic studies is shown in Figure 2.
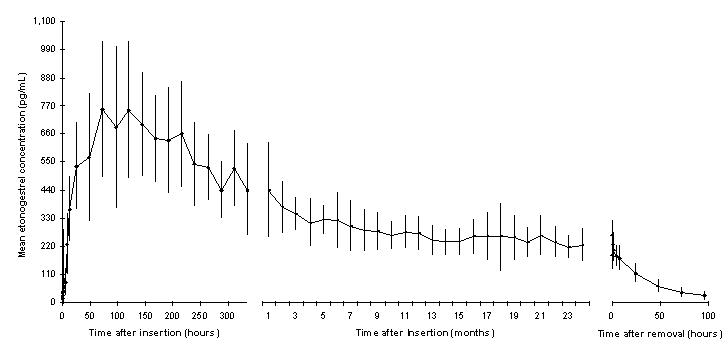
Figure 2. Mean serum concentration-time profile of ENG during 2 years of IMPLANON™ use and after removal in 20 healthy women.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution averages about 201 L. ENG is approximately 32% bound to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and 66% bound to albumin in blood.
Metabolism
In vitro data shows that ENG is metabolized in liver microsomes by the cytochrome P450 3A4 isoenzyme. The biological activity of ENG metabolites is unknown.
Excretion
The elimination half-life of ENG is approximately 25 hours. Excretion of ENG and its metabolites, either as free steroid or as conjugates, is mainly in urine and to a lesser extent in feces. After removal of IMPLANON™, ENG concentrations decreased below sensitivity of the assay by one week.
Special Populations
Overweight Women
The effectiveness of IMPLANON™ in overweight women has not been defined because women who weighed more than 130% of their ideal body weight were not studied. However, serum concentrations of ENG are inversely related to body weight and decrease with time after insertion. It is therefore possible that with time IMPLANON™ may be less effective in overweight women, especially in the presence of other factors that decrease etonogestrel concentrations such as concomitant use of hepatic enzyme inducers.
Race
No formal studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of race on the pharmacokinetics of IMPLANON™.
Hepatic Insufficiency
No formal studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic disease on the pharmacokinetics of IMPLANON™. However, ENG is metabolized by the liver, and therefore use in patients with active liver disease is contraindicated.
Renal Insufficiency
No formal studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of renal disease on the pharmacokinetics of IMPLANON™.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
IMPLANON™ (etonogestrel implant) is indicated for women for the prevention of pregnancy. IMPLANON™ is a long-acting (up to 3 years), reversible, contraceptive method. IMPLANON™ must be removed by the end of the third year and may be replaced by a new IMPLANON™ at the time of removal, if continued contraceptive protection is desired.
In clinical trials involving 923 subjects and 1,854 women-years of IMPLANON™ use, the total exposure in 28-day cycles by year was
- Year 1: 10,867 cycles
- Year 2: 8,595 cycles
- Year 3: 3,492 cycles
The clinical trials excluded women who
- Weighed more than 130% of their ideal body weight
- Were chronically taking medications that induce liver enzymes
Among women aged 18-35 years of age at entry, six pregnancies during 20,648 cycles of use were reported. Two pregnancies occurred in each of Years 1, 2 and 3. Each conception was likely to have occurred shortly before or within two weeks after IMPLANON™ removal. With these six pregnancies, the cumulative Pearl Index was 0.38 pregnancies per 100 women-years of use.
The efficacy of IMPLANON™ does not depend on patient self-administration. IMPLANON™ may be less effective in women who are overweight or who are taking medications that induce liver enzymes. See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Special Populations, Overweight Women, and PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions.
The following Table shows pregnancy rates in the first year of use for other contraceptive methods.
| % of Women Experiencing an Unintended Pregnancy within the First Year of Use | % of Women Continuing Use at One Year* | ||
| Method (1) | Typical Use†
(2) | Perfect Use‡
(3) |
(4) |
| Emergency Contraceptive Pills: Treatment initiated within 72 hours after unprotected intercourse reduces the risk of pregnancy by at least 75%.§ | |||
| Lactation Amenorrhea Method: LAM is a highly effective, temporary method of contraception.¶ | |||
| Adapted from Hatcher et al., Contraceptive Technology, 17th Revised Edition. New York, NY: Irvington Publishers, 1998. | |||
|
|||
| Chance# | 85 | 85 | |
| SpermicidesÞ | 26 | 6 | 40 |
| Periodic abstinence | 25 | 63 | |
| Calendar | 9 | ||
| Ovulation Method | 3 | ||
| Sympto-Thermalß | 2 | ||
| Post-Ovulation | 1 | ||
| Capà | |||
| Parous Women | 40 | 26 | 42 |
| Nulliparous Women | 20 | 9 | 56 |
| Sponge | |||
| Parous Women | 40 | 20 | 42 |
| Nulliparous Women | 20 | 9 | 56 |
| Diaphragmà | 20 | 6 | 56 |
| Withdrawal | 19 | 4 | |
| Condomè | |||
| Female (Reality) | 21 | 5 | 56 |
| Male | 14 | 3 | 61 |
| Pill | 5 | 71 | |
| Progestin Only | 0.5 | ||
| Combined | 0.1 | ||
| IUD | |||
| Progesterone T | 2.0 | 1.5 | 81 |
| Copper T 380A | 0.8 | 0.6 | 78 |
| LNg 20 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 81 |
| Depo-Provera | 0.3 | 0.3 | 70 |
| Norplant and Norplant-2 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 88 |
| Female sterilization | 0.5 | 0.5 | 100 |
| Male sterilization | 0.15 | 0.10 | 100 |
CONTRAINDICATIONS
IMPLANON™ (etonogestrel implant) should not be used in women who have
- Known or suspected pregnancy
- Current or past history of thrombosis or thromboembolic disorders
- Hepatic tumors (benign or malignant), active liver disease
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
- Known or suspected carcinoma of the breast or personal history of breast cancer
- Hypersensitivity to any of the components of IMPLANON™.
WARNINGS
A. WARNINGS BASED ON EXPERIENCE WITH IMPLANON™ AND OTHER PROGESTIN-ONLY CONTRACEPTIVES
1. Complications of Insertion and Removal
IMPLANON™ should be inserted subdermally so that it is palpable after insertion. Failure to insert IMPLANON™ properly may go unnoticed unless the implant is palpated immediately after insertion. Deep insertions may lead to difficult or impossible removals. Failure to remove IMPLANON™ may result in infertility, ectopic pregnancy, or inability to stop a drug-related adverse event. Undetected failure to insert IMPLANON™ may lead to an unintended pregnancy. See INSTRUCTIONS FOR INSERTION AND REMOVAL.
In clinical trials, 1.0% of patients had complications at implant insertion and 1.7% had complications at implant removal. Complications expected of a minor surgical procedure, such as pain, paresthesias, bleeding, hematoma, scarring or infection, have been reported. Occasionally in post-marketing use, implant insertions have failed because the implant fell out of the needle or remained in the needle during insertion. Implant removals may be difficult because the implant is deep, not palpable, encased in fibrous tissue, or has migrated. Implants have broken during difficult removals.
Deep insertions may result in the need for a surgical procedure in an operating room in order to remove IMPLANON™. Any of the possible complications of surgery may occur. In post-marketing use there have been cases of failure to localize and remove the implant, probably due to deep insertion. There has been one case of an intravascular insertion reported post-marketing which led to inability to remove the implant.
If infection develops at the insertion site, start suitable treatment. If infection persists, remove IMPLANON™. Incomplete insertions or infections may lead to expulsion.
2. Ectopic Pregnancies
Be alert to the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy among patients using IMPLANON™ who become pregnant or complain of lower abdominal pain. Although ectopic pregnancies should be uncommon among patients using IMPLANON™, a pregnancy that occurs in a patient using IMPLANON™ may be more likely to be ectopic than a pregnancy occurring in a patient using no contraception.
3. Bleeding Irregularities
Patients who use IMPLANON™ are likely to have changes in their vaginal bleeding patterns, which are often unpredictable. These may include changes in bleeding frequency or duration, or amenorrhea. Patients should be counseled regarding unpredictable bleeding irregularities so that they know what to expect. Abnormal bleeding should be evaluated as needed to exclude pathologic conditions or pregnancy.
In clinical trials, bleeding changes were the single most common reason for stopping treatment with IMPLANON™ (11.1%, or 105 of 942 patients using IMPLANON™). Most patients stopped treatment with IMPLANON™ because of irregular bleeding (10.8%), but some stopped because of amenorrhea (0.3%). In these studies, patients using IMPLANON™ had an average of 17.7 days of bleeding or spotting every 90 days (based on 3315 intervals of 90 days recorded by 780 patients). The percentages of patients having 0, 1-7, 8-21, or > 21 days of spotting or bleeding over a 90-day interval while using IMPLANON™ is shown in the following table.
| Total Days of Spotting or Bleeding | Percentage of Patients | ||
| Treatment Days 91-180 (N=566) | Treatment Days 270-360 (N=554) | Treatment Days 640-730 (N=547) |
|
| 0 Days | 19% | 24% | 17% |
| 1-7 Days | 15% | 13% | 12% |
| 8-21 Days | 30% | 30% | 37% |
| >21 Days | 36% | 33% | 35% |
Bleeding patterns observed with use of IMPLANON™ for up to 2 years, and the proportion of 90-day intervals with these bleeding patterns, are summarized in the following table.
| Bleeding Patterns | Definitions | % |
| % = Percentage of 90-day intervals with this pattern | ||
| Based on 3315 recording periods of 90 days duration in 780 women, excluding the first 90 days after implant insertion | ||
| Infrequent | Less than three bleeding and/or spotting episodes in 90 days (excluding amenorrhea) | 33.6 |
| Amenorrhea | No bleeding and/or spotting in 90 days | 22.2 |
| Prolonged | Any bleeding and/or spotting episode lasting more than 14 days in 90 days | 17.7 |
| Frequent | More than 5 bleeding and/or spotting episodes in 90 days | 6.7 |
4. Interaction with Anti-Epileptic and Other Drugs
IMPLANON™ is not recommended for women who chronically take drugs that are potent hepatic enzyme inducers because etonogestrel levels may be substantially reduced in these women. See also PRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions.
5. Ovarian Cysts
If follicular development occurs, atresia of the follicle is sometimes delayed, and the follicle may continue to grow beyond the size it would attain in a normal cycle. Generally, these enlarged follicles disappear spontaneously. Rarely, they can require surgery.
6. Thrombosis
There have been post-marketing reports of serious thromboembolic events, including cases of pulmonary emboli (some fatal) and strokes, in patients using IMPLANON™. IMPLANON™ should be removed in the event of a thrombosis. Consider removal of IMPLANON™ in case of long-term immobilization due to surgery or illness. Women with a history of thromboembolic disorders should be made aware of the possibility of a recurrence. See also WARNINGS BASED ON EXPERIENCE WITH COMBINATION (PROGESTIN PLUS ESTROGEN) ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES.
B. WARNINGS BASED ON EXPERIENCE WITH COMBINATION (PROGESTIN PLUS ESTROGEN) ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
1. Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems
Thromboembolism: Epidemiological investigations have associated the use of combination hormonal contraceptives with an increased incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE, deep venous thrombosis, retinal vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism).
The use of combination hormonal contraceptives is associated with increased risks of several serious conditions including myocardial infarction, thromboembolism, and stroke, although the risk of serious morbidity or mortality is very small in healthy women without underlying risk factors. The risk increases significantly in the presence of other underlying risk factors such as hypertension, hyperlipidemias, obesity, and diabetes.
2. Cigarette Smoking
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular side effects from the use of combination hormonal contraceptives. This risk increases with age and with heavy smoking (15 or more cigarettes per day) and is quite marked in women over 35 years old who smoke. While this is believed to be an estrogen-related effect, it is not known whether a similar risk exists with progestin only methods. However, patients should be strongly advised not to smoke.
3. Elevated Blood Pressure
An increase in blood pressure has been reported in women taking combination hormonal contraceptives and this increase is more likely with continued use and with those users who are older. Studies have shown that the incidence of hypertension increases with increasing concentrations of progestins.
Women with a history of hypertension-related diseases or renal disease should be discouraged from using hormonal contraceptives. If women with hypertension elect to use hormonal contraceptives, they should be monitored closely. lf sustained hypertension develops during the use of hormonal contraceptives, or if a significant increase in blood pressure does not respond adequately to antihypertensive therapy, hormonal contraceptives should be discontinued.
For most women, elevated blood pressure will return to normal after stopping hormonal contraceptives, and there is no difference in the occurrence of hypertension between ever- and never-users.
4. Carcinoma of the Breast and Reproductive Organs
Women with breast cancer should not use hormonal contraceptives because breast cancer may be hormonally sensitive.
The risk of having breast cancer diagnosed may be slightly increased among current and recent users of combination oral contraceptives. However, after combination oral contraceptive discontinuation this excess risk appears to decrease over time and within 10 years after cessation the increased risk disappears. Some studies report an increased risk with duration of use while other studies do not, and no consistent relationships have been found with dose or type of steroid. Some studies have found a small increase in risk for women who first used combination oral contraceptives before age 20. Most studies show a similar pattern of risk with combination oral contraceptive use regardless of a woman’s reproductive history or her family breast cancer history.
In addition, breast cancers diagnosed in current or ever combination oral contraceptive users may be less clinically advanced than in never-users.
Some studies suggest that oral contraceptive use has been associated with an increase in the risk of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in some populations of women. However, there continues to be controversy about the extent to which such findings may be due to differences in sexual behavior and other factors.
In spite of many studies on the relationship between combination oral contraceptive use and breast and cervical cancers, a cause-and-effect relationship has not been established.
5. Hepatic Neoplasia
Benign hepatic adenomas have been associated with the use of combination oral contraceptives, although the incidence of benign tumors is rare in the United States. Indirect calculations have estimated the attributable risk to be in the range of 3.3 cases/100,000 for users, a risk that increases after four or more years of use. Rupture of benign hepatic adenomas may cause death through intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
Studies from Britain have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in long-term (>8 years) oral contraceptive users. However, these cancers are extremely rare in the U.S. and the attributable risk (the excess incidence) of liver cancers in oral contraceptive users approaches less than one per million users.
6. Gallbladder Disease
Earlier studies have reported an increased lifetime relative risk of gallbladder surgery in users of combination oral contraceptives and estrogens. More recent studies, however, have shown that the relative risk of developing gallbladder disease among combination oral contraceptive users may be minimal. The recent findings of minimal risk may be related to the use of combination oral contraceptive formulations containing lower doses of estrogens and progestins.
PRECAUTIONS
1. General
Women should be informed that this product does not protect against infection from HIV (the virus that causes AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases.
IMPORTANT: Pregnancy must be excluded before inserting IMPLANON™.
2. Physical Examination and Follow-up
A complete medical evaluation, including history and physical examination and relevant laboratory tests, should be performed prior to IMPLANON™ insertion or reinsertion. It is good medical practice for patients using IMPLANON™ to have regular physical examinations. In case of undiagnosed, persistent, or recurrent abnormal vaginal bleeding, appropriate measures should be conducted to rule out malignancy. Women with a family history of breast cancer or who have breast nodules should be monitored with particular care.
3. Information for the Patient
Provide your patient with a copy of the Patient Labeling and ensure that she understands the information in the Patient Labeling before insertion and removal. A USER CARD and consent form are included in the packaging, Have the patient complete a consent form and retain it in your records. The USER CARD should be filled out and given to the patient after IMPLANON™ insertion so that she will have a record of the location of IMPLANON™ and when IMPLANON™ should be removed.
4. Weight Gain
In clinical studies, mean weight gain in U.S. IMPLANON™ users was 2.8 pounds after one year and 3.7 pounds after two years. How much of the weight gain was related to IMPLANON™ is unknown. In studies, 2.3% of IMPLANON™ users reported weight gain as the reason for having IMPLANON™ removed.
5. Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolic Effects
IMPLANON™ may induce mild insulin resistance and small changes in glucose concentrations of unknown clinical significance. Women with diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance should be carefully observed while using IMPLANON™.
Women who are being treated for hyperlipidemias should be followed closely if they elect to use hormonal contraceptives. Some progestins may elevate LDL levels and may render the control of hyperlipidemias more difficult.
6. Liver Function
If jaundice develops in any patient using IMPLANON™, remove IMPLANON™. The hormone in IMPLANON™ may be poorly metabolized in patients with impaired liver function.
7. Depression
Women with a history of depression should be carefully observed. Consideration should be given to removing IMPLANON™ in patients who become significantly depressed.
8. Contact Lenses
Contact lens wearers who develop visual changes or changes in lens tolerance should be assessed by an ophthalmologist.
9. Drug Interactions
Changes in Contraceptive Effectiveness Associated with Co-Administration of Other Drugs
a. Anti-Infective Agents and Anticonvulsants
IMPLANON™ is not recommended for women who require chronic use of drugs that are potent inducers of hepatic enzymes because IMPLANON™ is likely to be less effective for these women.
Contraceptive effectiveness may be reduced when hormonal contraceptives are co- administered with some antibiotics, antifungals, anticonvulsants, and other drugs that increase the metabolism of contraceptive steroids. This could result in an unintended pregnancy or breakthrough bleeding. Examples include barbiturates, griseofulvin, rifampin, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, carbamazepine, felbamate, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, and modafinil. Patients should use an additional nonhormonal contraceptive method when taking medications that may decrease the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives.
b. Anti-HIV Protease Inhibitors
Several of the anti-HIV protease inhibitors have been studied with co-administration of combination oral contraceptives; significant changes (increase and decrease) in the mean area under the curve (AUC) of the estrogen and progestin have been noted in some cases. The efficacy and safety of combination oral contraceptive products may be affected with co-administration of anti-HIV protease inhibitors; it is unknown whether this applies to IMPLANON™. Healthcare providers should refer to the labeling of the individual anti-HIV protease inhibitors for further drug-drug interaction information.
c. Herbal Products
Herbal products containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) may induce hepatic enzymes and p-glycoprotein transporter and may reduce the effectiveness of contraceptive steroids.
Increase in Plasma Hormone Levels Associated with Co-Administered Drugs
Inhibitors of hepatic enzymes such as itraconazole or ketoconazole may increase plasma hormone levels.
10. Interactions with Laboratory Tests
Certain endocrine tests may be affected by IMPLANON™ use:
- Sex hormone-binding globulin concentrations may be decreased for the first six months after IMPLANON™ insertion followed by a gradual recovery.
- Thyroxine concentrations may initially be slightly decreased followed by gradual recovery to baseline.
11. Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
In a 24-month carcinogenicity study in rats with subdermal implants releasing 10 and 20 µg etonogestrel (ENG) per day (equal to approximately 1.8-3.6 times the systemic steady state exposure of women using IMPLANON™), no drug-related carcinogenic potential was observed. ENG was not genotoxic in the in vitro Ames/Salmonella reverse mutation assay, the chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster ovary cells or in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test. Fertility returned after withdrawal from treatment.
12. Pregnancy
IMPLANON™ is not indicated for use during pregnancy (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Teratology studies have been performed in rats and rabbits, respectively using oral administration up to 390 and 790 times the human IMPLANON™ dose (based upon body surface) and revealed no evidence of fetal harm due to ENG exposure.
Studies have revealed no increased risk of birth defects in women who have used combination oral contraceptives before pregnancy or during early pregnancy. There is no evidence that the risk associated with IMPLANON™ is different from that of combination oral contraceptives.
IMPLANON™ should be removed if maintaining a pregnancy.
13. Nursing Mothers
Based on limited data, IMPLANON™ may be used during lactation after the 4th postpartum week. Use of IMPLANON™ before the 4th postpartum week has not been studied.
Small amounts of ENG are excreted in breast milk. During the first months after IMPLANON™ insertion, when maternal blood levels of ENG are highest, about 100 ng of ENG may be ingested by the child per day based on an average daily milk ingestion of 658 mL. Based on daily milk ingestion of 150 mL/kg, the mean daily infant ENG dose one month after insertion of IMPLANON™ is about 2.2% of the weight-adjusted maternal daily dose, or about 0.2% of the estimated absolute maternal daily dose. The health of breast-fed infants whose mothers began using IMPLANON™ during the 4th to 8th week postpartum (n=38) was evaluated in a comparative study with infants of mothers using a non-hormonal IUD (n=33). They were breast-fed for a mean duration of 14 months and followed up to 36 months of age. No significant effects and no differences between the groups were observed on the physical and psychomotor development of these infants. No differences between groups in the production or quality of breast milk were detected.
Healthcare providers should discuss both hormonal and non-hormonal contraceptive options, since steroids may not be the initial choice for these patients.
14. Return to Ovulation
In clinical trials, pregnancies occurred as early as during the first week after removal of IMPLANON™. Therefore, a patient should re-start contraception immediately after removal of IMPLANON™ if she still needs to prevent pregnancy.
15. Fluid Retention
Steroid contraceptives may cause some degree of fluid retention. They should be prescribed with caution, and only with careful monitoring, in patients with conditions which might be aggravated by fluid retention. It is unknown if IMPLANON™ causes fluid retention.
16. Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of IMPLANON™ have been established in women of reproductive age. Safety and efficacy are expected to be the same for postpubertal adolescents. However, no clinical studies have been conducted in women less than 18 years of age. Use of this product before menarche is not indicated.
17. Geriatric Use
This product has not been studied in women over 65 years of age and is not indicated in this population.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS for additional important adverse events.
In clinical trials including 942 subjects, bleeding irregularities were the most common adverse event causing discontinuation of IMPLANON™. (see following Table)
| Adverse Event | All Studies N=942 |
| Bleeding Irregularities* | 11.0% |
| Emotional Lability† | 2.3% |
| Weight Increase | 2.3% |
| Headache | 1.6% |
| Acne | 1.3% |
| Depression‡ | 1.0% |
Adverse events that were reported by more than 5% of subjects in clinical trials appear in the following Table.
| Adverse Event | All Studies N=942 |
|
|
| Headache | 24.9% |
| Vaginitis | 14.5% |
| Weight Increase | 13.7% |
| Acne | 13.5% |
| Breast Pain | 12.8% |
| Upper Respiratory Tract Infection | 12.6% |
| Abdominal Pain | 10.9% |
| Pharyngitis | 10.5% |
| Leukorrhoea | 9.6% |
| Influenza-like symptoms | 7.6% |
| Dizziness | 7.2% |
| Dysmenorrhoea | 7.2% |
| Back Pain | 6.8% |
| Emotional lability | 6.5% |
| Nausea | 6.4% |
| Pain | 5.6% |
| Nervousness | 5.6% |
| Sinusitis | 5.6% |
| Depression | 5.5% |
| Insertion site pain | 5.2% |
Other “Less Common Adverse Events” Reported in Less Than 5% of Subjects in Clinical Trials Include: Allergic Reaction, Alopecia, Anorexia, Anxiety, Appetite Increased, Arthralgia, Asthenia, Asthma, Breast Discharge, Breast Enlargement, Breast Fibroadenosis, Cervical Smear Test Positive, Constipation, Coughing, Crying Abnormal, Diarrhea, Dyspepsia, Dysuria, Edema, Edema Generalized, Fatigue, Fever, Flatulence, Gastritis, Hot Flushes, Hypertension, Hypoasthesia, Injection Site Reaction, Insomnia, Lactation Nonpuerperal, Libido Decreased, Migraine, Myalgia, Otitis Media, Ovarian Cyst, Pelvic Cramping, Premenstrual Tension, Pruritus, Pruritus Genital, Rash, Rhinitis, Sexual Function Abnormal, Skeletal Pain, Somnolence, Vaginal Discomfort, Vein Varicose, Vision Abnormal, Vomiting, and Weight Decrease.
Hypertrichosis has also been reported with use of progestin-only contraceptives.
Implant site complications were reported by 3.6% of subjects during any of the assessments in clinical trials. Pain was the most frequent implant site complication, reported during and/or after insertion, occurring in 2.9% of subjects. Additionally, hematoma, redness, and swelling were reported by 0.1%, 0.3%, and 0.3% of patients, respectively. See also WARNINGS, COMPLICATONS OF INSERTION AND REMOVAL.
OVERDOSAGE
Insertion of multiple rods has been reported. Overdosage may result if more than one IMPLANON™ (etonogestrel implant) rod is in place. In case of suspected overdose, IMPLANON™ should be removed. It is important to remove the IMPLANON™ rod or other contraceptive implant(s) before inserting a new IMPLANON™ rod.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
All healthcare providers performing insertions and/or removals of IMPLANON™ must receive instruction and training and where appropriate, supervision prior to inserting or removing IMPLANON™. Insert IMPLANON™ subdermally in the inner side of the upper arm (non-dominant arm) about 6-8 cm (2½-3 inches) above the elbow crease overlying the groove between the biceps and the triceps. See INSTRUCTIONS FOR INSERTION AND REMOVAL. IMPLANON™ must be inserted by the expiration date stated on the packaging. Remove IMPLANON™ no later than three years after the date of insertion.
When to Insert IMPLANON™
IMPORTANT: Rule out pregnancy before inserting IMPLANON™.
Timing of insertion depends on the patient’s recent history, as follows:
1. No preceding hormonal contraceptive use in the past month
Counting the first day of menstruation as “Day 1”, IMPLANON™ must be inserted between Days 1 through 5, even if the woman is still bleeding.
2. Switching from a combination hormonal contraceptive
IMPLANON™ may be inserted:
- Anytime within seven days after the last active (estrogen plus progestin) oral contraceptive tablet.
- Anytime during the seven-day ring-free period of NuvaRing® (etonogestrel/ ethinyl estradiol vaginal ring).
- Anytime during the seven-day patch-free period of a transdermal contraceptive system.
3. Switching from a progestin-only method
There are several types of progestin-only methods. IMPLANON™ insertion must be performed as follows:
- Any day of the month when switching from a progestin-only pill, do not skip any days between the last pill and insertion of IMPLANON™
- On the same day as contraceptive implant removal
- On the same day as removal of a progestin-containing IUD
- On the day when the next contraceptive injection would be due
4. Following first-trimester abortion or miscarriage
- IMPLANON™ may be inserted immediately following a complete first trimester abortion. If IMPLANON is not inserted within five days following a first trimester abortion, follow the instructions under "No preceding hormonal contraceptive use in the past month.”
5. Following delivery or a second-trimester abortion
- IMPLANON™ may be inserted between 21 to 28 days postpartum if not exclusively breast feeding or between 21 to 28 days following second trimester abortion. If more than four weeks have elapsed, pregnancy should be excluded and the patient should use a non-hormonal method of birth control during the first seven days after the insertion. If the patient is exclusively breast feeding, insert IMPLANON™ after the fourth postpartum week (see Nursing Mothers section under PRECAUTIONS).
If inserted as recommended above, back-up contraception is not necessary. If deviating from the recommended timing of insertion, rule out pregnancy and use back-up non-hormonal contraception for 7 days after IMPLANON™ insertion.
HOW SUPPLIED
One IMPLANON™ (etonogestrel implant) package consists of a single rod implant containing 68 mg etonogestrel that is 4 cm in length and 2 mm in diameter. IMPLANON™ is pre-loaded in the needle of a disposable applicator. The applicator consists of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene body with a stainless steel needle and a polypropylene shield. The sterile applicator containing IMPLANON™ is packed in a blister pack.
NDC 0052-0272-01
Storage
Store IMPLANON™ (etonogestrel implant) at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light. Avoid storing IMPLANON™ in direct sunlight or at temperatures above 30°C (86°F).
Rx only
REFERENCES
REFERENCES FURNISHED UPON REQUEST.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR INSERTION AND REMOVAL
The basis for successful use and subsequent removal of IMPLANON™ is a correct and carefully performed subdermal insertion of the single rod implant in accordance with the instructions. If the implant is placed improperly leading to deep location or migration, it will be more difficult to remove than a correctly placed subdermal implant. All healthcare providers performing insertions and removals of IMPLANON™ must receive instruction and training, and where appropriate, supervision prior to inserting or removing IMPLANON™.
Information concerning the insertion and removal of IMPLANON™ will be sent upon request free of charge [Organon USA Inc., telephone: 1-877-IMPLANON (1-877-467-5266)].
INSERTION PROCEDURE
Prior to inserting IMPLANON™ carefully read the instructions for insertion and removal as well as the full prescribing information.
Place IMPLANON™ subdermally. Both you and your patient should be able to feel IMPLANON™ under her skin after placement.
Follow instructions carefully. All healthcare providers must receive training before inserting or removing IMPLANON™. Proper IMPLANON™ insertion will facilitate removal. Correct timing of insertion is important. (See When to Insert IMPLANON™ in the DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section.) Perform a history and physical examination, including a gynecologic examination, before IMPLANON™ insertion. Ensure that the patient understands the risks and benefits of IMPLANON™ before insertion. Provide the patient with a copy of the Patient labeling included in packaging. Have the patient review and complete a consent form and maintain it with the patient’s chart.
Exclude pregnancy before insertion.
Insert IMPLANON™ under aseptic conditions.
The following equipment is needed for IMPLANON™ insertion:
- An examination table for the patient to lie on
- Sterile surgical drapes, talc-free sterile gloves, antiseptic solution, sterile marker (optional)
- Local anesthetic, needles, and syringe
- Sterile gauze, adhesive bandage, pressure bandage
An applicator and its parts are shown below (Figures 3a and 3b).
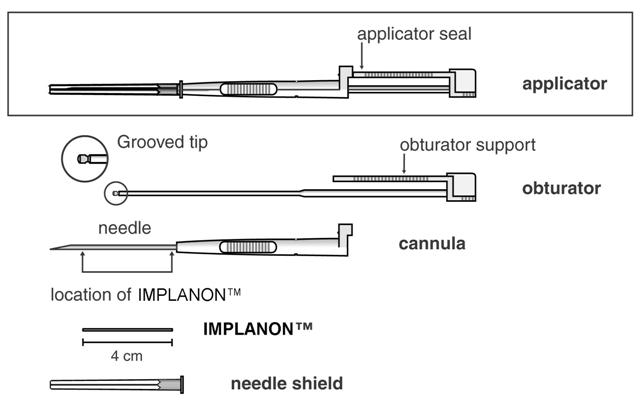
Figure 3a (Not to scale)
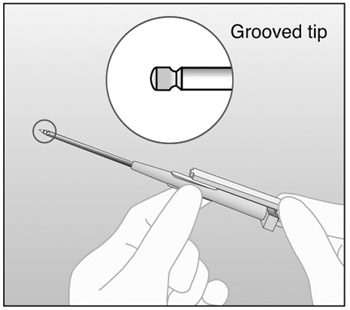
Figure 3b – Grooved Tip of Obturator (Enlarged)
The procedure used for IMPLANON™ insertion is opposite from that of an injection. The obturator keeps IMPLANON™ in place while the cannula is retracted. The obturator must remain fixed in place while the cannula with needle is retracted from the arm. Do not push the obturator.
- Confirm that the patient does not have allergies to IMPLANON™, as well as the antiseptic and anesthetic to be used during insertion.
- Have the patient lie on her back on the examination table
with her non-dominant arm flexed at the elbow and externally
rotated so that her wrist is parallel to her ear or her hand
is positioned next to her head (Figure 4).

Figure 4
- Identify the insertion site, which is 6-8 cm (2½ to 3 inches) above the elbow crease at the inner side of the upper arm overlying the groove between the biceps and the triceps of her non-dominant arm.
- Mark the insertion site with a sterile marker. Make two
marks: first, mark the spot where the IMPLANON™ rod will be
inserted, and second, mark a spot about 6-8 cm (2½ to 3
inches) proximal to the first mark (Figure 5). This second
mark will later serve as a direction guide during IMPLANON™
insertion.
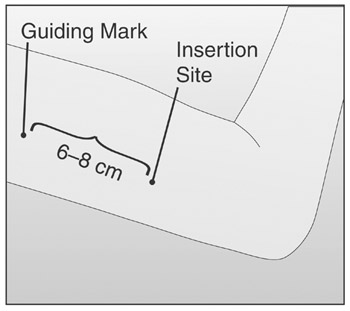
Figure 5
- Clean the insertion site with an antiseptic solution.
- Anesthetize the insertion area (for example, with anesthetic spray or by injecting 2 cc of 1% lidocaine just under the skin along the planned insertion tunnel).
- Carefully remove the IMPLANON™ applicator from its blister. Keep the shield on the needle and look for the IMPLANON™ rod, seen as a white cylinder inside the needle-tip.
- If you don’t see the IMPLANON™ rod, tap the top of the needle shield against a firm surface to bring the implant into the needle tip.
- Following visual confirmation, lower the IMPLANON™ rod back into the needle by tapping it back into the needle tip. Then remove the needle shield, while holding the applicator upright.
- Note that IMPLANON™ can fall out of the needle. Therefore, after you remove the needle shield, keep the applicator in the upright position until the moment of insertion.
- Keep the IMPLANON™ needle and rod sterile. If contamination occurs, use a new package of IMPLANON™ with a new sterile applicator.
- Apply counter-traction to the skin around the proposed
insertion site (Figure 6).
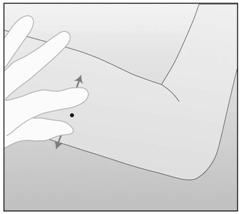
Figure 6
- At a slight angle (not greater than 20°), insert only the tip of the needle
with the beveled side up into the insertion site (Figure
7).
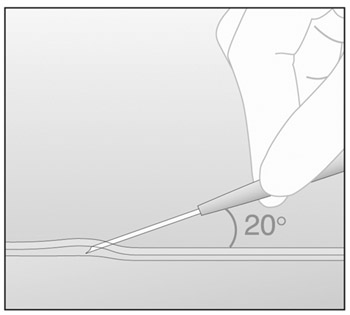
Figure 7
- Lower the applicator to a horizontal position. Lift the
skin up with the tip of the needle, but keep the needle in the subdermal
connective tissue (Figure 8).
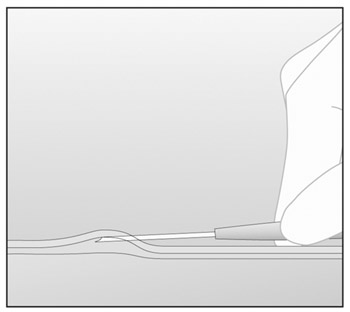
Figure 8
- While “tenting” (lifting) the skin, gently insert the
needle to its full length. Keep the needle parallel to the
surface of the skin during insertion (Figure
9).
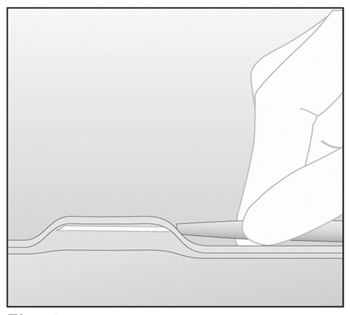
Figure 9
- If IMPLANON™ is placed too deeply the removal process can be difficult or impossible. If the needle is not inserted to its full length, the implant may protrude from the insertion site and fall out.
- Break the seal of the applicator by pressing the obturator
support (Figure 10).
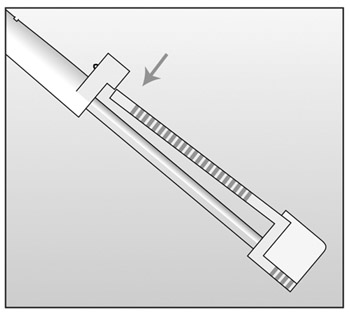
Figure 10
- Turn the obturator 90° in either direction with respect to
the needle (Figure 11).
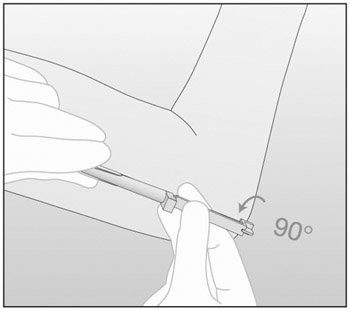
Figure 11
- While holding the obturator fixed in place on the arm,
fully retract the cannula (Figure 12). Note: This procedure is opposite from
an injection. Do not push the obturator. By holding the
obturator fixed in place on the arm and fully retracting
the cannula, IMPLANON™ will be left in its correct
subdermal position. Do not simultaneously retract the
obturator and cannula from the patient’s arm.
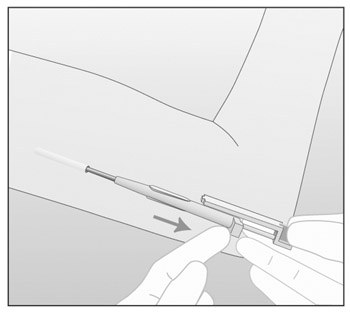
Figure 12: In this figure, the right hand is holding the obturator in place while the left hand is retracting the cannula.
- Confirm that IMPLANON™ has been inserted by checking the
tip of needle for the absence of IMPLANON™. After IMPLANON™
insertion, the grooved tip of the obturator will be visible
inside the needle. (Figure 13).
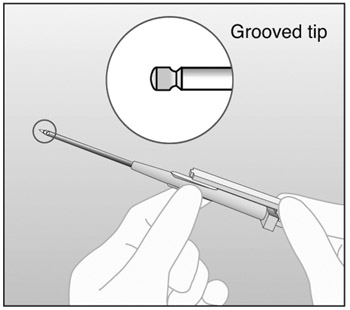
Figure 13
- Always verify the presence of IMPLANON™ in the patient’s arm immediately after insertion by palpation. By palpating both ends of the implant, you should be able to confirm the presence of the 4 cm rod.
- Place a small adhesive bandage over the insertion site. Request that the patient palpate IMPLANON™.
- If you cannot feel IMPLANON™ as a 4 cm long rod, confirm its presence using other methods. Suitable methods to locate IMPLANON™ are: ultrasound (US) with a high-frequency linear array transducer (10 MHz or greater) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Please note that the IMPLANON™ rod is not radio-opaque and cannot be seen by X-ray or CT scan. If ultrasound and MRI fail, call 1-877-IMPLANON (1-877-467-5266) for information on the procedure for measuring ENG blood levels. Until you confirm proper IMPLANON™ insertion, your patient must use a non-hormonal contraceptive method.
- Apply a pressure bandage with sterile gauze to minimize bruising. The patient may remove the pressure bandage in 24 hours and the small bandage over the insertion site in 3 to 5 days.
- Complete the User Card and give it to the patient to keep. Also, complete the Patient Chart Label and affix it to the patient's medical record.
- The applicator is for single use only. Dispose of the applicator in accordance with the Center for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines for handling of hazardous waste.
REMOVAL PROCEDURE
Before initiating the removal procedure, the healthcare provider may consult the USER CARD that is kept by the patient and/or the Patient Chart Label. The arm in which IMPLANON™ is located should be indicated on the USER CARD and the Patient Chart Label. IMPLANON™ should have been inserted in the medial aspect of the upper non-dominant arm. Prior to removing IMPLANON™ carefully read the instructions for removal. Find IMPLANON™ by palpation. If IMPLANON™ cannot be palpated, use either ultrasound with a high-frequency linear array transducer (10 MHz or greater) or magnetic resonance imaging to localize the implant. Consider conducting difficult removals with ultrasound guidance. Only remove a non-palpable implant once the location of IMPLANON™ has been established. If these imaging methods fail, call 1-877-IMPLANON (1-877-467-5266) for further instructions.
The patient’s position for removal is similar to the position for insertion. Use aseptic technique.
The following equipment is needed for removal:
- An examination table for the patient to lie on
- Sterile surgical drapes, talc-free sterile gloves, antiseptic solution, sterile marker (optional)
- Local anesthetic, needles, and syringe
- Sterile scalpel, forceps (straight and curved mosquito)
- Skin closure, sterile gauze, adhesive bandage and pressure bandages
- IMPLANON™ must only be removed by a healthcare provider who has been instructed and trained in the IMPLANON™ removal technique.
- The arm in which IMPLANON™ is located should be indicated on the USER CARD and the Patient Chart Label. IMPLANON™ should be in the medial aspect of the upper non-dominant arm.
- After confirming that the patient does not have any
allergies to the antiseptic, wash the patient's arm and
apply an antiseptic. Locate IMPLANON™ by palpation and mark
the end closest to the elbow, for example, with a sterile
marker (Figure a).
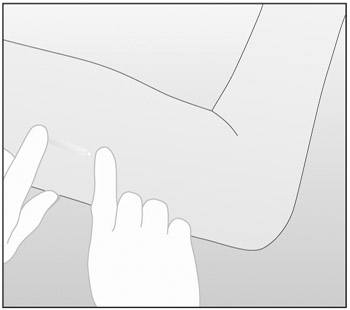
Figure a
- After determining the absence of allergies to the
anesthetic agent or related drugs, anesthetize the arm, for
example, with 0.5 to 1 cc 1% lidocaine at the site where the
incision will be made ( near the tip of IMPLANON™ that is
closest to the elbow) (Figure b). Be sure to inject the
local anesthetic under
IMPLANON™ to keep the implant close to the skin
surface.
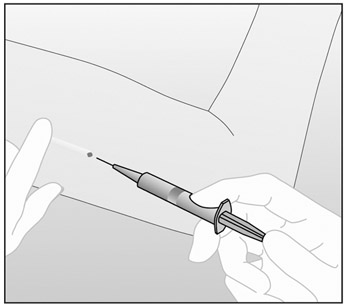
Figure b
- Make a 2-3 mm incision in the longitudinal direction of
the arm at the tip of the implant closest to the elbow
(Figure c).
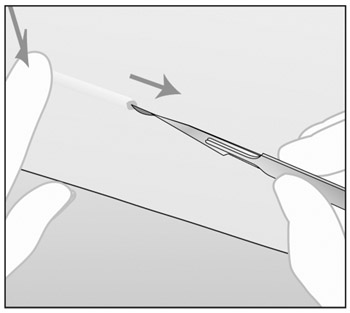
Figure c
- Gently push IMPLANON™ toward the incision until the tip is
visible. Grasp the implant with forceps (preferably curved
mosquito forceps) and pull it out gently. (Figure d).
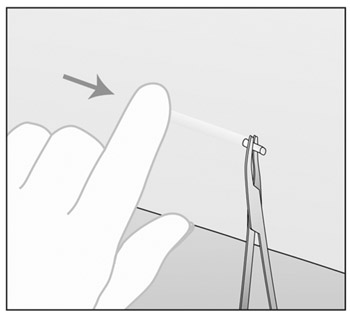
Figure d
- If IMPLANON™ is encapsulated, make an incision into the
tissue sheath and then remove IMPLANON™ with the forceps
(Figures e and f).
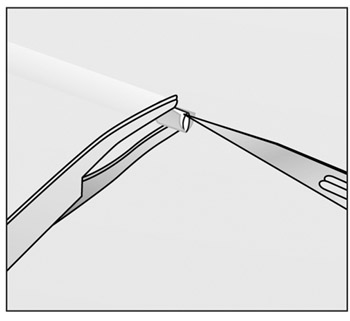
Figure e
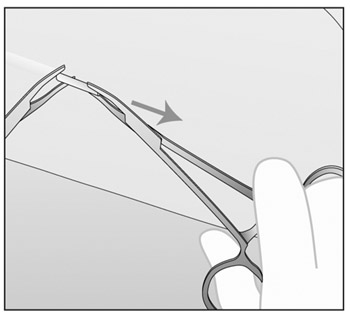
Figure f
- If the tip of the implant is still not visible after
gently pushing it towards the incision (as in step 6),
gently insert a forceps into the incision and grasp the
implant (Figures g and h). Turn the forceps around (Figure
h).
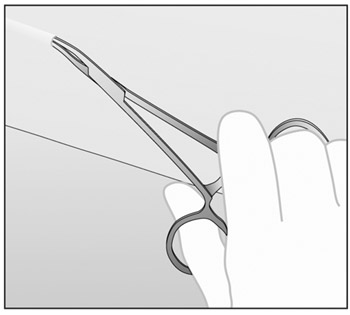
Figure g
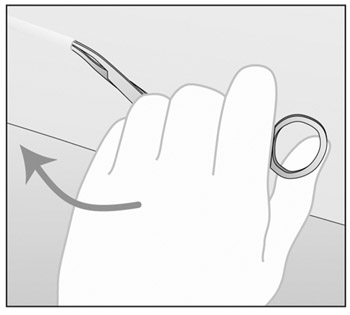
Figure h
- With a second forceps carefully dissect the tissue around
IMPLANON™ and then remove IMPLANON™ (Figure i). Be sure to
remove the IMPLANON™ rod entirely. Confirm that the entire
rod, which is 4 cm long, has been removed by measuring its
length.If the patient would like to continue using IMPLANON™, insert a new IMPLANON™ rod immediately after the old IMPLANON™ rod is removed. The new IMPLANON™ can be inserted in the same arm, and through the same incision, or a new IMPLANON™ can be inserted in the other arm. If the patient does not wish to continue using IMPLANON™ and does not want to become pregnant, recommend another contraceptive method.
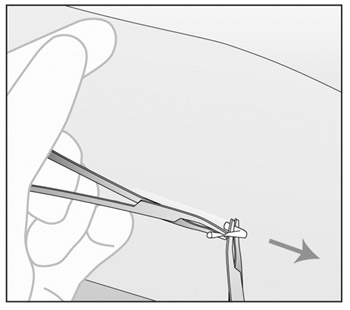
Figure i
- After removing IMPLANON™, close the incision with a butterfly closure and apply an adhesive bandage.
- Apply a pressure bandage with sterile gauze to minimize bruising.
SUPPLEMENTAL PATIENT MATERIAL
PATIENT LABELING
IMPLANON™ (etonogestrel implant)
IMPLANON™ does not protect against infection from HIV (the virus that causes AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases.
Read this leaflet carefully and have your healthcare provider answer all of your questions before you decide to use IMPLANON™.
What is the most important information I should know about IMPLANON™?
If IMPLANON™ is not placed properly, it may not prevent pregnancy or it may be difficult or impossible to remove. After you receive IMPLANON™, check that it is in place by pressing your fingertips over the skin in your arm where IMPLANON™ was placed. You should be able to feel the IMPLANON™ rod.
The most common side effect of IMPLANON™ is a change in your menstrual periods. Expect your menstrual period to be irregular and unpredictable throughout the time you are using IMPLANON™. You may have more bleeding, less bleeding, or no bleeding. The time between periods may vary, and in between periods you may have spotting.
What is IMPLANON™?
IMPLANON™ is a type of birth control for women. It is a flexible plastic rod the size of a matchstick that is put under the skin of your arm. IMPLANON™ contains a hormone called etonogestrel. You can use a single IMPLANON™ rod for up to three years. Because IMPLANON™ does not contain estrogen, your healthcare provider may recommend IMPLANON™ even if you cannot use estrogen.

What if I need birth control for more than three years?
You must have IMPLANON™ removed after three years. If you want to continue using IMPLANON™, your healthcare provider can put a new IMPLANON™ under your skin after taking out the old one.
What if I change my mind about birth control?
Your healthcare provider can remove IMPLANON™ at any time. If you want to become pregnant after IMPLANON™ removal, your ability to get pregnant may return quickly. If you don’t want to get pregnant, you should start another birth control method right away.
How does IMPLANON™ work?
IMPLANON™ prevents pregnancy in several ways. The most important way is by stopping release of an egg from your ovary. IMPLANON™ also changes the mucus in your cervix and this change may keep sperm from reaching the egg. Also, IMPLANON™ changes the lining of your uterus.
How well does IMPLANON™ work?
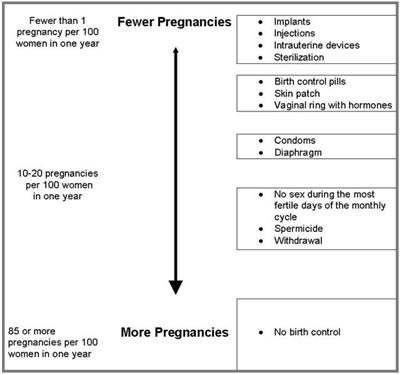
If IMPLANON™ is inserted correctly, your chance of getting pregnant is very low (less than 1 pregnancy per 100 women who use IMPLANON for one year). It is not known if IMPLANON™ is as effective in very overweight women because studies did not include many overweight women.
The following chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who use different methods of birth control. Each box on the chart contains a list of birth control methods that are similar in effectiveness. The most effective methods are at the top of the chart. The box on the bottom of the chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who do not use birth control and are trying to get pregnant.
Who should not use IMPLANON™?
Do not use IMPLANON™ if you
- are pregnant or think you may be pregnant
- have, or have had serious blood clots, such as blood clots in your legs (deep venous thrombosis), lungs (pulmonary embolism), eyes (retinal thrombosis), heart (heart attack), or head (stroke)
- have unexplained vaginal bleeding
- have liver disease
- have breast cancer, now or in the past
- are allergic to anything in IMPLANON™
Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had any of the conditions just listed. Your healthcare provider can suggest another method of birth control.
In addition, talk to your healthcare provider about using IMPLANON™ if you have or had
- diabetes
- high cholesterol or triglycerides
- headaches
- seizures or epilepsy
- gallbladder or kidney disease
- depression
- high blood pressure
- allergic reaction to anesthetics or antiseptics. These medicines will be used when IMPLANON™ is inserted into your arm.
If you have any of these conditions, your healthcare provider can explain what to do.
How do I use IMPLANON™?
Your healthcare provider will insert (or remove) IMPLANON™ in a minor surgical procedure in his or her office. IMPLANON™ is inserted just under the skin on the inner side of your upper arm.
The timing of insertion is important. Depending on your history, your healthcare provider may ask you to
- have a pregnancy test before insertion
- schedule the insertion at a specific time of your cycle (for example, within the first days of your regular menstrual bleeding)
- use a backup method of birth control, such as condoms, for seven days after IMPLANON™ insertion
Both you and your healthcare provider should check that IMPLANON™ is in your arm by feeling the IMPLANON™ implant.
If you and your healthcare provider cannot feel IMPLANON™, use a non-hormonal birth control method such as condoms until your healthcare provider confirms that IMPLANON™ is in place. You may need special tests to check that IMPLANON™ is in place or to help find IMPLANON™ when it is time to take it out.
You will be asked to review and sign a consent form prior to inserting IMPLANON™. You will also get a USER CARD to keep at home with your health records. Your healthcare provider will fill out the insertion and removal dates. Keep track of the removal date and schedule an appointment for removal with your healthcare provider on or before the removal date.
The insertion site is covered with two bandages. Leave the top bandage on for 24 hours. Keep the smaller bandage dry, clean, and in place for three to five days.
Be sure to have checkups as advised by your healthcare provider.
What are the most common side effects I can expect while using IMPLANON™?
Irregular and Unpredictable Bleeding
The most common side effect of IMPLANON™ is a change in your menstrual periods. In studies, about one out of ten women stopped using IMPLANON™ because of bleeding problems. Expect your menstrual periods to be irregular and unpredictable throughout the time you are using IMPLANON™. You may have more bleeding, less bleeding, or no bleeding. The time between periods may vary, and in between periods you may have spotting.
Talk with your healthcare provider if
- you think you may be pregnant
- your vaginal bleeding is heavy and prolonged
Besides irregular bleeding, the most frequent side effects that caused women to stop using IMPLANON™ in studies were
- mood swings
- weight gain
- headache
- acne
- depression
The most common side effects reported by women using IMPLANON™ in clinical trials were
- irregular bleeding
- headache
- vaginitis (inflammation of the vagina)
- weight gain
- acne
- breast pain
- viral infections such as colds, sore throats, sinus infections, or flu-like symptoms
- stomach pain
- painful periods
- mood swings, nervousness, or depression
- back pain
- nausea
- dizziness
- pain
- pain at the site of insertion
Rare side effects that have been reported include: extra hair on your face and body, trouble using contact lenses, and spotty darkening of the skin, especially on the face. This is not a complete list of possible side effects. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have any side effects that concern you.
What are the possible risks of using IMPLANON™?
Complications of Insertion and Removal
Rarely, removal of IMPLANON™ is difficult or even impossible because IMPLANON™ is not where it should be. If IMPLANON™ cannot be removed, then the effects of IMPLANON™ will continue for a longer period of time.
Rarely, IMPLANON™ is not inserted at all due to a failed insertion, or the implant has fallen out of the needle, and then you may become pregnant. After insertion, and with direction from your healthcare provider, you should be able to feel IMPLANON™ under your skin. If you can’t feel IMPLANON™, tell your healthcare provider.
Some other problems related to insertion and removal are
- Pain, irritation, swelling, or bruising
- Scarring, including a thick scar called a keloid
- Infection
- IMPLANON™ breaks making it difficult to remove IMPLANON™
- Thick scar tissue forming around IMPLANON™ making removal difficult
- Rarely, expulsion of the implant
- Rarely, need for surgery in the hospital for removal of IMPLANON™
- Removals of deeply inserted implants can lead to scarring or complications
Ectopic Pregnancy
If you become pregnant while using IMPLANON™, you have a slightly higher chance that the pregnancy will be ectopic (occurring outside the womb) than do women who are not using birth control. Ectopic pregnancies can cause serious internal bleeding and even death.
Interaction with other Medications
Certain medicines may make IMPLANON™ less effective and you may need to use back-up non-hormone birth control. Tell your healthcare provider about any medicines you are taking, or intend to take, including over-the-counter medicines and prescription medicines such as: barbiturates, griseofulvin, rifampin, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, carbamazepine, felbamate, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, and modafinil. Herbal remedies such as St. John's Wort may also reduce the effectiveness of contraceptive drug products. This is not a complete list of drugs that may interact with IMPLANON™.
When you are using IMPLANON™, tell all of your healthcare providers that you have IMPLANON™.
Ovarian Cysts
Cysts on the ovaries usually go away without treatment. Sometimes surgery is needed.
Breast Cancer
It is not known whether IMPLANON™ changes a woman’s risk for breast cancer. If you have breast cancer now, or have had it in the past, do not use IMPLANON™ because some breast cancers are sensitive to hormones.
Blood Clots (Thrombosis)
It is not known whether IMPLANON™ changes a woman's risk for serious blood clots called thrombosis. Thrombosis is a side effect of birth control pills and pregnancy. Because IMPLANON™ contains one of the two hormones that are in birth control pills, thrombosis may be a side effect of IMPLANON™. There have been post-marketing reports of thrombosis among IMPLANON™ users.
Some examples of thrombosis are
- Legs (deep vein thrombosis)
- Lung (pulmonary embolism)
- Brain (stroke)
- Heart (heart attack)
- Eyes (blindness)
The risk of thrombosis is increased in women who smoke. If you smoke, you should quit. Your healthcare provider may be able to help.
Tell your healthcare provider at least four weeks before if you are going to have surgery or will need to be on bed rest. You have an increased chance of getting thrombosis during surgery or bed rest.
Other Risks
A few women who use birth control that contains hormones may get
- High blood pressure
- Gallbladder problems
- Rare cancerous or noncancerous liver tumors
When should I call my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the symptoms listed below. They may be signs of a serious problem:
- sharp chest pain, coughing blood, or sudden shortness of breath (possible clot in the lung)
- pain in the calf (back of lower leg; possible clot in the leg)
- crushing chest pain or heaviness in the chest (possible heart attack)
- sudden severe headache or vomiting, dizziness or fainting, problems with vision or speech, weakness, or numbness in an arm or leg (possible stroke)
- sudden partial or complete loss of vision (possible clot in the eye)
- yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice), especially with fever, tiredness, loss of appetite, dark colored urine, or light colored bowel movements (possible liver problems)
- severe pain, swelling, or tenderness in the abdomen (possibly indicating an ectopic pregnancy, a ruptured or twisted ovarian follicle, or gallbladder, or liver problems)
- breast lumps
- difficulty in sleeping, weakness, lack of energy, tiredness, or sadness (possible severe depression)
- heavy vaginal bleeding
What if I become pregnant while using IMPLANON™?
You should see your healthcare provider right away. It is important to remove IMPLANON™ and make sure that the pregnancy is not ectopic (occurring outside the womb). Based on experience with birth control pills, IMPLANON™ is not likely to cause birth defects.
Can I use IMPLANON™ when I am breast feeding?
Based on a small study, you may start IMPLANON™ if you are breastfeeding and if you delivered your baby more than four weeks ago. A small amount of the active substance of IMPLANON™ passes into the breast milk. The health of breast fed children whose mothers were using IMPLANON™ has been studied up to three years of age in a small number of children. No effects on the growth and development of the children were seen. If you are breast feeding and want to use IMPLANON™, talk with your healthcare provider.
What if I want to become pregnant or want to stop using IMPLANON™ for another reason before three years?
Your healthcare provider can remove IMPLANON™ at any time with a minor surgical procedure in the office. The information on your USER CARD may help your healthcare provider find IMPLANON™.
After removal, keep the removal site clean, dry, and bandaged for three to five days to lessen the chance of infection.
If you want to become pregnant, your ability to get pregnant usually returns quickly. Some women have become pregnant within days after removal of IMPLANON™. If you do not want to become pregnant, you should start another birth control method right away.
Additional Information
This leaflet contains important information about IMPLANON™. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider for information about IMPLANON™ that is written for healthcare providers. You may also call 1-877-IMPLANON (1-877-467-5266) or visit www.IMPLANON-USA.com
Manufactured for Organon USA Inc.
Roseland, NJ
07068
by N.V. Organon, Oss, The Netherlands
©
2006 Organon USA Inc.
PATIENT CONSENT FORM
I understand the Patient Labeling for IMPLANON™. I have discussed IMPLANON™ with my healthcare provider who answered all my questions. I understand that there are benefits as well as risks from using IMPLANON™. I understand that there are other birth control methods and that each has its own benefits and risks.
I also understand that this Patient Consent Form is important. I understand that I need to sign this form to show that I am making an informed and careful decision to use IMPLANON™, and that I have read and understand the following points.
- IMPLANON™ helps to keep me from getting pregnant.
- No contraceptive method is 100% effective, including IMPLANON™.
- IMPLANON™ is made of a hormone mixed in a plastic rod.
- It is important to have IMPLANON™ inserted at the right time of my menstrual cycle.
- After IMPLANON™ is inserted, I should check that it is in place by gently pressing my fingertips over the skin in my arm where IMPLANON™ was inserted. I should be able to feel the small rod.
- IMPLANON™ must be removed at the end of three years. IMPLANON™ can be removed sooner if I want.
- If I have trouble finding a healthcare provider to remove IMPLANON™, I can call (877) 467-5266 for help.
- IMPLANON™ is placed under the skin of my arm during a procedure done in my healthcare provider’s office. There is a slight risk of getting a scar or an infection from this procedure.
- Removal is usually a small office procedure. However, removal may be difficult. Rarely, IMPLANON™ cannot be found when it is time to remove it. Special procedures, including surgery in the hospital, may be needed. Difficult removals may cause pain and scarring. If IMPLANON™ cannot be found, its effects may continue.
- Most women have changes in their menstrual bleeding while using IMPLANON™. I also will likely have changes in my menstrual bleeding while using IMPLANON™. My bleeding may be irregular, lighter or heavier, or my bleeding may completely stop. If I think I am pregnant, I should see my healthcare provider as soon as possible.
- I understand the warning signs for problems with IMPLANON™. I should seek medical attention if any warning signs appear.
- I should tell all my healthcare providers that I am using IMPLANON™.
- I need to have a medical checkup regularly and at any time I am having problems.
- IMPLANON™ does not protect me from HIV infection (AIDS) or any other sexually transmitted disease.
After learning about IMPLANON™, I choose to use IMPLANON™.
________________________________________________
(Name
of Healthcare Provider)
________________________________________________ ________________
(Patient
Signature) (Date)
WITNESSED BY:
The patient above has signed
this consent in my presence after I counseled her and answered
her questions.
________________________________________________ ________________
(Healthcare
Provider
Signature) (Date)
I have provided an accurate translation of this
information to the patient whose signature appears above. She
has stated that she understands the information and has had an
opportunity to have her questions answered.
________________________________________________ ________________
(Signature
of
Translator) (Date)
| Implanon (etonogestrel) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revised: 09/2007Organon USA, Inc.