INTUNIV- guanfacine hydrochloride tablet, extended release
INTUNIV- guanfacine
Shire US Manufacturing Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use INTUNIV® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for INTUNIV® .
INTUNIV® (guanfacine) extended-release tablets Initial U.S. Approval: 1986 RECENT MAJOR CHANGESINDICATIONS AND USAGEINTUNIV® is a selective alpha2A-adrenergic receptor agonist indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) as monotherapy and as adjunctive therapy to stimulant medications. The efficacy of INTUNIV® is based on results of two 8 to 9 week monotherapy studies and one 9 week adjunctive study in combination with psychostimulants in children and adolescents (14.1). Maintenance treatment has not been systematically evaluated, and patients who are continued on longer-term treatment require periodic reassessment (1). DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONFor all patients (2.1):
Dose selection (2.2):
Discontinuation (2.4):
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSExtended-release tablets: 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg and 4 mg (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSHistory of hypersensitivity to INTUNIV®, its inactive ingredients, or other products containing guanfacine (e.g. TENEX®) (4). WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost common adverse reactions (≥5% and at least twice placebo rate) in the monotherapy trials: somnolence, fatigue, nausea, lethargy, and hypertension (6). Most common adverse reactions (≥5% and at least twice placebo rate) in the adjunctive trial: somnolence, fatigue, insomnia, dizziness, and abdominal pain (6). To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Shire US Inc. at 1-800-828-2088 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSHepatic or Renal Impairment: dose reduction may be required in patients with clinically significant impairment of hepatic or renal function (8.6). See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 06/2011 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
INTUNIV® is indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) as monotherapy and as adjunctive therapy to stimulant medications. The efficacy of INTUNIV® was studied for the treatment of ADHD in two controlled monotherapy clinical trials (8 and 9 weeks in duration) and one controlled adjunctive trial with psychostimulants (9 weeks in duration) in children and adolescents ages 6-17 who met DSM-IV® criteria for ADHD [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The effectiveness of INTUNIV® for longer-term use (more than 9 weeks) has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials.
A diagnosis of ADHD implies the presence of hyperactive-impulsive and/or inattentive symptoms that cause impairment and were present before the age of 7 years. The symptoms must cause clinically significant impairment, e.g., in social, academic, or occupational functioning, and be present in two or more settings, e.g., school (or work) and at home. The symptoms must not be better accounted for by another mental disorder. For the Inattentive Type, at least six of the following symptoms must have persisted for at least 6 months: lack of attention to details/careless mistakes; lack of sustained attention; poor listener; failure to follow through on tasks; poor organization; avoids tasks requiring sustained mental effort; loses things; easily distracted; forgetful. For the Hyperactive-Impulsive Type, at least six of the following symptoms must have persisted for at least 6 months: fidgeting/squirming; leaving seat; inappropriate running/climbing; difficulty with quiet activities; "on the go"; excessive talking; blurting answers; can't wait turn; intrusive. The Combined Type requires both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive criteria to be met.
Special Diagnostic Considerations
Specific etiology of this syndrome is unknown, and there is no single diagnostic test. Adequate diagnosis requires the use not only of medical but also of special psychological, educational, and social resources. Learning may or may not be impaired. The diagnosis must be based upon a complete history and evaluation of the patient and not solely on the presence of the required number of DSM-IV® characteristics.
Need for Comprehensive Treatment Program
INTUNIV® is indicated as an integral part of a total treatment program for ADHD that may include other measures (psychological, educational, and social) for patients with this syndrome. Drug treatment may not be indicated for all patients with this syndrome. INTUNIV® is not intended for use in patients who exhibit symptoms secondary to environmental factors and/or other primary psychiatric disorders, including psychosis. Appropriate educational/vocational placement is essential and psychosocial intervention is often helpful. When remedial measures alone are insufficient, the decision to prescribe INTUNIV® will depend upon the physician's assessment of the chronicity and severity of the patient's symptoms and on the level of functional impairment.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
INTUNIV® is an extended-release tablet and should be dosed once daily. Tablets should not be crushed, chewed or broken before swallowing because this will increase the rate of guanfacine release. Do not administer with high fat meals, due to increased exposure.
Do not substitute for immediate-release guanfacine tablets on a mg-per-mg basis, because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles. INTUNIV® has a delayed Tmax, reduced Cmax and lower bioavailability compared to those of the same dose of immediate-release guanfacine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Dose Selection
If switching from immediate-release guanfacine, discontinue that treatment, and titrate with INTUNIV® according to the following recommended schedule.
Begin at a dose of 1 mg/day, and adjust in increments of no more than 1 mg/week, for both monotherapy and adjunctive therapy to a psychostimulant.
Maintain the dose within the range of 1 mg to 4 mg once daily, depending on clinical response and tolerability, for both monotherapy and adjunctive therapy to a psychostimulant. In clinical trials, patients were randomized or dose optomized to doses of 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg or 4 mg and received INTUNIV® once daily in the morning in monotherapy trials and once daily in the morning or the evening in the adjunctive therapy trial [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
In monotherapy trials, clinically relevant improvements were observed beginning at doses in the range 0.05-0.08 mg/kg once daily. Efficacy increased with increasing weight-adjusted dose (mg/kg). If well tolerated, doses up to 0.12 mg/kg once daily may provide additional benefit. Doses above 4 mg/day have not been systematically studied in controlled clinical trials.
In the adjunctive trial, the majority of subjects reached optimal doses in the 0.05-0.12 mg/kg/day range.
In clinical trials, there were dose-related and exposure-related risks for several clinically significant adverse reactions (hypotension, bradycardia, sedative events). Thus, consideration should be given to dosing INTUNIV® on a mg/kg basis, in order to balance the exposure-related potential benefits and risks of treatment.
2.3 Maintenance Treatment
The effectiveness of INTUNIV® for longer-term use (more than 9 weeks) has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials. Therefore the physician electing to use INTUNIV® for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
2.4 Discontinuation
In a pharmacodynamic study in healthy young adult volunteers receiving INTUNIV® (4 mg once daily) or placebo, the effects of abrupt discontinuation were compared to tapering. There were greater mean increases in systolic and diastolic blood pressure and heart rate after abrupt discontinuation of INTUNIV®, but these changes generally reflected a return to original baseline and were not meaningfully different for the two discontinuation strategies. However, infrequent, transient elevations in blood pressure above original baseline (i.e., rebound) have been reported to occur upon abrupt discontinuation of guanfacine. To minimize these effects, the dose should generally be tapered in decrements of no more than 1 mg every 3 to 7 days.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg and 4 mg extended-release tablets
| 1 mg | 2 mg | 3 mg | 4 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | White/off-white | White/off-white | Green | Green |
| Shape | Round | Caplet | Round | Caplet |
| Debossment (top/bottom) | 503 / 1mg | 503 / 2mg | 503 / 3mg | 503 / 4mg |
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to INTUNIV®, its inactive ingredients [see Description (11)], or other products containing guanfacine (e.g. TENEX®) should not take INTUNIV®.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypotension, Bradycardia, and Syncope
Treatment with INTUNIV® can cause decreases in blood pressure and heart rate. In the monotherapy, pediatric, short-term (8-9 weeks), controlled trials, the maximum mean changes from baseline in systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and pulse were -5 mm Hg, -3 mm Hg, and -6 bpm, respectively, for all dose groups combined (generally one week after reaching target doses of 1 mg/day, 2 mg/day, 3 mg/day or 4 mg/day). These changes were dose dependent. Decreases in blood pressure and heart rate were usually modest and asymptomatic; however, hypotension and bradycardia can occur. Hypotension was reported as an adverse event for 7% of the INTUNIV® group and 3% of the placebo group. This includes orthostatic hypotension, which was reported for 1% of the INTUNIV® group and none in the placebo group. In the adjunctive trial, hypotension (3%) and bradycardia (2%) were observed in patients treated with INTUNIV® as compared to none in the placebo group. In long-term, open label studies, (mean exposure of approximately 10 months), maximum decreases in systolic and diastolic blood pressure occurred in the first month of therapy. Decreases were less pronounced over time. Syncope occurred in 1% of pediatric subjects in the clinical program. The majority of these cases occurred in the long-term, open-label studies.
Measure heart rate and blood pressure prior to initiation of therapy, following dose increases, and periodically while on therapy. Use INTUNIV® with caution in patients with a history of hypotension, heart block, bradycardia, or cardiovascular disease, because it can decrease blood pressure and heart rate. Use caution in treating patients who have a history of syncope or may have a condition that predisposes them to syncope, such as hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, or dehydration. Use INTUNIV® with caution in patients treated concomitantly with antihypertensives or other drugs that can reduce blood pressure or heart rate or increase the risk of syncope. Advise patients to avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated.
5.2 Sedation and Somnolence
Somnolence and sedation were commonly reported adverse reactions in clinical studies (38% for INTUNIV® vs. 12% for placebo in monotherapy studies and 18% for INTUNIV® vs. 7% for placebo in the adjunctive study) in children and adolescents with ADHD, especially during initial use [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Before using INTUNIV® with other centrally active depressants (such as phenothiazines, barbiturates, or benzodiazepines), consider the potential for additive sedative effects. Caution patients against operating heavy equipment or driving until they know how they respond to treatment with INTUNIV®. Advise patients to avoid use with alcohol.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labelling:
- Hypotension, bradycardia, and syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Sedation and somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Monotherapy Trials
The most commonly observed adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5% and at least twice the rate for placebo) in the monotherapy trials with INTUNIV® were: somnolence, fatigue, nausea, lethargy, and hypotension.
Twelve percent (12%) of patients receiving INTUNIV® discontinued from the monotherapy clinical studies due to adverse events, compared to 4% in the placebo group. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of INTUNIV®-treated patients from the studies were somnolence/sedation (6%) and fatigue (2%). Less common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation (occurring in approximately 1% of patients) included: hypotension, headache, and dizziness.
Adjunctive Trial
The most commonly observed adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5% and at least twice the rate for placebo) in the adjunctive trial with INTUNIV® were: somnolence, fatigue, insomnia, dizziness, and abdominal pain.
Three percent of patients receiving INTUNIV® discontinued from the adjunctive clinical study due to adverse events, compared to 1% in the placebo group.
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Short Term Monotherapy Clinical Studies
Common Adverse Reactions - Two short-term, placebo-controlled, double-blind pivotal studies (Studies 1 and 2) were conducted in children and adolescents with ADHD, using fixed doses of INTUNIV® (1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg/day). The most commonly reported adverse reactions (occurring in ≥ 2% of patients) that were considered drug-related and reported in a greater percentage of patients taking INTUNIV® compared to patients taking placebo are shown in Table 1. Adverse reactions that were dose-related include: somnolence/sedation, abdominal pain, dizziness, hypotension, dry mouth and constipation.
| Table 1: Percentage of Patients Experiencing Common (≥2%) Adverse Reactions in Short-Term Monotherapy Studies 1 and 2 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | All Doses of INTUNIV® (N=513) | Placebo
(N=149) |
| Somnolencea | 38% | 12% |
| Headache | 24% | 19% |
| Fatigue | 14% | 3% |
| Abdominal painb | 11% | 9% |
| Hypotensionc | 7% | 3% |
| Nausea | 6% | 2% |
| Lethargy | 6% | 3% |
| Dizziness | 6% | 4% |
| Irritability | 6% | 4% |
| Decreased appetite | 5% | 3% |
| Dry mouth | 4% | 1% |
| Constipation | 3% | 1% |
|
a: The somnolence term includes somnolence, sedation, and hypersomnia. b: The abdominal pain term includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, and abdominal pain lower. c: The hypotension term includes hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, and decreased blood pressure. |
||
Short Term Adjunctive Clinical Study
A 9-week, placebo-controlled, double-blind, dose-optimized pivotal study (Study 3) was conducted in children and adolescents aged 6-17 years with a diagnosis of ADHD who were identified as having a sub-optimal response to psychostimulants. Patients received INTUNIV® (1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg/day) or placebo, dosed in the morning or in the evening, in combination with their morning dose of psychostimulant. The most commonly reported adverse reactions (occurring in ≥ 2% of patients in the overall INTUNIV® group) that were reported in a greater percentage of patients taking INTUNIV® compared to patients taking placebo are shown in Table 2.
| Table 2: Percentage of Patients Experiencing Common (≥ 2%) Adverse Reactions in Short-Term Adjunctive Study 3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction Term | All Doses of INTUNIV®
(N=302)a | Placebo
(N=153) |
| Headache | 21% | 13% |
| Somnolenceb | 18% | 7% |
| Insomniac | 12% | 6% |
| Fatigue | 10% | 3% |
| Abdominal paind | 10% | 3% |
| Dizziness | 8% | 4% |
| Decreased appetite | 7% | 4% |
| Nausea | 5% | 3% |
| Diarrhea | 4% | 1% |
| Hypotensione | 3% | 0% |
| Affect lability | 2% | 1% |
| Bradycardia | 2% | 0% |
| Constipation | 2% | 0% |
| Dry mouth | 2% | 0% |
|
a: The morning and evening dose groups of INTUNIV® are combined. b: The somnolence term includes somnolence, sedation, and hypersomnia. c: The insomnia term includes insomnia, initial insomnia, and middle insomnia. d: The abdominal pain term includes abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, and abdominal pain lower. e: The hypotension term includes hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, and decreased blood pressure. |
||
Effects on Height, Weight, and Body Mass Index (BMI)
Patients taking INTUNIV® demonstrated similar growth compared to normative data. Patients taking INTUNIV® had a mean increase in weight of 0.5 kg (1 lb) compared to those receiving placebo over a comparative treatment period. Patients receiving INTUNIV® for at least 12 months in open-label studies gained an average of 8 kg (17 lbs) in weight and 8 cm (3 in) in height. The height, weight, and BMI percentile remained stable in patients at 12 months in the long-term studies compared to when they began receiving INTUNIV®.
Laboratory Tests
In short and long-term studies, no clinically important effects were identified on any laboratory parameters.
Effects on Heart Rate and QT Interval
The effect of two dose levels of immediate-release guanfacine (4 mg and 8 mg) on the QT interval was evaluated in a double-blind, randomized, placebo- and active-controlled, cross-over study in healthy adults.
A dose-dependent decrease in heart rate was observed during the first 12 hours, at time of maximal concentrations. The mean change in heart rate was -13 bpm at 4 mg and -22 bpm at 8 mg.
An apparent increase in mean QTc was observed for both doses. However, guanfacine does not appear to interfere with cardiac repolarization of the form associated with pro-arrhythmic drugs. This finding has no known clinical relevance.
Other Adverse Reactions Observed in Clinical Studies
Table 3 includes additional adverse reactions observed in short-term, placebo-controlled and long-term, open-label clinical studies not included elsewhere in section 6.1, listed by organ system.
The mean duration of exposure of the 446 patients in two 2-year, open-label long-term studies was approximately 10 months. The percentage of patients at each dose upon completion or early withdrawal from the studies was 37% (n=164) for 4 mg, 33% (n=149) for 3 mg, 27% (n=119) for 2 mg, and 3% (n=14) for 1 mg, respectively. The number of patients at each dose (prior to tapering) that completed the 2-year studies was n=27 for 4 mg, n=24 for 3 mg, n=14 for 2 mg, and n=2 for 1 mg, respectively.
| Table 3: Other adverse reactions observed in clinical studies | |
|---|---|
| Body System | Adverse Reactions |
| Cardiac | Atrioventricular block, sinus arrhythmia |
| Gastrointestinal | Dyspepsia, stomach discomfort, vomiting |
| General | Asthenia, chest pain |
| Immune System Disorders | Hypersensitivity |
| Investigations | Increased alanine amino transferase, increased blood pressure, increased weight |
| Nervous system | Convulsion, postural dizziness, syncope |
| Psychiatric | Agitation, anxiety, depression, nightmare |
| Renal | Increased urinary frequency, enuresis |
| Respiratory | Asthma |
| Vascular | Hypertension, pallor |
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP3A4/5 Inhibitors
Use caution when INTUNIV® is administered to patients taking ketoconazole and other strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors, since elevation of plasma guanfacine concentration increases the risk of adverse events such as hypotension, bradycardia, and sedation. There was a substantial increase in the rate and extent of guanfacine exposure when administered with ketoconazole; the guanfacine exposure increased 3-fold (AUC).
7.2 CYP3A4 Inducers
When patients are taking INTUNIV® concomitantly with a CYP3A4 inducer, an increase in the dose of INTUNIV® within the recommended dose range may be considered. There was a significant decrease in the rate and extent of guanfacine exposure when co-administered with rifampin, a CYP3A4 inducer. The exposure to guanfacine decreased by 70% (AUC).
7.3 Valproic Acid
Co-administration of guanfacine and valproic acid can result in increased concentrations of valproic acid. The mechanism of this interaction is unknown, although both guanfacine (via a Phase I metabolite, 3-hydroxy guanfacine) and valproic acid are metabolized by glucuronidation, possibly resulting in competitive inhibition. When INTUNIV® is co-administered with valproic acid, monitor patients for potential additive CNS effects, and consider monitoring serum valproic acid concentrations. Adjustments in the dose of valproic acid may be indicated when co-administered with INTUNIV®.
7.4 Antihypertensive Drugs
Use caution when INTUNIV® is administered concomitantly with antihypertensive drugs, due to the potential for additive pharmacodynamic effects. (e.g., hypotension, syncope) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.5 CNS Depressant Drugs
Caution should be exercised when INTUNIV® is administered concomitantly with CNS depressant drugs (e.g. alcohol, sedative/hypnotics, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and antipsychotics) due to the potential for additive pharmacodynamic effects (e.g., sedation, somnolence) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7.6 Oral Methylphenidate
In a drug interaction study, (N=35) neither INTUNIV® (4 mg) nor CONCERTA® (methylphenidate HCl) (36 mg) were found to affect the pharmacokinetics of the other drug when co-administered.
7.7 Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate
In a drug interaction study, (N=40) administration of INTUNIV® in combination with VYVANSE® (lisdexamfetamine dimesylate) (50 mg) increased guanfacine maximum plasma concentration by 19% whereas exposure (area under the curve; AUC) was increased by 7%. These small changes are not expected to be clinically meaningful. In this study, no effect on d-amphetamine exposure was observed following co-administration of INTUNIV® and VYVANSE®.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B
Rat experiments have shown that guanfacine crosses the placenta. However, administration of guanfacine to rats and rabbits at 6 and 4 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose of 4 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis resulted in no evidence of harm to the fetus. Higher doses (20 times the maximum recommended human dose in both rabbits and rats) were associated with reduced fetal survival and maternal toxicity. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of guanfacine in pregnant women. INTUNIV® should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether guanfacine is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when INTUNIV® is administered to a nursing woman. Experiments with rats have shown that guanfacine is excreted in the milk.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of INTUNIV® in pediatric patients less than 6 years of age have not been established. For children and adolescents 6 years and older, efficacy beyond 9 weeks and safety beyond 2 years of treatment have not been established [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Clinical Studies (14)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
The safety and efficacy of INTUNIV® in geriatric patients have not been established.
8.6 Use in Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Renal Impairment
The impact of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of guanfacine in children was not assessed. In adult patients with impaired renal function, the cumulative urinary excretion of guanfacine and the renal clearance diminished as renal function decreased. In patients on hemodialysis, the dialysis clearance was about 15% of the total clearance. The low dialysis clearance suggests that the hepatic elimination (metabolism) increases as renal function decreases. It may be necessary to adjust the dose in patients with significant impairment of renal function.
Hepatic Impairment
The impact of hepatic impairment on PK of guanfacine in children was not assessed. Guanfacine in adults is cleared both by the liver and the kidney, and approximately 50% of the clearance of guanfacine is hepatic. It may be necessary to adjust the dose in patients with significant impairment of hepatic function.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms
Two cases of accidental overdose of INTUNIV® were reported in clinical trials in pediatric ADHD patients. These reports included adverse reactions of sedation and bradycardia in one patient and somnolence and dizziness in the other patient.
Post-marketing reports of guanfacine overdosage indicate that hypotension, drowsiness, lethargy, and bradycardia have been observed following overdose. Initial hypertension may develop early and may be followed by hypotension. Similar symptoms have been described in voluntary reports to the American Association of Poison Control Center's National Poison Data System. Miosis of the pupils may be noted on examination. No fatal overdoses of guanfacine have been reported in published literature.
Treatment
Consult a Certified Poison Control Center by calling 1-800-222-1222 for up to date guidance and advice.
Management of INTUNIV® overdose should include monitoring for and the treatment of initial hypertension, if that occurs, as well as hypotension, bradycardia, lethargy and respiratory depression. Children and adolescents who develop lethargy should be observed for the development of more serious toxicity including coma, bradycardia and hypotension for up to 24 hours, due to the possibility of delayed onset hypotension.
11 DESCRIPTION
INTUNIV® is a once-daily, extended-release formulation of guanfacine hydrochloride (HCl) in a matrix tablet formulation for oral administration only. The chemical designation is N-amidino-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl) acetamide monohydrochloride. The molecular formula is C9H9Cl2 N3O·HCl corresponding to a molecular weight of 282.55. The chemical structure is:
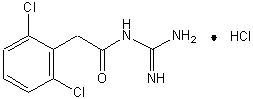
Guanfacine HCl is a white to off-white crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water (approximately 1 mg/mL) and alcohol and slightly soluble in acetone. The only organic solvent in which it has relatively high solubility is methanol (>30 mg/mL). Each tablet contains guanfacine HCl equivalent to 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, or 4 mg of guanfacine base. The tablets also contain hypromellose, methacrylic acid copolymer, lactose, povidone, crospovidone, microcrystalline cellulose, fumaric acid, and glyceryl behenate. In addition, the 3mg and 4mg tablets also contain green pigment blend PB-1763.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Guanfacine is a selective alpha2A-adrenergic receptor agonist. Guanfacine is not a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. The mechanism of action of guanfacine in ADHD is not known.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Guanfacine is a selective alpha2A-adrenergic receptor agonist in that it has a 15-20 times higher affinity for this receptor subtype than for the alpha2B or alpha2C subtypes.
Guanfacine is a known antihypertensive agent. By stimulating alpha2A-adrenergic receptors, guanfacine reduces sympathetic nerve impulses from the vasomotor center to the heart and blood vessels. This results in a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance and a reduction in heart rate.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Distribution
Guanfacine is readily absorbed and approximately 70% bound to plasma proteins independent of drug concentration. After oral administration of INTUNIV® the time to peak plasma concentration is approximately 5 hours in children and adolescents with ADHD.
Immediate-release guanfacine and INTUNIV® have different pharmacokinetic characteristics; dose substitution on a milligram for milligram basis will result in differences in exposure.
A comparison across studies suggests that the Cmax is 60% lower and AUC0-∞ 43% lower, respectively, for INTUNIV® compared to immediate-release guanfacine. Therefore, the relative bioavailability of INTUNIV® to immediate-release guanfacine is 58%. The mean pharmacokinetic parameters in adults following the administration of INTUNIV® 1 mg once daily and immediate-release guanfacine 1mg once daily are summarized in Table 4.
| Table 4: Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Adults | ||
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | INTUNIV®
1 mg once daily (n=52) | Immediate-release
guanfacine 1 mg once daily (n=12) |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 2.5 ± 0.6 |
| AUC0-∞ (ng.h/mL) | 32 ± 9 | 56 ± 15 |
| tmax (h) | 6.0 (4.0 - 8.0) | 3.0 (1.5-4.0) |
| t1/2 (h) | 18 ± 4 | 16 ± 3 |
| Note: Values are mean +/- SD, except for tmax which is median (range) | ||
Exposure to guanfacine was higher in children (ages 6-12) compared to adolescents (ages 13-17) and adults. After oral administration of multiple doses of INTUNIV® 4 mg, the Cmax was 10 ng/mL compared to 7 ng/mL and the AUC was 162 ng h/mL compared to 116 ng h/mL in children (ages 6-12) and adolescents (ages 13-17), respectively. These differences are probably attributable to the lower body weight of children compared to adolescents and adults.
The pharmacokinetics were affected by intake of food when a single dose of INTUNIV® 4 mg was administered with a high-fat breakfast. The mean exposure increased (Cmax ~75% and AUC ~40%) compared to dosing in a fasted state.
Dose Proportionality
Following administration of INTUNIV® in single doses of 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg to adults, Cmax and AUC0-∞ of guanfacine were proportional to dose.
Metabolism and Elimination
In vitro studies with human liver microsomes and recombinant CYP's demonstrated that guanfacine was primarily metabolized by CYP3A4. In pooled human hepatic microsomes, guanfacine did not inhibit the activities of the major cytochrome P450 isoenzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 or CYP3A4/5). Guanfacine is a substrate of CYP3A4/5 and exposure is affected by CYP3A4/5 inducers/inhibitors.
Renal and Hepatic Impairment
The impact of renal impairment on PK of guanfacine in children was not assessed [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenic effect of guanfacine was observed in studies of 78 weeks in mice or 102 weeks in rats at doses up to 6-7 times the maximum recommended human dose of 4 mg/day on a mg/ m2 basis.
Guanfacine was not genotoxic in a variety of test models, including the Ames test and an in vitro chromosomal aberration test; however, a marginal increase in numerical aberrations (polyploidy) was observed in the latter study.
No adverse effects were observed in fertility studies in male and female rats at doses up to 30 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/ m2 basis.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Safety and Efficacy Studies
The efficacy of INTUNIV® in the treatment of ADHD was established in 2 placebo-controlled monotherapy trials (Studies 1 and 2) and in 1 placebo-controlled adjunctive trial with psychostimulants (Study 3) in children and adolescents ages 6-17.
Studies 1 and 2: Fixed-dose INTUNIV® Monotherapy
Study 1 evaluated 2 mg, 3 mg and 4 mg of INTUNIV® dosed once daily in an 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, fixed dose design (n=345). Study 2 evaluated 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg and 4 mg of INTUNIV® dosed once daily in a 9-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, fixed-dose design (n=324). In Studies 1 and 2, patients were randomized to a fixed dose of INTUNIV®. Doses were titrated in increments of up to 1 mg/week. The lowest dose of 1 mg used in Study 2 was assigned only to patients less than 50 kg (110 lbs). Patients who weighed less than 25 kg (55 lbs) were not included in either study.
Signs and symptoms of ADHD were evaluated on a once weekly basis using the clinician administered and scored ADHD Rating Scale (ADHD-RS-IV), which includes both hyperactive/impulsive and inattentive subscales. The primary efficacy outcome was the change from baseline to endpoint in ADHD-RS-IV total scores. Endpoint was defined as the last post-randomization treatment week for which a valid score was obtained prior to dose tapering (up to Week 5 in Study 1 and up to Week 6 in Study 2).
The mean reductions in ADHD-RS-IV total scores at endpoint were statistically significantly greater for INTUNIV® compared to placebo for Studies 1 and 2. Placebo-adjusted changes from baseline were statistically significant for each of the 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg INTUNIV® randomized treatment groups in both studies, as well as the 1 mg INTUNIV® treatment group (for patients 55-110 lbs) that was included only in Study 2.
Dose-responsive efficacy was evident, particularly when data were examined on a weight-adjusted (mg/kg) basis. When evaluated over the dose range of 0.01-0.17 mg/kg/day, clinically relevant improvements were observed beginning at doses in the range 0.05-0.08 mg/kg/day. Doses up to 0.12 mg/kg/day were shown to provide additional benefit.
Controlled, monotherapy long-term efficacy studies (>9 weeks) have not been conducted.
In the monotherapy trials, subgroup analyses were performed to identify any differences in response based on gender or age (6-12 vs. 13-17). Analyses of the primary outcome did not suggest any differential responsiveness on the basis of gender. Analyses by age subgroup revealed a statistically significant treatment effect only in the 6-12 age subgroup. Due to the relatively small proportion of adolescent patients (ages 13-17) enrolled into these studies (approximately 25%), these data may not be sufficient to demonstrate efficacy in the adolescent subgroup. In these studies, patients were randomized to a fixed dose of INTUNIV® rather than optimized by body weight. Therefore, it is likely that some adolescent patients were randomized to a dose that resulted in relatively low plasma guanfacine concentrations compared to the younger sub-group. Over half (55%) of the adolescent patients received doses of 0.01-0.04mg/kg. In studies in which systematic pharmacokinetic data were obtained, there was a strong inverse correlation between body weight and plasma guanfacine concentrations.
Study 3: Flexible-dose INTUNIV® as Adjunctive Therapy to Psychostimulants
Study 3 evaluated 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg and 4 mg of INTUNIV® dosed once daily in an 9-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose optimization study. This study evaluated the safety and efficacy of INTUNIV®, dosed either in the morning or the evening, compared to placebo, when given in combination with a psychostimulant, in children and adolescents aged 6-17 years with a diagnosis of ADHD, with a sub-optimal response to stimulants (n=455). Subjects were started at the 1 mg INTUNIV® dose level and were titrated weekly over a 5-week dose optimization period to an optimal INTUNIV® dose not to exceed 4 mg/daybased on tolerability and clinical response. The dose was then maintained for a 3-week dose maintenance period before entry to 1 week of dose tapering. Subjects took INTUNIV® either in the morning or the evening while maintaining their current dose of psychostimulant treatment given each morning. Allowable psychostimulants in the study were ADDERALL XR®, VYVANSE®, CONCERTA®, FOCALIN XR®, RITALIN LA®, METADATE CD® or FDA-approved generic equivalents.
Symptoms of ADHD were evaluated on a weekly basis by clinicians using the ADHD Rating Scale (ADHD-RS-IV), which includes both hyperactive/impulsive and inattentive subscales. The primary efficacy outcome was the change from baseline to endpoint in ADHD-RS-IV total scores. Endpoint was defined as the last post-randomization treatment week prior to dose tapering for which a valid score was obtained (up to Week 8).
Mean reductions in ADHD-RS-IV total scores at endpoint were significantly greater for INTUNIV® given in combination with a psychostimulant compared to placebo given with a psychostimulant for Study 3, for both morning and evening INTUNIV® dosing. Nearly two-thirds (64.2%) of subjects reached optimal doses in the 0.05-0.12 mg/kg/day range.
Controlled adjunctive long-term efficacy studies (>9 weeks) have not been conducted.
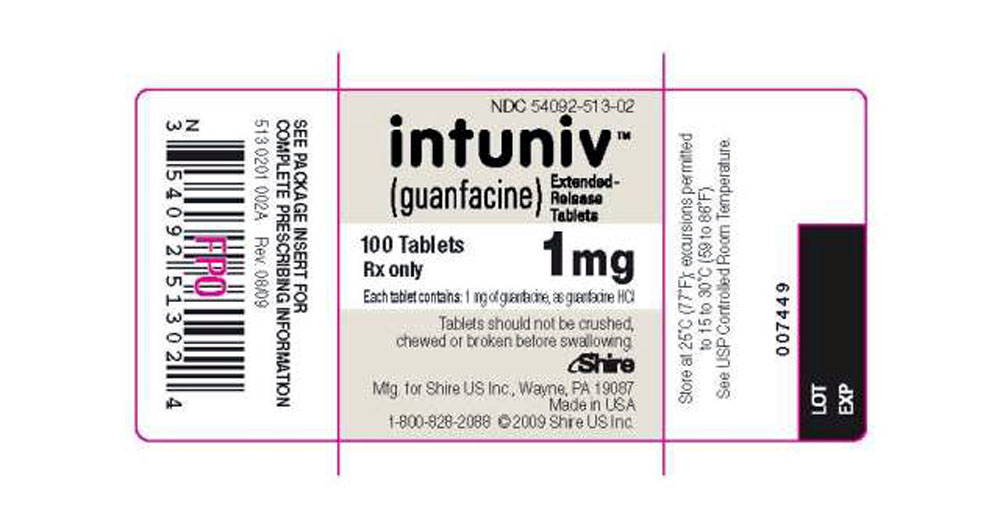
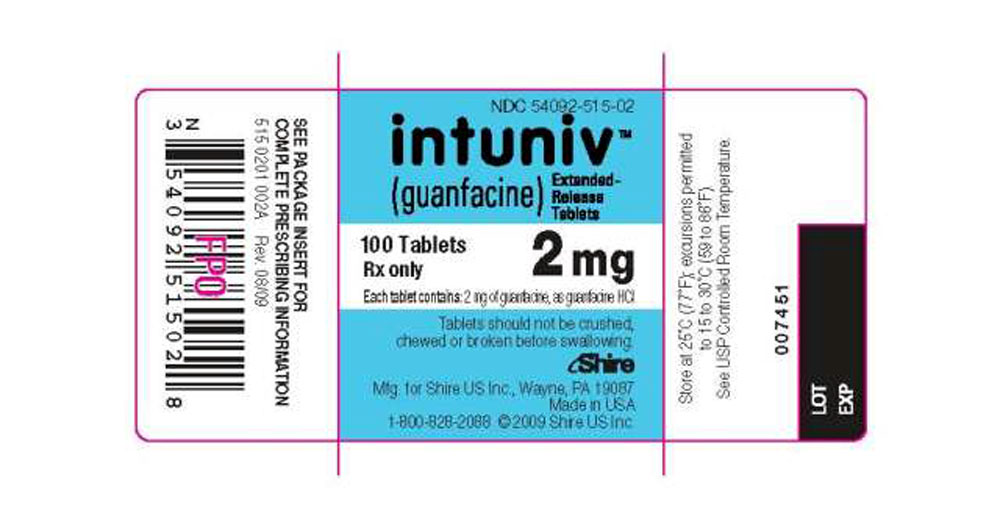
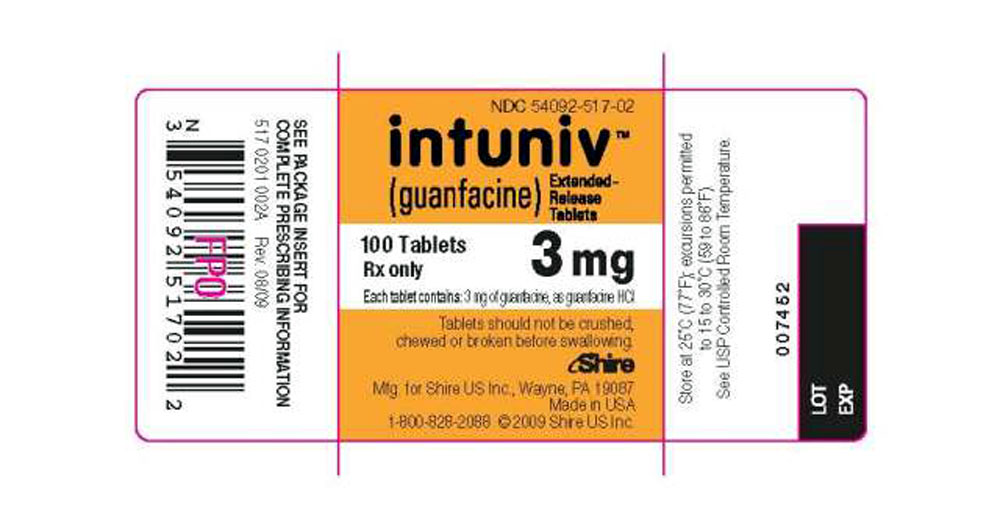
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
INTUNIV® is supplied in 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg strength extended-release tablets in 100 count bottles.
| 1 mg | 2 mg | 3 mg | 4 mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | White/off-white | White/off-white | Green | Green |
| Shape | Round | Caplet | Round | Caplet |
| Debossment (top/bottom) | 503 / 1mg | 503 / 2mg | 503 / 3mg | 503 / 4mg |
| NDC number | 54092-513-02 | 54092-515-02 | 54092-517-02 | 54092-519-02 |
Storage - Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
[See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling.]
17.1 Dosing and Administration
Instruct patients to swallow INTUNIV® whole with water, milk or other liquid. Tablets should not be crushed, chewed or broken prior to administration because this may increase the rate of release of the active drug. Patients should not take INTUNIV® together with a high-fat meal, since this can raise blood levels of INTUNIV®. Instruct the parent or caregiver to supervise the child or adolescent taking INTUNIV® and to keep the bottle of tablets out of reach of children.
Instruct patients on how to properly taper the medication, if the physician decides to discontinue treatment.
17.2 Adverse Reactions
Advise patients that sedation can occur, particularly early in treatment or with dose increases. Caution against operating heavy equipment or driving until they know how they respond to treatment with INTUNIV®. Headache and abdominal pain can also occur. If any of these symptoms persist, or other symptoms occur, the patient should be advised to discuss the symptoms with the physician.
Advise patients to avoid becoming dehydrated or overheated, and to avoid use with alcohol.
Patient Information
INTUNIV® (in-TOO-niv)
(guanfacine)
Extended-Release Tablets
Read the Patient Information that comes with INTUNIV® before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is INTUNIV®?
INTUNIV® is a prescription medicine used to treat the symptoms of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
INTUNIV® is not a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant.
INTUNIV® should be used as a part of a total treatment program for ADHD that may include counselling or other therapies.
It is not known if INTUNIV® is effective:
- for use longer than 9 weeks
It is not known if INTUNIV® is safe or effective:
- in children younger than 6 years old
- in adults
What should I tell my doctor before taking INTUNIV®?
Before you take INTUNIV®, tell your doctor if you:
- have heart problems or a low heart rate
- have fainted
- have low blood pressure
- have liver or kidney problems
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if INTUNIV® will harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. It is not known if INTUNIV® passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take INTUNIV® or breastfeed.
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
INTUNIV® may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how INTUNIV® works.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- ketoconazole
- medicines that can affect enzyme metabolism
- valproic acid
- high blood pressure medicine
- sedatives
- benzodiazepines
- barbiturates
- antipsychotics
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take INTUNIV®?
- Take INTUNIV® exactly as your doctor tells you.
- Your doctor may change your dose. Do not change your dose of INTUNIV® without talking to your doctor.
- Do not stop taking INTUNIV® without talking to your doctor.
- INTUNIV® should be taken 1 time a day, either alone or in combination with an ADHD stimulant medication that your doctor may prescribe. Your doctor will tell you when to take INTUNIV® and when to take your ADHD stimulant medication.
- INTUNIV® should be swallowed whole with a small amount of water, milk, or other liquid.
- Do not crush, chew, or break INTUNIV®. Tell your doctor if you can not swallow INTUNIV® whole.
- Do not take INTUNIV® with a high-fat meal.
- Your doctor will check your blood pressure and heart rate while you take INTUNIV®.
- If you take too much INTUNIV®, call your local Poison Control Center or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking INTUNIV®?
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how INTUNIV® affects you. INTUNIV® can slow your thinking and motor skills.
- Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking INTUNIV® until you talk with your doctor. INTUNIV® taken with alcohol or medicines that cause sleepiness or dizziness may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse.
What are the possible side effects of INTUNIV®?
INTUNIV® may cause serious side effects including:
- low blood pressure
- low heart rate
- fainting
- sleepiness
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of INTUNIV® include:
- sleepiness
- tiredness
- trouble sleeping
- low blood pressure
- nausea
- stomach pain
- dizziness
Tell the doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of INTUNIV®. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store INTUNIV®?
- Store INTUNIV® between 590F to 860F (15oC to 30oC)
Keep INTUNIV® and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about INTUNIV®
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information Leaflet. Do not use INTUNIV® for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give INTUNIV® to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about INTUNIV®. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about INTUNIV® that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.INTUNIV.com or call 1-800-828-2088.
What are the ingredients in INTUNIV®?
Active ingredient: guanfacine hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: hypromellose, methacrylic acid copolymer, lactose, povidone, crospovidone, microcrystalline cellulose, fumaric acid, and glycerol behenate. In addition, the 3mg and 4mg tablets also contain green pigment blend PB-1763.
Manufactured for Shire US Inc., Wayne, PA 19087.
INTUNIV® is a registered trademark of Shire LLC.
©2011 Shire Pharmaceuticals Inc.
This product is covered by US patents including 5,854,290; 6,287,599; 6,811,794.
Version: 06 2011
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 54092-513-02 - 1 mg 100 Count Bottle
NDC 54092-515-02 - 2 mg 100 Count Bottle
NDC 54092-517-02 - 3 mg 100 Count Bottle
NDC 54092-519-02 - 4 mg 100 Count Bottle
NDC 54092-513-03 - Physician Sample 1 mg 7 Count Bottle
NDC 54092-515-03 - Physician Sample 2 mg 7 Count Bottle
NDC 54092-517-03 - Physician Sample 3 mg 7 Count Bottle
| INTUNIV
guanfacine tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INTUNIV
guanfacine tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INTUNIV
guanfacine tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INTUNIV
guanfacine tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INTUNIV
guanfacine kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INTUNIV
guanfacine kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Shire US Manufacturing Inc. (964907406) |
| Registrant - Shire US Inc. (622467447) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
| Shire US Manufacturing Inc. | 964907406 | manufacture | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
| WellSpring Pharmaceutical Canada Corp. | 251086799 | pack | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
| DSM Pharmaceuticals Inc. | 076301910 | manufacture | |