GILENYA
-
fingolimod hydrochloride capsule
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
----------
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GILENYA is indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) to reduce the frequency of clinical exacerbations and to delay the accumulation of physical disability.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dose of GILENYA is 0.5 mg orally once daily. Patients should be observed for 6 hours after the first dose to monitor for signs and symptoms of bradycardia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Fingolimod doses higher than 0.5 mg are associated with a greater incidence of adverse reactions without additional benefit.
GILENYA can be taken with or without food.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
GILENYA is available as 0.5 mg hard capsules with a white opaque body and bright yellow cap imprinted with “FTY 0.5 mg” on the cap and two radial bands imprinted on the capsule body with yellow ink.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Bradyarrhythmia and Atrioventricular Blocks
Reduction in heart rate
Initiation of GILENYA treatment results in a decrease in heart rate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Observe all patients for a period of 6 hours for signs and symptoms of bradycardia. Should post-dose bradyarrhythmia-related symptoms occur, initiate appropriate management and continue observation until the symptoms have resolved.
To identify underlying risk factors for bradycardia and atrioventricular (AV) block, if a recent electrocardiogram (i.e. within 6 months) is not available, obtain one in patients using anti-arrhythmics including beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers, those with cardiac risk factors, as described below, and those who on examination have a slow or irregular heart beat prior to starting GILENYA.
Experience with GILENYA in patients receiving concurrent therapy with beta blockers or in those with a history of syncope is limited. GILENYA has not been studied in patients with sitting heart rate less than 55 bpm. GILENYA has not been studied in patients with second degree or higher AV block, sick sinus syndrome, prolonged QT interval, ischemic cardiac disease, or congestive heart failure. GILENYA has not been studied in patients with arrhythmias requiring treatment with Class Ia (e.g. quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic drugs. Class Ia and Class III antiarrhythmic drugs have been associated with cases of torsades de pointes in patients with bradycardia.
After the first dose of GILENYA, the heart rate decrease starts within an hour and the Day 1 decline is maximal at approximately 6 hours. Following the second dose a further decrease in heart rate may occur when compared to the heart rate prior to the second dose, but this change is of a smaller magnitude than that observed following the first dose. With continued dosing, the heart rate returns to baseline within one month of chronic treatment. The mean decrease in heart rate in patients on GILENYA 0.5 mg at 6 hours after the first dose was approximately 13 beats per minute (bpm). Heart rates below 40 bpm were rarely observed. Adverse reactions of bradycardia following the first dose were reported in 0.5% of patients receiving GILENYA 0.5 mg, but in no patient on placebo. Patients who experienced bradycardia were generally asymptomatic, but some patients experienced mild to moderate dizziness, fatigue, palpitations, and chest pain that resolved within the first 24 hours on treatment.
Atrioventricular blocks
Initiation of GILENYA treatment has resulted in transient AV conduction delays. In controlled clinical trials, adverse reactions of first degree AV block (prolonged PR interval on ECG) following the first dose were reported in 0.1% of patients receiving GILENYA 0.5 mg, but in no patient on placebo. Second degree AV blocks following the first dose were also identified in 0.1% of patients receiving GILENYA 0.5 mg, but in no patient on placebo. In a study of 698 patients with available 24-hour Holter monitoring data after their first dose (N=351 on GILENYA 0.5 mg and N=347 on placebo), second degree AV blocks, usually Mobitz type I (Wenckebach) were reported in 3.7% (N=13) of patients receiving GILENYA 0.5 mg and 2% (N=7) of patients on placebo. The conduction abnormalities were usually transient and asymptomatic, and resolved within the first 24 hours on treatment, but they occasionally required treatment with atropine or isoproterenol. One patient developed syncope and complete AV block following the first dose of fingolimod 1.25 mg (a dose higher than recommended) in an uncontrolled study.
Re-initiation of therapy following discontinuation
If GILENYA therapy is discontinued for more than two weeks the effects on heart rate and AV conduction may recur on reintroduction of GILENYA treatment and the same precautions as for initial dosing should apply.
5.2 Infections
Risk of infections
GILENYA causes a dose-dependent reduction in peripheral lymphocyte count to 20 - 30% of baseline values because of reversible sequestration of lymphocytes in lymphoid tissues. GILENYA may therefore increase the risk of infections, some serious in nature [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Before initiating treatment with GILENYA, a recent CBC (i.e. within 6 months) should be available. Consider suspending treatment with GILENYA if a patient develops a serious infection, and reassess the benefits and risks prior to re-initiation of therapy. Because the elimination of fingolimod after discontinuation may take up to two months, continue monitoring for infections throughout this period. Instruct patients receiving GILENYA to report symptoms of infections to a physician. Patients with active acute or chronic infections should not start treatment until the infection(s) is resolved.
Two patients died of herpetic infections during GILENYA controlled studies in the premarketing database (one disseminated primary herpes zoster and one herpes simplex encephalitis). In both cases, the patients were receiving a fingolimod dose (1.25 mg) higher than recommended for the treatment of MS (0.5 mg), and had received high dose corticosteroid therapy for suspected MS relapse. No deaths due to viral infections occurred in patients treated with GILENYA 0.5 mg in the premarketing database.
In MS controlled studies, the overall rate of infections (72%) and serious infections (2%) with GILENYA 0.5 mg was similar to placebo. However, bronchitis and, to a lesser extent, pneumonia were more common in GILENYA-treated patients.
Concomitant use with antineoplastic, immunosuppressive or immune modulating therapies
GILENYA has not been administered concomitantly with antineoplastic, immunosuppressive or immune modulating therapies used for treatment of MS. Concomitant use of GILENYA with any of these therapies would be expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Varicella zoster virus antibody testing/vaccination
As for any immune modulating drug, before initiating GILENYA therapy, patients without a history of chickenpox or without vaccination against varicella zoster virus (VZV) should be tested for antibodies to VZV. VZV vaccination of antibody-negative patients should be considered prior to commencing treatment with GILENYA, following which initiation of treatment with GILENYA should be postponed for 1 month to allow the full effect of vaccination to occur.
5.3 Macular Edema
In patients receiving GILENYA 0.5 mg, macular edema occurred in 0.4% of patients. An adequate ophthalmologic evaluation should be performed at baseline and 3-4 months after treatment initiation. If patients report visual disturbances at any time while on GILENYA therapy, additional ophthalmologic evaluation should be undertaken.
In MS controlled studies involving 1204 patients treated with GILENYA 0.5 mg and 861 patients treated with placebo, macular edema with or without visual symptoms was reported in 0.4% of patients treated with GILENYA 0.5 mg and 0.1% of patients treated with placebo; it occurred predominantly in the first 3-4 months of therapy. Some patients presented with blurred vision or decreased visual acuity, but others were asymptomatic and diagnosed on routine ophthalmologic examination. Macular edema generally improved or resolved with or without treatment after drug discontinuation, but some patients had residual visual acuity loss even after resolution of macular edema.
Continuation of GILENYA in patients who develop macular edema has not been evaluated. A decision on whether or not to discontinue GILENYA therapy should include an assessment of the potential benefits and risks for the individual patient. The risk of recurrence after rechallenge has not been evaluated.
Macular edema in patients with history of uveitis or diabetes mellitus
Patients with a history of uveitis and patients with diabetes mellitus are at increased risk of macular edema during GILENYA therapy. The incidence of macular edema is also increased in MS patients with a history of uveitis. The rate was approximately 20% in patients with a history of uveitis vs. 0.6% in those without a history of uveitis, in the combined experience with all doses of fingolimod. MS patients with diabetes mellitus or a history of uveitis should undergo an ophthalmologic evaluation prior to initiating GILENYA therapy and have regular follow-up ophthalmologic evaluations while receiving GILENYA therapy. GILENYA has not been tested in MS patients with diabetes mellitus.
5.4 Respiratory Effects
Dose-dependent reductions in forced expiratory volume over 1 second (FEV1) and diffusion lung capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) were observed in patients treated with GILENYA as early as 1 month after treatment initiation. At Month 24, the reduction from baseline in the percent of predicted values for FEV1 was 3.1% for GILENYA 0.5 mg and 2% for placebo. For DLCO, the reductions from baseline in percent of predicted values at Month 24 were 3.8% for GILENYA 0.5 mg and 2.7% for placebo. The changes in FEV1 appear to be reversible after treatment discontinuation. There is insufficient information to determine the reversibility of the decrease of DLCO after drug discontinuation. In MS controlled trials, dyspnea was reported in 5% of patients receiving GILENYA 0.5 mg and 4% of patients receiving placebo. Several patients discontinued GILENYA because of unexplained dyspnea during the extension (uncontrolled) studies. GILENYA has not been tested in MS patients with compromised respiratory function.
Spirometric evaluation of respiratory function and evaluation of DLCO should be performed during therapy with GILENYA if clinically indicated.
5.5 Hepatic Effects
Elevations of liver enzymes may occur in patients receiving GILENYA. Recent (i.e. within last 6 months) transaminase and bilirubin levels should be available before initiation of GILENYA therapy.
During clinical trials, 3-fold the upper limit of normal (ULN) or greater elevation in liver transaminases occurred in 8% of patients treated with GILENYA 0.5 mg, as compared to 2% of patients on placebo. Elevations 5-fold the ULN occurred in 2% of patients on GILENYA and 1% of patients on placebo. In clinical trials, GILENYA was discontinued if the elevation exceeded 5 times the ULN. Recurrence of liver transaminase elevations occurred with rechallenge in some patients, supporting a relationship to drug. The majority of elevations occurred within 6-9 months. Serum transaminase levels returned to normal within approximately 2 months after discontinuation of GILENYA.
Liver enzymes should be monitored in patients who develop symptoms suggestive of hepatic dysfunction, such as unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, anorexia, or jaundice and/or dark urine. GILENYA should be discontinued if significant liver injury is confirmed. Patients with pre-existing liver disease may be at increased risk of developing elevated liver enzymes when taking GILENYA.
Because GILENYA exposure is doubled in patients with severe hepatic impairment, these patients should be closely monitored, as the risk of adverse reactions is greater [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.6 Fetal Risk
Based on animal studies, GILENYA may cause fetal harm. Because it takes approximately 2 months to eliminate GILENYA from the body, women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception to avoid pregnancy during and for 2 months after stopping GILENYA treatment.
5.7 Blood Pressure Effects
In MS clinical trials, patients treated with GILENYA 0.5 mg had an average increase of approximately 2 mmHg in systolic pressure, and approximately 1 mmHg in diastolic pressure, first detected after approximately 2 months of treatment initiation, and persisting with continued treatment. In controlled studies involving 854 MS patients on GILENYA 0.5 mg and 511 MS patients on placebo, hypertension was reported as an adverse reaction in 5% of patients on GILENYA 0.5 mg and in 3% of patients on placebo. Blood pressure should be monitored during treatment with GILENYA.
5.8 Immune System Effects Following GILENYA Discontinuation
Fingolimod remains in the blood and has pharmacodynamic effects, including decreased lymphocyte counts, for up to 2 months following the last dose of GILENYA. Lymphocyte counts generally return to the normal range within 1-2 months of stopping therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Because of the continuing pharmacodynamic effects of fingolimod, initiating other drugs during this period warrants the same considerations needed for concomitant administration (e.g., risk of additive immunosuppressant effects) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
- Bradyarrhythmia and atrioventricular blocks [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Macular edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Respiratory effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hepatic effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
The most frequent adverse reactions (incidence ≥10% and > placebo) for GILENYA 0.5 mg were headache, influenza, diarrhea, back pain, liver enzyme elevations, and cough. The only adverse event leading to treatment interruption reported at an incidence >1% for GILENYA 0.5 mg was serum transaminase elevations (3.8%).
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
A total of 1703 patients on GILENYA (0.5 or 1.25 mg once daily) constituted the safety population in the 2 controlled studies in patients with relapsing remitting MS (RRMS) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Study 1 was a 2-year placebo-controlled clinical study in 1272 MS patients treated with GILENYA 0.5 mg (n=425), GILENYA 1.25 mg (n=429) or placebo (n= 418).
| Primary System Organ Class
Preferred Term | GILENYA 0.5 mg
N=425 % | Placebo
N=418 % |
| Infections | ||
| Influenza viral infections | 13 | 10 |
| Herpes viral infections | 9 | 8 |
| Bronchitis | 8 | 4 |
| Sinusitis | 7 | 5 |
| Gastroenteritis | 5 | 3 |
| Tinea infections | 4 | 1 |
| Cardiac Disorders | ||
| Bradycardia | 4 | 1 |
| Nervous system disorders | ||
| Headache | 25 | 23 |
| Dizziness | 7 | 6 |
| Paresthesia | 5 | 4 |
| Migraine | 5 | 1 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| Diarrhea | 12 | 7 |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
| Asthenia | 3 | 1 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Back pain | 12 | 7 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||
| Alopecia | 4 | 2 |
| Eczema | 3 | 2 |
| Pruritus | 3 | 1 |
| Investigations | ||
| ALT/AST increased | 14 | 5 |
| GGT increased | 5 | 1 |
| Weight decreased | 5 | 3 |
| Blood triglycerides increased | 3 | 1 |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | ||
| Cough | 10 | 8 |
| Dyspnea | 8 | 5 |
| Psychiatric disorders | ||
| Depression | 8 | 7 |
| Eye disorders | ||
| Vision blurred | 4 | 1 |
| Eye pain | 3 | 1 |
| Vascular disorders | ||
| Hypertension | 6 | 4 |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | ||
| Lymphopenia | 4 | 1 |
| Leukopenia | 3 | <1 |
Adverse reactions in Study 2, a 1-year active-controlled (vs. interferon beta-1a, n=431) study including 849 patients with MS treated with fingolimod, were generally similar to those in Study 1.
Vascular Events
Vascular events, including ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, peripheral arterial occlusive disease and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome were reported in premarketing clinical trials in patients who received GILENYA doses (1.25-5 mg) higher than recommended for use in MS. No vascular events were observed with GILENYA 0.5 mg in the premarketing database.
Lymphomas
Cases of lymphoma (cutaneous T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders or diffuse B-cell lymphoma) were reported in premarketing clinical trials in MS patients receiving GILENYA at, or above, the recommended dose of 0.5 mg. Based on the small number of cases and short duration of exposure, the relationship to GILENYA remains uncertain.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Class Ia or Class III antiarrhythmic drugs
GILENYA has not been studied in patients with arrhythmias requiring treatment with Class Ia (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic drugs. Class Ia and Class III antiarrhythmic drugs have been associated with cases of torsades de pointes in patients with bradycardia. Since initiation of GILENYA treatment results in decreased heart rate, patients on Class Ia or Class III antiarrhythmic drugs should be closely monitored [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Ketoconazole
The blood levels of fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate are increased by 1.7-fold when coadministered with ketoconazole. Patients who use GILENYA and systemic ketoconazole concomitantly should be closely monitored, as the risk of adverse reactions is greater.
Vaccines
Vaccination may be less effective during and for up to 2 months after discontinuation of treatment with GILENYA [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. The use of live attenuated vaccines should be avoided during and for 2 months after treatment with GILENYA because of the risk of infection.
Antineoplastic, immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapies
Antineoplastic, immunosuppressive or immune modulating therapies are expected to increase the risk of immunosuppression. Use caution when switching patients from long-acting therapies with immune effects such as natalizumab or mitoxantrone.
Heart rate-lowering drugs (e.g., beta blockers or diltiazem)
Experience with GILENYA in patients receiving concurrent therapy with beta blockers is limited. These patients should be carefully monitored during initiation of therapy. When GILENYA is used with atenolol, there is an additional 15% reduction of heart rate upon GILENYA initiation, an effect not seen with diltiazem [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Laboratory test interaction
Because GILENYA reduces blood lymphocyte counts via redistribution in secondary lymphoid organs, peripheral blood lymphocyte counts cannot be utilized to evaluate the lymphocyte subset status of a patient treated with GILENYA. A recent CBC should be available before initiating treatment with GILENYA.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. In oral studies conducted in rats and rabbits, fingolimod demonstrated developmental toxicity, including teratogenicity (rats) and embryolethality, when given to pregnant animals. In rats, the highest no-effect dose was less than the recommended human dose (RHD) of 0.5 mg/day on a body surface area (mg/m2) basis. The most common fetal visceral malformations in rats included persistent truncus arteriosus and ventricular septal defect. The receptor affected by fingolimod (sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor) is known to be involved in vascular formation during embryogenesis. Because it takes approximately 2 months to eliminate fingolimod from the body, potential risks to the fetus may persist after treatment ends [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8)]. GILENYA should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Pregnancy Registry
A pregnancy registry has been established to collect information about the effect of GILENYA use during pregnancy. Physicians are encouraged to enroll pregnant patients, or pregnant women may enroll themselves in the GILENYA pregnancy registry by calling 1-877-598-7237.
Animal Data
When fingolimod was orally administered to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis (0, 0.03, 0.1, and 0.3 mg/kg/day or 0, 1, 3, and 10 mg/kg/day), increased incidences of fetal malformations and embryo-fetal deaths were observed at all but the lowest dose tested (0.03 mg/kg/day), which is less than the RHD on a mg/m2 basis. Oral administration to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis (0, 0.5, 1.5, and 5 mg/kg/day) resulted in increased incidences of embryo-fetal mortality and fetal growth retardation at the mid and high doses. The no-effect dose for these effects in rabbits (0.5 mg/kg/day) is approximately 20 times the RHD on a mg/m2 basis.
When fingolimod was orally administered to female rats during pregnancy and lactation (0, 0.05, 0.15, and 0.5 mg/kg/day), pup survival was decreased at all doses and a neurobehavioral (learning) deficit was seen in offspring at the high dose. The low-effect dose of 0.05 mg/kg/day is similar to the RHD on a mg/m2 basis.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
The effects of GILENYA on labor and delivery are unknown.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Fingolimod is excreted in the milk of treated rats. It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from GILENYA, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of GILENYA in pediatric patients with MS below the age of 18 have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical MS studies of GILENYA did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients. GILENYA should be used with caution in patients aged 65 years and over, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, or renal, function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Because fingolimod, but not fingolimod-phosphate, exposure is doubled in patients with severe hepatic impairment, patients with severe hepatic impairment should be closely monitored, as the risk of adverse reactions may be greater [See Warnings and Precautions (5.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment.
8.7 Renal Impairment
The blood level of some GILENYA metabolites is increased (up to 13-fold) in patients with severe renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The toxicity of these metabolites has not been fully explored. The blood level of these metabolites has not been assessed in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment.
10 OVERDOSAGE
No cases of overdosage have been reported. However, single doses up to 80-fold the recommended dose (0.5 mg) resulted in no clinically significant adverse reactions. At 40 mg, 5 of 6 subjects reported mild chest tightness or discomfort which was clinically consistent with small airway reactivity.
Neither dialysis nor plasma exchange results in removal of fingolimod from the body.
11 DESCRIPTION
Fingolimod is a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator.
Chemically, fingolimod is 2-amino-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]propan-1,3-diol hydrochloride. Its structure is shown below:
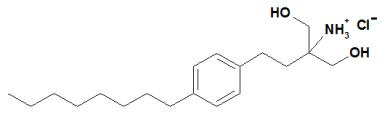
Fingolimod hydrochloride is a white to practically white powder that is freely soluble in water and alcohol and soluble in propylene glycol. It has a molecular weight of 343.93.
GILENYA is provided as 0.5 mg hard gelatin capsules for oral use. Each capsule contains 0.56 mg of fingolimod hydrochloride, equivalent to 0.5 mg of fingolimod.
Each GILENYA 0.5 mg capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: gelatin, magnesium stearate, mannitol, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Fingolimod is metabolized by sphingosine kinase to the active metabolite, fingolimod-phosphate. Fingolimod-phosphate is a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator, and binds with high affinity to sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors 1, 3, 4, and 5. Fingolimod-phosphate blocks the capacity of lymphocytes to egress from lymph nodes, reducing the number of lymphocytes in peripheral blood. The mechanism by which fingolimod exerts therapeutic effects in multiple sclerosis is unknown, but may involve reduction of lymphocyte migration into the central nervous system.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Heart rate and rhythm
Fingolimod causes a transient reduction in heart rate and AV conduction at treatment initiation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. The maximal decline of heart rate is seen in the first 6 hours post-dose, with 70% of the negative chronotropic effect achieved on the first day. Heart rate progressively increases after the first day, returning to baseline values within 1 month of the start of chronic treatment.
Autonomic responses of the heart, including diurnal variation of heart rate and response to exercise, are not affected by fingolimod treatment.
Fingolimod treatment is not associated with a decrease in cardiac output.
Potential to prolong the QT interval
In a thorough QT interval study of doses of 1.25 or 2.5 mg fingolimod at steady-state, when a negative chronotropic effect of fingolimod was still present, fingolimod treatment resulted in a prolongation of QTc, with the upper bound of the 90% confidence interval (CI) of 14.0 ms. There is no consistent signal of increased incidence of QTc outliers, either absolute or change from baseline, associated with fingolimod treatment. In MS studies, there was no clinically relevant prolongation of QT interval, but patients at risk for QT prolongation were not included in clinical studies.
Immune system
Effects on immune cell numbers in the blood
In a study in which 12 subjects received GILENYA 0.5 mg daily, the lymphocyte count decreased to approximately 60% of baseline within 4-6 hours after the first dose. With continued daily dosing, the lymphocyte count continued to decrease over a 2-week period, reaching a nadir count of approximately 500 cells/μL or approximately 30% of baseline. In a placebo-controlled study in 1272 MS patients (of whom 425 received fingolimod 0.5 mg daily and 418 received placebo), 18% (N=78) of patients on fingolimod 0.5 mg reached a nadir of < 200 cells/μL on at least one occasion. No patient on placebo reached a nadir of < 200 cells/μL. Low lymphocyte counts are maintained with chronic daily dosing of GILENYA 0.5 mg daily.
Chronic fingolimod dosing leads to a mild decrease in the neutrophil count to approximately 80% of baseline. Monocytes are unaffected by fingolimod.
Peripheral lymphocyte count increases are evident within days of stopping fingolimod treatment and typically normal counts are reached within 1 to 2 months.
Effect on antibody response
The immunogenicity of keyhole limpet Hemocyanin (KLH) and pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV-23) immunization were assessed by IgM and IgG titers in a steady-state, randomized, placebo-controlled study in healthy volunteers. Compared to placebo, antigen-specific IgM titers were decreased by 91% and 25% in response to KLH and PPV, respectively, in subjects on GILENYA 0.5 mg. Similarly, IgG titers were decreased by 45% and 50%, in response to KLH and PPV, respectively, in subjects on GILENYA 0.5 mg daily compared to placebo. The responder rate for GILENYA 0.5 mg as measured by the number of subjects with a >4-fold increase in KLH IgG was comparable to placebo and 25% lower for PPV-23 IgG, while the number of subjects with a >4 fold increase in KLH and PPV-23 IgM was 75% and 40% lower, respectively, compared to placebo. The capacity to mount a skin delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to Candida and tetanus toxoid was decreased by approximately 30% in subjects on GILENYA 0.5 mg daily, compared to placebo. Immunologic responses were further decreased with fingolimod 1.25 mg (a dose higher than recommended in MS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Pulmonary function
Single fingolimod doses ≥5 mg (10-fold the recommended dose) are associated with a dose-dependent increase in airway resistance. In a 14-day study of 0.5, 1.25, or 5 mg/day, fingolimod was not associated with impaired oxygenation or oxygen desaturation with exercise or an increase in airway responsiveness to methacholine. Subjects on fingolimod treatment had a normal bronchodilator response to inhaled beta-agonists.
In a 14-day placebo-controlled study of patients with moderate asthma, no effect was seen for GILENYA 0.5mg (recommended dose in MS). A 10% reduction in mean FEV1 at 6 hour after dosing was observed in patients receiving fingolimod 1.25 mg (a dose higher than recommended for use in MS) on Day 10 of treatment. Fingolimod 1.25 mg was associated with a 5-fold increase in the use of rescue short acting beta-agonists.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The Tmax of fingolimod is 12-16 hours. The apparent absolute oral bioavailability is 93%.
Food intake does not alter Cmax or exposure (AUC) of fingolimod or fingolimod-phosphate. Therefore GILENYA may be taken without regard to meals.
Steady-state blood concentrations are reached within 1 to 2 months following once-daily administration and steady-state levels are approximately 10-fold greater than with the initial dose.
Distribution
Fingolimod highly (86%) distributes in red blood cells. Fingolimod-phosphate has a smaller uptake in blood cells of <17%. Fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate are >99.7% protein bound. Fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate protein binding is not altered by renal or hepatic impairment.
Fingolimod is extensively distributed to body tissues with a volume of distribution of about 1200±260 L.
Metabolism
The biotransformation of fingolimod in humans occurs by three main pathways: by reversible stereoselective phosphorylation to the pharmacologically active (S)-enantiomer of fingolimod-phosphate, by oxidative biotransformation mainly via the cytochrome P450 4F2 isoenzyme and subsequent fatty acid-like degradation to inactive metabolites, and by formation of pharmacologically inactive non-polar ceramide analogs of fingolimod.
Fingolimod is primarily metabolized via human CYP4F2 with a minor contribution of CYP2D6, 2E1, 3A4, and 4F12. Inhibitors or inducers of these isozymes might alter the exposure of fingolimod or fingolimod-phosphate. The involvement of multiple CYP isoenzymes in the oxidation of fingolimod suggests that the metabolism of fingolimod will not be subject to substantial inhibition in the presence of an inhibitor of a single specific CYP isozyme.
Following single oral administration of [14C] fingolimod, the major fingolimod-related components in blood, as judged from their contribution to the AUC up to 816 hours post-dose of total radiolabeled components, are fingolimod itself (23.3%), fingolimod-phosphate (10.3%), and inactive metabolites [M3 carboxylic acid metabolite (8.3%), M29 ceramide metabolite (8.9%), and M30 ceramide metabolite (7.3%)].
Elimination
Fingolimod blood clearance is 6.3±2.3 L/h, and the average apparent terminal half-life (t1/2) is 6-9 days. Blood levels of fingolimod-phosphate decline in parallel with those of fingolimod in the terminal phase, yielding similar half-lives for both.
After oral administration, about 81% of the dose is slowly excreted in the urine as inactive metabolites. Fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate are not excreted intact in urine but are the major components in the feces with amounts of each representing less than 2.5% of the dose.
Special Populations
Renal Impairment
In patients with severe renal impairment, fingolimod Cmax and AUC are increased by 32% and 43%, respectively, and fingolimod-phosphate Cmax and AUC are increased by 25% and 14%, respectively, with no change in apparent elimination half-life. Based on these findings, the GILENYA 0.5 mg dose is appropriate for use in patients with renal impairment. The systemic exposure of two metabolites (M2 and M3) is increased by 3- and 13-fold, respectively. The toxicity of these metabolites has not been fully characterized.
A study in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment has not been conducted.
Hepatic Impairment
In subjects with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment, no change in fingolimod Cmax was observed, but fingolimod AUC was increased respectively by 12%, 44%, and 103%. In patients with severe hepatic impairment, fingolimod-phosphate Cmax was decreased by 22% and AUC was not substantially changed. The pharmacokinetics of fingolimod-phosphate were not evaluated in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. The apparent elimination half-life of fingolimod is unchanged in subjects with mild hepatic impairment, but is prolonged by about 50% in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment.
Patients with severe hepatic impairment should be closely monitored, as the risk of adverse reactions is greater [See Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
No dose adjustment is needed in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment.
Race
The effects of race on fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate pharmacokinetics cannot be adequately assessed due to a low number of non-white patients in the clinical program.
Gender
Gender has no clinically significant influence on fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate pharmacokinetics.
Geriatric patients
The mechanism for elimination and results from population pharmacokinetics suggest that dose adjustment would not be necessary in elderly patients. However, clinical experience in patients aged above 65 years is limited.
Pharmacokinetic interactions
Ketoconazole
The coadministration of ketoconazole (a potent inhibitor of CYP3A and CYP4F) 200 mg twice daily at steady-state and a single dose of fingolimod 5 mg led to a 70% increase in AUC of fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate. Patients who use GILENYA and systemic ketoconazole concomitantly should be closely monitored, as the risk of adverse reactions is greater. [See Drug Interactions (7)].
Potential of fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate to inhibit the metabolism of co-medications
In vitro inhibition studies in pooled human liver microsomes and specific metabolic probe substrates demonstrate that fingolimod has little or no capacity to inhibit the activity of the following CYP450 enzymes: CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP3A4/5, or CYP4A9/11, and similarly fingolimod-phosphate has little or no capacity to inhibit the activity of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, or CYP3A4 at concentrations up to three orders of magnitude of therapeutic concentrations. Therefore, fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate are unlikely to reduce the clearance of drugs that are mainly cleared through metabolism by the major cytochrome P450 isoenzymes described above. The potential of fingolimod to inhibit CYP2C8 and fingolimod-phosphate to inhibit CYP2B6 is unknown.
Potential of fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate to induce its own and/or the metabolism of co-medications
Fingolimod was examined for its potential to induce human CYP3A4, CYP1A2, CYP4F2, and MDR1 (P-glycoprotein) mRNA and CYP3A, CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, and CYP4F2 activity in primary human hepatocytes. Fingolimod did not induce mRNA or activity of the different CYP450 enzymes and MDR1 with respect to the vehicle control; therefore, no clinically relevant induction of the tested CYP450 enzymes or MDR1 by fingolimod are expected at therapeutic concentrations. The potential of fingolimod-phosphate to induce CYP450 isoenzymes is unknown.
Transporters
Fingolimod as well as fingolimod-phosphate are not expected to inhibit the uptake of co-medications and/or biologics transported by OATP1B1, OATP1B3, or NTCP. Similarly, they are not expected to inhibit the efflux of co-medications and/or biologics transported by the breast cancer resistant protein (MXR), the bile salt export pump (BSEP), the multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2), and MDR1-mediated transport at therapeutic concentrations.
Cyclosporine
The pharmacokinetics of single-dose fingolimod were not altered during coadministration with cyclosporine at steady-state, nor was cyclosporine steady-state pharmacokinetics altered by fingolimod. These data indicate that GILENYA is unlikely to reduce the clearance of drugs mainly cleared by CYP3A4 and show that the potent inhibition of transporters MDR1, MRP2, and OATP-C does not influence fingolimod disposition.
Isoproterenol, atropine, atenolol, and diltiazem
Single-dose fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate exposure was not altered by coadministered isoproterenol or atropine. Likewise, the single-dose pharmacokinetics of fingolimod and fingolimod-phosphate and the steady-state pharmacokinetics of both atenolol and diltiazem were unchanged during the coadministration of the latter two drugs individually with fingolimod.
Population pharmacokinetics analysis
A population pharmacokinetics evaluation performed in MS patients did not provide evidence for a significant effect of fluoxetine and paroxetine (strong CYP2D6 inhibitors) and carbamazepine (potent enzyme inducer) on fingolimod or fingolimod-phosphate pre-dose concentrations. In addition, the following commonly co-prescribed substances had no clinically relevant effect (<20%) on fingolimod or fingolimod-phosphate pre-dose concentrations: baclofen, gabapentin, oxybutynin, amantadine, modafinil, amitriptyline, pregabalin, and corticosteroids.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Oral carcinogenicity studies of fingolimod were conducted in mice and rats. In mice, fingolimod was administered at oral doses of 0, 0.025, 0.25, and 2.5 mg/kg/day for up to 2 years. The incidence of malignant lymphoma was increased in males and females at the mid and high dose. The lowest dose tested (0.025 mg/kg/day) is less than the recommended human dose (RHD) of 0.5 mg/day on a body surface area (mg/m2) basis. In rats, fingolimod was administered at oral doses of 0, 0.05, 0.15, 0.5, and 2.5 mg/kg/day. No increase in tumors was observed. The highest dose tested (2.5 mg/kg/day) is approximately 50 times the RHD on a mg/m2 basis.
Fingolimod was negative in a battery of in vitro (Ames, mouse lymphoma thymidine kinase, chromosomal aberration in mammalian cells) and in vivo (micronucleus in mouse and rat) assays.
When fingolimod was administered orally (0, 1, 3, and 10 mg/kg/day) to male and female rats prior to and during mating, and continuing to Day 7 of gestation in females, no effect on fertility was observed up to the highest dose tested (10 mg/kg), which is approximately 200 times the RHD on a mg/m2 basis.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Lung toxicity was observed in two different strains of rat and in dog and monkey. The primary findings included increase in lung weight, associated with smooth muscle hypertrophy, hyperdistension of the alveoli, and/or increased collagen. Insufficient or lack of pulmonary collapse at necropsy, generally correlated with microscopic changes, was observed in all species. In rat and monkey, lung toxicity was observed at all oral doses tested in chronic studies. The lowest doses tested in rat (0.05 mg/kg/day in the 2-year carcinogenicity study) and monkey (0.5 mg/kg/day in the 39-week toxicity study) are similar to and approximately 20 times the RHD on a mg/m2 basis, respectively.
In the 52-week oral study in monkey, respiratory distress associated with ketamine administration was observed at doses of 3 and 10 mg/kg/day; the most affected animal became hypoxic and required oxygenation. As ketamine is not generally associated with respiratory depression, this effect was attributed to fingolimod. In a subsequent study in rat, ketamine was shown to potentiate the bronchoconstrictive effects of fingolimod. The relevance of these findings to humans is unknown.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of GILENYA was demonstrated in 2 studies that evaluated once-daily doses of GILENYA 0.5 mg and 1.25 mg in patients with relapsing remitting MS (RRMS). Both studies included patients who had experienced at least 2 clinical relapses during the 2 years prior to randomization or at least 1 clinical relapse during the 1 year prior to randomization, and had an Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) score from 0 to 5.5. Study 1 was a 2-year randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with RRMS who had not received any interferon-beta or glatiramer acetate for at least the previous 3 months and had not received any natalizumab for at least the previous 6 months. Neurological evaluations were performed at screening, every 3 months and at time of suspected relapse. MRI evaluations were performed at screening, month 6, month 12, and month 24. The primary endpoint was the annualized relapse rate.
Median age was 37 years, median disease duration was 6.7 years and median EDSS score at baseline was 2.0. Patients were randomized to receive GILENYA 0.5 mg (n=425), 1.25 mg (n=429), or placebo (n=418) for up to 24 months. Median time on study drug was 717 days on 0.5 mg, 715 days on 1.25 mg and 719 days on placebo.
The annualized relapse rate was significantly lower in patients treated with GILENYA than in patients who received placebo. The secondary endpoint was the time to 3-month confirmed disability progression as measured by at least a 1-point increase from baseline in EDSS (0.5 point increase for patients with baseline EDSS of 5.5) sustained for 3 months. Time to onset of 3-month confirmed disability progression was significantly delayed with GILENYA treatment compared to placebo. The 1.25 mg dose resulted in no additional benefit over the GILENYA 0.5 mg dose. The results for this study are shown in Table 2 and Figure 1.
| GILENYA 0.5 mg N=425 | Placebo N=418 | p-value | |
| Clinical Endpoints | |||
| Annualized relapse rate (primary endpoint) | 0.18 | 0.40 | <0.001 |
| Percentage of patients without relapse | 70% | 46% | <0.001 |
| Hazard ratio‡ of disability progression (95% CI) | 0.70 (0.52, 0.96) | 0.02 | |
| MRI Endpoint | |||
| Mean (median) number of new or newly enlarging T2 lesions over 24 months | 2.5(0) | 9.8 (5.0) | <0.001 |
All analyses of clinical endpoints were intent-to–treat. MRI analysis used evaluable dataset.
‡ Hazard ratio is an estimate of the relative risk of having the event of disability progression on GILENYA as compared to placebo.
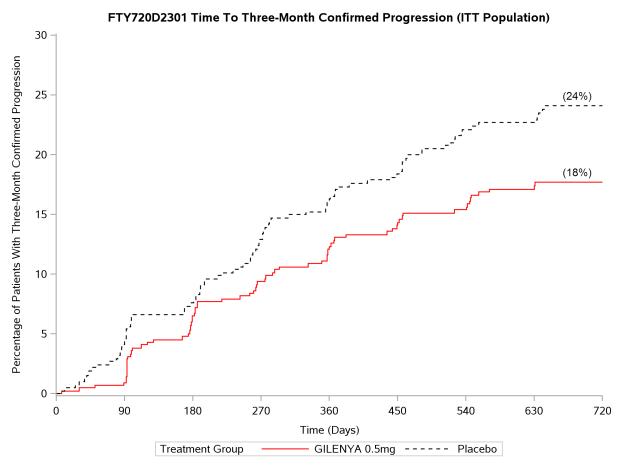
Figure 1 Time to 3-month Confirmed Disability Progression – Study 1 (ITT population)
Study 2 was a 1-year randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled study in patients with RRMS who had not received any natalizumab in the previous 6 months. Prior therapy with interferon-beta or glatiramer acetate up to the time of randomization was permitted.
Neurological evaluations were performed at screening, every 3 months, and at the time of suspected relapses. MRI evaluations were performed at screening and at month 12. The primary endpoint was the annualized relapse rate.
Median age was 36 years, median disease duration was 5.9 years, and median EDSS score at baseline was 2.0. Patients were randomized to receive GILENYA 0.5 mg (n=431), 1.25 mg (n=426), or interferon beta-1a, 30 micrograms via the intramuscular route (IM) once weekly (n=435) for up to 12 months. Median time on study drug was 365 days on GILENYA 0.5 mg, 354 days on 1.25 mg, and 361 days on interferon beta-1a IM.
The annualized relapse rate was significantly lower in patients treated with GILENYA 0.5 mg than in patients who received interferon beta-1a IM. The key secondary endpoints were number of new and newly enlarging T2 lesions and time to onset of 3-month confirmed disability progression as measured by at least a 1-point increase from baseline in EDSS (0.5 point increase for those with baseline EDSS of 5.5) sustained for 3 months. The number of new and newly enlarging T2 lesions was significantly lower in patients treated with GILENYA than in patients who received interferon beta-1a IM. There was no significant difference in the time to 3-month confirmed disability progression between GILENYA and interferon beta-1a-treated patients at 1 year. The 1.25 mg dose resulted in no additional benefit over the GILENYA 0.5 mg dose. The results for this study are shown in Table 3.
| GILENYA 0.5 mg N=429 | Interferon beta-1a IM 30 μg N=431 | p-value | |
| Clinical Endpoints | |||
| Annualized relapse rate (primary endpoint) | 0.16 | 0.33 | <0.001 |
| Percentage of patients without relapse | 83% | 70% | <0.001 |
| Hazard ratio‡ of disability progression (95% CI) | 0.71 (0.42, 1.21) | 0.21 | |
| MRI Endpoint | |||
| Mean (median) number of new or newly enlarging T2 lesions over 12 months | 1.6 (0) | 2.6 (1.0) | 0.002 |
All analyses of clinical endpoints were intent-to–treat. MRI analysis used evaluable dataset.
‡ Hazard ratio is an estimate of the relative risk of having the event of disability progression on GILENYA as compared to control.
Pooled results of study 1 and study 2 showed a consistent and statistically significant reduction of annualized relapse rate compared to comparator in subgroups defined by gender, age, prior MS therapy, and disease activity.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
0.5 mg GILENYA capsules are hard gelatin capsules with a white opaque body and bright yellow cap imprinted with “FTY 0.5 mg” on the cap and two radial bands imprinted on the capsule body with yellow ink.
GILENYA capsules are supplied in blister packs.
Carton of 28 capsules containing 2 folded blister cards of 14 capsules per blister card........ NDC 0078-0607-51
Carton of 7 capsules containing 1 blister card of 7 capsules per blister card........... NDC 0078-0607-89
GILENYA capsules should be stored at 25ºC (77ºF); excursions permitted to 15-30ºC (59-86ºF). Protect from moisture.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See Medication Guide.
A Medication Guide is required for distribution with GILENYA. Encourage patients to read the GILENYA Medication Guide. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of this document.
17.1 Benefits and Risks
Summarize for patients the benefits and potential risks of treatment with GILENYA. Tell patients to take GILENYA once daily as prescribed. Tell patients not to discontinue GILENYA without first discussing this with the prescribing physician.
17.2 Cardiac Effects
Advise patients that initiation of GILENYA treatment results in a transient decrease in heart rate. Inform patients that they will need to be observed in the doctor's office or other facility for 6 hours after the first dose. Advise patients that if GILENYA is discontinued for more than two weeks, effects similar to those observed on treatment initiation may be seen and observation for 6 hours will be needed on treatment re-initiation.
17.3 Risk of Infections
Inform patients that they may be more likely to get infections when taking GILENYA, and that they should contact their physician if they develop symptoms of infection. Advise patients that the use of some vaccines should be avoided during treatment with GILENYA and for 2 months after discontinuation. Advise patients who have not had chickenpox or vaccination to consider VZV vaccination prior to commencing treatment with GILENYA.
17.4 Macular Edema
Advise patients that GILENYA may cause macular edema, and that they should contact their physician if they experience any changes in their vision. Inform patients with diabetes mellitus or a history of uveitis that their risk of macular edema is increased.
17.5 Respiratory Effects
Advise patients that they should contact their physician if they experience new onset or worsening of dyspnea.
17.6 Hepatic Effects
Inform patients that GILENYA may increase liver enzymes. Advise patients that they should contact their physician if they have any unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, anorexia, or jaundice and/or dark urine.
17.7 Fetal Risk
Inform patients that, based on animal studies, GILENYA may cause fetal harm. Discuss with women of childbearing age whether they are pregnant, might be pregnant or are trying to become pregnant. Advise women of childbearing age of the need for effective contraception during GILENYA treatment and for two months after stopping GILENYA. Advise the patient that if she should nevertheless become pregnant, she should immediately inform her physician.
17.8 Persistence of GILENYA effects after drug discontinuation
Advise patients that GILENYA remains in the blood and continues to have effects, including decreased blood lymphocyte counts, for up to two months following the last dose.
T2011-77
MEDICATION GUIDE
GILENYA™ (je-LEN-yah)
(fingolimod)
capsules
Read this Medication Guide before you start using GILENYA and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about GILENYA?
GILENYA may cause serious side effects, including:
1. Slow Heart Rate (bradycardia or bradyarrhythmia) when you start taking GILENYA. GILENYA can cause your heart rate to slow down, especially after you take the first dose. Your heart rate will usually slow down the most about 6 hours after you take your first dose of GILENYA. You might feel dizzy or tired or be aware of a slow or irregular heartbeat if your heart rate slows down. Usually, if you experience these types of symptoms due to the slowing down of your heart rate, they will occur during the first 6 hours after the first dose. Your doctor will watch you for the first 6 hours after you take the first dose to see if you have any serious side effects. Your slow heart rate will usually return to normal within 1 month after you start taking GILENYA.
Call your doctor if at any time you have:
- dizziness
- tiredness
- a slow or irregular heartbeat
2. Infections. GILENYA can increase your risk of serious infections. GILENYA lowers the number of white blood cells (lymphocytes) in your blood. This will usually go back to normal within 2 months of stopping treatment. Your doctor may do a blood test before you start taking GILENYA. Call your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms of an infection:
- fever
- tiredness
- body aches
- chills
- nausea
- vomiting
3. A problem with your vision called macular edema. Macular edema can cause some of the same vision symptoms as an MS attack (optic neuritis). You may not notice any symptoms with macular edema. Macular edema usually starts in the first 3 to 4 months after you start taking GILENYA. Your doctor should test your vision before you start taking GILENYA and 3 to 4 months after you start taking GILENYA, or any time you notice vision changes during treatment with GILENYA. Your risk of macular edema may be higher if you have diabetes or have had an inflammation of your eye called uveitis.
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following:
- blurriness or shadows in the center of your vision
- a blind spot in the center of your vision
- sensitivity to light
- unusually colored (tinted) vision
What is GILENYA?
GILENYA is a prescription medicine used to treat relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS) in adults. GILENYA can decrease the number of MS flare-ups (relapses). GILENYA does not cure MS, but it can help slow down the physical problems that MS causes.
It is not known if GILENYA is safe and effective in children under age 18.
What should I tell my doctor before taking GILENYA?
Before you take GILENYA, tell your doctor about all your medical conditions, including if you had or now have:
- an irregular or abnormal heartbeat (arrhythmia)
- a heart rate less than 55 beats a minute
- heart problems
- a history of fainting (syncope)
- a fever or infection, or you are unable to fight infections. Tell your doctor if you have had chicken pox or have received the vaccine for chicken pox. Your doctor may do a blood test for chicken pox virus. You may need to get the vaccine for chicken pox and then wait 1 month before you start taking GILENYA.
- eye problems, especially an inflammation of the eye called uveitis.
- diabetes
- breathing problems
- liver problems
- high blood pressure
- Are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. GILENYA may harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant.
- Tell your doctor right away if you become pregnant while taking GILENYA or if you become pregnant within 2 months after you stop taking GILENYA.
- If you are a female who can become pregnant, you should use effective birth control during your treatment with GILENYA and for at least 2 months after you stop taking GILENYA.
- Tell your doctor right away if you become pregnant while taking GILENYA or if you become pregnant within 2 months after you stop taking GILENYA.
Pregnancy Registry: There is a registry for women who become pregnant during treatment with GILENYA. If you become pregnant while taking GILENYA, talk to your doctor about registering with the GILENYA Pregnancy Registry. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about your health and your baby’s health.
For more information, you can call the GILENYA Pregnancy Registry at 1-877-598-7237.
- Are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if GILENYA passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take GILENYA or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
Using GILENYA and other medicines together may affect each other causing serious side effects.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- Medicines for heart problems or high blood pressure
- Vaccines. Tell your doctor if you have been vaccinated within 1 month before you start taking GILENYA. You should not get certain vaccines while you take GILENYA and for at least 2 months after you stop taking GILENYA. If you take certain vaccines, you may get the infection the vaccine should have prevented. Vaccines may not work as well when given during GILENYA treatment.
- Medicines that could raise your chance of getting infections, such as medicines to treat cancer or to control your immune system.
- ketoconazole (an antifungal drug) by mouth
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure.
How should I take GILENYA?
- Your first dose of GILENYA will be given in a doctor’s office or clinic, where you will be observed for 6 hours after your first dose of GILENYA.
- Take GILENYA exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Take GILENYA 1 time each day.
- Take GILENYA with or without food.
- Do not stop taking GILENYA without talking with your doctor first.
- If you start GILENYA again after stopping for 2 weeks or more, you will start taking GILENYA again in your doctor’s office or clinic.
What are possible side effects of GILENYA?
GILENYA can cause serious side effects.
See “What is the most important information I should know about GILENYA?”
Serious side effects include:
-
Breathing Problems. Some people who take GILENYA have shortness of breath. Call your doctor right away if you have trouble breathing.
-
Liver problems. GILENYA may cause liver problems. Your doctor should do blood tests to check your liver before you start taking GILENYA. Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms of liver problems:
- nausea
- vomiting
- stomach pain
- loss of appetite
- tiredness
- your skin or the whites of your eyes turn yellow
- dark urine
- nausea
The most common side effects of GILENYA include:
- headache
- flu
- diarrhea
- back pain
- abnormal liver tests
- cough
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of GILENYA. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How do I store GILENYA?
- Store GILENYA in the original blister pack in a dry place.
- Store GILENYA at room temperature between 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
- Keep GILENYA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about GILENYA
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use GILENYA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give GILENYA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about GILENYA. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about GILENYA that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information, go to www.pharma.US.Novartis.com or call 1-888-669-6682.
What are the ingredients in GILENYA?
Active ingredient: fingolimod
Inactive ingredients: gelatin, magnesium stearate, mannitol, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
GILENYA is a trademark of Novartis AG.
Manufactured by:
Novartis Pharma Stein AG
Stein, Switzerland
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
© Novartis
T2011-77/T2010-82
May 2011/September 2010
Package Label – 0.5 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0607-51
GILENYA™
(fingolimod)
Capsules
28 Capsules
0.5 mg
Equivalent to 0.56 mg fingolimod hydrochloride
This package contains a four-week supply of capsules.
Dispense with enclosed Medication Guide.
| GILENYA
fingolimod hcl capsule |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA022527 | 09/21/2010 | |
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |