physiolyte (Sodium Chloride, Sodium Gluconate, Sodium Acetate Trihydrate, Potassium Chloride, and Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate) injection
[B. Braun Medical Inc.]
Balanced Electrolyte Solution for Irrigation.
For All General Irrigation, Washing, and Rinsing Purposes.
Not for Injection by Usual Parenteral Route.
DESCRIPTION
Physiolyte is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution of electrolytes in water for injection intended only for sterile irrigation, washing, and rinsing purposes.
Each 100 mL contains:
Sodium Chloride USP 0.53 g; Sodium Gluconate USP 0.5 g
Sodium Acetate Trihydrate USP 0.37 g; Potassium Chloride
USP 0.037 g; Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate USP 0.03 g
Water for Injection USP qs
Glacial Acetic Acid USP has been added to adjust the pH
pH: 6.8 (6.3–7.3)
Calculated Osmolarity: The solution is isotonic (295 mOsmol/liter)
Concentration of Electrolytes (mEq/liter): Sodium 140
Potassium 5; Magnesium 3; Chloride 98; Acetate (CH3COO−) 27
Gluconate (HOCH2(CHOH)4COO−) 23
It contains no bacteriostat, antimicrobial agent or added buffer (except for pH adjustment) and is intended only for use as a single-dose or short procedure irrigation. When smaller volumes are required the unused portion should be discarded.
Physiolyte may be classified as a sterile irrigant, wash, rinse and pharmaceutical vehicle.
The formulas of the active ingredients are:
| Ingredients | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium Chloride USP | NaCl | 58.44 |
| Sodium Acetate Trihydrate USP | CH3COONa•3H2O | 136.08 |
| Potassium Chloride USP | KCl | 74.55 |
| Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate USP | MgCl2•6H2O | 203.30 |
| Sodium Gluconate USP |
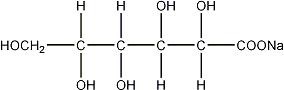 | 218.14 |
The plastic container is a copolymer of ethylene and propylene formulated and developed for parenteral drugs. The copolymer contains no plasticizers and exhibits virtually no leachability. The plastic container is also virtually impermeable to vapor transmission and therefore, requires no overwrap to maintain the proper drug concentration. The safety of the plastic container has been confirmed by biological evaluation procedures. The material passes Class VI testing as specified in the U.S. Pharmacopeia for Biological Tests. The safety of the plastic has been confirmed by tests in animals according to USP biological standards for plastic containers.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Physiolyte exerts a mechanical cleansing action for sterile irrigation of body cavities, tissues or wounds, indwelling urethral catheters and surgical drainage tubes, and for washing, rinsing or soaking surgical dressings, instruments and laboratory specimens. It also serves as a vehicle for drugs used for irrigation or other pharmaceutical preparations.
Physiolyte provides an isotonic calcium-free balanced electrolyte irrigation with the same ionic composition as Isolyte® S (Multi-Electrolyte Solution) a multiple electrolyte solution for IV replacement of acute extracellular fluid losses.
Physiological irrigation solutions are considered generally compatible with living tissues and organs.
Sodium, the major cation of the extracellular fluid, functions primarily in the control of water distribution, fluid balance, and osmotic pressure of body fluids. Sodium is also associated with chloride and bicarbonate in the regulation of the acid-base equilibrium of body fluid.
Potassium, the principal cation of intracellular fluid, participates in carbohydrate utilization and protein synthesis, and is critical in the regulation of nerve conduction and muscle contraction, particularly in the heart.
Chloride, the major extracellular anion, closely follows the metabolism of sodium, and changes in the acid-base balance of the body are reflected by changes in the chloride concentration.
Magnesium, a principal cation of soft tissue, is primarily involved in enzyme activity associated with the metabolism of carbohydrates and protein. Magnesium is also involved in neuromuscular and cardiac conduction and irritability.
Gluconate and acetate are organic ions which are hydrogen ion acceptors and contribute bicarbonate during their metabolism to carbon dioxide and water, and serve as alkalinizing agents.
Water is an essential constituent of all body tissues and accounts for approximately 70% of total body weight. Average normal adult daily requirement ranges from two to three liters (1.0 to 1.5 liters each for insensible water loss by perspiration and urine production).
Water balance is maintained by various regulatory mechanisms. Water distribution depends primarily on the concentration of electrolytes in the body compartments and sodium (Na+) plays a major role in maintaining physiologic equilibrium.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Physiolyte® (A Physiological Irrigating Solution) is indicated for all general irrigation, washing, and rinsing purposes which permit use of a sterile, nonpyrogenic electrolyte solution.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Physiolyte is not for injection by usual parenteral routes.
An electrolyte solution should not be used for irrigation during electrosurgical procedures.
WARNINGS
FOR IRRIGATION ONLY. NOT FOR INJECTION.
Irrigating fluids have been demonstrated to enter the systemic circulation in relatively large volumes; thus, irrigation solutions must be regarded as systemic drugs. Absorption of large amounts can cause fluid and/or solute overload resulting in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations, overhydration, congested states or pulmonary edema.
The risk of dilutional states is inversely proportional to the electrolyte concentrations of the administered parenteral solutions. The risk of solute overload causing congested states with peripheral and pulmonary edema is directly proportional to the electrolyte concentrations.
Do not warm above 150°F (66°C).
After opening container, it's contents should be used promptly to minimize the possibility of bacterial growth or pyrogen formation.
Discard unused portion of irrigating solution since it contains no preservatives.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Use aseptic technique when preparing and administering sterile irrigation solutions for irrigating body cavities, wounds and urethral catheters or for wetting dressings that come in contact with the body tissues.
Use only if solution is clear and container and seal are intact.
Do not use for irrigation that may result in absorption of large amounts into the blood.
Caution should be observed when the solution is used for continuous irrigation or allowed to "dwell" inside body cavities because of possible absorption into the blood stream and the production of circulatory overload.
When used as a "pour" irrigation, no part of the contents should be allowed to contact the surface below the outer protected thread area of the plastic irrigation container. When used for irrigation via appropriate irrigation equipment, the administration set should be attached promptly. Unused portions should be discarded and a fresh container of appropriate size used for the start up of each cycle or repeat procedure. For repeated irrigations of urethral catheters, a separate container should be used for each patient.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies with Physiolyte® (A Physiological Irrigating Solution) have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential, or effects on fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Physiolyte (A Physiological Irrigating Solution). It is also not known whether Physiolyte (A Physiological Irrigating Solution) can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Physiolyte (A Physiological Irrigating Solution) should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Caution should be exercised when Physiolyte is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Physiolyte in pediatric patients have not been established. Its limited use in pediatric patients has been inadequate to fully define proper dosage and limitations for use.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Physiolyte (A Physiological Irrigating Solution) have not been performed to determine whether patients over 65 years of age respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Use in Patients with Renal Insufficiency/Failure
Clinical studies of Physiolyte (a Physiological Irrigation Solution) have not been performed to determine whether patients with renal failure respond differently from those with normal renal function. Given the potential for systemic absorption, the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Increased caution should be exercised when administering Physiolyte to patients with impaired fluid and electrolyte homeostasis.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Possible adverse effects arising from the irrigation of body cavities, tissues, or indwelling catheters and tubes can be minimized when proper procedures are followed. Displaced catheters or drainage tubes can lead to irrigation or infiltration of unintended structures or cavities. Excessive volume or pressure during irrigation of closed cavities may cause undue distension or disruption of tissues. Accidental contamination from careless technique may transmit infection.
If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue administration of the irrigant, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures, and save the remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
OVERDOSAGE
In the event of overhydration or solute overload, reevaluate the patient's condition, and institute appropriate corrective treatment. Intravascular volume overload may respond to hemodialysis. See WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, and ADVERSE REACTIONS.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
As required for irrigation.
The dose is dependent upon the capacity or surface area of the structure to be irrigated and the nature of the procedure. When used as a vehicle for other drugs, the directions of the additive's manufacturer should be followed.
Some additives may be incompatible. Consult with pharmacist. When introducing additives, use aseptic techniques. Mix thoroughly. Do not store.
Solutions should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permits.
HOW SUPPLIED
Physiolyte® (A Physiological Irrigating Solution) is supplied sterile and nonpyrogenic in 1000 mL PIC™ (Plastic Irrigation Containers) packaged 16 per case.
| NDC | Cat. No. | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Physiolyte (A Physiological Irrigating Solution) | ||
| 0264-2205-00 | R5510-01 | 1000 mL |
Exposure of pharmaceutical products to heat should be minimized. Avoid excessive heat. Protect from freezing. It is recommended that the product be stored at room temperature (25°C); however, brief exposure up to 40°C does not adversely affect the product.
Do not warm above 150°F (66°C).
Rx only
Issued: July 2003
Physiolyte and Isolyte S are registered trademarks and PIC is a trademark of B. Braun Medical Inc.
Made in USA
Directions For Use of PIC Containers
Not for injection.
Aseptic technique is required.
- Caution – Before use, perform the following checks:
- (a)
- Read the label. Ensure solution is the one ordered and is within the expiration date.
- (b)
- Invert container and inspect the solution in good light for cloudiness, haze, or particulate matter; check the container for leakage or damage. Any container which is suspect should not be used.
Use only if solution is clear and container and seal are intact.
Single unit container. Discard unused portion.
- 2.
- Outer Closure Removal – Grasp the container with one hand and turn the breakaway ring counterclockwise with the other hand until slight resistance is felt. Then, twisting the container in the opposite direction, turn the breakaway ring sharply until the entire outer cap is loose and can be lifted off.
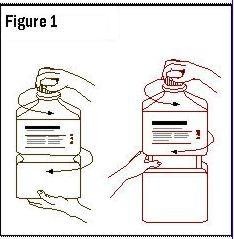
- 3.
- Connect the administration set through the sterile set port according to set instructions or remove screw cap and pour.
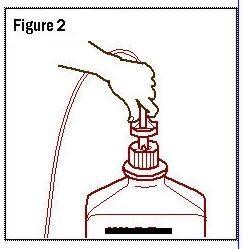
- 4.
- Do not warm above 150°F to assure minimal bottle distortion. Keep bottles upright.
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Irvine, CA USA 92614-5895
©2003 B. Braun Medical Inc.
Y36-002-478
| Physiolyte (Sodium Chloride, Sodium Gluconate, Sodium Acetate Trihydrate, Potassium Chloride, and Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revised: 08/2007B. Braun Medical Inc.