imipramine pamoate (imipramine pamoate) capsule
[Mallinckrodt Inc.]
For oral administration
Rx only
Prescribing Information
Suicidality in Children and Adolescents
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in short-term studies in children and adolescents with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Anyone considering the use of imipramine pamoate or any other antidepressant in a child or adolescent must balance this risk with the clinical need. Patients who are started on therapy should be observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Families and caregivers should be advised of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Imipramine pamoate is not approved for use in pediatric patients. (See Warnings and Precautions: Pediatric Use)
Pooled analyses of short-term (4 to 16 weeks) placebo-controlled trials of 9 antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and others) in children and adolescents with major depressive disorder (MDD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), or other psychiatric disorders (a total of 24 trials involving over 4400 patients) have revealed a greater risk of adverse events representing suicidal thinking or behavior (suicidality) during the first few months of treatment in those receiving antidepressants. The average risk of such events in patients receiving antidepressants was 4%, twice the placebo risk of 2%. No suicides occurred in these trials.
DESCRIPTION
Imipramine pamoate is a tricyclic antidepressant, available as capsules for oral administration. The 75-, 100-, 125-, and 150-mg capsules contain imipramine pamoate equivalent to 75, 100, 125, and 150 mg of imipramine hydrochloride. Imipramine pamoate is 5-[3- (dimethylamino)propyl]-10, 11-dihydro-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 4, 4'-methylenebis- (3-hydroxy-2-naphthoate) (2:1), and its structural formula is
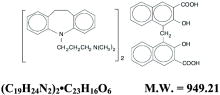
Imipramine pamoate is a fine, yellow, tasteless, odorless powder. It is soluble in ethanol, in acetone, in ether, in chloroform, and in carbon tetrachloride, and is insoluble in water.
Inactive Ingredients. D&C Red No. 28, FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Yellow No. 6, D&C Yellow No. 10 (100 mg and 125 mg capsules only), gelatin, magnesium stearate, parabens, starch, talc, and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The mechanism of action of imipramine is not definitely known. However, it does not act primarily by stimulation of the central nervous system. The clinical effect is hypothesized as being due to potentiation of adrenergic synapses by blocking uptake of norepinephrine at nerve endings.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
For the relief of symptoms of depression. Endogenous depression is more likely to be alleviated than other depressive states. One to three weeks of treatment may be needed before optimal therapeutic effects are evident.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
The concomitant use of monoamine oxidase inhibiting compounds is contraindicated. Hyperpyretic crises or severe convulsive seizures may occur in patients receiving such combinations. The potentiation of adverse effects can be serious, or even fatal. When it is desired to substitute imipramine pamoate capsules in patients receiving a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, as long an interval should elapse as the clinical situation will allow, with a minimum of 14 days. Initial dosage should be low and increases should be gradual and cautiously prescribed.
The drug is contraindicated during the acute recovery period after a myocardial infarction. Patients with a known hypersensitivity to this compound should not be given the drug. The possibility of cross-sensitivity to other dibenzazepine compounds should be kept in mind.
WARNINGS
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
Patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), both adult and pediatric, may experience worsening of their depression and/or the emergence of suicidal ideation and behavior (suicidality) or unusual changes in behavior, whether or not they are taking antidepressant medications, and this risk may persist until significant remission occurs. There has been a long-standing concern that antidepressants may have a role in inducing worsening of depression and the emergence of suicidality in certain patients. Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in short-term studies in children and adolescents with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders.
Pooled analyses of short-term placebo-controlled trials of 9 antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and others) in children and adolescents with MDD, OCD, or other psychiatric disorders (a total of 24 trials involving over 4400 patients) have revealed a greater risk of adverse events representing suicidal behavior or thinking (suicidality) during the first few months of treatment in those receiving antidepressants. The average risk of such events in patients receiving antidepressants was 4%, twice the placebo risk of 2%. There was considerable variation in risk among drugs, but a tendency toward an increase for almost all drugs studied. The risk of suicidality was most consistently observed in the MDD trials, but there were signals of risk arising from some trials in other psychiatric indications (obsessive compulsive disorder and social anxiety disorder) as well. No suicides occurred in any of these trials. It is unknown whether the suicidality risk in pediatric patients extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond several months. It is also unknown whether the suicidality risk extends to adults.
All pediatric patients being treated with antidepressants for any indication should be observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, and unusual changes in behavior, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases. Such observation would generally include at least weekly face-to-face contact with patients or their family members or caregivers during the first 4 weeks of treatment, then every other week visits for the next 4 weeks, then at 12 weeks, and as clinically indicated beyond 12 weeks. Additional contact by telephone may be appropriate between face-to-face visits.
Adults with MDD or co-morbid depression in the setting of other psychiatric illness being treated with antidepressants should be observed similarly for clinical worsening and suicidality, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases.
The following symptoms, anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, and mania, have been reported in adult and pediatric patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder as well as for other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric. Although a causal link between the emergence of such symptoms and either the worsening of depression and/or the emergence of suicidal impulses has not been established, there is concern that such symptoms may represent precursors to emerging suicidality.
Consideration should be given to changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing the medication, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidality or symptoms that might be precursors to worsening depression or suicidality, especially if these symptoms are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms.
Families and caregivers of pediatric patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder or other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric, should be alerted about the need to monitor patients for the emergence of agitation, irritability, unusual changes in behavior, and the other symptoms described above, as well as the emergence of suicidality, and to report such symptoms immediately to health care providers. Such monitoring should include daily observation by families and caregivers. Prescriptions for imipramine pamoate should be written for the smallest quantity of tablets consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose. Families and caregivers of adults being treated for depression should be similarly advised.
Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder - A major depressive episode may be the initial presentation of bipolar disorder. It is generally believed (though not established in controlled trials) that treating such an episode with an antidepressant alone may increase the likelihood of precipitation of a mixed/manic episode in patients at risk for bipolar disorder. Whether any of the symptoms described above represent such a conversion is unknown. However, prior to initiating treatment with an antidepressant, patients with depressive symptoms should be adequately screened to determine if they are at risk for bipolar disorder; such screening should include a detailed psychiatric history, including a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression. It should be noted that imipramine pamoate is not approved for use in treating bipolar depression.
Extreme caution should be used when this drug is given to patients with cardiovascular disease because of the possibility of conduction defects, arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, strokes, and tachycardia. These patients require cardiac surveillance at all dosage levels of the drug; patients with increased intraocular pressure, history of urinary retention, or history of narrow-angle glaucoma because of the drug's anticholinergic properties; hyperthyroid patients or those on thyroid medication because of the possibility of cardiovascular toxicity; patients with a history of seizure disorder because this drug has been shown to lower the seizure threshold; patients receiving guanethidine, clonidine, or similar agents, since imipramine pamoate may block the pharmacologic effects of these drugs; patients receiving methylphenidate hydrochloride. Since methylphenidate hydrochloride may inhibit the metabolism of imipramine pamoate, downward dosage adjustment of imipramine pamoate may be required when given concomitantly with methylphenidate hydrochloride.
Since imipramine pamoate may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks, such as operating an automobile or machinery, the patient should be cautioned accordingly.
Imipramine pamoate capsules may enhance the CNS depressant effects of alcohol. Therefore, it should be borne in mind that the dangers inherent in a suicide attempt or accidental overdosage with the drug may be increased for the patient who uses excessive amounts of alcohol. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
PRECAUTIONS
General
An ECG recording should be taken prior to the initiation of larger-than-usual doses of imipramine pamoate and at appropriate intervals thereafter until steady state is achieved. (Patients with any evidence of cardiovascular disease require cardiac surveillance at all dosage levels of the drug. See WARNINGS.) Elderly patients and patients with cardiac disease or a prior history of cardiac disease are at special risk of developing the cardiac abnormalities associated with the use of imipramine pamoate. It should be kept in mind that the possibility of suicide in seriously depressed patients is inherent in the illness and may persist until significant remission occurs. Such patients should be carefully supervised during the early phase of treatment with imipramine pamoate and may require hospitalization. Prescriptions should be written for the smallest amount feasible.
Hypomanic or manic episodes may occur, particularly in patients with cyclic disorders. Such reactions may necessitate discontinuation of the drug. If needed, imipramine pamoate may be resumed in lower dosage when these episodes are relieved. Administration of a tranquilizer may be useful in controlling such episodes.
An activation of the psychosis may occasionally be observed in schizophrenic patients and may require reduction of dosage and the addition of a phenothiazine.
Concurrent administration of imipramine pamoate with electroshock therapy may increase the hazards: such treatment should be limited to those patients for whom it is essential, since there is limited clinical experience.
Patients taking imipramine pamoate should avoid excessive exposure to sunlight since there have been reports of photosensitization.
Both elevation and lowering of blood sugar levels have been reported with imipramine pamoate use.
Imipramine pamoate should be used with caution in patients with significantly impaired renal or hepatic function.
Patients who develop a fever and a sore throat during therapy with imipramine pamoate should have leukocyte and differential blood counts performed.
Imipramine pamoate should be discontinued if there is evidence of pathological neutrophil depression.
Prior to elective surgery, imipramine pamoate should be discontinued for as long as the clinical situation will allow.
Information for Patients
Prescribers or other health professionals should inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with imipramine pamoate and should counsel them in its appropriate use. A patient Medication Guide About Using Antidepressants in Children and Teenagers is available for imipramine pamoate. The prescriber or health professional should instruct patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide and should assist them in understanding its contents. Patients should be given the opportunity to discuss the contents of the Medication Guide and to obtain answers to any questions they may have. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of this document.
Patients should be advised of the following issues and asked to alert their prescriber if these occur while taking imipramine pamoate.
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk - Patients, their families, and their caregivers should be encouraged to be alert to the emergence of anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, mania, other unusual changes in behavior, worsening of depression, and suicidal ideation, especially early during antidepressant treatment and when the dose is adjusted up or down. Families and caregivers of patients should be advised to observe for the emergence of such symptoms on a day-to-day basis, since changes may be abrupt. Such symptoms should be reported to the patient's prescriber or health professional, especially if they are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms. Symptoms such as these may be associated with an increased risk for suicidal thinking and behavior and indicate a need for very close monitoring and possibly changes in the medication.
Drug Interactions
Drugs Metabolized by P450 2D6 - The biochemical activity of the drug metabolizing isozyme cytochrome P450 2D6 (debrisoquin hydroxylase) is reduced in a subset of the Caucasian population (about 7% to 10% of Caucasians are so-called “poor metabolizers”); reliable estimates of the prevalence of reduced P450 2D6 isozyme activity among Asian, African, and other populations are not yet available. Poor metabolizers have higher than expected plasma concentrations of tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) when given usual doses. Depending on the fraction of drug metabolized by P450 2D6, the increase in plasma concentration may be small, or quite large (8-fold increase in plasma AUC of the TCA).
In addition, certain drugs inhibit the activity of this isozyme and make normal metabolizers resemble poor metabolizers. An individual who is stable on a given dose of TCA may become abruptly toxic when given one of these inhibiting drugs as concomitant therapy. The drugs that inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 include some that are not metabolized by the enzyme (quinidine; cimetidine) and many that are substrates for P450 2D6 (many other antidepressants, phenothiazines, and the Type 1C antiarrhythmics propafenone and flecainide). While all the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), e.g., fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine, inhibit P450 2D6, they may vary in the extent of inhibition. The extent to which SSRI-TCA interactions may pose clinical problems will depend on the degree of inhibition and the pharmacokinetics of the SSRI involved. Nevertheless, caution is indicated in the co-administration of TCAs with any of the SSRIs and also in switching from one class to the other. Of particular importance, sufficient time must elapse before initiating TCA treatment in a patient being withdrawn from fluoxetine, given the long half-life of the parent and active metabolite (at least 5 weeks may be necessary).
Concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants with drugs that can inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 may require lower doses than usually prescribed for either the tricyclic antidepressant or the other drug. Furthermore, whenever one of these other drugs is withdrawn from co-therapy, an increased dose of tricyclic antidepressant may be required. It is desirable to monitor TCA plasma levels whenever a TCA is going to be co-administered with another drug known to be an inhibitor of P450 2D6.
The plasma concentration of imipramine may increase when the drug is given concomitantly with hepatic enzyme inhibitors (e.g., cimetidine, fluoxetine) and decrease by concomitant administration with hepatic enzyme inducers (e.g., barbiturates, phenytoin), and adjustment of the dosage of imipramine may therefore be necessary.
In occasional susceptible patients or in those receiving anticholinergic drugs (including antiparkinsonism agents) in addition, the atropine-like effects may become more pronounced (e.g., paralytic ileus). Close supervision and careful adjustment of dosage is required when imipramine pamoate is administered concomitantly with anticholinergic drugs.
Avoid the use of preparations, such as decongestants and local anesthetics, that contain any sympathomimetic amine (e.g., epinephrine, norepinephrine), since it has been reported that tricyclic antidepressants can potentiate the effects of catecholamines.
Caution should be exercised when imipramine pamoate is used with agents that lower blood pressure. Imipramine pamoate may potentiate the effects of CNS depressant drugs.
Patients should be warned that imipramine pamoate may enhance the CNS depressant effects of alcohol. (See WARNINGS.)
Pregnancy
Animal reproduction studies have yielded inconclusive results. (See also ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY.)
There have been no well-controlled studies conducted with pregnant women to determine the effect of imipramine on the fetus. However, there have been clinical reports of congenital malformations associated with the use of the drug. Although a causal relationship between these effects and the drug could not be established, the possibility of fetal risk from the maternal ingestion of imipramine cannot be excluded. Therefore, imipramine should be used in women who are or might become pregnant only if the clinical condition clearly justifies potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Limited data suggest that imipramine is likely to be excreted in human breast milk. As a general rule, a woman taking a drug should not nurse since the possibility exists that the drug may be excreted in breast milk and be harmful to the child.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in the pediatric population have not been established (see BOX WARNING and WARNINGS-Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk).
It is generally recommended that imipramine pamoate capsules should not be used in children because of the increased potential for acute overdosage due to the high unit potency (75 mg, 100 mg, 125 mg, and 150 mg). Each capsule contains imipramine pamoate equivalent to 75 mg, 100 mg, 125 mg, or 150 mg imipramine hydrochloride. Anyone considering the use of imipramine pamoate in a child or adolescent must balance the potential risks with the clinical need.
Geriatric Use
In the literature, there were four well-controlled, randomized, double-blind, parallel group comparison clinical studies done with Tofranil® in the elderly population. There was a total number of 651 subjects included in these studies. These studies did not provide a comparison to younger subjects. There were no additional adverse experiences identified in the elderly.
Clinical studies of Tofranil® in the original application did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Post-marketing clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger subjects. In general, dose selection for the elderly should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
(see also DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION in Adolescent and Geriatric Patients)
(see also PRECAUTIONS General)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Note: Although the listing which follows includes a few adverse reactions which have not been reported with this specific drug, the pharmacological similarities among the tricyclic antidepressant drugs require that each of the reactions be considered when imipramine is administered.
Cardiovascular: Orthostatic hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, palpitation, myocardial infarction, arrhythmias, heart block, ECG changes, precipitation of congestive heart failure, stroke.
Psychiatric: Confusional states (especially in the elderly) with hallucinations, disorientation, delusions; anxiety, restlessness, agitation; insomnia and nightmares; hypomania; exacerbation of psychosis.
Neurological: Numbness, tingling, paresthesias of extremities; incoordination, ataxia, tremors; peripheral neuropathy; extrapyramidal symptoms; seizures, alterations in EEG patterns; tinnitus.
Anticholinergic: Dry mouth, and, rarely, associated sublingual adenitis; blurred vision, disturbances of accommodation, mydriasis; constipation, paralytic ileus; urinary retention, delayed micturition, dilation of the urinary tract.
Allergic: Skin rash, petechiae, urticaria, itching, photosensitization; edema (general or of face and tongue); drug fever; cross-sensitivity with desipramine.
Hematologic: Bone marrow depression including agranulocytosis; eosinophilia; purpura; thrombocytopenia.
Gastrointestinal: Nausea and vomiting, anorexia, epigastric distress, diarrhea; peculiar taste, stomatitis, abdominal cramps, black tongue.
Endocrine: Gynecomastia in the male; breast enlargement and galactorrhea in the female; increased or decreased libido, impotence; testicular swelling; elevation or depression of blood sugar levels; inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion syndrome.
Other: Jaundice (simulating obstructive); altered liver function; weight gain or loss; perspiration; flushing; urinary frequency; drowsiness, dizziness, weakness and fatigue; headache; parotid swelling; alopecia; proneness to falling.
Withdrawal Symptoms: Though not indicative of addiction, abrupt cessation of treatment after prolonged therapy may produce nausea, headache and malaise.
OVERDOSAGE
Deaths may occur from overdosage with this class of drugs. Multiple drug ingestion (including alcohol) is common in deliberate tricyclic overdose. As the management is complex and changing, it is recommended that the physician contact a poison control center for current information on treatment. Signs and symptoms of toxicity develop rapidly after tricyclic overdose. Therefore, hospital monitoring is required as soon as possible.
Children have been reported to be more sensitive than adults to an acute overdosage of imipramine pamoate. An acute overdose of any amount in infants or young children, especially, must be considered serious and potentially fatal.
Manifestations
These may vary in severity depending upon factors such as the amount of drug absorbed, the age of the patient, and the interval between drug ingestion and the start of treatment. Critical manifestations of overdose include cardiac dysrhythmias, severe hypotension, convulsions, and CNS depression including coma. Changes in the electrocardiogram, particularly in QRS axis or width, are clinically significant indicators of tricyclic toxicity.
Other CNS manifestations may include drowsiness, stupor, ataxia, restlessness, agitation, hyperactive reflexes, muscle rigidity, athetoid and choreiform movements.
Cardiac abnormalities may include tachycardia, and signs of congestive failure. Respiratory depression, cyanosis, shock, vomiting, hyperpyrexia, mydriasis, and diaphoresis may also be present.
Management
Obtain an ECG and immediately initiate cardiac monitoring. Protect the patient's airway, establish an intravenous line, and initiate gastric decontamination. A minimum of 6 hours of observation with cardiac monitoring and observation for signs of CNS or respiratory depression, hypotension, cardiac dysrhythmias and/or conduction blocks, and seizures is necessary. If signs of toxicity occur at any time during this period, extended monitoring is required. There are case reports of patients succumbing to fatal dysrhythmias late after overdose; these patients had clinical evidence of significant poisoning prior to death and most received inadequate gastrointestinal decontamination. Monitoring of plasma drug levels should not guide management of the patient.
Gastrointestinal Decontamination - All patients suspected of tricyclic overdose should receive gastrointestinal decontamination. This should include large volume gastric lavage followed by activated charcoal. If consciousness is impaired, the airway should be secured prior to lavage. Emesis is contraindicated.
Cardiovascular - A maximal limb-lead QRS duration of ≥ 0.10 seconds may be the best indication of the severity of the overdose. Intravenous sodium bicarbonate should be used to maintain the serum pH in the range of 7.45 to 7.55. If the pH response is inadequate, hyperventilation may also be used. Concomitant use of hyperventilation and sodium bicarbonate should be done with extreme caution, with frequent pH monitoring. A pH >7.60 or a Pco2 < 20 mmHg is undesirable.
Dysrhythmias unresponsive to sodium bicarbonate therapy/ hyperventilation may respond to lidocaine, bretylium, or phenytoin. Type 1A and 1C antiarrhythmics are generally contraindicated (e.g., quinidine, disopyramide, and procainamide).
In rare instances, hemoperfusion may be beneficial in acute refractory cardiovascular instability in patients with acute toxicity. However, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, exchange transfusions, and forced diuresis generally have been reported as ineffective in tricyclic poisoning.
CNS - In patients with CNS depression, early intubation is advised because of the potential for abrupt deterioration. Seizures should be controlled with benzodiazepines, or if these are ineffective, other anticonvulsants (e.g., phenobarbital, phenytoin). Physostigmine is not recommended except to treat life-threatening symptoms that have been unresponsive to other therapies, and then only in consultation with a poison control center.
Psychiatric Follow-up - Since overdosage is often deliberate, patients may attempt suicide by other means during the recovery phase. Psychiatric referral may be appropriate.
Pediatric Management - The principles of management of child and adult overdosages are similar. It is strongly recommended that the physician contact the local poison control center for specific pediatric treatment.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The following recommended dosages for imipramine pamoate capsules should be modified as necessary by the clinical response and any evidence of intolerance.
Initial Adult Dosage
Outpatients - Therapy should be initiated at 75 mg/day. Dosage may be increased to 150 mg/day which is the dose level at which optimum response is usually obtained. If necessary, dosage may be increased to 200 mg/day.
Dosage higher than 75 mg/day may also be administered on a once-a-day basis after the optimum dosage and tolerance have been determined. The daily dosage may be given at bedtime. In some patients it may be necessary to employ a divided-dose schedule.
As with all tricyclics, the antidepressant effect of imipramine may not be evident for one to three weeks in some patients.
Hospitalized Patients - Therapy should be initiated at 100 to 150 mg/day and may be increased to 200 mg/day. If there is no response after two weeks, dosage should be increased to 250 to 300 mg/day.
Dosage higher than 150 mg/day may also be administered on a once-a-day basis after the optimum dosage and tolerance have been determined. The daily dosage may be given at bedtime. In some patients it may be necessary to employ a divided-dose schedule.
As with all tricyclics, the antidepressant effect of imipramine may not be evident for one to three weeks in some patients.
Adult Maintenance Dosage - Following remission, maintenance medication may be required for a longer period of time at the lowest dose that will maintain remission after which the dosage should gradually be decreased.
The usual maintenance dosage is 75 to 150 mg/day. The total daily dosage can be administered on a once-a-day basis, preferably at bedtime. In some patients it may be necessary to employ a divided-dose schedule.
In cases of relapse due to premature withdrawal of the drug, the effective dosage of imipramine should be reinstituted.
Adolescent and Geriatric Patients - Therapy in these age groups should be initiated with Tofranil®, brand of imipramine hydrochloride, tablets at a total daily dosage of 25 to 50 mg, since imipramine pamoate capsules are not available in these strengths. Dosage may be increased according to response and tolerance, but it is generally unnecessary to exceed 100 mg/day in these patients. Imipramine pamoate capsules may be used when total daily dosage is established at 75 mg or higher.
The total daily dosage can be administered on a once-a-day basis, preferably at bedtime. In some patients it may be necessary to employ a divided-dose schedule.
As with all tricyclics, the antidepressant effect of imipramine may not be evident for one to three weeks in some patients.
Adolescent and geriatric patients can usually be maintained at lower dosage. Following remission, maintenance medication may be required for a longer period of time at the lowest dose that will maintain remission after which the dosage should gradually be decreased.
The total daily maintenance dosage can be administered on a once-a-day basis, preferably at bedtime. In some patients it may be necessary to employ a divided-dose schedule.
In cases of relapse due to premature withdrawal of the drug, the effective dosage of imipramine should be reinstituted.
HOW SUPPLIED
Imipramine Pamoate Capsules
Capsules 75 mg - coral body imprinted in black “
Bottles of 30............................................NDC 0406-9931-03
Capsules 100 mg - maize body imprinted in black “
Bottles of 30...........................................NDC 0406-9932-03
Capsules 125 mg - ivory body imprinted in black “
Bottles of 30...........................................NDC 0406-9933-03
Capsules 150 mg - coral body imprinted in black “
Bottles of 30...........................................NDC 0406-9934-03
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in tight container (USP) with a child-resistant closure.
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY
A. Acute: Oral LD50:
Mouse 2185 mg/kg
Rat (F) 1142 mg/kg
(M) 1807 mg/kg
Rabbit 1016 mg/kg
Dog 693 mg/kg (Emesis ED50)
B. Subacute:
Two three-month studies in dogs gave evidence of an adverse drug effect on the testes, but only at the highest dose level employed, i.e., 90 mg/kg (10 times the maximum human dose). Depending on the histological section of the testes examined, the findings consisted of a range of degenerative changes up to and including complete atrophy of the seminiferous tubules, with spermatogenesis usually arrested.
Human studies show no definitive effect on sperm count, sperm motility, sperm morphology or volume of ejaculate.
Rat
One three-month study was done in rats at dosage levels comparable to those of the dog studies. No adverse drug effect on the testes was noted in this study, as confirmed by histological examination.
C. Reproduction/Teratogenic:
Oral: Imipramine pamoate was fed to male and female albino rats for 28 weeks through two breeding cycles at dose levels of 15 mg/kg/day and 40 mg/kg/day (equivalent to 2 1/2 and 7 times the maximum human dose).
No abnormalities which could be related to drug administration were noted in gross inspection. Autopsies performed on pups from the second breeding likewise revealed no pathological changes in organs or tissues; however, a decrease in mean litter size from both matings was noted in the drug-treated groups and significant growth suppression occurred in the nursing pups of both sexes in the high group as well as in the females of the low-level group. Finally, the lactation index (pups weaned divided by number left to nurse) was significantly lower in the second litter of the high-level group.
Tofranil and
tyco
Healthcare
Mallinckrodt
Manufactured by
Patheon Inc.
Whitby, Ontario, Canada
L1N 5Z5
Manufactured for
Mallinckrodt Inc.
St. Louis, MO 63134
Printed in U.S.A.
Rev 081106
Medication Guide
About Using Antidepressants in Children and Teenagers
What is the most important information I should know if my child is being prescribed an antidepressant?
Parents or guardians need to think about 4 important things when their child is prescribed an antidepressant:
- There is a risk of suicidal thoughts or actions
- How to try to prevent suicidal thoughts or actions in your child
- You should watch for certain signs if your child is taking an antidepressant
- There are benefits and risks when using antidepressants
1. There is a Risk of Suicidal Thoughts or Actions
Children and teenagers sometimes think about suicide, and many report trying to kill themselves.
Antidepressants increase suicidal thoughts and actions in some children and teenagers. But suicidal thoughts and actions can also be caused by depression, a serious medical condition that is commonly treated with antidepressants. Thinking about killing yourself or trying to kill yourself is called suicidality or being suicidal.
A large study combined the results of 24 different studies of children and teenagers with depression or other illnesses. In these studies, patients took either a placebo (sugar pill) or an antidepressant for 1 to 4 months. No one committed suicide in these studies, but some patients became suicidal. On sugar pills, 2 out of every 100 became suicidal. On the antidepressants, 4 out of every 100 patients became suicidal.
For some children and teenagers, the risks of suicidal actions may be especially high. These include patients with
- Bipolar illness (sometimes called manic-depressive illness)
- A family history of bipolar illness
- A personal or family history of attempting suicide
If any of these are present, make sure you tell your health care provider before your child takes an antidepressant.
2. How to Try to Prevent Suicidal Thoughts and Actions
To try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions in your child, pay close attention to changes in her or his moods or actions, especially if the changes occur suddenly. Other important people in your child's life can help by paying attention as well (e.g., your child, brothers and sisters, teachers, and other important people). The changes to look out for are listed in Section 3, on what to watch for.
Whenever an antidepressant is started or its dose is changed, pay close attention to your child.
After starting an antidepressant, your child should generally see his or her health care provider:
- Once a week for the first 4 weeks
- Every 2 weeks for the next 4 weeks
- After taking the antidepressant for 12 weeks
- After 12 weeks, follow your health care provider's advice about how often to come back
- More often if problems or questions arise (see Section 3)
You should call your child's health care provider between visits if needed.
3. You Should Watch for Certain Signs If Your Child is Taking an Antidepressant
Contact your child's health care provider right away if your child exhibits any of the following signs for the first time, or if they seem worse, or worry you, your child, or your child's teacher:
- Thoughts about suicide or dying
- Attempts to commit suicide
- New or worse depression
- New or worse anxiety
- Feeling very agitated or restless
- Panic attacks
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
- New or worse irritability
- Acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- Acting on dangerous impulses
- An extreme increase in activity and talking
- Other unusual changes in behavior or mood
Never let your child stop taking an antidepressant without first talking to his or her health care provider. Stopping an antidepressant suddenly can cause other symptoms.
4. There are Benefits and Risks When Using Antidepressants
Antidepressants are used to treat depression and other illnesses. Depression and other illnesses can lead to suicide. In some children and teenagers, treatment with an antidepressant increases suicidal thinking or actions. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and also the risks of not treating it. You and your child should discuss all treatment choices with your health care provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
Other side effects can occur with antidepressants (see section below).
Of all the antidepressants, only fluoxetine (Prozac®)* has been FDA approved to treat pediatric depression.
For obsessive compulsive disorder in children and teenagers, FDA has approved only fluoxetine (Prozac®)*, sertraline (Zoloft®)*, fluvoxamine, and clomipramine (Anafranil®)*.
Your health care provider may suggest other antidepressants based on the past experience of your child or other family members.
Is this all I need to know if my child is being prescribed an antidepressant?
No. This is a warning about the risk for suicidality. Other side effects can occur with antidepressants. Be sure to ask your health care provider to explain all the side effects of the particular drug he or she is prescribing. Also ask about drugs to avoid when taking an antidepressant. Ask your health care provider or pharmacist where to find more information.
*Prozac® is a registered trademark of Eli Lilly and Company
*Zoloft® is a registered trademark of Pfizer Pharmaceuticals
*Anafranil® is a registered trademark of Mallinckrodt Inc.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for all antidepressants.
| imipramine pamoate (imipramine pamoate) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| imipramine pamoate (imipramine pamoate) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| imipramine pamoate (imipramine pamoate) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| imipramine pamoate (imipramine pamoate) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revised: 08/2007Mallinckrodt Inc.