PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE, GUAIFENESIN
-
pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and
guaifenesin tablet
Prasco Laboratories
----------
Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride 120 mgGuaifenesin 1200 mg
Tablets
11 DESCRIPTION
Each extended-release tablet contains:
Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride .... 120 mg
Guaifenesin.......... 1200 mg
Inactive ingredients: calcium phosphate, Eudagit NE 30, magnesium stearate, methylcellulose.
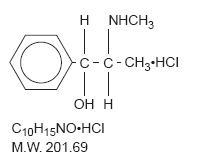
Chemically, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is benzenemethanol, α-[1-(methylamino)ethyl]-,[SR*, R*)]-, hydrochloride. It has the following structural formula:
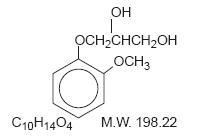
Chemically, guaifenesin is 1,2-propanediol,3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-,(±)-. It has the following structural formula:
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pseudoephedrine hydrochloride is an α-adrenergic receptor agonist (sympathomimetic) which produces vasoconstriction by stimulating α-receptors within the mucosa of the respiratory tract. Clinically pseudoephedrine shrinks swollen mucous membranes, reduces tissue hyperemia, edema, and nasal congestion, and increases nasal airway patency. The vasoconstriction action of pseudoephedrine is similar to that of ephedrine. In the usual dose it has minimal vasopressor effects. Pseudoephedrine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It has a plasma half-life of 6 to 8 hours. Acidic urine is associated with faster elimination of the drug. The drug is distributed to body tissues and fluids, including the fetal tissue, breast milk and the central nervous system central nervous system (CNS). Approximately 50% to 75% of the administered dose is excreted unchanged in the urine; the remainder is apparently metabolized in the liver to inactive compounds by N-demethylation, parahydroxylation and oxidative deamination.
Guaifenesin is an expectorant which increases respiratory tract fluid secretions and helps to loosen phlegm and bronchial secretions. By reducing the viscosity of secretions, guaifenesin increases the efficiency of the cough reflex and of ciliary action in removing accumulated secretions from the trachea and bronchi. Guaifenesin is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is rapidly metabolized and excreted i n the urine. Guaifenesin has a plasma half-life of one hour. The major urinary metabolite is â-(2-methoxy-phenoxy) lactic acid.
As a result of these drugs, sinus and bronchial drainage is improved, and dry, nonproductive coughs become more productive and less frequent.
1 INDICATIONS & USAGE
For temporary relief of nasal congestion and cough associated with respiratory tract infections and related conditions such as sinusitis, pharyngitis, bronchitis, and asthma, when these conditions are complicated by tenacious mucus and/or mucus plugs and congestion. The product is effective in a productive as well as a nonproductive cough, but is of particular value in a dry, nonproductive cough which tends to injure the mucous membrane of the air passages.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
This product is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to guaifenesin, or with hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to sympathomimetic amines which may be manifested by insomnia, dizziness, weakness, tremor or arrhythmias.
Sympathomimetic amines are contraindicated in patients with severe hypertension, severe coronary artery disease and patients on monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor therapy (see Drug Interactions section).
This product is contraindicated in women who are pregnant or nursing. This product is not recommended for use in pediatric patients under six years of age. Geriatric patients may be more sensitive to the effects of this medication.
WARNINGS
Sympathomimetic amines should be used with caution in patients with hypertension, ischemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, or prostatic hypertrophy. Sympathomimetics may produce central nervous system stimulation with convulsions or cardiovascular collapse with accompanying hypotension. Do not exceed recommended dosage.
Hypertensive crises can occur with concurrent use of pseudoephedrine and monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, indomethacin, or with beta blockers and methyldopa. If a hypertensive crisis occurs, these drugs should be discontinued immediately and theraued immediately and therapy to lower blood pressure should be instituted. Fever should be managed by means of external cooling.
GENERAL PRECAUTIONS
Pseudoephedrine-containing preparations should be used with caution in the presence of: hypertension; coronary artery disease; any other cardiovascular disease; glaucoma; prostatic hypertrophy; hyperthyroidism; diabetes.
Before prescribing medication to suppress or modify cough, it is important to ascertain that the underlying cause of cough is identified, that modification of cough does not increase the risk of clinical or physiologic complications, and that appropriate therapy for the primary disease is instituted.
17 INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Patient consultation should include the following information regarding proper use of this medication:
- Do not take more medication than the amount recommended.
- Take medication with food, water, or milk to minimize gastric irritation.
- Do not ingest monoamine oxidase inhibitors while taking this medication.
- If a dose is missed, the medication should be taken as soon as possible unless it is almost time for the next dose; not doubling doses.
- This medication should be stored in a tight, light-resistant container at temperatures between 59°-86°F (15°- 30°C).
- Keep all medications out of the reach of children. In case of accidental overdose, seek professional assistance or contact a poison control center immediately.
4 PEDIATRIC USE
This product is not recommended for use in children under 6 years of age. Pseudoephedrine may be more likely to cause side effects in infants, especially newborn and premature infants, than in older children and adults. No age specific problems related to guaifenesin have been documented in the pediatric population to date.
Demonstrate safe use of a short-acting sympathomimetic amine before use of a sustained-action formulation in pediatric patients.
5 GERIATRIC USE
Use in Patients Approximately 60 Years and Older: Geriatric patients taking sympathomimetics may be more likely to experience confusion, hallucinations, seizures, and CNS depression. Geriatric patients may also be more sensitive to the effects, especially to the vasopressor effects of sympathomimetic amines. No age specific problems related to guaifenesin have been documented in the geriatric population to date.
Demonstrate safe use of a short-acting sympathomimetic formulation before use of a sustained action formulation in elderly patients.
DRUG & OR LABORATORY TEST INTERACTIONS
The in vitro addition of pseudoephedrine to sera containing the cardiac isoenzyme MB of serum creatine phosphokinase progressively inhibits the activity of the enzyme. The inhibition becomes complete over six hours.
Guaifenesin may increase renal clearance for urate and thereby lower serum uric acid levels.
Guaifenesin may produce an increase in urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid and may therefore interfere with the interpretation of this test for the diagnosis of carcinoid syndrome. It may also falsely elevate the VMA test for catechols. Administration of this drug should be discontinued 48 hours prior to the collection of urine specimens for such tests.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Do not take this product if you are presently taking, or have taken within the preceding two weeks, a prescription drug for high blood pressure or depression without first consulting your physician.
- MAO Inhibitors and Tricyclic Antidepressants – hypertensive reactions, including hypertensive crises may occur when sympathomimetic drugs are given to patients receiving monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors.
- Antihypertensives - the antihypertensive effects of guanethidine, methyldopa, mecamylamine, reserpine, and veratrum alkaloids may be reduced by sympathomimetics. Beta-adrenergic blocking agents may also interact with sympathomimetics.
- Digitalis – increased ectopic pacemaker activity can occur when pseudoephedrine is used concomitantly with digitalis.
- Antacids – increase the rate of absorption of pseudoephedrine, while kaolin decreases it.
1 CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY
No data are available on the long-term potential of the components of this product for carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility in animals or humans.
1 PREGNANCY
Category C.
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with the components of this product. It is also not known whether these drugs can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Accordingly, this product should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
This product is contraindicated in women who are pregnant.
3 NURSING MOTHERS
Pseudoephedrine is excreted in breast milk. Use of this product by nursing mothers is not recommended because of the higher than usual risk for infants from sympathomimetic amines.
This product is contraindicated in women who are nursing.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Hyperreactive individuals may display ephedrine-like reactions such as tachycardia, palpitations, headache, dizziness, or nausea. Sympathomimetics have been associated with certain untoward reactions including fear, anxiety, nervousness, restlessness, tremor, weakness, pallor, respiratory difficulty, dysuria, insomnia, hallucinations, convulsions, CNS depression, arrhythmias, and cardiovascular collapse with hypotension.
No serious side effects have been reported with the use of guaifenesin.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Since this product contains two pharmacologically different compounds, treatment of overdosage should be based upon the symptomatology of the patient as it relates to the individual ingredients. Treatment of acute overdosage would probably be based upon treating the patient for pseudoephedrine toxicity which may manifest itself as excessive CNS stimulation resulting in excitement, tremor, restlessness, and insomnia. Other effects may include tachycardia, hypertension, pallor, mydriasis, hyperglycemia and urinary retention. Severe overdosage may cause tachypnea or hyperpnea, hallucinations, convulsions or delirium, but in some individuals there may be CNS depression with somnolence, stupor or respiratory depression. Arrhythmias (including ventricular fibrillation) may lead to hypotension and circulatory collapse. Severe hypokalemia can occur, probably due to a compartmental shift rather than a depletion of potassium. No organ damage or significant metabolic derangement is associated with pseudoephedrine overdosage. Overdosage with guaifenesin is unlikely to produce toxic effects since its toxicity is much lower than that of pseudoephedrine. The LD64 of pseudoephedrine (single oral dose) has been reported to be 726 mg/kg in the mouse, 2206 mg/kg in the rat and 1177 mg/kg in the rabbit. An oral TDLo of 714 μg/kg has been reported for humans. Urinary excretion increases with acidification and decreases with alkalinization of the urine. There are few published reports of toxicity due to pseudoephedrine and no case of fatal overdose has been reported. Guaifenesin, when administered by stomach tube to test animals in doses up to 5 gm/kg produced no signs of toxicity.
Since the action of sustained-release products may continue for as long as 12 hours, treatment of as 12 hours, treatment of overdosage should be directed toward reducing further absorption and supporting the patient for at least that length of time. Gastric emptying (Syrup of Ipecac)and/or lavage is recommended as soon as possible after ingestion, even if the patient has vomited spontaneously. Either isotonic or half-isotonic saline may be used for lavage. Administration of an activated charcoal slurry is beneficial after lavage and/or emesis if less than four hours have passed since ingestion. Saline cathartics, such as Milk of Magnesia, are useful for hastening the evacuation of unreleased medication.
Adrenergic receptor blocking agents are antidotes to pseudoephedrine. In practice, the most useful is the beta blocker propanolol which is indicated when there are signs of cardiac toxicity. Theoretically, pseudoephedrine is dialyzable but procedures have not been clinically established.
In severe cases of overdosage, it is essential to monitor both the heart (by electrocardiograph) and plasma electrolytes, and to give intravenous potassium as indicated. Vasopressors may be used to treat hypotension. Excessive CNS stimulation may be counteracted with parenteral diazepam. Stimulants should not be used.
Hyperpyrexia, especially in children, may require treatment with tepid water sponge baths or a hyperthermic blanket. Apnea is treated with ventilatory support.
Overdosage with guaifenesin is unlikely to produce toxic effects since its toxicity is low. Guaifenesin, when administered by stomach tube to test animals in doses up to 5 gm/kg, produced no signs of toxicity.
2 DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Adults and children 12 years and older: 1 tablet every 12 hours not to exceed 2 tablets in 24 hours.
Children 6 to under 12 years: One-half (1/2) tablet every 12 hours not to exceed 1 tablet in 24 hours.
This product is not recommended for children under 6 years of age.
Tablets may be broken in half for ease of administration without affecting release of medication but should not be crushed or chewed prior to swallowing.
16 HOW SUPPLIED
Supplied as white, capsule-shaped tablets, scored and debossed “332” on top, Prasco Laboratories logo on bottom. Bottles of 100 tablets, NDC 66993-332-02.
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATION OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN. IN
CASE OF ACCIDENTAL OVERDOSE, SEEK PROFESSIONAL ASSISTANCE OR CONTACT A POISON CONTROL CENTER IMMEDIATELY.
Dispense in tight, light-resistant containers as defined in USP-NF.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted at 15-30°C (59-86°F). [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] Protect from light and moisture.
Manufactured For:
PRASCO LABORATORIES
Cincinnati, OH 45249
by:
Sovereign Pharmaceuticals, Ltd.
Fort Worth, TX 76118
PIPRAS-06
Iss. 3/2002
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

| PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE, GUAIFENESIN
pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, guaifenesin tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| Unapproved drug other | 01/01/2008 | 07/31/2009 | |
| Labeler - Prasco Laboratories (065969375) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Sovereign Pharmaceuticals, Ltd. | 623168267 | MANUFACTURE | |