GAMUNEX-C
-
human immunoglobulin g injection
TALECRIS BIOTHERAPEUTICS, INC.
----------
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
GAMUNEX®-C, [Immune Globulin Injection (Human) 10% Caprylate/Chromatography Purified]
WARNING: RENAL DYSFUNCTION AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
- Renal dysfunction, acute renal failure, osmotic nephrosis, and death may occur with immune globulin intravenous (IGIV) products in predisposed patients. Patients predisposed to renal dysfunction include those with any degree of pre-existing renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, age greater than 65, volume depletion, sepsis, paraproteinemia, or patients receiving known nephrotoxic drugs.
- Renal dysfunction and acute renal failure occur more commonly in patients receiving IGIV products containing sucrose. [1] GAMUNEX-C does not contain sucrose.
- For patients at risk of renal dysfunction or failure, administer GAMUNEX-C at the minimum concentration available and the minimum infusion rate practicable. (see Warnings and Precautions [5.2])
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
GAMUNEX-C is an immune globulin injection (human) 10% liquid that is indicated for the treatment of:
1.1 Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency (PI)
GAMUNEX-C is indicated as replacement therapy of primary humoral immunodeficiency. This includes, but is not limited to, congenital agammaglobulinemia, common variable immunodeficiency, X-linked agammaglobulinemia, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, and severe combined immunodeficiencies. [2-5]
1.2 Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
GAMUNEX-C is indicated for the treatment of patients with Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura to raise platelet counts to prevent bleeding or to allow a patient with ITP to undergo surgery [6-7].
1.3 Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP)
GAMUNEX-C is indicated for the treatment of CIDP to improve neuromuscular disability and impairment and for maintenance therapy to prevent relapse.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
GAMUNEX-C consists of 9%–11% protein in 0.16–0.24 M glycine. The buffering capacity of GAMUNEX-C is 35.0 mEq/L (0.35 mEq/g protein). A dose of 1 g/kg body weight therefore represents an acid load of 0.35 mEq/kg body weight. The total buffering capacity of whole blood in a normal individual is 45–50 mEq/L of blood, or 3.6 mEq/kg body weight. Thus, the acid load delivered with a dose of 1 g/kg of GAMUNEX-C would be neutralized by the buffering capacity of whole blood alone, even if the dose was infused instantaneously.
2.1 Preparation and Handling
- GAMUNEX-C should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if turbid.
- Do not freeze. Solutions that have been frozen should not be used.
- The GAMUNEX-C vial is for single use only. GAMUNEX-C contains no preservative. Any vial that has been entered should be used promptly. Partially used vials should be discarded.
- GAMUNEX-C should be infused using a separate line by itself, without mixing with other intravenous fluids or medications the subject might be receiving.
- GAMUNEX-C is not compatible with saline. If dilution is required, GAMUNEX-C may be diluted with 5% dextrose in water (D5/W). No other drug interactions or compatibilities have been evaluated.
- Content of vials may be pooled under aseptic conditions into sterile infusion bags and infused within 8 hours after pooling.
- Do not mix with immune globulin intravenous (IGIV) products from other manufacturers.
- Do not use after expiration date.
2.2 Treatment of Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency
As there are significant differences in the half-life of IgG among patients with primary humoral immunodeficiencies, the frequency and amount of immunoglobulin therapy may vary from patient to patient. The proper amount can be determined by monitoring clinical response.
Intravenous (IV)
The dose of GAMUNEX-C for patients with PI is 300 to 600 mg/kg body weight (3-6 mL/kg) administered every 3 to 4 weeks. The dosage may be adjusted over time to achieve the desired trough levels and clinical responses.
The recommended initial infusion rate is 1 mg/kg/min (0.01 mL/kg/min). If the infusion is well-tolerated, the rate may be gradually increased to a maximum of 8 mg/kg/min (0.08 mL/kg/min). For patients judged to be at risk for renal dysfunction or thrombotic events, administer GAMUNEX-C at the minimum infusion rate practicable. (see Warnings and Precautions [5.2,5.5])
If a patient routinely receives a dose of less than 400 mg/kg of GAMUNEX-C every 3 to 4 weeks (less than 4 mL/kg), and is at risk of measles exposure (i.e., traveling to a measles endemic area), administer a dose of at least 400 mg/kg (4 mL/kg) just prior to the expected measles exposure. If a patient has been exposed to measles, a dose of 400 mg/kg (4 mL/kg) should be administered as soon as possible after exposure.
Subcutaneous (SC)
The dose should be individualized based on the patient’s clinical response to GAMUNEX-C therapy and serum IgG trough levels. Begin treatment with GAMUNEX-C one week after the patient’s last IGIV infusion. See below under "Initial Weekly Dose". Prior to switching treatment from IGIV to GAMUNEX-C, obtain the patient’s serum IgG trough level to guide subsequent dose adjustments. See below under "Dose Adjustment".
Establish the initial weekly dose of GAMUNEX-C by converting the monthly IGIV dose into a weekly equivalent and increasing it using a dose adjustment factor. The goal is to achieve a systemic serum IgG exposure (Area Under the Concentration-Time Curve [AUC]) not inferior to that of the previous IGIV treatment. If the patient has not been previously treated with IV GAMUNEX-C, convert the weekly IGIV dose by multiplying by 1.37, then dividing this dose into weekly doses based on the patient’s previous IGIV treatment interval. Monitor the patient’s clinical response, and adjust dose accordingly.
Initial Weekly Dose
To calculate the initial weekly dose of subcutaneous administration of GAMUNEX-C, multiply the previous IGIV dose in grams by the dose adjustment factor of 1.37; then divide this by the number of weeks between doses during the patient’s IGIV treatment (i.e., 3 or 4).
Initial SC dose = 1.37 × previous IGIV dose (in grams)
Number of weeks between IGIV doses
To convert the GAMUNEX-C dose (in grams) to milliliters (mL), multiply the calculated dose (in grams) by 10.
Dose adjustment
Over time, the dose may need to be adjusted to achieve the desired clinical response and serum IgG trough level. To determine if a dose adjustment may be considered, measure the patient’s serum IgG trough level on IGIV and as early as 5 weeks after switching from IGIV to subcutaneous. The target serum IgG trough level on weekly SC treatment is projected to be the last IGIV trough level plus 340 mg/dL. To determine if further dose adjustments are necessary, monitor the patients IgG trough level every 2 to 3 months.
To adjust the dose based on trough levels, calculate the difference (in mg/dL) of the patient’s serum IgG trough level from the target IgG trough level (the last IGIV trough level + 340 mg/dL). Then find this difference in Table 1 and the corresponding amount (in mL) by which to increase or decrease the weekly dose based on the patient’s body weight. However, the patient’s clinical response should be the primary consideration in dose adjustment.
|
|||||||||||||
| Difference From Target IgG Trough Level (mg/dL) | Body Weight (kg) | ||||||||||||
| 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 | |
| Dose Adjustment (mL per Week)* | |||||||||||||
| 50 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 100 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 20 |
| 150 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 13 | 15 | 18 | 20 | 23 | 25 | 28 | 30 |
| 200 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 17 | 20 | 23 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 37 | 40 |
| 250 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 13 | 17 | 21 | 25 | 29 | 33 | 38 | 42 | 46 | 50 |
| 300 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 |
| 350 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 18 | 23 | 29 | 35 | 41 | 47 | 53 | 58 | 64 | 70 |
| 400 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 20 | 27 | 33 | 40 | 47 | 53 | 60 | 67 | 73 | 80 |
| 450 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 23 | 30 | 38 | 45 | 53 | 60 | 68 | 75 | 83 | 90 |
| 500 | 8 | 13 | 17 | 25 | 33 | 42 | 50 | 58 | 67 | 75 | 83 | 92 | 100 |
For example, if a patient with a body weight of 70 kg has an actual IgG trough level of 900 mg/dL and the target level is 1000 mg/dL, this results in a difference of 100 mg/dL. Therefore, increase the weekly dose of subcutaneous dose by 12 mL.
Monitor the patient’s clinical response, and repeat the dose adjustment as needed.
Dosage requirements for patients switching to GAMUNEX-C from another Immune Globulin Subcutaneous (IGSC) product have not been studied. If a patient on GAMUNEX-C does not maintain an adequate clinical response or a serum IgG trough level equivalent to that of the previous IGSC treatment, the physician may want to adjust the dose. For such patients, Table 1 also provides guidance for dose adjustment to achieve a desired IGSC trough level.
2.3 Treatment of Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
DO NOT ADMINISTER SUBCUTANEOUSLY (see Warnings and Precautions [5.3])
GAMUNEX-C may be administered at a total dose of 2 g/kg, divided in two doses of 1 g/kg (10 mL/kg) given on two consecutive days or into five doses of 0.4 g/kg (4 mL/kg) given on five consecutive days. If after administration of the first of two daily 1 g/kg (10 mL/kg) doses, an adequate increase in the platelet count is observed at 24 hours, the second dose of 1g/kg (10 mL/kg) body weight may be withheld.
Forty-eight ITP subjects were treated with 2 g/kg GAMUNEX-C, divided in two 1 g/kg doses (10 mL/kg) given on two successive days. With this dose regimen 35/39 subjects (90%) responded with a platelet count from less than or equal to 20 x109/L to more than or equal to 50 x109/L within 7 days after treatment. The high dose regimen (1 g/kg × 1-2 days) is not recommended for individuals with expanded fluid volumes or where fluid volume may be a concern.
The recommended initial infusion rate is 1 mg/kg/min (0.01 mL/kg/min). If the infusion is well-tolerated, the rate may be gradually increased to a maximum of 8 mg/kg/min (0.08 mL/kg/min). For patients judged to be at risk for renal dysfunction or thrombotic events, GAMUNEX-C should be administered at the minimum infusion rate practicable (see Warnings and Precautions [5.2,5.5]).
2.4 Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
GAMUNEX-C may be initially administered as a total loading dose of 2 g/kg (20 mL/kg) given in divided doses over two to four consecutive days. GAMUNEX-C may be administered as a maintenance infusion of 1 g/kg (10 mL/kg) administered over 1 day or divided into two doses of 0.5 g/kg (5 mL/kg) given on two consecutive days, every 3 weeks.
The recommended initial infusion rate is 2 mg/kg/min (0.02 mL/kg/min). If the infusion is well tolerated, the rate may be gradually increased to a maximum of 8 mg/kg/min (0.08 mL/kg/min). For patients judged to be at risk for renal dysfunction or thrombotic events, GAMUNEX-C should be administered at the minimum infusion rate practicable. (see Warnings and Precautions [5.2,5.5])
2.5 Administration
Administer intravenously for treatment of PI, ITP and CIDP.
GAMUNEX-C may also be administered subcutaneously for the treatment of PI.
GAMUNEX-C should be at room temperature during administration.
GAMUNEX-C should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever the solution and container permit. Do not use if turbid and/or if discoloration is observed.
Intravenous
Only 18 gauge needles should be used to penetrate the stopper for dispensing product from the 10 mL vial; 16 gauge needles or dispensing pins should only be used with 25 mL vial sizes and larger. Needles or dispensing pins should only be inserted once and be within the stopper area delineated by the raised ring. The stopper should be penetrated perpendicular to the plane of the stopper within the ring.
| GAMUNEX® -C vial size | Gauge of needle to penetrate stopper |
| 10 mL | 18 gauge |
| 25, 50, 100, 200 mL | 16 gauge |
Any vial that has been opened should be used promptly. Partially used vials should be discarded.
If dilution is required, GAMUNEX-C may be diluted with 5% dextrose in water (D5/W). Do not dilute with saline.
Subcutaneous for PI only
Instructions for Administration
Prior to use, allow the solution to reach ambient room temperature. DO NOT SHAKE. Do not use if the solution is cloudy or has particulates. Check the product expiration date on the vial. Do not use beyond the expiration date.
- Use aseptic technique when preparing and administering GAMUNEX-C for injection.
- Remove the protective cap from the vial to expose the central portion of the rubber stopper.
- Wipe the rubber stopper with alcohol and allow to dry.
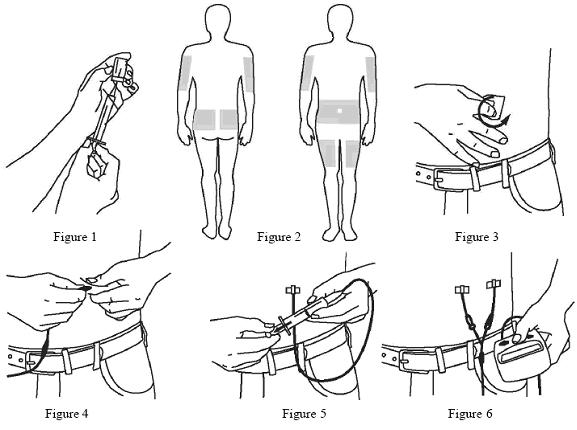
- Using a sterile syringe and needle, prepare to withdraw GAMUNEX-C by first injecting air into the vial that is equivalent to the amount of GAMUNEX-C to be withdrawn. Then withdraw the desired volume of GAMUNEX-C. If multiple vials are required to achieve the desired dose, repeat this step. (Figure 1)
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for filling the pump reservoir and preparing the pump, administration tubing and Y-site connection tubing, if needed. Be sure to prime the administration tubing to ensure that no air is left in the tubing or needle by filling the tubing/needle with GAMUNEX-C.
- Select the number and location of injection sites. (Figure 2)
- Cleanse the injection site(s) with antiseptic solution using a circular motion working from the center of the site and moving to the outside. Sites should be clean, dry, and at least two inches apart. (Figure 3)
- Grasp the skin between two fingers and insert the needle into the subcutaneous tissue. (Figure 4)
- Repeat priming and needle insertion steps using a new needle, administration tubing and a new infusion site. Secure the needle in place by applying sterile gauze or transparent dressing over the site. (Figure 5)
- If using multiple, simultaneous injection sites, use Y-site connection tubing and secure to the administration tubing.
- Infuse GAMUNEX-C following the manufacturer’s instructions for the pump. (Figure 6)
Rate of Administration
Intravenous
Following initial infusion (see table below), the infusion rate may be gradually increased to a maximum of 0.08 mL/kg per minute (8 mg/kg per minute) as tolerated.
| Indication | Initial Infusion Rate (first 30 minutes) | Maximum infusion rate (if tolerated) |
| PI | 1 mg/kg/min | 8 mg/kg/min |
| ITP | 1 mg/kg/min | 8 mg/kg/min |
| CIDP | 2 mg/kg/min | 8 mg/kg/min |
Monitor patient vital signs throughout the infusion. Slow or stop infusion if adverse reactions occur. If symptoms subside promptly, the infusion may be resumed at a lower rate that is comfortable for the patient.
Certain severe adverse drug reactions may be related to the rate of infusion. Slowing or stopping the infusion usually allows the symptoms to disappear promptly.
Ensure that patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency are not volume depleted. For patients at risk of renal dysfunction or thromboembolic events, administer GAMUNEX-C at the minimum infusion rate practicable and discontinue GAMUNEX-C if renal function deteriorates.
Subcutaneous for PI only
For PI, it is recommended that GAMUNEX-C is infused at a rate of 20 mL/hr per infusion site.
In the SC clinical study, the mean volume administered per infusion site was 34 mL (17-69 mL) and the majority of infusions were administered at a rate of 20 mL/hr per site. Multiple simultaneous infusion sites were enabled by administration tubing and Y-site connection tubing. Most subjects utilized 4 infusion sites per infusion with abdomen and thighs being the most commonly used sites. The maximum number of infusion sites is 8. Injection sites should be at least 2 inches apart.
Incompatibilities with Saline
GAMUNEX-C is not compatible with saline. If dilution is required GAMUNEX-C may be diluted with 5% dextrose in water (D5/W). No other drug interactions or compatibilities have been evaluated.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
GAMUNEX-C is supplied in 1 g, 2.5 g, 5 g, 10 g, or 20 g single use bottles.
- 1 g protein in 10 mL solution
- 2.5 g protein in 25 mL solution
- 5 g protein in 50 mL solution
- 10 g protein in 100 mL solution
- 20 g protein in 200 mL solution
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity reaction to immune globulins
GAMUNEX-C is contraindicated in patients who have had an anaphylactic or severe systemic reaction to the administration of human immune globulin.
4.2 IgA sensitive patients with history of hypersensitivity reaction
GAMUNEX-C is contraindicated in IgA deficient patients with antibodies against IgA and history of hypersensitivity.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur with IGIV products, including GAMUNEX-C. In case of hypersensitivity, discontinue GAMUNEX-C infusion immediately and institute appropriate treatment. Medications such as epinephrine should be available for immediate treatment of acute hypersensitivity reaction.
GAMUNEX-C contains trace amounts of IgA (average 46 micrograms/mL). Patients with known antibodies to IgA may have a greater risk of developing potentially severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions. It is contraindicated in IgA deficient patients with antibodies against IgA and history of hypersensitivity reaction.(see Contraindications [4])
5.2 Renal Failure
Assure that patients are not volume depleted prior to the initiation of the infusion of GAMUNEX-C. Periodic monitoring of renal function and urine output is particularly important in patients judged to have a potential increased risk for developing acute renal failure. Assess renal function, including measurement of blood urea nitrogen (BUN)/serum creatinine, prior to the initial infusion of GAMUNEX-C and again at appropriate intervals thereafter. If renal function deteriorates, consider discontinuation of GAMUNEX-C. (see Patient Counseling Information [17]) For patients judged to be at risk for developing renal dysfunction, including patients with any degree of pre-existing renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, age greater than 65, volume depletion, sepsis, paraproteinemia, or patients receiving known nephrotoxic drugs, administer GAMUNEX-C at the minimum infusion rate practicable [less than 8 mg IG/kg/min (0.08 mL/kg/min)]. (see Dosage and Administration [2.5])
5.3 Hematoma Formation
Do not administer GAMUNEX-C subcutaneously in patients with ITP because of the risk of hematoma formation.
5.4 Hyperproteinemia, Increased Serum Viscosity, and Hyponatremia
Hyperproteinemia, increased serum viscosity and hyponatremia may occur in patients receiving IGIV treatment, including GAMUNEX-C. It is clinically critical to distinguish true hyponatremia from a pseudohyponatremia that is associated with concomitant decreased calculated serum osmolality or elevated osmolar gap, because treatment aimed at decreasing serum free water in patients with pseudohyponatremia may lead to volume depletion, a further increase in serum viscosity and a possible predisposition to thromboembolic events. [8]
5.5 Thrombotic Events
Thrombotic events have been reported following IGIV treatment and may occur in patients receiving IGIV treatment, including GAMUNEX-C. [9-11] Patients at risk may include those with a history of atherosclerosis, multiple cardiovascular risk factors, advanced age, impaired cardiac output, coagulation disorders, prolonged periods of immobilization and/or known or suspected hyperviscosity. Consider baseline assessment of blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity, including those with cryoglobulins, fasting chylomicronemia/markedly high triacylglycerols (triglycerides), or monoclonal gammopathies. For patients judged to be at risk of developing thrombotic events, administer GAMUNEX-C at the minimum rate of infusion practicable. (see Dosage and Administration [2.5])
5.6 Aseptic Meningitis Syndrome (AMS)
AMS may occur infrequently with IGIV treatment, including GAMUNEX-C. Discontinuation of IGIV treatment has resulted in remission of AMS within several days without sequelae. The syndrome usually begins within several hours to two days following IGIV treatment. AMS is characterized by the following symptoms and signs: severe headache, nuchal rigidity, drowsiness, fever, photophobia, painful eye movements, nausea and vomiting. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) studies are frequently positive with pleocytosis up to several thousand cells per cu mm, predominantly from the granulocytic series, and with elevated protein levels up to several hundred mg/dL, but negative culture results. Conduct a thorough neurological examination on patients exhibiting such symptoms and signs including CSF studies, to rule out other causes of meningitis. AMS may occur more frequently in association with high doses (2 g/kg) and/or rapid infusion of IGIV.
5.7 Hemolysis
IGIV products, including GAMUNEX-C, may contain blood group antibodies which may act as hemolysins and induce in vivo coating of red blood cells (RBCs) with immunoglobulin, causing a positive direct antiglobulin reaction and, rarely, hemolysis.[12-14] Delayed hemolytic anemia can develop subsequent to IGIV therapy due to enhanced RBC sequestration, and acute hemolysis consistent with intravascular hemolysis, has been reported. Monitor patients for clinical signs and symptoms of hemolysis. [15] (see Patient Counseling Information [17]) If signs and/or symptoms of hemolysis are present after GAMUNEX-C infusion, perform appropriate confirmatory laboratory testing.
5.8 Transfusion-related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI)
Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema may occur in patients following treatment with IGIV products, including GAMUNEX-C. [16] TRALI is characterized by severe respiratory distress, pulmonary edema, hypoxemia, normal left ventricular function, and fever. Symptoms typically occur within 1 to 6 hours after treatment.
Monitor patients for pulmonary adverse reactions. (see Patient Counseling Information [17]) If TRALI is suspected, perform appropriate tests for the presence of anti-neutrophil and anti-HLA antibodies in both the product and patient serum. TRALI may be managed using oxygen therapy with adequate ventilatory support.
5.9 Volume Overload
The high dose regimen (1g/kg x 1-2 days) is not recommended for individuals with expanded fluid volumes or where fluid volume may be a concern.
5.10 Transmissible Infectious Agents
Because GAMUNEX-C is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. No cases of transmission of viral diseases or CJD have ever been identified for GAMUNEX-C. ALL infections suspected by a physician possibly to have been transmitted by this product should be reported by the physician or other healthcare provider to Talecris Biotherapeutics, Inc. [1-800-520-2807]
5.11 Laboratory Tests
After infusion of IgG, the transitory rise of the various passively transferred antibodies in the patient’s blood may yield positive serological testing results, with the potential for misleading interpretation.
Passive transmission of antibodies to erythrocyte antigens (e.g., A, B, and D) may cause a positive direct or indirect antiglobulin (Coombs’) test. Patients with known renal dysfunction or renal failure, including patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, age greater than 65, volume depletion, sepsis, paraproteinemia, or those receiving nephrotoxic agents, should be clinically assessed and monitored (BUN, creatinine), as appropriate, during therapy with GAMUNEX-C.
Consider baseline assessment of blood viscosity in patients at risk for hypervisocosity, including those with cryoglobulins, fasting chylomicronemia/markedly high triacylglycerols (triglycerides), or monoclonal gammopathies.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions observed at a rate ≥5% in subjects treated with IV GAMUNEX-C for PI were headache, cough, injection site reaction, nausea, pharyngitis and urticaria.
The most common adverse reactions observed at a rate ≥5% of subjects treated with SC GAMUNEX-C for PI were infusion site reactions, headache, fatigue, arthralgia and pyrexia.
The most common adverse reactions observed at a rate ≥5% in subjects treated with GAMUNEX-C for ITP were headache, vomiting, fever, nausea, back pain and rash.
The most common adverse reactions observed at a rate ≥5% in subjects with GAMUNEX-C for CIDP were headache, fever, chills, hypertension, rash, nausea and asthenia.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of one drug cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Treatment of Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency by the Intravenous Route
The most serious adverse event observed in clinical study subjects receiving GAMUNEX-C IV for PI was an exacerbation of autoimmune pure red cell aplasia in one subject.
In four different clinical trials to study PI, out of 157 subjects treated with GAMUNEX-C, 4 subjects discontinued due to the following adverse events: Coombs negative hypochromic anemia, Autoimmune pure red cell aplasia, arthralgia/hyperhidrosis/fatigue/myalgia/nausea and migraine.
In a study of 87 subjects, 9 subjects in each treatment group were pretreated with non-steroidal medication prior to infusion, such as diphenhydramine and acetaminophen.
Table 2 lists all adverse events occurring in greater than 10% of subjects irrespective of the causality assessment.
| Adverse Event | GAMUNEX-C® | GAMIMUNE® N, 10% |
| No. of subjects: 87 | No. of subjects: 85 | |
| No. of subjects with AE | No. of subjects with AE | |
| (percentage of all subjects) | (percentage of all subjects) | |
| Cough increased | 47 (54%) | 46 (54%) |
| Rhinitis | 44 (51%) | 45 (53%) |
| Pharyngitis | 36 (41%) | 39 (46%) |
| Headache | 22 (25%) | 28 (33%) |
| Fever | 24 (28%) | 27 (32%) |
| Diarrhea | 24 (28%) | 27 (32%) |
| Asthma | 25 (29%) | 17 (20%) |
| Nausea | 17 (20%) | 22 (26%) |
| Ear Pain | 16 (18%) | 12 (14%) |
| Asthenia | 9 (10%) | 13 (15%) |
Table 3 lists the adverse reactions reported by at least 5% of subjects during the 9-month treatment.
| Adverse Reactions | GAMUNEX-C® | GAMIMUNE® N, 10% |
| No. of subjects: 87 | No. of subjects: 85 | |
| No. of subjects with adverse reaction | No. of subjects with adverse reaction | |
| (percentage of all subjects) | (percentage of all subjects) | |
| Headache | 7 (8%) | 8 (9%) |
| Cough increased | 6 (7%) | 4 (5%) |
| Injection site reaction | 4 (5%) | 7 (8%) |
| Nausea | 4 (5%) | 4 (5%) |
| Pharyngitis | 4 (5%) | 3 (4%) |
| Urticaria | 4 (5%) | 1 (1%) |
Table 4 lists the frequency of adverse reactions, which were reported by at least 5% of subjects, and their relationship to infusions administered.
|
GAMUNEX® -C | GAMIMUNE® N, 10% | |
| Adverse Experience | No. of infusions: 825 |
No. of infusions: 865 |
| Number (percentage of all infusions) | (percentage of all subjects) | |
| Cough increased | ||
| All | 154 (18.7%) | 148 (17.1%) |
| Drug related | 14 (1.7%) | 11 (1.3%) |
| Pharyngitis | ||
| All |
96 (11.6%) | 99 (11.4%) |
| Drug related | 7 (0.8%) | 9 (1.0%) |
| Headache | ||
| All |
57 (6.9%) |
69 (8.0%) |
| Drug related | 7 (0.8%) | 11 (1.3%) |
| Fever | ||
| All |
41 (5.0%) | 65 (7.5%) |
| Drug rela ted | 1 (0.1%) | 9 (1.0%) |
| Nausea | ||
| All |
31 (3.8%) |
43 (5.0%) |
| Drug related | 4 (0.5%) | 4 (0.5%) |
|
Urticaria | ||
| All |
5 (0.6%) | 8 (0.9%) |
| Drug related | 4 (0.5%) | 5 (0.6%) |
The mean number of adverse reactions per infusion that occurred during or on the same day as an infusion was 0.21 in both the GAMUNEX-C and GAMIMUNE®N, Immune Globulin Intravenous (Human), 10%, treatment groups.
In all three trials in primary humoral immundeficiencies, the maximum infusion rate was 0.08 mL/kg/min (8 mg/kg/min). The infusion rate was reduced for 11 of 222 exposed subjects (7 GAMUNEX-C, 4 GAMIMUNE N, 10%) at 17 occasions. In most instances, mild to moderate hives/urticaria, itching, pain or reaction at infusion site, anxiety or headache was the main reason. There was one case of severe chills. There were no anaphylactic or anaphylactoid reactions to GAMUNEX-C or GAMIMUNE N, 10% in clinical trials.
In the IV efficacy and safety study, serum samples were drawn to monitor the viral safety at baseline and one week after the first infusion (for parvovirus B19), eight weeks after first and fifth infusion, and 16 weeks after the first and fifth infusion of IGIV (for hepatitis C) and at any time of premature discontinuation of the study. Viral markers of hepatitis C, hepatitis B, HIV-1, and parvovirus B19 were monitored by nucleic acid testing (NAT, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)), and serological testing.
Treatment of Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency by the Subcutaneous Route (SC PK and Safety Study)
Adverse experiences were divided into 2 types: 1) Local infusion site reactions, and 2) Non-infusion site adverse events. Table 5 lists those adverse events occurring in ≥ 2% of infusions during the SC phase of the study.
|
|
| Adverse Experience | |
| (≥2% of infusions) | Number |
| (Number of infusions: 725) | (Rate*) |
| Local Infusion Site reactions | 427 (0.59) |
| Mild | 389 (0.54) |
| Moderate | 29 (0.04) |
| Severe | 9 (0.01) |
| Non-infusion site adverse events | |
| Headache | 37 (0.05) |
| Sinusitis | 11 (0.02) |
Table 6 lists the adverse reactions occurring in ≥5% of subjects and the frequency of adverse reactions per infusion. All local infusion site reactions were a priori considered drug-related.
|
||
| Adverse Reactions |
No. of Subjects | No. of Adverse Reactions |
| (≥5% of subjects) | n=32 (% ) | (Rate*) |
| Local Infusion Site Reactions | 24 (75%) | 427 (0.59) |
| Non-infusion Site Adverse Reactions | ||
| Headache | 4 (13%) | 21 (0.03) |
| Arthralgia | 2 (6.3%) | 4 (0.01) |
| Fatigue | 2 (6.3%) | 3 (≤0.01) |
| Pyrexia | 2 (6.3%) | 2 (≤0.01) |
There were no serious bacterial infections in the SC phase of the PK and safety study.
Local Infusion Site Reactions
Local infusion site reactions with SC GAMUNEX-C consisted of erythema, pain and swelling. The majority of local infusion site reactions resolved within 3 days. The number of subjects experiencing an infusion site reaction and the number of infusion site reactions decreased over time as subjects received continued weekly SC infusions. At the beginning of the SC phase (week 1), a rate of approximately 1 infusion site reaction per infusion was reported, whereas at the end of the study (week 24) this rate was reduced to 0.5 infusion site reactions per infusion, a reduction of 50%.
Treatment of Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
In two different clinical trials to study ITP, out of 76 subjects treated with GAMUNEX-C, 2 subjects discontinued due to the following adverse events: Hives and Headache/Fever/Vomiting.
One subject, a 10-year-old boy, died suddenly from myocarditis 50 days after his second infusion of GAMUNEX-C. The death was judged to be unrelated to GAMUNEX-C.
No pre-medication with corticosteroids was permitted by the protocol. Twelve (12) ITP subjects treated in each treatment group were pretreated with medication prior to infusion. Generally, diphenhydramine and/or acetaminophen were used. More than 90% of the observed drug related adverse events were of mild to moderate severity and of transient nature.
The infusion rate was reduced for 4 of the 97 exposed subjects (1 GAMUNEX-C, 3 GAMIMUNE N, 10%) on 4 occasions. Mild to moderate headache, nausea, and fever were the reported reasons.
Table 7 lists any adverse events, irrespective of the causality, reported by at least 5% of subjects during the 3-month efficacy and safety study.
|
GAMUNEX® -C |
GAMIMUNE® N, 10% |
|
|
Adverse Event | No. of subjects: 48 | No. of subjects: 49 |
| No. of subjects with AE | No. of subjects with AE | |
| (percentage of all subjects) | (percentage of all subjects) | |
| Headache | 28 (58%) | 30 (61%) |
| Ecchymosis, Purpura | 19 (40%) | 25 (51%) |
| Hemorrhage (All systems) | 14 (29%) | 16 (33%) |
| Epistaxis | 11 (23%) | 12 (24%) |
| Petechiae | 10 (21%) | 15 (31%) |
| Fever | 10 (21%) | 7 (14%) |
| Vomiting | 10 (21%) | 10 (20%) |
| Nausea | 10 (21%) | 7 (14%) |
| Thrombocytopenia | 7 (15%) | 8 (16%) |
| Accidental injury | 6 (13%) | 8 (16%) |
| Rhinitis | 6 (13%) | 6 (12%) |
| Pharyngitis | 5 (10%) | 5 (10%) |
| Rash | 5 (10%) | 6 (12%) |
| Pruritis | 4 (8%) | 1 (2%) |
| Asthenia | 3 (6%) | 5 (10%) |
| Abdominal Pain | 3 (6%) | 4 (8%) |
| Arthralgia | 3 (6%) | 6 (12%) |
| Back Pain | 3 (6%) | 3 (6%) |
| Dizziness | 3 (6%) | 3 (6%) |
| Flu Syndrome | 3 (6%) | 3 (6%) |
| Neck Pain | 3 (6%) | 1 (2%) |
| Anemia | 3 (6%) | 0 (0%) |
| Dyspepsia | 3 (6%) | 0 (0%) |
Table 8 lists the adverse reactions reported by at least 5% of subjects during the 3-month efficacy and safety study.
|
GAMUNEX® -C |
GAMIMUNE® N, 10% |
|
|
Adverse Event | No. of subjects: 48 | No. of subjects: 49 |
| Number (percentage of all subjects) | Number (percentage of all subjects) | |
| Headache | 24 (50%) | 24 (49%) |
| Vomiting | 6 (13%) | 8 (16%) |
| Fever | 5 (10%) | 5 (10%) |
| Nausea | 5 (10%) | 4 (8%) |
| Back Pain | 3 (6%) | 2 (4%) |
| Rash | 3 (6%) | 0 (0%) |
Serum samples were drawn to monitor the viral safety of the ITP subjects at baseline, nine days after the first infusion (for parvovirus B19), and 3 months after the first infusion of IGIV and at any time of premature discontinuation of the study. Viral markers of hepatitis C, hepatitis B, HIV-1, and parvovirus B19 were monitored by nucleic acid testing (NAT, PCR), and serological testing. There were no treatment related emergent findings of viral transmission for either GAMUNEX®-C, Immune Globulin Injection (Human), 10% Caprylate/Chromatography Purified or GAMIMUNE® N, Immune Globulin Intravenous (Human), 10%.
Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
In the CIDP efficacy and safety study, 113 subjects were exposed to GAMUNEX-C and 95 were exposed to Placebo. (see Clinical Studies [14.3]) As a result of the study design, the drug exposure with GAMUNEX-C was almost twice that of Placebo, with 1096 GAMUNEX-C infusions versus 575 Placebo infusions. Therefore, adverse reactions are reported per infusion (represented as frequency) to correct for differences in drug exposure between the 2 groups. The majority of loading-doses were administered over 2 days. The majority of maintenance-doses were administered over 1 day. Infusions were administered in the mean over 2.7 hours.
Table 9 shows the numbers of subjects per treatment group in the CIDP clinical trial, and the reason for discontinuation due to adverse events:
| Number of Subjects | Number of Subjects Discontinued due to Adverse Events | Adverse Event | |
| GAMUNEX® -C | 113 | 3 (2.7%) | Urticaria, Dyspnea, Bronchopneumonia |
| Placebo | 95 | 2 (2.1%) |
Cerebrovascular Accident, |
Table 10 shows adverse events reported by at least 5% of subjects in any treatment group irrespective of causality.
| MedDRA Preferred Term* | GAMUNEX® -C No. of subjects: 113 | Placebo No. of subjects: 95 |
||||
|
No. of | No. of Adverse Events | Incidence density † |
No. of | No. of Adverse Events | Incidence density† |
|
| Any Adverse Event | 85 (75) | 377 | 0.344 | 45 (47) | 120 | 0.209 |
| Headache | 36 (32) | 57 | 0.052 | 8 (8) | 15 | 0.026 |
| Pyrexia (fever) | 15 (13) | 27 | 0.025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hypertension | 10 (9) | 20 | 0.018 | 4 (4) | 6 | 0.010 |
| Rash | 8 (7) | 13 | 0.012 | 1 (1) | 1 | 0.002 |
| Arthralgia | 8 (7) | 11 | 0.010 | 1 (1) | 1 | 0.002 |
| Asthenia | 9 (8) | 10 | 0.009 | 3 (3) | 4 | 0.007 |
| Chills | 9 (8) | 10 | 0.009 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Back pain | 9 (8) | 10 | 0.009 | 3 (3) | 3 | 0.005 |
| Nausea | 7 (6) | 9 | 0.008 | 3 (3) | 3 | 0.005 |
| Dizziness | 7 (6) | 3 | 0.006 | 1 (1) | 1 | 0.002 |
| Influenza | 6 (5) | 6 | 0.005 | 2 (2) | 2 | 0.003 |
The most common adverse reactions with GAMUNEX-C were headache and pyrexia. Table 11 lists adverse reactions reported by at least 5% of subjects in any treatment group.
| MedDRA Preferred Term* | GAMUNEX® -C No. of subjects: 113 | Placebo No. of subjects: 95 |
||||
|
No. of | No. of Adverse Events | Incidence density † |
No. of | No. of Adverse Events | Incidence density† |
|
| Any Adverse Event | 62 (55) | 194 | 0.177 | 16 (17) | 25 | 0.043 |
| Headache | 31 (27) | 44 | 0.040 | 6 (6) | 7 | 0.012 |
| Pyrexia (fever) | 15 (13) | 26 | 0.024 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Chills | 8 (7) | 9 | 0.008 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hypertension | 7 (6) | 16 | 0.015 | 3 (3) | 3 | 0.005 |
| Rash | 6 (5) | 8 | 0.007 | 1 (1) | 1 | 0.002 |
| Nausea | 6 (5) | 7 | 0.006 | 3 (3) | 3 | 0.005 |
| Asthenia | 6 (5) | 6 | 0.005 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
The most serious adverse reaction observed in clinical study subjects receiving GAMUNEX-C for CIDP was pulmonary embolism (PE) in one subject with a history of PE.
Laboratory Abnormalities
During the course of the clinical program, ALT and AST elevations were identified in some subjects.
- For ALT, in the IV PI study treatment emergent elevations above the upper limit of normal were transient and observed among 14/80 (18%) of subjects in the GAMUNEX-C group versus 5/88 (6%) of subjects in the GAMIMUNE N, 10% group (p = 0.026).
- In the SC PI study treatment emergent laboratory abnormalities during the SC phase occurred in several subjects. Four subjects (4/32, 13%) had elevated Alkaline Phosphatase and one subject (1/32, 3%) had a low Alkaline Phosphatase. One subject (1/32, 3%) had an elevated ALT and three subjects (3/32, 9%) had an elevated AST. No elevations were >1.6 times the upper limit of normal.
- In the ITP study which employed a higher dose per infusion, but a maximum of only two infusions, the reverse finding was observed among 3/44 (7%) of subjects in the GAMUNEX-C group versus 8/43 (19%) of subjects in the GAMIMUNE N, 10% group (p = 0.118).
- In the CIDP study, 15/113 (13%) of subjects in the GAMUNEX-C group and 7/95 (7%) in the Placebo group (p=0.168) had a treatment emergent transient elevation of ALT.
Elevations of ALT and AST were generally mild (<3 times upper limit of normal), transient, and were not associated with obvious symptoms of liver dysfunction.
GAMUNEX-C may contain low levels of anti-Blood Group A and B antibodies primarily of the IgG4 class. Direct antiglobulin tests (DAT or direct Coombs tests), which are carried out in some centers as a safety check prior to red blood cell transfusions, may become positive temporarily. Hemolytic events not associated with positive DAT findings were observed in clinical trials.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because adverse reactions are voluntary and reported post-approval from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequencies or establish a causal relationship to product exposure.
GAMUNEX-C Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified and reported during the post marketing use of GAMUNEX-C:
| Hematologic: | Hemolytic anemia |
| Infections and Infestations: | Aseptic meningitis |
The following adverse reactions have been identified and reported during the overall post marketing use of IGIV products [17]:
- Respiratory: Apnea, Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), TRALI, cyanosis, hypoxemia, pulmonary edema, dyspnea, bronchospasm
- Cardiovascular: Cardiac arrest, thromboembolism, vascular collapse, hypotension
- Neurological: Coma, loss of consciousness, seizures/convulsions, tremor
- Integumentary: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, epidermolysis, erythema multiforme, bullous dermatitis
- Hematologic: Pancytopenia, leukopenia, hemolysis, positive direct antiglobulin (Coombs test)
- General/Body as a Whole: Pyrexia, rigors
- Musculoskeletal: Back pain
- Gastrointestinal: Hepatic dysfunction, abdominal pain
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
GAMUNEX-C may be diluted with 5% dextrose in water (D5/W). Admixtures of GAMUNEX-C with other drugs and intravenous solutions have not been evaluated. It is recommended that GAMUNEX-C be administered separately from other drugs or medications which the patient may be receiving. The product should not be mixed with IGIVs from other manufacturers.
The infusion line may be flushed before and after administration of GAMUNEX-C with D5/W.
Various passively transferred antibodies in immunoglobulin preparations can confound the results of serological testing.
Passive transfer of antibodies may transiently interfere with the immune response to live virus vaccines such as measles, mumps, rubella and varicella. Inform the immunizing physician of recent therapy with GAMUNEX-C so that appropriate measures may be taken. (see Patient Counseling Information [17])
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with GAMUNEX-C. It is not known whether GAMUNEX-C can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. GAMUNEX-C should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed. Immunoglobulins cross the placenta from maternal circulation increasingly after 30 weeks of gestation. [18-19]
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Use of GAMUNEX-C has not been evaluated in nursing mothers.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Treatment of Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency
IV
GAMUNEX-C was evaluated in 18 pediatric subjects (age range 0-16 years). Twenty-one percent of PI subjects exposed to GAMUNEX-C were children. Pharmacokinetics, safety and efficacy were similar to those in adults with the exception that vomiting was more frequently reported in pediatrics (3 of 18 subjects). No pediatric-specific dose requirements were necessary to achieve serum IgG levels.
SC
SC GAMUNEX-C was evaluated in only three pediatric subjects (age range 13-15) with PI. This number of pediatric subjects was too small for separate evaluation of pharmacokinetics and safety to determine whether they respond differently from adults. (see Clinical Studies [14]) Efficacy and safety in pediatric patients using the SC route of administration have not been established.
Treatment of Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
For treatment of ITP, GAMUNEX-C must be administered by the intravenous route.
GAMUNEX-C was evaluated in 12 pediatric subjects with acute ITP. Twenty-five percent of the acute ITP subjects exposed to GAMUNEX-C were children. Pharmacokinetics, safety and efficacy were similar to those in adults with the exception that fever was more frequently reported in pediatrics (6 of 12 subjects). No pediatric-specific dose requirements were necessary to achieve serum IgG levels. One subject, a 10-year-old boy, died suddenly from myocarditis 50 days after his second infusion of GAMUNEX-C. The death was judged to be unrelated to GAMUNEX-C.
Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
The safety and effectiveness of GAMUNEX-C has not been established in pediatric subjects with CIDP.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Use caution when administering GAMUNEX-C to patients age 65 and over who are judged to be at increased risk for developing thromboembolic events or renal insufficiency. (see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions [5.2]) Do not exceed recommended doses, and administer GAMUNEX-C at the minimum infusion rate practicable. Clinical studies of GAMUNEX-C did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
11 DESCRIPTION
GAMUNEX-C is a ready-to-use sterile solution of human immune globulin protein for intravenous and subcutaneous (PI indication only) administration. GAMUNEX-C consists of 9%–11% protein in 0.16–0.24 M glycine. Not less than 98% of the protein has the electrophoretic mobility of gamma globulin. GAMUNEX-C contains trace levels of fragments, IgA (average 0.046 mg/mL), and IgM. The distribution of IgG subclasses is similar to that found in normal serum. GAMUNEX-C doses of 1 g/kg correspond to a glycine dose of 0.15 g/kg. While toxic effects of glycine administration have been reported, the doses and rates of administration were 3 – 4 fold greater than those for GAMUNEX-C. In another study it was demonstrated that intravenous bolus doses of 0.44 g/kg glycine were not associated with serious adverse effects. [20] Caprylate is a saturated medium-chain (C8) fatty acid of plant origin. Medium chain fatty acids are considered to be essentially non-toxic. Human subjects receiving medium chain fatty acids parenterally have tolerated doses of 3.0 to 9.0 g/kg/day for periods of several months without adverse effects. [21] Residual caprylate concentrations in the final container are no more than 0.216 g/L (1.3 mmol/L).The measured buffer capacity is 35 mEq/L and the osmolality is 258 mOsmol/kg solvent, which is close to physiological osmolality (285-295 mOsmol/kg). The pH of GAMUNEX-C is 4.0 – 4.5. GAMUNEX-C contains no preservative and is latex-free.
GAMUNEX-C is made from large pools of human plasma by a combination of cold ethanol fractionation, caprylate precipitation and filtration, and anion-exchange chromatography. Isotonicity is achieved by the addition of glycine. GAMUNEX-C is incubated in the final container (at the low pH of 4.0 – 4.3). The product is intended for intravenous administration and may be administered subcutaneously in treatment of PI.
The capacity of the manufacturing process to remove and/or inactivate enveloped and non-enveloped viruses has been validated by laboratory spiking studies on a scaled down process model, using the following enveloped and non-enveloped viruses: human immunodeficiency virus, type I (HIV-1) as the relevant virus for HIV-1 and HIV–2; bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) as a model for hepatitis C virus; pseudorabies virus (PRV) as a model for large DNA viruses (e.g. herpes viruses); Reo virus type 3 (Reo) as a model for non-enveloped viruses and for its resistance to physical and chemical inactivation; hepatitis A virus (HAV) as relevant non-enveloped virus, and porcine parvovirus (PPV) as a model for human parvovirus B19.
Overall virus reduction was calculated only from steps that were mechanistically independent from each other and truly additive. In addition, each step was verified to provide robust virus reduction across the production range for key operating parameters.
|
||||||
| Process Step | Log 10 Virus Reduction | |||||
| Enveloped Viruses | Non-enveloped Viruses | |||||
| HIV | PRV | BVDV | Reo | HAV | PPV | |
| Caprylate Precipitation/Depth Filtration | C/I * | C/I | 2.7 | ≥ 3.5 | ≥ 3.6 | 4.0 |
| Caprylate Incubation | ≥ 4.5 | ≥ 4.6 | ≥ 4.5 | NA† | NA | NA |
| Depth Filtration‡ | CAP§ | CAP | CAP | ≥ 4.3 | ≥ 2.0 | 3.3 |
| Column Chromatography | ≥ 3.0 | ≥ 3.3 | 4.0 | ≥ 4.0 | ≥ 1.4 | 4.2 |
| Low pH Incubation | ≥ 6.5 | ≥ 4.3 | ≥ 5.1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Global Reduction | ≥ 14.0 | ≥ 12.2 | ≥ 16.3 | ≥ 7.5 | ≥ 5.0 | 8.2 |
Additionally, the manufacturing process was investigated for its capacity to decrease the infectivity of an experimental agent of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE), considered as a model for the vCJD and CJD agents. [22-26]
Several of the individual production steps in the GAMUNEX-C manufacturing process have been shown to decrease TSE infectivity of that experimental model agent. TSE reduction steps include two depth filtrations (in sequence, a total of ≥ 6.6 logs). These studies provide reasonable assurance that low levels of CJD/vCJD agent infectivity, if present in the starting material, would be removed.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Treatment of Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency
GAMUNEX-C supplies a broad spectrum of opsonic and neutralizing IgG antibodies against bacteria, viral, parasitic, mycoplasma agents, and their toxins. The mechanism of action in PI has not been fully elucidated.
Treatment of Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
The mechanism of action of high doses of immunoglobulins in the treatment of ITP has not been fully elucidated.
Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
The precise mechanism of action in CIDP has not been fully elucidated.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Immunoglobulins are fractionated blood products made from pooled human plasma. Immunoglobulins are endogenous proteins produced by B lymphocyte cells. The main component of GAMUNEX-C is IgG (≥98%) with a sub-class distribution of IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4 of approximately 62.8%, 29.7%, 4.8% and 2.7% respectively.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Intravenous Administration:
Two randomized pharmacokinetic crossover trials were carried out with GAMUNEX-C in 38 subjects with Primary Humoral Immunodeficiencies given 3 infusions 3 or 4 weeks apart of test product at a dose of 100-600 mg/kg body weight per infusion. One trial compared the pharmacokinetic characteristics of GAMUNEX-C to GAMIMUNE N, 10% and the other trial compared the pharmacokinetics of GAMUNEX-C (10% strength) with a 5% concentration of this product. The ratio of the geometric least square means for dose-normalized IgG peak levels of GAMUNEX-C and GAMIMUNE N, 10% was 0.996. The corresponding value for the dose-normalized area under the curve (AUC) of IgG levels was 0.990. The results of both PK parameters were within the pre-established limits of 0.080 and 1.25. Similar results were obtained in the comparison of GAMUNEX-C 10% to a 5% concentration of GAMUNEX-C.
The main pharmacokinetic parameters of GAMUNEX-C, measured as total IgG in study 100152 are displayed below:
| GAMUNEX® -C | GAMIMUNE® N, 10% | |||||||
| N | Mean | SD | Median | N | Mean | SD | Median | |
| Cmax (mg/mL) | 17 | 19.04 | 3.06 | 19.71 | 17 | 19.31 | 4.17 | 19.30 |
| Cmax-norm (kg/mL) | 17 | 0.047 | 0.007 | 0.046 | 17 | 0.047 | 0.008 | 0.047 |
| AUC(0-tn)* (mg*hr/mL) | 17 | 6746.48 | 1348.13 | 6949.47 | 17 | 6854.17 | 1425.08 | 7119.86 |
| AUC(0-tn) norm* (kg*hr/mL) | 17 | 16.51 | 1.83 | 16.95 | 17 | 16.69 | 2.04 | 16.99 |
| T 1/2†
(days) | 16 | 35.74 | 8.69 | 33.09 | 16 | 34.27 | 9.28 | 31.88 |
The two pharmacokinetic trials with GAMUNEX-C show the IgG concentration/time curve follows a biphasic slope with a distribution phase of about 5 days characterized by a fall in serum IgG levels to about 65-75% of the peak levels achieved immediately post-infusion. This phase is followed by the elimination phase with a half-life of approximately 35 days. IgG trough levels were measured over nine months in the therapeutic equivalence trial. Mean trough levels were 7.8 ± 1.9 mg/mL for the GAMUNEX-C treatment group and 8.2 ± 2.0 mg/mL for the GAMIMUNE N, 10% control group.
Subcutaneous Administration
Treatment of Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency by the Subcutaneous (SC) Route
In a single sequence, open-label, crossover trial, the pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of SC administered GAMUNEX-C in subjects with PI were evaluated. A total of 32 and 26 subjects received GAMUNEX-C as IV or SC for PK study, respectively. Subjects received GAMUNEX-C 200-600 mg/kg IV every 3-4 weeks for at least 3 months, at which time they entered the IV phase of the study. Subjects were crossed over to weekly SC infusions. The weekly SC dose was determined by multiplying the total IV dose by 1.37 and dividing the resultant new total dose by 3 or 4 depending on the previous IV interval. The PK endpoint parameter (AUC of total plasma IgG) following IV and SC administration is summarized below in Table 14. The lower bound of the 90% confidence interval for the geometric mean ratio of AUC (SC vs. IV) was 0.861, therefore, meeting the pre-specified non-inferiority margin between the two modes of administration.
| Route of Administration | Statistics | AUC0-τ,IV
(mg*h/mL) | AUC0-τ,SC
(mg*h/mL) | AUC0-τ,SC *
(mg*h/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| IV (n = 32) | Mean | 7640 | NA | NA |
| %CV | 15.9 | |||
| Range | 5616-10400 | |||
| SC (n = 26) | Mean | NA | 1947 | 6858 |
| %CV | 20.4 | 18.1 | ||
| Range | 1300-2758 | 5169-10364 | ||
| CV, coefficient of variation; NA, not applicable | ||||
The mean trough concentration ( mean Ctrough) of plasma total IgG following IV and SC administration are presented in Table 15.
| IV Mean Ctrough | SC Mean Ctrough | |
|---|---|---|
| n | 32 | 28 |
| Mean (mg/mL) | 9.58 | 11.4 |
| %CV | 22.3 | 20.4 |
| Range | 6.66-14.0 | 8.10-16.2 |
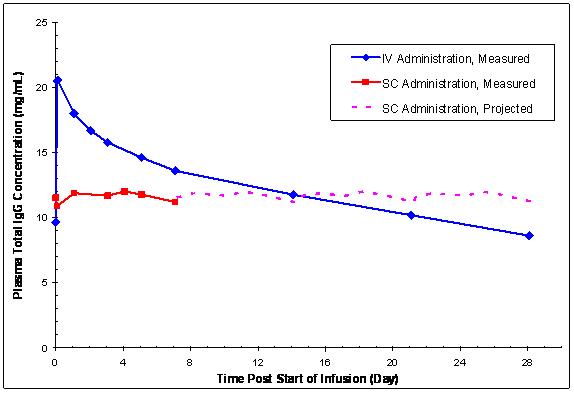
In contrast to plasma total IgG levels observed with monthly IV GAMUNEX-C treatment (rapid peaks followed by a slow decline), the plasma IgG levels in subjects receiving weekly SC GAMUNEX-C therapy were relatively stable (Figure 7).
Figure 7: Mean Steady-state Plasma Total IgG Concentration vs. Time Curves Following IV Administration or Weekly SC Administration
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Treatment of Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency by the Intravenous (IV) Route
In a randomized, double-blind, parallel group clinical trial with 172 subjects with primary humoral immunodeficiencies GAMUNEX-C was demonstrated to be at least as efficacious as GAMIMUNE N, 10% in the prevention of any infection, i.e., validated plus clinically defined, non-validated infections of any organ system, during a nine month treatment period. Twenty-six subjects were excluded from the Per Protocol analysis (2 due to non-compliance and 24 due to protocol violations). The analysis for efficacy was based on the annual rate of bacterial infections pneumonia, acute sinusitis and acute exacerbations of chronic sinusitis.
| GAMUNEX®-C | GAMIMUNE® N, 10% | Mean Difference | p-Value | |
| (n=73) | (n=73) | (90% confidence interval) | ||
| No. of subjects with | No. of subjects with | |||
| at least one infection | at least one infection | |||
| Validated Infections | 9 (12%) | 17 (23%) | -0.117 | 0.06 |
| (-0.220, -0.015) | ||||
| Acute Sinusitis | 4 (5%) | 10 (14%) | ||
| Exacerbation of | ||||
| Chronic Sinusitis | 5 (7%) | 6 (8%) | ||
| Pneumonia | 0 (0%) | 2 (3%) | ||
| Any Infection | 56 (77%) | 57 (78%) | -0.020 | 0.78 |
| (Validated plus | (-0.135, 0.096) | |||
| Clinically defined | ||||
| non-validated Infections) |
The annual rate of validated infections (Number of Infection/year/subject) was 0.18 in the group treated with GAMUNEX-C and 0.43 in the group treated with GAMIMUNE N, 10% (p=0.023). The annual rates for any infection (validated plus clinically-defined, non-validated infections of any organ system) were 2.88 and 3.38, respectively (p=0.300).
14.2 Treatment of Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
A double-blind, randomized, parallel group clinical trial with 97 ITP subjects was carried out to prove the hypothesis that GAMUNEX-C was at least as effective as GAMIMUNE N, 10% in raising platelet counts from less than or equal to 20 x109/L to more than 50 x109/L within 7 days after treatment with 2 g/kg IGIV. Twenty-four percent of the subjects were less than or equal to 16 years of age.
GAMUNEX-C was demonstrated to be at least as effective as GAMIMUNE N, 10% in the treatment of adults and children with acute or chronic ITP.
| GAMUNEX®-C | GAMIMUNE® N, 10% | Mean Difference | |
| (n=39) | (n=42) | (90% confidence interval) | |
| By Day 7 | 35 (90%) | 35 (83%) | 0.075 |
| (-0.037, 0.186) | |||
| By Day 23 | 35 (90%) | 36 (86%) | 0.051 |
| (-0.058, 0.160) | |||
| Sustained for 7 days | 29 (74%) | 25 (60%) | 0.164 |
| (0.003, 0.330) |
A trial was conducted to evaluate the clinical response to rapid infusion of GAMUNEX-C in patients with ITP. The study involved 28 chronic ITP subjects, wherein the subjects received 1 g/kg GAMUNEX-C on three occasions for treatment of relapses. The infusion rate was randomly assigned to 0.08, 0.11, or 0.14 mL/kg/min (8, 11 or 14 mg/kg/min). Pre-medication with corticosteroids to alleviate infusion-related intolerability was not permitted. Pre-treatment with antihistamines, anti-pyretics and analgesics was permitted. The average dose was approximately 1 g/kg body weight at all three prescribed rates of infusion (0.08, 0.11 and 0.14 mL/kg/min). All patients were administered each of the three planned infusions except seven subjects. Based on 21 patients per treatment group, the a posteriori power to detect twice as many drug-related adverse events between groups was 23%. Of the seven subjects that did not complete the study, five did not require additional treatment, one withdrew because he refused to participate without concomitant medication (prednisone) and one experienced an adverse event (hives); however, this was at the lowest dose rate level (0.08 mL/kg/min).
14.3 Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
A multi-center, randomized, double-blind, Placebo-controlled trial (The Immune Globulin Intravenous (Human), 10% Caprylate/Chromatography Purified CIDP Efficacy or ICE study) was conducted with GAMUNEX-C. [27] This study included two separately randomized periods to assess whether GAMUNEX-C was more effective than Placebo for the treatment of CIDP (assessed in the Efficacy Period for up to 24 weeks) and whether long-term administration of GAMUNEX-C could maintain long-term benefit (assessed in the 24 week Randomized Withdrawal Period).
In the Efficacy Period, there was a requirement for Rescue (crossover) to the alternate study drug if the subject did not improve and maintain this improvement until the end of the 24 week treatment period. Subjects entering the Rescue phase followed the same dosing and schedule as in the Efficacy period. Any subject who was rescued (crossed over) and did not improve and maintain this improvement was withdrawn from the study.
Subjects who completed 24 weeks treatment in the Efficacy period or Rescue phase and responded to therapy were eligible for entry into a double-blind Randomized Withdrawal Period. Eligible subjects were re-randomized to GAMUNEX-C or Placebo. Any subject who relapsed was withdrawn from the study.
The Efficacy Period and the Rescue treatment started with a loading dose of 2 g/kg body weight of GAMUNEX-C or equal volume of Placebo given over 2-4 consecutive days. All other infusions (including the first infusion of the Randomized Withdrawal Period) were given as maintenance doses of 1 g/kg bw (or equivalent volume of Placebo) every three weeks.
The Responder rates of the GAMUNEX-C and Placebo treatment groups was measured by the INCAT score. The INCAT (Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment) scale is used to assess functional disability of both upper and lower extremities in demyelinating polyneuropathy. The INCAT scale has upper and lower extremity components (maximum of 5 points for upper (arm disability) and maximum of 5 points for lower (leg disability)) that add up to a maximum of 10-points (0 is normal and 10 is severely incapacitated). [28] At the start of the efficacy portion of the study, the INCAT scores were as follows: Upper Extremity mean was 2.2 ± 1.0, and median was 2.0 with a range of 0 to 5; Lower Extremity mean was 1.9 ± 0.9, and median was 2.0 with a range of 1 to 5; Total Overall Score mean was 4.2 ± 1.4, and median was 4.0 with a range of 2 to 9. A Responder was defined as a subject with at least 1-point improvement from baseline in the adjusted INCAT score that was maintained through 24 weeks.
More subjects with CIDP responded to GAMUNEX-C: 28 of 59 subjects (47.5%) responded to GAMUNEX-C compared with 13 of 58 subjects (22.4%) administered Placebo (25% difference; 95% CI 7%-43%; p=0.006). The study included both subjects who were IGIV naive and subjects who had previous IGIV experience. The outcome was influenced by the group of subjects who experienced prior therapy with IGIV, as shown by the outcomes table, below.
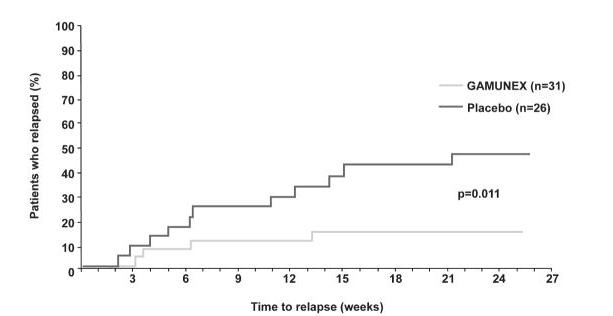
Time to relapse for the subset of 57 subjects who previously responded to GAMUNEX-C was evaluated: 31 were randomly reassigned to continue to receive GAMUNEX-C and 26 subjects were randomly reassigned to Placebo in the Randomized Withdrawal Period. Subjects who continued to receive GAMUNEX-C experienced a longer time to relapse versus subjects treated with Placebo (p=0.011). The probability of relapse was 13% with GAMUNEX-C versus 45% with Placebo (hazard ratio, 0.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.05, 0.70).
|
|||||
| Efficacy Period | GAMUNEX®-C | Placebo | p-value* | ||
| Responder | Non-Responder | Responder | Non-Responder | ||
| All Subjects | 28/59 (47.5%) | 31/59 (52.5%) | 13/58 (22.4%) | 45/58 (77.6%) | 0.006 |
| IGIV Naïve Subjects |
17/39 (43.6%) |
22/39 (56.4%) |
13/46 (28.3%) |
33/46 (71.7%) |
0.174 |
| IGIV Experienced Subjects |
11/20 (55.0%) |
9/20 (45.0%) |
0/12 (0%) |
12/12 (100%) |
0.002 |
The following table shows outcomes for the Rescue Phase (which are supportive data):
|
|||||
| Rescue Phase | GAMUNEX®-C | Placebo | p-value* | ||
| Success | Failure | Success | Failure | ||
| All Subjects | 25/45 (55.6%) | 20/45 (44.4%) | 6/23 (26.1%) | 17/23 (73.9%) | 0.038 |
| IGIV - Naïve Subjects | 19/33(57.6%) | 14/33 (42.4%) | 6/18 (33.3%) | 12/18 (66.7%) | 0.144 |
| IGIV - Experienced Subjects | 6/12 (50%) | 6/12 (50%) | 0/5 (0%) | 5/5 (100%) | 0.102 |
The following Kaplan-Meier curves show the outcomes for the Randomized Withdrawal Period:
|
||
| Secondary Endpoint Randomized Withdrawal Period | Time to Relapse | p-value*
p= 0.011 |
 |
||
15 REFERENCES
-
Cayco AV, Perazella MA, Hayslett JP. Renal insufficiency after intravenous immune globulin therapy: a report of two cases and an analysis of the literature. J Am Soc Nephrol, 1997. 8(11): p. 1788-94.
-
Buckley RH, Schiff RI. The use of intravenous immune globulin in immunodeficiency diseases. N Engl J Med, 1991. 325(2): p. 110-7.
-
Cunningham-Rundles C, Bodian C. Common variable immunodeficiency: clinical and immunological features of 248 patients. Clin Immunol, 1999. 92(1): p. 34-48.
-
Pruzanski W, et al. Relationship of the dose of intravenous gammaglobulin to the prevention of infections in adults with common variable immunodeficiency. Inflammation, 1996. 20(4): p. 353-9.
-
Stephan JL, et al. Severe combined immunodeficiency: a retrospective single-center study of clinical presentation and outcome in 117 patients. J Pediatr, 1993. 123(4): p. 564-72.
-
Blanchette VS, Kirby MA, and Turner C. Role of intravenous immunoglobulin G in autoimmune hematologic disorders. Semin Hematol, 1992. 29(3 Suppl 2): p. 72-82.
-
Lazarus AH, Freedman J, Semple JW. Intravenous immunoglobulin and anti-D in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP): mechanisms of action. Transfus Sci, 1998. 19(3): p. 289-94.
-
Steinberger BA, Ford SM, Coleman TA. Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy Results in Post-infusional Hyperproteinemia, Increased Serum Viscosity, and Pseudohyponatremia. Am J Hematol 73:97-100 (2003).
-
Dalakas MC. High-dose intravenous Immunoglobulin and serum viscosity: risk of precipitating thromboembolic events. Neurology, 44:223-226.
-
Woodruff RK, Grigg AP, Firkin FC, Smith IL. Fatal thrombotic events during treatment of autoimmune thrombocytopenia with intravenous immunoglobulin in elderly patients. Lancet 1986;2:217-218.
-
Wolberg AS, Kon RH, Monroe DM, Hjoffman M. Coagulation factor XI is a contaminant in intravenous immunoglobulin preparations. Am J Hematol 2000; 65,30-34.
-
Copelan EA, Stohm PL, Kennedy MS, Tutschka PJ. Hemolysis following intravenous immune globulin therapy. Transfusion 1986;26:410-412.
-
Thomas MJ, Misbah SA, Chapel HM, Jones M, Elrington G, Newsom-Davis J. Hemolysis after high-dose intravenous Ig. Blood 1993;15:3789.
-
Wilson JR, Bhoopalam N, Fisher M. Hemolytic anemia associated with intravenous immunoglobulin. Muscle & Nerve 1997; 20:1142-1145.
-
Kessary-Shoham H, Levy Y, Shoenfeld Y, Lorber M, Gershon H. In vivo administration of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) can lead to enhanced erythrocyte sequestration. J Autoimmune 1999; 13:129-135.
-
Rizk A, Gorson KC, Kenney L, Weinstein R. Transfusion-related acute lung injury after the infusion of IVIG. Transfusion 2001:41:264-268.
-
Pierce LR, Jain N. Risks associated with the use of intravenous immunoglobulin. Trans Med Rev 2003; 17,241-251.
-
Hammarstrom L, Smith CIE. Placental transfer of intravenous immunoglobulin. Lancet 1986: 1:681.
-
Sidiropoulos D, Herrmann U, Morell A, von Muralt G, Barandun S. Transplacental passage of intravenous immunoglobulin in the last trimester of pregnancy. J Pediatr 1986; 109:505-508.
-
Tai VM, M.E., Lee-Brotherton V, Manley JJ, Nestmann ER, Daniels JM. Safety Evaluation of Intravenous Glycine in Formulation Development. in J Pharm Pharmaceut Sci. 2000.
-
Traul KA, et al. Review of the toxicologic properties of medium-chain triglycerides. Food Chem Toxicol, 2000. 38(1): p. 79-98.
-
Stenland CJ, Lee DC, Brown P, et al. Partitioning of human and sheep forms of the pathogenic prion protein during the purification of therapeutic proteins from human plasma. Transfusion 2002. 42(11):1497-500.
-
Lee DC, Stenland CJ, Miller JL, et al. A direct relationship between the partitioning of the pathogenic prion protein and transmissible spongiform encephalopathy infectivity during the purification of plasma proteins. Transfusion 2001. 41(4):449-55.
-
Lee DC, Stenland CJ, Hartwell RC, et al. Monitoring plasma processing steps with a sensitive Western blot assay for the detection of the prion protein. J Virol Methods 2000. 84(1):77-89.
-
Cai K, Miller JL, Stenland CJ, et al. Solvent-dependent precipitation of prion protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002. 1597(1):28-35.
-
Trejo SR, Hotta JA, Lebing W, et al. Evaluation of virus and prion reduction in a new intravenous immunoglobulin manufacturing process. Vox Sang 2003. 84(3):176-87.
-
Hughes RAC, Donofrio P, Bril V, et al. Intravenous immune globulin (10% caprylate/chromatography purified) for the treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (ICE study): a randomized Placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2008. 7:136-144.
-
Hughes R, Bensa S, Willison H, Van den BP, Comi G, Illa I, et al. Randomized controlled trial of intravenous immunoglobulin versus oral prednisolone in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Ann Neurol 2001 Aug;50(2):195-201.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
GAMUNEX-C is supplied in single-use, tamper evident vials (shrink band) containing the labeled amount of functionally active IgG. The three larger vial size labels incorporate integrated hangers. The components used in the packaging for GAMUNEX-C are latex-free. GAMUNEX-C is supplied in the following sizes:
| NDC Number | Size | Grams Protein |
| 13533-800-12 | 10 mL | 1.0 |
| 13533-800-15 | 25 mL | 2.5 |
| 13533-800-20 | 50 mL | 5.0 |
| 13533-800-71 | 100 mL | 10.0 |
| 13533-800-24 | 200 mL | 20.0 |
Do not freeze
GAMUNEX-C may be stored for 36 months at 2 - 8°C (36 - 46°F) from the date of manufacture, AND product may be stored at temperatures not to exceed 25°C (77°F) for up to 6 months anytime during the 36 month shelf life, after which the product must be immediately used or discarded. Do not use after expiration date.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
(see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions Sections)
Inform patients to immediately report the following signs and symptoms to their healthcare provider:
- Decreased urine output, sudden weight gain, fluid retention/edema, and/or shortness of breath (see Warnings and Precautions [5.2])
- Acute chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, and swelling of the legs/feet (see Warnings and Precautions [5.5])
- Severe headache, neck stiffness, drowsiness, fever, sensitivity to light, painful eye movements, nausea, and vomiting (see Warnings and Precautions [5.6]).
- Increased heart rate, fatigue, yellowing of the skin or eyes, and dark-colored urine (see Warnings and Precautions [5.7])
- Trouble breathing, chest pain, blue lips or extremities, and fever. (see Warnings and Precautions [5.8])
Inform patients that GAMUNEX-C is made from human plasma and may contain infectious agents that can cause disease. While the risk GAMUNEX-C can transmit an infectious agent has been reduced by screening plasma donors for prior exposure, testing donated plasma, and by inactivating or removing certain viruses during manufacturing, patients should report any symptoms that concern them. (see Warnings and Precautions [5.10])
Inform patients that GAMUNEX-C can interfere with their immune response to live viral vaccines such as measles, mumps and rubella. Inform patients to notify their healthcare professional of this potential interaction when they are receiving vaccinations. (see Drug Interaction [7])
Home Treatment for Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency with Subcutaneous Infusion
Provide the patient with instructions on subcutaneous infusion for home treatment, if the physician believes that home administration is appropriate for the patient. Include the type of equipment to be used along with its maintenance, proper infusion techniques, selection of appropriate infusion sites (e.g., abdomen, thighs, upper arms, and/or lateral hip), maintenance of a treatment diary, and measures to be taken in case of adverse reactions in the patient instructions.
Rx only
Manufactured by:
Talecris BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Talecris Biotherapeutics, Inc.
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709 USA
U.S. License No. 1716
08939771
(Rev. October 2010)
GAMUNEX®-C
Immune Globulin Injection (Human), 10% Caprylate/Chromatography Purified
Subcutaneous Infusion for Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency
Information for Patients
Please read this information about GAMUNEX-C carefully before using this medicine. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare professional, and it does not include all of the important information about GAMUNEX-C. If you have any questions after reading this, contact your healthcare professional.
What is the most important information I should know about GAMUNEX-C?
GAMUNEX-C should be infused under your skin (in the subcutaneous tissue). DO NOT inject GAMUNEX-C into a blood vessel or directly into a muscle.
What is GAMUNEX-C?
GAMUNEX-C (Găm-yōō-nĕx) is an immunoglobulin used to treat primary immune deficiency (PI). Immunoglobulin is another name for the purified antibodies from human plasma that defend the body against infections such as viruses and bacteria. People with PI lack the healthy antibodies needed to fight off these infections. GAMUNEX-C provides those healthy antibodies and will help lower the number and severity of infections you could get.
Who should NOT take GAMUNEX-C?
Do not take GAMUNEX-C if you have known severe allergic reactions or a severe response to Immune Globulin (Human). Tell your doctor if you have had a serious reaction to other medicines that contain immune globulin. Also tell your doctor if you have an immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficiency.
How should I take GAMUNEX-C?
You will take GAMUNEX-C through infusions given just below the skin (in the subcutaneous tissue). As directed by your physician, one or more injection sites on your body will be selected. The number and location of the injection sites depends on the amount you need to receive. Typically, people use 1 to 4 needles in different locations on your body at one time. You may use up to 8 needles as directed by your doctor. The needles are attached with a tube to the pump. You will need to have infusions once a week.
Instructions for administering GAMUNEX-C are at the end of this patient package insert (see "Steps for Administration"). Only use GAMUNEX-C by yourself after you have been instructed by your doctor or healthcare professional.
What should I avoid while taking GAMUNEX-C?
Certain types of vaccines (ones containing a live virus) may not work as well for you if you are also receiving immunoglobulin products like GAMUNEX-C. The antibodies in GAMUNEX-C may prevent the vaccine from working. Before you get a vaccine, tell the doctor or nurse that you are taking GAMUNEX-C.
Tell your doctor or healthcare professional if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant, or if you are nursing.
What are possible side effects of GAMUNEX-C?
The most common side effects with GAMUNEX-C when given under the skin (subcutaneously) are:
- Redness, swelling, and itching at the injection site
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Pain (including pain in the back, joints, arms, legs)
- Fever
Tell your doctor right away or go to the emergency room if you have hives, trouble breathing, wheezing, dizziness, or fainting. These could be signs of a bad allergic reaction.
Tell your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms. They could be signs of a rare, but serious problem.
- Decreased urination, sudden weight gain, fluid retention/swelling in your legs, and/or shortness of breath. They could be signs of a serious kidney problem called renal failure.
- Chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, and swelling of the legs/feet. These could be signs of a blood clot in your body (thromboembolism).
- Severe headache, stiff neck, fatigue, fever, sensitivity to light, painful eye movements, nausea and vomiting. These could be signs of a type of brain inflammation called aseptic meningitis.
- Increased heart rate, fatigue, yellow skin or eyes, and dark colored urine. These could be signs of a type of blood problem called hemolytic anemia.
- Chest pains, trouble breathing, blue lips or extremities, and fever. These could be signs of a lung problem called TRALI (transfusion-related acute lung injury).
- Fever over 100° F. This could be a sign of an infection.
Tell your doctor about any side effects that concern you. You can ask your doctor to give you the full prescribing information available to healthcare professionals.
Steps for Administration
Infuse GAMUNEX-C only after you have been trained by your doctor or healthcare professional. Below are step-by-step instructions to help you remember how to use GAMUNEX-C. Ask your doctor or healthcare professional about any instructions you do not understand.
Before Using GAMUNEX-C
- GAMUNEX-C comes in single-use vials. Do not let it freeze. Keep it refrigerated. If needed, GAMUNEX-C can be stored at room temperature for up to 6 months but you must use it within that time or you must throw it away.
- Do not shake the vials.
- Prior to use, allow the solution to come to room temperature (68-77°F or 20-25°C). This can take 60 minutes or longer.
- Do not use the vial if:
- the solution is cloudy, discolored or contains particles. The solution should be clear and colorless to pale yellow.
- the protective cap or plastic shrink band around the cap is missing.
- the expiration date has passed.
- Sanitize your infusion set-up area by preparing a clean, flat, non-porous surface such as a kitchen counter. Avoid using porous surfaces such as wood. Clean the surface with an alcohol wipe using a circular motion from the center outward.
Step 1:
Wash and dry your hands thoroughly before administering GAMUNEX-C
- Your healthcare provider may recommend that you use antibacterial soap or that you wear gloves.
Step 2:
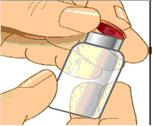
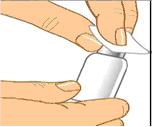
Remove the protective cap and sanitize the rubber stopper
- Remove the protective cap from the vial to expose the central portion of the rubber stopper.
- Wipe the rubber stopper with alcohol and allow to dry.
Step 3:
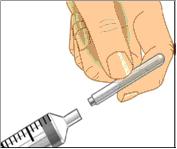
Use aseptic technique when preparing and administering GAMUNEX-C
- Do not allow your fingers or other objects to touch the inner stem of the plunger, the syringe tip, or other areas that will come in contact with your GAMUNEX-C solution. This is called aseptic technique and is designed to prevent transmission of germs.
- Using aseptic technique, attach each needle to the syringe tip.
Step 4:
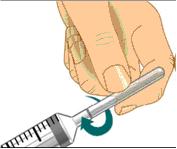
Prepare the syringe and draw GAMUNEX-C solution into syringe
- Remove cap from needle.
- Pull the syringe plunger back to the level matching the amount of GAMUNEX-C to be withdrawn from the vial.
- Place the GAMUNEX-C bottle on a clean flat surface and insert the needle into the center of the vial stopper.
- Inject air into the vial. The amount of air should match the amount of GAMUNEX-C to be withdrawn.
- Turn the vial upside down and withdraw the correct amount of GAMUNEX-C. If multiple vials are required to achieve the correct dose, repeat Step 4.
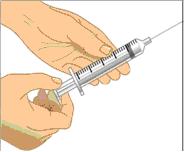
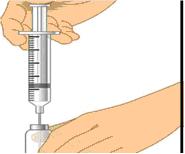
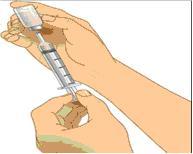
Step 5:
Fill the pump reservoir and prepare the infusion pump
- Follow the pump manufacturer’s instructions for filling the pump reservoir and preparing the infusion pump, administration tubing and Y-site connection tubing, if needed.
- Be sure to prime the administration tubing to ensure that no air is left in the tubing or needle by filling the tubing/needle with GAMUNEX-C. To prime, hold the syringe in one hand and the administration tubing’s capped needle in the other. Gently squeeze on the plunger until you see a drop of GAMUNEX-C exit from the needle.
Example Equipment
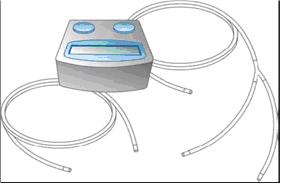
Step 6:
Select the number and location of infusion sites
- Select one or more infusion sites as directed by your healthcare provider.
- The number and location of injection sites depends on the volume of the total dose.
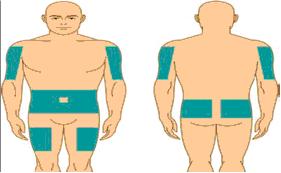
Step 7:
Prepare the infusion site
- Cleanse the infusion site(s) with antiseptic solution using a circular motion working from the center of the site and moving to the outside.
- Sites should be clean, dry, and at least 2 inches apart.
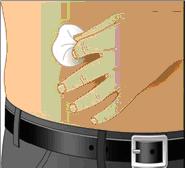
Step 8:
Insert the needle
- Grasp the skin between two fingers and insert the needle into the subcutaneous tissue.
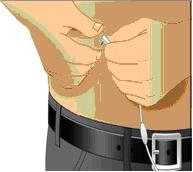
Step 9:
Do not inject GAMUNEX-C into a blood vessel
- After inserting each needle into tissue (and before your infusion), make sure that a blood vessel has not been accidentally entered. To do this, attach a sterile syringe to the end of the primed administration tubing. Pull back on the syringe plunger and watch for any blood flowing back into administration tubing.
- If you see any blood, remove and discard the needle and administration tubing.
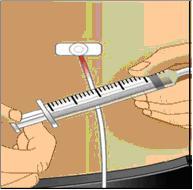
- Repeat priming and needle insertion steps using a new needle, administration tubing and a new infusion site.
- Secure the needle in place by applying sterile gauze or transparent dressing over the site.
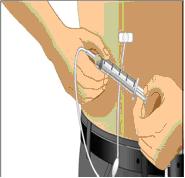
Step 10:
Repeat for other sites, as needed
- If using multiple, simultaneous infusion sites, use Y-site connection tubing and secure to the administration tubing.
Step 11:
Infuse GAMUNEX-C following the pump manufacturer’s instructions for the infusion pump
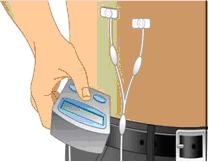
Step 12:
After infusion, turn off pump and dispose of used supplies
- Follow manufacturer’s instructions to turn off pump.
- Undo and discard any dressing or tape.
- Gently remove the inserted needle(s) or catheter(s).
- Discard any unused solution in an appropriate waste container as instructed.
-
Discard any used administration equipment in an appropriate waste container.
- Store your supplies in a safe place.
- Discard any used administration equipment in an appropriate waste container.
Step 13:
Record each infusion
- Remove the peel-off label with the product lot number from the GAMUNEX-C vial and use this to complete the patient record.
- Remember to bring your journal with you when you visit your physician or healthcare provider.
Be sure to tell your doctor about any problems you have doing your infusions. Your doctor may ask to see your journal, so be sure to take it with you each time you visit the doctor’s office.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You can also report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Manufactured by:
Talecris BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Distributed by:
Talecris Biotherapeutics, Inc.
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709 USA
U.S. License No. 1716
08939771
(Rev. October 2010)
PACKAGE LABEL

Immune
Globulin
Injection
(Human), 10%
gamunex®-c
Caprylate/Chromatography Purified
Solution for Infusion
NDC
13533-800-12
1 Gram Protein in 10 ml
Talecris
BIOTHERAPEUTICS
Contents:
One bottle of
Gamunex-C
No preservative
Sterile, Non-pyrogenic
Gamunex-C may be stored for
36 months at 2–8°C (36–46°F),
AND product may be stored at
temperatures not to exceed 25°C
(77°F) for up to 6 months
anytime during the 36 month
shelf life, after which the product
must be immediately used or
discarded.
Date removed
from refrigeration:
The patient and physician should
discuss the risks and benefits of this
product.
FOR INTRAVENOUS OR SUBCUTANEOUS
ADMINISTRATION.
Refer to package insert for dosage
and administration and compatibility
with other solutions.
Single Dose Vial
Do not use if turbid.
Discard unused portion. Do not store
after entry into bottle.
Contains no preservative
Do not freeze.
Each milliliter (mL) contains approximately
100 mg of protein, not less than
98% of which is immunoglobulin, and
approximately 15 mg glycine.
If the shrink band is absent or shows
any sign of tampering, do not use the
product and notify Talecris Biotherapeutics,
Inc. immediately.
Not Returnable for Credit or
Exchange
Rx only
08939777
Talecris Biotherapeutics, Inc.
Research Triangle Park,
NC 27709 USA
U.S. License No. 1716

NDC 13533-800-12
Immune Globulin
Injection (Human), 10%
gamunex®-c
Caprylate/Chromatography Purified
Talecris Biotherapeutics, Inc.
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709 USA
U.S. License No. 1716
Gamunex-C, 1 g Protein in 10 mL
Lot
Lot
Exp:
| GAMUNEX-C
immune globulin intravenous (human), 10% caprylate chromatography purified injection |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| BLA | BLA125046 | 10/13/2010 | |
| Labeler - TALECRIS BIOTHERAPEUTICS, INC. (839731507) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| TALECRIS BIOTHERAPEUTICS HOLDINGS CORP | 611019113 | MANUFACTURE | |