COLDCOUGH PD
-
dihydrocodeine bitartrate,
chlorpheniramine maleate and
phenylephrine hydrochloride syrup
Breckenridge Pharmaceutical, Inc.
----------
Coldcough™ PDSyrup
CV
Rx ONLY
DESCRIPTION
This product contains ingredients in the following therapeutic classes: Antitussive, Decongestant and Antihistamine.
Coldcough™ PD is sugar free and alcohol free.
Each 5 mL (one teaspoonful) for oral administration contains:
|
|
| Dihydrocodeine Bitartrate* | 3.0 mg |
| Chlorpheniramine Maleate | 2.0 mg |
| Phenylephrine Hydrochloride | 7.5 mg |
Inactive Ingredients: Sodium benzoate, Citric acid, Sodium saccharin, Sorbitol, Propylene glycol, D&C Red No. 33, FD&C Blue No. 1, Grape flavor, Purified water.
Dihydrocodeine Bitartrate is a semi-synthetic narcotic/analgesic, its structure is as follows:
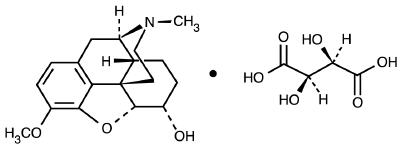
C18H23NO3 • C4H6O6 M.W. 451.47
Morphinan-6-ol, 4,5-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methyl-,(5α,6α)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate (1:1) (salt).
Chlorpheniramine Maleate is an antihistaminic, its structure is as follows:
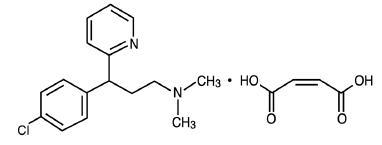
C16H19ClN2 • C4H4O4 M.W. 390.86
2-Pyridinepropanamine, γ-(4-chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-, (Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1).
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride is an orally effective nasal decongestant, its structure is as follows:
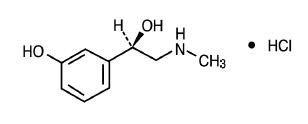
C9H13NO2 • HCl M.W. 203.67
Benzenemethanol, 3-hydroxy-α-[(methylamino)methyl]-,hydrochloride (R)-.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Dihydrocodeine is a semi-synthetic narcotic analgesic related to codeine, with multiple actions qualitatively similar to those of codeine; the most prominent of these involve the central nervous system and organs with smooth muscle components. Chlorpheniramine maleate is an alkylamine type antihistamine. This group of antihistamines is among the most active histamine antagonists and is generally effective in relatively low doses. The drugs are not so prone to produce drowsiness and are among the most suitable agents for daytime use, but a significant proportion of patients do experience this effect. Phenylephrine HCl is a sympathomimetic, which acts predominately on alpha-receptors and has little action on beta-receptors. It therefore functions as an oral nasal decongestant with minimal CNS stimulation.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Coldcough™ PD is indicated to control cough and provide for temporary relief from congestion associated with the upper respiratory tract.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
This combination product is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to dihydrocodeine, codeine, or any of the active and inactive components listed above, or in any situation where opioids are contraindicated including significant respiratory depression (in unmonitored settings or in the absence of resuscitation equipment), acute or severe bronchial asthma or hypercapnia, and paralytic ileus.
Antihistamines and sympathomimetics are contraindicated in patients receiving antihypertensive or antidepressant drugs containing monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (and for 14 days after stopping MAOI therapy). Antihistamines should not be used to treat lower respiratory tract symptoms or be given to premature or newborn infants.
Sympathomimetic agents are contraindicated in patients with severe hypertension, severe coronary artery disease, patients with narrow angle glaucoma, bronchial asthma, urinary retention, peptic ulcer, and during an asthma attack. This product is contraindicated in women who are pregnant.
WARNINGS
Do not exceed recommended dosage. If nervousness, dizziness, or sleeplessness occurs, discontinue use and consult a doctor. If symptoms do not improve within 7 days or are accompanied by a fever, consult a doctor.
General
Considerable caution should be exercised in patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, ischemic heart disease, hyperthyroidism, increased intraocular pressure and prostatic hypertrophy. The elderly (60 years and older) are more likely to exhibit adverse reactions. Antihistamines may cause excitability, especially in children. At dosages higher than the recommended dose, nervousness, dizziness, or sleeplessness may occur.
Sympathomimetic amines should be used with caution in patients with hypertension, ischemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism or prostatic hypertrophy. Sympathomimetics may produce central nervous system stimulation with convulsions or cardiovascular collapse with accompanying hypotension.
Codeine Warning
Nursing infants whose mothers are taking codeine and are ultra-rapid metabolizers of codeine may be at increased risk for morphine overdose.
When physicians prescribe codeine-containing drugs to nursing women, they should inform their patients about the potential risks and the signs of morphine overdose. Nursing women taking codeine need to carefully watch their infants for signs of morphine overdose and seek medical attention immediately if the infant develops increased sleepiness (more than usual), difficulty breastfeeding or breathing, or decreased tone (limpness). Nursing mothers may also experience overdose symptoms such as extreme sleepiness, confusion, shallow breathing or severe constipation. When prescribing codeine to nursing mothers, physicians should choose the lowest effective dose for the shortest period of time and should closely monitor mother-infant pairs.
Drug metabolism is a complex process involving multiple genetic, environmental and physiologic factors. Limited evidence suggests that individuals who are ultra-rapid metabolizers (those with a specific CYP2D6 genotype) may convert codeine to its active metabolite, morphine, more rapidly and completely than other people. In nursing mothers, this metabolism can result in higher than expected serum and breast milk morphine levels. One published case report of an infant death raises concern that nursing babies may be at increased risk of morphine overdose if their mothers are taking codeine and are ultra-rapid metabolizers of the drug.
Usage in Ambulatory Patients
Dihydrocodeine may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery.
Respiratory Depression
Respiratory depression is the most dangerous acute reaction produced by opioid agonist preparations, although it is rarely severe with usual doses. Opioids decrease the respiratory rate, tidal volume, minute ventilation, and sensitivity to carbon dioxide. Respiratory depression occurs most frequently in elderly more debilitated patients, usually after large initial doses in non-tolerant patients, or when opioids are given in conjunction with other agents that depress respiration. This combination product should be used with caution in patients with significant chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or cor pulmonale and in patients with a substantially decreased respiratory reserve, hypoxia hypercapnia, or respiratory depression.
Hypotensive Effect
Dihydrocodeine, like all opioid analgesics, may cause hypotension in patients whose ability to maintain blood pressure has been compromised by a depleted blood volume or who receive concurrent therapy with drugs such as phenothiazines or other agents, which compromise vasomotor tone. Coldcough™ PD may produce orthostatic hypotension in ambulatory patients. This combination product should be administered with caution to patients in circulatory shock, since vasodilation produced by the drug may further reduce cardiac output and blood pressure.
Dependence
Dihydrocodeine can produce drug dependence of the codeine type and has the potential of being abused. This product should be prescribed and administered with the appropriate degree of caution. (See Drug Abuse and Dependence section).
PRECAUTIONS
General
This combination product should be used with caution in elderly or debilitated patients or those with any of the following conditions: adrenocortical insufficiency (e.g., Addison's disease); asthma; central nervous system depression or coma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; decreased respiratory reserve (including emphysema, severe obesity, cor pulmonale, or kyphoscoliosis); delirium tremens; diabetes; head injury; hypotension; hypertension; increased intracranial pressure; myxedema or hypothyroidism; prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture; and toxic psychosis. The benefits and risks of opioids in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors and in those with a history of drug abuse should be carefully considered. This combination product may aggravate convulsions in patients with convulsive disorders, and, like all opioids, may induce or aggravate seizures in some clinical settings.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in the pediatric population, under 6, have not been established.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
General
Sympathomimetics may reduce the antihypertensive effects of methyldopa, mecamylamine, reserpine and veratrum alkaloids.
Other Central Nervous System Depressants
Patients receiving other opioid analgesics, sedatives or hypnotics, muscle relaxants, general anesthetics, centrally acting anti-emetics, phenothiazines or other tranquilizers, or alcohol concomitantly with this combination product may exhibit additive depressant effects on the central nervous system. When such combined therapy is contemplated, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced. Concomitant use of hydrocodeine and antihistamines with alcohol and other CNS depressants may have an additive effect.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Dihydrocodeine, like all opioids, interact with monoamine oxidase inhibitors causing central nervous system excitation and hypertension. MAO inhibitors and beta-adrenergic blockers increase the effects of sympathomimetics. They may also prolong and intensify the anticholinergic effects of antihistamines.
Information for Patient/Caregivers
Patients receiving Coldcough™ PD should be given the following information:
- Patients should be advised that Coldcough™ PD may impair the mental or physical abilites required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery.
- Patients should be advised to report adverse experiences occurring during therapy.
- Patients should be advised not to adjust the dose of Coldcough™ PD without consulting the prescribing professional. Patients should not combine Coldcough™ PD with alcohol or other central nervous system stimulants.
- Women of childbearing potential who become, or are planning to become pregnant should be advised to consult their physician regarding the effects of opioids and other drug use during pregnancy on themselves and their unborn child.
Patients should be advised that Coldcough™ PD is a potential drug of abuse. They should protect it from theft, and it should never be given to anyone other than the individual for whom it was prescribed.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Coldcough™ PD. It is also not known whether this combination product can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women or can affect reproduction capacity in males and females. This combination product should be given to pregnant women only if clearly needed, especially during the first trimester.
Non-Teratogenic Effects
Babies born to mothers who have been taking opioids regularly prior to delivery will be physically dependent. The withdrawal signs include irritability and excessive crying, tremors, hyperactive reflexes, increased respiratory rate, increased stools, sneezing, yawning, vomiting and fever. The intensity of the syndrome does not always correlate with the duration of maternal opioid use or dose. There is no consensus on the best method of managing withdrawal, Chlorpromazine 0.7-1.0 mg/kg q6h, phenobarbital 2 mg/kg q6h, and paregoric 2-4 drops/kg q4h, have been used to treat withdrawal symptoms in infants. The duration of therapy is 4 to 28 days, with the dosages decreased as tolerated.
Labor and Delivery
Coldcough™ PD is not recommended for use by women during and immediately before labor and delivery because oral opioids may cause respiratory depression in the newborn.
Geriatric Use
Coldcough™ PD should be given with caution to the elderly.
Hepatic Impairment
Coldcough™ PD should be given with caution to patients with hepatic insufficiency. Since dihydrocodeine is metabolized by the liver, the effects of this combination product should be monitored closely in such patients.
Renal Impairment
Coldcough™ PD should be used with caution and at reduced dosage in the presence of impaired renal function.
Pancreatic/Biliary Tract Disease
Opioids may cause spasms of the sphincter of Oddi and should be used with caution in patients with biliary tract disease including pancreatitis.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently observed adverse reactions with hydrocodeine include light-headedness, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, fatigue, sedation, sweating, nausea, vomiting, constipation, pruritus, and skin reactions. With the exception of constipation, tolerance develops to most of these effects. Other reactions that have been observed with dihydrocodeine or other opioids include respiratory depression, orthostatic hypotension, cough suppression, confusion, diarrhea, miosis, abdominal pain, dry mouth, indigestion, anorexia, spasm of biliary tract, and urinary retention. Physical and pyschological dependence are possibilities. Hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylactoid reactions), hallucinations, vivid dreams, granulomatous interstitial nephritis, severe narcosis and acute renal failure have been reported rarely during dihydrocodeine administration.
Other adverse reactions observed with the ingredients in Coldcough™ PD include lassitude, nausea, giddiness, dryness of mouth, blurred vision, cardiac palpitations, flushing, increased irritability or excitement (especially in children).
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
This combination product is subject to the provisions of the Controlled Substance Act and has been placed in Schedule V. Dihydrocodeine can produce drug dependence of the codeine type and therefore has the potential of being abused. Psychological dependence, physical dependence, and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration of dihydrocodeine, and it should be prescribed and administered with the same degree of caution appropriate to the use of other oral opioid medications. Symptoms of dihydrocodeine withdrawal consist of irritability, restlessness, insomnia, diaphoresis, anxiety and palpitations.
OVERDOSAGE
An overdose of Coldcough™ PD is a potentially lethal poly-drug overdose situation, and consultation with a regional Poison Control Center is recommended. A listing of the Poison Control Centers can be found in standard references such as the Physicians Desk Reference.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of overdosage include pinpoint pupils, respiratory depression, extreme somnolence progressing to stupor, loss of consciousness, or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin and other symptoms common with narcotic overdosage. Convulsions, cardiovascular collapse, and death may occur. A single case of acute rhabdomyolysis associated with an overdose of dihydrocodeine has been reported.
Recommended Treatment
Immediate treatment of an overdosage of Coldcough™ PD includes support of cardiorespiratory function and measures to reduce drug absorption. Vomiting should be induced with syrup of ipecac, if the patient is alert and has adequate laryngeal reflexes. Oral activated charcoal should follow. The first dose should be accompanied by an appropriate cathartic. Gastric lavage may be necessary. Hypotension is usually hypovolemic and should be treated with fluids. Endotracheal intubation and artificial respiration may be necessary. The pure opioid antagonist naloxone or nalmefene is a specific antidote against respiratory depression that results from opioid overdose. Opioid antagonists should not be given in the absence of clinically significant respiratory or circulatory depression secondary to opioid overdose. They should be administered cautiously to persons who are known, or suspected to be, physically dependent on any opioid agonist including dihydrocodeine. In such cases, an abrupt or complete reversal of opioid effects may precipitate an acute abstinence syndrome. The prescribing information for the specific opioid antagonist should be consulted for details of their proper use.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults and Adolescents over 12 years
1 to 2 teaspoonfuls (5 mL to 10 mL). (Not to exceed 8 teaspoonfuls (40 mL) in 24 hours).
Children 6 to 12 years of age
1/2 to 1 teaspoonful (2.5 mL to 5 mL). (Not to exceed 4 teaspoonfuls (20 mL) in 24 hours).
These doses may be given every four to six hours as needed.
This product is not indicated for use in children under 6 years of age. (See PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use.)
HOW SUPPLIED
Coldcough™ PD is a sugar-free, alcohol-free, purple liquid with a grape flavor supplied in 4 x 4 fl. oz. (118 mL) bottles (Unit of use with a 10 mL graduated oral dosing syringe and bottle Adaptor included) (NDC 51991-224-04).
STORAGE
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature.
Dispense in original tight, light-resistant container with a child-resistant closure as defined in the USP/NF. Protect from freezing.
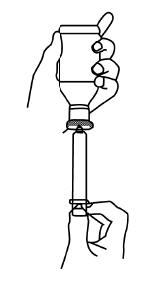
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF SYRINGE
Important: follow Instructions carefully to ensure proper dosing.
To insert dispensing Plug
- 1)
- Shake bottle well.
- 2)
- Remove Child-Resistant cap and the safety seal from bottle.
- 3)
- Push Dispensing Plug into neck of bottle.
- 4)
- To ensure that the dispensing plug is fully seated, replace the child safety cap onto the bottle and turn it down completely. This will seat the dispensing plug securely in the bottle. Remove child safety cap.
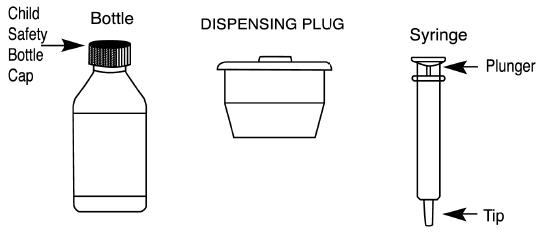
To withdraw medication into syringe
|
|
|
|
|
|
|  |
|
|
|
|
NOTE: TO MAINTAIN CHILD-RESISTANT STATUS OF MEDICATION, REPLACE CHILD SAFETY CAP AFTER EACH USE.
Caution: Forceful squirting into the back of mouth can cause choking. Dispensing plug and syringe should be used for one drug product and one patient only. The dispensing plug is not a childproof closure.
Keep this and all medications out of the reach of children. In case of accidental overdose seek professional assistance or contact a poison control center immediately.
All prescription substitutions using this product shall be pursuant to state statutes as applicable. This is not an Orange Book product.
Rx Only
Manufactured by: Deltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Rosenberg, TX 77471
Distributed by: Breckenridge Pharmaceutical, Inc.
Boca Raton, FL 33487
ISS. 10/07
MG #21477
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 118 mL Bottle Carton
Breckenridge
Pharmaceutical, Inc.
NDC 51991-224-04
Updated Labeling
CV
Coldcough™ PD
Syrup
Antitussive/Decongestant/Antihistamine
Alcohol Free • Sugar Free
| Each 5 mL (one teaspoonful) contains: | |
|---|---|
| Dihydrocodeine Bitartrate* | 3.0 mg |
| *(Warning: May be habit-forming) | |
| Chlorpheniramine Maleate | 2.0 mg |
| Phenylephrine Hydrochloride | 7.5 mg |
Grape Flavor
DO NOT USE IF INNER SEAL
IS BROKEN OR MISSING
Rx Only
4 fl. oz. (118 mL)

| COLDCOUGH PD
dihydrocodeine bitartrate, chlorpheniramine maleate, and phenylephrine hydrochloride syrup |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| UNAPPROVED DRUG OTHER | 07/01/2003 | 12/31/2011 | |
| Labeler - Breckenridge Pharmaceutical, Inc. (150554335) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Deltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 019851778 | MANUFACTURE | |