FORTESTA
-
testosterone gel, metered
Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc.
----------
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: SECONDARY EXPOSURE TO TESTOSTERONE
- Virilization has been reported in children who were secondarily exposed to testosterone gel [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- Children should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application sites in men using FORTESTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Healthcare providers should advise patients to strictly adhere to recommended instructions for use [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FORTESTA is an androgen indicated for replacement therapy in males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone:
- Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) – testicular failure due to conditions such as cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, orchiectomy, Klinefelter’s syndrome, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol, heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone concentrations and gonadotropins (Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH)) above the normal range.
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) – idiopathic gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These men have low serum testosterone concentrations but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range.
Important limitations of use: - Safety and efficacy of FORTESTA in males <18 years old have not been established [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing and Dose Adjustment
The recommended starting dose of FORTESTA is 40 mg of testosterone (4 pump actuations) applied once daily to the thighs in the morning. The dose can be adjusted between a minimum of 10 mg of testosterone and a maximum of 70 mg of testosterone. To ensure proper dosing, the dose should be titrated based on the serum testosterone concentration from a single blood draw 2 hours after applying FORTESTA and at approximately 14 days and 35 days after starting treatment or following dose adjustment. In addition, serum testosterone concentration should be assessed periodically thereafter. Table 1 describes the dose adjustments required at each titration step.
| Total Serum Testosterone Concentration 2 hours Post FORTESTA Application | Dose Titration |
|---|---|
| Equal to or greater than 2,500 ng/dL | Decrease daily dose by 20 mg (2 pump actuations) |
| Equal to or greater than 1,250 and less than 2,500 ng/dL | Decrease daily dose by 10 mg (1 pump actuation) |
| Equal to or greater than 500 and less than 1,250 ng/dL | No change: continue on current dose |
| Less than 500 ng/dL | Increase daily dose by 10 mg (1 pump actuation) |
The application site and dose of FORTESTA are not interchangeable with other topical testosterone products.
2.2 Administration Instructions
FORTESTA should be applied directly to clean, dry, intact skin of the front and inner thighs. Do not apply FORTESTA to the genitals or other parts of the body. Patients should be instructed to use one finger to gently rub FORTESTA evenly onto the front and inner area of each thigh as directed in Table 2.
| Total Dose of Testosterone | Total Pump Actuations | Pump Actuations per Thigh | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thigh #1 | Thigh #2 | ||
| 10 mg | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 20 mg | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 30 mg | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 40 mg | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| 50 mg | 5 | 3 | 2 |
| 60 mg | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| 70 mg | 7 | 4 | 3 |
Once the application site is dry, the site should be covered with clothing [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water. Avoid applying the gel to the thigh adjacent to the scrotum. Avoid fire, flames or smoking until the gel has dried since alcohol based products, including FORTESTA, are flammable.
The patient should avoid swimming or showering or washing the administration site for a minimum of 2 hours after application [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
To obtain a full first dose, it is necessary to prime the canister pump. To do so, with the canister in the upright position, slowly and fully depress the actuator eight times. The first three actuations may result in no discharge of gel. Safely discard the gel from the first eight actuations. It is only necessary to prime the pump before the first dose.
Strict adherence to the following precautions is advised in order to minimize the potential for secondary exposure to testosterone from FORTESTA-treated skin:
- Children and women should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application site(s) of men using FORTESTA.
- FORTESTA should only be applied to the front and inner thighs (area of application should be limited to the area that will be covered by the patient’s shorts or pants).
- Patients should wash their hands immediately with soap and water after applying FORTESTA.
- Patients should cover the application site(s) with clothing (e.g., shorts of sufficient length or pants) after the gel has dried.
- Prior to any situation in which skin-to-skin contact with the application site is anticipated, patients should wash the application site(s) thoroughly with soap and water to remove any testosterone residue.
- In the event that unwashed or unclothed skin to which FORTESTA has been applied comes in direct contact with the skin of another person, the general area of contact on the other person should be washed with soap and water as soon as possible.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
FORTESTA (testosterone) Gel for topical use only, is supplied in a metered-dose pump. One pump actuation delivers 10 mg of testosterone.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- FORTESTA is contraindicated in men with carcinoma of the breast or known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
- FORTESTA is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant, or who are breastfeeding. FORTESTA may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. FORTESTA may cause serious adverse reactions in nursing infants. Exposure of a female fetus or nursing infant to androgens may result in varying degrees of virilization. Pregnant women or those who may become pregnant need to be aware of the potential for transfer of testosterone from men treated with FORTESTA. If a pregnant woman is exposed to FORTESTA, she should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Worsening of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Potential Risk of Prostate Cancer
- Patients with BPH treated with androgens are at an increased risk of worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH. Monitor patients with BPH for worsening signs and symptoms.
- Patients treated with androgens may be at increased risk for prostate cancer. Evaluation of the patients for the presence of prostate cancer prior to initiating and during treatment with androgens is appropriate [see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Potential for Secondary Exposure to Testosterone
Cases of secondary exposure resulting in virilization of children have been reported in postmarketing surveillance of testosterone gel products. Signs and symptoms have included enlargement of the penis or clitoris, development of pubic hair, increased erections and libido, aggressive behavior, and advanced bone age. In most cases, these signs and symptoms regressed with removal of the exposure to testosterone gel. In a few cases, however, enlarged genitalia did not fully return to age-appropriate normal size, and bone age remained modestly greater than chronological age. The risk of transfer was increased in some of these cases by not adhering to precautions for the appropriate use of the topical testosterone product. Children and women should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application sites in men using FORTESTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Inappropriate changes in genital size or development of pubic hair or libido in children, or changes in body hair distribution, significant increase in acne, or other signs of virilization in adult women should be brought to the attention of a physician and the possibility of secondary exposure to testosterone gel should also be brought to the attention of a physician. Testosterone gel should be promptly discontinued until the cause of virilization has been identified.
5.3 Polycythemia
Increases in hematocrit, reflective of increases in red blood cell mass, may require lowering or discontinuation of testosterone. Check hematocrit prior to initiating treatment. It would also be appropriate to re-evaluate the hematocrit 3 to 6 months after starting treatment, and then annually. If hematocrit becomes elevated, stop therapy until hematocrit decreases to an acceptable concentration. An increase in red blood cell mass may increase the risk of thromboembolic events.
5.4 Use in Women
Due to the lack of controlled evaluations in women and potential virilizing effects, FORTESTA is not indicated for use in women [see Contraindications (4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
5.5 Potential for Adverse Effects on Spermatogenesis
With large doses of exogenous androgens, including FORTESTA, spermatogenesis may be suppressed through feedback inhibition of pituitary FSH which could possibly lead to adverse effects on semen parameters including sperm count.
5.6 Hepatic Adverse Effects
Prolonged use of high doses of orally active 17-alpha-alkyl androgens (e.g. methyltestosterone) has been associated with serious hepatic adverse effects (peliosis hepatis, hepatic neoplasms, cholestatic hepatitis and jaundice). Peliosis hepatis can be a life-threatening or fatal complication. Long-term therapy with testosterone enanthate has produced multiple hepatic adenomas. FORTESTA is not known to cause these adverse effects.
5.7 Edema
Androgens, including FORTESTA, may promote retention of sodium and water. Edema, with or without congestive heart failure, may be a serious complication in patients with pre-existing cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.8 Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia may develop and persist in patients being treated with androgens, including FORTESTA, for hypogonadism.
5.9 Sleep Apnea
The treatment of hypogonadal men with testosterone may potentiate sleep apnea in some patients, especially those with risk factors such as obesity or chronic lung diseases.
5.10 Lipids
Changes in serum lipid profile may require dose adjustment or discontinuation of testosterone therapy.
5.11 Hypercalcemia
Androgens, including FORTESTA, should be used with caution in cancer patients at risk of hypercalcemia (and associated hypercalciuria). Regular monitoring of serum calcium concentrations is recommended in these patients.
5.12 Decreased Thyroxine-binding globulin
Androgens, including FORTESTA, may decrease concentrations of thyroxin-binding globulins, resulting in decreased total T4 serum concentrations and increased resin uptake of T3 and T4. Free thyroid hormone concentrations remain unchanged, however, and there is no clinical evidence of thyroid dysfunction.
5.13 Flammability
Alcohol based products, including FORTESTA, are flammable; therefore, patients should be advised to avoid smoking, fire or flame until the FORTESTA gel has dried.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
In a controlled multicenter, open label, non-comparative 90-day clinical study, 149 hypogonadal patients were treated with FORTESTA [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Adverse reactions occurred in 22.8% (34/149) of patients. The most common adverse reaction reported in this study was skin reactions associated with the site of application (16.1%; 24/149) of which 79% (19/24) were mild, and the remainder were moderate (21%; 5/24) (Table 3).
| Adverse Reaction | Number (%) of Patients N = 149 |
|---|---|
| Skin reaction | 24 (16.1%) |
| Prostatic specific antigen increased | 2 (1.3%) |
| Abnormal dreams | 2 (1.3%) |
During the 90 day trial 5 patients (3.4%) discontinued treatment because of adverse reactions. These reactions were: 1 patient with contact dermatitis (considered probably related to FORTESTA application), 1 with application site reaction (considered probably related to FORTESTA application), 1 with gastrointestinal hypomotility (considered possibly related to FORTESTA application), 1 with severe dyspnea (considered not related to FORTESTA application), and 1 with moderate contusion (considered not related to FORTESTA application).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of FORTESTA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure (Table 4).
| System Organ Class | Adverse Reaction |
|---|---|
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Polycythemia |
| Eye disorders | Vitreous detachment |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Abdominal symptoms |
| General disorders and administrative site conditions | Application site erythema, irritation, pruritus, and swelling; fatigue, influenza like illness, and malaise. |
| Investigations | Decreased serum testosterone, increased hematocrit and hemoglobin |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Pain in extremity |
| Nervous system disorders | Dizziness, headache, and migraine |
| Reproductive system and breast disorders | Erectile dysfunction, and priapism |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Allergic dermatitis, erythema, rash, and papular rash. |
Secondary Exposure to Testosterone in Children
Cases of secondary exposure to testosterone resulting in virilization of children have been reported in postmarketing surveillance of testosterone gel products. Signs and symptoms of these reported cases have included enlargement of the clitoris (with surgical intervention) or the penis, development of pubic hair, increased erections and libido, aggressive behavior, and advanced bone age. In most cases with a reported outcome, these signs and symptoms were reported to have regressed with removal of the testosterone gel exposure. In a few cases, however, enlarged genitalia did not fully return to age appropriate normal size, and bone age remained modestly greater than chronological age. In some of the cases, direct contact with the sites of application on the skin of men using testosterone gel was reported. In at least one reported case, the reporter considered the possibility of secondary exposure from items such as the testosterone gel user’s shirts and/or other fabric, such as towels and sheets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Insulin
Changes in insulin sensitivity or glycemic control may occur in patients treated with androgens. In diabetic patients, the metabolic effects of androgens may decrease blood glucose and, therefore, may decrease insulin requirements.
7.2 Oral Anticoagulants
Changes in anticoagulant activity may be seen with androgens, therefore more frequent monitoring of international normalized ratio (INR) and prothrombin time are recommended in patients taking anticoagulants, especially at the initiation and termination of androgen therapy.
7.3 Corticosteroids
The concurrent administration of testosterone with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) or corticosteroids may result in increased fluid retention and requires careful monitoring particularly in patients with cardiac, renal or hepatic disease.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category X [see Contraindications (4)]. – FORTESTA is contraindicated during pregnancy or in women who may become pregnant. Testosterone is teratogenic and may cause fetal harm. Exposure of a female fetus to androgens may result in varying degrees of virilization. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be made aware of the potential hazard to the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Although it is not known how much testosterone transfers into human milk, FORTESTA is contraindicated in nursing women because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants. Testosterone and other androgens may adversely affect lactation [see Contraindications (4)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of FORTESTA in pediatric patients <18 years old has not been established. Improper use may result in acceleration of bone age and premature closure of epiphyses.
8.5 Geriatric Use
There have not been sufficient numbers of geriatric patients involved in controlled clinical studies utilizing FORTESTA to determine whether efficacy in those over 65 years of age differs from younger subjects. Of the 149 patients enrolled in the pivotal clinical study utilizing FORTESTA, 20 were over 65 years of age. Additionally, there are insufficient long-term safety data in geriatric patients to assess the potential risks of cardiovascular disease and prostate cancer.
Geriatric patients treated with androgens may also be at risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No studies were conducted in patients with renal impairment.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No studies were conducted in patients with hepatic impairment.
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
FORTESTA contains testosterone, a Schedule III controlled substance as defined under the Anabolics Steroid Control Act.
9.2 Abuse
Anabolic steroids, such as testosterone, are abused. Abuse is often associated with adverse physical and psychological effects.
9.3 Dependence
Although drug dependence is not documented in individuals using therapeutic doses of anabolic steroids for approved indications, dependence is observed in some individuals abusing high doses of anabolic steroids. In general, anabolic steroid dependence is characterized by any three of the following:
- Taking more drug than intended
- Continued drug use despite medical and social problems
- Significant time spent in obtaining adequate amounts of drug
- Desire for anabolic steroids when supplies of the drugs are interrupted
- Difficulty in discontinuing use of the drug despite desires and attempts to do so
- Experience of a withdrawal syndrome upon discontinuation of anabolic steroid use.
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is a single report of acute overdosage after parenteral administration of an approved testosterone product in the literature. This subject had serum testosterone concentrations of up to 11,400 ng/dL, which were implicated in a cerebrovascular accident. There were no reports of overdose in the FORTESTA clinical trial.
Treatment of overdosage would consist of discontinuation of FORTESTA, washing the application site with soap and water, and appropriate symptomatic and supportive care.
11 DESCRIPTION
FORTESTA is a clear, colorless, odorless, gel containing testosterone. FORTESTA is available in a metered-dose pump. Each pump actuation provides 10 mg of testosterone and each container is capable of dispensing 120 pump actuations. One pump actuation dispenses 0.5 g of gel.
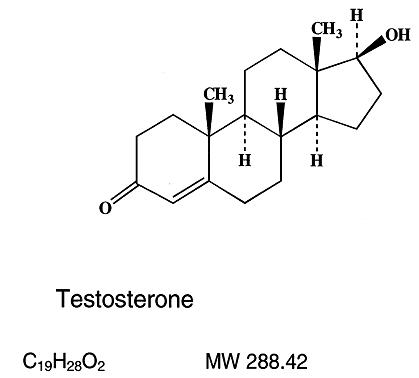
The active pharmacologic ingredient in FORTESTA is testosterone. Testosterone USP is a white to almost white powder described chemically as 17-beta hydroxyandrost-4-en-3-one.
Pharmacologically inactive ingredients in FORTESTA are: propylene glycol, purified water, ethanol, 2-propanol, oleic acid, carbomer 1382, triethanolamine and butylated hydroxytoluene.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Endogenous androgens, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), are responsible for the normal growth and development of the male sex organs and for the maintenance of secondary sex characteristics. These effects include the growth and maturation of the prostate, seminal vesicles, penis and scrotum; the development of male hair distribution, such as facial, pubic, chest and axillary hair; laryngeal enlargement, vocal cord thickening, alterations in body musculature and fat distribution. Testosterone and DHT are necessary for the normal development of secondary sex characteristics. Male hypogonadism results from insufficient production of testosterone and is characterized by low serum testosterone concentrations. Symptoms associated with male hypogonadism include erectile dysfunction and decreased sexual desire, fatigue and loss of energy, mood depression, regression of secondary sexual characteristics, and osteoporosis.
Male hypogonadism can present as primary hypogonadism caused by defects of the gonads, such as Klinefelter’s Syndrome or Leydig cell aplasia while secondary hypogonadism is the failure of the hypothalamus or pituitary to produce sufficient gonadotropins (FSH, LH).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
No specific pharmacodynamic studies were conducted using FORTESTA.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
FORTESTA delivers physiologic amounts of testosterone, producing serum testosterone concentrations that approximate normal concentrations (> 300 ng/dL) seen in healthy men.
FORTESTA provides continuous transdermal delivery of testosterone for 24 hours following a single application to clean, dry, intact skin of the front and inner thighs (Figure 1).
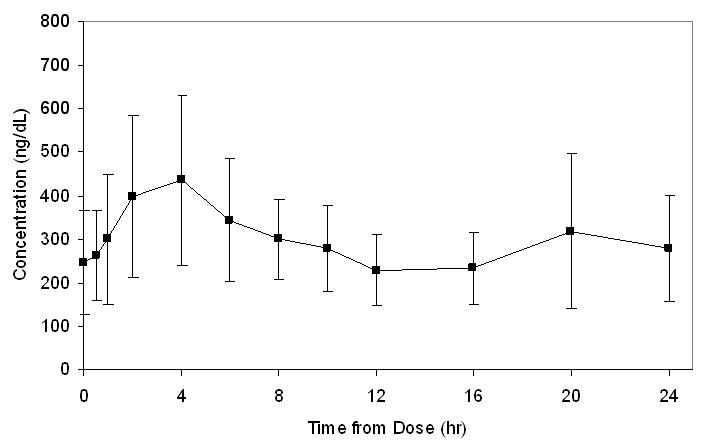
Figure 1: Mean (±SD) Serum Total Testosterone Concentrations on Day 7 in Patients Following FORTESTA Once-Daily Application of 40 mg of Testosterone (N=12)
Distribution
Circulating testosterone is primarily bound in the serum to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin. Approximately 40% of testosterone in plasma is bound to SHBG, 2% remains unbound (free) and the rest is loosely bound to albumin and other proteins.
Metabolism
Testosterone is metabolized to various 17-keto steroids through two different pathways. The major active metabolites of testosterone are estradiol and DHT.
Excretion
There is considerable variation in the half-life of testosterone concentration as reported in the literature, ranging from 10 to 100 minutes. About 90% of a dose of testosterone given intramuscularly is excreted in the urine as glucuronic acid and sulfuric acid conjugates of testosterone and its metabolites. About 6% is excreted in the feces, mostly in the unconjugated form. Inactivation of testosterone occurs primarily in the liver.
Potential for testosterone transfer
The potential for testosterone transfer from healthy males dosed with FORTESTA to healthy females was evaluated in a placebo-controlled, three-way crossover study. The washout period was approximately 29 days. Six males were treated with either FORTESTA (30 mg testosterone) or placebo to one thigh only. At 2 hours after the application of FORTESTA to males, the females rubbed their forearms for 15 minutes on the thigh of the males. Serum concentrations of testosterone were monitored in females for 24 hours after the transfer procedure. When direct skin-to-skin transfer occurred with FORTESTA mean Cavg increased by 134% and mean Cmax increased by 191%, compared to direct skin-to-skin transfer with placebo. When transfer occurred with FORTESTA while covering a thigh with boxer shorts, mean Cavg decreased by 3% and mean Cmax increased by 2%, compared to direct skin-to-skin transfer with placebo [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Effect of showering
In a two-way crossover study, the effects of showering on the pharmacokinetics of total testosterone following application of FORTESTA (30 mg testosterone to each thigh; total 60 mg testosterone) were assessed in 7 hypogonadal males. There were two 7-day treatment phases, with showering 2 hours post FORTESTA application, and without showering on Day 7 of each treatment phase. Showering decreased Cavg by 3% and it increased Cmax by 13%. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Testosterone has been tested by subcutaneous injection and implantation in mice and rats. In mice, implant induced cervical-uterine tumors metastasized in some cases. There is suggestive evidence that injection of testosterone into some strains of female mice increases their susceptibility to hepatoma. Testosterone is also known to increase the number of tumors and decrease the degree of differentiation of chemically induced carcinomas of the liver in rats. Testosterone was negative in the in vitro Ames and in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assays. The administration of exogenous testosterone has been reported to suppress spermatogenesis in the rat, dog and non-human primates, which was reversible on cessation of the treatment.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Study in Hypogonadal Males
FORTESTA was evaluated in a multicenter, 90 day open-label, non-comparative trial of 149 hypogonadal males with body mass index (BMI) ≥ 22 kg/m2 and < 35 kg/m2 and 18-75 years of age (mean age 54.5 years). The patients were screened for a single serum total testosterone concentration < 250 ng/dL, or two consecutive serum total testosterone concentrations < 300 ng/dL. Patients were Caucasian (80.5%), Black (10.1%), Hispanic (7.4%) and other (2.0%).
FORTESTA was applied once each morning to the thighs at a starting dose of 40 mg of testosterone (4 pump actuations) per day. The dose was adjusted between a minimum of 10 mg and a maximum of 70 mg testosterone on the basis of total serum testosterone concentration obtained 2 hours post FORTESTA application on Days 14, 35, and 60 (± 3 days).
The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients with Cavg within the normal range (greater than or equal to 300 ng/dL and less than or equal to 1140 ng/dL) on Day 90. In patients treated with FORTESTA, 77.5% (100/129) had Cavg within the normal range on Day 90. The secondary endpoint was the percentage of patients with Cmax above three pre-determined limits. The percentages of patients with Cmax greater than 1500 ng/dL, and between 1800 and 2499 ng/dL on Day 90 were 5.4% and 1.6%, respectively. No patient had a Cmax greater than or equal to 2500 ng/dL on Day 90.
Dose titrations on Days 14, 35 and 60 resulted in mean (SD) Cavg and Cmax for final doses of 10 mg – 70 mg on Day 90 shown in Table 5.
| Final Dose | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg (n=1) | 20mg (n=6) | 30mg (n=16) | 40mg (n=30) | 50mg (n=26) | 60mg (n=27) | 70mg (n=23) |
||
| Cavg
(ng/dL) | Mean | 196 | 464 | 392 | 444 | 483 | 441 | 415 |
| SD | 205 | 164 | 176 | 156 | 163 | 136 | ||
| Cmax
(ng/dL) | Mean | 503 | 971 | 775 | 855 | 964 | 766 | 724 |
| SD | 399 | 278 | 417 | 389 | 292 | 313 | ||
Figure 2 summarizes the pharmacokinetic profiles of total testosterone in patients completing 90 days of FORTESTA treatment administered as 40 mg of testosterone once-daily for the initial 14 days followed by possible titration according to follow-up testosterone measurements.
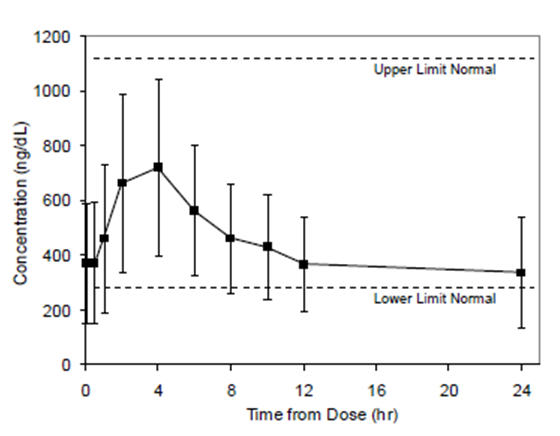
Figure 2 Mean (±SD) Steady-State Serum Total Testosterone Concentrations on Day 90 (N=129)
Additionally, there were no clinically significant changes from baseline for sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) (slight decrease), E2 (slight increase) and ratio of DHT to total testosterone (slight increase) at Day 90.
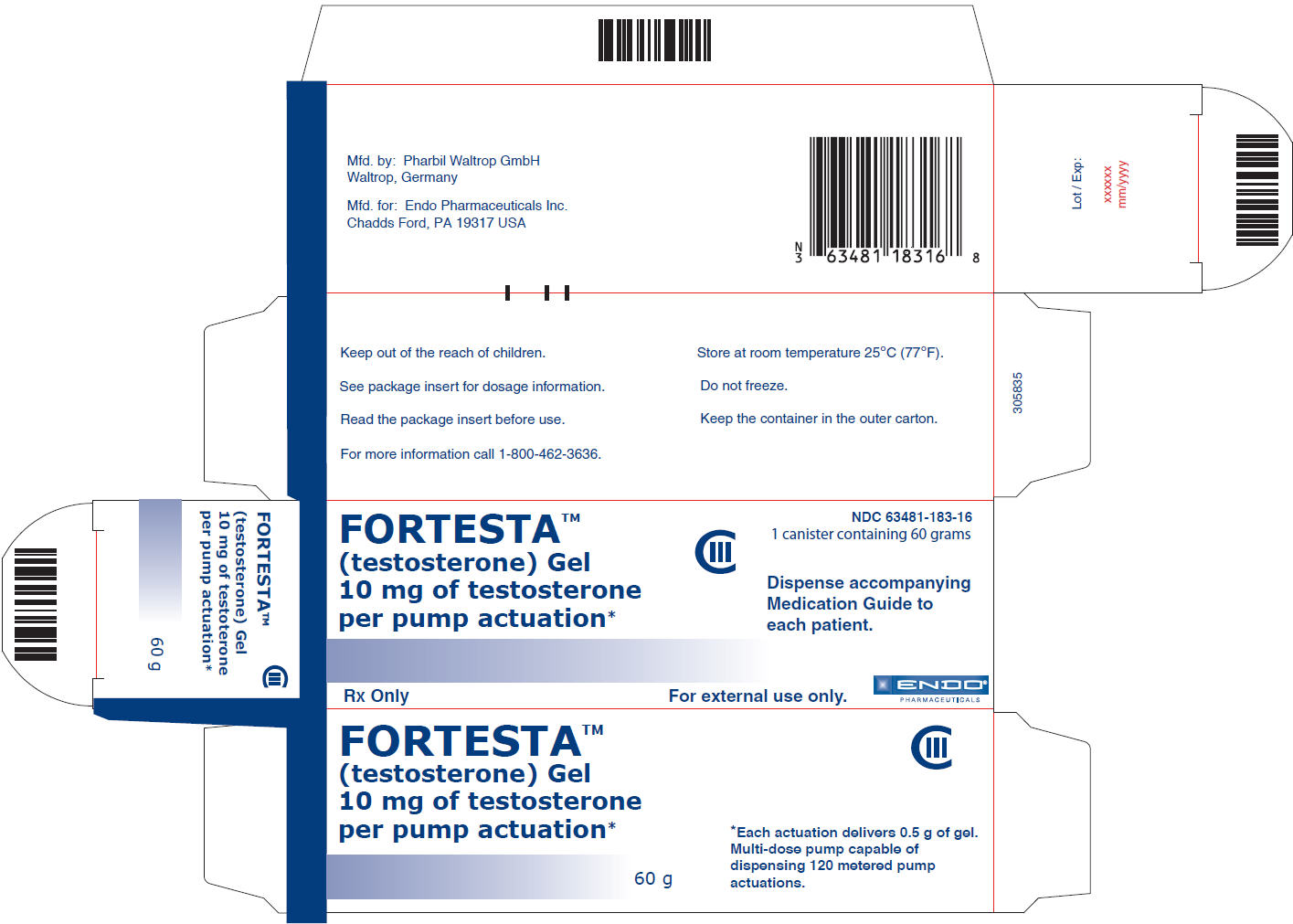
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
FORTESTA is supplied in 60 g canisters with a metered dose pump that delivers 10 mg of testosterone per complete pump actuation. The metered dose pump is capable of dispensing 120 metered pump actuations. One pump actuation dispenses 0.5 g of gel.
FORTESTA is available in packages of 1, 2 and 3 canisters (NDC 63481-183-16, NDC 63481-183-17 and NDC 63481-183-18, respectively).
Store at controlled room temperature 20-25oC (68-77oF); excursions permitted to 15o-30oC (59o-86oF). [See USP]. Do Not Freeze.
Used FORTESTA canisters should be discarded in household trash in a manner that prevents accidental application or ingestion by children or pets.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved Medication Guide.
Patients should be informed of the following information:
17.1 Use in Men with Known or Suspected Prostate or Breast Cancer
Men with known or suspected prostate or breast cancer should not use FORTESTA [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precaution (5.1)].
17.2 Potential for Secondary Exposure to Testosterone and Steps to Prevent Secondary Exposure
Secondary exposure to testosterone in children and women can occur with the use of testosterone gel in men. Cases of secondary exposure to testosterone in children have been reported.
Physicians should advise patients of the reported signs and symptoms of secondary exposure which may include the following:
- In children; unexpected sexual development including inappropriate enlargement of the penis or clitoris, premature development of pubic hair, increased erections, and aggressive behavior.
- In women; changes in hair distribution, increase in acne, or other signs of testosterone effects.
- The possibility of secondary exposure to FORTESTA should be brought to the attention of a healthcare provider.
- FORTESTA should be promptly discontinued until the cause of virilization is identified.
Strict adherence to the following precautions is advised to minimize the potential for secondary exposure to testosterone from FORTESTA in men [see Medication Guide]:
- Children and women should avoid contact with unwashed or unclothed application site(s) of men using FORTESTA.
- Patients using FORTESTA should apply the product as directed and strictly adhere to the following:
- Wash hands with soap and water after application.
- Cover the application site(s) with clothing after the gel has dried.
- Wash the application site(s) thoroughly with soap and water prior to any situation where skin-to-skin contact of the application site with another person is anticipated.
- In the event that unwashed or unclothed skin to which FORTESTA has been applied comes in contact with the skin of another person, the general area of contact on the other person should be washed with soap and water as soon as possible [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
17.3 Potential Adverse Reactions with Androgens
Patients should be informed that treatment with androgens may lead to adverse reactions which include:
- Changes in urinary habits such as increased urination at night, trouble starting your urine stream, passing urine many times during the day, having an urge that you have to go to the bathroom right away, having a urine accident, being unable to pass urine and weak urine flow.
- Breathing disturbances, including those associated with sleep, or excessive daytime sleepiness.
- Too frequent or persistent erections of the penis.
- Nausea, vomiting, changes in skin color, or ankle swelling.
17.4 Patients Should Be Advised of the Following Instructions for Use
- Read the Medication Guide before starting FORTESTA therapy and reread it each time the prescription is renewed.
- FORTESTA should be applied and used appropriately to maximize the benefits and to minimize the risk of secondary exposure in children and women.
- Keep FORTESTA out of the reach of children.
- FORTESTA is an alcohol based product and is flammable; therefore avoid fire, flame or smoking until the gel has dried.
- It is important to adhere to all recommended monitoring.
- Report any changes in their state of health, such as changes in urinary habits, breathing, sleep, and mood.
- FORTESTA is prescribed to meet the patient’s specific needs, therefore, the patient should never share FORTESTA with anyone.
Manufactured by: Pharbil Waltrop GmbH, Im Wirrigen 25, 45731 Waltrop, Germany
Manufactured for: Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc., 100 Endo Boulevard, Chadds Ford, PA 19317
110093
| FORTESTA is a trademark of Endo Pharmaceuticals |
MEDICATION GUIDE
FORTESTA™ (FOR-tes-ta) CIII
(testosterone) Gel
Read this Medication Guide before you start using FORTESTA and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about FORTESTA?
FORTESTA can transfer from your body to others. This can happen if other people come into contact with the area where the FORTESTA was applied.
Signs of puberty that are not expected (for example, pubic hair) have happened in young children who were accidentally exposed to testosterone through contact with men using topical testosterone products like FORTESTA.
- Women and children should avoid contact with the unwashed or unclothed area where FORTESTA has been applied. If a woman or child makes contact with the FORTESTA application area, that area on the woman or child should be washed well with soap and water right away.
- To lower the risk of transfer of FORTESTA from your body to others, you should follow these important instructions:
- Apply FORTESTA only to the front and inside area of your thighs that will be covered by clothing.
- Wash your hands right away with soap and water after applying FORTESTA.
- After the FORTESTA gel has dried, cover the application area with clothing. Keep the area covered until you have washed the application area well or have showered.
- If you expect another person to have skin-to-skin contact with your thigh, first wash the application area well with soap and water.
Stop using FORTESTA and call your healthcare provider right away if you see any signs and symptoms in a child or a woman that may have occurred through accidental exposure to FORTESTA:
Signs and symptoms in children may include:
- enlarged penis or clitoris
- early development of pubic hair
- increased erections or sex drive
- aggressive behavior
Signs and symptoms in women may include:
- changes in body hair
- a large increase in acne
What is FORTESTA?
FORTESTA is a prescription medicine that contains testosterone. FORTESTA is used to treat adult males who have low or no testosterone.
Your healthcare provider will test your blood before you start taking and while you are taking FORTESTA.
It is not known if FORTESTA is safe or effective in children younger than 18 years old. Improper use of FORTESTA may affect bone growth in children.
FORTESTA is a controlled substance (CIII) because it contains testosterone that can be a target for people who abuse prescription medicines. Keep your FORTESTA in a safe place to protect it. Never give FORTESTA to anyone else, even if they have the same symptoms you have. Selling or giving away this medicine may harm others and is against the law.
FORTESTA is not meant for use in women.
Who should not use FORTESTA?
Do not use FORTESTA if you:
- have breast cancer
- have or might have prostate cancer
- are pregnant or may become pregnant or breast-feeding. FORTESTA may harm your unborn or breast-feeding baby.
Women who are pregnant or who may become pregnant should avoid contact with the area of skin where FORTESTA has been applied.
Talk to your healthcare provider before taking this medicine if you have any of the above conditions.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using FORTESTA?
Before you use FORTESTA, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have breast cancer
- have or might have prostate cancer
- have urinary problems due to an enlarged prostate
- have heart problems
- have liver or kidney problems
- have problems breathing while you sleep (sleep apnea)
- have any other medical conditions
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Using FORTESTA with certain other medicines can affect each other.
Especially, tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- insulin
- medicines that decrease blood clotting
- corticosteroids
Know the medicines you take. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use FORTESTA?
- It is important that you apply FORTESTA exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you how much FORTESTA to apply and when to apply it.
- Your healthcare provider may change your FORTESTA dose. Do not change your FORTESTA dose without talking to your healthcare provider.
- FORTESTA should be applied to the front and inner part of your thighs only. Do not apply FORTESTA to any other parts of your body such as your stomach area (abdomen), penis, scrotum, shoulders or upper arms.
- Apply FORTESTA in the morning. If you shower or bathe, FORTESTA should be applied afterwards.
- Avoid swimming, showering, or bathing for at least 2 hours after you apply FORTESTA.
- FORTESTA is flammable until dry. Let FORTESTA dry before smoking or going near an open flame.
- Apply FORTESTA only to areas that will be covered by shorts or pants.
- Wash your hands with soap and water right after you apply FORTESTA.
Applying FORTESTA:
- Before using a new canister of FORTESTA for the first time, you will need to prime the pump. To prime the FORTESTA pump, gently push down on the pump 8 times. Do not use any FORTESTA that comes out while priming. Wash it down the sink or throw it in the trash to avoid accidental exposure to others. Your FORTESTA pump is now ready to use.
- Use FORTESTA exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it. Your healthcare provider will tell you the dose of FORTESTA that is right for you.
- Depress the pump to apply the medicine directly on clean, dry, intact skin of the front and inner part of your thighs. Use one finger to gently rub FORTESTA evenly onto the front and inner part of each thigh.
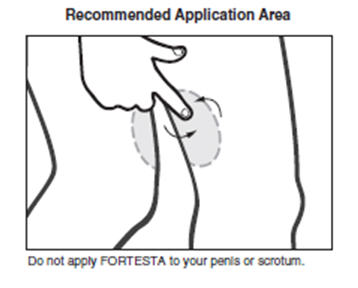
- Let the application site dry completely before putting on shorts or pants.
- Wash your hands right away with soap and water.
What are the possible side effects of FORTESTA?
See “What is the most important information I should know about FORTESTA?”
FORTESTA can cause serious side effects including:
-
-
If you already have enlargement of your prostate gland your signs and symptoms can get worse while using FORTESTA. This can include:
- increased urination at night
- trouble starting your urine stream
- having to pass urine many times during the day
- having an urge that you have to go to the bathroom right away
- having a urine accident
- being unable to pass urine or weak urine flow
- Possible increased risk of prostate cancer. Your healthcare provider should check you for prostate cancer or any other prostate problems before you start and while you use FORTESTA.
- In large doses FORTESTA may lower your sperm count.
- Swelling of your ankles, feet, or body, with or without heart failure.
- Enlarged or painful breasts.
- Have problems breathing while you sleep (sleep apnea).
- Increased red blood cell count
- Blood clots in the legs. This can include pain, swelling or redness of your legs.
-
If you already have enlargement of your prostate gland your signs and symptoms can get worse while using FORTESTA. This can include:
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the serious side effects listed above.
-
The most common side effects of FORTESTA include:
- skin redness or irritation where FORTESTA is applied
- increased in blood level of Prostate Specific Antigen (a test used to screen for prostate cancer)
- abnormal dreams
Other side effects include more erections than are normal for you or erections that last a long time.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of FORTESTA. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store FORTESTA?
- Store FORTESTA at 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
- When it is time to throw away the canister, safely throw away used FORTESTA in household trash. Be careful to prevent accidental exposure of children or pets.
- Keep FORTESTA away from fire.
- Do not freeze FORTESTA.
Keep FORTESTA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about FORTESTA
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use FORTESTA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give FORTESTA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about FORTESTA. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about FORTESTA that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.FORTESTA.com or call 1-800-462-3636.
What are the ingredients in FORTESTA?
Active ingredient: testosterone
Inactive ingredients: propylene glycol, purified water, ethanol, 2-propanol, oleic acid, carbomer 1382, triethanolamine and butylated hydroxytoluene.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
© 2010 Endo Pharmaceuticals
110094
Issued 12/2010
Package Label – Principle Display Panel – 60 g Canister Label

Package Label – Principle Display Panel – Principle Display Panel – 60 g Canister Carton
| FORTESTA
testosterone gel, metered |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA021463 | 12/29/2010 | |
| Labeler - Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc. (178074951) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Pharbil Waltrop GmbH | 343740283 | MANUFACTURE | |