LAMISIL
-
terbinafine hydrochloride granule
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
----------
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules are indicated for the treatment of tinea capitis in patients 4 years of age and older.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules should be taken once a day for 6 weeks based upon body weight (See Table 1). Sprinkle the contents of each packet on a spoonful of pudding or other soft, non-acidic food such as mashed potatoes and swallow the entire spoonful (without chewing); do not use applesauce or fruit-based foods. Take with food. If two packets (250 mg) are required with each dose, either the content of both packets may be sprinkled on one spoonful, or the contents of both packets may be sprinkled on two spoonfuls of non-acidic food as directed above.
| <25 kg | 125 mg/day |
| 25-35 kg | 187.5 mg/day |
| >35 kg | 250 mg/day |
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oral Granules, 125 mg or 187.5 mg (terbinafine base equivalent) per packet. The film-coated granules are off-white to yellowish, round, biconvex, each having a diameter of approximately 2.1 mm.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules are contraindicated in individuals with a history of allergic reaction to oral terbinafine because of the risk of anaphylaxis.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hepatotoxicity
Cases of liver failure, some leading to liver transplant or death, have occurred with the use of oral terbinafine during postmarketing experience in individuals with and without pre-existing liver disease. In the majority of liver cases reported, the patients had serious underlying systemic conditions. The severity of hepatic events and/or their outcome may be worse in patients with active or chronic liver disease. Treatment with Lamisil Oral Granules should be discontinued if biochemical or clinical evidence of liver injury develops.
Lamisil Oral Granules are not recommended for patients with chronic or active liver disease. Before prescribing Lamisil Oral Granules, pre-existing liver disease should be assessed. Hepatotoxicity may occur in patients with and without pre-existing liver disease. Pretreatment serum transaminase (ALT and AST) tests are advised for all patients before taking Lamisil Oral Granules. Patients prescribed Lamisil Oral Granules and/or their guardians should be warned to report immediately to their physician any symptoms of persistent nausea, anorexia, fatigue, vomiting, right upper abdominal pain or jaundice, dark urine or pale stools. Patients with these symptoms should discontinue taking Lamisil Oral Granules, and the patient’s liver function should be immediately evaluated.
5.2 Taste Disturbance Including Loss of Taste
Taste disturbance, including taste loss, has been reported with the use of terbinafine. It can be severe enough to result in decreased food intake, weight loss, and depressive symptoms. Taste disturbance may resolve within several weeks after discontinuation of treatment, but may be prolonged (greater than one year). If symptoms of a taste disturbance occur, Lamisil Oral Granules should be discontinued.
5.3 Depressive Symptoms
Depressive symptoms have occurred during post-marketing use of terbinafine. Prescribers should be alert to depressive symptoms, and patients should be instructed to report depressive symptoms to their physician.
5.4 Hematologic Effects
Transient decreases in absolute lymphocyte counts (ALC) have been observed in clinical trials. In placebo-controlled trials, 8/465 subjects receiving Lamisil Tablets (1.7%) and 3/137 subjects receiving placebo (2.2%) had decreases in ALC to below 1,000/mm3 on two or more occasions. In patients with known or suspected immunodeficiency, physicians should consider monitoring complete blood counts if treatment continues for more than six weeks. Cases of severe neutropenia have been reported; these were reversible upon discontinuation of terbinafine, with or without supportive therapy. If clinical signs and symptoms suggestive of secondary infection occur, a complete blood count should be obtained. If the neutrophil count is <1,000 cells/mm3, Lamisil Oral Granules should be discontinued and supportive management started.
5.5 Skin Reactions
There have been postmarketing reports of serious skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis) with oral terbinafine. If progressive skin rash occurs, treatment with Lamisil Oral Granules should be discontinued.
5.6 Lupus Erythematosus
During postmarketing experience, precipitation and exacerbation of cutaneous and systemic lupus erythematosus have been reported in patients taking oral terbinafine. Therapy should be discontinued in patients with clinical signs and symptoms suggestive of lupus erythematosus.
5.7 Laboratory Monitoring
Measurement of serum transaminases (ALT and AST) is advised for all patients before taking Lamisil Oral Granules.
6. ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules
The data described below reflect exposure to terbinafine including 1,042 subjects exposed for a median of 42 days. Lamisil Oral Granules was studied in 2 active-controlled trials (n=1,042). The population was children aged 4 to 12 years old, 64% male and 36% female, 21% Caucasian, 47% Black, 32% Other. Baseline disease (dermatophyte) characteristics of subjects included 49% having T. tonsurans, 15% T. violaceum, 15% M. canis, 2% M. audouinii, and 1% others. Subjects received once daily, for 6 weeks, oral doses of Lamisil Oral Granules based on body weight: <25 kg 125 mg/day, 25-35 kg 187.5 mg/day, and >35 kg 250 mg/day.
Adverse events reported in the 2 trials are listed in the table below.
| Lamisil® Oral Granules (%) N=1,042 | Griseofulvin Oral Suspension (%) N=507 |
|
| Nasopharyngitis | 10 | 11 |
| Headache | 7 | 8 |
| Pyrexia | 7 | 6 |
| Cough | 6 | 5 |
| Vomiting | 5 | 5 |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 5 | 5 |
| Upper abdominal pain | 4 | 4 |
| Diarrhea | 3 | 4 |
| Influenza | 2 | 1 |
| Abdominal pain | 2 | 1 |
| Pharyngolaryngeal pain | 2 | 2 |
| Nausea | 2 | 2 |
| Rash | 2 | 2 |
| Rhinorrhea | 2 | 0 |
| Nasal congestion | 2 | 1 |
| Pruritus | 1 | 1 |
| Toothache | 1 | 1 |
In the pooled pivotal trials, 2% (17/1,042) of subjects in the terbinafine group and 2% (6/507) in the griseofulvin group experienced discontinuation of study drug due to adverse events. The most common categories of adverse events causing discontinuation in those exposed to terbinafine included gastrointestinal disorders, skin and subcutaneous disorders, and infections and infestations.
No ophthalmologic safety signal was identified in the pooled pivotal trials. Ophthalmologic assessments included dilated fundoscopy to assess for refractile bodies in the retina, visual acuity assessment, and color vision testing. Of the 940 subjects in the terbinafine group and 471 subjects in the griseofulvin group who completed dilated fundoscopy at post-treatment visits, none of the subjects were found to have refractile bodies of the retina at baseline or end of treatment. For visual acuity, 1% (11/837) of subjects treated with terbinafine and 2% (7/426) of subjects treated with griseofulvin showed a doubling of visual angle after 6 weeks of treatment, while 2% (15/837) treated with terbinafine and 3% (12/426) treated with griseofulvin showed a halving of the visual angle after 6 weeks of treatment. Of subjects who completed yellow-blue color vision assessment for acquired defects, 5% (13/262) of subjects treated with terbinafine and 6% (8/129) of subjects treated with griseofulvin had color confusion on more than one symbol at week 6 than at baseline, while 13% (33/262) of subjects treated with terbinafine and 13% (17/129) of subjects treated with griseofulvin identified more symbols correctly at week 6 than at baseline.
Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Tablets
Adverse events reported in three US/Canadian placebo-controlled trials included diarrhea (6%), rashes (6%), dyspepsia (4%), nausea (3%), liver abnormalities (3%), pruritus (3%), taste disturbances (3%), abdominal pain (2%), and urticaria (1%).
Changes in the ocular lens and retina have been reported following the use of Lamisil Tablets in clinical trials in adult subjects with onychomycosis. The clinical significance of these changes is unknown.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse events have been identified during post-approval use of Lamisil. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse events reported with oral terbinafine use include: idiosyncratic and symptomatic hepatic injury and, cases of liver failure, some leading to liver transplant or death, serious skin reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis), severe neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, anemia, angioedema and allergic reactions (including anaphylaxis). [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.4, and 5.5)].
Psoriasiform eruptions or exacerbation of psoriasis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis and precipitation and exacerbation of cutaneous and systemic lupus erythematosus have been reported in patients taking Lamisil. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Cases of taste disturbance, including taste loss, have been reported with the use of terbinafine. It can be severe enough to result in decreased food intake, weight loss, and depressive symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Depressive symptoms independent of taste disturbance have been reported with terbinafine use. In some cases, depressive symptoms have been reported to subside with discontinuance of therapy and to recur with reinstitution of therapy. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Other adverse reactions which have been reported include malaise, fatigue, arthralgia, myalgia, vomiting, acute pancreatitis, rhabdomyolysis, reduced visual acuity, visual field defects, and hair loss. Adverse events reported spontaneously since the drug was marketed include altered prothrombin time (prolongation and reduction) in patients concomitantly treated with warfarin.
7. DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drug-Drug Interactions
In vivo studies have shown that terbinafine is an inhibitor of the CYP450 2D6 isozyme. Drugs predominantly metabolized by the CYP450 2D6 isozyme include the following drug classes: tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, beta-blockers, antiarrhythmics class 1C (e.g., flecainide and propafenone) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors Type B. Coadministration of Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules should be done with careful monitoring and may require a reduction in dose of the 2D6-metabolized drug. In a study to assess the effects of terbinafine on desipramine in healthy volunteers characterized as normal metabolizers, the administration of terbinafine resulted in a 2-fold increase in Cmax and a 5-fold increase in AUC. In this study, these effects were shown to persist at the last observation at 4 weeks after discontinuation of Lamisil. In studies in healthy subjects characterized as extensive metabolizers of dextromethorphan, terbinafine increases the dextromethorphan/dextrorphan metabolite ratio in urine by 16- to 97-fold, on average. In vitro studies with human liver microsomes showed that terbinafine does not inhibit the metabolism of tolbutamide, ethinylestradiol, ethoxycoumarin, cyclosporine, cisapride and fluvastatin.
In vivo drug-drug interaction studies conducted in healthy volunteer subjects showed that terbinafine does not affect the clearance of antipyrine or digoxin. Terbinafine decreases the clearance of caffeine by 19%. Terbinafine increases the clearance of cyclosporine by 15%.
The influence of terbinafine on the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole, trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole, zidovudine or theophylline was not considered to be clinically significant.
Co-administration of a single dose of fluconazole (100 mg) with a single dose of terbinafine resulted in a 52% and 69% increase in terbinafine Cmax and AUC, respectively. Fluconazole is an inhibitor of CYP2C9 and CYP3A enzymes. Based on this finding, it is likely that other inhibitors of both CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole, amiodarone) may also lead to a substantial increase in the systemic exposure (Cmax and AUC) of terbinafine.
There have been spontaneous reports of increase or decrease in prothrombin times in patients concomitantly taking oral terbinafine and warfarin, however, a causal relationship between terbinafine and these changes has not been established.
Terbinafine clearance is increased 100% by rifampin, a CYP450 enzyme inducer, and decreased 33% by cimetidine, a CYP450 enzyme inhibitor. Terbinafine clearance is unaffected by cyclosporine. There is no information available from adequate drug-drug interaction studies with the following classes of drugs: oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapies, hypoglycemics, phenytoins, thiazide diuretics, and calcium channel blockers.
7.2 Food Interactions
An evaluation of the effect of food on Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules was not conducted. However, in the clinical trials, Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules was administered with food [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, and because treatment of tinea capitis can be postponed until after pregnancy is completed, it is recommended that Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules not be initiated during pregnancy.
Oral reproduction studies have been performed in rabbits and rats at doses up to 300 mg/kg/day [12x to 23x the Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD), in rabbits and rats, respectively, based on body surface area (BSA) comparisons] and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to terbinafine.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
After oral administration, terbinafine is present in breast milk of nursing mothers. The ratio of terbinafine in milk to plasma is 7:1. Treatment with Lamisil Oral Granules is not recommended in nursing mothers.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Lamisil Oral Granules was studied in two randomized, active-controlled trials in which 1,021 subjects, 4 to 12 years old, having a clinical diagnosis of tinea capitis confirmed by KOH microscopy were treated with Lamisil Oral Granules at the labeled dose for up to 6 weeks. The most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis, headache, pyrexia, cough, vomiting, and upper respiratory tract infection [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Lamisil Oral Granules has not been studied in geriatric patients.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical experience regarding overdose with oral terbinafine is limited. Doses up to 5 grams in adults (20 times the therapeutic daily adult dose) have been reported without inducing serious adverse reactions. The symptoms of overdose included nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dizziness, rash, frequent urination, and headache.
11 DESCRIPTION
Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules 125 mg and 187.5 mg contain the synthetic allylamine antifungal compound, terbinafine hydrochloride.
Chemically, terbinafine hydrochloride is (E)-N-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethanamine hydrochloride. It has the empirical formula C21H26ClN with a molecular weight of 327.90, and the following structural formula:
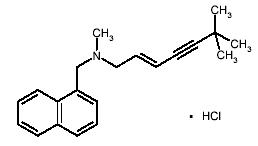
Terbinafine hydrochloride is a white to off-white fine crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in methanol and methylene chloride, soluble in ethanol, and slightly soluble in water.
Each packet of Lamisil Oral Granules contains:
Active Ingredients: terbinafine hydrochloride (equivalent to 125 mg or 187.5 mg terbinafine base)
Inactive Ingredients: basic butylated methacrylate copolymer, colloidal silicon dioxide NF, dibutyl sebacate NF, hypromellose USP, magnesium stearate NF, microcrystalline cellulose NF, nitrogen NF (filling gas), polyethylene glycol NF, sodium lauryl sulfate NF, and sodium starch glycolate NF.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Terbinafine is an allylamine antifungal [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics in children 4 to 8 years of age with tinea capitis was investigated in a pharmacokinetic study after single and repeated (for 42 days) oral administration of Lamisil Oral Granules (N=16), once daily, using the body weight groups and doses described in section 2.2. The systemic exposure (Cmax and AUC0-24) of terbinafine in children had a relatively high inter-individual variability (ranging from 36% to 64%). At steady state the AUC0-24 increased by a mean factor of 1.9 to 2.1 across doses. The mean (SD) effective half-life obtained from the observed accumulation was 26.7 (13.8) hrs and 30.5 (9.3) hrs for the 125 mg and 187.5 mg doses, respectively.
Systemic exposure to terbinafine in the children did not exceed the highest values of the systemic exposure in adults receiving repeated once daily doses of 250 mg Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Tablets. A population pharmacokinetic evaluation of oral terbinafine that included children 4-12 years of age and adults 18-45 years of age (N=113) found that clearance (CL/F) of terbinafine is dependent on body weight in a nonlinear manner. For a typical child of 25 kg CL/F was predicted to be 19 L/h and for a typical adult of 70 kg body weight it was predicted to be 27 L/h. Over the weight range for pediatric patients included in the analysis (14.1 kg-68 kg), the predicted CL/F ranged between 15.6-26.7 L/hr. In plasma, terbinafine is >99% bound to plasma proteins. Prior to excretion, terbinafine is rapidly and extensively metabolized by at least seven CYP isoenzymes with major contributions from CYP2C9, CYP1A2, CYP3A4, CYP2C8 and CYP2C19. No metabolites have been identified that have antifungal activity similar to terbinafine. Approximately 70% of the administered dose is eliminated in the urine. In adult patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≤50 mL/min) or hepatic cirrhosis, the clearance of terbinafine is decreased by approximately 50% compared to normal volunteers.
12.4 Microbiology
Terbinafine, an allylamine antifungal, inhibits biosysnthesis of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membrane, via inhibition of squalene epoxidase enzyme. This results in fungal cell death primarily due to the increased membrane permeability mediated by the accumulation of high concentrations of squalene but not due to ergosterol deficiency. Depending on the concentration of the drug and the fungal species tested in vitro, terbinafine may be fungicidal. However, the clinical significance of in vitro data is unknown.
Lamisil Oral Granules has been studied in tinea capitis [see Clinical Studies (14)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 28-month oral carcinogenicity study in rats, an increase in the incidence of liver tumors was observed in males at the highest dose tested, 69 mg/kg/day (2x the MRHD based on AUC comparisons of the parent terbinafine); however, even though dose-limiting toxicity was not achieved at the highest tested dose, higher doses were not tested.
The results of a variety of in vitro (mutations in E. coli and S. typhimurium, DNA repair in rat hepatocytes, mutagenicity in Chinese hamster fibroblasts, chromosome aberration and sister chromatid exchanges in Chinese hamster lung cells), and in vivo (chromosome aberration in Chinese hamsters, micronucleus test in mice) genotoxicity tests gave no evidence of a mutagenic or clastogenic potential.
Oral reproduction studies in rats at doses up to 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 12x the MRHD based on BSA comparisons) did not reveal any specific effects on fertility or other reproductive parameters. Intravaginal application of terbinafine hydrochloride at 150 mg/day in pregnant rabbits did not increase the incidence of abortions or premature deliveries nor affect fetal parameters.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
A wide range of in vivo studies in mice, rats, dogs, and monkeys, and in vitro studies using rat, monkey, and human hepatocytes suggest that peroxisome proliferation in the liver is a rat-specific finding. However, other effects, including increased liver weights and APTT, occurred in dogs and monkeys at doses giving Css trough levels of the parent terbinafine 2-3x those seen in humans at the MRHD. Higher doses were not tested.
In a 52-week oral toxicology study conducted in juvenile maturing dogs, increased heart and liver weights were noted in males and signs of CNS disturbance including 3 cases of single episodes of seizures were noted in females at the highest dose tested, 100 mg/kg/day [19x (males) and 10x (females) the MRHD based on AUC comparisons of the parent terbinafine]. No treatment related findings were noted at 30 mg/kg/day [1.6x (males) and 1.9x (females) the MRHD based on AUC comparisons of the parent terbinafine] in this study.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Two randomized, multinational trials were conducted to investigate the safety and efficacy of Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules in the treatment of subjects 4 to 12 years old with tinea capitis. Lamisil Oral Granules was dosed based on body weight. Griseofulvin dosed at 10-20 mg/kg was used as a comparator. Subjects were dosed for 6 weeks and followed for an additional 4 weeks.
The two trials enrolled 50% of subjects from the U.S. Additionally, among those with positive cultures, 65% and 54% of infections were due to T. tonsurans, and 19% and 17% due to M. canis in Studies 1 and 2, respectively.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of subjects with complete cure (negative KOH, negative culture and absence of clinical signs of infection) at week 10. Table 3 below lists the efficacy results for Studies 1 and 2 overall and according to the dermatophyte species (T. tonsurans, M. canis, or Other).
| Study 1 | Study 2 | ||||
| Terbinafine | Griseofulvin | Terbinafine | Griseofulvin | ||
| All Dermatophytes | (N=411) | (N=197) | (N=441) | (N=237) | |
| Complete Cure | 190 (46.2%) | 67 (34.0%) | 194 (44.0%) | 103 (43.5%) | |
| T. tonsurans | (N=264) | (N=131) | (N=243) | (N=126) | |
| Complete Cure | 148 (56.1%) | 45 (34.4%) | 116 (47.7%) | 46 (36.5%) | |
| M. canis | (N=80) | (N=37) | (N=72) | (N=45) | |
| Complete Cure | 19 (23.8%) | 13 (35.1%) | 22 (30.6%) | 23 (51.1%) | |
| Other* | (N=67) | (N=29) | (N=126) | (N=66 ) | |
| Complete Cure | 23 (34.2%) | 9 (31.0%) | 56 (44.4%) | 34 (51.5%) | |
| * T. violaceum, M. audouinii, T. mentagrophytes, T. rubrum, M. gypseum, and M. vanbreuseghemii. | |||||
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Lamisil (terbinafine hydrochloride ) Oral Granules 125 mg and 187.5 mg
Lamisil Oral Granules are supplied in cartons containing 14 laminated aluminum packets. Each packet contains approximately either 30 or 45 off-white to yellowish, round, biconvex, film-coated granules, corresponding to a single total dose of 125 mg or 187.5 mg (terbinafine base equivalent) per packet.
125 mg per packet
Carton of 14 packets………..………………………….………..NDC 0078-0499-58
Pack of 3 cartons each containing 14 packets (42 packets).........NDC 0078-0499-59
187.5 mg per packet
Carton of 14 packets………….………………………………....NDC 0078-0500-58
Pack of 3 cartons each containing 14 packets (42 packets)..........NDC 0078-0500-59
Storage conditions of Lamisil Oral Granules 125 mg and 187.5 mg: Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15–30°C (59–86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
[See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information)]
Patients taking Lamisil®(terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules should receive the following information and instructions:
• Patients should be informed that Lamisil Oral Granules should be taken once a day with food. Patients should sprinkle the contents of each packet on a spoonful of pudding or other soft, non-acidic food such as mashed potatoes and swallow the entire spoonful; applesauce or fruit-based foods should not be used. The combination of food and granules should be swallowed without chewing. If two packets are required with each dose, the patient may either sprinkle the content of both packets on one spoonful of non-acidic food, or sprinkle the contents of both packets on two spoonfuls of non-acidic food as directed above.
•Patients prescribed Lamisil Oral Granules and/or their guardian should be warned to report immediately to their physician any symptoms of persistent nausea, anorexia, fatigue, vomiting, right upper abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine or pale stools. Lamisil Oral Granules treatment should be discontinued.
• Patients and/or their guardian should be advised to report to their physician any signs of taste disturbance and/or depressive symptoms. Lamisil Oral Granules treatment should be discontinued.
• Patients should be advised to immediately report to their physician or get emergency help if they experience any of the following symptoms: hives, mouth sores, blistering and peeling of skin, swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty swallowing or breathing. Lamisil Oral Granules treatment should be discontinued.
• Patients should be advised to report to their physician any symptoms of new onset or worsening lupus erythematosus. Symptoms can include erythema, scaling, loss of pigment, and unusual photosensitivity that can result in a rash. Lamisil Oral Granules treatment should be discontinued.
• Patients should be informed that if a progressive skin rash occurs, treatment with Lamisil Oral Granules should be discontinued.
• Measurement of serum transaminases (ALT and AST) is advised for all patients before taking Lamisil Oral Granules.
• Patients should be advised that if they take too many Lamisil Oral Granules they should call their physician.
T2010-116
Patient Information
Lamisil (Lam-i-sil)
(terbinafine hydrochloride) Oral Granules
Read the Patient Information that comes with Lamisil Oral Granules before you start using it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your specific scalp condition or treatment.
What is Lamisil Oral Granules?
Lamisil Oral Granules is a prescription antifungal medicine used to treat tinea capitis in patients 4 years of age and older.
What is tinea capitis?
Tinea capitis is a dermatophyte infection of the scalp hair follicles which occurs primarily in children.
Who Should not take Lamisil?
Do not take Lamisil if you are allergic to terbinafine hydrochloride when taken by mouth.
What should I tell my doctor before taking Lamisil?
Before you take Lamisil, tell your doctor if you:
- have or had liver problems
- have a weakened immune system (immunocompromised)
- have lupus (an autoimmune disease)
- have kidney problems
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Lamisil will harm your unborn baby. You should not start using Lamisil during pregnancy without talking to your doctor.
- Are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. Some Lamisil passes into your milk and may harm your baby. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you take Lamisil.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Lamisil may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect how Lamisil works. Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- a medicine for depression
- a medicine for high blood pressure
- a medicine for heart problems
- desipramine (Norpramin)
- caffeine
- cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune)
- fluconazole (Diflucan)
- rifampin (Rifater, Rifamate, Rimactane, Rifadine)
- cimetidine (Tagamet)
If you are not sure if your medicine is one listed above, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Lamisil?
- Take Lamisil exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Lamisil comes as oral granules that are sprinkled on food and taken by mouth.
One to two packets should be taken each day with a soft non-acidic food, (see patient instructions below). You physician will prescribe a dose based on your body weight. For best results you should take the complete course of prescribed medicine. If two packets are required with each dose, you may either sprinkle the content of both packets on one spoonful of non-acidic food, or sprinkle the contents of both packets on two spoonfuls of non-acidic food as directed below.
Patient instructions:
- Hold packet with cut line on top.
- Shake packet gently to settle contents.
- Tear packet open along cut line, or use scissors to cut across line.
- Carefully pour entire contents of packet onto a spoonful of a soft food, such as pudding or other soft, non-acidic food such as mashed potatoes (do not use applesauce or a fruit-based food).
- Make sure that no granules remain in the packet.
- Swallow combination of food and granules without chewing.
If you take too much Lamisil call your doctor. You may have the following symptoms:
• nausea
• vomiting
• stomach (abdominal) pain
• dizziness
• rash
• frequent urination
• headache
What are the possible side effects of Lamisil?
Lamisil may cause serious side effects, including:
-
liver problems that can lead to the need for liver transplant, or death. Tell your doctor right away if you get any of these symptoms of a liver problem:
• nausea • upper right stomach (abdominal) pain
• poor appetite • yellowing of your skin or eyes (jaundice)
• tiredness • dark (tea-colored) urine
• vomiting • pale or light colored stools
Your doctor should do a blood test to check you for liver problems before you take Lamisil.
-
change in taste or loss of taste may happen with Lamisil. This usually improves within several weeks after stopping Lamisil, but may last for a long time. Tell your doctor if you have:
• change in taste or loss of taste
• poor appetite
• unwanted weight loss, or
• change in mood or depressive symptoms
-
depressive symptoms. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of these signs or symptoms:
• feel sad or worthless
• change in sleep pattern
• loss of energy or interest in daily activities
• restlessness
• mood changes
-
serious skin or allergic reactions. Tell your doctor right away or get emergency help if you get any of these symptoms:
• skin rash, hives, sores in your mouth, or your skin blisters and peels
• swelling of your face, eyes, lips, tongue or throat
• trouble swallowing or breathing
-
new or worsening lupus (an autoimmune disease). Stop taking Lamisil and tell your doctor if you experience any of the following:
• progressive skin rash that is scaly, red, shows scarring, or loss of pigment
• unusual sensitivity to the sun that can lead to a rash
The most common side effects of Lamisil include: headache, fever, vomiting, upper respiratory tract infection, abdominal pain, nausea, and itching.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of Lamisil. For information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects.
You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Lamisil Oral Granules?
Store Lamisil Oral Granules at 59-86°F and keep this and all other medications away from children.
Lamisil Oral Granules were prescribed only for you; do NOT share the medication with anyone else.
General information about the safe and effective use of Lamisil.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in Patient Information. Do not use Lamisil for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Lamisil to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information summarizes the most important information about Lamisil. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about Lamisil that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in Lamisil?
Active ingredient: terabinafine hydrochloride.
Inactive ingredients: basic butylated methacrylate copolymer, colloidal silicon dioxide, dibutyl sebacate, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, nitrogen (filling gas), polyethylene glycol, sodium lauryl sulfate, sodium starch glycolate.
T2010-117
Manufactured by:
Novartis Pharma Stein AG
Stein, Switzerland
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
© Novartis
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 125 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0499-58
Lamisil® (terbinafine hydrochloride)
Oral Granules
125 mg
terbinafine base equivalent per packet
Contains 14 packets

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label – 187.5 mg
Rx Only NDC 0078-0500-58
Lamisil® (terbinafine hydrochloride)
Oral Granules
187.5 mg
terbinafine base equivalent per packet
Contains 14 packets

| LAMISIL
terbinafine hydrochloride granule |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA022071 | 09/28/2007 | |
| LAMISIL
terbinafine hydrochloride granule |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA022071 | 09/28/2007 | |
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |