MEDEBAR PLUS
-
barium sulfate suspension
Mallinckrodt, Inc.
----------
LAFAYETTEMEDEBAR™ PLUS
BARIUM SULFATE SUSPENSION
Rx only
DESCRIPTION
Medebar Plus is a fruity-cola flavored, low viscosity (rapid flow), ready-to-use suspension, for x-ray examinations of the gastrointestinal tract.
It contains 100% w/v (55% w/w) barium sulfate USP, dispersing agent, vegetable gums, simethicone, preservatives, flavoring, saccharin sodium and water. Barium sulfate has the empirical formula of BaSO4.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Barium sulfate is an insoluble material which, because of its density, provides a positive contrast during x-ray examination. Barium sulfate is an inert radiopaque material which is not absorbed or metabolized and is eliminated intact from the body in a manner similar to other non-absorbed inorganic materials. Excretion rate is a function of gastrointestinal transit time.INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Medebar Plus is indicated for use as a contrast medium in x-ray diagnosis of the gastrointestinal tract. The suspension may be administered without dilution for double contrast colon, single contrast esophagus, small bowel and enteroclysis examinations. Aqueous dilutions of Medebar Plus may be used for single contrast stomach and single contrast colon examinations.CONTRAINDICATIONS
Barium sulfate products are contraindicated in patients with known or suspected obstruction of the colon, known or suspected gastrointestinal tract perforation, suspected tracheoesophageal fistula, obstructing lesions of the small intestine, pyloric stenosis, inflammation or neoplastic lesions of the rectum, recent rectal biopsy, or known hypersensitivity to barium sulfate formulations.
Known hypersensitivity or allergy to latex is a contraindication for the use of balloon retention enema tips containing latex. The use of a retention cuff enema tip is not necessary or desirable in patients with normal sphincter tone. The presence of adequate sphincter tone can be judged by preliminary rectal digital examination.
The use of rectal balloon is contraindicated in patients having a history of pencil stools, recent rectal surgery or low rectal anastomosis, perianal inflammation, colitis, rectal stricture or other suspected lesions that could lead to further injury through distention by a rectal balloon or when proctitis or other rectal conditions such as inflammatory or neoplastic diseases are suspected.
WARNINGS
Serious adverse reactions, including death, have been reported with the administration of barium sulfate formulations and are usually associated with the technique of administration, the underlying pathological condition and/or patient hypersensitivities.
Oral administration of barium sulfate suspension by an infant sucking a bottle and administration of large quantities by catheter are reported to be likely to result in aspiration into the tracheobronchial tree.
Vomiting following oral administration of barium sulfate may lead to aspiration pneumonitis. Cardiopulmonary arrest leading to fatality has been reported in infants following aspiration. Aspiration of smaller amounts may cause inflammation.
Barium sulfate preparations used as radiopaque media contain a number of additives to provide diagnostic properties and patient palatability. Allergic responses following the use of barium sulfate suspensions have been reported. In patients with increased cranial pressure, barium sulfate suspension enemas present an additional risk of further increasing intracranial pressure.
Barium sulfate suspension intravasation can be a serious complication. Mortality has been reported as a result of vaginal or rectal intravasation and is believed to be due to massive pulmonary embolism occurring within minutes of the inciting event.
Skin irritation, redness, inflammation and hives have been reported in infants and small children following spillage of barium sulfate suspension on their skin. These responses are thought to be caused by the flavors and/or preservatives used in the product.
Barium sulfate suspension has been reported to cause obstruction of the small bowel (impaction) in pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis. It has also been reported to cause fluid overload from the absorption of water during studies in infants when Hirschsprung’s Disease is suspected.
Care must be taken during the insertion of an enema tip into the patient to prevent application of pressure to the vagus nerve which can lead to vasovagal reactions and syncopal episodes. Cardiac arrhythmia or other cardiovascular side effects can occur as a result of colon distension.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Diagnostic procedures which involve the use of radiopaque contrast agents should be carried out under the direction of personnel with the requisite training and with a thorough knowledge of the particular procedure to be performed. A history of bronchial asthma, atopy, as evidenced by hay fever and eczema, a family history of allergy, or a previous reaction to a contrast agent warrant special attention. Caution should be exercised with the use of radiopaque media in severely debilitated patients and in those with marked hypertension or advanced cardiac disease.
Anaphylactic and allergic reactions have been reported during double contrast examinations in which glucagon has been used.
Ingestion of barium sulfate suspension is not recommended in patients with a history of food aspiration. If barium sulfate suspension is aspirated into the larynx, further administration of the suspension should be immediately discontinued.
Patient preparation for diagnostic gastrointestinal examinations frequently requires cathartics and a liquid diet. The various preparations can result in water loss for the patient. Patients should be rehydrated quickly following a barium sulfate suspension examination of the gastrointestinal tract. In patients with reduced colon motility, saline cathartics may be required after the barium sulfate suspension enema. Saline cathartics are recommended on a routine basis in patients with a history of constipation unless clinically contraindicated.
Where enema tips are used, care must be taken during insertion into the patient, since forceful or too deep insertion may cause tearing or perforation of the rectum. Insertion of an enema tip should be done only after digital examination by qualified medical personnel. When balloon retention tips are used, care should be taken to avoid over-inflation of the balloon, since overfilling or asymmetrical filling may cause displacement of the tip. Such a displacement can lead to rectal perforation or barium sulfate granulomas. Inflation of the balloon should be done under fluoroscopic control by qualified medical personnel. Do not unnecessarily move the enema tip once inserted.
A specially designed enema tip is required for a barium sulfate suspension examination of a colostomy patient.
Intubation of an enteroclysis catheter should be done by qualified medical personnel. Perforation of the duodenum has been reported.
Because of reported anaphylactoid reactions to latex, the use of non-latex gloves during the procedure should be considered.
Pregnancy
Safe use of barium sulfate during pregnancy has not been established. Barium sulfate should be used in pregnant women only if the possible benefits outweigh the potential risks. Elective radiography of the abdomen is considered to be contraindicated during pregnancy due to the risk to the fetus from radiation exposure. Radiation is known to cause harm to the unborn fetus exposed in utero.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions accompanying the use of barium sulfate formulations are infrequent and usually mild, though severe reactions (approximately 1 in 500,000) and fatalities (approximately 1 in 2,000,000) have occurred. Procedural complications are rare, but may include aspiration pneumonitis, barium sulfate impaction, granuloma formation, intravasation, embolization and peritonitis following intestinal perforation, vasovagal and syncopal episodes, and fatalities. EKG changes have been shown to occur following or during barium sulfate suspension enemas. It is of the utmost importance to be completely prepared to treat any such occurrence.
Due to the increased likelihood of allergic reactions in atopic patients, a complete history of known and suspected allergies as well as allergic-like symptoms, such as rhinitis, bronchial asthma, eczema and urticaria, must be obtained prior to any medical procedure.
Aspiration of large amounts of barium sulfate suspension may cause pneumonitis or nodular granulomas of interstitial lung tissues and lymph nodes; asphyxiation and death have been reported.
Transient bacteremia, beginning almost immediately and lasting up to 15 minutes, may occur during rectal administration of barium sulfate suspension, and rarely septicemia has been reported.
A rare mild allergic reaction would most likely be generalized pruritis, erythema or urticaria (approximately 1 in 100,000 reactions). Such reactions will often respond to an antihistamine. More serious reactions (approximately 1 in 500,000) may result in laryngeal edema, bronchospasm or hypotension.
Severe reactions which may require emergency measures are often characterized by peripheral vasodilation, hypotension, reflex tachycardia, dyspnea, bronchospasm, agitation, confusion and cyanosis, progressing to unconsciousness. Treatment should be initiated immediately according to established standard of care.
Apprehensive patients may develop weakness, pallor, tinnitus, diaphoresis and bradycardia following the administration of any diagnostic agent. Such reactions are usually non-allergic in nature.
Allergic reactions to the enema examination accessories, in particular to retention catheters (tips) with latex cuffs, can occur. Such reactions could occur immediately and result in the previously mentioned acute allergic-like responses or might be delayed in appearance and result in a contact dermatitis. Known atopic patients, particularly those with a history of asthma or eczema, should be evaluated for alternative methods of administration in order to avoid these adverse reactions. These plastic / rubber accessories are disposable, single-use devices that must not be reused or left in the body cavity for an extended period of time.
Postmarketing Experiences
The following adverse experiences have been reported in patients receiving products containing barium sulfate. These adverse experiences are listed alphabetically: abdominal cramping, abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, foreign body trauma relating to procedural complications, headache, laryngeal burning and irritation, leukocytosis, nausea, procedural site reactions, rash and vomiting.
OVERDOSAGE
In rare instances, immediate repeat oral examinations utilizing standard dosages may lead to severe stomach cramps and diarrhea. Cases reported implicate total dose in the range of 30 ounces (900 mL) of suspension. Instances of this type have resolved spontaneously and they are not considered to be life-threatening.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Patient Preparation
Successful examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract requires that the stomach be empty and essentially free of fluid. This can usually be accomplished by instructing the patient to abstain from eating or drinking anything after the evening meal before the examination. The preparation for small bowel examinations, done separately or combined with an upper gastrointestinal series, is the same.For examinations of the colon, the patient should be given a low solid diet for a minimum of 24 hours before the examination. Laxatives should also be used to clean the colon. In order to obtain thorough cleansing of the colon, a 2 liter water enema one hour before the examination may be necessary.
Suspension Preparation
The volume and concentration used will vary depending upon the method of patient preparation, the desired level of contrast density, individual variation in patient anatomy and radiographic equipment. The following dilutions are suggested for Medebar Plus:
| TEST | DILUTION FORMULA | % BARIUM SULFATE (w/v) |
| Double Contrast Colon | Medebar Plus undiluted | 100 |
| Single Contrast Esophagus | Medebar Plus undiluted | 100 |
| Small Bowel, Enteroclysis | Medebar Plus undiluted | 100 |
| Single Contrast Stomach | Medebar Plus undiluted or diluted 1:1 with water | 100 50 |
| Single Contrast Colon | From 7 to 3 parts water to 1 part Medebar Plus | 14-33 |
| Shake VIGOROUSLY prior to use. | ||
Double Contrast Colon Examination:
The examination should be performed by properly trained medical personnel only. Approximately 500 mL Medebar Plus is required to reach the splenic flexure, and it should be introduced by an enema administration system.
An enema administration system with 1/2” ID tubing, such as Medebar Plus Kit or Aircon is used for ease of administration. The usual method uses introduced air to move the column of barium sulfate suspension around the hepatic flexure and into the cecum. Patient positioning is critical during this process to ensure that air does not get ahead of the barium column. Such an eventuality may reduce the volume of suspension that reaches the cecum, and will adversely affect the quality of its coating. Conversely, should excessive quantities of suspension flood the cecum, double contrast views may be obscured by the barium pool.
Double Contrast Colon Examination with Medebar Plus Kit
The following procedure is suggested for double contrast examination of a well prepared, adult colon using Medebar Plus Kit (650 mL Medebar Plus). The actual procedure used will depend upon patient symptoms and conditions as well as physician preference and judgement.
Shake the Medebar Plus bottle well and attach the tubing unit.
With the patient in the left lateral position and the right knee flexed, insert the enema tip and inflate the retention cuff. Introduce a small amount of Medebar Plus into the rectal area. Check the rectal area by fluoroscopy for contraindications.
Place the table slightly Trendelenburg. With the fluoroscopy unit off, introduce the remainder of the Medebar Plus. Close the clamp on the large bore tubing. Introduce approximately five pumps of air into the patient using the blue multi-puff insufflator provided with each case.
Turn the patient LAO and introduce five pumps of air. Turn the patient prone, bring the table horizontal and introduce five pumps of air. Turn the patient RAO and introduce five pumps of air. Position the patient right lateral and introduce five pumps of air. If, at this point, the barium sulfate suspension has not coated the cecum, tilt the patient slightly head up. This should bring the barium sulfate suspension pool to the cecum.
Next turn the patient supine and tilt the table slightly Trendelenburg. Turn the patient LPO and bring the table to horizontal. Turn the patient left lateral and position the table with the patient slightly head up. This should cause the barium sulfate suspension pool to collect in the rectal area.
Place the Medebar Plus bottle on the floor and open the 1/2” tubing clamp to drain excess barium sulfate suspension from the rectum. The physician may prefer to have the patient either left lateral or prone for rectal drainage. When drainage is complete, close the tubing clamp. Spot films of the rectosigmoid may now be obtained.
Fluoroscopy is then used to evaluate colon distension. Introduce additional air to provide optimum distension as determined by the physician. Removal of the enema tip at this time is optional, according to the preference of the examiner. Rotate the patient slowly 360° taking spot films and overhead radiographs.
For single patient use only. Properly discard unused portion.
HOW SUPPLIED
Catalog No. 129794. NDC 68240-737-90. 900 mL bottle; twelve (12) bottles per case.
Medebar Plus Kit. Catalog No. 129722. NDC 68240-737-65. 650 mL bottles. Six (6) bottles with six (6) enema tip-tubing assemblies per case.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). Protect from freezing.
Shake VIGOROUSLY prior to use.
Medebar™ All trademark rights reserved.
DIN: 02216388
Distributed in Canada by:
tyco Healthcare
Pointe-Claire, QC, Canada H9R 5H8
Establishment License # 100689-A
Made in Mexico
Manufactured by:
Mallinckrodt Inc.
St. Louis, MO 63042 USA
www.Mallinckrodt.com
MID 1295215
Rev 03/2009
LOWER G.I.
- Fast-flowing
- 100% w/v
- Dilute for single contrast
tyco
Healthcare
Mallinckrodt
Package Label - Principal Display Panel - 900 mL Bottle
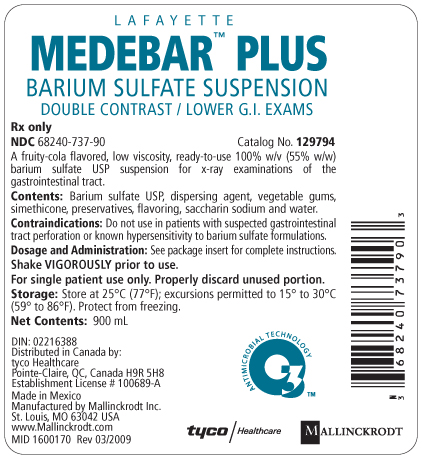
L A F A Y E T T E
MEDEBAR™ PLUS
BARIUM SULFATE SUSPENSION
DOUBLE CONTRAST / LOWER G.I. EXAMS
Rx only
NDC 68240-737-90
Catalog No. 129794
A fruity-cola flavored, low viscosity, ready-to-use 100% w/v (55% w/w) barium sulfate USP suspension for x-ray examinations of the gastrointestinal tract.
Contents: Barium sulfate USP, dispersing agent, vegetable gums, simethicone, preservatives, flavoring, saccharin sodium and water.
Contraindications: Do not use in patients with suspected gastrointestinal tract perforation or known hypersensitivity to barium sulfate formulations.
Dosage and Administration: See package insert for complete instructions.
Shake VIGOROUSLY prior to use.
For single patient use only. Properly discard unused portion.
Storage: Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). Protect from freezing.
Net Contents: 900 mL
DIN: 02216388
Distributed in Canada by:
tyco Healthcare
Pointe-Claire, QC, Canada H9R 5H8
Establishment License # 100689-A
Made in Mexico
Manufactured by Mallinckrodt Inc.
St. Louis, MO 63042 USA
www.Mallinckrodt.com
MID 1600170
Rev 03/2009
O3™ ANTIMICROBIAL TECHNOLOGY
tyco/Healthcare
MALLINCKRODT
| MEDEBAR
PLUS
barium sulfate suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| unapproved drug other | 12/01/2009 | 09/30/2010 | |
| Labeler - Mallinckrodt, Inc. (810407189) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Mallinckrodt Medical, S.A. de C.V. | 810407189 | analysis, manufacture | |