INVIRASE
-
saquinavir mesylate capsule
INVIRASE
-
saquinavir mesylate tablet, film coated
Genentech, Inc.
----------
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Product identification in this document includes: INVIRASE in reference to saquinavir mesylate; saquinavir 200 mg soft gel capsule formulation1 in reference to saquinavir active base.
- 1
- The term "saquinavir soft gel capsules" used in this label refers to the drug product formerly marketed as "Fortovase" (saquinavir 200 mg soft gel capsule formulation). This formulation has been withdrawn from the market.
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
The following points should be considered when initiating therapy with INVIRASE:
- –
- The twice daily administration of INVIRASE in combination with ritonavir is supported by safety data from the MaxCmin 1 study [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] and pharmacokinetic data [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- –
- –
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
INVIRASE must be used in combination with ritonavir, because it significantly inhibits saquinavir's metabolism to provide increased plasma saquinavir levels.
2.1 Adults (Over the Age of 16 Years)
- INVIRASE 1000-mg twice daily (5 × 200-mg capsules or 2 × 500-mg tablets) in combination with ritonavir 100-mg twice daily.
- Ritonavir should be taken at the same time as INVIRASE.
- INVIRASE and ritonavir should be taken within 2 hours after a meal.
2.2 Concomitant Therapy: INVIRASE with Lopinavir/Ritonavir
When administered with lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily, the appropriate dose of INVIRASE is 1000 mg twice daily (with no additional ritonavir).
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 200 mg
Film-coated tablets: 500 mg
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
QT interval prolongation and torsades de pointes have been reported rarely with INVIRASE/ritonavir use. Do not use in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, those with refractory hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, and in combination with drugs that both increase saquinavir plasma concentrations and prolong the QT interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
INVIRASE is contraindicated in patients with complete atrioventricular (AV) block without implanted pacemakers, or patients who are at high risk of complete AV block [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
INVIRASE is contraindicated in patients with clinically significant hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reaction, Stevens-Johnson syndrome) to saquinavir, saquinavir mesylate, or any of its ingredients including ritonavir.
INVIRASE when administered with ritonavir is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Coadministration of INVIRASE/ritonavir is contraindicated with drugs that are CYP3A substrates for which increased plasma levels may result in serious or life-threatening reactions. These drugs and potentially related adverse events are listed in Table 1.
| Drug Class | Drugs Within Class That Are Contraindicated With INVIRASE | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Alpha 1-adrenoreceptor antagonist | Alfuzosin | Potentially increased alfuzosin concentrations can result in hypotension. |
| Antiarrhythmics | Amiodarone, bepridil, dofetilide, flecainide, lidocaine (systemic), propafenone, quinidine | Potential for serious and/or life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. |
| Antidepressant | Trazodone | Increased trazodone concentrations can result in potentially life threatening cardiac arrhythmia. |
| Antimycobacterial Agents | Rifampin | Rifampin should not be administered in patients taking ritonavir-boosted INVIRASE part of an ART regimen due to the risk of severe hepatocellular toxicity. |
| Ergot Derivatives | Dihydroergotamine, ergonovine, ergotamine, methylergonovine | Potential for serious and life threatening reactions such as ergot toxicity characterized by peripheral vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities and other tissues. |
| GI Motility Agent | Cisapride | Potential for serious and/or life threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias. |
| HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors | Lovastatin, Simvastatin | Potential for myopathy including rhabdomyolysis. |
| Neuroleptics | Pimozide | Potential for serious and/or life threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias. |
| PDE5 Inhibitors | Sildenafil (Revatio®)[for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension] | Increased potential for sildenafil-associated adverse events (which include visual disturbances, hypotension, prolonged erection, and syncope). A safe and effective dose has not been established when used with INVIRASE/ritonavir. |
| Sedative/Hypnotics | Triazolam, orally administered midazolam | Potential for serious and/or life threatening reactions such as prolonged or increased sedation or respiratory depression. Triazolam and orally administered midazolam are extensively metabolized by CYP3A4. Coadministration of triazolam and orally administered midazolam with INVIRASE/ritonavir may cause large increases in the concentration of these benzodiazepines. |
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
INVIRASE must be used in combination with ritonavir. Please refer to the ritonavir full prescribing information for additional precautionary measures.
If a serious or severe toxicity occurs during treatment with INVIRASE, INVIRASE should be interrupted until the etiology of the event is identified or the toxicity resolves. At that time, resumption of treatment with full-dose INVIRASE may be considered. For antiretroviral agents used in combination with INVIRASE, physicians should refer to the complete product information for these drugs for dose adjustment recommendations and for information regarding drug-associated adverse reactions.
5.1 Drug Interactions
The combination INVIRASE/ritonavir is a potent inhibitor of CYP3A and may significantly increase the exposure of drugs primarily metabolized by CYP3A. See Table 1 for a listing of drugs that are contraindicated for use with INVIRASE/ritonavir due to potentially life-threatening adverse events or significant drug interactions [see Contraindications (4)]. See Table 3 for established and other potentially significant drug interactions [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
5.2 PR Interval Prolongation
5.3 QT Interval Prolongation
Saquinavir/ritonavir causes dose-dependent QT prolongation. Torsades de pointes has been reported rarely post-marketing. Avoid saquinavir/ritonavir in patients with long QT syndrome. ECG monitoring is recommended if therapy is initiated in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, hepatic impairment and electrolyte abnormalities. Correct hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia prior to initiating saquinavir/ritonavir and monitor these electrolytes periodically during therapy. Do not use in combination with drugs that both increase saquinavir plasma concentrations and prolong the QT interval (see Tables 1 and 3) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Patients initiating therapy with ritonavir-boosted INVIRASE:
An ECG should be performed prior to initiation of treatment. Patients with a QT interval > 450 msec should not receive ritonavir-boosted INVIRASE. For patients with a QT interval < 450 msec, an on-treatment ECG is suggested after approximately 3 to 4 days of therapy; patients with a QT interval > 480 msec or prolongation over pre-treatment by > 20 msec should discontinue ritonavir-boosted INVIRASE.
Patients requiring treatment with medications with the potential to increase the QT interval and concomitant ritonavir-boosted INVIRASE:
A cardiology consult is recommended if drug discontinuation or interruption is being considered on the basis of ECG assessment.
5.4 Diabetes Mellitus and Hyperglycemia
New onset diabetes mellitus, exacerbation of preexisting diabetes mellitus and hyperglycemia have been reported during postmarketing surveillance in HIV-1-infected patients receiving protease-inhibitor therapy. Some patients required either initiation or dose adjustments of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents for the treatment of these events. In some cases diabetic ketoacidosis has occurred. In those patients who discontinued protease-inhibitor therapy, hyperglycemia persisted in some cases. Because these events have been reported voluntarily during clinical practice, estimates of frequency cannot be made and a causal relationship between protease-inhibitor therapy and these events has not been established.
5.5 Hepatotoxicity
In patients with underlying hepatitis B or C, cirrhosis, chronic alcoholism and/or other underlying liver abnormalities, there have been reports of worsening liver disease.
5.6 Hemophilia
There have been reports of spontaneous bleeding in patients with hemophilia A and B treated with protease inhibitors. In some patients additional factor VIII was required. In the majority of reported cases treatment with protease inhibitors was continued or restarted. A causal relationship between protease inhibitor therapy and these episodes has not been established.
5.7 Hyperlipidemia
Elevated cholesterol and/or triglyceride levels have been observed in some patients taking saquinavir in combination with ritonavir. Marked elevation in triglyceride levels is a risk factor for development of pancreatitis. Cholesterol and triglyceride levels should be monitored prior to initiating combination dosing regimen of INVIRASE with ritonavir, and at periodic intervals while on such therapy. In these patients, lipid disorders should be managed as clinically appropriate.
5.8 Lactose Intolerance
Each capsule contains lactose (anhydrous) 63.3 mg. This quantity should not induce specific symptoms of intolerance.
5.9 Fat Redistribution
Redistribution/accumulation of body fat including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), facial wasting, peripheral wasting, breast enlargement, and "cushingoid appearance" have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. A causal relationship between protease-inhibitor therapy and these events has not been established and the long-term consequences are currently unknown.
5.10 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including INVIRASE. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia [PCP], or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
5.11 Resistance/Cross-resistance
Varying degrees of cross-resistance among HIV-1 protease inhibitors have been observed. Continued administration of INVIRASE therapy following loss of viral suppression may increase the likelihood of cross resistance to other protease inhibitors [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- PR Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- QT Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The original INVIRASE safety database consisted of a total of 574 patients who received saquinavir 600 mg alone or in combination with ZDV or ddC. Combination dosing with ritonavir is based on 352 HIV-1 infected patients and 166 healthy subjects who received various combinations of either saquinavir (hard gel or soft-gel capsules) with ritonavir.
The recommended dose of INVIRASE is 1000 mg twice daily co-administered with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily, in combination with other antiretroviral agents. Table 2 lists grade 2, 3 and 4 adverse events that occurred in ≥2% of patients receiving saquinavir soft gel capsules with ritonavir (1000/100 mg bid).
| Adverse Events | Saquinavir soft gel capsules 1000 mg plus Ritonavir 100 mg bid (48 weeks) N=148 n (%=n/N) |
|---|---|
|
|
| Endocrine Disorders | |
| Diabetes mellitus/hyperglycemia | 4 (2.7) |
| Lipodystrophy | 8 (5.4) |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | |
| Nausea | 16 (10.8) |
| Vomiting | 11 (7.4) |
| Diarrhea | 12 (8.1) |
| Abdominal Pain | 9 (6.1) |
| Constipation | 3 (2.0) |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | |
| Fatigue | 9 (6.1) |
| Fever | 5 (3.4) |
| Musculoskeletal Disorders | |
| Back Pain | 3 (2.0) |
| Respiratory Disorders | |
| Pneumonia | 8 (5.4) |
| Bronchitis | 4 (2.7) |
| Influenza | 4 (2.7) |
| Sinusitis | 4 (2.7) |
| Dermatological Disorders | |
| Rash | 5 (3.4) |
| Pruritus | 5 (3.4) |
| Dry lips/skin | 3 (2.0) |
| Eczema | 3 (2.0) |
Limited experience is available from three studies investigating the pharmacokinetics of the INVIRASE 500 mg film-coated tablet compared to the INVIRASE 200 mg capsule in healthy volunteers (n=140). In two of these studies saquinavir was boosted with ritonavir; in the other study, saquinavir was administered as single drug. The INVIRASE tablet and the capsule formulations were similarly tolerated. The most common adverse events were gastrointestinal disorders (such as diarrhea). Similar bioavailability was demonstrated and no clinically significant differences in saquinavir exposures were seen. Thus, similar safety profiles are expected between the two INVIRASE formulations.
In a study investigating the drug-drug interaction of rifampin 600 mg/day daily and INVIRASE 1000 mg/ritonavir 100 mg twice daily (ritonavir-boosted INVIRASE) involving 28 healthy volunteers, 11 of 17 healthy volunteers (65%) exposed concomitantly to rifampin and ritonavir-boosted INVIRASE developed severe hepatocellular toxicity which presented as increased hepatic transaminases. In some subjects, transaminases increased up to >20-fold the upper limit of normal and were associated with gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal pain, gastritis, nausea, and vomiting. Following discontinuation of all three drugs, clinical symptoms abated and the increased hepatic transaminases normalized [see Contraindications (4)].
Additional Adverse Reactions Reported During Clinical Trials with Saquinavir
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: anemia, hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, lymphadenopathy, neutropenia, pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia
Cardiac disorders: heart murmur, syncope
Ear and labyrinth disorders: tinnitus
Eye disorders: visual impairment
Gastrointestinal disorders: abdominal discomfort, ascites, dyspepsia, dysphagia, eructation, flatulence, gastritis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, intestinal obstruction, mouth dry, mucosal ulceration, pancreatitis
General disorders and administration site conditions: anorexia, asthenia, chest pain, edema, lethargy, wasting syndrome, weight increased
Hepatobiliary disorders: chronic active hepatitis, hepatitis, hepatomegaly, hyperbilirubinemia, jaundice, portal hypertension
Immune system disorders: allergic reaction
Investigations: ALT increase, AST increase, blood creatine phosphokinase increased, increased alkaline phosphatase, GGT increase, raised amylase, raised LDH
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: increased or decreased appetite, dehydration, hypertriglyceridemia
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: arthralgia, muscle spasms, myalgia, polyarthritis
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified (incl cysts and polyps): acute myeloid leukemia, papillomatosis
Nervous system disorders: confusion, convulsions, coordination abnormal, dizziness, dysgeusia, headache, hypoaesthesia, intracranial hemorrhage leading to death, loss of consciousness, paresthesia, peripheral neuropathy, somnolence, tremor
Psychiatric disorders: anxiety, depression, insomnia, libido disorder, psychotic disorder, sleep disorder, suicide attempt
Renal and urinary disorders: nephrolithiasis
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: cough, dyspnea
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: acne, alopecia, dermatitis bullous, drug eruption, erythema, severe cutaneous reaction associated with increased liver function tests, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, sweating increased, urticaria
Vascular disorders: hypertension, hypotension, thrombophlebitis, peripheral vasoconstriction
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Additional adverse events that have been observed during the postmarketing period are similar to those seen in clinical trials with INVIRASE and saquinavir soft gel capsules alone or in combination with ritonavir. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to INVIRASE exposure.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drug interaction studies have been completed with both INVIRASE and saquinavir soft gel capsules. Observations from drug interaction studies with saquinavir soft gel capsules may not be predictive for INVIRASE/ritonavir. Because ritonavir is coadministered with INVIRASE, prescribers should also refer to the prescribing information for ritonavir regarding drug interactions associated with this agent.
7.1 Potential for INVIRASE to Affect Other Drugs
The combination INVIRASE/ritonavir is a potent inhibitor of CYP3A and may significantly increase the exposure of drugs primarily metabolized by CYP3A. Drugs that are contraindicated specifically due to the observed or expected magnitude of interaction and potential for serious or life-threatening adverse events are listed in Table 1 [see Contraindications (4)]. Coadministration with other CYP3A substrates may require a dose adjustment or additional monitoring (Table 3).
7.2 Potential for Other Drugs to Affect INVIRASE
The metabolism of saquinavir is mediated primarily by CYP3A. Additionally, saquinavir is a substrate for P-glycoprotein (P-gp). Therefore, drugs that affect CYP3A and/or P-gp may modify the pharmacokinetics of saquinavir. Coadministration with drugs that are potent inducers of CYP3A (e.g., phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine) may result in decreased plasma concentrations of saquinavir and reduced therapeutic effect.
7.3 Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
Based on the finding of dose-dependent prolongations of QT and PR intervals in healthy volunteers receiving INVIRASE/ritonavir, additive effects on QT and/or PR interval prolongation may occur with certain members of the following drug classes: antiarrhythmics class IA or class III, neuroleptics, antidepressive agents, PDE5 inhibitors (when used for pulmonary arterial hypertension), antimicrobials, antihistaminics and others. This effect might lead to an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias, notably torsades de pointes. Therefore, concurrent administration of these agents with INVIRASE/ritonavir is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)].
Table 3 provides a listing of established or potentially clinically significant drug interactions. Alteration in dose or avoidance of the combination may be recommended depending on the interaction.
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration of Saquinavir or Concomitant Drug | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| HIV-1 Antiviral Agents | ||
| Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor:
Delavirdine* | ↑ Saquinavir Effect on delavirdine is not well established | Appropriate doses of the combination with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. |
| Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor:
Efavirenz†, nevirapine* | ↓ Saquinavir ↔ Efavirenz | Appropriate doses of the combination of efavirenz or nevirapine and INVIRASE/ritonavir with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. |
| HIV-1 protease inhibitor:
Atazanavir† | INVIRASE/ritonavir
↑ Saquinavir ↑ Ritonavir ↔ Atazanavir | Atazanavir in combination with INVIRASE/ritonavir should be used with caution. Additive effects on PR interval prolongation may occur with INVIRASE/ritonavir [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| HIV-1 protease inhibitor:
Indinavir* | ↑ Saquinavir Effect on indinavir is not well established | Appropriate doses of the combination of indinavir and INVIRASE/ritonavir with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. |
| HIV-1 protease inhibitor:
Lopinavir/ritonavir† (coformulated tablet) | ↔ Saquinavir ↔ Lopinavir ↓ Ritonavir | Evidence from several clinical trials indicates that saquinavir concentrations achieved with the saquinavir and lopinavir/ritonavir combination are similar to those achieved following saquinavir/ritonavir 1000/100 mg. The recommended dose for this combination is saquinavir 1000 mg plus lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg bid. Lopinavir/ritonavir in combination with INVIRASE should be used with caution. Additive effects on QT and/or PR interval prolongation may occur with INVIRASE [Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]. |
| HIV-1 protease inhibitor:
Tipranavir/ritonavir† | ↓ Saquinavir | Combining saquinavir with tipranavir/ritonavir is not recommended. |
| HIV-1 fusion inhibitor:
Enfuvirtide† | Saquinavir soft gel capsules/ritonavir ↔ enfuvirtide | No clinically significant interaction was noted from a study in 12 HIV-1 patients who received enfuvirtide concomitantly with saquinavir soft gel capsules/ritonavir 1000/100 mg bid. No dose adjustments are required. |
| HIV-1 CCR5 antagonist:
Maraviroc | ↑ maraviroc | Maraviroc dose should be 150 mg twice daily when coadministered with INVIRASE/ritonavir. For further details see complete prescribing information for Selzentry® (maraviroc). |
| Other Agents | ||
| Ibutilide Sotalol | Use with caution. Additive effects on QT and/or PR interval prolongation may occur with INVIRASE/ritonavir [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]. |
|
| Anticoagulant:
Warfarin* | ↑ Warfarin | Concentrations of warfarin may be affected. It is recommended that INR (international normalized ratio) be monitored. |
| Anticonvulsants:
Carbamazepine*, phenobarbital*, phenytoin* | ↓ Saquinavir Effect on carbamazepine, phenobarbital, and phenytoin is not well established | Use with caution. Saquinavir may be less effective due to decreased saquinavir plasma concentrations in patients taking these agents concomitantly. |
| Anti-gout:
Colchicine | ↑ Colchicine | Treatment of gout flares-coadministration of colchicine in patients on INVIRASE/ritonavir:
0.6 mg (1 tablet) × 1 dose, followed by 0.3 mg (half tablet) 1 hour later. Dose to be repeated no earlier than 3 days. Treatment of familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) coadministration of colchicine in patients on INVIRASE/ritonavir: Maximum daily dose of 0.6 mg (may be given as 0.3 mg twice a day). Prophylaxis of gout-flares-co-administration of colchicine in patients on INVIRASE/ritonavir: If the original colchicine regimen was 0.6 mg twice a day, the regimen should be adjusted to 0.3 mg once a day. If the original colchicine regimen was 0.6 mg once a day, the regimen should be adjusted to 0.3 mg once every other day. Patients with renal or hepatic impairment should not be given colchicine with INVIRASE/ritonavir. |
| Anti-infective:
Clarithromycin† | ↑ Saquinavir ↑ Clarithromycin | Due to the known effect of ritonavir on clarithromycin concentrations, the following dose adjustments are recommended for patients with renal impairment:
|
| Erythromycin Halofantrine Pentamidine | Use with caution. Additive effects on QT and/or PR interval prolongation may occur with INVIRASE/ritonavir [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]. |
|
| Antifungal:
Ketoconazole†, itraconazole* | ↔ Saquinavir ↔ Ritonavir ↑ Ketoconazole | When INVIRASE/ritonavir and ketoconazole are coadministered, plasma concentrations of ketoconazole are increased (see Table 3). Hence, doses of ketoconazole or itraconazole >200 mg/day are not recommended. |
| Antimycobacterial:
Rifabutin† | ↔ Saquinavir ↑ Rifabutin ↔ Ritonavir | No dose adjustment of INVIRASE/ritonavir (1000/100 mg bid) is required if ritonavir-boosted INVIRASE is administered in combination with rifabutin. Dosage reduction of rifabutin by at least 75% of the usual dose of 300 mg/day is recommended (i.e., a maximum dose of 150 mg every other day or three times per week). Increased monitoring for adverse events is warranted in patients receiving the combination. Consider monitoring rifabutin concentrations to ensure adequate exposure. |
| Benzodiazepines*:
Alprazolam, clorazepate, diazepam, flurazepam | ↑ Benzodiazepines | Clinical significance is unknown; however, a decrease in benzodiazepine dose may be needed. |
| Benzodiazepine*:
Intravenously administered Midazolam | ↑ Midazolam | Midazolam is extensively metabolized by CYP3A4. Increases in the concentration of midazolam are expected to be significantly higher with oral than parenteral administration. Therefore, INVIRASE should not be given with orally administered midazolam [see Contraindications (4)]. If INVIRASE is coadministered with parenteral midazolam, close clinical monitoring for respiratory depression and/or prolonged sedation should be exercised and dosage adjustment should be considered. |
| Calcium channel blockers*:
Diltiazem, felodipine, nifedipine, nicardipine, nimodipine, verapamil, amlodipine, nisoldipine, isradipine | ↑ Calcium channel blockers | Caution is warranted and clinical monitoring of patients is recommended. |
| Corticosteroid:
Dexamethasone* | ↓ Saquinavir | Use with caution. Saquinavir may be less effective due to decreased saquinavir plasma concentrations. |
| Digitalis Glycosides: Digoxin† | ↑ Digoxin Increases in serum digoxin concentration were greater in female subjects as compared to male subjects when digoxin was coadministered with INVIRASE/ritonavir. | Concomitant use of INVIRASE/ritonavir with digoxin results in a significant increase in serum concentrations of digoxin. Caution should be exercised when INVIRASE/ritonavir and digoxin are coadministered; serum digoxin concentrations should be monitored and the dose of digoxin may need to be reduced when coadministered with INVIRASE/ritonavir. |
| Endothelin receptor antagonists:
Bosentan | ↑ Bosentan | Coadministration of bosentan in patients on INVIRASE/ritonavir:
In patients who have been receiving INVIRASE/ritonavir for at least 10 days, start bosentan at 62.5 mg once daily or every other day based upon individual tolerability. Coadministration of INVIRASE/ritonavir in patients on bosentan: Discontinue use of bosentan at least 36 hours prior to initiation of INVIRASE/ritonavir. After at least 10 days following the initiation of INVIRASE/ritonavir, resume bosentan at 62.5 mg once daily or every other day based upon individual tolerability. |
| Inhaled beta agonist:
Salmeterol | ↑ Salmeterol | Concurrent administration of salmeterol with INVIRASE/ritonavir is not recommended. The combination may result in increased risk of cardiovascular adverse events associated with salmeterol, including QT prolongation, palpitations and sinus tachycardia. |
| Inhaled/nasal steroid:
Fluticasone* | INVIRASE/ritonavir
↑ Fluticasone | Concomitant use of fluticasone propionate and INVIRASE/ritonavir may increase plasma concentrations of fluticasone propionate, resulting in significantly reduced serum cortisol concentrations. Coadministration of fluticasone propionate and INVIRASE/ritonavir is not recommended unless the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the risk of systemic corticosteroid side effects. |
| HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors*:
Atorvastatin, rosuvastatin | ↑ Atorvastatin ↑ Rosuvastatin | Use lowest possible dose of atorvastatin or rosuvastatin with careful monitoring, or consider other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors such as fluvastatin in combination with INVIRASE/ritonavir. |
| Immunosuppressants*:
Cyclosporine, tacrolimus, rapamycin | ↑ Immunosuppressants | Therapeutic concentration monitoring is recommended for immunosuppressant agents when coadministered with INVIRASE/ritonavir. |
| Narcotic analgesic:
Methadone† | ↓ Methadone | Dosage of methadone may need to be increased when coadministered with INVIRASE/ritonavir. Use with caution. Additive effects on QT and/or PR interval prolongation may occur with INVIRASE/ritonavir [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]. |
| Neuroleptics:
Clozapine Haloperidol Mesoridazine Phenothiazines Thioridazine Ziprasidone | Use with caution. Additive effects on QT and/or PR interval prolongation may occur with INVIRASE/ritonavir [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]. |
|
| Oral contraceptives:
Ethinyl estradiol* | ↓ Ethinyl estradiol | Alternative or additional contraceptive measures should be used when estrogen-based oral contraceptives and INVIRASE/ritonavir are coadministered. |
| PDE5 inhibitors (phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors):
Sildenafil†, vardenafil*, tadalafil* | ↑ Sildenafil ↔ Saquinavir ↑ Vardenafil ↑ Tadalafil Only the combination of sildenafil with saquinavir soft gelatin capsules has been studied at doses used for treatment of erectile dysfunction. | May result in an increase in PDE5 inhibitor-associated adverse events, including hypotension, syncope, visual disturbances, and priapism. Use of PDE-5 inhibitors for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH):
Coadministration of ADCIRCA in patients on INVIRASE/ritonavir: In patients receiving INVIRASE/ritonavir for at least one week, start ADCIRCA at 20 mg once daily. Increase to 40 mg once daily based upon individual tolerability. Coadministration of INVIRASE/ritonavir in patients on ADCIRCA: Avoid use of ADCIRCA during the initiation of INVIRASE/ritonavir. Stop ADCIRCA at least 24 hours prior to starting INVIRASE/ritonavir. After at least one week following the initiation of INVIRASE/ritonavir, resume ADCIRCA at 20 mg once daily. Increase to 40 mg once daily based upon individual tolerability. Use of PDE5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction: Use sildenafil with caution at reduced doses of 25 mg every 48 hours with increased monitoring of adverse events when administered concomitantly with INVIRASE/ritonavir. Use vardenafil with caution at reduced doses of no more than 2.5 mg every 72 hours with increased monitoring of adverse events when administered concomitantly with INVIRASE/ritonavir. Use tadalafil with caution at reduced doses of no more than 10 mg every 72 hours with increased monitoring of adverse events when administered concomitantly with INVIRASE/ritonavir. |
| Tricyclic antidepressants*: Amitriptyline, imipramine | ↑ Tricyclics | Therapeutic concentration monitoring is recommended for tricyclic antidepressants when coadministered with INVIRASE/ritonavir. |
| Proton pump inhibitors: Omeprazole† | ↑ Saquinavir | When INVIRASE/ritonavir is co-administered with omeprazole, saquinavir concentrations are increased significantly. If omeprazole or another proton pump inhibitor is taken concomitantly with INVIRASE/ritonavir, caution is advised and monitoring for potential saquinavir toxicities is recommended, particularly gastrointestinal symptoms, increased triglycerides, deep vein thrombosis, and QT prolongation. |
| Herbal Products:
St. John's wort* (hypericum perforatum) | ↓ Saquinavir | Coadministration may lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to INVIRASE or to the class of protease inhibitors. |
| Garlic Capsules* | ↓ Saquinavir | Coadministration of garlic capsules and saquinavir is not recommended due to the potential for garlic capsules to induce the metabolism of saquinavir which may result in sub-therapeutic saquinavir concentrations. |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies conducted with saquinavir have shown no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity in both rats and rabbits. Because of limited bioavailability of saquinavir in animals and/or dosing limitations, the plasma exposures (AUC values) in the respective species were approximately 29% (using rat) and 21% (using rabbit) of those obtained in humans at the recommended clinical dose boosted with ritonavir. Clinical experience in pregnant women is limited. Saquinavir should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry
To monitor maternal-fetal outcomes of pregnant women exposed to antiretroviral medications, including INVIRASE, an Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry has been established. Physicians are encouraged to register patients by calling 1-800-258-4263.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend that HIV-infected mothers not breast-feed their infants to avoid risking postnatal transmission of HIV. It is not known whether saquinavir is excreted in human milk. Because of both the potential for HIV transmission and the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, mothers should be instructed not to breast-feed if they are receiving INVIRASE.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of INVIRASE in HIV-1-infected pediatric patients younger than 16 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of INVIRASE did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, caution should be taken when dosing INVIRASE in elderly patients due to the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Impaired Renal Function
Renal clearance is a minor elimination pathway; the principal route of excretion for saquinavir is by hepatic metabolism. Therefore, no initial dose adjustment is necessary for patients with renal impairment. However, patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) have not been studied, and caution should be exercised when prescribing INVIRASE in this population.
8.7 Impaired Hepatic Function
No dosage adjustment is necessary for HIV-1-infected patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment based on limited data. In patients with underlying hepatitis B or C, cirrhosis, chronic alcoholism and/or other underlying liver abnormalities, there have been reports of worsening liver disease [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is limited experience of overdose with saquinavir.
No acute toxicities or sequelae were noted in 1 patient who ingested 8 grams of INVIRASE as a single dose. The patient was treated with induction of emesis within 2 to 4 hours after ingestion. A second patient ingested 2.4 grams of INVIRASE in combination with 600 mg of ritonavir and experienced pain in the throat that lasted for 6 hours and then resolved. In an exploratory Phase II study of oral dosing with INVIRASE at 7200 mg/day (1200 mg q4h), there were no serious toxicities reported through the first 25 weeks of treatment.
Treatment of overdose with saquinavir should consist of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and ECG and observations of the patient's clinical status. Since saquinavir is highly protein bound, dialysis is unlikely to be beneficial in significant removal of the active substance.
11 DESCRIPTION
INVIRASE brand of saquinavir mesylate is an inhibitor of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) protease.
The chemical name for saquinavir mesylate is N-tert-butyl-decahydro-2-[2(R)-hydroxy-4-phenyl-3(S)-[[N-(2-quinolylcarbonyl)-L-asparaginyl]amino]butyl]-(4aS,8aS)-isoquinoline-3(S)-carboxamide methanesulfonate with a molecular formula C38H50N6O5∙CH4O3S and a molecular weight of 766.96. The molecular weight of the free base is 670.86. Saquinavir mesylate has the following structural formula:
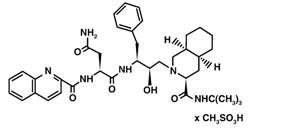
Saquinavir mesylate is a white to off-white, very fine powder with an aqueous solubility of 2.22 mg/mL at 25°C.
INVIRASE is available as light brown and green, opaque hard gelatin capsules for oral administration in a 200-mg strength (as saquinavir free base). Each capsule also contains the inactive ingredients lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone K30, sodium starch glycolate, talc, and magnesium stearate. Each capsule shell contains gelatin and water with the following dye systems: red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide, black iron oxide, FD&C Blue #2, and titanium dioxide.
INVIRASE is also available as a light orange to greyish- or brownish-orange, oval cylindrical, biconvex film-coated tablet for oral administration in a 500-mg strength (as saquinavir free base). Each tablet also contains the inactive ingredients lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone K30, croscarmellose sodium, and magnesium stearate. Each film coat contains hypromellose, titanium dioxide, talc, iron oxide yellow, iron oxide red, and triacetin.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
INVIRASE is an antiviral agent [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)]
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
QTcS interval was evaluated in a randomized, placebo and active (moxifloxacin 400 mg once daily) controlled crossover study in 59 healthy adults, with ECG measurements on Day 3. The maximum mean (95% upper confidence bound) differences in QTcS interval from placebo after baseline-correction were 18.9 (22.0) and 30.2 (33.4) ms for 1000/100 mg twice daily and supratherapeutic 1500/100 mg twice daily of INVIRASE/ritonavir, respectively. There is a delayed effect between QTc interval change and drug concentrations, with the maximum placebo-adjusted baseline-corrected QTcS observed at about 12-20 h post-dose. INVIRASE/ritonavir 1500/100 mg twice daily resulted in a Day 3 mean Cmax of INVIRASE approximately 1.4-fold higher than the mean Cmax observed on Day 3 with the approved therapeutic dose in healthy volunteers (within the same study). QTcS in this study was QT/RR0.319 for males and QT/RR0.337 for females, which are similar to Fridericia's correction (QTcF=QT/RR0.3333).
PR and QRS interval prolongations were also noted in subjects receiving INVIRASE/ritonavir in the same study on Day 3. The maximum mean (95% upper confidence bound) difference from placebo in the PR interval after baseline-correction were 28.6 (31.6) and 38.4 (41.4) ms for 1000/100 mg twice daily and supratherapeutic 1500/100 mg twice daily saquinavir/ritonavir respectively. The maximum mean (95% upper confidence bound) difference from placebo in QRS interval after baseline correction were 2.9 (3.9) and 4.4 (5.3) ms for 1000/100 mg twice daily and supratherapeutic 1500/100 mg twice daily INVIRASE/ritonavir respectively. In this study using healthy subjects, PR interval prolongation of >200 ms was also observed in 40% and 47% of subjects receiving INVIRASE/ritonavir 1000/100 mg bid and 1500/100 mg bid, respectively, on Day 3. Three (3%) of subjects in the active control moxifloxacin arm and 5% in the placebo arm experienced PR prolongation of >200 ms.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of INVIRASE/ritonavir 1000/100 mg twice daily have been evaluated in HIV-1-infected patients and healthy subjects. Steady-state saquinavir AUC, Cmax, and Cmin in healthy subjects are approximately 50% higher than observed in HIV-1-infected patients.
Absorption and Bioavailability in Adults
Similar bioavailability was demonstrated when INVIRASE 500 mg film-coated tablet (2 × 500 mg) and INVIRASE 200 mg capsule (5 × 200 mg) were administered with low-dose ritonavir (100 mg) under fed conditions. The ratio of mean exposures (90% confidence intervals) of tablets vs capsules was 1.10 (1.04-1.16) for AUC0-∞ and 1.19 (1.14-1.25) for Cmax.
Absolute bioavailability of saquinavir administered as INVIRASE averaged 4% (CV 73%, range: 1% to 9%) in 8 healthy volunteers who received a single 600-mg dose (3 × 200 mg) of saquinavir mesylate following a high-fat breakfast (48 g protein, 60 g carbohydrate, 57 g fat; 1006 kcal). The low bioavailability is thought to be due to a combination of incomplete absorption and extensive first-pass metabolism.
INVIRASE in combination with ritonavir at a dose of 1000/100 mg twice daily provides saquinavir systemic exposures over a 24-hour period that are similar to those achieved with saquinavir soft gel capsules (FORTOVASE) with ritonavir 1000/100 mg twice daily and greater than that achieved with saquinavir soft gel capsules 1200 mg three times daily (see Table 4).
| Dosing Regimen | N | AUCτ
(ng∙h/mL) | AUC24h
(ng∙h/mL) | Cmin
(ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| τ is the dosing interval (i.e., 8h if three times daily and 12h if twice daily) | ||||
| INVIRASE 600 mg tid (arithmetic mean, %CV) | 10 | 866 (62) | 2598 | 79 |
| Saquinavir soft gel capsules (FORTOVASE) 1200 mg tid (arithmetic mean) | 31 | 7249 | 21747 | 216 |
| INVIRASE 1000 mg bid + ritonavir 100 mg bid (geometric mean and 95% CI) | 24 | 14607 (10218-20882) | 29214 | 371 (245-561) |
| Saquinavir soft gel capsules 1000 mg bid + ritonavir 100 mg bid (geometric mean and 95% CI) | 24 | 19085 (13943-26124) | 38170 | 433 (301-622) |
Food Effect
The mean 24-hour AUC after a single 600-mg oral dose (6 × 100 mg) in healthy volunteers (n=6) was increased from 24 ng∙h/mL (CV 33%), under fasting conditions, to 161 ng∙h/mL (CV 35%) when INVIRASE was given following a high-fat breakfast (48 g protein, 60 g carbohydrate, 57 g fat; 1006 kcal). Saquinavir 24-hour AUC and Cmax (n=6) following the administration of a higher calorie meal (943 kcal, 54 g fat) were on average 2 times higher than after a lower calorie, lower fat meal (355 kcal, 8 g fat). The effect of food has been shown to persist for up to 2 hours.
INVIRASE/ritonavir should be taken within 2 hours after a meal.
Distribution in Adults
The mean steady-state volume of distribution following intravenous administration of a 12-mg dose of saquinavir (n=8) was 700 L (CV 39%), suggesting saquinavir partitions into tissues. Saquinavir was approximately 98% bound to plasma proteins over a concentration range of 15 to 700 ng/mL. In 2 patients receiving saquinavir mesylate 600 mg three times daily, cerebrospinal fluid concentrations were negligible when compared to concentrations from matching plasma samples.
Metabolism and Elimination in Adults
In vitro studies using human liver microsomes have shown that the metabolism of saquinavir is cytochrome P450 mediated with the specific isoenzyme, CYP3A4, responsible for more than 90% of the hepatic metabolism. Based on in vitro studies, saquinavir is rapidly metabolized to a range of mono- and di-hydroxylated inactive compounds. In a mass balance study using 600 mg 14C-saquinavir mesylate (n=8), 88% and 1% of the orally administered radioactivity was recovered in feces and urine, respectively, within 5 days of dosing. In an additional 4 subjects administered 10.5 mg 14C-saquinavir intravenously, 81% and 3% of the intravenously administered radioactivity was recovered in feces and urine, respectively, within 5 days of dosing. In mass balance studies, 13% of circulating radioactivity in plasma was attributed to unchanged drug after oral administration and the remainder attributed to saquinavir metabolites. Following intravenous administration, 66% of circulating radioactivity was attributed to unchanged drug and the remainder attributed to saquinavir metabolites, suggesting that saquinavir undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism.
Systemic clearance of saquinavir was rapid, 1.14 L/h/kg (CV 12%) after intravenous doses of 6, 36, and 72 mg. The mean residence time of saquinavir was 7 hours (n=8).
Special Populations
Renal Impairment
Saquinavir pharmacokinetics in patients with renal impairment has not been investigated. Only 1% of saquinavir is excreted in the urine, so the impact of renal impairment on saquinavir elimination would likely be minimal. However, patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) have not been studied, and concentrations of saquinavir may be elevated in these populations.
Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the steady state pharmacokinetics of INVIRASE/ritonavir (1000/100 mg bid for 14 days) was investigated in 7 HIV-1-infected patients with moderate liver impairment (6 with Child-Pugh score of 7 and 1 with Child-Pugh score of 9). The study included a control group consisting of 7 HIV-1-infected patients with normal hepatic function matched with hepatically impaired patients for age, gender, weight and tobacco use. The mean (% coefficient of variation in parentheses) values for INVIRASE AUC0-12 and Cmax were 24.3 (102%) µg∙hr/mL and 3.6 (83%) µg/mL, respectively, for HIV-1-infected patients with moderate hepatic impairment. The corresponding values in the control group were 28.5 (71%) µg∙hr/mL and 4.3 (68%) µg/mL. The geometic mean ratio (ratio of pharmacokinetic parameters in hepatically impaired patients to patients with normal liver function) (90% confidence interval) was 0.7 (0.3 to 1.6) for both AUC0-12 and Cmax, which suggests approximately 30% reduction in saquinavir exposure in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. No dose adjustment is warranted for INVIRASE in HIV-1-infected patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Gender, Race, and Age
A gender difference was observed, with females showing higher saquinavir exposure than males (mean AUC 56% higher, mean Cmax 26% higher), in the relative bioavailability study comparing INVIRASE 500 mg film-coated tablets to the INVIRASE 200 mg capsules in combination with ritonavir. There was no evidence that age and body weight explained the gender difference in this study. A clinically significant difference in safety and efficacy between men and women has not been reported with the approved dosage regimen (saquinavir 1000-mg/ritonavir 100-mg twice daily).
The effect of race on the pharmacokinetics of saquinavir has not been investigated.
The pharmacokinetics of saquinavir have not been evaluated in the elderly.
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of saquinavir have not been evaluated in pediatric patients.
Drug Interactions
Table 5 summarizes the effect of saquinavir soft gel capsules and INVIRASE with and without ritonavir on the geometric mean AUC and Cmax of coadministered drugs. Table 6 summarizes the effect of coadministered drugs on the geometric mean AUC and Cmax of saquinavir.
| Coadministered Drug | Saquinavir soft gel capsules or saquinavir soft gel capsules/ ritonavir | N | % Change for Coadministered Drug | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ Denotes an average increase in exposure by the percentage indicated. | ||||
| ↓ Denotes an average decrease in exposure by the percentage indicated. | ||||
| ↔ Denotes no statistically significant change in exposure was observed. | ||||
| P Patient | ||||
| V Healthy Volunteers | ||||
| M Methadone-dependent, HIV negative patients | ||||
| NA Not Available | ||||
| Dose | AUC (95% CI) | Cmax (95% CI) | ||
| Clarithromycin 500 mg bid × 7 days Clarithromycin 14-OH clarithromycin metabolite | 1200 mg tid × 7 days | 12V | ↑45% (17-81%) ↓24% (5-40%) | ↑39% (10-76%) ↓34% (14-50%) |
| Enfuvirtide 90 mg SC q12h (bid) for 7 days | 1000/100 mg bid | 12P | ↔ | ↔ |
| Sildenafil 100-mg single dose | 1200 mg tid × 8 days | 27V | ↑210% (150-300%) | ↑140% (80-230%) |
| Efavirenz 600 mg qd | 1200 mg tid | 13V | ↓12% | ↓13% |
| INVIRASE/ritonavir Dose | ||||
| Digoxin 0.5 mg single dose | 1000/100 mg bid × 16 days | 16V | ↑49% (32-69%)* | ↑27% (5-54%)* |
| R-Methadone 60-120 mg qd | 1000/100 mg bid × 14 days | 12M | ↓19% (9-29%)* | NA |
| Ketoconazole 200 mg/day | 1000/100 mg bid | 12V | ↑168% (146-193%)* | ↑45% (32-59%)* |
| Midazolam 7.5 mg oral single dose | 1000/100 mg bid | 16V | ↑1144% (975-1339%)* | ↑327% (264 -402%)* |
| Rifabutin 150 mg q4d | 1000/100 mg bid | 11V | ↑60%†‡
(43-79%)* ↔§ (-10 to 13%)* | ↑111%†‡
(75-153%)* ↑68%§ (38-105%)* |
| Coadministered Drug | Saquinavir soft gel capsules | N | % Change for Saquinavir | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | AUC (95% CI) | Cmax (95% CI) | ||
| ↑ Denotes an average increase in exposure by the percentage indicated. | ||||
| ↓ Denotes an average decrease in exposure by the percentage indicated. | ||||
| ↔ Mean change <10% | ||||
| P Patient | ||||
| V Healthy Volunteers | ||||
| Clarithromycin 500 mg bid × 7 days | 1200 mg tid × 7 days | 12V | ↑177% (108-269%) | ↑187% (105-300%) |
| Efavirenz 600 mg qd | 1200 mg tid | 13V | ↓62% | ↓50% |
| Indinavir 800 mg q8h × 2 days | 1200 mg single dose | 6V | ↑364% (190-644%) | ↑299% (138-568%) |
| Ritonavir 400 mg bid × 14 days | 400 mg bid × 14 days* | 8V | ↑121% (7-359%) | ↑64%† |
| Lopinavir/ritonavir Evidence from several clinical trials indicates that saquinavir concentrations achieved with saquinavir 1000 mg + lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg BID are similar to those achieved following saquinavir/ritonavir 1000/100 mg BID. |
||||
| Coadministered Drug | INVIRASE or INVIRASE/ritonavir | N | % Change for Saquinavir | |
| Dose | AUC (95% CI) | Cmax (95% CI) | ||
| Atazanavir 300 mg qd | 1600/100 mg qd | 18P | ↑60% (16-122%) | ↑42% (10-84%) |
| Fosamprenavir 700 mg bid | 1000 mg bid/100 mg bid | 18P | ↓15% (-33% to 9%) | ↔ |
| Ritonavir 100 mg bid | 1000 mg bid‡ | 24P | ↑1124% | ↑1325% |
| Tenofovir 300 mg qd | 1000 mg bid/100 mg bid | 18P | ↔ | ↔ |
| Tipranavir 500 mg + ritonavir 200 mg bid | 600 mg bid/100 mg bid | 20P | ↓76% (68-81%)§ | ↓70% (60-77%)§ |
| Omeprazole 40 mg qd × 5 days | 1000/100 mg bid × 15 days | 19V | ↑82% (37-234%)§ | ↑ 75% (31-234%)§ |
| Ketoconazole 200 mg/day | 1000 mg bid/100 mg bid | 20V | ↔§ | ↔ |
| Rifabutin 150 mg q3d | 1000 mg bid/100 mg bid | 19V | ↓13% (-31% to 9%)§ | ↓15% (-32% to 7%)§ |
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Saquinavir is an inhibitor of HIV-1 protease. HIV-1 protease is an enzyme required for the proteolytic cleavage of viral polyprotein precursors into individual functional proteins found in HIV-1 particles. Saquinavir is a peptide-like substrate analogue that binds to the protease active site and inhibits the activity of the enzyme. Saquinavir inhibition prevents cleavage of the viral polyproteins resulting in the formation of immature noninfectious viral particles
Antiviral Activity
The antiviral activity of saquinavir was assessed in lymphoblastoid and monocytic cell lines and in peripheral blood lymphocytes in cell culture. Saquinavir inhibited HIV-1 activity in both acutely and chronically infected cells. EC50 and EC90 values (50% and 90% inhibitory concentrations) ranged from 1 to 30 nM and 5 to 80 nM, respectively. In the presence of 40% human serum, the mean IC50 of saquinavir against laboratory strain HIV-1 RF in MT4 cells was 37.7± 5 nM representing a 4-fold increase in the EC50 value. In cell culture, saquinavir demonstrated additive to synergistic effects against HIV-1 in combination with reverse transcriptase inhibitors (didanosine, lamivudine, nevirapine, stavudine and zidovudine) without enhanced cytotoxicity. Saquinavir in combination with the protease inhibitors amprenavir, atazanavir, or lopinavir resulted in synergistic antiviral activity. Saquinavir displayed antiviral activity in cell culture against HIV-1 clades A-H (EC50 values ranged from 0.9 to 2.5 nM). The EC50 and EC90 values of saquinavir against HIV-2 isolates in cell culture ranged from 0.25 nM to 14.6 nM and 4.65 nM to 28.6 nM, respectively.
Drug Resistance
HIV-1 with reduced susceptibility to saquinavir have been selected during passage in cell culture. Genotypic analyses of these isolates showed several amino acid substitutions in the HIV-1 protease. Only the G48V and L90M substitutions were associated with reduced susceptibility to saquinavir, and conferred an increase in the EC50 value of 8- and 3-fold, respectively.
HIV-1 isolates with reduced susceptibility (≥4-fold increase in the EC50 value) to saquinavir emerged in some patients treated with INVIRASE. Genotypic analysis of these isolates identified resistance conferring primary amino acid substitutions in the protease G48V and L90M, and secondary substitutions L10I/R/V, I54V/L, A71V/T, G73S, V77I, V82A and I84V that contributed additional resistance to saquinavir. Forty-one isolates from 37 patients failing therapy with INVIRASE had a median decrease in susceptibility to saquinavir of 4.3-fold.
The degree of reduction in cell culture susceptibility to saquinavir of clinical isolates bearing substitutions G48V and L90M depends on the number of secondary substitutions present. In general, higher levels of resistance are associated with greater number of substitutions only in association with either or both of the primary substitutions G48V and L90M. No data are currently available to address the development of resistance in patients receiving saquinavir/ritonavir.
Cross-resistance
Among protease inhibitors, variable cross-resistance has been observed. In one clinical study, 22 HIV-1 isolates with reduced susceptibility (>4-fold increase in the EC50 value) to saquinavir following therapy with INVIRASE were evaluated for cross-resistance to amprenavir, indinavir, nelfinavir and ritonavir. Six of the 22 isolates (27%) remained susceptible to all 4 protease inhibitors, 12 of the 22 isolates (55%) retained susceptibility to at least one of the protease inhibitors and 4 out of the 22 isolates (18%) displayed broad cross-resistance to all protease inhibitors. Sixteen (73%) and 11 (50%) of the 22 isolates remained susceptible (<4-fold) to amprenavir and indinavir, respectively. Four of 16 (25%) and nine of 21 (43%) with available data remained susceptible to nelfinavir and ritonavir, respectively.
After treatment failure with amprenavir, cross-resistance to saquinavir was evaluated. HIV-1 isolates from 22/22 patients failing treatment with amprenavir and containing one or more substitutions M46L/I, I50V, I54L, V32I, I47V, and I84V were susceptible to saquinavir.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies found no indication of carcinogenic activity in rats and mice administered saquinavir for approximately 2 years. Because of limited bioavailability of saquinavir in animals, the plasma exposures (AUC values) in the respective species were approximately 29% (using rat) and 65% (using mouse) of those obtained in humans at the recommended clinical dose boosted with ritonavir.
Mutagenesis
Mutagenicity and genotoxicity studies, with and without metabolic activation where appropriate, have shown that saquinavir has no mutagenic activity in vitro in either bacterial (Ames test) or mammalian cells (Chinese hamster lung V79/HPRT test). Saquinavir does not induce chromosomal damage in vivo in the mouse micronucleus assay or in vitro in human peripheral blood lymphocytes, and does not induce primary DNA damage in vitro in the unscheduled DNA synthesis test.
Impairment of Fertility
No adverse effects were reported in fertility and reproductive performance study conducted in rats. Because of limited bioavailability of saquinavir in animals, the maximal plasma exposures achieved in rats were approximately 26% of those obtained in humans at the recommended clinical dose boosted with ritonavir.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Description of Clinical Studies
In a randomized, double-blind clinical study (NV14256) in zidovudine-experienced, HIV-1-infected patients, INVIRASE in combination with zalcitabine2 was shown to be superior to either INVIRASE or zalcitabine monotherapy in decreasing the cumulative incidence of clinical disease progression to AIDS-defining events or death. Furthermore, in a randomized study (ACTG229/NV14255), patients with advanced HIV-1 infection with history of prolonged zidovudine treatment and who were given INVIRASE 600 mg (three times daily) + zidovudine + zalcitabine experienced greater increases in CD4+ cell counts as compared to those who received INVIRASE + zidovudine or zalcitabine + zidovudine. It should be noted that HIV-1 treatment regimens that were used in these initial clinical studies of INVIRASE are no longer considered standard of care.
Saquinavir gel capsule 1000 mg twice daily coadministered with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily was studied in a heterogeneous population of 148 HIV-1-infected patients (MaxCmin 1 study). At baseline 42 were treatment naïve and 106 were treatment experienced (of which 52 had an HIV-1 RNA level <400 copies/mL at baseline). Results showed that 91/148 (61%) subjects achieved and/or sustained an HIV-1 RNA level <400 copies/mL at the completion of 48 weeks.
- 2
- No longer available in the US.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
INVIRASE 200-mg capsules are light brown and green opaque capsules with ROCHE and 0245 imprinted on the capsule shell—bottles of 270 (NDC 0004-0245-15).
INVIRASE 500-mg film-coated tablets are light orange to greyish- or brownish-orange, oval cylindrical, biconvex tablets with ROCHE and SQV 500 imprinted on the tablet face—bottles of 120 (NDC 0004-0244-51).
The capsules and tablets should be stored at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature] in tightly closed bottles.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved Medication Guide.
A statement to patients and health care providers is included on the product's bottle label: ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with INVIRASE.
Patients should be informed that INVIRASE is not a cure for HIV-1 infection and that they may continue to acquire illnesses associated with advanced HIV-1 infection, including opportunistic infections. They should be informed that INVIRASE therapy has not been shown to reduce the risk of transmitting HIV-1 to others through sexual contact or blood contamination.
17.1 Drug Interactions
INVIRASE may interact with some drugs; therefore, patients should be advised to report to their doctor the use of any other prescription, nonprescription medication, or herbal products, particularly St. John's wort.
17.2 PR and QT Interval Prolongation
Patients should be informed that INVIRASE may produce changes in the electrocardiogram (PR interval or QT interval prolongation). Patients should consult their health care provider if they are experiencing symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or palpitations.
17.3 Fat Redistribution
Patients should be informed that redistribution or accumulation of body fat may occur in patients receiving protease inhibitors and that the cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known at this time.
17.4 Dosing Instructions
Patients should be advised that INVIRASE must be used in combination with ritonavir, which significantly inhibits saquinavir's metabolism to provide increased plasma saquinavir levels.
Patients should be advised that INVIRASE administered with ritonavir should be taken within 2 hours after a full meal [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. When INVIRASE is taken without food, concentrations of saquinavir in the blood are substantially reduced and may result in no antiviral activity. Patients should be advised of the importance of taking their medication every day, as prescribed, to achieve maximum benefit. Patients should not alter the dose or discontinue therapy without consulting their physician. If a dose is missed, patients should take the next dose as soon as possible. However, the patient should not double the next dose.
FDA-approved Medication Guide
Medication Guide
INVIRASE® (in-ver-ase)
(saquinavir mesylate)
Capsules and Tablets
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking INVIRASE and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. You and your healthcare provider should talk about your treatment with INVIRASE before you start taking it and at regular checkups. You should stay under a healthcare provider's care when taking INVIRASE.
Also read the Medication Guide for ritonavir (Norvir).
What is the most important information I should know about INVIRASE?
- INVIRASE must be taken along with NORVIR® (ritonavir).
INVIRASE may cause serious side effects including:
- Interactions with other medicines. It is important to know the medicines that should not be taken with INVIRASE. Read the section "What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking INVIRASE?"
-
Changes in your heart rhythm and the electrical activity of your heart. These changes may be seen on an EKG (electrocardiogram) and can lead to serious heart problems. Your risk for these problems may be higher if you:
- already have a history of abnormal heart rhythm, including Congenital Long QT Syndrome, or other types of heart disease.
- take other medicines that can affect your heart rhythm while you take INVIRASE.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms while taking INVIRASE:
- dizziness
- lightheadedness
- fainting
- sensation of abnormal heartbeats
See the section below "What are the possible side effects of INVIRASE?" for more information about serious side effects.
What is INVIRASE?
INVIRASE is a prescription anti-HIV medicine used in people 16 years and older. INVIRASE belongs to a class of anti-HIV medicines called protease inhibitors. INVIRASE is used with ritonavir and other anti-HIV medicines to treat people with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection. HIV-1 is the virus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome).
It is not known if INVIRASE is safe and effective in children younger than 16 years old.
Who should not take INVIRASE?
Do not take INVIRASE if:
- you are taking certain medicines. For more information about medicines you should not take with INVIRASE, please see "What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking INVIRASE?" and talk with your healthcare provider about all other medicines you take.
- your healthcare provider has told you that you have a condition called Congenital Long QT Syndrome.
- your healthcare provider has told you that you have complete AV (atrioventricular) block and you do not have a pacemaker or you are at risk for complete AV block.
- your healthcare provider has told you that you have low potassium or low magnesium in your blood.
- you have severe liver problems.
- you have had a severe allergic reaction to INVIRASE or any of the ingredients in INVIRASE.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking INVIRASE?
INVIRASE may not be right for you. Before you take INVIRASE, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have any heart problems, including a condition called Congenital Long QT Syndrome.
- have diabetes.
- have liver problems, including Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C.
- have hemophilia. People who take INVIRASE may have increased bleeding.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if INVIRASE will harm your unborn baby.
Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry. If you take INVIRASE during pregnancy, talk with your healthcare provider about how you can take part in an antiretroviral pregnancy registry. The purpose of the pregnancy registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if INVIRASE passes into your breast milk. You should not breastfeed if you are taking INVIRASE. If you are a woman who has or will have a baby while taking INVIRASE, talk with your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that HIV-infected mothers not breastfeed to avoid the risk of passing HIV infection to your baby.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescriptions and non-prescriptions medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. INVIRASE and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. Do not start taking a new medicine without talking with your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to take INVIRASE with other medicines.
Taking INVIRASE with certain other medicines can cause serious problems or life threatening reactions.
Medicines you should not take with INVIRASE and NORVIR include:
- alfuzosin (UROXATRAL®)
- amiodarone (CORDARONE®, PACERONE®)
- dofetilide (TIKOSYN®)
- flecainide (TAMBOCOR®)
- lidocaine
- propafenone (RHYTHMOL®)
- quinidine
- trazodone (OLEPTRO®)
- rifampin (RIFADIN®, RIFAMATE®, RIFATER®, RIMACTANE®)
- Ergot containing medicines, including:
- dihydroergotamine mesylate (D.H.E 45, EMBOLEX, MIGRANAL)
- ergonovine, ergonovine and methylergonovine (Ergotrate, Methergine), ergotamine and methylergonovine
- ergotamine tartrate (CAFERGOT, MIGERGOT, ERGOMAR, ERGOSTATE, MEDIHALER ERGOTAMINE, WIGRAINE, WIGRETTES)
- lovastatin (ADVICOR®, ALTOPREV®, MEVACOR®)
- simvastatin (SIMCOR®, VYTORIN®, ZOCOR®)
- pimozide (ORAP®)
- sildenafil (REVATIO®)
- triazolam (HALCION®)
- midazolam hydrochloride oral syrup
The following medicines may increase blood levels and side effects of INVIRASE when taken with INVIRASE and NORVIR:
- delavirdine (RESCRIPTOR®)
- atazanavir (REYATAZ®)
- omeprazole (PRILOSEC®)
- clarithromycin (BIAXIN®)
- indinavir (CRIXIVAN®)
INVIRASE and NORVIR may not work as well when taken together with the following medicines, herbal products, or dietary supplements:
- efavirenz (SUSTIVA®)
- nevirapine (VIRAMUNE®)
- tipranavir and ritonavir (APTIVUS®, NORVIR® used for HIV infection)
- Anticonvulsants such as carbamazepine (CARBATROL®, TEGRETOL®), phenobarbital, and phenytoin (DILANTIN®)
- dexamethasone
- Garlic capsules, an herbal product sold as a dietary supplement
- the herbal supplement St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) or products containing St. John's wort
Your healthcare provider may need to monitor your therapy more closely if you take INVIRASE and NORVIR with the following medicines:
- medicines for erectile problems, such as tadalafil (CIALIS®), vardenafil (LEVITRA®), or sildenafil citrate (VIAGRA®)
- a blood thinner medicine such as warfarin (COUMADIN®, JANTOVEN®)
- Antidepressants such as trazodone (DESYREL®), (amitriptyline (ELAVIL®), or imipramine (TORFRANIL®)
- Benzodiazepines used as sedatives or sleeping pills such as alprazolam (XANAX®), clorazepate (TRANXENE®), diazepam (VALIUM®), and flurazepam (DALMANE®)
- atorvastatin (LIPITOR®) and rosuvastatin (CRESTOR®) used for lowering cholesterol
- Calcium channel blockers used for treatment of high blood pressure or heart disease, such as diltiazem (CARDIZEM®, CARTIA XT®, DILACOR XR®, DILTZAC®, TAZTIA XT®, TIAZAC®), felodipine (PLENDIL®), nifedipine (PROCARDIA®), nicardipine (CARDENE®), nimodipine (NIMOTOP®), verapamil-containing medications (such as CALAN®, VERELAN®), amlodipine-containing medications (such as CADUET®, NORVASC®), nisoldipine (SULAR®), and isradipine (DYNACIRC®)
- ketoconazole (NIZORAL®) and itraconazole (SPORANOX®) used to treat fungal infections
- Medicines to prevent organ transplant rejection: cyclosporine SANDIMMUNE®), cyclosporine (NEORAL®), sirolimus (RAPAMUNE®), or tacrolimus (PROGRAF®)
- fluticasone propionate (FLONASE®, FLOVENT®, ADVAIR®), given by nose or inhaled to treat allergic symptoms or asthma
- digoxin (LANOXIN®) used to treat of heart rhythm problems or other heart conditions
- bosentan (TRACLEER®) and tadalafil (ADCIRCA®) used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension
- medicines for gout, such as colchicine (COLCRYS®)
- Oral contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol used for preventing pregnancy
- Methadone
- rifabutin (MYCOBUTIN®)
If you are not sure if you take a medicine above, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take INVIRASE?
- Take INVIRASE exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- INVIRASE comes as a 500 mg tablet or a 200 mg capsule.
- Do not change your dose of INVIRASE or stop treatment without first talking with your healthcare provider.
- INVIRASE must be used along with ritonavir (Norvir).
- Take INVIRASE with meals or up to 2 hours after a meal.
- Do not miss a dose of INVIRASE. It is very important to take your medicine every day. If you skip doses or take less than the prescribed dose the medicine will not work as well, and the virus may become harder to treat.
- If you miss a dose of INVIRASE, you should take the next dose as soon as possible. Do not double your dose.
- If you take more than your prescribed dose of INVIRASE, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of INVIRASE?
INVIRASE can cause serious side effects.
Diabetes and high blood sugar. Some people who take protease inhibitors get new or more serious diabetes, or high blood sugar. Tell your healthcare provider if you notice an increase in thirst or urinate more often than normal while taking INVIRASE.
-
Liver problems. People with liver problems such as Hepatitis B or C, cirrhosis or have a history of alcoholism may have worsening liver problems.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these signs and symptoms of liver problems:- loss of appetite
- yellowing of your skin or whites of your eyes (jaundice)
- dark-colored urine
- pale colored stools
- itchy skin
- stomach area (abdominal) pain
- Increased bleeding in people with hemophilia. Some people with hemophilia have increased bleeding with protease inhibitors including INVIRASE.
- Increase in certain fat (cholesterol and triglycerides) levels in your blood. Your healthcare provider will check your blood for high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides before you start INVIRASE and during treatment with INVIRASE.
- Changes in body fat. Changes in body fat have been seen in some people who take anti-HIV medications. These changes may include increased amount of fat in the upper back and neck ("buffalo hump"), breasts, and around the trunk. Loss of fat from the legs, arms and face may also happen. The cause and long-term health effects of these conditions are not known at this time.
- Immune System Changes (Immune Reconstitution Syndrome). Your immune system may get stronger and begin to fight infections that have been hidden in your body for a long time. Tell your healthcare provider if you start having new or worse symptoms of infection after you start taking INVIRASE.
The most common side effects of INVIRASE include:
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- stomach area (abdominal) pain
- tiredness
- pneumonia
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of INVIRASE. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to Genentech at 1-800-835-2555.
How should I store INVIRASE?
- Store INVIRASE at room temperature between 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
- Keep INVIRASE in a tightly closed container.
Keep INVIRASE and all medicine out of the reach of children.
General information about INVIRASE.
INVIRASE does not cure HIV, and it does not prevent you from getting other illness from advanced HIV infections. INVIRASE does not stop you from passing HIV infections to others. Do not share needles, or personal items that can have blood or body fluids on them, like toothbrushes and razor blades. Always practice safer sex by using condoms to lower the chance of sexual contact with semen, vaginal secretions, or blood.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use INVIRASE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give INVIRASE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about INVIRASE. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about INVIRASE that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to http://www.gene.com/gene/products/information/invirase or call 1-877-436-3683 (1-877-Genentech).
What are the ingredients in INVIRASE?
Active ingredient: saquinavir mesylate
Inactive ingredients:
200 mg Capsule: lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone K30, sodium starch glycolate, talc, and magnesium stearate.
Capsule shell: gelatin and water with the following dye systems: red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide, black iron oxide, FD&C Blue #2, and titanium dioxide.
500 mg Tablet: lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone K30, croscarmellose sodium, and magnesium stearate.
Film coat: hypromellose, titanium dioxide, talc, iron oxide yellow, iron oxide red, and triacetin.
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Roche Laboratories, Inc. The makers of these brands are not affiliated with and do not endorse Roche Laboratories, Inc. or its products.
INVIRASE is a registered trademark of Hoffmann-La Roche Inc.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Capsules Manufactured by:
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Basel, Switzerland
Tablets Manufactured by:
Roche Farma, S.A., Leganes, Spain
Distributed by:
Genentech USA, Inc.
A Member of the Roche Group
1 DNA Way
South San Francisco, CA 94080-4990
IET_318959_PI_042010_K
IEC_318959_PI_042010_N
IET_318959_MG_062010_K
IEC_318959_MG_062010_N
Revised: 10/2010
© 2010 Genentech, Inc. All rights reserved.
Representative sample of labeling (see the HOW SUPPLIED section for complete listing):
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 500 mg Bottle Label
NDC 0004-0244-51
Invirase®
(saquinavir mesylate)
Tablets
500 mg
Each tablet contains saquinavir mesylate
equivalent to 500 mg saquinavir (free base).
Rx only
ALERT: Find out about medicines that
should NOT be taken with INVIRASE.
Attention Pharmacist: Dispense the attached
Medication Guide to each patient. Do not cover
ALERT box with pharmacy label.
120 tablets
Genentech
| INVIRASE
saquinavir mesylate capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA020628 | 12/06/1995 | |
| INVIRASE
saquinavir mesylate tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA021785 | 12/17/2004 | |
| Labeler - Genentech, Inc. (080129000) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd | 482242971 | ANALYSIS, API MANUFACTURE, MANUFACTURE | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Roche Farma S.A. | 462011388 | ANALYSIS, MANUFACTURE | |