DYPHYLLINE GG
-
dyphylline and
guaifenesin tablet
Pegasus Laboratories
----------
DESCRIPTION
Dyphylline and Guaifenesin Tablets are a bronchodilator/expectorant combination available for oral administration.
Each tablet contains:
Dyphylline . . . . . 200mg
Guaifenesin . . . . 200mg
Other ingredients: dextrose, povidone, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose.
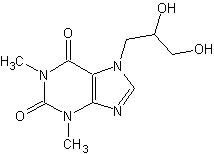
Dyphylline is 7-(2,3-dihyroxypropyl)-theophylline, a white, extremely bitter, amorphous powder that is fully soluble in water and soluble alcohol to the extent of 2g/100mL. Dyphylline forms a neutral solution that is stable in gastrointestinal fluids over a wide range of pH.
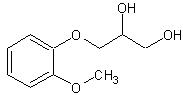
Guaifenesin is an expectorant which occurs as a white to slightly gray, crystalline powder, having a bitter taste. It may have a slight characteristic odor. It is soluble in water, alcohol, chloroform, glycerin, and propylene glycol. The chemical name is 1,2-propanediol, 3-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Dyphylline is a xanthine derivative with pharmacological actions similar to theophylline and other members of this class of drugs. Its primary action is that of bronchodilation, but it also exhibits peripheral vasodilatory and other smooth muscle relaxant activity to a lesser degree. The bronchodilatory action of dyphylline, as with other xanthines, is through to be mediated through competitive inhibition of phsphodiesterase with a resulting increase in cyclic AMP producing relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle.
Dyphylline is well tolerated and produces less nausea than aminophylline and other alkaline theophylline compounds when administered orally. Unlike the hydrolyzable salts of theophylline, dyphylline is not converted to free theophylline in vivo. It is absorbed rapidly in therapeutically active form and in healthy volunteers reaches a mean peak plasma concentration of 17.1 mcg/mL in approximately 45 minutes following a single oral dose of 1000 mg of dyphylline.
Dyphylline exerts its bronchodilatory effects directly and, unlike theophylline, is excreted unchanged by the kidneys without being metabolized by the liver. Because of this, dyphylline pharmacokinetics and plasma levels are not influenced by various factors that affect liver function and hepatic enzyme activity, such as smoking, age, or concomitant use of drugs which affect liver function.
The elimination half-life of dyphylline is approximately two hours (1.8 - 2.1 hr) and approximately 88% of a single oral dose can be recovered from the urine unchanged. The renal clearance would be correspondingly reduced in patients with impaired function. In anuric patients, the half-life may be increased to 3 to 4 times normal.
Dyphylline plasma levels are dose-related and generally predictable. The therapeutic range of plasma levels within which dyphylline can be expected to produce effective bronchodilation has not been determined.
Dyphylline plasma concentrations can be accurately determined using high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) or gas-liquid chromatography (GLC).
Guaifenesin is an expectorant whose action helps increase the output of then respiratory tract fluid to facilitate mucociliary clearance and removal of inspissated mucus.
Guaifenesin is an expectorant which increases respiratory tract fluid secretions and helps to loosed phlegm and bronchial secretions. By reducing the viscosity of secretions, guaifenesin increases the efficiency of the cough reflex and of cilliary action in removing accumulated secretion from the trachea and bronchi.
Guaifenesin is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is rapidly metabolized and excreted in the urine. Guaifenesin has a plasma half-life of one hour. The major urinary metabolite is p-(2-methoxyphenoxy) lactic acid.
INDICATION AND USAGE
For relief of acute bronchial asthma and for reversible bronchospasm associated with chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients or related compounds.
WARNINGS
This product is not indicated in the management of status asthmaticus, which is a serous medical emergency.
Although the relationship between plasma levels of dyphylline and appearance of toxicity is unknown, excessive doses may be expected to be associated with an increased risk of adverse effects.
PRECAUTIONS
General: Use this product with caution in patients with severe cardiac disease, hypertension, hypothyroidism, acute myocardial injury or peptic ulcer.
Drug Interactions: Synergism, between xanthine bronchodilators (e.g., theophylline), ephedrine and other sympathomimetic bronchodilators has been reported. This should be considered whenever these agents are prescribed concomitantly. Concurrent administration of dyphylline and probenecid, which competes for tubular secretion, has been shown to increase plasma half-life and dyphylline (See Clinical Pharmacology).
Carcinogenesis,Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility: No long-term animal studies have been performed with this product.
Pregnancy: Teratogenic effects - Pregnancy Category C, Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with this formulation. It is also not known whether this product can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. This medication should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers: Dyphylline is present in human milk at approximately twice the maternal plasma concentration. Caution should be exercised when this product is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness in children below the age of six have not been established. Use caution when administering to children six years of age or older.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
This formulation may cause nausea, headache, cardiac palpitation and CNS stimulation, Postprandial administration may help avoid gastric discomfort. The following adverse reactions which have been reported with other xanthine bronchodilators, and which have most often been related to excessive drug plasma levels, should be considered as potential adverse effects when dyphylline is administered.
Gastrointestinal: nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, hematemesis, diarrhea.
Central Nervous System: headache, irritability, restlessness, insomnia, hyperexcitability, agitation, muscle twitching, generalized clonic and tonic convulsions.
Cardiovascular: palpitation, tachycardia, extrasystoles, flushing, hypotension, circulatory failure, ventricular arrhythmias.
Respiratory: tachypnea.
Renal: albuminuria, gross and microscopic hematuria, diuresis.
Other: hyperglycemia, inappropriate ADH syndrome.
OVERDOSAGE
There have been no reports, in the literature, of overdosage with the product. However, the following information based on reports of theophylline overdosage are considered typical of the xanthine class of drugs and should be kept in mind.
Signs and Symptoms: Restlessness, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, insomina, irritability, and headache. Marked overdosage with resulting severe toxicity has produced agitation, severe vomiting, dehydration, excessive thirst, tinnitus, cardiac arrhythmias, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, and generalized clonic and tonic convulsions. Cardiovascular collapse has also occurred, with some fatalities. Seizures have occurred in some cases associated with very high theophylline plasma concentrations, without any premonitory symptoms of toxicity.
Treatment: There is no specific antidote for overdosage with drugs of the xanthine class. Symptomatic treatment and general supportive measures should be instituted with careful monitoring and maintenance of vital signs, fluids and electrolytes. The stomach should be emptied by inducing emesis if the patient is conscious and responsive, or by gastric lavage, taking care to protect against aspiration, especially in stuporous or comatose patients. Maintenance of an adequate airway is essential is case oxygen or assisted respiration is needed. Sympathomimetic agents should be avoided but sedatives such as short acting barbiturates may be useful.
Dyphylline is dialyzable and although not recommended as routine procedure in overdosage cases, hemodialysis may be of some benefit with severe intoxication is present or when the patient has not responded to general supportive and symptomatic treatment.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage should be individually titrated according to the severity of the condition and the response of the patient.
Usual Adult Dosage:1 tablet four times daily
Children Above Age Six:
1/2 tablet 3 to 4 times daily.
Not recommended for use in children under the age of six (see Precautions)
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN. IN CASE OF ACCIDENTAL OVERDOSE, SEEK PROFESSIONAL ASSISTANCE OR CONTACT A POISON CONTROL CENTER IMMEDIATELY.
HOW SUPPLIED
DYPHYLLINE AND GUAIFENESIN TABLETS, USP: round, white tablets scored on one side, and debossed on the scored side with "PL1" and "001". They are packaged in bottles of 100 tablets, NDC 60258-336-001
STORAGE: Tablets - Avoid excessive heat - above 40°C (104°F)

| DYPHYLLINE GG
dyphylline and guaifenesin tablet |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| unapproved drug other | 12/18/2006 | 06/30/2012 | |
| Labeler - Pegasus Laboratories (007124357) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Pegasus Laboratories | 007124357 | manufacture, analysis | |