ASCORBIC ACID
-
ascorbic acid injection, solution
American Therapeutic Medicines Inc.
----------
Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP(500 mg/mL)
Ascorbic Acid for Parenteral Use
Pharmacy Bulk Package, Not for Direct Infusion
DESCRIPTION
Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution of ascorbic acid prepared with the aid of sodium bicarbonate in water for injection. Ascorbic Acid is an essential water-soluble vitamin. Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP is indicated for injection by the intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous routes. Each mL contains 500 mg of ascorbic acid, and edetate disodium 0.025% (w/v). It also contains sodium bicarbonate and may contain sodium hydroxide to aid in preparation and pH adjustment. The pH is 5.5-7.0. It contains no bacteriostat, antimicrobial agent or added buffer. It must be protected from light.
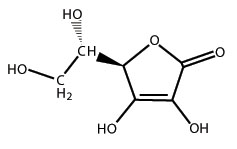
The chemical name of Ascorbic Acid is L-ascorbic acid. The molecular formula is C6H8O6. It occurs as white or slightly yellow crystals or powder. It has the following structural formula:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) has few strictly pharmacological actions. Administration in amounts greatly in excess of physiologic requirements causes no demonstrable effects. The vitamin is an essential coenzyme for collagen formation, tissue repair and synthesis of lipids and proteins. It acts both as a reducing agent and as an antioxidant and is necessary for many physiologic functions, e.g., metabolism of iron and folic acid, resistance to infection, and preservation of blood vessel integrity. Signs and symptoms of early vitamin C deficiency include malaise, irritability, arthralgia, hyperkeratosis of hair follicles, nosebleed, and petechial hemorrhages. Prolonged deficiency leads to clinical scurvy.
Ascorbic acid is normally present in both plasma and cells. The absorbed vitamin is ubiquitous in all body tissues. The highest concentrations are found in glandular tissue, the lowest in muscle and stored fat. Ascorbic acid is partially destroyed and partially excreted by the body. There is a renal threshold for vitamin C; the vitamin is excreted by the kidney in large amounts only when the plasma concentration exceeds this threshold, which is approximately 1.4 mg/100 mL. When the body is saturated with ascorbic acid, the plasma concentration will be about the same as that of the renal threshold; if further amounts are then administered, most of it escapes into the urine. When body tissues are not saturated and plasma concentration is low, administration of ascorbic acid results in little or no renal excretion.
A major route of metabolism of ascorbic acid involves its conversion to urinary oxalate, presumably through intermediate formation of its oxidized product, dehydroascorbic acid.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP is indicated for ascorbic acid deficiency. Parenteral ascorbic acid supplementation may be necessary in the treatment of scurvy for patients with gastric disorders, for patients with extensive injuries, for surgical patients and other who cannot take oral vitamins. Acute ascorbic acid deficiency may be associated with extensive injuries and other states of extreme stress. Vitamin C requirements are also significantly increased in certain diseases and conditions such as tuberculosis, hyperthyroidism, peptic ulcer, neoplastic disease, pregnancy and lactation.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Contraindicated in those persons who have a known hypersensitivity to any component of this preparation.
PRECAUTIONS
General Precautions:Excessivly rapid intravenous administration is to be avoided. Temporary faintness or dizziness may result.
Since high internal pressure may develop on long storage, precautions should be taken when withdrawing the solution from the vial.
Do not administer unless solution is clear and container is intact. Discard unused portion.
Laboratory tests: Because ascorbic acid is a strong reducing agent, it interferes with numerous laboratory tests based on oxidation-reduction reactions. Diabetics taking more than 500 mg of ascorbic acid daily may obtain false readings of their urinary glucose test. No exogenous ascorbic acid should be ingested for 48 to 72 hours before amine-dependent stool occult blood tests are conducted because false negative results may occur.
Drug Interactions: Acidification of the urine by ascorbic acid may cause precipitation of cysteine, urate or oxalate stones and will alter the excretion of certain other drugs administered concurrently. Large doses interfere with the anticoagulant effect of warfarin.
Ascorbic acid has on occasion been used as a specific antidote for symptoms resulting from interaction between ethanol and disulfiram (Antabuse), it may be expected that the concurrent administration of Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP will interfere with the effectiveness of disulfiram given to patients to encourage abstention from alcohol.
Usage in pregnancy: Pregnancy Category C (in doses greater than the RDA). Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with ascorbic acid injection. It is not known whether ascorbic acid injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nonteratogenic effects: High doses of vitamin C taken during pregnancy have been reported to cause scurvy in infants removed from this environment at birth.
Nursing mothers: Ascorbic acid is excreted in breast milk. Caution should be exercised when ascorbic acid injection is administered to a nursing woman, and excessive doses should be avoided.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Pain and swelling at the site of injection have been reported in some patients. Excessively rapid intravenous injection may result in temporary faintness or dizziness.
OVERDOSAGE
Due to loss in the urine of excessively high doses of parenterally administered ascorbic acid are wasteful after saturation of body tissues. Serious toxicity is very uncommon. In the event of severe or unusual untoward effects, ascorbic acid therapy should be terminated, pending further evaluation.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP is usually injected intramuscularly or subcutaneously. The solution has a pH of 5.5 to 7.0 and is not usually irritating to the tissues. The solution also may be injected intravenously, but a higher percentage of the drug will be excreted in the urine than when the subcutaneous or intramuscular route is employed. When administered intravenously, Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP should be slowly infused with large volume solutions. Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP should be added to such solutions shortly before venoclysis; any of the mixture remaining after administration should be discarded.
It is difficult to establish an exact dosage of ascorbic acid suitable for the treatment of deficiencies. In general, therapeutic doses should substantially exceed the recommended daily dietary allowances for healthy persons: Adult males 19 years of age and beyond, 90 mg; adult females 19 years of age and beyond, 75 mg; boys 14 to 18 years of age, 75 mg; girls 14 to 18 years of age, 65 mg; boys and girls 9-13 years of age, 45 mg; children 4-8 years of age, 25 mg; children 1-3 years of age, 15mg; infants through 12 months of age, 6 mg/kg/day. The blood level of ascorbic acid in normal persons ranges from 0.4 to 1.5 mg/100 mL.
The usual therapeutic parenteral dose ranges from 100 to 250 mg (0.2 to 0.5 mL of Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP, once or twice daily. If the deficiency is extreme, 1 to 2 g (2 to 4 mL) may be given. There is no appreciable danger from excessive dosage because superfluous amounts of the vitamin are rapidly excreted in the urine.
When extensive injuries are treated, ascorbic acid may be given if any doubt exists regarding previous nutrition with the vitamin. Patients with deep and extensive burns may require 200 to 500 mg (0.4 to 1.0 mL) daily to maintain measurable blood concentrations. Doses of 1 to 2 g daily for 4 to 7 days may be given before operation in gastrectomy patients. Similar doses also have been used postoperatively to aid wound healing following extensive surgical procedures.
Directions for Dispensing: The pharmacy bulk package is for use in a pharmacy admixture service only. A single entry through the vial closure should be made with a sterile dispensing set or transfer device. Multiple entries will increase the potential for microbial and particulate contamination. Use aseptic technique, preferably in a laminar flow environment. Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP contains no preservative. Any unused portion must be discarded within 6 hours.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, as the solution and container permit.
HOW SUPPLIED
Ascorbic Acid Injection, USP, 500 mg/mL, is available in trays of twenty-five, 50 mL, sterile, pharmacy bulk bottles, containing no preservative.
Protect from light.
Store in refrigerator 2oC – 8oC (36oF – 46oF). Do not allow to stand at room temperature before use. Failure to follow this caution may lead to excessive pressure inside the vial.
CAUTION: Pressure may develop within the vial during storage. Exercise caution when withdrawing.
Rx ONLY
Manufactured for:
American Therapeutic Medicines Inc. Santa Ana, CA 92704 U.S.A.
MD381-0034 rev:NEW 12/2007
VIAL LABEL

| ASCORBIC ACID
ascorbic acid injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| unapproved drug other | 03/01/2008 | ||
| Labeler - American Therapeutic Medicines Inc. (134632103) |