CALOMIST
-
cyanocobalamin spray, metered
Fleming & Company, Pharmaceuticals
----------
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Vitamin B12 Maintenance Therapy
CaloMist is indicated for maintenance of vitamin B12 concentrations after normalization with intramuscular vitamin B12 therapy in patients with vitamin B12 deficiency who have no nervous system involvement.
1.2 Important Limitations of Use
CaloMist has not been evaluated for the treatment of newly diagnosed vitamin B12 deficiency.
CaloMist is not suitable for use in the vitamin B12 absorption test (Schilling Test).
The effectiveness of CaloMist in patients with nasal pathology (e.g., nasal congestion, allergic rhinitis, upper respiratory infections) has not been determined. Treatment with CaloMist should be deferred until nasal symptoms have subsided [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dose
The recommended initial dose of CaloMist is one spray in each nostril once daily (25 mcg per nostril, total daily dose 50 mcg). The dose should be increased to one spray in each nostril twice daily (total daily dose 100 mcg) for patients with an inadequate response to once daily dosing.
The dosing of CaloMist and other intranasal medications should be separated by several hours, and these patients should have more frequent monitoring of vitamin B12 concentrations because of the potential for erratic absorption.
2.2 Priming (Activation) of Pump
The pump must be primed before the bottle is used for the first time. To prime the pump, place the nozzle between the first and second finger with the thumb on the bottom of the bottle. Pump the unit firmly and quickly then repeat this priming an additional 6 times for a total of 7 priming sprays. Now the nasal spray is ready for first-time use. If 5 or more days elapse since last use, the pump must be re-primed with two re-priming sprays.
Additional instructions are provided in the patient instruction sheet [see Patient Counseling Information (17.2)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CaloMist (cyanocobalamin, USP) Nasal Spray is a solution of cyanocobalamin, USP, for administration as a metered spray to the nasal mucosa. Each bottle of CaloMist contains 10.7 mL of a 25 mcg/0.1 mL solution of cyanocobalamin. The spray solution has a pH between 6.5 and 7.5. After initial priming, each spray delivers 25 mcg of cyanocobalamin. Each bottle will deliver 60 sprays for a total of thirty 50 mcg doses of CaloMist.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sensitivity to cobalt, vitamin B 12, or any component of this product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Laboratory Monitoring
Hematocrit, reticulocyte count, vitamin B12, folate, and iron levels should be obtained prior to treatment. All hematologic parameters, including vitamin B12 concentrations, should be normal before initiating treatment with CaloMist. Periodic monitoring of serum vitamin B12 concentrations must be obtained to confirm adequacy of therapy. Vitamin B12 concentrations and complete blood counts should be monitored one month after starting CaloMist and then at 3 to 6 month intervals thereafter. Patients with borderline-low vitamin B12 concentrations (<300 ng/L) should also undergo measurement of methylmalonic acid and homocysteine concentrations, which are more sensitive measures of vitamin B12 deficiency in this setting.
Patients with declining or abnormally low vitamin B 12 concentrations despite maximal doses of CaloMist should be switched back to intramuscular vitamin B12 injections. Vitamin B12 deficiency that is inadequately treated for longer than three months may produce irreversible neurological damage.
5.2 Use in Patients With Nasal Pathology
CaloMist has not been evaluated in patients with nasal pathology. Treatment with CaloMist should be deferred until nasal symptoms have subsided. Patients with chronic nasal symptoms or significant nasal pathology are not ideal candidates for intranasal vitamin B12 therapy. If CaloMist therapy is attempted in these patients, vitamin B12 concentrations should be monitored more frequently than in patients without nasal pathology because of the potential for erratic or blunted absorption.
5.3 Use in Patients with Leber’s Disease
Patients with early Leber’s disease (hereditary optic nerve atrophy) who were treated with cyanocobalamin suffered severe and swift optic atrophy. Cyanocobalamin should not be used in these patients.
5.4 Anaphylaxis and Angioedema
Anaphylactic shock, death, and angioedema were not reported in the CaloMist clinical trial but have been reported with parenteral vitamin B12 administration.
5.5 Megaloblastic Anemia
Megaloblastic anemia has many causes, including vitamin B12 deficiency and folate deficiency. Folic acid may result in a hematological response in patients with vitamin B12 deficiency, but will not prevent irreversible neurological manifestations. Vitamin B12 is not an appropriate treatment for folate deficiency.
Hypokalemia, thrombocytosis, and sudden death may occur when severe megaloblastic anemia is treated intensely with vitamin B12. Serum potassium and the platelet count should be carefully monitored in this setting.
5.6 Blunted Response to Vitamin B12 Therapy
Infections, uremia, concurrent iron or folic acid deficiency, and drugs with bone marrow suppressant properties (e.g., chloramphenicol) may blunt the therapeutic response to vitamin B12 products, including CaloMist.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below and in Table 1 reflect exposure in 25 subjects (age range 27-82 years; 17 women; 21 Caucasians) with vitamin B12 deficiency (12 with pernicious anemia, 4 secondary to gastrointestinal surgery, 9 with unknown cause) who received CaloMist 50 mcg daily for 8 weeks in an uncontrolled clinical trial. Prior to enrollment, all subjects were required to have normal vitamin B12 levels with intramuscular vitamin B12 injections. One patient who completed the study developed epistaxis on Day 12 of dosing and was noted to have irritation of the right nasal septum at study end. This patient had pre-existing allergic rhinitis and required a doubling of the CaloMist dose during the last week of the study because of declining vitamin B12 concentrations.
| Preferred Term | CaloMist
(N=25)n (%) |
| Arthralgia | 3 (12%) |
| Dizziness | 3 (12%) |
| Headache | 3 (12%) |
| Nasopharyngitis | 3 (12%) |
| Rhinorrhea | 3 (12%) |
| Bronchitis | 2 (8%) |
| Nasal Discomfort | 2 (8%) |
| Pain | 2 (8%) |
| Rash | 2 (8%) |
| Asthma | 1 (4%) |
| Back Pain | 1 (4%) |
| Cough | 1 (4%) |
| Epistaxis | 1 (4%) |
| Hypersomnia | 1 (4%) |
| Influenza Like Illness | 1 (4%) |
| Malaise | 1 (4%) |
| Pharyngolaryngeal Pain | 1 (4%) |
| Postnasal Drip | 1 (4%) |
| Procedural Pain | 1 (4%) |
| Pyrexia | 1 (4%) |
| Scab | 1 (4%) |
| Sinus Headache | 1 (4%) |
| Sinusitis | 1 (4%) |
| Tooth Abscess | 1 (4%) |
6.2 Experience with Parenteral Vitamin B12
The following adverse reactions have been reported with parenteral vitamin B12:
| Generalized: | Anaphylactic shock and death |
| Cardiovascular: | Pulmonary edema and congestive heart failure early in treatmentPeripheral vascular thrombosis |
| Hematological | Polycythemia vera |
| Gastrointestinal: | Mild transient diarrhea |
| Dermatological: | Itching; transitory exanthema |
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of cyanocobalamin. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Angioedema and angioedema-like reactions [See Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Most antibiotics, methotrexate, and pyrimethamine invalidate the vitamin B12 diagnostic blood assays.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with CaloMist. Although vitamin B12 is an essential vitamin and requirements are increased during pregnancy, it is not known whether CaloMist can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. CaloMist should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed. Adequate and well-controlled studies have not been conducted in pregnant women.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Although vitamin B12 is an essential vitamin and requirements are increased during lactation, it is not known whether CaloMist can cause harm to an infant when administered to a nursing woman. Vitamin B12 appears in the milk of nursing mothers in concentrations that approximate the mother's vitamin B12 blood level. Caution should be exercised when CaloMist is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Because CaloMist has not been studied in children, safety and effectiveness have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of CaloMist did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal/Hepatic Impairment
Patients with vitamin B12 deficiency and concurrent renal or hepatic disease may require increased doses or more frequent administration of vitamin B12 therapy.
11 DESCRIPTION
Cyanocobalamin is a synthetic form of vitamin B12 with activity equivalent to the endogenous form of vitamin B12. The chemical name is α-(5,6-dimethylbenzimidazolyl) cyanocobamide. The cobalt content is 4.35%. The molecular formula is C63H88CoN14O14P, which corresponds to a molecular weight of 1355.4 and the following structural formula:
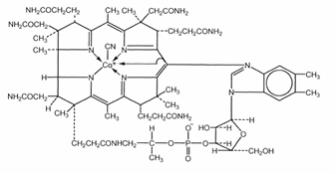
Cyanocobalamin occurs as dark red crystals, orthorhombic needles, or crystalline red powder and is very hygroscopic in the anhydrous form, and sparingly to moderately soluble in water (1:80). The pharmacologic activity of cyanocobalamin is destroyed by heavy metals (iron) and strong oxidizing or reducing agents (Vitamin C), but not by autoclaving for short periods of time (15-20 minutes) at 121°C. The vitamin B12 coenzymes are very unstable in light.
Each bottle of CaloMist contains cyanocobalamin, sodium chloride, sodium phosphate monobasic, benzyl alcohol, sodium hydroxide, and benzalkonium chloride in purified water with an attached spray pump unit.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Vitamin B12 is essential for growth, cell reproduction, hematopoiesis, and nucleoprotein and myelin synthesis. Rapidly dividing cells (e.g., epithelial cells, bone marrow, myeloid cells) have the greatest requirement for vitamin B12. In tissues, vitamin B12 is essential for the conversion of methylmalonate to succinate and for the synthesis of methionine from homocysteine. In the absence of vitamin B12, tetrahydrofolate cannot be regenerated from 5-methyl tetrahydrofolate, and functional folate deficiency occurs. Vitamin B12 also may be involved in sulfhydryl-activated enzyme systems associated with fat and carbohydrate metabolism and protein synthesis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In 24 vitamin B12 deficient patients who were stabilized on intramuscular (IM) vitamin B12 therapy, once daily intranasal dosing with CaloMist for 8 weeks resulted in serum vitamin B12 concentrations that were within the target range (>200 ng/L) and slightly higher than those seen 2 to 4 weeks after administration of IM vitamin B12 (see Figure 1 - average mean increase from Visit 1 to Visits 3-6 = 45 ng/L). Twenty-three of these 24 patients received 50 mcg of CaloMist daily for the duration of the trial; the remaining patient required doubling of the CaloMist dose from 50 mcg to 100 mcg daily during the last week of the study because of declining vitamin B12 concentrations. One of the 25 patients dosed with CaloMist was excluded from the efficacy analyses because a diagnosis of vitamin B12 deficiency could not be confirmed.
Figure 1. Mean Vitamin B12 Serum Levels Over 8 Weeks of Intranasal (IN) Vitamin B12 Dosing in 24 Subjects Stabilized on Intramuscular (IM) Vitamin B12
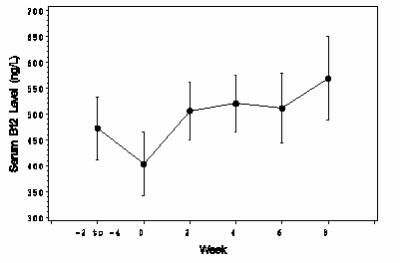
Notes:
- Weeks -2 to -4 correspond to 2 to 4 weeks post last IM injection
- CaloMist was initiated at Week 0
- Figure shows mean vitamin B12 serum levels with 95% confidence intervals.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Distribution
In the blood, vitamin B12 is bound to transcobalamin II (a specific B-globulin carrier protein) and is distributed to tissues and stored primarily in the liver and bone marrow.
Elimination
About 3-8 mcg of vitamin B12 is secreted into the gastrointestinal tract daily via the bile. In subjects with sufficient intrinsic factor, all but about 1 mcg is reabsorbed. When vitamin B12 is administered in doses that saturate the binding capacity of plasma proteins and the liver, the unbound vitamin B12 is rapidly eliminated in the urine. Retention of vitamin B12 in the body is dose-dependent.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
There are no long-term studies in animals that have evaluated the carcinogenic potential of any of the vitamin B12 products, including CaloMist. There is no evidence from long-term use in patients with pernicious anemia that vitamin B12 is carcinogenic. Pernicious anemia is associated with an increased incidence of carcinoma of the stomach, but this malignancy has been attributed to the underlying pathology of pernicious anemia and not to treatment with vitamin B12.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
CaloMist is available as a metered dose spray in 30 mL plastic bottles containing 10.7 mL of solution. CaloMist is available in a dosage strength of 25 mcg cyanocobalamin, USP, per actuation (0.1 mL/actuation). CaloMist is provided in a carton containing one bottle of nasal spray solution affixed with a nasal spray pump, a package insert, and a patient instruction sheet. One bottle delivers thirty 50 mcg doses (60 sprays) (NDC 0256-0203-01).
Storage
Protect from light. Store upright at a controlled temperature of 15 to 30°C (59 to 86°F).
Protect from freezing.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
[See FDA-approved Patient Labeling (17.2)]
17.1 Important Information for Patients
Patients with a chronic underlying cause of vitamin B12 deficiency will require indefinite administration of a vitamin B12 product, such as CaloMist. Noncompliance or inadequate treatment with vitamin B12 therapy may result in recurrence of anemia and the development or worsening of irreversible neurological damage.
The dosing of CaloMist and other intranasal medications should be separated by several hours.
Vitamin B12 concentrations should be monitored one month after CaloMist initiation or dose change and every 3-6 months thereafter.
Careful instructions on the priming of the actuator and nasal administration of CaloMist should be given to the patient, and the procedures for use should be demonstrated.
17.2 Patient Instruction Sheet
Instructions for Using CaloMist. Read the following instructions carefully before using CaloMist.
- Use CaloMist as directed by your doctor.
NOTE: CaloMist is prefilled to give 30 doses (60 sprays of medicine). One dose is one spray in each nostril once a day.
CaloMist Pump Priming: Before you use the medicine for the first time the nasal spray pump unit must be readied (primed).
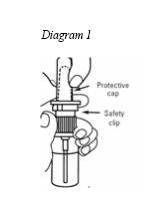
1. Hold the nasal spray bottle upright with your index finger on top of one of the two arms of the pump. Remove the clear protective cap from the top of the nozzle. (See Diagram 1)
2. Remove the safety clip from the nasal spray pump. (See Diagram 1)
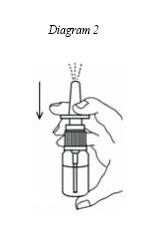
3. While holding the nasal spray bottle upright with your index and middle fingers on the two side arms of the pump, and your thumb on the bottom of the bottle, press the arms down firmly and quickly. (See Diagram 2)
4. Repeat Step 3, 6 more times for a total of 7 priming sprays. You should see a full spray of medicine with the 7 th priming spray. (See Diagram 2)
NOTE: You must prime CaloMist with two re-priming sprays if you do not use for five days or more.
Your CaloMist is now ready to use.

1. Blow your nose gently to clear both nostrils. (See Diagram 3)
2. Hold the nasal spray bottle upright with your first and second fingers on the two side arms of the pump. Place your thumb on the bottom of the bottle. (See Diagram 4)
3. Gently insert the nasal spray pump into one nostril (about ½ inch), pointing the tip towards the back of the nose. (See Diagram 4)
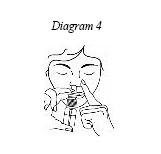
4. With your other hand (the one not holding the bottle) use a finger to gently push close your other nostril (the one without a spray pump inserted). (See Diagram 4)
5. Tilt your head forward. Firmly and quickly press down the arms of the nasal spray bottle.
6. Sniff in gently during and right after a spray and return your head to an upright position. Repeat these steps for the other nostril.
7. After use, wipe the nozzle of the nasal spray pump with a clean tissue. Replace the safety clip and clear cover on the nasal spray pump.
8. Store CaloMist upright at room temperature, 15° - 30° C (59° - 86° F). Do not freeze.
Discard CaloMist after 30 doses (60 sprays).
- Unscrew the cap. Rinse the bottle and pump assembly under a water faucet.
- Dispose of all parts in a trashcan.
Keep CaloMist and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Manufactured by:
Fleming Pharmaceuticals
St. Louis County, MO 63026 USA
calomist@flemingpharma.com
1-800-343-0164
Principal Display Panel - carton
principal display panel - carton
Principal Display Panel - bottle

principal display panel - bottle
| CALOMIST
cyanocobalamin spray, metered |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA022102 | 10/01/2007 | |
| Labeler - Fleming & Company, Pharmaceuticals (006491351) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Fleming & Company, Pharmaceuticals | 006491351 | MANUFACTURE, ANALYSIS, RELABEL, REPACK | |