CUVPOSA- glycopyrrolate solution
Shionogi Pharma, Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use CUVPOSA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CUVPOSA.
CUVPOSA (glycopyrrolate) oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 1961 INDICATIONS AND USAGECUVPOSA is an anticholinergic indicated to reduce chronic severe drooling in patients aged 3-16 with neurologic conditions associated with problem drooling (e.g., cerebral palsy). (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS1 mg/5 mL, oral solution in 16 ounce bottles. (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSThe most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥30%) are dry mouth, vomiting, constipation, flushing, and nasal congestion. (6) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Shionogi Drug Safety Department at 1-800-849-9707 ext. 1454 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSSee 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling. Revised: 8/2014 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CUVPOSA is indicated to reduce chronic severe drooling in patients aged 3 to 16 years with neurologic conditions associated with problem drooling (e.g. cerebral palsy).
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
CUVPOSA must be measured and administered with accurate measuring device [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Initiate dosing at 0.02 mg/kg orally three times daily and titrate in increments of 0.02 mg/kg every 5-7 days based on therapeutic response and adverse reactions. The maximum recommended dosage is 0.1 mg/kg three times daily not to exceed 1.5-3 mg per dose based upon weight. For greater detail, see Table 1.
During the four-week titration period, dosing can be increased consistent with the recommended dose titration schedule while ensuring that the anticholinergic adverse events are tolerable. Prior to each increase in dose, review the tolerability of the current dose level with the patient's caregiver.
CUVPOSA should be dosed at least one hour before or two hours after meals.
The presence of high fat food reduces the oral bioavailability of CUVPOSA if taken shortly after a meal [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Weight | Dose Level 1 | Dose Level 2 | Dose Level 3 | Dose Level 4 | Dose Level 5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kg | lb | (~0.02 mg/kg) | (~0.04 mg/kg) | (~0.06 mg/kg) | (~0.08 mg/kg) | (~0.1 mg/kg) | |||||
| 13-17 | 27-38 | 0.3 mg | 1.5 mL | 0.6 mg | 3 mL | 0.9 mg | 4.5 mL | 1.2 mg | 6 mL | 1.5 mg | 7.5 mL |
| 18-22 | 39-49 | 0.4 mg | 2 mL | 0.8 mg | 4 mL | 1.2 mg | 6 mL | 1.6 mg | 8 mL | 2.0 mg | 10 mL |
| 23-27 | 50-60 | 0.5 mg | 2.5 mL | 1.0 mg | 5 mL | 1.5 mg | 7.5 mL | 2.0 mg | 10 mL | 2.5 mg | 12.5 mL |
| 28-32 | 61-71 | 0.6 mg | 3 mL | 1.2 mg | 6 mL | 1.8 mg | 9 mL | 2.4 mg | 12 mL | 3.0 mg | 15 mL |
| 33-37 | 72-82 | 0.7 mg | 3.5 mL | 1.4 mg | 7 mL | 2.1 mg | 10.5 mL | 2.8 mg | 14 mL | 3.0 mg | 15 mL |
| 38-42 | 83-93 | 0.8 mg | 4 mL | 1.6 mg | 8 mL | 2.4 mg | 12 mL | 3.0 mg | 15 mL | 3.0 mg | 15 mL |
| 43-47 | 94-104 | 0.9 mg | 4.5 mL | 1.8 mg | 9 mL | 2.7 mg | 13.5 mL | 3.0 mg | 15 mL | 3.0 mg | 15 mL |
| ≥48 | ≥105 | 1.0 mg | 5 mL | 2.0 mg | 10 mL | 3.0 mg | 15 mL | 3.0 mg | 15 mL | 3.0 mg | 15 mL |
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CUVPOSA is available as a 1 mg/5 mL clear, cherry-flavored solution for oral administration in 16 ounce bottles.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
CUVPOSA is contraindicated in:
- Patients with medical conditions that preclude anticholinergic therapy (e.g., glaucoma, paralytic ileus, unstable cardiovascular status in acute hemorrhage, severe ulcerative colitis, toxic megacolon complicating ulcerative colitis, myasthenia gravis).
- Patients taking solid oral dosage forms of potassium chloride. The passage of potassium chloride tablets through the gastrointestinal (GI) tract may be arrested or delayed with coadministration of CUVPOSA.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Constipation or Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction
Constipation is a common dose-limiting adverse reaction which sometimes leads to glycopyrrolate discontinuation [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Assess patients for constipation, particularly within 4-5 days of initial dosing or after a dose increase. Intestinal pseudo-obstruction has been reported and may present as abdominal distention, pain, nausea or vomiting.
5.2 Incomplete Mechanical Intestinal Obstruction
Diarrhea may be an early symptom of incomplete mechanical intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. If incomplete mechanical intestinal obstruction is suspected, discontinue treatment with CUVPOSA and evaluate for intestinal obstruction.
5.3 High Ambient Temperatures
In the presence of high ambient temperature, heat prostration (fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating) can occur with use of anticholinergic drugs such as CUVPOSA. Advise parents/caregivers to avoid exposure of the patient to hot or very warm environmental temperatures.
5.4 Operating Machinery or an Automobile
CUVPOSA may produce drowsiness or blurred vision. As appropriate for a given age, warn the patient not to engage in activities requiring mental alertness such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery, or performing hazardous work while taking CUVPOSA.
5.5 Anticholinergic Drug Effects
Use CUVPOSA with caution in patients with conditions that are exacerbated by anticholinergic drug effects including:
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Renal disease
- Ulcerative colitis – Large doses may suppress intestinal motility to the point of producing a paralytic ileus and for this reason may precipitate or aggravate "toxic megacolon," a serious complication of the disease.
- Hyperthyroidism
- Coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, cardiac tachyarrhythmias, tachycardia, and hypertension
- Hiatal hernia associated with reflux esophagitis, since anticholinergic drugs may aggravate this condition
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Constipation or intestinal pseudo-obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Incomplete mechanical intestinal obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
The most common adverse reactions reported with CUVPOSA are dry mouth, vomiting, constipation, flushing, and nasal congestion.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to CUVPOSA in 151 subjects, including 20 subjects who participated in a 8-week placebo-controlled study (Study 1) and 137 subjects who participated in a 24-week open-label study (six subjects who received CUVPOSA in the placebo-controlled study and 131 new subjects).
Table 2 presents adverse reactions reported by ≥ 15% of CUVPOSA-treated subjects from the placebo-controlled clinical trial.
| CUVPOSA (N=20) n (%) | Placebo (N=18) n (%) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Dry Mouth | 8 (40%) | 2 (11%) |
| Vomiting | 8 (40%) | 2 (11%) |
| Constipation | 7 (35%) | 4 (22%) |
| Flushing | 6 (30%) | 3 (17%) |
| Nasal Congestion | 6 (30%) | 2 (11%) |
| Headache | 3 (15%) | 1 (6%) |
| Sinusitis | 3 (15%) | 1 (6%) |
| Upper Respiratory Tract Infection | 3 (15%) | 0 |
| Urinary Retention | 3 (15%) | 0 |
The following adverse reactions occurred at a rate of <2% of patients receiving CUVPOSA in the open-label study.
- Gastrointestinal: Abdominal distention, abdominal pain, stomach discomfort, chapped lips, flatulence, retching, dry tongue
- General Disorders: Irritability, pain
- Infections: Pneumonia, sinusitis, tracheostomy infection, upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection
- Investigations: Heart rate increased
- Metabolism and Nutrition: Dehydration
- Nervous System: Headache, convulsion, dysgeusia, nystagmus
- Psychiatric: Agitation, restlessness, abnormal behavior, aggression, crying, impulse control disorder, moaning, mood altered
- Respiratory: Increased viscosity of bronchial secretion, nasal congestion, nasal dryness
- Skin: Dry skin, pruritus, rash
- Vascular: Pallor
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of other formulations of glycopyrrolate for other indications. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Additional adverse reactions identified during postapproval use of glycopyrrolate tablets include: loss of taste and suppression of lactation.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drugs Affected by Reduced GI Transit Time
Glycopyrrolate reduces GI transit time, which may result in altered release of certain drugs when formulated in delayed- or controlled-release dosage forms.
- The passage of potassium chloride tablets through the GI tract may be arrested or delayed with coadministration of glycopyrrolate. Solid dosage forms of potassium chloride are contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)].
- Digoxin administered as slow dissolution oral tablets may have increased serum levels and enhanced action when administered with glycopyrrolate. Monitor patients receiving slow dissolution digoxin for increased action if glycopyrrolate is coadministered regularly. Consider the use of other oral dosage forms of digoxin (e.g., elixir or capsules).
Amantadine
The anticholinergic effects of glycopyrrolate may be increased with concomitant administration of amantadine. Consider decreasing the dose of glycopyrrolate during coadministration of amantadine.
Drugs Whose Plasma Levels May be Increased by Glycopyrrolate
Coadministration of glycopyrrolate may result in increased levels of certain drugs.
- Atenolol's bioavailability may be increased with coadministration of glycopyrrolate. A reduction in the atenolol dose may be needed.
- Metformin plasma levels may be elevated with coadministration of glycopyrrolate, increasing metformin's pharmacologic and toxic effects. Monitor clinical response to metformin with concomitant glycopyrrolate administration; consider a dose reduction of metformin if warranted.
Drugs Whose Plasma Levels May be Decreased by Glycopyrrolate
Coadministration of glycopyrrolate may result in decreased levels of certain drugs.
- Haloperidol's serum levels may be decreased when coadministered with glycopyrrolate, resulting in worsening of schizophrenic symptoms, and development of tardive dyskinesia. Closely monitor patients if coadministration cannot be avoided.
- Levodopa's therapeutic effect may be reduced with glycopyrrolate administration. Consider increasing the dose of levodopa.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with glycopyrrolate. It is also not known whether glycopyrrolate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. CUVPOSA should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when CUVPOSA is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
CUVPOSA was evaluated for chronic severe drooling in patients aged 3 to 16 years with neurologic conditions associated with problem drooling. CUVPOSA has not been studied in subjects under the age of 3 years.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Because glycopyrrolate is largely renally eliminated, CUVPOSA should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment (see Clinical Pharmacology 12.3).
10 OVERDOSAGE
Because glycopyrrolate is a quaternary amine which does not easily cross the blood-brain barrier, symptoms of glycopyrrolate overdosage are generally more peripheral in nature rather than central compared to other anticholinergic agents. In case of accidental overdose, therapy may include:
- Maintaining an open airway, providing ventilation as necessary.
- Managing any acute conditions such as hyperthermia, coma and or seizures as applicable, and managing any jerky myoclonic movements or choreoathetosis which may lead to rhabdomyolysis in some cases of anticholinergic overdosage.
- Administering a quaternary ammonium anticholinesterase such as neostigmine to help alleviate peripheral anticholinergic effects such as anticholinergic induced ileus.
- Administering activated charcoal orally as appropriate.
11 DESCRIPTION
CUVPOSA is an anticholinergic drug available as an oral solution containing 1 mg glycopyrrolate per 5 mL. The chemical name for glycopyrrolate is pyrrolidinium, 3-[(cyclopentylhydroxyphenylacetyl)oxy]-1,1-dimethyl-, bromide. The chemical structure is:
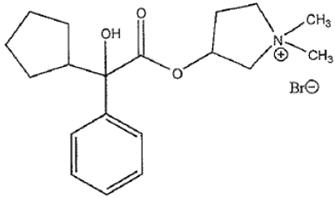
The empirical formula for CUVPOSA is C19H28BrNO3 and the molecular weight is 398.33. The inactive ingredients in CUVPOSA are: citric acid, glycerin, natural and artificial cherry flavor, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, saccharin sodium, sodium citrate, sorbitol solution, and purified water.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Glycopyrrolate is a competitive inhibitor of acetylcholine receptors that are located on certain peripheral tissues, including salivary glands. Glycopyrrolate indirectly reduces the rate of salivation by preventing the stimulation of these receptors.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Glycopyrrolate inhibits the action of acetylcholine on salivary glands thereby reducing the extent of salivation.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
In a parallel study of children (n=6 per group) aged 7-14 years undergoing intraocular surgery receiving either intravenous (IV) or oral glycopyrrolate as a premedication, the mean absolute bioavailability of glycopyrrolate tablets was low (approximately 3%) and highly variable among subjects (range 1.3 to 13.3%). A similar pattern of low and variable relative bioavailability is seen in adults.
Analysis of population pharmacokinetic data from normal adults and children with cerebral palsy associated chronic moderate to severe drooling failed to demonstrate linear pharmacokinetics across the dose range. In the same analysis, population estimates of the apparent oral clearance (scaled by weight in children and adults) ranged from 5.28 ~ 38.95 L/hr/kg for healthy adults and 8.07 ~ 25.65 L/hr/kg for patients with cerebral palsy, a reflection of the low and highly variable oral bioavailability of glycopyrrolate.
Absorption of CUVPOSA (fasting) was compared to that of a marketed glycopyrrolate oral tablet. The Cmax after oral solution administration was 23% lower compared to tablet administration and the AUC0-inf was 28% lower after oral solution administration. Mean Cmax after oral solution administration in the fasting state was 0.318 ng/mL, and mean AUC0-24 was 1.74 ng.hr/mL. Mean time to maximum plasma concentration for CUVPOSA was 3.1 hours, and mean plasma half-life was 3.0 hours.
In healthy adults, a high fat meal was shown to significantly affect the absorption of glycopyrrolate oral solution (10 mL, 1 mg/5 mL). The mean Cmax under fed high fat meal conditions was approximately 74% lower than the Cmax observed under fasting conditions. Similarly, mean AUC0-T was reduced by about 78% by the high fat meal compared with the fasting AUC0-T. A high fat meal markedly reduces the oral bioavailability of CUVPOSA. Therefore, CUVPOSA should be dosed at least one hour before or two hours after meals. Pharmacokinetic results (mean ± SD) are described in Table 3.
| Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (hrs) | AUC0-T
(ng∙hr/mL) | AUC0-Inf
(ng∙hr/mL) | T½ (hrs) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
| Fasting | 0.318 | 3.10 | 1.74 | 1.81 | 3.0 |
| (n=37) | ± 0.190 | ± 1.08 | ± 1.07 | ± 1.09 | ± 1.2 |
| Fed | 0.084 | 2.60 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 3.2 |
| (n=36) | ± 0.081 | ± 1.12 | ± 0.14 | ± 0.13* | ±1.1* |
Distribution
After IV administration, glycopyrrolate has a mean volume of distribution in children aged 1 to 14 years of approximately 1.3 to 1.8 L/kg, with a range from 0.7 to 3.9 L/kg. In adults aged 60-75 years, the volume of distribution was lower (0.42 L/kg +/- 0.22).
Metabolism
In adult patients who underwent surgery for cholelithiasis and were given a single IV dose of tritiated glycopyrrolate, approximately 85% of total radioactivity was excreted in urine and < 5% was present in T-tube drainage of bile. In both urine and bile, > 80% of the radioactivity corresponded to unchanged drug. These data suggest a small proportion of IV glycopyrrolate is excreted as one or more metabolites.
Elimination
Approximately 65-80% of an IV glycopyrrolate dose was eliminated unchanged in urine in adults. In two studies, after IV administration to pediatric patients ages 1-14 years, mean clearance values ranged from 1.01- 1.41 L/kg/hr (range 0.32 – 2.22 L/kg/hr). In adults, IV clearance values were 0.54 ± 0.14 L/kg/hr.
Pediatrics
The estimated apparent clearance of glycopyrrolate from a population pharmacokinetic analysis (scaled by weight in children and adults) of oral and IV data was found to be 13.2 L/hr/Kg or 92 7L/hr for a typical 70 kg subject. In the same population based analysis, gender was not identified as having an effect on either glycopyrrolate clearance or systemic exposure.
Gender
Population pharmacokinetic evaluation of adults and children administered IV or oral glycopyrrolate identified no effect of gender on glycopyrrolate clearance or systemic exposure.
Renal Impairment
In one study, glycopyrrolate 4 mcg/kg was administered intravenously in uremic patients undergoing renal transplantation surgery. Mean AUC (10.6 mcg∙h/L), mean plasma clearance (0.43 L/hr/kg) and mean 3-hour urinary excretion (0.7%) for glycopyrrolate were significantly different than those of control patients (3.73 µg∙h/L, 1.14 L/hr/kg, and 50%, respectively). These results suggest that elimination of glycopyrrolate is severely impaired in patients with renal failure.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of glycopyrrolate.
Glycopyrrolate did not elicit any genotoxic effects in the Ames mutagenicity assay, the human lymphocyte chromosome aberration assay, or the micronucleus assay.
Glycopyrrolate has not been evaluated for potential to impair fertility.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
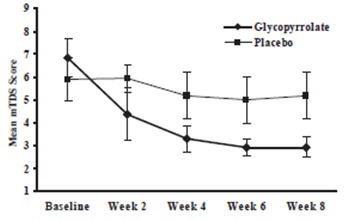
CUVPOSA was evaluated in a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel, eight-week study for the control of pathologic drooling in children (Study 1). The study enrolled 38 subjects aged 3-23 years; thirty-six subjects were aged 3-16 years and two patients were greater than 16 years. The subjects were male or female, weighed at least 13 kg (27 lbs), and had cerebral palsy, mental retardation, or another neurologic condition associated with problem drooling defined as drooling in the absence of treatment so that clothing became damp on most days (approximately five to seven days per week). Subjects were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive CUVPOSA or placebo. Doses of study medication were titrated over a 4-week period to optimal response beginning at 0.02 mg/kg given three times a day increasing doses in increments of approximately 0.02 mg/kg three times per day every 5-7 days, not to exceed the lesser of approximately 0.1 mg/kg three times per day or 3 mg three times per day.
Subjects were evaluated on the 9-point modified Teacher's Drooling Scale (mTDS), which is presented below. The mTDS evaluations were recorded by parents/caregivers 3 times daily approximately two hours post-dose on evaluation days during pre-treatment baseline and at Weeks 2, 4, 6 and 8 of therapy.
Modified Teacher's Drooling Scale
1 = Dry: never drools
2 = Mild: only the lips are wet; occasionally
3 = Mild: only the lips are wet; frequently
4 = Moderate: wet on lips and chin; occasionally
5 = Moderate: wet on the lips and chin; frequently
6 = Severe: drools to the extent that clothing becomes damp; occasionally
7 = Severe: drools to the extent that clothing becomes damp; frequently
8 = Profuse: clothing, hands, tray and objects become wet; occasionally
9 = Profuse: clothing, hands, tray and objects become wet; frequently
Responders were defined as subjects with at least a 3-point reduction in mean daily mTDS scores from baseline to Week 8. Table 4 presents the proportion of responders at Week 8 and Figure 1 presents mean mTDS values from baseline through Week 8.
| CUVPOSA Group (N=20) | Placebo Group (N=18) |
|---|---|
| 15/20 (75%) | 2/18 (11%) |
Figure 1. Mean (± 2 Standard Errors) mTDS Scores
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
NDC 59630-206-16: 1 mg/5 mL clear, cherry-flavored solution; 16 oz. bottle.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling.
- Advise parent/caregivers to measure CUVPOSA with an accurate measuring device. A household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device. Parents/caregivers should use a dosing cup available in pharmacies to accurately measure the correct milliliter dose for the patient. An oral syringe, also available in pharmacies, should be used to dispense CUVPOSA into the child's mouth from the cup. A pharmacist can recommend an appropriate measuring device and can provide instructions for measuring the correct dose.
- Administering CUVPOSA with a high fat meal substantially reduces the amount of glycopyrrolate absorbed. Administer CUVPOSA at least one hour before or two hours after meals.
- CUVPOSA is started at a low dose and gradually titrated over a period of weeks based on therapeutic response and adverse reactions. Parents/caregivers should not increase the dose without the physician's permission.
- Common adverse reactions from CUVPOSA include overly dry mouth, constipation, vomiting, flushing of the skin or face, and urinary retention. Side effects can sometimes be difficult to detect in some patients with neurologic problems who cannot adequately communicate how they feel. If side effects become troublesome after increasing a dose, decrease the dose to the prior one and contact your physician.
- Constipation is the most common side effect of glycopyrrolate, and if constipation occurs, stop administering glycopyrrolate to the patient and call a healthcare practitioner.
- Inability of the patient to urinate, dry diapers or undergarments, irritability or crying may be signs of urinary retention, and if urinary retention occurs, parents/caregivers should stop administering glycopyrrolate and call their healthcare practitioner.
- If the patient develops a skin rash, hives or an allergic reaction, parents/caregivers should stop administering glycopyrrolate and call their healthcare practitioner as this could be a sign of hypersensitivity to this product.
- Drugs like glycopyrrolate can reduce sweating, and if the patient is in a hot environment and flushing of the skin occurs, this may be due to overheating. Parents/caregivers should be advised to avoid exposure of the patient to hot or very warm environmental temperatures to avoid overheating and the possibility of heat exhaustion or heat stroke.
Manufactured by:
Mikart, Inc.
Atlanta, GA 30318
Manufactured for:
SHIONOGI PHARMA, INC.
Atlanta, GA 30328
GLY-PI-01
PATIENT and CAREGIVER INFORMATION
CUVPOSA (glycopyrrolate) Oral Solution
Please read the Patient and Caregiver Information that comes with CUVPOSA before you start giving it to your child, and each time you get a refill. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your child's medical condition or treatment.
What is CUVPOSA?
CUVPOSA is a prescription medicine used in children with medical conditions that cause too much (abnormal) drooling.
Who should not take CUVPOSA?
Do not give CUVPOSA to anyone who:
- has problems urinating
- has a bowel problem called paralytic ileus
- lacks normal bowel tone or tension
- has severe ulcerative colitis or certain other serious bowel problems with severe ulcerative colitis
- has myasthenia gravis
What should I tell the doctor before giving CUVPOSA to my child?
Tell your doctor if your child:
- has any allergies
- has any stomach or bowel problems, including ulcerative colitis
- has any problems with constipation
- has thyroid problems
- has high blood pressure
- has heart problems or abnormal heart beats
- has a hiatal hernia with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- has any eye problems
- has any problems urinating
- has any other medical conditions
- is pregnant or plans to become pregnant. It is not known if CUVPOSA can harm an unborn baby.
- is breastfeeding or plans to breastfeed. It is not known if CUVPOSA passes into breast milk and if it can harm the baby.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines that your child takes, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicine may affect the way CUVPOSA works, and CUVPOSA may affect how some other medicines work.
How should I give CUVPOSA?
- Give CUVPOSA exactly as prescribed by your child's doctor.
- Give CUVPOSA 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals.
- Your doctor will tell you how much (milliliters or mLs) of CUVPOSA to give your child.
- Do not change the dose of CUVPOSA unless your doctor tells you to.
- You must measure the dose of CUVPOSA before giving it to your child. Use a specially marked dose measuring cup (available at most pharmacies) to measure the right dose of CUVPOSA.
- To help make sure that your child swallows the dose, you should use an oral syringe to give the child each dose of CUVPOSA, after you measure the dose needed with a dose measuring cup. Oral syringes are also available at most pharmacies.
- If you have questions about how to measure the dose or how to use an oral syringe, ask your pharmacist or doctor.
- The dose of CUVPOSA that is needed to control drooling may be different for each child. CUVPOSA is usually started at a low dose, and slowly increased as directed by your doctor. This slow increase in dose continues until the best dose for your child is reached, to control drooling.
- During this time it is important to stay in close contact with your child's doctor, and tell the doctor about any side effects that your child has. See "What are the possible side effects of CUVPOSA?"
What should I avoid while taking CUVPOSA?
- CUVPOSA may cause sleepiness or blurred vision. Do not drive a car, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities while taking CUVPOSA.
- Avoid overheating. See "What are the possible side effects of CUVPOSA?"
What are the possible side effects of CUVPOSA?
CUVPOSA can cause serious side effects including:
- Constipation. Constipation is common with CUVPOSA. Tell your doctor if your child strains with bowel movements, goes longer between bowel movements, can not have a bowel movement, or their stomach is firm and large. The dose of CUVPOSA may need to be decreased or stopped.
- Diarrhea and intestinal blockage. Diarrhea can be an early symptom of a blockage in the intestine. This is especially true if your child has a colostomy or ileostomy. Tell your doctor if your child has any diarrhea while taking CUVPOSA.
-
Problems with control of body temperature (overheating or heat stroke). CUVPOSA can cause your child to sweat less. Your child can become overheated, and develop heat stroke if they are in an area that is very hot. Avoid overheating. Call your doctor right away if your child becomes sick and has any of these symptoms of heatstroke:
- hot, red skin
- decreased alertness or passing out (unconsciousness)
- fast, weak pulse
- fast, shallow breathing
- increased body temperature (fever)
The most common side effects of CUVPOSA include:
- dry mouth
- vomiting
- flushing of the face or skin
- nasal congestion
- headache
- swollen sinuses (sinusitis)
- upper respiratory tract infection
- problems urinating, difficulty starting urination
Tell your doctor if your child has any side effect that concerns you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of CUVPOSA.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store CUVPOSA?
Store CUVPOSA between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep CUVPOSA out of the reach of children.
General information about CUVPOSA:
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use CUVPOSA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give CUVPOSA to other people even if they have the same condition. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about CUVPOSA. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about CUVPOSA that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to: www.cuvposa.com or call 1-800-849-9707 ext.1454.
What are the ingredients in CUVPOSA?
Active Ingredient: glycopyrrolate
Inactive Ingredients: citric acid glycerin, natural and artificial cherry flavor, methylparaben, propylene glycol, propylparaben, saccharin sodium, sodium citrate, sorbitol solution, and purified water
Issued July 2010
Manufactured by:
Mikart, Inc.
Atlanta, GA 30318
Manufactured for:
SHIONOGI PHARMA, INC.
Atlanta, GA 30328
GLY-PPI-01 Rev 07/2010
| CUVPOSA
glycopyrrolate solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Shionogi Pharma, Inc. (949127786) |
