PREMPHASE
-
conjugated estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate
PREMPRO
-
estrogens, conjugated and
medroxyprogesterone acetate tablet, sugar coated
Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc.
----------
PREMPRO®(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
PREMPHASE®
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
Rx only
WARNINGS
CARDIOVASCULAR AND OTHER RISKS
Estrogens plus progestins should not be used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular disorders and Dementia.)
The estrogen plus progestin substudy of the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) reported increased risks of myocardial infarction, stroke, invasive breast cancer, pulmonary emboli, and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 5.6 years of treatment with daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE 0.625 mg) combined with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA 2.5 mg), relative to placebo. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular disorders and Malignant neoplasms, Breast cancer.)
The estrogen alone substudy of the WHI reported increased risks of stroke and DVT in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 6.8 years and 7.1 years, respectively, of treatment with daily CE 0.625 mg, relative to placebo. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular disorders.)
The Women's Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS), a substudy of WHI, reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age or older during 4 years of treatment with daily CE 0.625 mg combined with MPA 2.5 mg and during 5.2 years of treatment with daily CE 0.625 mg alone, relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women. (See CLINICAL STUDIES, and WARNINGS, Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use.)
In the absence of comparable data, these risks should be assumed to be similar for other doses of CE and MPA and other combinations and dosage forms of estrogens and progestins. Because of these risks, estrogens with or without progestins should be prescribed at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
DESCRIPTION
PREMPRO® 0.3 mg/1.5 mg therapy consists of a single tablet containing 0.3 mg of the conjugated estrogens (CE) found in Premarin® tablets and 1.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) for oral administration.
PREMPRO 0.45 mg/1.5 mg therapy consists of a single tablet containing 0.45 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 1.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate for oral administration.
PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg therapy consists of a single tablet containing 0.625 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 2.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate for oral administration.
PREMPRO 0.625 mg/5 mg therapy consists of a single tablet containing 0.625 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate for oral administration.
PREMPHASE® therapy consists of two separate tablets, a maroon Premarin tablet containing 0.625 mg of conjugated estrogens that is taken orally on days 1 through 14 and a light-blue tablet containing 0.625 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate that is taken orally on days 15 through 28.
Premarin (conjugated estrogens tablets, USP) for oral administration contains a mixture obtained exclusively from natural sources, occurring as the sodium salts of water-soluble estrogen sulfates blended to represent the average composition of material derived from pregnant mares' urine. It is a mixture of sodium estrone sulfate and sodium equilin sulfate. It contains as concomitant components, as sodium sulfate conjugates, 17 α-dihydroequilin, 17 α-estradiol and 17 β‑dihydroequilin.
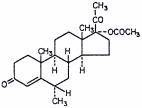
Medroxyprogesterone acetate is a derivative of progesterone. It is a white to off-white, odorless, crystalline powder, stable in air, melting between 200°C and 210°C. It is freely soluble in chloroform, soluble in acetone and in dioxane, sparingly soluble in alcohol and in methanol, slightly soluble in ether, and insoluble in water. The chemical name for MPA is pregn-4-ene-3, 20-dione, 17-(acetyloxy)-6-methyl-, (6α)-. Its molecular formula is C24H34O4, with a molecular weight of 386.53. Its structural formula is:
PREMPRO 0.3 mg/1.5 mg
Each cream tablet for oral administration contains 0.3 mg conjugated estrogens, 1.5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate, and the following inactive ingredients: calcium phosphate tribasic, microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, sucrose, Eudragit NE 30D, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, povidone, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide, and iron oxide black.
PREMPRO 0.45 mg/1.5 mg
Each gold tablet for oral administration contains 0.45 mg conjugated estrogens, 1.5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate and the following inactive ingredients: calcium phosphate tribasic, microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, sucrose, Eudragit NE 30D, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, povidone, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide, and iron oxide black.
PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg
Each peach tablet for oral administration contains 0.625 mg conjugated estrogens, 2.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate and the following inactive ingredients: calcium phosphate tribasic, calcium sulfate, carnauba wax, cellulose, glyceryl monooleate, lactose, magnesium stearate, methylcellulose, pharmaceutical glaze, polyethylene glycol, sucrose, povidone, titanium dioxide, red ferric oxide, and black iron oxide.
PREMPRO 0.625 mg/5 mg
Each light-blue tablet for oral administration contains 0.625 mg conjugated estrogens, 5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate and the following inactive ingredients: calcium phosphate tribasic, calcium sulfate, carnauba wax, cellulose, glyceryl monooleate, lactose, magnesium stearate, methylcellulose, pharmaceutical glaze, polyethylene glycol, sucrose, povidone, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue No. 2, and black iron oxide.
PREMPHASE
Each maroon Premarin tablet for oral administration contains 0.625 mg of conjugated estrogens and the following inactive ingredients: calcium phosphate tribasic, hydroxypropyl cellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, powdered cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, sucrose, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue No. 2, and FD&C Red No. 40. These tablets comply with USP Dissolution Test 5.
Each light-blue tablet for oral administration contains 0.625 mg of conjugated estrogens, 5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate, and the following inactive ingredients: calcium phosphate tribasic, calcium sulfate, carnauba wax, cellulose, glyceryl monooleate, lactose, magnesium stearate, methylcellulose, pharmaceutical glaze, polyethylene glycol, sucrose, povidone, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue No. 2, and black iron oxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Endogenous estrogens are largely responsible for the development and maintenance of the female reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics. Although circulating estrogens exist in a dynamic equilibrium of metabolic interconversions, estradiol is the principal intracellular human estrogen and is substantially more potent than its metabolites, estrone and estriol, at the receptor level.
The primary source of estrogen in normally cycling adult women is the ovarian follicle, which secretes 70 to 500 mcg of estradiol daily, depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. After menopause, most endogenous estrogen is produced by conversion of androstenedione, secreted by the adrenal cortex, to estrone by peripheral tissues. Thus, estrone and the sulfate-conjugated form, estrone sulfate, are the most abundant circulating estrogens in postmenopausal women.
Estrogens act through binding to nuclear receptors in estrogen-responsive tissues. To date, two estrogen receptors have been identified. These vary in proportion from tissue to tissue.
Circulating estrogens modulate the pituitary secretion of the gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), through a negative feedback mechanism. Estrogens act to reduce the elevated levels of these gonadotropins seen in postmenopausal women.
Parenterally administered medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) inhibits gonadotropin production, which in turn prevents follicular maturation and ovulation, although available data indicate that this does not occur when the usually recommended oral dosage is given as single daily doses. MPA may achieve its beneficial effect on the endometrium in part by decreasing nuclear estrogen receptors and suppression of epithelial DNA synthesis in endometrial tissue. Androgenic and anabolic effects of MPA have been noted, but the drug is apparently devoid of significant estrogenic activity.
Pharmacokinetics
A. Absorption
Conjugated estrogens are water‑soluble and are well-absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after release from the drug formulation. However, PREMPRO and PREMPHASE contain a formulation of medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) that is immediately released and conjugated estrogens that are slowly released over several hours. MPA is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Table 1 summarizes the mean pharmacokinetic parameters for unconjugated and conjugated estrogens, and medroxyprogesterone acetate following administration of 2 PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg and 2 PREMPRO 0.625 mg/5 mg tablets to healthy postmenopausal women.
Table 2 summarizes the mean pharmacokinetic parameters for unconjugated and conjugated estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate following administration of 4 PREMPRO 0.45 mg/1.5 mg tablets to healthy, postmenopausal women.
Food-Effect: Single dose studies in healthy, postmenopausal women were conducted to investigate any potential drug interaction when PREMPRO or PREMPHASE is administered with a high fat breakfast. Administration with food decreased the Cmax of total estrone by 18 to 34 percent and increased total equilin Cmax by 38 percent compared to the fasting state, with no other effect on the rate or extent of absorption of other conjugated or unconjugated estrogens. Administration with food approximately doubles MPA Cmax and increases MPA AUC by approximately 20 to 30 percent.
Dose Proportionality: The Cmax and AUC values for MPA observed in two separate pharmacokinetic studies conducted with 2 PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg or 2 PREMPRO or PREMPHASE 0.625 mg/5 mg tablets exhibited nonlinear dose proportionality; doubling the MPA dose from 2 x 2.5 to 2 x 5.0 mg increased the mean Cmax and AUC by 3.2 and 2.8 folds, respectively.
The dose proportionality of estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate was assessed by combining pharmacokinetic data across another two studies totaling 61 healthy, postmenopausal women. Single conjugated estrogens doses of 2 x 0.3 mg, 2 x 0.45 mg, or 2 x 0.625 mg were administered either alone or in combination with medroxyprogesterone acetate doses of 2 x 1.5 mg or 2 x 2.5 mg. Most of the estrogen components demonstrated dose proportionality; however, several estrogen components did not. Medroxyprogesterone acetate pharmacokinetic parameters increased in a dose-proportional manner.
B. Distribution
The distribution of exogenous estrogens is similar to that of endogenous estrogens. Estrogens are widely distributed in the body and are generally found in higher concentrations in the sex hormone target organs. Estrogens circulate in the blood largely bound to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin. MPA is approximately 90% bound to plasma proteins but does not bind to SHBG.
C. Metabolism
Exogenous estrogens are metabolized in the same manner as endogenous estrogens. Circulating estrogens exist in a dynamic equilibrium of metabolic interconversions. These transformations take place mainly in the liver. Estradiol is converted reversibly to estrone, and both can be converted to estriol, which is the major urinary metabolite. Estrogens also undergo enterohepatic recirculation via sulfate and glucuronide conjugation in the liver, biliary secretion of conjugates into the intestine, and hydrolysis in the intestine followed by reabsorption. In postmenopausal women a significant proportion of the circulating estrogens exists as sulfate conjugates, especially estrone sulfate, which serves as a circulating reservoir for the formation of more active estrogens. Metabolism and elimination of MPA occur primarily in the liver via hydroxylation, with subsequent conjugation and elimination in the urine.
D. Excretion
Estradiol, estrone, and estriol are excreted in the urine, along with glucuronide and sulfate conjugates. Most metabolites of MPA are excreted as glucuronide conjugates with only minor amounts excreted as sulfates.
E. Special Populations
No pharmacokinetic studies were conducted in special populations, including patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
F. Drug Interactions
Data from a single-dose drug-drug interaction study involving conjugated estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate indicate that the pharmacokinetic disposition of both drugs is not altered when the drugs are coadministered. No other clinical drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted with conjugated estrogens.
In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that estrogens are metabolized partially by cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4). Therefore, inducers or inhibitors of CYP3A4 may affect estrogen drug metabolism. Inducers of CYP3A4, such as St. John's Wort preparations (Hypericum perforatum), phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and rifampin, may reduce plasma concentrations of estrogens, possibly resulting in a decrease in therapeutic effects and/or changes in the uterine bleeding profile. Inhibitors of CYP3A4, such as erythromycin, clarithromycin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir and grapefruit juice, may increase plasma concentrations of estrogens and may result in side effects.
CLINICAL STUDIES
Effects on vasomotor symptoms
In the first year of the Health and Osteoporosis, Progestin and Estrogen (HOPE) Study, a total of 2,805 postmenopausal women (average age 53.3 ± 4.9 years) were randomly assigned to one of eight treatment groups of either placebo or conjugated estrogens, with or without medroxyprogesterone acetate. Efficacy for vasomotor symptoms was assessed during the first 12 weeks of treatment in a subset of symptomatic women (n = 241) who had at least seven moderate to severe hot flushes daily, or at least 50 moderate to severe hot flushes during the week before randomization. PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg, 0.45 mg/1.5 mg, and 0.3 mg/1.5 mg were shown to be statistically better than placebo at weeks 4 and 12 for relief of both the frequency and severity of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms. Table 3 shows the adjusted mean number of hot flushes in the PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg, 0.45 mg/1.5 mg, 0.3 mg /1.5 mg, and placebo groups during the initial 12-week period.
Effects on vulvar and vaginal atrophy
Results of vaginal maturation indexes at cycles 6 and 13 showed that the differences from placebo were statistically significant (p < 0.001) for all treatment groups (conjugated estrogens alone and conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate treatment groups).
Effects on the endometrium
In a 1-year clinical trial of 1,376 women (average age 54.0 ± 4.6 years) randomized to PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg (n=340), PREMPRO 0.625 mg/5 mg (n=338), PREMPHASE 0.625 mg/5 mg (n=351), or Premarin 0.625 mg alone (n=347), results of evaluable biopsies at 12 months (n=279, 274, 277, and 283, respectively) showed a reduced risk of endometrial hyperplasia in the two PREMPRO treatment groups (less than 1 percent) and in the PREMPHASE treatment group (less than 1 percent; 1 percent when focal hyperplasia was included) compared to the Premarin group (8 percent; 20 percent when focal hyperplasia was included). See Table 4.
| ---------------------------Groups---------------------------- | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PREMPRO | PREMPRO | PREMPHASE | Premarin | |
| 0.625 mg/2.5 mg | 0.625 mg/5 mg | 0.625 mg/5 mg | 0.625 mg | |
| * Significant (p < 0.001) in comparison with Premarin (0.625 mg) alone. | ||||
| Total number of patients | 340 | 338 | 351 | 347 |
| Number of patients with evaluable biopsies | 279 | 274 | 277 | 283 |
| No. (%) of patients with biopsies | ||||
| ● all focal and non-focal hyperplasia | 2 (<1)* | 0 (0)* | 3 (1)* | 57 (20) |
| ● excluding focal cystic hyperplasia | 2 (<1)* | 0 (0)* | 1 (<1)* | 25 (8) |
In the first year of the Health and Osteoporosis, Progestin and Estrogen (HOPE) Study, 2,001 women (average age 53.3 ± 4.9 years) of whom 88 percent were Caucasian were treated with either Premarin 0.625 mg alone (n = 348), Premarin 0.45 mg alone (n = 338), Premarin 0.3 mg alone (n = 326) or PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg (n = 331), PREMPRO 0.45 mg/1.5 mg (n = 331) or PREMPRO 0.3 mg/1.5 mg (n = 327). Results of evaluable endometrial biopsies at 12 months showed a reduced risk of endometrial hyperplasia or cancer in the PREMPRO treatment groups compared with the corresponding Premarin alone treatment groups, except for the PREMPRO 0.3 mg/1.5 mg and Premarin 0.3 mg alone groups, in each of which there was only 1 case. See Table 5.
No endometrial hyperplasia or cancer was noted in those patients treated with the continuous combined regimens who continued for a second year in the osteoporosis and metabolic substudy of the HOPE study. See Table 6.
Effects on uterine bleeding or spotting
The effects of PREMPRO on uterine bleeding or spotting, as recorded on daily diary cards, were evaluated in 2 clinical trials. Results are shown in Figures 1 and 2.
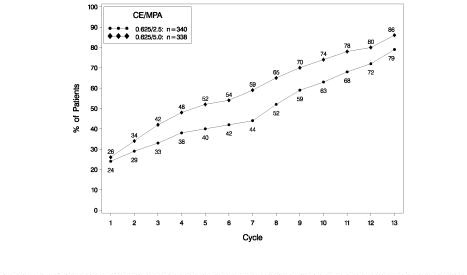
FIGURE 1. PATIENTS WITH CUMULATIVE AMENORRHEA OVER TIME PERCENTAGES OF WOMEN WITH NO BLEEDING OR SPOTTING AT A GIVEN CYCLE THROUGH CYCLE 13 INTENT-TO-TREAT POPULATION, LOCF
Note: The percentage of patients who were amenorrheic in a given cycle and through cycle 13 is shown. If data were missing, the bleeding value from the last reported day was carried forward (LOCF).
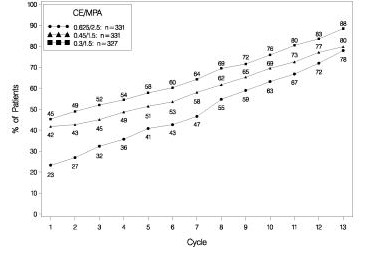
FIGURE 2. PATIENTS WITH CUMULATIVE AMENORRHEA OVER TIME PERCENTAGES OF WOMEN WITH NO BLEEDING OR SPOTTING AT A GIVEN CYCLE THROUGH CYCLE 13 INTENT-TO-TREAT POPULATION, LOCF
Note: The percentage of patients who were amenorrheic in a given cycle and through cycle 13 is shown. If data were missing, the bleeding value from the last reported day was carried forward (LOCF).
Effects on bone mineral density
Health and Osteoporosis, Progestin and Estrogen (HOPE) Study
The HOPE study was a double-blind, randomized, placebo/active-drug-controlled, multicenter study of healthy postmenopausal women with an intact uterus. Subjects (mean age 53.3 ± 4.9 years) were 2.3 ± 0.9 years on average since menopause and took one 600-mg tablet of elemental calcium (Caltrate™) daily. Subjects were not given Vitamin D supplements. They were treated with PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg, 0.45 mg/1.5 mg or 0.3 mg/1.5 mg, comparable doses of Premarin alone, or placebo. Prevention of bone loss was assessed by measurement of bone mineral density (BMD), primarily at the anteroposterior lumbar spine (L2 to L4). Secondarily, BMD measurements of the total body, femoral neck, and trochanter were also analyzed. Serum osteocalcin, urinary calcium, and N-telopeptide were used as bone turnover markers (BTM) at cycles 6, 13, 19, and 26.
Intent-to-treat subjects
All active treatment groups showed significant differences from placebo in each of the four BMD endpoints. These significant differences were seen at cycles 6, 13, 19, and 26. With PREMPRO, the mean percent increases in the primary efficacy measure (L2 to L4 BMD) at the final on-therapy evaluation (cycle 26 for those who completed and the last available evaluation for those who discontinued early) were 3.28 percent with 0.625 mg/2.5 mg, 2.18 percent with 0.45 mg/1.5 mg, and 1.71 percent with 0.3 mg/1.5 mg. The placebo group showed a mean percent decrease from baseline at the final evaluation of 2.45 percent. These results show that the lower dose regimens of PREMPRO were effective in increasing L2 to L4 BMD compared with placebo, and therefore support the efficacy of lower doses of PREMPRO.
The analysis for the other three BMD endpoints yielded mean percent changes from baseline in femoral trochanter that were generally larger than those seen for L2 to L4, and changes in femoral neck and total body that were generally smaller than those seen for L2 to L4. Significant differences between groups indicated that each of the PREMPRO treatment groups was more effective than placebo for all three of these additional BMD endpoints. With regard to femoral neck and total body, the continuous combined treatment groups all showed mean percent increases in BMD, while the placebo group showed mean percent decreases. For femoral trochanter, each of the PREMPRO groups showed a mean percent increase that was significantly greater than the small increase seen in the placebo group. The percent changes from baseline to final evaluation are shown in Table 7.
| Region Evaluated Treatment Groupa | No. of Subjects | Baseline (g/cm2) Mean ± SD | Change from Baseline (%) Adjusted Mean ± SE | p-Value vs Placebo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a: Identified by dosage (mg/mg) of Premarin/MPA or placebo. | ||||
| L2 to L4 BMD | ||||
| 0.625/2.5 | 81 | 1.14 ± 0.16 | 3.28 ± 0.37 | <0.001 |
| 0.45/1.5 | 89 | 1.16 ± 0.14 | 2.18 ± 0.35 | <0.001 |
| 0.3/1.5 | 90 | 1.14 ± 0.15 | 1.71 ± 0.35 | <0.001 |
| Placebo | 85 | 1.14 ± 0.14 | -2.45 ± 0.36 | |
| Total body BMD | ||||
| 0.625/2.5 | 81 | 1.14 ± 0.08 | 0.87 ± 0.17 | <0.001 |
| 0.45/1.5 | 89 | 1.14 ± 0.07 | 0.59 ± 0.17 | <0.001 |
| 0.3/1.5 | 91 | 1.13 ± 0.08 | 0.60 ± 0.16 | <0.001 |
| Placebo | 85 | 1.13 ± 0.08 | -1.50 ± 0.17 | |
| Femoral neck BMD | ||||
| 0.625/2.5 | 81 | 0.89 ± 0.14 | 1.62 ± 0.46 | <0.001 |
| 0.45/1.5 | 89 | 0.89 ± 0.12 | 1.48 ± 0.44 | <0.001 |
| 0.3/1.5 | 91 | 0.86 ± 0.11 | 1.31 ± 0.43 | <0.001 |
| Placebo | 85 | 0.88 ± 0.14 | -1.72 ± 0.45 | |
| Femoral trochanter BMD | ||||
| 0.625/2.5 | 81 | 0.77 ± 0.14 | 3.35 ± 0.59 | 0.002 |
| 0.45/1.5 | 89 | 0.76 ± 0.12 | 2.84 ± 0.57 | 0.011 |
| 0.3/1.5 | 91 | 0.76 ± 0.12 | 3.93 ± 0.56 | <0.001 |
| Placebo | 85 | 0.75 ± 0.12 | 0.81 ± 0.58 | |
Figure 3 shows the cumulative percentage of subjects with percent changes from baseline in spine BMD equal to or greater than the percent change shown on the x-axis.
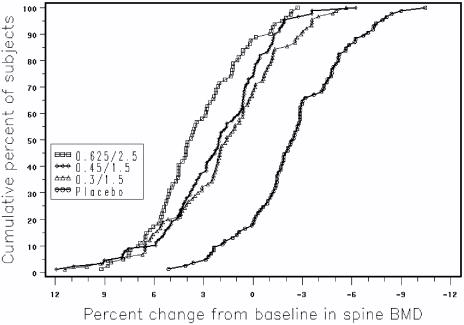
FIGURE 3. CUMULATIVE PERCENT OF SUBJECTS WITH CHANGES FROM BASELINE IN SPINE BMD OF GIVEN MAGNITUDE OR GREATER IN PREMARIN/MPA AND PLACEBO GROUPS
The mean percent changes from baseline in L2 to L4 BMD for women who completed the bone density study are shown with standard error bars by treatment group in Figure 4. Significant differences between each of the PREMPRO dosage groups and placebo were found at cycles 6, 13, 19, and 26.
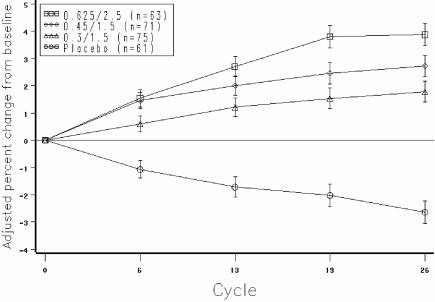
FIGURE 4. ADJUSTED MEAN (SE) PERCENT CHANGE FROM BASELINE AT EACH CYCLE IN SPINE BMD: SUBJECTS COMPLETING IN PREMARIN/MPA GROUPS AND PLACEBO
The bone turnover markers, serum osteocalcin and urinary N-telopeptide, significantly decreased (p < 0.001) in all active-treatment groups at cycles 6, 13, 19, and 26 compared with the placebo group. Larger mean decreases from baseline were seen with the active groups than with the placebo group. Significant differences from placebo were seen less frequently in urine calcium; only with PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg and 0.45 mg/1.5 mg were there significantly larger mean decreases than with placebo at 3 or more of the 4 time points.
Women's Health Initiative Studies
The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) enrolled approximately 27,000 predominantly healthy postmenopausal women in two substudies to assess the risks and benefits of either the use of daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE 0.625 mg) alone or in combination with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA 2.5 mg) compared to placebo in the prevention of certain chronic diseases. The primary endpoint was the incidence of coronary heart disease (CHD) (nonfatal myocardial infarction [MI], silent MI and CHD death), with invasive breast cancer as the primary adverse outcome. A “global index” included the earliest occurrence of CHD, invasive breast cancer, stroke, pulmonary embolism (PE), endometrial cancer (only in CE/MPA substudy), colorectal cancer, hip fracture, or death due to other causes. The study did not evaluate the effects of CE/MPA or CE on menopausal symptoms.
The estrogen plus progestin substudy was stopped early. According to the predefined stopping rule, after an average follow-up of 5.2 years of treatment, the increased risk of breast cancer and cardiovascular events exceeded the specified benefits included in the “global index.” The absolute excess risk of events included in the “global index” was 19 per 10,000 women-years (relative risk [RR] 1.15, 95 percent nominal confidence interval [nCI] 1.03-1.28).
For those outcomes included in the WHI “global index” that reached statistical significance after 5.6 years of follow-up, the absolute excess risks per 10,000 women-years in the group treated with CE/MPA were 6 more CHD events, 7 more strokes, 10 more PEs, and 8 more invasive breast cancer, wile the absolute risk reductions per 10,000 women-years were 7 fewer colorectal cancers and 5 fewer hip fractures. (See BOXED WARNINGS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS.)
Results of the estrogen plus progestin substudy, which included 16,608 women (average age 63 years, range 50 to 79; 83.9 percent White, 6.8 percent Black, 5.4 percent Hispanic, 3.9 percent Other) are presented in Table 8. These results reflect centrally adjudicated data after an average follow-up of 5.6 years.
The estrogen alone substudy was also stopped early because an increased risk of stroke was observed, and it was deemed that no further information would be obtained regarding the risks and benefits of estrogen alone in predetermined primary endpoints. Results of the estrogen alone substudy, which included 10,739 women (average age of 63 years, range 50 to 79; 75.3 percent White, 15.1 percent Black, 6.1 percent Hispanic, 3.6 percent Other) after an average follow-up of 6.8 years, are presented in Table 9.
For those outcomes included in the WHI “global index” that reached statistical significance, the absolute excess risk per 10,000 women-years in the group treated with CE alone were 12 more strokes while the absolute risk reduction per 10,000 women-years was 6 fewer hip fractures. The absolute excess risk of events included in the “global index” was a nonsignificant 2 events per 10,000 women-years. There was no difference between the groups in terms of all‑cause mortality. (See BOXED WARNINGS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS.)
Final centrally adjudicated results for CHD events and centrally adjudicated results for invasive breast cancer incidence from the estrogen alone substudy, after an average follow-up of 7.1 years, reported no overall difference for primary CHD events (nonfatal MI, silent MI and CHD death) and invasive breast cancer incidence in women receiving CE alone compared with placebo (see Table 9).
Centrally adjudicated results for stroke events from the estrogen alone substudy, after an average follow-up of 7.1 years, reported no significant difference in distribution of stroke subtype or severity, including fatal strokes, in women receiving CE alone compared to placebo. Estrogen alone increased the risk of ischemic stroke, and this excess was present in all subgroups of women examined (see Table 9).
Women's Health Initiative Memory Study
The estrogen plus progestin Women's Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS), a substudy of WHI, enrolled 4,532 predominantly healthy postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older (47 percent, age 65 to 69 years; 35 percent, 70 to 74 years; 18 percent, 75 years of age and older) to evaluate the effects of daily CE/MPA 0.625 mg conjugated estrogens/2.5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate on the incidence of probable dementia (primary outcome) compared with placebo.
After an average follow-up of 4 years, 40 women in the estrogen-plus-progestin group (45 per 10,000 women-years) and 21 in the placebo group (22 per 10,000 women-years) were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia in the hormone therapy group was 2.05 (95 percent CI 1.21–3.48) compared to placebo. It is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women. (See BOXED WARNINGS, WARNINGS, Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use.)
The estrogen alone WHIMS substudy enrolled 2,947 predominantly healthy postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older (45 percent, age 65 to 69 years; 36 percent, 70 to 74 years; 19 percent, 75 years of age and older) to evaluate the effects of daily CE 0.625 mg on the incidence of probable dementia (primary outcome) compared with placebo.
After an average follow-up of 5.2 years, 28 women in the estrogen alone group (37 per 10,000 women-years) and 19 in the placebo group (25 per 10,000 women-years) were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia in the estrogen alone group was 1.49 (95 percent CI 0.83–2.66) compared to placebo. It is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women. (See BOXED WARNINGS, WARNINGS, Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use.)
When data from the two populations were pooled as planned in the WHIMS protocol, the reported overall relative risk for probable dementia was 1.76 (95 percent CI 1.19-2.60). Differences between groups became apparent in the first year of treatment. It is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women. (See BOXED WARNINGS, WARNINGS, Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use.)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PREMPRO or PREMPHASE therapy is indicated in women who have a uterus for the:
- Treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause.
- Treatment of moderate to severe symptoms of vulvar and vaginal atrophy due to menopause. When prescribing solely for the treatment of symptoms of vulvar and vaginal atrophy, topical vaginal products should be considered.
- Prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. When prescribing solely for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis, therapy should only be considered for women at significant risk of osteoporosis and for whom non-estrogen medications are not considered to be appropriate. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
The mainstays for decreasing the risk of postmenopausal osteoporosis are weight-bearing exercise, adequate calcium and Vitamin D intake, and when indicated, pharmacologic therapy. Postmenopausal women require an average of 1500 mg/day of elemental calcium. Therefore, when not contraindicated, calcium supplementation may be helpful for women with suboptimal dietary intake. Vitamin D supplementation of 400-800 IU/day may also be required to ensure adequate daily intake in postmenopausal women.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
PREMPRO or PREMPHASE therapy should not be used in women with any of the following conditions:
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding.
- Known, suspected, or history of cancer of the breast.
- Known or suspected estrogen-dependent neoplasia.
- Active deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism or a history of these conditions.
- Active or recent (within past year) arterial thromboembolic disease (for example, stroke, myocardial infarction).
- Liver dysfunction or disease.
- Known hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in PREMPRO or PREMPHASE.
- Known or suspected pregnancy.
WARNINGS
See BOXED WARNINGS.
1. Cardiovascular disorders
An increased risk of stroke, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism, and myocardial infarction has been reported with estrogen plus progestin therapy.
An increased risk of stroke and DVT has been reported with estrogen alone therapy.
Should any of these events occur or be suspected, estrogens with or without progestins should be discontinued immediately.
Risk factors for arterial vascular disease (for example, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, tobacco use, hypercholesterolemia, and obesity) and/or venous thromboembolism (for example, personal history or family history of VTE, obesity, and systemic lupus erythematosus) should be managed appropriately.
a. Stroke
In the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) estrogen plus progestin substudy, a statistically significant increased risk of stroke was reported in women receiving daily conjugated estrogens (CE 0.625 mg) plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA 2.5 mg) compared to placebo (31 versus 24 per 10,000 women-years). The increase in risk was demonstrated after the first year and persisted. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
In the estrogen alone substudy of the WHI, a statistically significant increased risk of stroke was reported in women receiving daily CE 0.625 mg compared to placebo (44 versus 32 per 10,000 women-years). The increase in risk was demonstrated in year 1 and persisted. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
b. Coronary heart disease
In the estrogen plus progestin substudy of WHI, no statistically significant increase of CHD events (defined as nonfatal MI, silent MI, or death, due to CHD) was reported in women receiving CE/MPA compared to placebo (39 versus 33 per 10,000 women years). An increase in relative risk was demonstrated in year 1, and a trend toward decreasing relative risk was reported in years 2 through 5. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
In the estrogen alone substudy of WHI, no overall effect on coronary heart disease (CHD) events was reported in women receiving estrogen alone compared to placebo. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
In postmenopausal women with documented heart disease (n = 2,763, average age 66.7 years), in a controlled clinical trial of secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease (Heart and Estrogen/progestin Replacement Study; HERS), treatment with daily CE 0.625 mg/MPA 2.5 mg demonstrated no cardiovascular benefit. During an average follow-up of 4.1 years, treatment with CE/MPA did not reduce the overall rate of CHD events in postmenopausal women with established coronary heart disease. There were more CHD events in the CE/MPA-treated group than in the placebo group in year one, but not during the subsequent years. Two thousand three hundred and twenty one (2,321) women from the original HERS trial agreed to participate in an open-label extension of HERS, HERS II. Average follow-up in HERS II was an additional 2.7 years, for a total of 6.8 years overall. Rates of CHD events were comparable among women in the CE/MPA group and the placebo group in the HERS, the HERS II, and overall.
c. Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
In the estrogen plus progestin substudy of WHI, a statistically significant 2-fold greater rate of VTE (DVT and pulmonary embolism [PE]), was reported in women receiving daily CE/MPA compared to placebo (35 versus 17 per 10,000 women-years). Statistically significant increases in risk for both DVT (26 versus 13 per 10,000 women-years) and PE (18 versus 8 per 10,000 women-years) were also demonstrated. The increase in VTE risk was demonstrated during the first year and persisted. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
In the estrogen alone substudy of WHI, the risk of VTE was reported to be increased for women receiving daily CE compared to placebo (30 versus 22 per 10,000 women-years), although only the increased risk of DVT reached statistical significance (23 versus 15 per 10,000 women years). The increase in VTE risk was demonstrated during the first 2 years. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
If feasible, estrogens should be discontinued at least 4 to 6 weeks before surgery of the type associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism, or during periods of prolonged immobilization.
2. Malignant neoplasms
a. Breast cancer
The most important randomized clinical trial providing information about this issue in estrogen plus progestin users is the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) substudy of daily conjugated estrogens (CE 0.625 mg) plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA 2.5 mg). In the estrogen plus progestin substudy, after a mean follow-up of 5.6 years, the WHI substudy reported an increased risk of breast cancer in women who took daily CE/MPA. In this substudy, prior use of estrogen alone or estrogen plus progestin therapy was reported by 26 percent of the women. The relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.24 (95 percent nominal confidence interval [nCI] 1.01-1.54), and the absolute risk was 41 versus 33 cases per 10,000 women-years, for estrogen plus progestin compared with placebo, respectively. Among women who reported prior use of hormone therapy, the relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.86, and the absolute risk was 46 versus 25 cases per 10,000 women-years, for estrogen plus progestin compared with placebo. Among women who reported no prior use of hormone therapy, the relative risk of invasive breast cancer was 1.09, and the absolute risk was 40 versus 36 cases per 10,000 women-years for estrogen plus progestin compared with placebo. In the same substudy, invasive breast cancers were larger and diagnosed at a more advanced stage in the CE/MPA group compared with the placebo group. Metastatic disease was rare, with no apparent difference between the two groups. Other prognostic factors, such as histologic subtype, grade and hormone receptor status did not differ between the groups. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
The most important randomized clinical trial providing information about this issue in estrogen alone users is the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) substudy of daily CE 0.625 mg. In the estrogen alone substudy of WHI, after an average of 7.1 years of follow-up, daily CE 0.625 mg was not associated with an increased risk of invasive breast cancer (RR 0.80, 95 percent nCI 0.62-1.04). (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
The results from observational studies are generally consistent with those of the WHI clinical trial. Observational studies have also reported an increased risk of breast cancer for estrogen plus progestin therapy, and a smaller increased risk for estrogen alone therapy, after several years of use. The risk increased with duration of use, and appeared to return to baseline over about 5 years after stopping treatment (only the observational studies have substantial data on risk after stopping). Observational studies also suggest that the risk of breast cancer was greater, and became apparent earlier, with estrogen plus progestin therapy as compared to estrogen alone therapy. However, these studies have not found significant variation in the risk of breast cancer among different estrogens or among different estrogen plus progestin combinations, doses, or routes of administration.
The use of estrogen alone and estrogen plus progestin has been reported to result in an increase in abnormal mammograms requiring further evaluation.
All women should receive yearly breast examinations by a healthcare provider and perform monthly breast self-examinations. In addition, mammography examinations should be scheduled based on patient age, risk factors, and prior mammogram results.
b. Endometrial cancer
An increased risk of endometrial cancer has been reported with the use of unopposed estrogen therapy in women with a uterus. The reported endometrial cancer risk among unopposed estrogen users is about 2 to 12 times greater than in nonusers, and appears dependent on duration of treatment and on estrogen dose. Most studies show no significant increased risk associated with the use of estrogens for less than 1 year. The greatest risk appears associated with prolonged use, with increased risks of 15- to 24-fold for 5 to 10 years or more, and this risk has been shown to persist for at least 8 to 15 years after estrogen therapy is discontinued.
Clinical surveillance of all women using estrogen plus progestin therapy is important. Adequate diagnostic measures, including endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in all cases of undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal vaginal bleeding. There is no evidence that the use of natural estrogens results in a different endometrial risk profile than synthetic estrogens of equivalent estrogen dose.
Endometrial hyperplasia (a possible precursor of endometrial cancer) has been reported to occur at a rate of approximately 1 percent or less with PREMPRO or PREMPHASE in two large clinical trials. In the two large clinical trials described above, two cases of endometrial cancer were reported to occur among women taking combination Premarin/medroxyprogesterone acetate therapy.
3. Dementia
In the estrogen plus progestin Women's Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS), a substudy of WHI, a population of 4,532 postmenopausal women 65 to 79 years of age was randomized to daily conjugated estrogens (CE 0.625 mg) plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA 2.5 mg) or placebo. In the estrogen alone WHIMS substudy, a population of 2,947 hysterectomized women 65 to 79 years of age, was randomized to daily CE 0.625 mg or placebo.
In the estrogen plus progestin substudy, after an average follow-up of 4 years, 40 women in the CE/MPA group and 21 women in the placebo group were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia for CE/MPA versus placebo was 2.05 (95 percent CI 1.21-3.48). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE/MPA versus placebo was 45 versus 22 cases per 10,000 women-years. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use.)
In the estrogen alone substudy, after an average follow-up of 5.2 years, 28 women in the estrogen-alone group and 19 women in the placebo group were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia for CE alone versus placebo was 1.49 (95 percent CI 0.83-2.66). The absolute risk of probable dementia for CE alone versus placebo was 37 versus 25 cases per 10,000 women-years. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use.)
When data from the two populations were pooled as planned in the WHIMS protocol, the reported overall relative risk for probable dementia was 1.76 (95 percent CI 1.19-2.60). Since both substudies were conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women. (See BOXED WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use.)
4. Gallbladder Disease
A 2- to 4-fold increase in the risk of gallbladder disease requiring surgery in postmenopausal women receiving estrogens has been reported.
5. Hypercalcemia
Estrogen administration may lead to severe hypercalcemia in patients with breast cancer and bone metastases. If hypercalcemia occurs, use of the drug should be stopped and appropriate measures taken to reduce the serum calcium level.
6. Visual Abnormalities
Retinal vascular thrombosis has been reported in patients receiving estrogens. Discontinue medication pending examination if there is sudden partial or complete loss of vision, or a sudden onset of proptosis, diplopia, or migraine. If examination reveals papilledema or retinal vascular lesions, estrogens should be permanently discontinued.
PRECAUTIONS
A. General
1. Addition of a progestin when a woman has not had a hysterectomy
Studies of the addition of a progestin for 10 or more days of a cycle of estrogen administration, or daily with estrogen in a continuous regimen, have reported a lowered incidence of endometrial hyperplasia than would be induced by estrogen treatment alone. Endometrial hyperplasia may be a precursor to endometrial cancer.
There are, however, possible risks that may be associated with the use of progestins with estrogens compared with estrogen-alone regimens. These include a possible increased risk of breast cancer, adverse effects on lipoprotein metabolism (lowering HDL, raising LDL) and impairment of glucose tolerance.
2. Elevated blood pressure
In a small number of case reports, substantial increases in blood pressure have been attributed to idiosyncratic reactions to estrogens. In a large, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial, a generalized effect of estrogen therapy on blood pressure was not seen. Blood pressure should be monitored at regular intervals with estrogen use.
3. Hypertriglyceridemia
In patients with pre-existing hypertriglyceridemia, estrogen therapy may be associated with elevations of plasma triglycerides leading to pancreatitis and other complications. Consider discontinuation of treatment if pancreatitis or other complications develop.
In the HOPE study, the mean percent increase from baseline in serum triglycerides after one year of treatment with PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg, 0.45 mg/1.5 mg, and 0.3 mg/1.5 mg compared with placebo were 32.8, 24.8, 23.3, and 10.7, respectively. After two years of treatment, the mean percent changes were 33.0, 17.1, 21.6, and 5.5, respectively.
4. Impaired liver function and past history of cholestatic jaundice
Estrogens may be poorly metabolized in patients with impaired liver function. For patients with a history of cholestatic jaundice associated with past estrogen use or with pregnancy, caution should be exercised, and in the case of recurrence, medication should be discontinued.
5. Hypothyroidism
Estrogen administration leads to increased thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) levels. Patients with normal thyroid function can compensate for the increased TBG by making more thyroid hormone, thus maintaining free T4 and T3 serum concentrations in the normal range. Patients dependent on thyroid hormone replacement therapy who are also receiving estrogens may require increased doses of their thyroid replacement therapy. These patients should have their thyroid function monitored in order to maintain their free thyroid hormone levels in an acceptable range.
6. Fluid retention
Estrogens/progestins may cause some degree of fluid retention.Patients with conditions that might be influenced by this factor, such as cardiac or renal dysfunction, warrant careful observation when estrogens are prescribed.
7. Hypocalcemia
Estrogens should be used with caution in individuals with severe hypocalcemia.
8. Ovarian cancer
The estrogen plus progestin substudy of WHI reported a non-statistically significant increased risk of ovarian cancer. After an average follow-up of 5.6 years, the relative risk for ovarian cancer for CE/MPA versus placebo was 1.58 (95 percent nCI 0.77 – 3.24). The absolute risk for CE/MPA versus placebo was 4.2 versus 2.7 cases per 10,000 women-years. In some epidemiologic studies, the use of estrogen-only products, in particular for 5 or more years, has been associated with an increased risk of ovarian cancer. However, the duration of exposure associated with increased risk is not consistent across all epidemiologic studies and some report no association.
9. Exacerbation of endometriosis
Endometriosis may be exacerbated with administration of estrogen therapy.
A few cases of malignant transformation of residual endometrial implants has been reported in women treated post-hysterectomy with estrogen alone therapy. For patients known to have residual endometriosis post-hysterectomy, the addition of progestin should be considered.
10. Exacerbation of other conditions
Estrogen therapy may cause an exacerbation of asthma, diabetes mellitus, epilepsy, migraine, porphyria, systemic lupus erythematosus, and hepatic hemangiomas and should be used with caution in women with these conditions.
B. Patient Information
Physicians are advised to discuss the contents of the PATIENT INFORMATION leaflet with patients for whom they prescribe PREMPRO or PREMPHASE.
C. Laboratory Tests
Serum follicle stimulating hormone and estradiol levels have not been shown to be useful in the management of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms and moderate to severe symptoms of vulvar and vaginal atrophy.
D. Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
- Accelerated prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and platelet aggregation time; increased platelet count; increased factors II, VII antigen, VIII coagulant activity, IX, X, XII, VII-X complex, II-VII-X complex, and beta-thromboglobulin; decreased levels of anti-factor Xa and antithrombin III, decreased antithrombin III activity; increased levels of fibrinogen and fibrinogen activity; increased plasminogen antigen and activity.
- Increased thyroid binding globulin (TBG) levels leading to increased circulating total thyroid hormone levels as measured by protein-bound iodine (PBI), T4 levels (by column or by radioimmunoassay), or T3 levels by radioimmunoassay. T3 resin uptake is decreased, reflecting the elevated TBG. Free T4 and free T3 concentrations are unaltered. Patients on thyroid replacement therapy may require higher doses of thyroid hormone.
- Other binding proteins may be elevated in serum, i.e., corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG), sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), leading to increased total circulating corticosteroids and sex steroids, respectively. Free hormone concentrations may be decreased. Other plasma proteins may be increased (angiotensinogen/renin substrate, alpha-1-antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin).
- Increased plasma HDL and HDL2 cholesterol subfraction concentrations, reduced LDL cholesterol concentration, increased triglyceride levels.
- Impaired glucose tolerance.
- Aminoglutethimide administered concomitantly with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) may significantly depress the bioavailability of MPA.
E. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
(See BOXED WARNINGS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS.)
Long-term continuous administration of natural and synthetic estrogens in certain animal species increases the frequency of carcinomas of the breasts, uterus, cervix, vagina, testis, and liver.
In a two-year oral study of medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) in which female rats were exposed to dosages of up to 5000 mcg/kg/day in their diets (50 times higher – based on AUC values – than the level observed experimentally in women taking 10 mg of MPA), a dose-related increase in pancreatic islet cell tumors (adenomas and carcinomas) occurred. Pancreatic tumor incidence was increased at 1000 and 5000 mcg/kg/day, but not at 200 mcg/kg/day.
A decreased incidence of spontaneous mammary gland tumors was observed in all three MPA-treated groups, compared with controls, in the two-year rat study. The mechanism for the decreased incidence of mammary gland tumors observed in the MPA-treated rats may be linked to the significant decrease in serum prolactin concentration observed in rats.
Beagle dogs treated with MPA developed mammary nodules, some of which were malignant. Although nodules occasionally appeared in control animals, they were intermittent in nature, whereas the nodules in the drug-treated animals were larger, more numerous, persistent, and there were some breast malignancies with metastases. It is known that progestogens stimulate synthesis and release of growth hormone in dogs. The growth hormone, along with the progestogen, stimulates mammary growth and tumors. In contrast, growth hormone in humans is not increased, nor does growth hormone have any significant mammotrophic role. No pancreatic tumors occurred in dogs.
F. Pregnancy
PREMPRO and PREMPHASE should not be used during pregnancy. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
G. Nursing Mothers
PREMPRO and PREMPHASE should not be used during lactation. Estrogen administration to nursing mothers has been shown to decrease the quantity and quality of the milk. Detectable amounts of estrogen and progestin have been identified in the milk of mothers receiving these drugs.
H. Pediatric Use
PREMPRO and PREMPHASE are not indicated for pediatric use and no clinical data have been collected in children.
I. Geriatric Use
With respect to efficacy in the approved indications, there have not been sufficient numbers of geriatric patients involved in studies utilizing Premarin and medroxyprogesterone acetate to determine whether those over 65 years of age differ from younger subjects in their response to PREMPRO or PREMPHASE.
Of the total number of subjects in the estrogen plus progestin substudy of the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) study, 44 percent (n=7,320) were 65 years of age and older, while 6.6 percent (n=1,095) were 75 years and older. In women 75 years of age and older compared to women less than 74 years of age, there was a higher relative risk of nonfatal stroke and invasive breast cancer in the estrogen plus progestin group versus placebo. In women greater than 75, the increased risk of nonfatal stroke and invasive breast cancer observed in the estrogen plus progestin group compared to placebo was 75 versus 24 per 10,000 women-years and 52 versus 12 per 10,000 women-years, respectively.
In the estrogen plus progestin substudy of the Women's Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS), a substudy of WHI, a population of 4,532 hysterectomized women, 65 to 79 years of age, was randomized to daily CE 0.625 mg/MPA 2.5 mg or placebo. In the estrogen plus progestin group, after an average follow-up of 4 years, the relative risk (CE/MPA versus placebo) of probable dementia was 2.05 (95 percent CI 1.21-3.48). The absolute risk of developing probable dementia with CE/MPA was 45 versus 22 cases per 10,000 women-years with placebo.
Of the total number of subjects in the estrogen alone substudy of WHI, 46 percent (n=4,943) were 65 years of age and older, while 7.1% (n=767) were 75 years of age and older. There was a higher relative risk (daily CE versus placebo) of stroke in women less than 75 years of age compared to women 75 years and older.
In the estrogen alone WHIMS substudy, a population of 2,947 hysterectomized women, 65 to 79 years of age, was randomized to daily CE 0.625 mg or placebo. After an average follow-up of 5.2 years, the relative risk (CE versus placebo) of probable dementia was 1.49 (95 percent CI 0.83-2.66). The absolute risk of developing probable dementia with estrogen alone was 37 versus 25 cases per 10,000 women-years compared with placebo.
Seventy-nine percent of the cases of probable dementia occurred in women that were older than 70 for the CE alone group, and 82 percent of the cases of probable dementia occurred in women who were older than 70 in the CE/MPA group. The most common classification of probable dementia in both the treatment groups and placebo groups was Alzheimer’s disease.
When data from the two populations were pooled as planned in the WHIMS protocol, the reported overall relative risk for probable dementia was 1.76 (95 percent CI 1.19-2.60). Since both substudies were conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women. (See BOXED WARNINGS and WARNINGS, Dementia.)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
See BOXED WARNINGS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In a 1-year clinical trial that included 678 postmenopausal women treated with PREMPRO, 351 postmenopausal women treated with PREMPHASE, and 347 postmenopausal women treated with Premarin, the following adverse events occurred at a rate ≥ 5% (see Table 10).
| PREMPRO | PREMPRO | PREMPHASE | PREMARIN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body System | 0.625 mg/2.5 mg continuous | 0.625 mg/5.0 mg continuous | 0.625 mg/5.0 mg sequential | 0.625 mg daily |
| Adverse event | (n=340) | (n=338) | (n=351) | (n=347) |
| Body as a whole | ||||
| abdominal pain | 16% | 21% | 23% | 17% |
| accidental injury | 5% | 4% | 5% | 5% |
| asthenia | 6% | 8% | 10% | 8% |
| back pain | 14% | 13% | 16% | 14% |
| flu syndrome | 10% | 13% | 12% | 14% |
| headache | 36% | 28% | 37% | 38% |
| infection | 16% | 16% | 18% | 14% |
| pain | 11% | 13% | 12% | 13% |
| pelvic pain | 4% | 5% | 5% | 5% |
| Digestive system | ||||
| diarrhea | 6% | 6% | 5% | 10% |
| dyspepsia | 6% | 6% | 5% | 5% |
| flatulence | 8% | 9% | 8% | 5% |
| nausea | 11% | 9% | 11% | 11% |
| Metabolic and Nutritional | ||||
| peripheral edema | 4% | 4% | 3% | 5% |
| Musculoskeletal system | ||||
| arthralgia | 9% | 7% | 9% | 7% |
| leg cramps | 3% | 4% | 5% | 4% |
| Nervous system | ||||
| depression | 6% | 11% | 11% | 10% |
| dizziness | 5% | 3% | 4% | 6% |
| hypertonia | 4% | 3% | 3% | 7% |
| Respiratory system | ||||
| pharyngitis | 11% | 11% | 13% | 12% |
| rhinitis | 8% | 6% | 8% | 7% |
| sinusitis | 8% | 7% | 7% | 5% |
| Skin and appendages | ||||
| pruritus | 10% | 8% | 5% | 4% |
| rash | 4% | 6% | 4% | 3% |
| Urogenital system | ||||
| breast pain | 33% | 38% | 32% | 12% |
| cervix disorder | 4% | 4% | 5% | 5% |
| dysmenorrhea | 8% | 5% | 13% | 5% |
| leukorrhea | 6% | 5% | 9% | 8% |
| vaginal hemorrhage | 2% | 1% | 3% | 6% |
| vaginitis | 7% | 7% | 5% | 3% |
During the first year of a 2-year clinical trial with 2,333 postmenopausal women between 40 and 65 years of age (88% Caucasian), 2,001 women received continuous regimens of either 0.625 mg of CE with or without 2.5 mg MPA, or 0.45 mg or 0.3 mg of CE with or without 1.5 mg MPA, and 332 received placebo tablets. Table 11 summarizes adverse events that occurred at a rate ≥ 5% in at least 1 treatment group.
| Body System | Premarin 0.625 mg daily | Prempro 0.625 mg/ 2.5 mg continuous | Premarin 0.45 mg daily | Prempro 0.45 mg/ 1.5 mg continuous | Premarin 0.3 mg daily | Prempro 0.3 mg/ 1.5 mg continuous | Placebo daily |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse event | (n = 348) | (n = 331) | (n = 338) | (n = 331) | (n = 326) | (n = 327) | (n = 332) |
| Any adverse event | 93% | 92% | 90% | 89% | 90% | 90% | 85% |
| Body as a whole | |||||||
| abdominal pain | 16% | 17% | 15% | 16% | 17% | 13% | 11% |
| accidental injury | 6% | 10% | 12% | 9% | 6% | 9% | 9% |
| asthenia | 7% | 8% | 7% | 8% | 8% | 6% | 5% |
| back pain | 14% | 12% | 13% | 13% | 13% | 12% | 12% |
| flu syndrome | 11% | 8% | 11% | 11% | 10% | 10% | 11% |
| headache | 26% | 28% | 32% | 29% | 29% | 33% | 28% |
| infection | 18% | 21% | 22% | 19% | 23% | 18% | 22% |
| pain | 17% | 14% | 18% | 15% | 20% | 20% | 18% |
| Digestive system | |||||||
| diarrhea | 6% | 7% | 7% | 7% | 6% | 6% | 6% |
| dyspepsia | 9% | 8% | 9% | 8% | 11% | 8% | 14% |
| flatulence | 7% | 7% | 7% | 8% | 6% | 5% | 3% |
| nausea | 9% | 7% | 7% | 10% | 6% | 8% | 9% |
| Musculoskeletal system | |||||||
| arthralgia | 14% | 9% | 12% | 13% | 7% | 10% | 12% |
| leg cramps | 5% | 7% | 7% | 5% | 3% | 4% | 2% |
| myalgia | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 9% | 4% | 8% |
| Nervous system | |||||||
| anxiety | 5% | 4% | 4% | 5% | 4% | 2% | 4% |
| depression | 7% | 11% | 8% | 5% | 5% | 8% | 7% |
| dizziness | 6% | 3% | 6% | 5% | 4% | 5% | 5% |
| insomnia | 6% | 6% | 7% | 7% | 7% | 6% | 10% |
| nervousness | 3% | 3% | 5% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| Respiratory system | |||||||
| cough increased | 4% | 8% | 7% | 5% | 4% | 6% | 4% |
| pharyngitis | 10% | 11% | 10% | 8% | 12% | 9% | 11% |
| rhinitis | 6% | 8% | 9% | 9% | 10% | 10% | 13% |
| sinusitis | 6% | 8% | 11% | 8% | 7% | 10% | 7% |
| upper respiratory infection | 12% | 10% | 10% | 9% | 9% | 11% | 11% |
| Skin and appendages | |||||||
| pruritus | 4% | 4% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 2% |
| Urogenital system | |||||||
| breast enlargement | <1% | 5% | 1% | 3% | 2% | 2% | <1% |
| breast pain | 11% | 26% | 12% | 21% | 7% | 13% | 9% |
| dysmenorrhea | 4% | 5% | 3% | 6% | 1% | 3% | <1% |
| leukorrhea | 5% | 4% | 7% | 5% | 4% | 3% | 3% |
| vaginal hemorrhage | 14% | 6% | 4% | 4% | 2% | 2% | 0% |
| vaginal moniliasis | 6% | 8% | 5% | 7% | 5% | 4% | 2% |
| vaginitis | 7% | 5% | 6% | 6% | 5% | 4% | 1% |
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported with estrogen and/or progestin therapy:
1. Genitourinary system
Abnormal uterine bleeding/spotting, dysmenorrhea/pelvic pain, change in amount of cervical secretion, premenstrual-like syndrome, cystitis-like syndrome, increase in size of uterine leiomyomata, vaginal candidiasis, amenorrhea, changes in cervical erosion, ovarian cancer, endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial cancer.
2. Breasts
Tenderness, enlargement, pain, nipple discharge, galactorrhea, fibrocystic breast changes, breast cancer.
3. Cardiovascular
Deep and superficial venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, thrombophlebitis, myocardial infarction, stroke, increase in blood pressure.
4. Gastrointestinal
Nausea, cholestatic jaundice, changes in appetite, vomiting, abdominal cramps, bloating, increased incidence of gallbladder disease, pancreatitis, enlargement of hepatic hemangiomas.
5. Skin
Chloasma or melasma that may persist when drug is discontinued, erythema multiforme, erythema nodosum, hemorrhagic eruption, loss of scalp hair, hirsutism, itching, urticaria, pruritus, generalized rash, rash (allergic) with and without pruritus, acne.
6. Eyes
Neuro-ocular lesions, for example, retinal vascular thrombosis and optic neuritis, intolerance of contact lenses.
7. Central Nervous System (CNS)
Headache, dizziness, mental depression, mood disturbances, anxiety, irritability, nervousness, migraine, exacerbation of chorea, insomnia, somnolence, exacerbation of epilepsy, dementia.
8. Miscellaneous
Increase or decrease in weight, edema, changes in libido, fatigue, backache, reduced carbohydrate tolerance, aggravation of porphyria, pyrexia, urticaria, angioedema, anaphylactoid/anaphylactic reactions, hypocalcemia, exacerbation of asthma, increased triglycerides.
OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of estrogen/progestin may cause nausea and vomiting, breast tenderness, abdominal pain, drowsiness/fatigue and withdrawal bleeding may occur in females. Treatment of overdose consists of discontinuation of PREMPRO or PREMPHASE together with institution of appropriate symptomatic care.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Use of estrogens, alone or in combination with a progestin, should be with the lowest effective dose and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman. Patients should be reevaluated periodically as clinically appropriate (for example, at 3-month to 6-month intervals) to determine if treatment is still necessary (see BOXED WARNINGS and WARNINGS.) For women who have a uterus, adequate diagnostic measures, such as endometrial sampling, when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in cases of undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal vaginal bleeding.
PREMPRO therapy consists of a single tablet to be taken once daily.
PREMPHASE therapy consists of two separate tablets; one maroon 0.625 mg Premarin tablet taken daily on days 1 through 14 and one light-blue tablet, containing 0.625 mg conjugated estrogens and 5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate, taken on days 15 through 28.
1. For treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms and/or moderate to severe symptoms of vulvar and vaginal atrophy due to menopause. When prescribing solely for the treatment of symptoms of moderate to severe vulvar and vaginal atrophy, topical vaginal products should be considered.
- PREMPRO 0.3 mg/1.5 mg
- PREMPRO 0.45 mg/1.5 mg
- PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg
- PREMPRO 0.625 mg/5 mg
- PREMPHASE
Patients should be treated with the lowest effective dose. Generally, women should be started at 0.3 mg/1.5 mg PREMPRO daily. Subsequent dosage adjustment may be made based upon the individual patient response. In patients where bleeding or spotting remains a problem, after appropriate evaluation, consideration should be given to changing the dose level. This dose should be periodically reassessed by the healthcare provider.
2. For prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. When prescribing solely for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis, therapy should be considered only for women at significant risk of osteoporosis and for whom non-estrogen medications are not considered to be appropriate.
- PREMPRO 0.3 mg/1.5 mg
- PREMPRO 0.45 mg/1.5 mg
- PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg
- PREMPRO 0.625 mg/5 mg
- PREMPHASE
Patients should be treated with the lowest effective dose. Generally, women should be started at 0.3 mg/1.5 mg PREMPRO daily. Dosage may be adjusted depending on individual clinical and bone mineral density responses. This dose should be periodically reassessed by the healthcare provider.
In patients where bleeding or spotting remains a problem, after appropriate evaluation, consideration should be given to changing the dose level. This dose should be periodically reassessed by the healthcare provider.
HOW SUPPLIED
PREMPRO therapy consists of a single tablet to be taken once daily.
PREMPRO 0.3 mg/1.5 mg
NDC 0046-1105-11, carton includes 1 blister card containing 28 oval, cream tablets.
PREMPRO 0.45 mg/1.5 mg
NDC 0046-1106-11, carton includes 1 blister card containing 28 oval, gold tablets.
PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg
NDC 0046-0875-06, carton includes 3 EZ DIAL® dispensers each containing 28 oval, peach tablets.
NDC 0046-0875-11, carton includes 1 blister card containing 28 oval, peach tablets.
PREMPRO 0.625 mg/5 mg
NDC 0046-0975-06, carton includes 3 EZ DIAL dispensers each containing 28 oval, light‑blue tablets.
NDC 0046-0975-11, carton includes 1 blister card containing 28 oval, light-blue tablets.
PREMPHASE therapy consists of two separate tablets; one maroon Premarin tablet taken daily on days 1 through 14 and one light-blue tablet taken on days 15 through 28.
NDC 0046-2579-11, carton includes 1 blister card containing 28 tablets (14 oval, maroon Premarin tablets and 14 oval, light-blue tablets).
The appearance of PREMPRO tablets is a trademark of Wyeth Pharmaceuticals.
The appearance of PREMARIN tablets is a trademark of Wyeth Pharmaceuticals. The appearance of the conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate combination tablets is a trademark.
Store at 20° - 25°C (68° - 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
United States Patent Number: 5,547,948 (PREMPRO).
PATIENT INFORMATION
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
Read this PATIENT INFORMATION before you start taking PREMPRO or PREMPHASE and read what you get each time you refill PREMPRO or PREMPHASE. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about PREMPRO and PREMPHASE (combinations of estrogens and a progestin)?
Do not use estrogens and progestins to prevent heart disease, heart attacks, strokes, or dementia.
Using estrogens and progestins may increase your chances of getting heart attacks, strokes, breast cancer, or blood clots. Using estrogens, with or without progestins, may increase your chance of getting dementia, based on a study of women age 65 years or older. You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly about whether you still need treatment with PREMPRO or PREMPHASE.
What is PREMPRO or PREMPHASE?
PREMPRO or PREMPHASE are medicines that contain two kinds of hormones, estrogens and a progestin.
PREMPRO or PREMPHASE is used after menopause to:
- Reduce moderate to severe hot flashes. Estrogens are hormones made by a woman's ovaries. The ovaries normally stop making estrogens when a woman is between 45 and 55 years old. This drop in body estrogen levels causes the “change of life” or menopause (the end of monthly menstrual periods). Sometimes, both ovaries are removed during an operation before natural menopause takes place. The sudden drop in estrogen levels causes “surgical menopause.”
- When the estrogen levels begin dropping, some women get very uncomfortable symptoms, such as feelings of warmth in the face, neck, and chest, or sudden strong feelings of heat and sweating (“hot flashes” or “hot flushes”). In some women the symptoms are mild, and they will not need to take estrogens. In other women, symptoms can be more severe. You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly about whether you still need treatment with PREMPRO or PREMPHASE.
- Treat moderate to severe dryness, itching, and burning, in and around the vagina. You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly about whether you still need treatment with PREMPRO or PREMPHASE to control these problems. If you use PREMPRO or PREMPHASE only to treat your dryness, itching, and burning in and around your vagina, talk with your healthcare provider about whether a topical vaginal product would be better for you.
- Help reduce your chances of getting osteoporosis (thin weak bones). Osteoporosis from menopause is a thinning of the bones that makes them weaker and easier to break. If you use PREMPRO or PREMPHASE only to prevent osteoporosis due to menopause, talk with your healthcare provider about whether a different treatment or medicine without estrogens might be better for you. You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly about whether you should continue with PREMPRO or PREMPHASE. Weight-bearing exercise, like walking or running, and taking calcium and vitamin D supplements may also lower your chances of getting postmenopausal osteoporosis. It is important to talk about exercise and supplements with your healthcare provider before starting them.
Who should not take PREMPRO or PREMPHASE?
Do not take PREMPRO or PREMPHASE if you have had your uterus (womb) removed (hysterectomy).
PREMPRO and PREMPHASE contain a progestin to decrease the chance of getting cancer of the uterus. If you do not have a uterus, you do not need a progestin and you should not take PREMPRO or PREMPHASE.
Do not start taking PREMPRO or PREMPHASE if you:
- Have unusual vaginal bleeding.
-
Currently have or have had certain cancers.
Estrogens may increase the chances of getting certain types of cancers, including cancer of the breast or uterus. If you have or had cancer, talk with your healthcare provider about whether you should take PREMPRO or PREMPHASE.
- Had a stroke or heart attack in the past year.
- Currently have or have had blood clots.
- Currently have or have had liver problems.
- Are allergic to PREMPRO or PREMPHASE or any of their ingredients. See the end of this leaflet for a list of all the ingredients in PREMPRO and PREMPHASE.
- Think you may be pregnant.
Tell your healthcare provider:
- If you are breastfeeding. The hormones in PREMPRO and PREMPHASE can pass into your milk.
- About all of your medical problems. Your healthcare provider may need to check you more carefully if you have certain conditions, such as asthma (wheezing), epilepsy (seizures), migraine, endometriosis, lupus, problems with your heart, liver, thyroid, kidneys, or have high calcium levels in your blood.
- About all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicines may affect how PREMPRO or PREMPHASE works. PREMPRO or PREMPHASE may also affect how your other medicines work.
- If you are going to have surgery or will be on bedrest. You may need to stop taking estrogens and progestins.
How should I take PREMPRO or PREMPHASE?
- Take one PREMPRO or PREMPHASE tablet at the same time each day.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as possible. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your normal schedule. Do not take 2 doses at the same time.
- Estrogens should be used at the lowest dose possible for your treatment only as long as needed. You and your healthcare provider should talk regularly (for example, every 3 to 6 months) about the dose you are taking and whether you still need treatment with PREMPRO or PREMPHASE.
What are the possible side effects of PREMPRO or PREMPHASE?
Side effects are grouped by how serious they are and how often they happen when you are treated.
Serious but less common side effects:
- Breast cancer
- Cancer of the uterus
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Blood clots
- Dementia
- Gallbladder disease
- Ovarian cancer
- High blood pressure
- Liver problems
- High blood sugar
- Enlargement of benign tumors of the uterus (“fibroids”)
- Mental depression
Some of the warning signs of these serious side effects include:
- Breast lumps
- Unusual vaginal bleeding
- Dizziness and faintness
- Changes in speech
- Severe headaches
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Pains in your legs
- Changes in vision
- Vomiting
- Yellowing of the skin, eyes or nail beds
Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of these warning signs, or any other unusual symptoms that concern you.
Less serious but common side effects include:
- Headache
- Breast pain
- Irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Stomach/abdominal cramps/bloating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hair loss
- Fluid retention
- Vaginal yeast infection
These are not all the possible side effects of PREMPRO or PREMPHASE. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
What can I do to lower my chances of getting a serious side effect with PREMPRO or PREMPHASE?
- Talk with your healthcare provider regularly about whether you should continue taking PREMPRO or PREMPHASE.
- See your healthcare provider right away if you get vaginal bleeding while taking PREMPRO or PREMPHASE.
- Have a breast exam and mammogram (breast X-ray) every year unless your healthcare provider tells you something else. If members of your family have had breast cancer or if you have ever had breast lumps or an abnormal mammogram, you may need to have breast exams more often.
- If you have high blood pressure, high cholesterol (fat in the blood), diabetes, are overweight, or if you use tobacco, you may have higher chances for getting heart disease. Ask your healthcare provider for ways to lower your chances of getting heart attacks.
General Information about the safe and effective use of PREMPRO and PREMPHASE
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not take PREMPRO or PREMPHASE for conditions for which it was not prescribed. Do not give PREMPRO or PREMPHASE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
Keep PREMPRO and PREMPHASE out of the reach of children.
This leaflet provides a summary of the most important information about PREMPRO and PREMPHASE. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist. You can ask for information about PREMPRO and PREMPHASE that is written for health professionals. You can get more information by calling the toll free number 800‑934-5556.
What are the ingredients in PREMPRO and PREMPHASE?
PREMPRO contains the same conjugated estrogens found in Premarin which are a mixture of sodium estrone sulfate and sodium equilin sulfate and other components including sodium sulfate conjugates, 17α-dihydroequilin, 17α-estradiol and 17β-dihydroequilin. PREMPRO also contains either 1.5, 2.5, or 5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate.
PREMPRO 0.3 mg/1.5 mg and 0.45 mg/1.5 mg also contain calcium phosphate tribasic, microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, hydromellose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, sucrose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, Eudragit NE 30D, povidone, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide, and iron oxide black.
PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg and 0.625 mg/5 mg also contain calcium phosphate tribasic, calcium sulfate, carnauba wax, cellulose, glyceryl monooleate, lactose, magnesium stearate, methylcellulose, pharmaceutical glaze, polyethylene glycol, sucrose, povidone, titanium dioxide, black iron oxide, and FD&C Blue No. 2 or red ferric oxide.
PREMPHASE is two separate tablets. One tablet (maroon color) is 0.625 mg of Premarin which is a mixture of sodium estrone sulfate and sodium equilin sulfate and other components including sodium sulfate conjugates, 17 α-dihydroequilin, 17 α-estradiol and 17 β-dihydroequilin. The maroon tablet also contains calcium phosphate tribasic, hydroxypropyl cellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, powdered cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, sucrose, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue No. 2, FD&C Red No. 40. The second tablet (light blue color) contains 0.625 mg of the same ingredients as the maroon color tablet plus 5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate. The light blue tablet also contains calcium phosphate tribasic, calcium sulfate, carnauba wax, cellulose, glyceryl monooleate, lactose, magnesium stearate, methylcellulose, pharmaceutical glaze, polyethylene glycol, sucrose, povidone, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue No. 2, and black iron oxide.
PREMPRO therapy consists of a single tablet to be taken once daily.
PREMPRO 0.3 mg/1.5 mg
Blister Card - Each carton includes 1 blister card containing 28 oval, cream tablets. Each tablet contains 0.3 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 1.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate for oral administration.
PREMPRO 0.45 mg/1.5 mg
Blister Card - Each carton includes 1 blister card containing 28 oval, gold tablets. Each tablet contains 0.45 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 1.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate for oral administration.
PREMPRO 0.625 mg/2.5 mg
EZ DIAL dispenser - Each carton includes 3 EZ DIAL® dispensers containing 28 tablets. One EZ DIAL dispenser contains 28 oval, peach tablets. Each tablet contains 0.625 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 2.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate for oral administration.
Blister Card – Each carton includes 1 blister card containing 28 oval, peach tablets. Each tablet contains 0.625 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 2.5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate for oral administration.
PREMPRO 0.625 mg/5 mg
EZ DIAL dispenser - Each carton includes 3 EZ DIAL dispensers containing 28 tablets. One EZ DIAL dispenser contains 28 oval, light-blue tablets. Each tablet contains 0.625 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate for oral administration.
Blister Card – Each carton includes 1 blister card containing 28 oval, light-blue tablets. Each tablet contains 0.625 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate for oral administration.
PREMPHASE therapy consists of two separate tablets; one maroon Premarin tablet taken daily on days 1 through 14 and one light-blue tablet taken on days 15 through 28.
Each carton includes 1 blister card containing 28 tablets. One blister card contains 14 oval, maroon Premarin tablets containing 0.625 mg of conjugated estrogens and 14 oval, light-blue tablets that contain 0.625 mg of the conjugated estrogens found in Premarin tablets and 5 mg of medroxyprogesterone acetate for oral administration.
The appearance of PREMPRO tablets is a trademark of Wyeth Pharmaceuticals.
The appearance of PREMARIN tablets is a trademark of Wyeth Pharmaceuticals. The appearance of the conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate combination tablets is a trademark.
Store at 20° - 25°C (68° - 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
United States Patent Number: 5,547,948 (PREMPRO).
 | This product's label may have been updated. For current package insert and further product information, please visit www.wyeth.com or call our medical communications department toll-free at 1‑800‑934‑5556. |  |
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.3 mg / 1.5 mg - BLISTER CARD
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
This blister card contains 28 tablets.
Finish all the tablets in this blister card.
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.3 mg / 1.5 mg - CARTON
Package contains 1 blister card of 28 Tablets
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.45 mg / 1.5 mg - BLISTER CARD
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
This blister card contains 28 tablets.
Finish all the tablets in this blister card.
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.45 mg / 1.5 mg - CARTON
Package contains 1 blister card of 28 tablets
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.625 mg / 2.5 mg - BLISTER CARD
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
This blister card contains 28 tablets.
Finish all the tablets in this blister card.
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.625 mg / 2.5 mg - CARTON
Package contains 1 blister card of 28 tablets.
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.625 mg / 2.5 mg - EZ DIAL
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
Package includes 1 EZ DIAL® dispenser containing 28 tablets

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.625 mg / 2.5 mg - CARTON
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
Package consists of 3 pouches, each includes one EZ DIAL® dispenser containing 28 tablets

PACKAGE LABEL – PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 0.625 mg / 5 mg – BLISTER CARD
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
This blister card contains 28 tablets.
Finish all the tablets in this blister card.
PACKAGE LABEL – PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 0.625 mg / 5 mg - CARTON
Package contains 1 blister card of 28 tablets
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.625 mg / 5 mg - EZ DIAL
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
Package includes 1 EZ DIAL® dispenser containing 28 tablets

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.625 mg / 5 mg - CARTON
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
Package consists of 3 pouches, each includes one EZ DIAL® dispenser containing 28 tablets

PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.625 mg / 5 mg - BLISTER CARD
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
14 maroon tablets of 0.625 mg conjugated estrogens
14 light-blue tablets of 0.625 mg conjugated estrogens
5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.625 mg / 5 mg - CARTON
Package contains 1 blister card of 28 tablets
(conjugated estrogens/medroxyprogesterone acetate tablets)
14 maroon tablets of 0.625 mg conjugated estrogens
14 light-blue tablets of 0.625 mg conjugated estrogens
5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate

| PREMPHASE
conjugated estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA020527 | 12/01/1995 | |
| PREMPRO
conjugated estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate tablet, sugar coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA020527 | 09/21/2009 | |
| PREMPRO
conjugated estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate tablet, sugar coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA020527 | 09/21/2009 | |
| PREMPRO
conjugated estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate tablet, sugar coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA020527 | 12/01/1995 | |
| PREMPRO
conjugated estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate tablet, sugar coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA020527 | 12/01/1995 | |
| Labeler - Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. (828831441) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Company | 071170729 | MANUFACTURE, ANALYSIS | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Wyeth Pharmaceuticals Inc. | 828831441 | MANUFACTURE, ANALYSIS | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Wyeth Organics Division of Wyeth Canada | 200006526 | MANUFACTURE, ANALYSIS | |