MINOCYCLINE HYDROCHLORIDE
-
minocycline hydrochloride tablet
Sandoz Inc
----------
MINOCYCLINE HCl EXTENDED RELEASE TABLETS (MINOCYCLINE HCl, USP)To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria as well as to maintain the effectiveness of other antibacterial drugs, Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets should be used only as indicated.
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets are indicated to treat only inflammatory lesions of non-nodular moderate to severe acne vulgaris.
This formulation of minocycline has not been evaluated in the treatment of infections.
DESCRIPTION
Minocycline hydrochloride, a semi synthetic derivative of tetracycline, is [4S-(4α,4aα,5aα,12aα)]-4,7-Bis(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,10,12,12a-tetrahydroxy-1,11-dioxo-2-naphthacenecarboxamide mono hydrochloride. The structural formula is represented below:
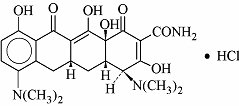
C23H27N3O7.HCl M. W. 493.95
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets for oral administration contain minocycline hydrochloride USP equivalent to 45 mg, 90 mg or 135 mg of minocycline. In addition, 45 mg, 90 mg, and 135 mg tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate NF, hypromellose type 2208 USP, hypromellose type 2910 USP, magnesium stearate NF and colloidal silicon dioxide NF.
The 45 mg tablets also contain opadry grey 04K57541, which contains: hypromellose type 2910 USP, titanium dioxide USP, triacetin USP, iron oxide black NF and iron oxide yellow NF.
The 90 mg tablets also contain opadry orange 04K53924, which contains: hypromellose type 2910 USP, titanium dioxide USP, triacetin USP, iron oxide yellow NF, FD&C yellow #6, and iron oxide red NF.
The 135 mg tablets also contain opadry yellow 04K82628, which contains: hypromellose type 2910 USP, titanium dioxide USP, triacetin USP and iron oxide yellow NF.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacokinetics
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets are not bioequivalent to minocycline products. Based on pharmacokinetic studies in healthy adults, Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets produce a delayed Tmax at 3.5 –4.0 hours as compared to a non-modified release reference minocycline product (Tmax at 2.25 - 3 hours). At steady-state (Day 6), the mean AUC (0-24) and Cmax were 33.32 μg x hr/mL and 2.63 μg/mL for Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets and 46.35 μg x hr/mL and 2.92 μg/mL for Minocin® capsules, respectively. These parameters are based on dose adjusted to 135 mg per day for both products.
A single-dose, four-way crossover study demonstrated that all strengths of Minocycline Extended Release Tablets (45 mg, 90 mg, 135 mg) exhibited dose-proportional pharmacokinetics.
When Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets were administered concomitantly with a meal that included dairy products, the extent and timing of absorption of minocycline did not differ from that of administration under fasting conditions.
Microbiology
Minocycline is bacteriostatic exerting its antimicrobial effect by the inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis. Minocycline is lipid soluble and distributes in to the skin and sebum. Minocycline has been shown to have in vitro activity against Propionibacterium acnes, an organism associated with acne vulgaris, however, the clinical significance of this activity against P. acnes in patients with acne vulgaris is not known.
CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets in the treatment of inflammatory lesions of non-nodular moderate to severe acne vulgaris was assessed in two 12-week, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, studies in subjects ≥ 12 years. The mean age of subjects was 20 years and subjects were from the following racial groups: White (73%), Hispanic (13%), Black (11%), Asian/Pacific Islander (2%), and Other (2%).
In two efficacy and safety trials, a total of 924 subjects with non-nodular moderate to severe acne vulgaris received 1 mg/kg of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets or placebo for a total of 12 weeks. The two primary efficacy endpoints were:
- Mean percent change in inflammatory lesion counts from Baseline to 12 weeks.
- Percentage of subjects with an Evaluator’s Global Severity Assessment (EGSA) of clear or almost clear at 12 weeks.
Efficacy results are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 – Efficacy Results at Week 12
| Study1 | Study2 | |||
|
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets (1 mg/kg) N = 300 |
Placebo N = 151 |
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets (1 mg/kg) N = 315 |
Placebo N = 158 |
|
| Mean Percent Improvement in inflammatory Lesions. | 43.1% | 31.7% | 45.8% | 30.8% |
| No. (%) of Subject Clear or Almost Clear on the EGSA* | 52 (17.3%) | 12 (7.9%) | 50 (15.9%) | 15 (9.5%) |
*Evaluator’s Global Severity Assessment
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets did not demonstrate any effect on non-inflammatory lesions (benefit or worsening).
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets are indicated to treat only inflammatory lesions of non-nodular moderate to severe acne vulgaris in patients 12 years of age and older. Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets did not demonstrate any effect on non-inflammatory lesions. Safety of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets has not been established beyond 12 weeks of use.
This formulation of minocycline has not been evaluated in the treatment of infections.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria as well as to maintain the effectiveness of other antibacterial drugs, Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets should be used only as indicated.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
This drug is contraindicated in persons who have shown hypersensitivity to any of the tetracyclines.
WARNINGS
Teratogenic effects
1) MINOCYCLINE, LIKE OTHER TETRACYCLINE-CLASS ANTIBIOTICS, CAN CAUSE FETAL HARM WHEN ADMINISTERED TO A PREGNANT WOMAN. IF ANY TETRACYCLINE IS USED DURING PREGNANCY OR IF THE PATIENT BECOMES PREGNANT WHILE TAKING THESE DRUGS, THE PATIENT SHOULD BE APPRISED OF THE POTENTIAL HAZARD TO THE FETUS.
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets should not be used during pregnancy nor by individuals of either gender who are attempting to conceive a child (see PRECAUTIONS: Impairment of Fertility ).
2) THE USE OF DRUGS OF THE TETRACYCLINE CLASS DURING TOOTH DEVELOPMENT (LAST HALF OF PREGNANCY, INFANCY, AND CHILDHOOD UP TO THE
AGE OF 8 YEARS) MAY CAUSE PERMANENT DISCOLORATION OF THE TEETH (YELLOW-GRAY-BROWN).
This adverse reaction is more common during long-term use of the drug but has been observed following repeated short-term courses. Enamel hypoplasia has also been reported. TETRACYCLINE DRUGS, THEREFORE, SHOULD NOT BE USED DURING TOOTH DEVELOPMENT.
3) All tetracyclines form a stable calcium complex in any bone-forming tissue. A decrease in fibula growth rate has been observed in premature human infants given oral tetracycline in doses of 25 mg/kg every 6 hours. This reaction was shown to be reversible when the drug was discontinued.
Results of animal studies indicate that tetracyclines cross the placenta, are found in fetal tissues, and can cause retardation of skeletal development on the developing fetus.Evidence of embryotoxicity has been noted in animals treated early in pregnancy (see PRECAUTIONS:Pregnancy section).
Gastro-intestinal effects
1. Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents and may range from mild to life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents.
Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon and may permit overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile is a primary cause of “antibiotic-associated colitis”.
After the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, therapeutic measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to discontinuation of the drug alone. In moderate to severe cases, consideration should be given to management with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation, and treatment with an antibacterial drug clinically effective against Clostridium difficile colitis.
2. Hepatotoxicity – Post-marketing cases of serious liver injury, including irreversible druginduced hepatitis and fulminant hepatic failure (sometimes fatal) have been reported with minocycline use in the treatment of acne.
Metabolic effects
The anti-anabolic action of the tetracyclines may cause an increase in BUN. While this is not a problem in those with normal renal function, in patients with significantly impaired function, higher serum levels of tetracycline-class antibiotics may lead to azotemia, hyperphosphatemia, and acidosis. If renal impairment exists, even usual oral or parenteral doses may lead to excessive systemic accumulations of the drug and possible liver toxicity. Under such conditions, lower than usual total doses are indicated, and if therapy is prolonged, serum level determinations of the drug may be advisable.
Central nervous system effects
1. Central nervous system side effects including light-headedness, dizziness or vertigo have been reported with minocycline therapy. Patients who experience these symptoms should be cautioned about driving vehicles or using hazardous machinery while on minocycline therapy. These symptoms may disappear during therapy and usually rapidly disappear when the drug is discontinued.
2. Pseudotumor cerebri (benign intracranial hypertension) in adults and adolescents has been associated with the use of tetracyclines. Minocycline has been reported to cause or precipitate pseudotumor cerebri, the hallmark of which is papilledema. Clinical manifestations include headache and blurred vision. Bulging fontanels have been associated with the use of tetracyclines in infants. Although signs and symptoms of pseudotumor cerebri resolve after discontinuation of treatment, the possibility for permanent sequelae such as visual loss that may be permanent or severe exists. Patients should be questioned for visual disturbances prior to initiation of treatment with tetracyclines and should be routinely checked for papilledema while on treatment.
Concomitant use of isotretinoin and minocycline should be avoided because isotretinoin, a systemic retinoid, is also known to cause pseudotumor cerebri.
Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity manifested by an exaggerated sunburn reaction has been observed in some individuals taking tetracyclines. This has been reported rarely with minocycline. Patients should minimize or avoid exposure to natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while using minocycline. If patients need to be outdoors while using minocycline, they should wear loose-fitting clothes that protect skin from sun exposure and discuss other sun protection measures with their physician.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Safety of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets beyond 12 weeks of use has not been established.
As with other antibiotic preparations, use of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi. If superinfection occurs, the antibiotic should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted.
Bacterial resistance to the tetracyclines may develop in patients using Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets, therefore the susceptibility of bacteria associated with infection should be considered in selecting antimicrobial therapy. Because of the potential for drug-resistant bacteria to develop during the use of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets it should be used only as indicated.
Autoimmune Syndromes
Tetracyclines have been associated with the development of autoimmune syndromes. The long-term use of minocycline in the treatment of acne has been associated with drug-induced lupus-like syndrome, autoimmune hepatitis and vasculitis. Sporadic cases of serum sickness have presented shortly after minocycline use. Symptoms may be manifested by fever, rash, arthralgia, and malaise. In symptomatic patients, liver function tests, ANA, CBC, and other appropriate tests should be performed to evaluate the patients. Use of all tetracycline-class drugs should be discontinued immediately.
Serious Skin/Hypersensitivity Reaction
Post-marketing cases of anaphylaxis and serious skin reactions such as Stevens Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme have been reported with minocycline use in treatment of acne.
Tissue Hyperpigmentation
Tetracycline class antibiotics are known to cause hyperpigmentation. Tetracycline therapy may induce hyperpigmentation in many organs, including nails, bone, skin, eyes, thyroid, visceral tissue, oral cavity (teeth, mucosa, alveolar bone), sclerae and heart valves. Skin and oral pigmentation has been reported to occur independently of time or amount of drug administration, whereas other tissue pigmentation has been reported to occur upon prolonged administration. Skin pigmentation includes diffuse pigmentation as well as over sites of scars or injury.
Information for patients
(See Patient Package Insert that accompanies this Package Insert for additional information to give patients)
- Photosensitivity manifested by an exaggerated sunburn reaction has been observed in some individuals taking tetracyclines, including minocycline. Patients should minimize or avoid exposure to natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while using minocycline. If patients need to be outdoors while using minocycline, they should wear loose-fitting clothes that protect skin from sun exposure and discuss other sun protection measures with their physician. Treatment should be discontinued at the first evidence of skin erythema.
- Patients who experience central nervous system symptoms (see WARNINGS) should be cautioned about driving vehicles or using hazardous machinery while on minocycline therapy. Patients should also be cautioned about seeking medical help for headaches or blurred vision.
- Concurrent use of tetracycline may render oral contraceptives less effective (seeDrug interactions).
- Autoimmune syndromes, including drug-induced lupus-like syndrome, autoimmune hepatitis, vasculitis and serum sickness have been observed with tetracycline-class antibiotics, including minocycline. Symptoms may be manifested by arthralgia, fever, rash and malaise. Patients who experience such symptoms should be cautioned to stop the drug immediately and seek medical help.
- Patients should be counseled about discoloration of skin, scars, teeth or gums that can arise from minocycline therapy.
- Take Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may decrease the effectiveness of the current treatment course and increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets should not be used by pregnant women or women attempting to conceive a child (SeeCarcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility sections).
- It is recommended that Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets not be used by men who are attempting to father a child (SeeImpairment of Fertility section).
Laboratory tests
Periodic laboratory evaluations of organ systems, including hematopoietic, renal and hepatic studies should be performed. Appropriate tests for autoimmune syndromes should be performed as indicated.
Drug interactions
- Because tetracyclines have been shown to depress plasma prothrombin activity, patients who are on anticoagulant therapy may require downward adjustment of their anticoagulant dosage.
- Since bacteriostatic drugs may interfere with the bactericidal action of penicillin, it is advisable to avoid giving tetracycline-class drugs in conjunction with penicillin.
- The concurrent use of tetracycline and methoxyflurane has been reported to result in fatal renal toxicity.
- Absorption of tetracyclines is impaired by antacids containing aluminum, calcium or magnesium and iron-containing preparations.
- In a multi-center study to evaluate the effect of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets on low dose oral contraceptives, hormone levels over one menstrual cycle with and without Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets 1 mg/kg once-daily were measured.
Based on the results of this trial, minocycline-related changes in estradiol, progestinic hormone, FSH and LH plasma levels, of breakthrough bleeding, or of contraceptive failure, can not be ruled out. To avoid contraceptive failure, female patients are advised to use a second form of contraceptive during treatment with minocycline.
Drug/laboratory test interactions
False elevations of urinary catecholamine levels may occur due to interference with the fluorescence test.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of minocycline. A structurally related compound, oxytetracycline, was found to produce adrenal and pituitary tumors in rats.
Mutagenesis
Minocycline was not mutagenic in vitro in a bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) or CHO/HGPRT mammalian cell assay in the presence or absence of metabolic activation. Minocycline was not clastogenic in vitro using human peripheral blood lymphocytes or in vivo in a mouse micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
Male and female reproductive performance in rats was unaffected by oral doses of minocycline of up to 300 mg/kg/day (which resulted in up to approximately 40 times the level of systemic exposure to minocycline observed in patients as a result of use of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets). However, oral administration of 100 or 300 mg/kg/day of minocycline to male rats (resulting in approximately 15 to 40 times the level of systemic exposure to minocycline observed in patients as a result of use of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets) adversely affected spermatogenesis. Effects observed at 300 mg/kg/day included a reduced number of sperm cells per gram of epididymis, an apparent reduction in the percentage of sperm that were motile, and (at 100 and 300 mg/kg/day) increased numbers of morphologically abnormal sperm cells. Morphological abnormalities observed in sperm samples included absent heads, misshapen heads, and abnormal flagella.
Limited human studies suggest that minocycline may have a deleterious effect on spermatogenesis.
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets should not be used by individuals of either gender who are attempting to conceive a child.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy category D (See WARNINGS)
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcome regardless of drug exposure. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies on the use of minocycline in pregnant women. Minocycline, like other tetracycline-class antibiotics, crosses the placenta and may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Rare spontaneous reports of congenital anomalies including limb reduction have been reported with minocycline use in pregnancy in post-marketing experience. Only limited information is available regarding these reports; therefore, no conclusion on causal association can be established.
Minocycline induced skeletal malformations (bent limb bones) in fetuses when administered to pregnant rats and rabbits in doses of 30 mg/kg/day and 100 mg/kg/day, respectively, (resulting in approximately 3 times and 2 times, respectively, the systemic exposure to minocycline observed in patients as a result of use of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets). Reduced mean fetal body weight was observed in studies in which minocycline was administered to pregnant rats at a dose of 10 mg/kg/day (which resulted in approximately the same level of systemic exposure to minocycline as that observed in patients who use Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets).
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets should not be used during pregnancy. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus and stop treatment immediately.
Nursing mothers
Tetracycline-class antibiotics are excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse effects on bone and tooth development in nursing infants from the tetracycline-class antibiotics, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother (see WARNINGS).
Pediatric use
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets are indicated to treat only inflammatory lesions of non-nodular moderate to severe acne vulgaris in patients 12 years and older. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 12 has not been established.
Use of tetracycline-class antibiotics below the age of 8 is not recommended due to the potential for tooth discoloration (see WARNINGS).
Geriatric use
Clinical studies of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical trials are conducted under prescribed conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trial may not reflect the rates observed in practice. However, adverse reaction information from clinical trials provides a basis for identifying the adverse events that appear to be related to drug use.
Adverse events reported in clinical trials for Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets are described below in Table 2.
Table 2 – Selected Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events in at least 1% of Clinical Trial Subjects
| Adverse Event |
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets (1 mg/kg) N=674(%) |
PLACEBO N=364(%) |
| At least one treatment-emergent event | 379(56) | 197(54) |
| Headache | 152(23) | 83(23) |
| Fatigue | 62(9) | 24(7) |
| Dizziness | 59(9) | 17(5) |
| Pruitus | 31(5) | 16(4) |
| Malaise | 26(4) | 9(3) |
| Mood alteration | 17(3) | 9(3) |
| Somnolence | 13(2) | 3(1) |
| Urticaria | 10(2) | 1(0) |
| Tinnitus | 10(2) | 5(1) |
| Arthralgia | 9(1) | 2(0) |
| Vertigo | 8(1) | 3(1) |
| Dry mouth | 7(1) | 5(1) |
| Myalgia | 7(1) | 4(1) |
Adverse reactions not observed in the clinical trials, but that have been reported with minocycline hydrochloride use in a variety of indications include:
Skin and hypersensitivity reactions: fixed drug eruptions, balanitis, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, anaphylactoid purpura, photosensitivity, pigmentation of skin and mucous membranes, hypersensitivity reactions, angioneurotic edema, anaphylaxis.
Autoimmune conditions: polyarthralgia, pericarditis, exacerbation of systemic lupus, pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia, transient lupus-like syndrome.
Central nervous system: pseudotumor cerebri, bulging fontanels in infants, decreased hearing.
Endocrine: thyroid discoloration, abnormal thyroid function.
Oncology: papillary thyroid cancer.
Oral: glossitis, dysphagia, tooth discoloration.
Gastrointestinal: enterocolitis, pancreatitis, hepatitis, liver failure.
Renal: reversible acute renal failure.
Hematology: hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia.
Preliminary studies suggest that use of minocycline may have deleterious effects on human spermatogenesis (see Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility section).
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
OVERDOSAGE
In case of overdosage, discontinue medication, treat symptomatically and institute supportive measures. Minocycline is not removed in significant quantities by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets are a once-daily tablet to be prescribed based on the patient’s weight to achieve approximately a 1 mg/kg dosage without any loading dose. The following table shows tablet strength and body weight to achieve approximately 1 mg/kg.
Table 3: Dosing Table for Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
| Patient’s Weight (lbs) |
Patient’s Weight (kg) |
Tablet Strength (mg) |
Actual mg/kg Dose |
| 99-131 | 45-59 | 45 | 1-0.76 |
| 132-199 | 60-90 | 90 | 1.5-1 |
| 200-300 | 91-136 | 135 | 1.48-0.99 |
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets may be taken with or without food (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY). Ingestion of food along with Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets may help reduce the risk of esophageal irritation and ulceration.
The recommended dosage of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets per clinical trials is 1 mg/kg daily for 12 weeks. Higher doses have not shown to be of additional benefit in the treatment of inflammatory lesions of acne, and may be associated with more acute vestibular side effects.
In patients with renal impairment (see WARNINGS), the total dosage should be decreased by either reducing the recommended individual doses and/or by extending the time intervals between doses.
HOW SUPPLIED
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets are supplied as aqueous film coated tablets containing minocycline hydrochloride equivalent to 45 mg, 90 mg or 135 mg minocycline.
The 45 mg extended release tablets are grey colored, capsule shaped, biconvex, film coated, debossed with ‘I113’ on one side and plain on the other side. Each tablet contains minocycline hydrochloride equivalent to 45 mg minocycline, supplied as follows:
NDC 0781-5385-31 Bottle of 30
NDC 0781-5385-01 Bottle of 100
NDC 0781-5385-10 Bottle of 1000
The 90 mg extended release tablets are light orange colored, capsule shaped, biconvex, film coated, debossed with ‘I112’ on one side and plain on the other side. Each tablet contains minocycline hydrochloride equivalent to 90 mg minocycline, supplied as follows:
NDC 0781-5386-31 Bottle of 30
NDC 0781-5386-01 Bottle of 100
NDC 0781-5386-10 Bottle of 1000
The 135 mg extended release tablets are light yellow colored, capsule shaped, biconvex film coated, debossed with ‘I111’ on one side and plain on the other side. Each tablet contains minocycline hydrochloride equivalent to 135 mg minocycline, supplied as follows:
NDC 0781-5387-31 Bottle of 30
NDC 0781-5387-01 Bottle of 100
NDC 0781-5387-10 Bottle of 1000
Store at 20º-25ºC (68º-77ºF); excursions are permitted to 15º-30ºC (59º-86ºF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from light, moisture, and excessive heat.
Dispense in tight, light-resistant container with child-resistant closure.
Patient Information
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets (Minocycline HCl, USP)
Rx only
Read all patient information that comes with Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of speaking with your doctor about your condition or treatment.
What is Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets?
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets are a tetracycline-class antibiotic medicine that contains minocycline. Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets are only for the treatment of pimples and red bumps (non-nodular inflammatory lesions) that happen with moderate to severe acne in patients 12 years and older.
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets have not been studied for use longer than 12 weeks.
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets have not been studied for the treatment of infections.
Who should not take Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets?
Do not take Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets if you are allergic to minocycline or any other tetracycline antibiotics. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets.
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets should not be used by pregnant women, women attempting to conceive a child, or children up to 8 years old because:
- Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets may harm an unborn baby
- Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets may permanently turn a baby or child’s teeth yellow-grey-brown during tooth development. Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets should not be used during tooth development. Tooth development happens in the last half of pregnancy and birth to age 8 years.
It is recommended that Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets not be used by men who are attempting to father a child.
What should I tell my doctor before taking Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets?
Tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions including if you:
- have kidney problems. Your doctor may prescribe a lower dose of medicine for you.
- have any vision problems such as blurred vision
- are pregnant or attempting to conceive a child. Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets may harm your unborn baby. Stop taking Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets and call your doctor if you become pregnant while taking it.
- are breastfeeding. Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets passes into your milk and may harm your baby.
You should decide whether to use Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets or breastfeed, but not both.
Tell your doctor about all the other medicines you take including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets and other medicines may interact. Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- birth control pills. Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets may make your birth control pills less effective. You should use a second form of birth control while taking Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets.
- a blood thinner medicine. The dose of your blood thinner may be lowered.
- a penicillin antibiotic medicine. Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets and penicillins should not be used together.
- antacids that contain aluminum, calcium, or magnesium or iron-containing products. These can affect how much Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets passes into your body.
- Isotretinoin products
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist.
How should I take Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets?
- Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets comes in 3 strengths. Your doctor will prescribe the strength that is best for your body weight. The usual dose of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets is 1 tablet each day for 12 weeks.
- Take Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets at the same time each day, with or without food. Taking Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets with food may lower your chances of getting irritation or ulcers in your esophagus. Your esophagus is the tube that connects your mouth to your stomach.
- Swallow Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets whole. Do not chew, crush, or split the tablets.
- If you forget to take Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets, take it as soon as you remember. Do not take more than one tablet of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets in one day.
- If you take too much Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets at a time, call your doctor.
- If you do not notice an improvement in your acne after 12 weeks of treatment with Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets, call your doctor.
What are possible side effects of Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets?
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets may cause serious side effects. Stop Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets and call your doctor if you have:
- watery diarrhea
- bloody stools
- stomach cramps
- unusual headaches
- blurred vision
- fever
- rash
- joint pain
- feeling very tired
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets may also cause:
- central nervous system effects. Symptoms include light-headedness, dizziness, and a spinning feeling (vertigo). You should not drive or operate dangerous machines if you have these symptoms.
- sun sensitivity (photosensitivity). You may get a worse sunburn with Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets. Avoid sun exposure and the use of sunlamps or tanning beds. Protect your skin while out in sunlight. Stop Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets and call your doctor at the first sign of redness or sunburn.
- darkening of skin, scars, teeth, and gums
The most common side effects with Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets include:
- headache
- nauseaBarbara Lopiccolo/GX/Novartis@PH, Joy John/GX/Novartis@PH, Marya Fradlina/GX/Novartis@PH, Shirley Fernandez/GX/Novartis@PH, Vamsi Nama/GX/Novartis@PH
- tiredness
- dizziness or spinning feeling
- diarrhea
- stomach area pain
- itching
Call your doctor if you have a side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the side effects with Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
How should I store Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets?
- Store Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets at room temperature. Keep Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets in the bottle you received from the pharmacy and store away from moisture and light.
- Keep Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed.
Do not give Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets. If you would like more information, talk to your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets that is written for health professionals.
What are the Ingredients in Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets?
Active Ingredient: minocycline HCl USP equivalent to 45 mg, 90 mg or 135 mg of minocycline
Inactive Ingredients: lactose monohydrate NF, hypromellose type 2208 USP, hypromellose type 2910 USP, magnesium stearate NF and colloidal silicon dioxide NF.
The 45 mg tablets also contain opadry grey 04K57541, which contains: hypromellose type 2910 USP, titanium dioxide USP, triacetin USP, iron oxide black NF and iron oxide yellow NF.
The 90 mg tablets also contain opadry orange 04K53924, which contains: hypromellose type 2910 USP, titanium dioxide USP, triacetin USP, iron oxide yellow NF, FD&C yellow #6, and iron oxide red NF.
The 135 mg tablets also contain opadry yellow 04K82628, which contains: hypromellose type 2910 USP, titanium dioxide USP, triacetin USP and iron oxide yellow NF.
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets are manufactured by USV LIMITED, H-17/H-18, OIDC, Mahatma Gandhi Udyog Nagar, Daman 396 210, India
For Sandoz Inc. Princeton, NJ 08540
March 2009
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0781-5385-31
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
45 mg
Rx only
30 Tablets

NDC 0781-5385-01
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
45 mg
Rx only
100 Tablets

NDC 0781-5385-10
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
45 mg
Rx only
1000 Tablets

NDC 0781-5386-31
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
90 mg
Rx only
30 Tablets

NDC 0781-5386-01
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
90 mg
Rx only
100 Tablets

NDC 0781-5386-10
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
90 mg
Rx only
1000 Tablets

NDC 0781-5387-31
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
135 mg
Rx only
30 Tablets

NDC 0781-5387-01
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
90 mg
Rx only
100 Tablets

NDC 0781-5387-10
Minocycline HCl Extended Release Tablets
90 mg
Rx only
1000 Tablets

| MINOCYCLINE HYDROCHLORIDE
minocycline hydrochloride tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| ANDA | ANDA090422 | 08/13/2009 | |
| MINOCYCLINE HYDROCHLORIDE
minocycline hydrochloride tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| ANDA | ANDA090422 | 08/13/2009 | |
| MINOCYCLINE HYDROCHLORIDE
minocycline hydrochloride tablet |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| ANDA | ANDA090422 | 08/13/2009 | |
| Labeler - Sandoz Inc (110342024) |