LOVAZA
-
omega-3-acid ethyl esters capsule, liquid filled
SmithKline Beecham Corporation
----------
LOVAZA® (omega-3-acid ethyl esters) CapsulesDESCRIPTION
LOVAZA, a lipid-regulating agent, is supplied as a liquid-filled gel capsule for oral administration. Each 1-gram capsule of LOVAZA (omega-3-acid ethyl esters) contains at least 900 mg of the ethyl esters of omega-3 fatty acids. These are predominantly a combination of ethyl esters of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA - approximately 465 mg) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA - approximately 375 mg).
The structural formula of EPA ethyl ester is:
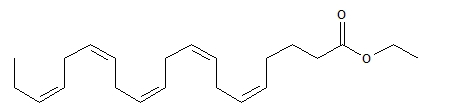
The empirical formula of EPA ethyl ester is C22H34O2, and the molecular weight of EPA ethyl ester is 330.51.
The structural formula of DHA ethyl ester is:
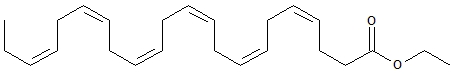
The empirical formula of DHA ethyl ester is C24H36O2, and the molecular weight of DHA ethyl ester is 356.55.
LOVAZA capsules also contain the following inactive ingredients: 4 mg α-tocopherol (in a carrier of partially hydrogenated vegetable oils including soybean oil), and gelatin, glycerol, and purified water (components of the capsule shell).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of LOVAZA is not completely understood. Potential mechanisms of action include inhibition of acyl CoA:1,2-diacylglycerol acyltransferase, increased mitochondrial and peroxisomal β-oxidation in the liver, decreased lipogenesis in the liver, and increased plasma lipoprotein lipase activity. LOVAZA may reduce the synthesis of triglycerides (TGs) in the liver because EPA and DHA are poor substrates for the enzymes responsible for TG synthesis, and EPA and DHA inhibit esterification of other fatty acids.
Pharmacokinetic and Bioavailability Studies
In healthy volunteers and in patients with hypertriglyceridemia (HTG), EPA and DHA were absorbed when administered as ethyl esters orally. Omega-3-acids administered as ethyl esters (LOVAZA) induced significant, dose–dependent increases in serum phospholipid EPA content, though increases in DHA content were less marked and not dose-dependent when administered as ethyl esters. Uptake of EPA and DHA into serum phospholipids in subjects t reated with LOVAZA was independent of age (<49 years versus ≥49 years). Females tended to have more uptake of EPA into serum phospholipids than males. Pharmacokinetic data on LOVAZA in children are not available.
Drug Interactions
Cytochrome P450-Dependent Monooxygenase Activities
The effect of a mixture of free fatty acids (FFA), EPA/DHA and their FFA-albumin conjugate on cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase activities was assessed in human liver microsomes. At the 23 micromole concentration, FFA resulted in a less than 32% inhibition of CYP1A2, 2A6, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A. At the 23 micromole concentration, the FFA-albumin conjugate resulted in a less than 20% inhibition of CYP2A6, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A, with a 68% inhibition being seen for CYP2E1. Since the free forms of the EPA and DHA are undetectable in the circulation (<1 micromole), clinically significant drug-drug interactions due to inhibition of P450-mediated metabolism EPA/DHA combinations are not expected in humans.
CLINICAL STUDIES
High Triglycerides
Add-on to HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor therapy
The effects of LOVAZA 4 g per day as add-on therapy to treatment with simvastatin were evaluated in a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group study of 254 adult patients (122 on LOVAZA and 132 on placebo) with persistent high triglycerides (200 to 499 mg/dL) despite simvastatin therapy (Table 1). Patients were treated with open-label simvastatin 40 mg per day for 8 weeks prior to randomization to control their LDL-C to no greater than 10% above NCEP ATP III goal and remained on this dose throughout the study. Following 8 weeks of open-label treatment with simvastatin, patients were randomized to either LOVAZA 4 g per day or placebo for an additional 8 weeks with simvastatin co-therapy. The median baseline triglyceride and LDL-C levels in these patients were 268 mg/dL and 89 mg/dL, respectively. Median baseline non-HDL-C and HDL-C levels were 138 mg/dL and 45 mg/dL, respectively.
The changes in the major lipoprotein lipid parameters for the groups receiving LOVAZA plus simvastatin and placebo plus simvastatin are shown in Table 1.
| Parameter |
LOVAZA + Simvastatin N = 122 |
Placebo + Simvastatin N = 132 | Difference | P-Value | ||||
| BL | EOT | Median % Change | BL | EOT | Median % Change | |||
| Non-HDL-C | 137 | 123 | -9.0 | 141 | 134 | -2.2 | -6.8 | <0.0001 |
| TG | 268 | 182 | -29.5 | 271 | 260 | -6.3 | -23.2 | <0.0001 |
| TC | 184 | 172 | -4.8 | 184 | 178 | -1.7 | -3.1 | <0.05 |
| VLDL-C | 52 | 37 | -27.5 | 52 | 49 | -7.2 | -20.3 | <0.05 |
| Apo-B | 86 | 80 | -4.2 | 87 | 85 | -1.9 | -2.3 | <0.05 |
| HDL-C | 46 | 48 | +3.4 | 43 | 44 | -1.2 | +4.6 | <0.05 |
| LDL-C | 91 | 88 | +0.7 | 88 | 85 | -2.8 | +3.5 | =0.05 |
BL = Baseline (mg/dL); EOT = End of Treatment (mg/dL); Median % Change = Median Percent Change from Baseline; Difference = LOVAZA Median % Change – Placebo Median % Change
LOVAZA 4 g per day significantly reduced non-HDL-C, TG, TC, VLDL-C, and Apo-B levels and increased HDL-C and LDL-C from baseline relative to placebo.
Very High Triglycerides
Monotherapy
The effects of LOVAZA 4 g per day were assessed in 2 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group studies of 84 adult patients (42 on LOVAZA, 42 on placebo) with very high triglyceride levels (Table 2). Patients whose baseline triglyceride levels were between 500 and 2,000 mg/dL were enrolled in these 2 studies of 6 and 16 weeks’ duration. The median triglyceride and LDL-C levels in these patients were 792 mg/dL and 100 mg/dL, respectively. Median HDL-C level was 23.0 mg/dL.
The changes in the major lipoprotein lipid parameters for the groups receiving LOVAZA or placebo are shown in Table 2.
| Parameter |
LOVAZA N = 42 |
Placebo N = 42 | Difference | ||
| BL | % Change | BL | % Change | ||
| TG | 816 | -44.9 | 788 | +6.7 | -51.6 |
| Non-HDL-C | 271 | -13.8 | 292 | -3.6 | -10.2 |
| TC | 296 | -9.7 | 314 | -1.7 | -8.0 |
| VLDL-C | 175 | -41.7 | 175 | -0.9 | -40.8 |
| HDL-C | 22 | +9.1 | 24 | 0.0 | +9.1 |
| LDL-C | 89 | +44.5 | 108 | -4.8 | +49.3 |
BL = Baseline (mg/dL); % Chg = Median Percent Change from Baseline; Difference = LOVAZA Median % change – Placebo Median % Change
LOVAZA 4 g per day reduced median TG, VLDL-C, and non-HDL-C levels and increased median HDL-C from baseline relative to placebo. Treatment with LOVAZA to reduce very high TG levels may result in elevations in LDL-C and non-HDL-C in some individuals. Patients should be monitored to ensure that the LDL-C level does not increase excessively.
The effect of LOVAZA on the risk of pancreatitis in patients with very high TG levels has not been evaluated.
The effect of LOVAZA on cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in patients with elevated TG levels has not been determined.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Very High Triglycerides
LOVAZA is indicated as an adjunct to diet to reduce triglyceride (TG) levels in adult patients with very high (≥500 mg/dL) triglyceride levels.
Usage Considerations
In individuals with hypertriglyceridemia (HTG), excess body weight and excess alcohol intake may be important contributing factors and should be addressed before initiating any drug therapy. Physical exercise can be an important ancillary measure. Diseases contributory to hyperlipidemia, (such as hypothyroidism or diabetes mellitus) should be looked for and adequately treated. Estrogen therapy, thiazide diuretics, and beta blockers are sometimes associated with massive rises in plasma TG levels. In such cases, discontinuation of the specific etiologic agent, if medically indicated, may obviate the need for specific drug therapy for HTG.
The use of lipid-regulating agents should be considered only when reasonable attempts have been made to obtain satisfactory results with non-drug methods. If the decision is made to use lipid-regulating agents, the patient should be advised that use of lipid-regulating agents does not reduce the importance of adhering to diet (see PRECAUTIONS).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
LOVAZA is contraindicated in patients who exhibit hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reaction) to any component of this medication.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Initial Therapy
Laboratory studies should be performed to ascertain that the patient’s TG levels are consistently abnormal before instituting therapy with LOVAZA. Every attempt should be made to control serum TG levels with appropriate diet, exercise, weight loss in overweight patients, and control of any medical problems (such as diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism) that may be contributing to the patient’s TG abnormalities. Medications known to exacerbate HTG (such as beta blockers, thiazides, and estrogens) should be discontinued or changed, if possible, before considering TG–lowering drug therapy.
Continued Therapy
Laboratory studies should be performed periodically to measure the patient’s TG levels during therapy with LOVAZA. Therapy with LOVAZA should be withdrawn in patients who do not have an adequate response after 2 months of treatment.
Information for Patients
LOVAZA should be used with caution in patients with known sensitivity or allergy to fish.
Patients should be advised that use of lipid-regulating agents does not reduce the importance of adhering to diet.
Laboratory Tests
In some patients, increases in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels without a concurrent increase in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels were observed. Alanine aminotransferase levels should be monitored periodically during therapy with LOVAZA.
In some patients, LOVAZA increased low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels. As with any lipid-regulating product, LDL-C levels should be monitored periodically during therapy with LOVAZA.
Drug Interactions
Anticoagulants
Some studies with omega-3-acids demonstrated prolongation of bleeding time. The prolongation of bleeding time reported in these studies has not exceeded normal limits and did not produce clinically significant bleeding episodes. Clinical studies have not been done to thoroughly examine the effect of LOVAZA and concomitant anticoagulants. Patients receiving treatment with both LOVAZA and anticoagulants should be monitored periodically.
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
In a 14-day study of 24 healthy adult subjects, daily co-administration of simvastatin 80 mg with LOVAZA 4 g did not affect the extent (AUC) or rate (Cmax) of exposure to simvastatin or the major active metabolite, beta-hydroxy simvastatin at steady state.
Cytochrome P450-Dependent Monooxygenase Activities
Omega-3 fatty-acid-containing products have been shown to increase hepatic concentrations of cytochrome P450 and activities of certain P450 enzymes in rats. The potential of LOVAZA to induce P450 activities in humans has not been studied.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a rat carcinogenicity study with oral gavage doses of 100, 600, and 2,000 mg/kg/day, males were treated with omega-3-acid ethyl esters for 101 weeks and females for 89 weeks without an increased incidence of tumors (up to 5 times human systemic exposures following an oral dose of 4 g/day based on a body surface area comparison). Standard lifetime carcinogenicity bioassays were not conducted in mice.
Omega-3-acid ethyl esters were not mutagenic or clastogenic with or without metabolic activation in the bacterial mutagenesis (Ames) test with Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli or in the chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster V79 lung cells or human lymphocytes. Omega-3-acid ethyl esters were negative in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
In a rat fertility study with oral gavage doses of 100, 600, and 2,000 mg/kg/day, males were treated for 10 weeks prior to mating and females were treated for 2 weeks prior to and throughout mating, gestation, and lactation. No adverse effect on fertility was observed at 2,000 mg/kg/day (5 times human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 g/day based on a body surface area comparison).
Pregnancy Category C
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. It is unknown whether LOVAZA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. LOVAZA should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Omega-3-acid ethyl esters have been shown to have an embryocidal effect in pregnant rats when given in doses resulting in exposures 7 times the recommended human dose of 4 g/day based on a body surface area comparison.
In female rats given oral gavage doses of 100, 600, and 2,000 mg/kg/day beginning 2 weeks prior to mating and continuing through gestation and lactation, no adverse effects were observed in the high dose group (5 times human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 g/day based on body surface area comparison).
In pregnant rats given oral gavage doses of 1,000, 3,000, and 6,000 mg/kg/day from gestation day 6 through 15, no adverse effects were observed (14 times human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 g/day based on a body surface area comparison).
In pregnant rats given oral gavage doses of 100, 600, and 2,000 mg/kg/day from gestation day 14 through lactation day 21, no adverse effects were seen at 2,000 mg/kg/day (5 times the human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 g/day based on a body surface area comparison). However, decreased live births (20% reduction) and decreased survival to postnatal day 4 (40% reduction) were observed in a dose-ranging study using higher doses of 3,000 mg/kg/day (7 times the human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 g/day based on a body surface area comparison).
In pregnant rabbits given oral gavage doses of 375, 750, and 1,500 mg/kg/day from gestation day 7 through 19, no findings were observed in the fetuses in groups given 375 mg/kg/day (2 times human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 g/day based on a body surface area comparison). However, at higher doses, evidence of maternal toxicity was observed (4 times human systemic exposure following an oral dose of 4 g/day based on a body surface area comparison).
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether omega-3-acid ethyl esters are excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when LOVAZA is administered to a woman who is breastfeeding.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Geriatric Use
A limited number of patients older than 65 years were enrolled in the clinical studies. Safety and efficacy findings in subjects older than 60 years did not appear to differ from those of subjects younger than 60 years.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Treatment-emergent adverse events reported in at least 1% of patients treated with LOVAZA 4 g per day or placebo during 8 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group studies for HTG are listed in Table 3. Adverse events led to discontinuation of treatment in 3.5% of patients treated with LOVAZA and 2.6% of patients treated with placebo.
|
BODY SYSTEM Adverse Event |
LOVAZA (N = 226) |
Placebo* (N = 228) |
||
| n | % | n | % | |
| Subjects with at least 1 adverse event | 80 | 35.4 | 63 | 27.6 |
| Body as a whole | ||||
| Back pain | 5 | 2.2 | 3 | 1.3 |
| Flu syndrome | 8 | 3.5 | 3 | 1.3 |
| Infection | 10 | 4.4 | 5 | 2.2 |
| Pain | 4 | 1.8 | 3 | 1.3 |
| Cardiovascular | ||||
| Angina pectoris | 3 | 1.3 | 2 | 0.9 |
| Digestive | ||||
| Dyspepsia | 7 | 3.1 | 6 | 2.6 |
| Eructation | 11 | 4.9 | 5 | 2.2 |
| Skin | ||||
| Rash | 4 | 1.8 | 1 | 0.4 |
| Special senses | ||||
| Taste perversion | 6 | 2.7 | 0 | 0.0 |
Adverse events were coded using COSTART, version 5.0. Subjects were counted only once for each body system and for each preferred term.
*Placebo was corn oil for all studies.
Additional adverse events reported by 1 or more patients from 22 clinical studies for HTG are listed below:
Body as a Whole
Enlarged abdomen, asthenia, body odor, chest pain, chills, suicide, fever, generalized edema, fungal infection, malaise, neck pain, neoplasm, rheumatoid arthritis, and sudden death.
Cardiovascular System
Arrhythmia, bypass surgery, cardiac arrest, hyperlipemia, hypertension, migraine, myocardial infarct, myocardial ischemia, occlusion, peripheral vascular disorder, syncope, and tachycardia.
Digestive System
Anorexia, constipation, dry mouth, dysphagia, colitis, fecal incontinence, gastritis, gastroenteritis, gastrointestinal disorder, increased appetite, intestinal obstruction, melena, pancreatitis, tenesmus, and vomiting.
Hematologic-Lymphatic System
Lymphadenopathy.
Infections and Infestations
Viral infection.
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders
Edema, hyperglycemia, increased ALT, and increased AST.
Musculoskeletal System
Arthralgia, arthritis, myalgia, pathological fracture, and tendon disorder.
Nervous System
Central nervous system neoplasia, depression, dizziness, emotional lability, facial paralysis, insomnia, vasodilatation, and vertigo.
Respiratory System
Asthma, bronchitis, increased cough, dyspnea, epistaxis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, pneumonia, rhinitis, and sinusitis.
Skin
Alopecia, eczema, pruritus, and sweating.
Special Senses
Cataract.
Urogenital System
Cervix disorder, endometrial carcinoma, epididymitis, and impotence.
Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the events described below have been identified during post-approval use of LOVAZA. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or to always establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following events have been reported: anaphylactic reaction, hemorrhagic diathesis.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
LOVAZA does not have any known drug abuse or withdrawal effects.
OVERDOSAGE
In the event of an overdose, the patient should be treated symptomatically, and general supportive care measures instituted, as required.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Patients should be placed on an appropriate lipid-lowering diet before receiving LOVAZA, and should continue this diet during treatment with LOVAZA. In clinical studies, LOVAZA was administered with meals.
The daily dose of LOVAZA is 4 g per day. The daily dose may be taken as a single 4-g dose (4 capsules) or as two 2-g doses (2 capsules given twice daily).
HOW SUPPLIED
LOVAZA (omega-3-acid ethyl esters) capsules are supplied as 1-gram transparent soft-gelatin capsules filled with light-yellow oil and bearing the designation REL900.
Bottles of 60: NDC 0173-0783-01
Bottles of 120: NDC 0173-0783-02
Recommended Storage: Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not freeze. Keep out of reach of children.
Distributed by:
GlaxoSmithKline
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709
©2008 GlaxoSmithKline. All rights reserved.
November 2008 LVZ:3PI
PHARMACIST-DETACH HERE AND GIVE INSTRUCTIONS TO PATIENT
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ __ _ _ _ _ _
PATIENT INFORMATION
LOVAZA® (lō-vā-ză)
(omega-3-acid ethyl esters) Capsules
Read the Patient Information that comes with LOVAZA before you start taking it, and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your condition or treatment.
What is LOVAZA?
LOVAZA is a prescription medicine for adults called a lipid-regulating medicine. LOVAZA is made of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are natural substances that your body needs. They are found naturally in some plants and in the oil of certain fish, such as salmon and mackerel.
LOVAZA is used along with a low-fat and low-cholesterol diet to lower very high triglycerides (fats) in your blood. Before taking LOVAZA, talk to your healthcare provider about how you can lower high blood fats by:
- losing weight, if you are overweight
- increasing physical exercise
- lowering alcohol use
- treating diseases such as diabetes and low thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- adjusting the dose or changing other medicines that raise triglyceride levels such as certain blood pressure medicines and estrogens
Treatment with LOVAZA has not been shown to prevent heart attacks or strokes.
LOVAZA has not been studied in children under the age of 18 years.
Who should not take LOVAZA?
Do not take LOVAZA if you:
- are allergic to LOVAZA or any of its ingredients. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in LOVAZA.
What should I tell my doctor before taking LOVAZA?
Tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- drink more than 2 glasses of alcohol daily
- have diabetes
- have a thyroid problem called hypothyroidism
- have a liver problem
- have a pancreas problem
- are allergic to fish. LOVAZA may not be right for you.
- are pregnant, or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if LOVAZA can harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding. It is not known if LOVAZA passes into your milk and if it can harm your baby.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicine, vitamins and herbal supplements. LOVAZA and certain other medicines can interact causing serious side effects. Especially tell your doctor if you take medicines:
- to reduce clotting – known as anticoagulants or blood thinners. These include aspirin, warfarin, coumarin and clopidogrel (PLAVIX).
Know all the medicines you take. Keep a list of them with you to show your doctor and pharmacist.
How should I take LOVAZA?
- Take LOVAZA exactly as prescribed. Do not change your dose or stop LOVAZA without talking to your doctor.
- The usual dose of LOVAZA is 4 capsules:
- Take all 4 capsules at the same time, or
- Take 2 capsules two times a day
- Take LOVAZA at the same time or times each day.
- Take LOVAZA with or without food. You may find it easier to take LOVAZA with food.
- Do not take more than 4 capsules a day. Taking more than 4 capsules per day may increase the chance of side effects.
- Your doctor should start you on a low-fat and low-cholesterol diet before giving you LOVAZA. Stay on this low-fat and low-cholesterol diet while taking LOVAZA.
- Your doctor should do blood tests to check your triglyceride and cholesterol levels, and liver function during treatment with LOVAZA.
- If you miss a dose of LOVAZA, take it as soon as you remember. However, if you miss one day of LOVAZA, do not double your dose when you next take it.
- If you take too much LOVAZA or overdose, call your doctor or Poison Control Center right away.
What are the possible side effects of LOVAZA?
- The most common side effects with LOVAZA are burping, infection, flu symptoms, upset stomach, a change in your sense of taste, back pain, and skin rash.
- LOVAZA may affect certain blood tests. It may change:
- one of the tests to check liver function (ALT)
- one of the tests to measure cholesterol levels (LDL-C)
Talk to your doctor if you have side effects that bother you or that will not go away. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
These are not all the side effects with LOVAZA. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a complete list.
How should I store LOVAZA?
- Store LOVAZA at room temperature, 59° to 86°F (15° to 30°C). Do not freeze.
- Do not keep medicine that is out of date or that you no longer need.
- Keep LOVAZA out of the reach of children. Be sure that if you throw medicines away, it is out of the reach of children.
General information about LOVAZA
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use LOVAZA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give LOVAZA to other people, even if they have the same problem you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about LOVAZA. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about LOVAZA that is written for health professionals or go to www.LOVAZA.com.
What are the ingredients in LOVAZA?
Active Ingredient: Omega-3-acid ethyl esters
Inactive Ingredients: Gelatin, glycerol, purified water, alpha-tocopherol (in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils, including soybean oil)
LOVAZA is a registered trademark of the GlaxoSmithKline group of companies.
PLAVIX is a registered trademark of Sanofi-Synthelabo.
Distributed by:
GlaxoSmithKline
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709
©2008 GlaxoSmithKline. All rights reserved.
June 2008 LVZ:1PIL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0173-0783-01
Lovaza®
(omega-3-acid ethyl esters)
Capsules
60 Capsules
Rx only
Each capsule contains 1 gram omega-3-acid ethyl ester liquid concentrate consisting of at least 900 mg omega-3-acid ethyl esters.
Each capsule provides: Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) ethyl ester: 465 mg Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) ethyl ester: 375 mg
Usual Dosage: See accompanying prescribing information.
Store at 25oC (77oF); excursions permitted to 15o-30oC (59o-86oF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not freeze.
Mfd for:
GlaxoSmithKline, RTP, NC 27709
Mfd by:
Catalent Pharma Solutions
St. Petersburg, FL 33716 or
Accucaps Industries, Ltd.
Windsor, ON, Canada N9C 3R5
Made in Norway
059191 Rev. 8/08

| LOVAZA
omega-3-acid ethyl esters capsule, liquid filled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NDA | NDA021654 | 10/21/2008 | |
| Labeler - SmithKline Beecham Corporation (167380711) |