LUCENTIS- ranibizumab injection, solution
Genentech, Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use LUCENTIS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LUCENTIS.
LUCENTIS® (ranibizumab injection) Intravitreal Injection Initial U.S. Approval: 2006 RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGEDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONFor Ophthalmic Intravitreal Injection Only (2.1) Neovascular (Wet) Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) (2.2) LUCENTIS 0.5 mg (0.05 mL) is recommended to be administered by intravitreal injection once a month (approximately 28 days). Although not as effective, patients may be treated with three monthly doses followed by less frequent dosing with regular assessment. In the nine months after three initial monthly doses, less frequent dosing with 4-5 doses on average is expected to maintain visual acuity while monthly dosing may be expected to result in an additional average 1-2 letter gain. Patients should be assessed regularly. Although not as effective, patients may also be treated with one dose every 3 months after 4 monthly doses. Compared to continued monthly dosing, dosing every 3 months over the next 9 months will lead to an approximate 5-letter (1-line) loss of visual acuity benefit, on average. Patients should be assessed regularly. Macular Edema Following Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) (2.3)
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) (2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Genentech at 1-888-835-2555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 02/2013 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.2 Neovascular (Wet) Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
LUCENTIS 0.5 mg (0.05 mL of 10 mg/mL LUCENTIS solution) is recommended to be administered by intravitreal injection once a month (approximately 28 days).
Although not as effective, patients may be treated with three monthly doses followed by less frequent dosing with regular assessment. In the nine months after three initial monthly doses, less frequent dosing with 4-5 doses on average is expected to maintain visual acuity while monthly dosing may be expected to result in an additional average 1-2 letter gain. Patients should be assessed regularly [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Although not as effective, patients may also be treated with one dose every 3 months after 4 monthly doses. Compared to continued monthly dosing, dosing every 3 months over the next 9 months will lead to an approximate 5-letter (1-line) loss of visual acuity benefit, on average. Patients should be assessed regularly [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
2.3 Macular Edema Following Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO)
LUCENTIS 0.5 mg (0.05 mL of 10 mg/mL LUCENTIS solution) is recommended to be administered by intravitreal injection once a month (approximately 28 days).
In Studies RVO-1 and RVO-2, patients received monthly injections of LUCENTIS for 6 months. In spite of being guided by optical coherence tomography and visual acuity re-treatment criteria, patients who were then not treated at Month 6 experienced on average, a loss of visual acuity at Month 7, whereas patients who were treated at Month 6 did not. Patients should be treated monthly [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
2.4 Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
LUCENTIS 0.3 mg (0.05 mL of 6 mg/mL LUCENTIS solution) is recommended to be administered by intravitreal injection once a month (approximately 28 days).
2.5 Preparation for Administration
Using aseptic technique, all of the LUCENTIS vial contents are withdrawn through a 5-micron, 19-gauge filter needle attached to a 1-cc tuberculin syringe. The filter needle should be discarded after withdrawal of the vial contents and should not be used for intravitreal injection. The filter needle should be replaced with a sterile 30-gauge × 1/2-inch needle for the intravitreal injection. The contents should be expelled until the plunger tip is aligned with the line that marks 0.05 mL on the syringe.
2.6 Administration
The intravitreal injection procedure should be carried out under controlled aseptic conditions, which include the use of sterile gloves, a sterile drape, and a sterile eyelid speculum (or equivalent). Adequate anesthesia and a broad-spectrum microbicide should be given prior to the injection.
Prior to and 30 minutes following the intravitreal injection, patients should be monitored for elevation in intraocular pressure using tonometry. Monitoring may also consist of a check for perfusion of the optic nerve head immediately after the injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Patients should also be monitored for and instructed to report any symptoms suggestive of endophthalmitis without delay following the injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Each vial should only be used for the treatment of a single eye. If the contralateral eye requires treatment, a new vial should be used and the sterile field, syringe, gloves, drapes, eyelid speculum, filter, and injection needles should be changed before LUCENTIS is administered to the other eye.
No special dosage modification is required for any of the populations that have been studied (e.g., gender, elderly).
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Single-use glass vial designed to provide 0.05 mL for intravitreal injection.
- 10 mg/mL solution (LUCENTIS 0.5 mg)
- 6 mg/mL solution (LUCENTIS 0.3 mg)
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Endophthalmitis and Retinal Detachments
Intravitreal injections, including those with LUCENTIS, have been associated with endophthalmitis and retinal detachments. Proper aseptic injection technique should always be used when administering LUCENTIS. In addition, patients should be monitored following the injection to permit early treatment should an infection occur [see Dosage and Administration (2.5, 2.6) and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.2 Increases in Intraocular Pressure
Increases in intraocular pressure have been noted both pre-injection and post-injection (at 60 minutes) while being treated with LUCENTIS. Monitor intraocular pressure prior to and following intravitreal injection with LUCENTIS and manage appropriately [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.3 Thromboembolic Events
Although there was a low rate of arterial thromboembolic events (ATEs) observed in the LUCENTIS clinical trials, there is a potential risk of ATEs following intravitreal use of VEGF inhibitors. ATEs are defined as nonfatal stroke, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or vascular death (including deaths of unknown cause).
Neovascular (Wet) Age-Related Macular Degeneration
The ATE rate in the three controlled neovascular AMD studies (AMD-1, AMD-2, AMD-3) during the first year was 1.9% (17 of 874) in the combined group of patients treated with 0.3 mg or 0.5 mg LUCENTIS compared with 1.1% (5 of 441) in patients from the control arms [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. In the second year of Studies AMD-1 and AMD-2, the ATE rate was 2.6% (19 of 721) in the combined group of LUCENTIS-treated patients compared with 2.9% (10 of 344) in patients from the control arms. In Study AMD-4, the ATE rates observed in the 0.5 mg arms of the study during the first year were similar to rates observed in AMD-1, AMD-2, and AMD-3.
In a pooled analysis of 2-year controlled studies (AMD-1, AMD-2, and a study of LUCENTIS used adjunctively with verteporfin photodynamic therapy), the stroke rate (including both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke) was 2.7% (13 of 484) in patients treated with 0.5 mg LUCENTIS compared to 1.1% (5 of 435) in patients in the control arms (odds ratio 2.2 (95% confidence interval (0.8-7.1))).
Macular Edema Following Retinal Vein Occlusion
The ATE rate in the two controlled RVO studies during the first 6 months was 0.8% in both the LUCENTIS and control arms of the studies (4 of 525 in the combined group of patients treated with 0.3 mg or 0.5 mg LUCENTIS and 2 of 260 in the control arms) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. The stroke rate was 0.2% (1 of 525) in the combined group of LUCENTIS-treated patients compared to 0.4% (1 of 260) in the control arms.
Diabetic Macular Edema
In a pooled analysis of Studies DME-1 and DME-2 [see Clinical Studies (14.3)], the ATE rate at 2 years was 7.2% (18 of 250) with 0.5 mg LUCENTIS, 5.6% (14 of 250) with 0.3 mg LUCENTIS, and 5.2% (13 of 250) with control. The stroke rate at 2 years was 3.2% (8 of 250) with 0.5 mg LUCENTIS, 1.2% (3 of 250) with 0.3 mg LUCENTIS, and 1.6% (4 of 250) with control. At 3 years, the ATE rate was 10.4% (26 of 249) with 0.5 mg LUCENTIS and 10.8% (27 of 250) with 0.3 mg LUCENTIS; the stroke rate was 4.8% (12 of 249) with 0.5 mg LUCENTIS and 2.0% (5 of 250) with 0.3 mg LUCENTIS.
5.4 Fatal Events in DME Patients
A pooled analysis of Studies DME-1 and DME-2 [see Clinical Studies (14.3)] showed that fatalities in the first 2 years occurred in 4.4% (11 of 250) of patients treated with 0.5 mg LUCENTIS, in 2.8% (7 of 250) of patients treated with 0.3 mg LUCENTIS, and in 1.2% (3 of 250) of control patients. Over 3 years, fatalities occurred in 6.4% (16 of 249) of patients treated with 0.5 mg LUCENTIS and in 4.4% (11 of 250) of patients treated with 0.3 mg LUCENTIS. Although the rate of fatal events was low and included causes of death typical of patients with advanced diabetic complications, a potential relationship between these events and intravitreal use of VEGF inhibitors cannot be excluded.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in the Warnings and Precautions (5) section of the label:
- Endophthalmitis and Retinal Detachments
- Increases in Intraocular Pressure
- Thromboembolic Events
- Fatal Events in DME Patients
6.1 Injection Procedure
Serious adverse reactions related to the injection procedure have occurred in < 0.1% of intravitreal injections, including endophthalmitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)], rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, and iatrogenic traumatic cataract.
6.2 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in one clinical trial of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of the same or another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data below reflect exposure to 0.5 mg LUCENTIS in 440 patients with neovascular AMD in Studies AMD-1, AMD-2, and AMD-3, and 259 patients with macular edema following RVO. The data also reflect exposure to 0.3 mg LUCENTIS in 250 patients with DME [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Safety data observed in Study AMD-4 were consistent with these results. On average, the rates and types of adverse reactions in patients were not significantly affected by dosing regimen.
Ocular Reactions
Table 1 shows frequently reported ocular adverse reactions in LUCENTIS-treated patients compared with the control group.
| DME 2-year | AMD 2-year | AMD 1-year | RVO 6-month |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | LUCENTIS 0.3 mg | Control | LUCENTIS 0.5 mg | Control | LUCENTIS 0.5 mg | Control | LUCENTIS 0.5 mg | Control |
| n=250 | n=250 | n=379 | n=379 | n=440 | n=441 | n=259 | n=260 | |
| Conjunctival hemorrhage | 47% | 32% | 74% | 60% | 64% | 50% | 48% | 37% |
| Eye pain | 17% | 13% | 35% | 30% | 26% | 20% | 17% | 12% |
| Vitreous floaters | 10% | 4% | 27% | 8% | 19% | 5% | 7% | 2% |
| Intraocular pressure increased | 18% | 7% | 24% | 7% | 17% | 5% | 7% | 2% |
| Vitreous detachment | 11% | 15% | 21% | 19% | 15% | 15% | 4% | 2% |
| Intraocular inflammation | 4% | 3% | 18% | 8% | 13% | 7% | 1% | 3% |
| Cataract | 28% | 32% | 17% | 14% | 11% | 9% | 2% | 2% |
| Foreign body sensation in eyes | 10% | 5% | 16% | 14% | 13% | 10% | 7% | 5% |
| Eye irritation | 8% | 5% | 15% | 15% | 13% | 12% | 7% | 6% |
| Lacrimation increased | 5% | 4% | 14% | 12% | 8% | 8% | 2% | 3% |
| Blepharitis | 3% | 2% | 12% | 8% | 8% | 5% | 0% | 1% |
| Dry eye | 5% | 3% | 12% | 7% | 7% | 7% | 3% | 3% |
| Visual disturbance or vision blurred | 8% | 4% | 18% | 15% | 13% | 10% | 5% | 3% |
| Eye pruritis | 4% | 4% | 12% | 11% | 9% | 7% | 1% | 2% |
| Ocular hyperemia | 9% | 9% | 11% | 8% | 7% | 4% | 5% | 3% |
| Retinal disorder | 2% | 2% | 10% | 7% | 8% | 4% | 2% | 1% |
| Maculopathy | 5% | 7% | 9% | 9% | 6% | 6% | 11% | 7% |
| Retinal degeneration | 1% | 0% | 8% | 6% | 5% | 3% | 1% | 0% |
| Ocular discomfort | 2% | 1% | 7% | 4% | 5% | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| Conjunctival hyperemia | 1% | 2% | 7% | 6% | 5% | 4% | 0% | 0% |
| Posterior capsule opacification | 4% | 3% | 7% | 4% | 2% | 2% | 0% | 1% |
| Injection site hemorrhage | 1% | 0% | 5% | 2% | 3% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
Non-Ocular Reactions
Non-ocular adverse reactions with an incidence of ≥ 5% in patients receiving LUCENTIS for DME, AMD, and/or RVO and which occurred at a ≥ 1% higher frequency in patients treated with LUCENTIS compared to control are shown in Table 2. Though less common, wound healing complications were also observed in some studies.
| DME 2-year | AMD 2-year | AMD 1-year | RVO 6-month |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Reaction | LUCENTIS 0.3 mg | Control | LUCENTIS 0.5 mg | Control | LUCENTIS 0.5 mg | Control | LUCENTIS 0.5 mg | Control |
| n=250 | n=250 | n=379 | n=379 | n=440 | n=441 | n=259 | n=260 | |
| Nasopharyngitis | 12% | 6% | 16% | 13% | 8% | 9% | 5% | 4% |
| Anemia | 11% | 10% | 8% | 7% | 4% | 3% | 1% | 1% |
| Nausea | 10% | 9% | 9% | 6% | 5% | 5% | 1% | 2% |
| Cough | 9% | 4% | 9% | 8% | 5% | 4% | 1% | 2% |
| Constipation | 8% | 4% | 5% | 7% | 3% | 4% | 0% | 1% |
| Seasonal allergy | 8% | 4% | 4% | 4% | 2% | 2% | 0% | 2% |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 7% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 3% | 2% | 1% | 1% |
| Influenza | 7% | 3% | 7% | 5% | 3% | 2% | 3% | 2% |
| Renal failure | 7% | 6% | 1% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 7% | 7% | 9% | 8% | 5% | 5% | 2% | 2% |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 6% | 4% | 4% | 6% | 3% | 4% | 1% | 0% |
| Headache | 6% | 8% | 12% | 9% | 6% | 5% | 3% | 3% |
| Edema peripheral | 6% | 4% | 3% | 5% | 2% | 3% | 0% | 1% |
| Renal failure chronic | 6% | 2% | 0% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Neuropathy peripheral | 5% | 3% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Sinusitis | 5% | 8% | 8% | 7% | 5% | 5% | 3% | 2% |
| Bronchitis | 4% | 4% | 11% | 9% | 6% | 5% | 0% | 2% |
| Atrial fibrillation | 3% | 3% | 5% | 4% | 2% | 2% | 1% | 0% |
| Arthralgia | 3% | 3% | 11% | 9% | 5% | 5% | 2% | 1% |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 1% | 1% | 6% | 3% | 3% | 1% | 0% | 0% |
| Wound healing complications | 1% | 0% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
6.3 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is the potential for an immune response in patients treated with LUCENTIS. The immunogenicity data reflect the percentage of patients whose test results were considered positive for antibodies to LUCENTIS in immunoassays and are highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assays.
The pre-treatment incidence of immunoreactivity to LUCENTIS was 0%-5% across treatment groups. After monthly dosing with LUCENTIS for 6 to 24 months, antibodies to LUCENTIS were detected in approximately 1%-8% of patients.
The clinical significance of immunoreactivity to LUCENTIS is unclear at this time. Among neovascular AMD patients with the highest levels of immunoreactivity, some were noted to have iritis or vitritis. Intraocular inflammation was not observed in DME or RVO patients with the highest levels of immunoreactivity.
6.4 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of LUCENTIS. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Ocular: Tear of retinal pigment epithelium among patients with neovascular AMD
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drug interaction studies have not been conducted with LUCENTIS.
LUCENTIS intravitreal injection has been used adjunctively with verteporfin photodynamic therapy (PDT). Twelve (12) of 105 (11%) patients with neovascular AMD developed serious intraocular inflammation; in 10 of the 12 patients, this occurred when LUCENTIS was administered 7 days (± 2 days) after verteporfin PDT.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. There are no studies of LUCENTIS in pregnant women. An embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study was performed on pregnant cynomolgus monkeys. Pregnant animals received intravitreal injections of ranibizumab every 14 days starting on Day 20 of gestation, until Day 62 at doses of 0, 0.125, and 1 mg/eye. Skeletal abnormalities including incomplete and/or irregular ossification of bones in the skull, vertebral column, and hindlimbs and shortened supernumerary ribs were seen at a low incidence in fetuses from animals treated with 1 mg/eye of ranibizumab. The 1 mg/eye dose resulted in trough serum ranibizumab levels up to 13 times higher than predicted Cmax levels with single eye treatment in humans. No skeletal abnormalities were seen at the lower dose of 0.125 mg/eye, a dose which resulted in trough exposures equivalent to single eye treatment in humans. No effect on the weight or structure of the placenta, maternal toxicity, or embryotoxicity was observed.
Animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response. It is also not known whether ranibizumab can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Based on the anti-VEGF mechanism of action for ranibizumab [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], treatment with LUCENTIS may pose a risk to embryo-fetal development (including teratogenicity) and reproductive capacity. LUCENTIS should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether ranibizumab is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because the potential for absorption and harm to infant growth and development exists, caution should be exercised when LUCENTIS is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of LUCENTIS in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the clinical studies, approximately 79% (2387 of 3005) of patients randomized to treatment with LUCENTIS were ≥ 65 years of age and approximately 54% (1636 of 3005) were ≥ 75 years of age [see Clinical Studies (14)]. No notable differences in efficacy or safety were seen with increasing age in these studies. Age did not have a significant effect on systemic exposure.
10 OVERDOSAGE
More concentrated doses as high as 2 mg ranibizumab in 0.05 mL have been administered to patients. No additional unexpected adverse reactions were seen.
11 DESCRIPTION
LUCENTIS® (ranibizumab injection) is a recombinant humanized IgG1 kappa isotype monoclonal antibody fragment designed for intraocular use. Ranibizumab binds to and inhibits the biologic activity of human vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A). Ranibizumab, which lacks an Fc region, has a molecular weight of approximately 48 kilodaltons and is produced by an E. coli expression system in a nutrient medium containing the antibiotic tetracycline. Tetracycline is not detectable in the final product.
LUCENTIS is a sterile, colorless to pale yellow solution in a single-use glass vial. LUCENTIS is supplied as a preservative-free, sterile solution in a single-use glass vial designed to deliver 0.05 mL of 10 mg/mL LUCENTIS (0.5 mg dose vial) or 6 mg/mL LUCENTIS (0.3 mg dose vial) aqueous solution with 10 mM histidine HCl, 10% α,α-trehalose dihydrate, 0.01% polysorbate 20, pH 5.5.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ranibizumab binds to the receptor binding site of active forms of VEGF-A, including the biologically active, cleaved form of this molecule, VEGF110. VEGF-A has been shown to cause neovascularization and leakage in models of ocular angiogenesis and vascular occlusion and is thought to contribute to pathophysiology of neovascular AMD, macular edema following RVO, and DME. The binding of ranibizumab to VEGF-A prevents the interaction of VEGF-A with its receptors (VEGFR1 and VEGFR2) on the surface of endothelial cells, reducing endothelial cell proliferation, vascular leakage, and new blood vessel formation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Increased retinal thickness (i.e., center point thickness (CPT) or central foveal thickness (CFT)), as assessed by optical coherence tomography (OCT) is associated with neovascular AMD, macular edema following RVO, and DME. Leakage from choroidal neovascularization (CNV) as assessed by fluorescein angiography (FA) is associated with neovascular AMD.
Neovascular (Wet) Age-Related Macular Degeneration
In Study AMD-3, CPT was assessed by time domain (TD)-OCT in 118 of 184 patients. TD-OCT measurements were collected at baseline, Months 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, and 12. In patients treated with LUCENTIS, CPT decreased, on average, more than in the sham group from baseline through Month 12. CPT decreased by Month 1 and decreased further at Month 3, on average. In this study, CPT data did not provide information useful in influencing treatment decisions [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
In Study AMD-4, CFT was assessed by spectral domain (SD)-OCT in all patients; on average, CFT reductions were observed beginning at Day 7 following the first LUCENTIS injection through Month 12 in both arms. CFT data did not provide information capable of predicting final visual acuity results [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
In patients treated with LUCENTIS, the area of CNV leakage, on average, decreased by Month 3 as assessed by FA. The area of CNV leakage for an individual patient was not correlated with visual acuity.
Macular Edema Following Retinal Vein Occlusion
On average, CPT reductions were observed in Studies RVO-1 and RVO-2 beginning at Day 7 following the first LUCENTIS injection through Month 6. CPT was not evaluated as a means to guide treatment decisions [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Diabetic Macular Edema
On average, CPT reductions were observed in Studies DME-1 and DME-2 beginning at Day 7 following the first LUCENTIS injection through Month 36. CPT data did not provide information useful in influencing treatment decisions [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In animal studies, following intravitreal injection, ranibizumab was cleared from the vitreous with a half-life of approximately 3 days. After reaching a maximum at approximately 1 day, the serum concentration of ranibizumab declined in parallel with the vitreous concentration. In these animal studies, systemic exposure of ranibizumab was more than 2000-fold lower than in the vitreous.
In patients with neovascular AMD, following monthly intravitreal administration, maximum ranibizumab serum concentrations were low (0.3 ng/mL to 2.36 ng/mL). These levels were below the concentration of ranibizumab (11 ng/mL to 27 ng/mL) thought to be necessary to inhibit the biological activity of VEGF-A by 50%, as measured in an in vitro cellular proliferation assay. The maximum observed serum concentration was dose proportional over the dose range of 0.05 to 1 mg/eye. Serum ranibizumab concentrations in RVO and DME patients were similar to those observed in neovascular AMD patients.
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis of patients with neovascular AMD, maximum serum concentrations of 1.5 ng/mL are predicted to be reached at approximately 1 day after monthly intravitreal administration of LUCENTIS 0.5 mg/eye. Based on the disappearance of ranibizumab from serum, the estimated average vitreous elimination half-life was approximately 9 days. Steady-state minimum concentration is predicted to be 0.22 ng/mL with a monthly dosing regimen. In humans, serum ranibizumab concentrations are predicted to be approximately 90,000-fold lower than vitreal concentrations.
In pharmacokinetic covariate analyses, 48% (520/1091) of patients had renal impairment (35% mild, 11% moderate, and 2% severe). Because the increases in plasma ranibizumab exposures in these patients are not considered clinically significant, no dosage adjustment is needed based on renal impairment status.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity or mutagenicity data are available for ranibizumab injection in animals or humans.
No studies on the effects of ranibizumab on fertility have been conducted. Although systemic exposure following ocular administration is expected to be low, effects on female fertility are possible due to the anti-VEGF mechanism of action for ranibizumab [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Unless otherwise noted, visual acuity was measured at a distance of 4 meters.
14.1 Neovascular (Wet) Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
The safety and efficacy of LUCENTIS were assessed in three randomized, double-masked, sham- or active-controlled studies in patients with neovascular AMD. A total of 1323 patients (LUCENTIS 879, control 444) were enrolled in the three studies.
Studies AMD-1 and AMD-2
In Study AMD-1, patients with minimally classic or occult (without classic) CNV lesions received monthly LUCENTIS 0.3 mg or 0.5 mg intravitreal injections or monthly sham injections. Data are available through Month 24. Patients treated with LUCENTIS in Study AMD-1 received a mean of 22 total treatments out of a possible 24 from Day 0 to Month 24.
In Study AMD-2, patients with predominantly classic CNV lesions received one of the following: 1) monthly LUCENTIS 0.3 mg intravitreal injections and sham PDT; 2) monthly LUCENTIS 0.5 mg intravitreal injections and sham PDT; or 3) sham intravitreal injections and active verteporfin PDT. Sham PDT (or active verteporfin PDT) was given with the initial LUCENTIS (or sham) intravitreal injection and every 3 months thereafter if fluorescein angiography showed persistence or recurrence of leakage. Data are available through Month 24. Patients treated with LUCENTIS in Study AMD-2 received a mean of 21 total treatments out of a possible 24 from Day 0 through Month 24.
In both studies, the primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients who maintained vision, defined as losing fewer than 15 letters of visual acuity at 12 months compared with baseline. Almost all LUCENTIS-treated patients (approximately 95%) maintained their visual acuity. Among LUCENTIS-treated patients, 31% to 37% experienced a clinically significant improvement in vision, defined as gaining 15 or more letters at 12 months. The size of the lesion did not significantly affect the results. Detailed results are shown in Table 3, Table 4, and Figure 1 below.
| Outcome Measure | Month | Sham n=229 | LUCENTIS 0.5 mg n=230 | Estimated Difference (95% CI)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Loss of <15 letters in visual acuity (%) | 12 | 60% | 91% | 30% (23%, 37%) |
| 24 | 56% | 89% | 33% (26%, 41%) |
|
| Gain of ≥15 letters in visual acuity (%) | 12 | 6% | 31% | 25% (18%, 31%) |
| 24 | 4% | 30% | 25% (18%, 31%) |
|
| Mean change in visual acuity (letters) (SD) | 12 | −11.0 (17.9) | +6.3 ( 14.1) | 17.1 (14.2, 20.0) |
| 24 | −15.0 (19.7) | +5.5 ( 15.9) | 20.1 (16.9, 23.4) |
|
| Outcome Measure | Month | Verteporfin PDT n=141 | LUCENTIS 0.5 mg n=139 | Estimated Difference (95% CI)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Loss of <15 letters in visual acuity (%) | 12 | 66% | 98% | 32% (24%, 40%) |
| 24 | 65% | 93% | 28% (19%, 37%) |
|
| Gain of ≥15 letters in visual acuity (%) | 12 | 11% | 37% | 26% (17%, 36%) |
| 24 | 9% | 37% | 29% (20%, 39%) |
|
| Mean change in visual acuity (letters) (SD) | 12 | −8.5 (17.8) | +11.0 (15.8) | 19.8 (15.9, 23.7) |
| 24 | −9.1 (18.7) | +10.9 (17.3) | 20 (16.0, 24.4) |
|
| Figure 1
Mean Change in Visual Acuity from Baseline to Month 24 in Study AMD-1 and Study AMD-2 |
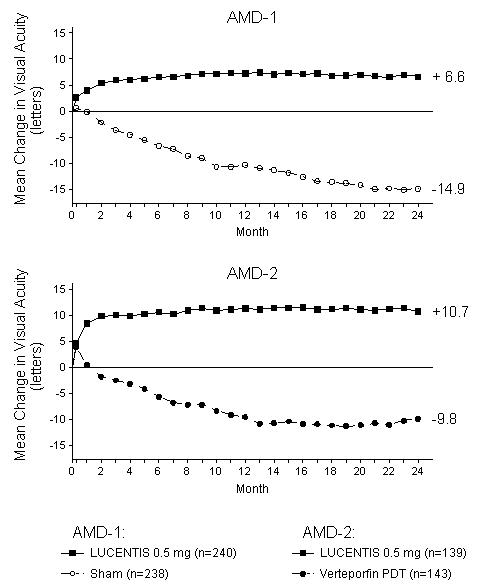 |
Visual acuity was measured at a distance of 2 meters
Patients in the group treated with LUCENTIS had minimal observable CNV lesion growth, on average. At Month 12, the mean change in the total area of the CNV lesion was 0.1-0.3 disc areas (DA) for LUCENTIS versus 2.3-2.6 DA for the control arms. At Month 24, the mean change in the total area of the CNV lesion was 0.3-0.4 DA for LUCENTIS versus 2.9-3.1 DA for the control arms.
Study AMD-3
Study AMD-3 was a randomized, double-masked, sham-controlled, two-year study designed to assess the safety and efficacy of LUCENTIS in patients with neovascular AMD (with or without a classic CNV component). Data are available through Month 12. Patients received LUCENTIS 0.3 mg or 0.5 mg intravitreal injections or sham injections once a month for 3 consecutive doses, followed by a dose administered once every 3 months for 9 months. A total of 184 patients were enrolled in this study (LUCENTIS 0.3 mg, 60; LUCENTIS 0.5 mg, 61; sham, 63); 171 (93%) completed 12 months of this study. Patients treated with LUCENTIS in Study AMD-3 received a mean of 6 total treatments out of a possible 6 from Day 0 through Month 12.
In Study AMD-3, the primary efficacy endpoint was mean change in visual acuity at 12 months compared with baseline (see Figure 2). After an initial increase in visual acuity (following monthly dosing), on average, patients dosed once every 3 months with LUCENTIS lost visual acuity, returning to baseline at Month 12. In Study AMD-3, almost all LUCENTIS-treated patients (90%) lost fewer than 15 letters of visual acuity at Month 12.
| Figure 2
Mean Change in Visual Acuity from Baseline to Month 12 in Study AMD-3 |
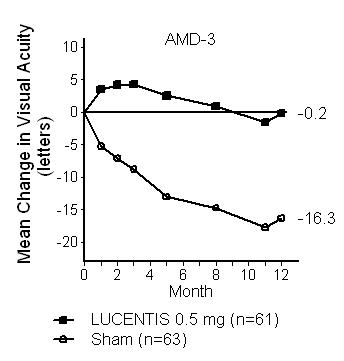 |
Study AMD-4
Study AMD-4 was a randomized, double-masked, active treatment-controlled, two-year study designed to assess the safety and efficacy of LUCENTIS 0.5 mg administered monthly or less frequently than monthly in patients with neovascular AMD. Patients randomized to the LUCENTIS 0.5 mg less frequent dosing arm received 3 monthly doses followed by monthly assessments where patients were eligible to receive LUCENTIS injections guided by pre-specified re-treatment criteria. A total of 550 patients were enrolled in the two 0.5 mg treatment groups; 521 (95%) of these patients completed Month 12 of this study. Data are available through Month 12.
From Month 3 through Month 12, patients in the 0.5 mg less frequent dosing arm gained an average of 0.1 letters in visual acuity and patients in the 0.5 mg monthly arm gained an average of 1.7 letters (see Figure 3). Over the same time period, patients in the 0.5 mg less frequent dosing and 0.5 mg monthly arms averaged 4.8 and 8.3 injections, respectively. The distribution of injections received in the less frequent dosing arm is shown in Figure 4.
| Figure 3
Mean Change in Visual Acuity from Baseline to Month 12 in Study AMD-4 |
 |
| Figure 4
Distribution of Injections from Month 3 to Month 12 in the Less Frequent Dosing Arm in Study AMD-4 |
 |
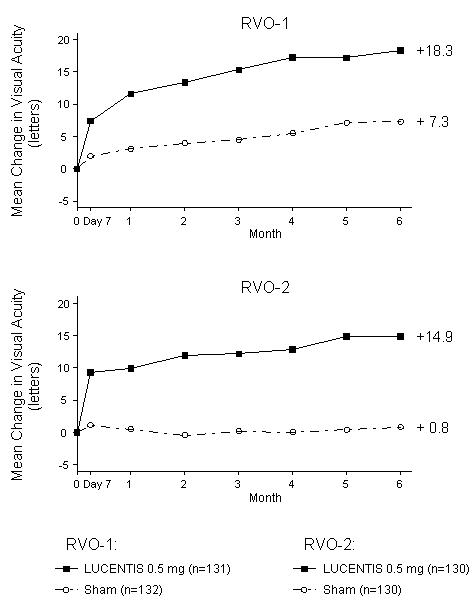
14.2 Macular Edema Following Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO)
The safety and efficacy of LUCENTIS were assessed in two randomized, double-masked, 1-year studies in patients with macular edema following RVO. Sham controlled data are available through Month 6. Patient age ranged from 20 to 91 years, with a mean age of 67 years. A total of 789 patients (LUCENTIS 0.3 mg, 266 patients; LUCENTIS 0.5 mg, 261 patients; sham, 262 patients) were enrolled, with 739 (94%) patients completing through Month 6. All patients completing Month 6 were eligible to receive LUCENTIS injections guided by pre-specified re-treatment criteria until the end of the studies at Month 12.
In Study RVO-1, patients with macular edema following branch or hemi-RVO, received monthly LUCENTIS 0.3 mg or 0.5 mg intravitreal injections or monthly sham injections for 6 months. All patients were eligible for macular focal/grid laser treatment beginning at Month 3 of the 6-month treatment period. Macular focal/grid laser treatment was given to 26 of 131 (20%) patients treated with 0.5 mg LUCENTIS and 71 of 132 (54%) patients treated with sham.
In Study RVO-2, patients with macular edema following central RVO received monthly LUCENTIS 0.3 mg or 0.5 mg intravitreal injections or monthly sham injections for 6 months.
At Month 6, after monthly treatment with 0.5 mg LUCENTIS, the following clinical results were observed:
| Outcome Measure | Study * | Sham | LUCENTIS 0.5 mg | Estimated Difference (95% CI) † |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gain of ≥15 letters in visual acuity (%) | RVO-1 | 29% | 61% | 31% (20%, 43%) |
| Gain of ≥15 letters in visual acuity (%) | RVO-2 | 17% | 48% | 30% (20%, 41%) |
| Figure 5
Mean Change in Visual Acuity from Baseline to Month 6 in Study RVO-1 and Study RVO-2 |
 |
p < 0.01 for all time points
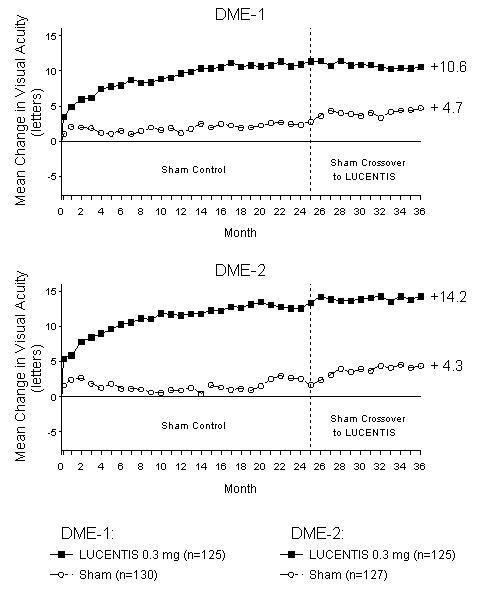
14.3 Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)
The safety and efficacy of LUCENTIS were assessed in two randomized, double-masked, 3-year studies in patients with DME. The studies were sham-controlled through Month 24. Patient age ranged from 21 to 91 years, with a mean age of 62 years. A total of 759 patients (LUCENTIS 0.3 mg, 250 patients; LUCENTIS 0.5 mg, 252 patients; sham, 257 patients) were enrolled, with 582 (77%) completing through Month 36.
In Studies DME-1 and DME-2, patients received monthly LUCENTIS 0.3 mg or 0.5 mg intravitreal injections or monthly sham injections during the 24-month controlled treatment period. From Months 25 through 36, patients who previously received sham were eligible to receive monthly LUCENTIS 0.5 mg and patients originally randomized to monthly LUCENTIS 0.3 mg or 0.5 mg continued to receive their assigned dose. All patients were eligible for macular focal/grid laser treatment beginning at Month 3 of the 24-month treatment period or panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) as needed. Through Month 24, macular focal/grid laser treatment was administered in 94 of 250 (38%) patients treated with LUCENTIS 0.3 mg and 185 of 257 (72%) patients treated with sham; PRP was administered in 2 of 250 (1%) patients treated with LUCENTIS 0.3 mg and 30 of 257 (12%) patients treated with sham.
Compared to monthly LUCENTIS 0.3 mg, no additional benefit was observed with monthly treatment with LUCENTIS 0.5 mg. At Month 24, after monthly treatment with LUCENTIS 0.3 mg, the following clinical results were observed:
| Outcome Measure | Study* | Sham | LUCENTIS 0.3 mg | Estimated Difference (95% CI)† |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gain of ≥15 letters in visual acuity (%) | DME-1 | 12% | 34% | 21% (11%, 30%) |
| DME-2 | 18% | 45% | 24% (14%, 35%) |
|
| Loss of <15 letters in visual acuity (%) | DME-1 | 92% | 98% | 7% (2%, 13%) |
| DME-2 | 90% | 98% | 8% (2%, 14%) |
|
| Mean change in visual acuity (letters) | DME-1 | 2.3 | 10.9 | 8.5 (5.4, 11.5) |
| DME-2 | 2.6 | 12.5 | 9.6 (6.1, 13.0) |
|
| Figure 6
Mean Change in Visual Acuity from Baseline to Month 36 in Study DME-1 and Study DME-2 |
 |
p < 0.01 for all time points comparing LUCENTIS 0.3 mg to sham through Month 24
VA outcomes observed at Month 24 in patients treated with LUCENTIS 0.3 mg were maintained with continued treatment through Month 36 in both DME studies. Patients in the sham arms who received LUCENTIS 0.5 mg beginning at Month 25 achieved lesser VA gains compared to patients who began treatment with LUCENTIS at the beginning of the studies.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- Each LUCENTIS 0.5 mg carton (NDC 50242-080-01) contains a single-use, 2-cc glass vial with a BLUE CAP designed to deliver 0.05 mL of 10 mg/mL ranibizumab.
- Each LUCENTIS 0.3 mg carton (NDC 50242-082-01) contains a single-use, 2-cc glass vial with a WHITE CAP designed to deliver 0.05 mL of 6 mg/mL ranibizumab.
In addition, each carton contains one 5-micron, 19-gauge × 1-1/2-inch filter needle for withdrawal of the vial contents; one 30-gauge × 1/2-inch injection needle for the intravitreal injection; and one package insert [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)]. VIALS ARE FOR SINGLE-EYE USE ONLY.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
In the days following LUCENTIS administration, patients are at risk of developing endophthalmitis. If the eye becomes red, sensitive to light, painful, or develops a change in vision, the patient should seek immediate care from an ophthalmologist [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
LUCENTIS® [ranibizumab injection]
Manufactured by:
Genentech, Inc.
A Member of the Roche Group
1 DNA Way
South San Francisco, CA 94080-4990
LUCENTIS® is a registered
trademark of Genentech, Inc.
©2013 Genentech, Inc.
Representative sample of labeling (see the HOW SUPPLIED section for complete listing):
| LUCENTIS
ranibizumab injection, solution |
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| LUCENTIS
ranibizumab injection, solution |
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Genentech, Inc. (080129000) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
| Genentech, Inc. (SSF) | 080129000 | API MANUFACTURE(50242-080, 50242-082), ANALYSIS(50242-080, 50242-082) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
| Roche Singapore Technical Operations Pte. Ltd. | 937189173 | API MANUFACTURE(50242-080, 50242-082), ANALYSIS(50242-080, 50242-082) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
| Novartis Pharma Stein AG | 488152505 | MANUFACTURE(50242-080, 50242-082), ANALYSIS(50242-080, 50242-082) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
| Novartis Pharma AG | 482347168 | ANALYSIS(50242-080, 50242-082) | |

